New Insights on Iron-Trimesate MOFs for Inorganic As(III) and As(V) Adsorption from Aqueous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Batch Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of Basolite®F300 and Nano-{Fe-BTC}
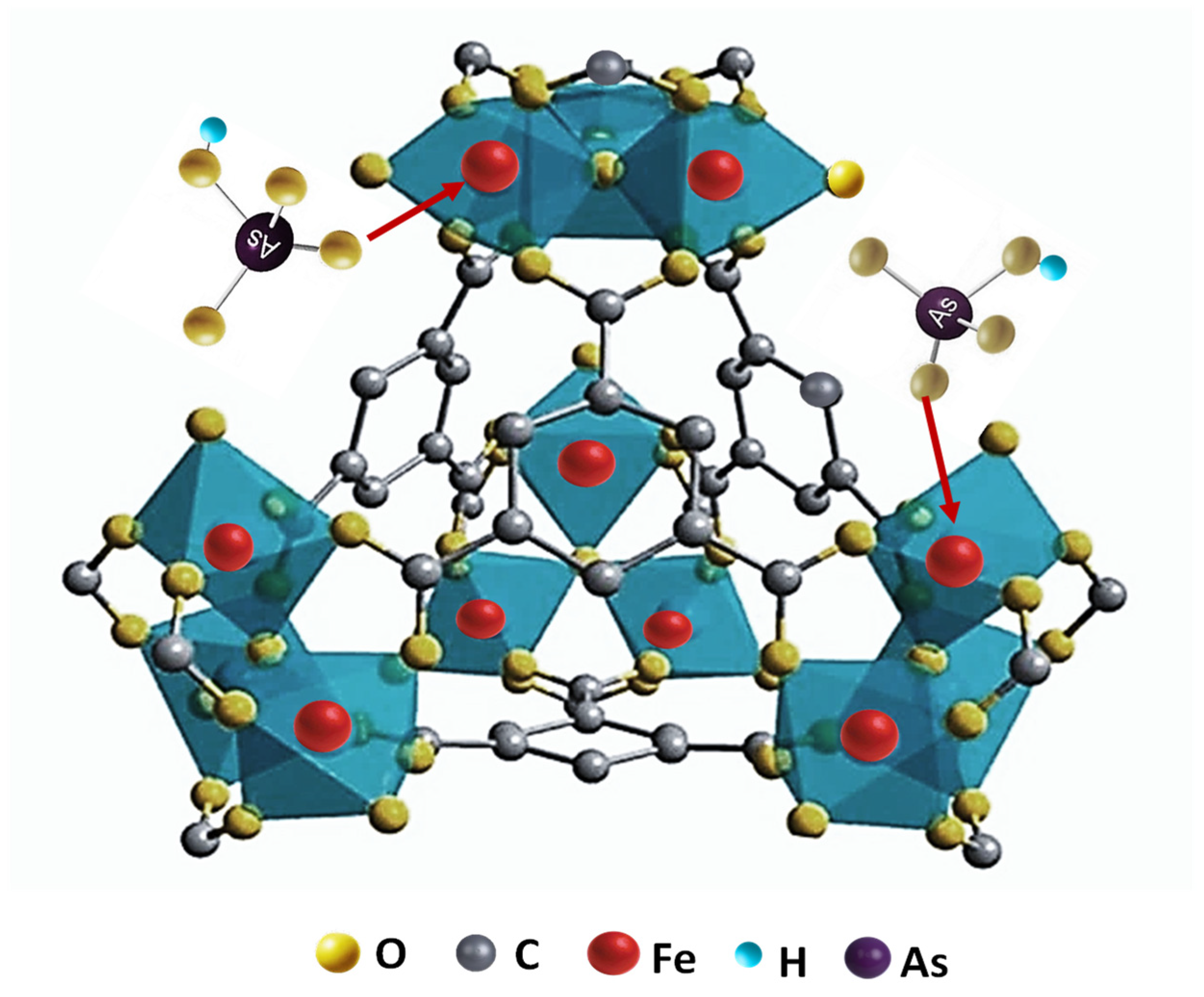
3.2. Characterisation of the Sorption Processes
3.3. Kinetics of the Sorption Processes
3.4. The Effect of pH
3.5. The Effect of Initial Arsenic Concentration
3.6. The Effect of the Sorbent Concentration
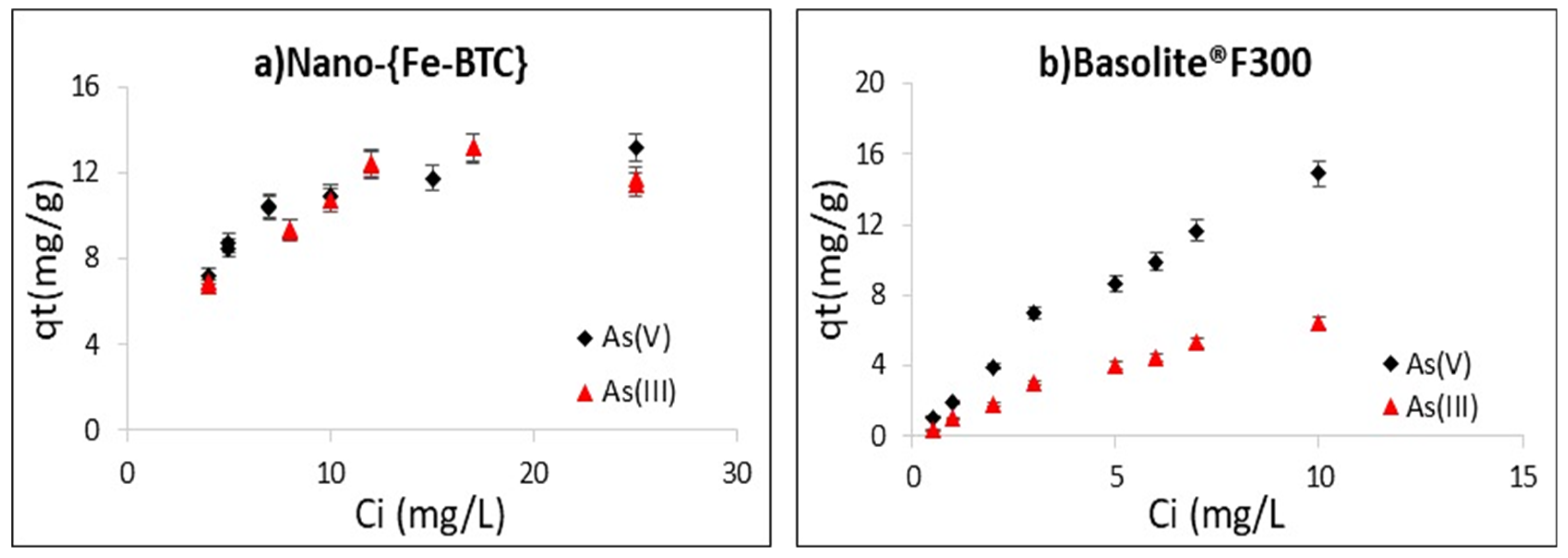
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, K.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Corns, W.T.; Varol, P.; Bhattacharya, P.; Zhu, Y. A review on arsenic in the environment: Contamination, mobility, sources, and exposure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8803–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi-Darani, K.; Rehman, Y.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kokkinos, E.; Zouboulis, A.I. Arsenic Exposure via Contaminated Water and Food Sources. Water 2022, 14, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Abdul, K.S.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C.S. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.D.; Vucic, E.A.; Becker-Santos, D.D.; Gil, L.; Lam, W.L. Arsenic exposure and the induction of human cancers. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 431287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization, Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khan, M.I.; Amjad, M.; Hussain, M. Arsenic Uptake, Toxicity, Detoxification, and Speciation in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsamman, M.T.; Sotelo, S.; Sánchez, J.; Rivas, B.L. Arsenic oxidation and its subsequent removal from water: An overview. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, A.; Park, J.; Kwak, H.; Park, P.-K. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hydrous iron oxide-impregnated alginate beads. