Engineering Zn/Fe Mixed Metal Oxides with Tunable Structural and Magnetic Properties for Magnetic Particle Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
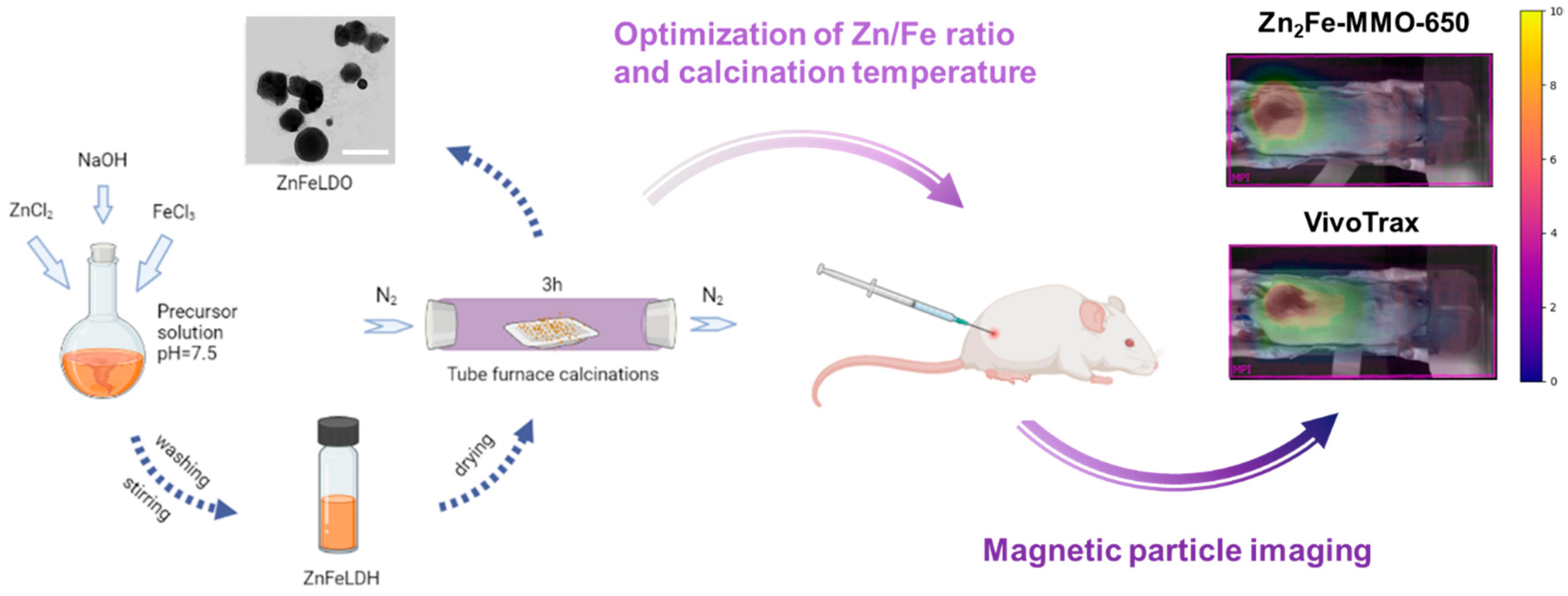
2.2. Synthesis of ZnFe-MMO Nanoparticles in Different Zn/Fe Ratios
2.3. Synthesis of Zn2Fe-MMO in Different Calcination Temperatures
2.4. Measurement of Saturation Magnetization
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cytotoxicity Study of Zn2Fe-MMO-650 Nanoparticles
2.7. Tumor Model
2.8. Magnetic Particle Imaging Evaluation
2.9. Characterization
3. Results
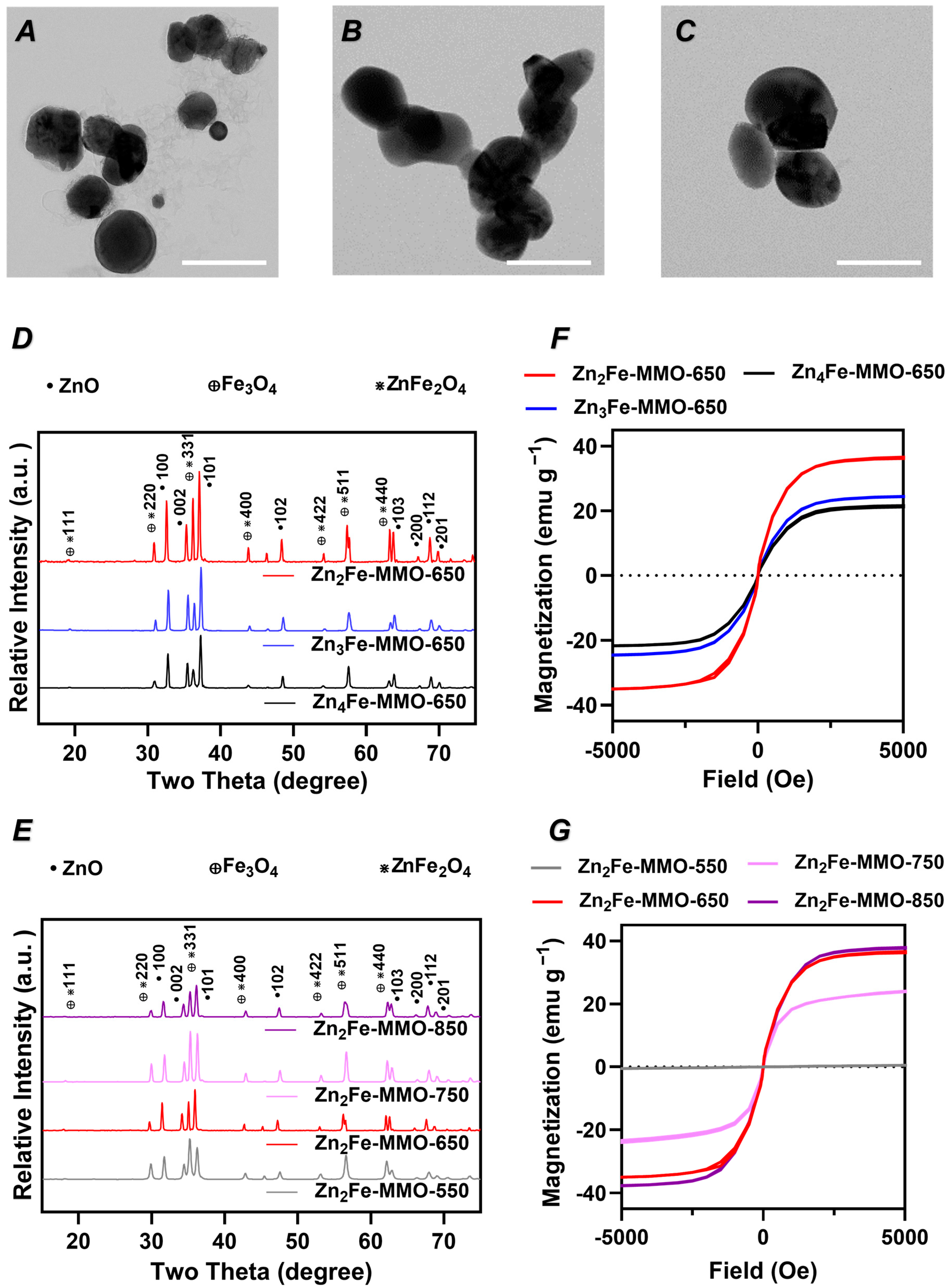
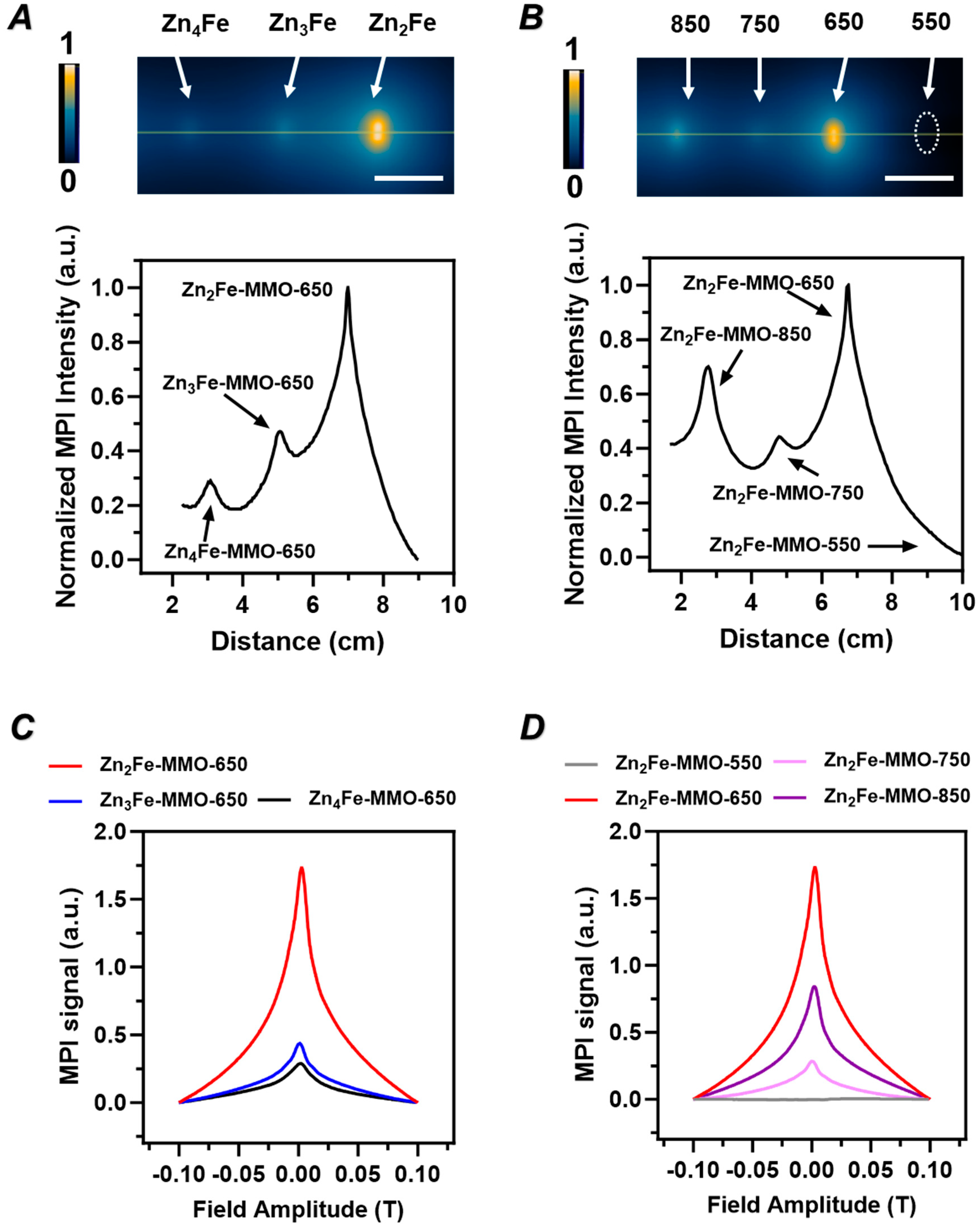
3.1. Effect of Zn/Fe Molar Ratio on Physicochemical Properties, Magnetic Properties, and MPI Signal of ZnFe-MMO Nanoparticles
3.2. Effect of Synthesis Temperature on Physicochemical Properties, Magnetic Properties, and MPI Signal of ZnFe-MMO
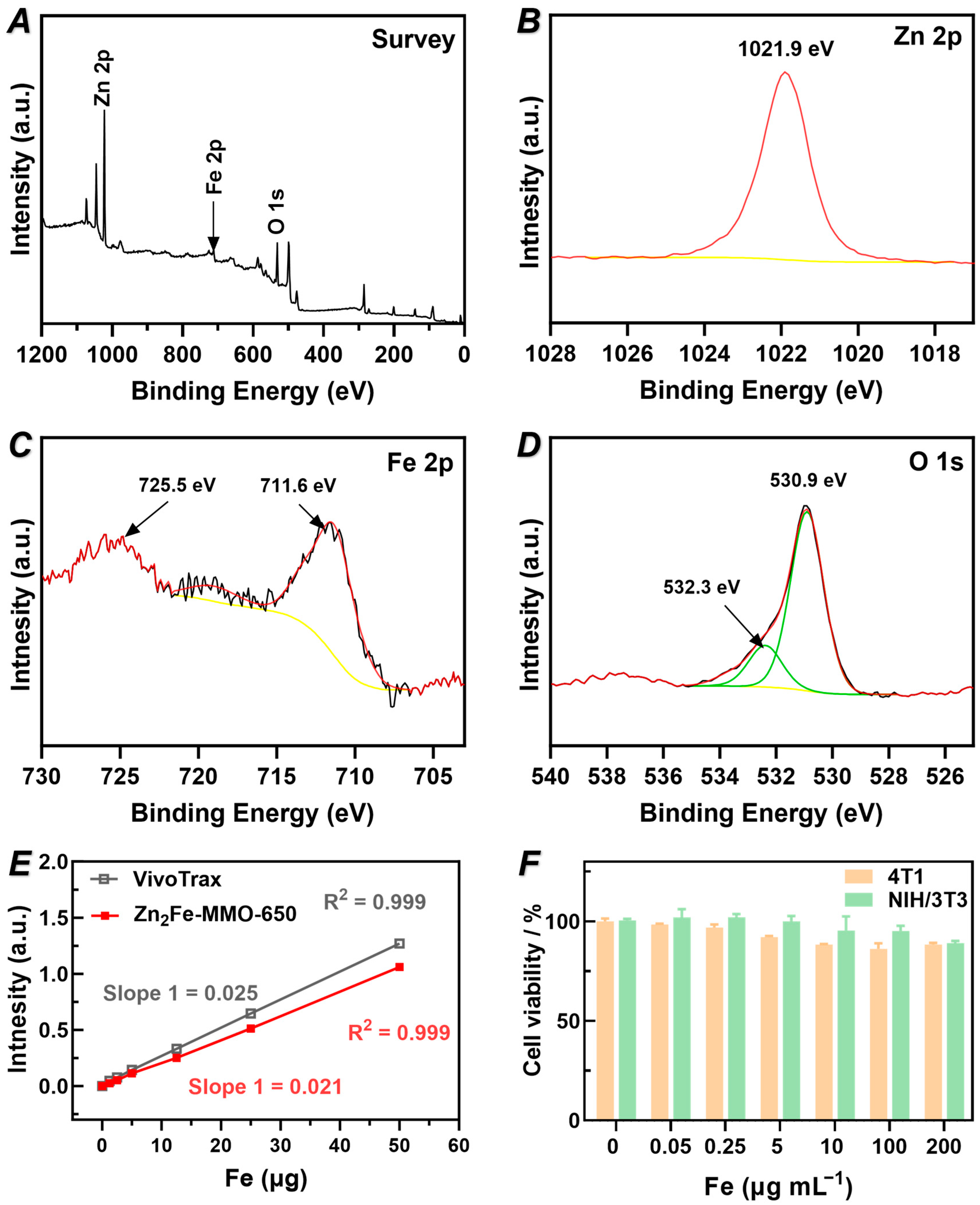
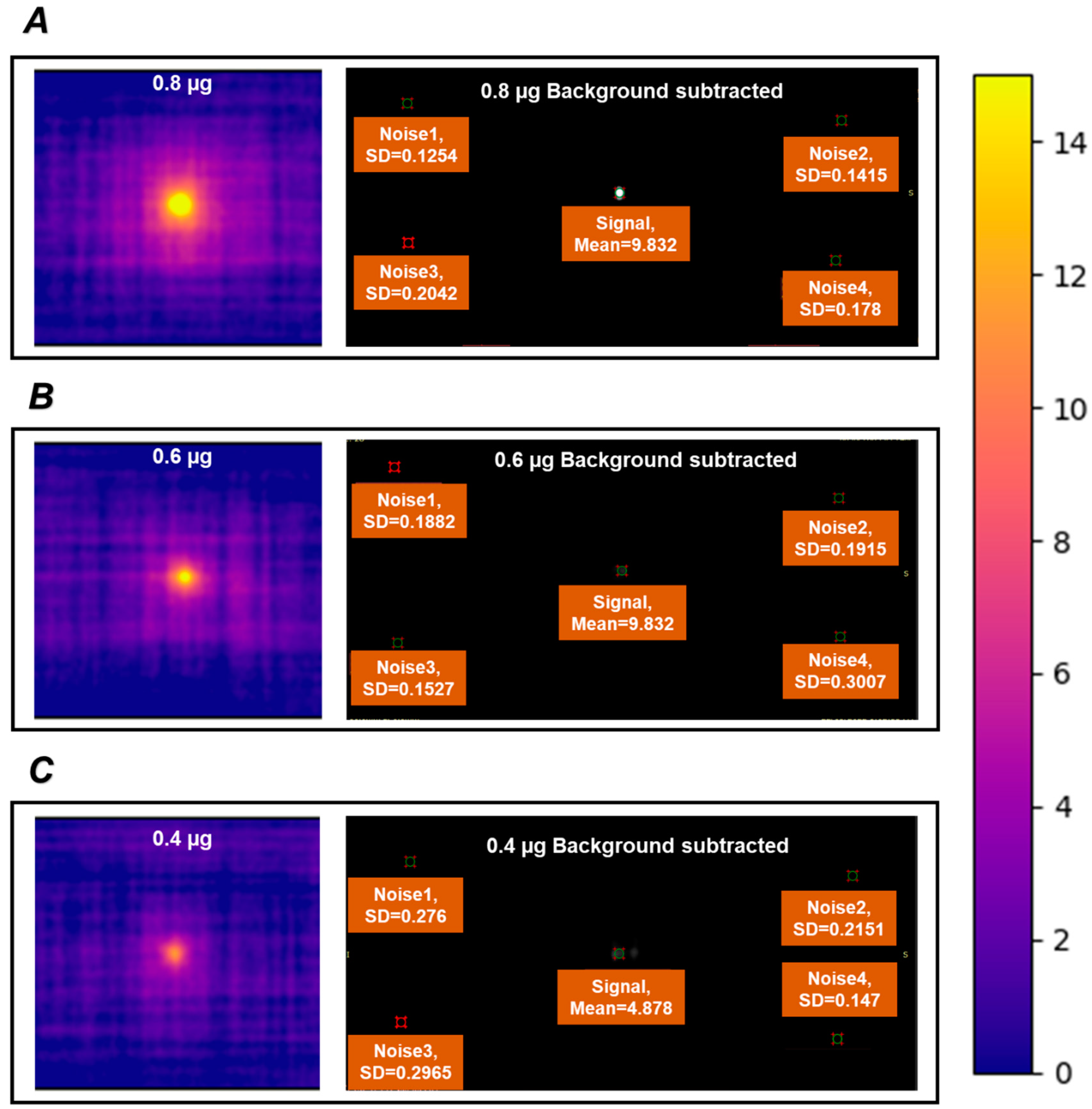
3.3. Chemical Composition, MPI Performance, and Cytotoxicity of Zn2Fe-MMO-650
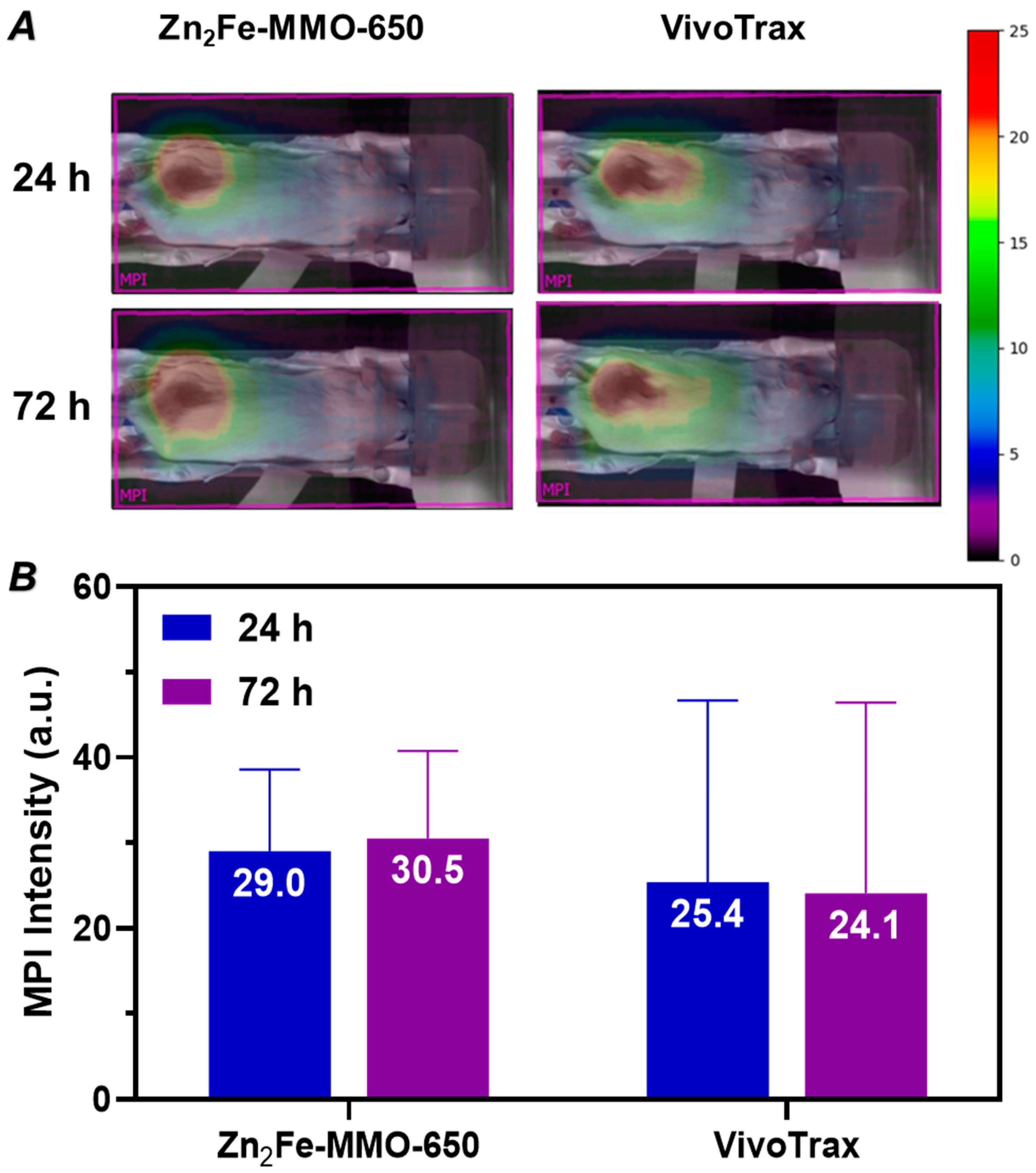
3.4. In Vivo MP Imaging Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, X.; Zhai, J.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Z.; Lo, P.-C.; Zhu, G.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Yang, M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: From Tracer Design to Biomedical Applications in Vasculature Abnormality. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2306450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleich, B.; Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 2005, 435, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebloo, N.; Gudi, M.; Robertson, N.; Wang, P. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current Applications in Biomedical Research. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanomaterials for In Vivo Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.; Jo, A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.-u.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Cheon, J. Engineered nanoparticles for clinical assays. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, Q.; Liang, X.-J.; Tian, J. Optimization and Design of Magnetic Ferrite Nanoparticles with Uniform Tumor Distribution for Highly Sensitive MRI/MPI Performance and Improved Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3618–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Z.W.; Hensley, D.; Ma, J.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Zheng, B.; Goodwill, P.; Conolly, S. Pulsed Excitation in Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2389–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Song, G.; Rao, J. Engineering of magnetic nanoparticles as magnetic particle imaging tracers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8102–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvell-Smith, S.; Tung, L.D.; Thanh, N.T.K. Magnetic particle imaging: Tracer development and the biomedical applications of a radiation-free, sensitive, and quantitative imaging modality. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 3658–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.K.; Abdibastami, A.; Gloag, L.; Barrera, L.; Gooding, J.J.; Tilley, R.D. A guide to the design of magnetic particle imaging tracers for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 13890–13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, X.; Liao, H.; Liang, Z.; Li, F.; Tian, J.; Ling, D. Artificially Engineered Cubic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle as a High-Performance Magnetic Particle Imaging Tracer for Stem Cell Tracking. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Chu, S.; Rao, J. A Magneto-Optical Nanoplatform for Multimodality Imaging of Tumors in Mice. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7750–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avugadda, S.K.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Niculaes, D.; Ju, M.; Lak, A.; Silvestri, N.; Nitti, S.; Roy, I.A.-O.; Samia, A.C.S.; Pellegrino, T. Uncovering the Magnetic Particle Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features of Iron Oxide Nanocube Clusters. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshkina, O.; Lajoinie, G.