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Nguyen, D.V.; Jeong, G.; Asghar, N.; Jang, A. Critical evaluation of hybrid metal–organic framework composites for efficient treatment of arsenic–contaminated solutions by adsorption and membrane–separation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alka, S.; Shahir, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Ndejiko, M.J.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Manan, F.A. Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: A mini review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhar, R.; Derco, J.; Čacho, F. An overview of main arsenic removal technologies. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2018, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Patel, M.; Singh, P.; Bundschuh, J.; Pittman, C.U.; Trakal, L.; Mohan, D. Emerging technologies for arsenic removal from drinking water in rural and peri-urban areas: Methods, experience from, and options for Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicomel, N.R.; Leus, K.; Folens, K.; Van Der Voort, P.; Du Laing, G. Technologies for Arsenic Removal from Water: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, V.; Kim, S. A review of functional sorbents for adsorptive removal of arsenic ions in aqueous systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuda-Stanić, M.; Nujić, M. Arsenic removal by nanoparticles: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8094–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lata, S.; Samadder, S.R. Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angodi, M.; Mameli, V.; Fantasia, A.; Cara, C.; Secci, F.; Enzo, S.; Gerina, M.; Cannas, C. As(III, V) Uptake from Nanostructured Iron Oxides and Oxyhydroxides: The complex Interplay between Sorbent Surface Chemistry and Arsenic Equilibria. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, B.; Kamboj, A.; Kamal Singh, V.; Gurjaspreet Singh, P.; Pombeiro, A.J.; Ren, P. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) materials for pesticides, heavy metals, and drugs removal: Environmental safety. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luan, J.; Wu, C. Metal-organic frameworks for aquatic arsenic removal. Water Res. 2019, 158, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamim, M.A.; Zia, H.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Shahid, M. Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as a cutting-edge tool for the selective detection and rapid removal of heavy metal ions from water: Recent progress. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Hassan, A.A.; Bilal, M.; Hussain, T.; Rizwan, K. Metal-organic frameworks based adsorbents: A review from removal perspective of various environmental contaminants from wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydiuk, T.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Shuai, Q.; Le, X.C. Removal of inorganic arsenic from water using metal organic frameworks. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi, M.; Zakeri, M.; Alobaid, F.; Aghel, B. A Brief Review of Recent Results in Arsenic Adsorption Process from Aquatic Environments by Metal-Organic Frameworks: Classification Based on Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamics Behaviors. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, K. Superior removal of arsenic from water with zirconium metal-organic framework UiO-66. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.A.; Le, G.H.; Dao, C.D.; Dang, L.Q.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Dang, P.T.; Tran, H.T.K.; Duong, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; et al. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption using novel MIL-53(Fe) as a highly efficient adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C. Selective adsorption of arsenate and the reversible structure transformation of the mesoporous metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 10864–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Wu, Y.; Feng, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Morlay, C.; Li, F. Green synthesis and evaluation of an iron-based metal–organic framework MIL-88B for efficient decontamination of arsenate from water. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, I.B.J.; Yu, X.; Jia, Y.; Peng, F.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Huang, X. Iron and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic metal–organic coordination polymers prepared by solvothermal method and their application in efficient As(V) removal from aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8601–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Torrente, M.; Filez, M.; Hardian, R.; Reynolds, E.; Seoane, B.; Coulet, M.V.; Oropeza Palacio, F.E.; Hofmann, J.P.; Fischer, R.A.; Goodwin, A.L.; et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Catalyst Supports: Influence of Lattice Disorder on Metal Nanoparticle Formation. Chem.—Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7498–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.-B.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.-C.E.; Cui, H.-J.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. Magnetic responsive Fe3O4-ZIF-8 core-shell composites for efficient removal of As(III) from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-González, J.E.; Peña-Méndez, E.M.; Melián-Fernández, A.M.; Havel, J.; Salvadó, V. Synthesis, performance and mechanism of nanoporous Fe-(1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid) metal-organic framework in the removal of anionic dyes from water. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshina Moorthy, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Horcajada, M.M.; Gibson, P.; Vishnuvarthan, E.; Vimont, M.; Grenèche, A.; Serre, J.M.; Daturi, C.; García, M.; et al. Comparison of porous iron trimesates basolite F300 and MIL-100(Fe) as heterogeneous catalysts for lewis acid and oxidation reactions: Roles of structural defects and stability. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption behavior of arsenicals on MIL-101(Fe): The role of arsenic chemical structures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-González, J.E.; Lorenzo-Luis, P.; Salvadó, V.; Havel, J.; Peña-Méndez, E. A new cotton functionalized with iron(III) trimer-like metal framework as an effective strategy for the adsorption of triarylmethane dye: An insight into the dye adsorption processes. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Luo, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Huang, W.; Zeng, K.; Luo, F. Metal-organic framework (MOF) showing both ultrahigh As(V) and As(III) removal from aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 269, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardozzi, E.; Tuninetti, J.S.; Einschlag, F.S.G.; Azzaroni, O.; Ceolín, M.; Rafti, M. Comparison of Arsenate Adsorption from Neutral pH Aqueous Solutions Using Two Different Iron-Trimesate Porous Solids: Kinetics, Equilibrium Isotherms, and Synchrotron X-Ray Absorption Experiments. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Mao, X.; Song, W.-G. Adsorption behavior and structure transformation of mesoporous metal–organic frameworks towards arsenates and organic pollutants in aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, M.A.; Muntean, S.G.; Maranescu, B.; Visa, A. Phosphonate metal-organic frameworks used as dye removal materials from wastewaters. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, Y.; Perman, J.A.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Deligiannakis, Y. Highly Efficient Arsenite [As(III)] Adsorption by an [MIL-100(Fe)] Metal–Organic Framework: Structural and Mechanistic Insights. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 4859–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Jiang, N.; Chai, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, X. Efficient removal of arsenic from wastewater using aminated Fe-BTC-based Metal-Organic frameworks. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 305, 117397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