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Swider, E.; Cruz, L.J.; White, P.B.; Schweins, R.; Dolen, Y.; van Dinther, E.A.W.; van Riessen, N.K.; et al. Multicore Liquid Perfluorocarbon-Loaded Multimodal Nanoparticles for Stable Ultrasound and 19F MRI Applied to In Vivo Cell Tracking. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.T.; Nah, H.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, M.G.; Cheon, J. Critical enhancements of MRI contrast and hyperthermic effects by dopant-controlled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Dogan, N.; Bingolbali, A.; Aliew, F. Synthesis and characterization of NiFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles with different coating materials for magnetic particle imaging (MPI). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 537, 168150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, C.; Sra, A.K.; Chaubey, G.S.; Khemtong, C.; Liu, J.P.; Gao, J. Zinc ferrite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Chem. Commun. 2008, 19, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.P.; Gu, Z. 2D Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles: Recent Progress toward Preclinical/Clinical Nanomedicine. Small Methods 2019, 4, 1900343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Choi, G.; Choy, J.-H. Multifunctional Layered Double Hydroxides for Drug Delivery and Imaging. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Szerlauth, A.; Muráth, S.; Varga, G.; Szilagyi, I. Surface modification of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanoparticles with biopolymers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 191, 114590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K. Nanoarchitectured two-dimensional layered double hydroxides-based nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Stoichiometric Synthesis of Pure MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Co, and Ni) Spinel Ferrites from Tailored Layered Double Hydroxide (Hydrotalcite-Like) Precursors. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, S.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. From Layered Double Hydroxides to ZnO-based Mixed Metal Oxides by Thermal Decomposition: Transformation Mechanism and UV-Blocking Properties of the Product. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 3933–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Duong, H.T.; Abdibastami, A.; Gloag, L.; Bongers, A.; Shanehsazzadeh, S.; Nelson, M.; Cousins, A.; Bayat, N.; McCalmont, H.; Lock, R.B.; et al. Small zinc doped iron oxide tracers for magnetic particle imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 587, 171304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.; Cheong, S.; Boyer, C.; Wang, Z.; Yun, S.L.J.; Amal, R.; Gu, Z. Two-Dimensional Ultra-Thin Nanosheets with Extraordinarily High Drug Loading and