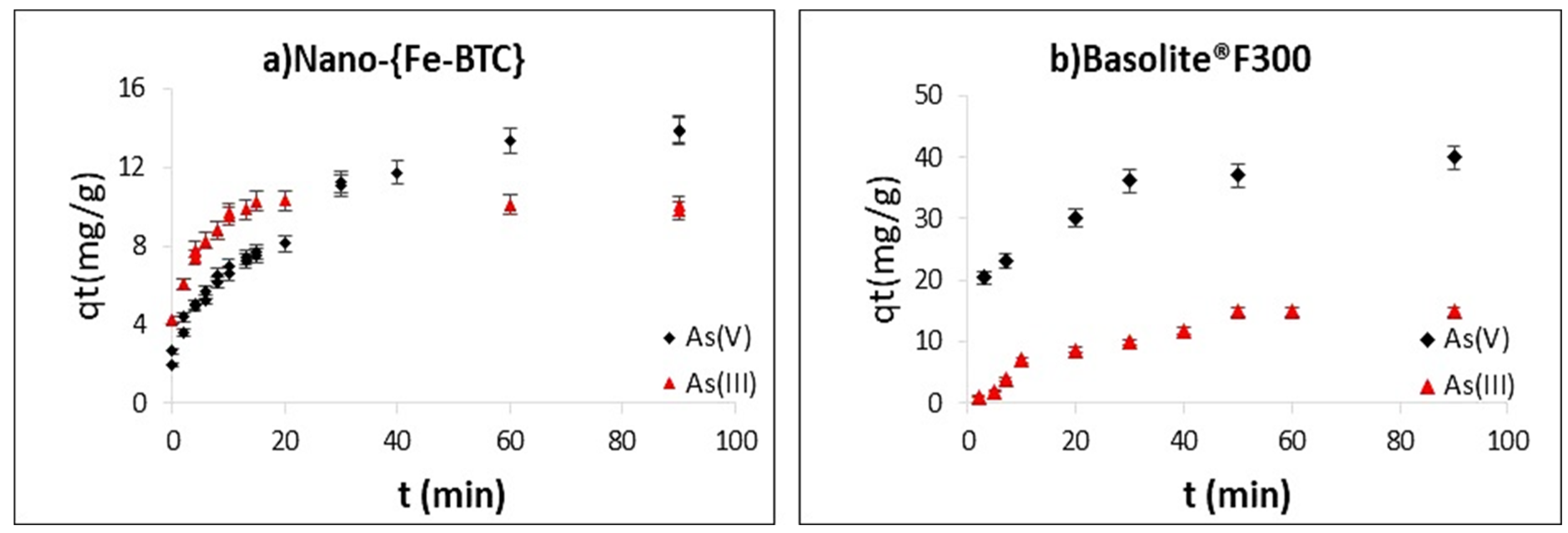
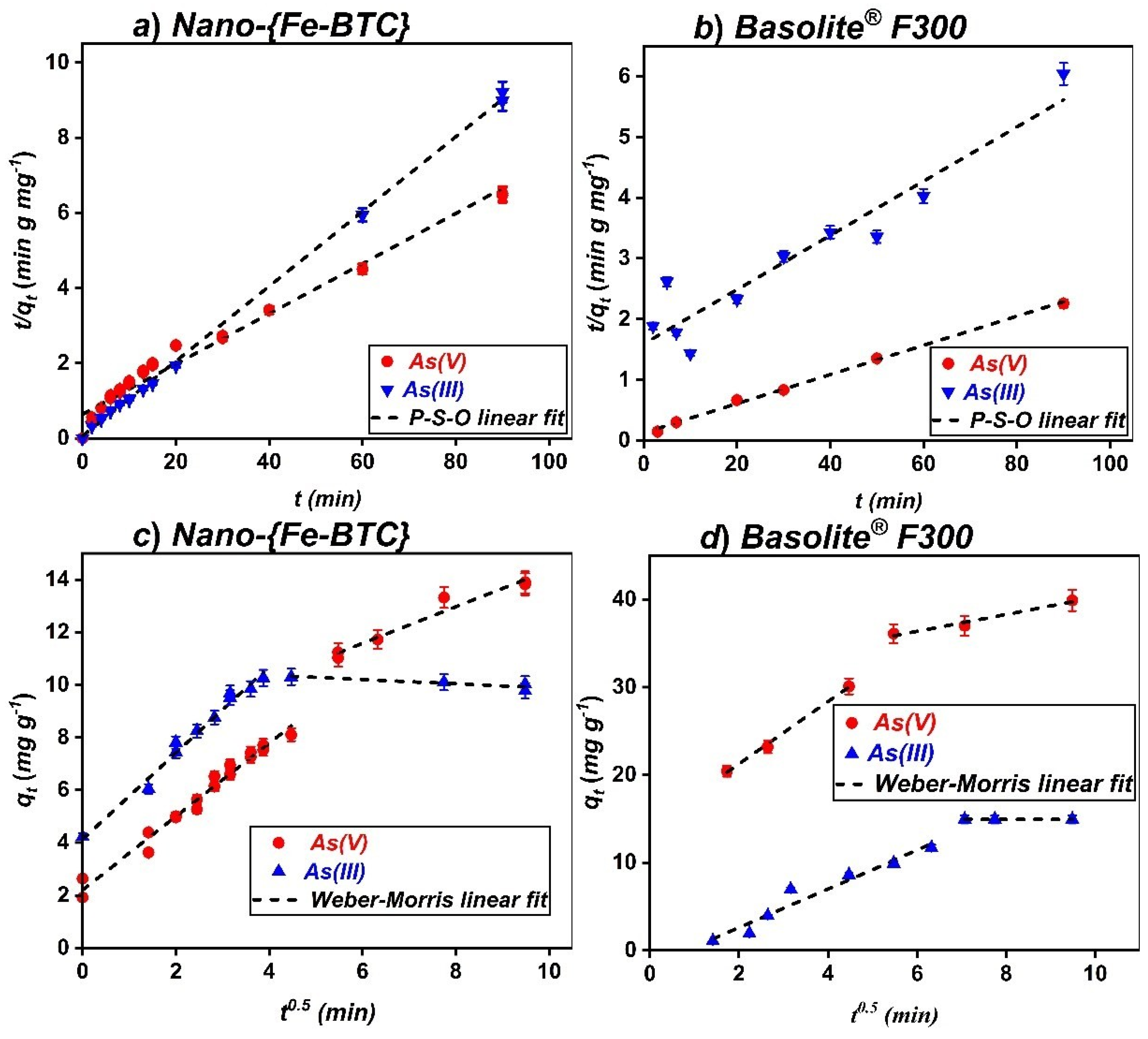
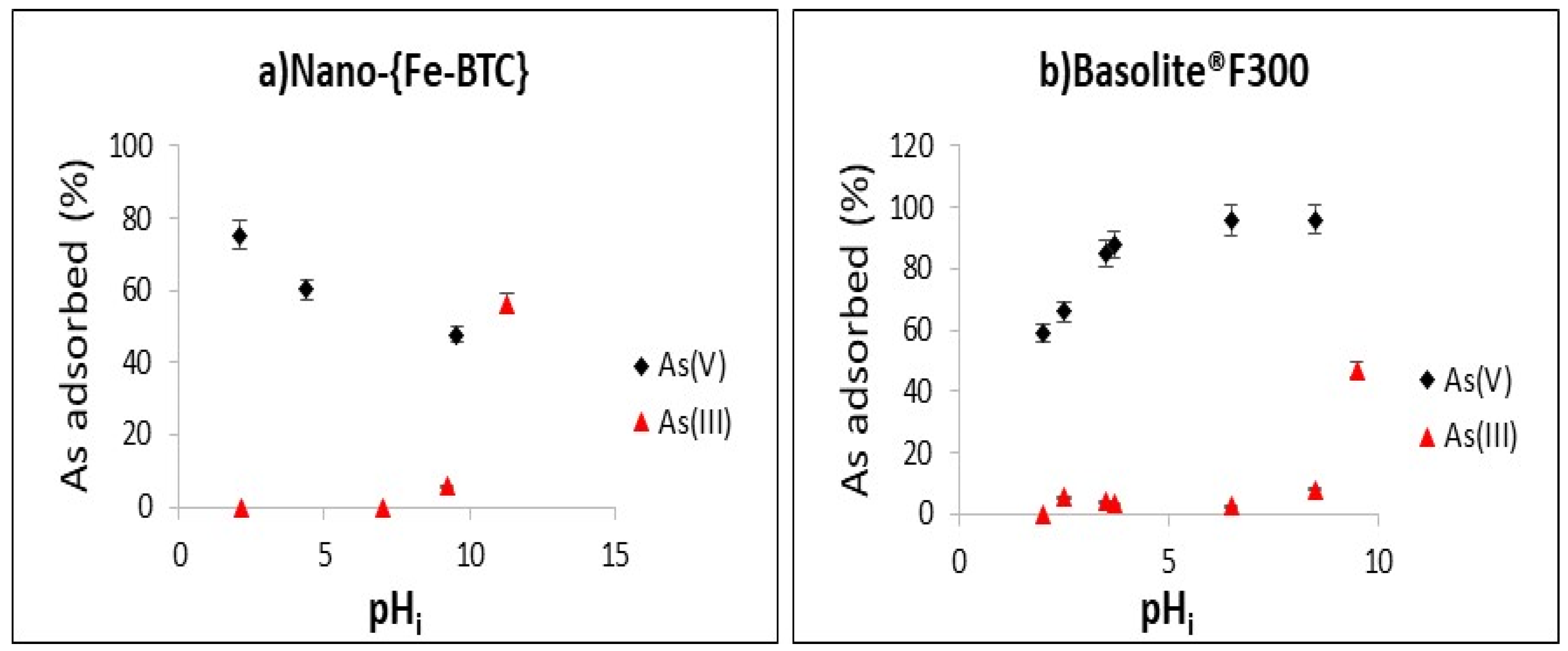

| Model | Parameters | Basolite® F300 | Nano-{Fe-BTC} | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) 50 rpm | (b) 20 rpm | (c) 20 rpm | ||||
| As(V) | As(III) | As(V) | As(V) | As(III) | ||
| PFO | qe (mg g−1) | 21.827 | 13.996 | 4.943 | 12.359 | 1.832 |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.044 | 0.037 | 0.090 | 0.053 | 0.025 | |
| R2 | 0.936 | 0.962 | 0.969 | 0.981 | 0.336 | |
| PSO | qe (mg g−1) | 41.667 | 22.222 | 12.195 | 14.925 | 10.000 |
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.075 | 0.007 | 0.156 | |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.904 | 0.999 | 0.974 | 0.999 | |
| Elovich M1 | α (mg g−1 min−1) | 85.426 | 1.889 | 271.792 | 7.142 | 19.427 |
| β (g mg−1) | 0.195 | 0.266 | 0.749 | 0.541 | 0.483 | |
| R2 | 0.980 | 0.948 | 0.992 | 0.962 | 0.987 | |
| Elovich M2 | α’ (mg g−1 min−1) | 3.26∙103 | - | 1.44∙106 | 6.55 | - |
| β’ (g mg−1) | 0.29 | −2.29∙1014 | 1.53 | 0.39 | −3.83 | |
| R2 | 0.94 | - | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.71 | |
| W-M M1 | KWM1 (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 3.552 | 2.203 | 1.216 | 1.392 | 1.643 |
| DWM1 | 14.142 | −1.812 | 6.334 | 2.209 | 4.122 | |
| R2 | 0.998 | 0.945 | 0.972 | 0.978 | 0.985 | |
| W-M M2 | KWM2 (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 0.968 | −1.02∙1015 | 0.230 | 0.696 | −0.081 |
| DWM2 | 30.554 | 14.900 | 10.459 | 7.400 | 10.683 | |
| R2 | 0.969 | - | 0.991 | 0.958 | 0.753 | |
| LF-D M1 | D | 0.040 | 0.037 | 0.112 | 0.036 | 0.202 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.907 | 0.998 | 0.933 | 0.975 | |
| LF-D M2 | D | 0.014 | - | 0.036 | 0.061 | −0.030 |
| R2 | 1.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.988 | 0.920 | |
| Nano-{Fe-BTC} | Basolite®F300 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Parameters | As(V) | As(III) | As(V) | As(III) |
| Langmuir | qm (mg g−1) | 13.61 | 12.20 | 16.16 | 11.72 |
| KL (L mg−1) | 1.05 | 1.99 | 2.38 | 0.17 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.94 | |
| SS(AIC) | 0.64 | 3.23 | - | 0.21 | |
| Freundlich | n | 4.84 | 4.76 | 2.02 | 1.39 |
| KF (L g−1) | 7.90 | 7.29 | 10.12 | 1.70 | |
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SS(AIC) | - | - | 1.12 | - | |
| Temkin | KT (L mg−1) | 44.76 | 39.82 | 80.65 | 2.52 |
| B (mg g−1) | 2.05 | 1.98 | 2.40 | 2.10 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.95 | |
| Redlich–Peterson | βRP | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.51 | 0.28 |
| KRP (L g−1) | 7.90 | 7.29 | 10.01 | 1.70 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |
| SS(AIC) | 4.07 | 6.29 | 6.19 | 0.37 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azri, A.; Amar, M.B.; Walha, K.; Fontàs, C.; Conde-González, J.E.; Salvadó, V.; Peña-Méndez, E.M. New Insights on Iron-Trimesate MOFs for Inorganic As(III) and As(V) Adsorption from Aqueous Media. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010036
Azri A, Amar MB, Walha K, Fontàs C, Conde-González JE, Salvadó V, Peña-Méndez EM. New Insights on Iron-Trimesate MOFs for Inorganic As(III) and As(V) Adsorption from Aqueous Media. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzri, Afef, Marwa Ben Amar, Khaled Walha, Clàudia Fontàs, José Elías Conde-González, Victoria Salvadó, and Eladia M. Peña-Méndez. 2025. "New Insights on Iron-Trimesate MOFs for Inorganic As(III) and As(V) Adsorption from Aqueous Media" Nanomaterials 15, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010036
APA StyleAzri, A., Amar, M. B., Walha, K., Fontàs, C., Conde-González, J. E., Salvadó, V., & Peña-Méndez, E. M. (2025). New Insights on Iron-Trimesate MOFs for Inorganic As(III) and As(V) Adsorption from Aqueous Media. Nanomaterials, 15(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010036