Long Blood Circulation for Cancer Therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2200299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, T.; Palapa, N.R.; Mohadi, R.; Lesbani, A. Thermal reconstruction properties of ZnFe LDH prepared by facile hydrothermal route. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2242, 040058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Samaei, L. ZnFe-Cl nanolayered double hydroxide as a novel catalyst for sonocatalytic degradation of an organic dye. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Aguilar, C.A.; Diaz-Puerto, Z.J.; Tecuapa-Flores, E.D.; Thangarasu, P. Crystal Plane Impact of ZnFe2O4–Ag Nanoparticles Influencing Photocatalytical and Antibacterial Properties: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 33985–34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Luo, K.; Sun, J.; Gong, C.; Yao, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; et al. Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic removal of refractory pollutants by Zn/Fe mixed metal oxide derived from layered double hydroxide. Catal. Commun. 2017, 99, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bid, S.; Pradhan, S.K. Preparation of zinc ferrite by high-energy ball-milling and microstructure characterization by Rietveld’s analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.K.; Taha, M.; Zaher, A.; Amin, R.M. Understanding the physicochemical properties of Zn–Fe LDH nanostructure as sorbent material for removing of anionic and cationic dyes mixture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, D.; Mahmoud, R.; El-Salam, H.M.A.; Shehata, N. Utilization of residual zinc–iron-layered double hydroxide after methyl orange management as a new sorbent for wastewater treatment. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nie, J.; Zhao, J.; Yao, S.; Wang, J.; Feng, X. Prussian blue-derived transition metal oxide ZnO/ZnFe2O4 microcubes as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 21416–21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.M.; Situ, S.F.; Griswold, M.A.; Samia, A.C. High-performance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic particle imaging–guided hyperthermia (hMPI). Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12162–12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmer, J.; Wirtz, D.; Bontus, C.; Borgert, J.; Gleich, B. Interactive Magnetic Catheter Steering With 3-D Real-Time Feedback Using Multi-Color Magnetic Particle Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloag, L.; Mehdipour, M.; Ulanova, M.; Mariandry, K.; Nichol, M.A.; Hernández-Castillo, D.J.; Gaudet, J.; Qiao, R.; Zhang, J.; Nelson, M.; et al. Zero valent iron core–iron oxide shell nanoparticles as small magnetic particle imaging tracers. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3504–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Kenney, M.; Chen, Y.S.; Zheng, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.X.; Gambhir, S.S.; Dai, H.; Rao, J. Carbon-coated FeCo nanoparticles as sensitive magnetic-particle-imaging tracers with photothermal and magnetothermal properties. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Sun, B.; Shanehsazzadeh, S.; Bongers, A.; Gu, Z. Engineering Zn/Fe Mixed Metal Oxides with Tunable Structural and Magnetic Properties for Magnetic Particle Imaging. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231964
Zhang Q, Sun B, Shanehsazzadeh S, Bongers A, Gu Z. Engineering Zn/Fe Mixed Metal Oxides with Tunable Structural and Magnetic Properties for Magnetic Particle Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(23):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231964
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qianyi, Bing Sun, Saeed Shanehsazzadeh, Andre Bongers, and Zi Gu. 2024. "Engineering Zn/Fe Mixed Metal Oxides with Tunable Structural and Magnetic Properties for Magnetic Particle Imaging" Nanomaterials 14, no. 23: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231964
APA StyleZhang, Q., Sun, B., Shanehsazzadeh, S., Bongers, A., & Gu, Z. (2024). Engineering Zn/Fe Mixed Metal Oxides with Tunable Structural and Magnetic Properties for Magnetic Particle Imaging. Nanomaterials, 14(23), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231964







