Antibacterial Electrospun Membrane with Hierarchical Bead-on-String Structured Fibres for Wound Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
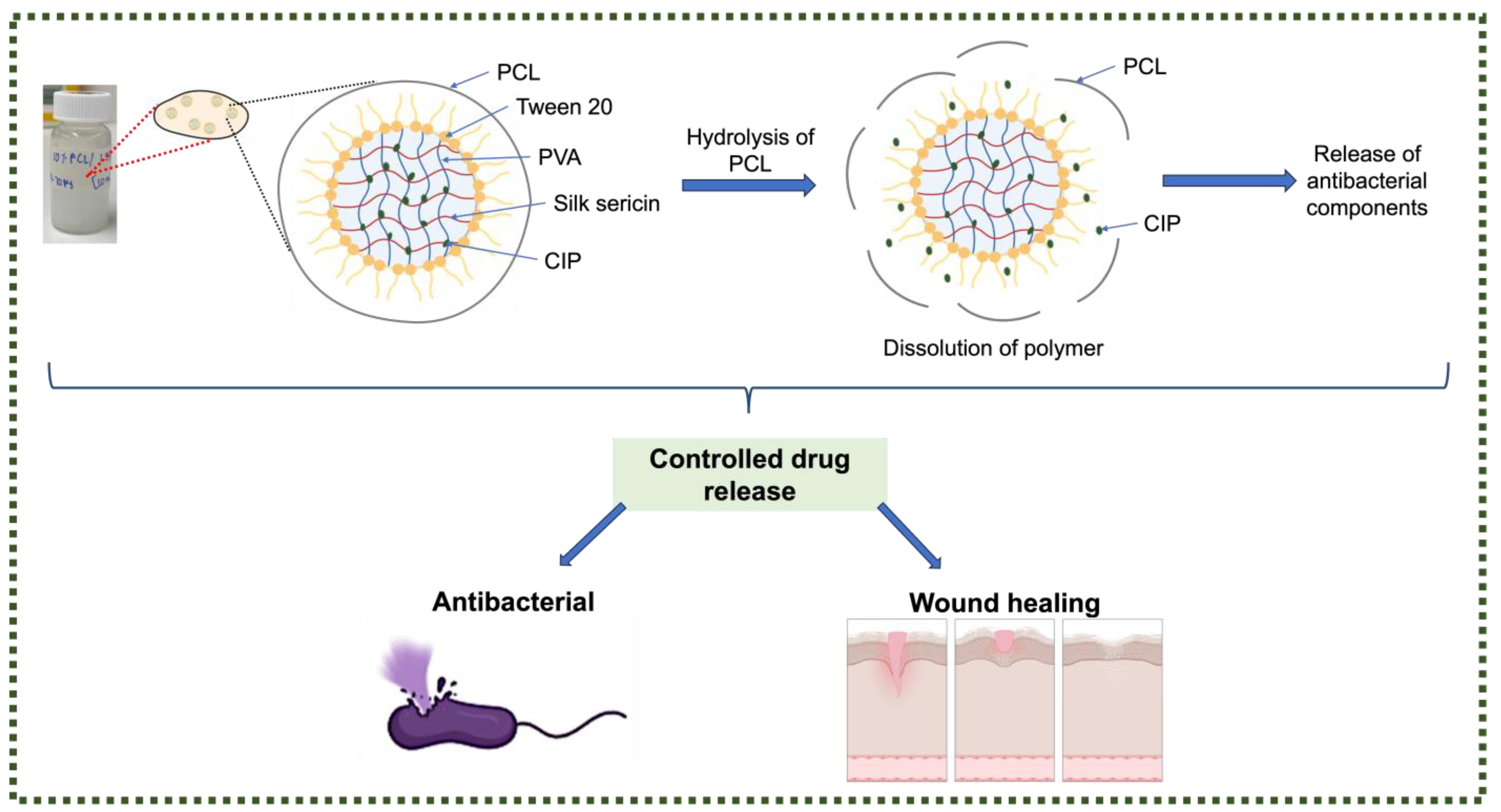
2.2.1. Nanofibre Fabrication
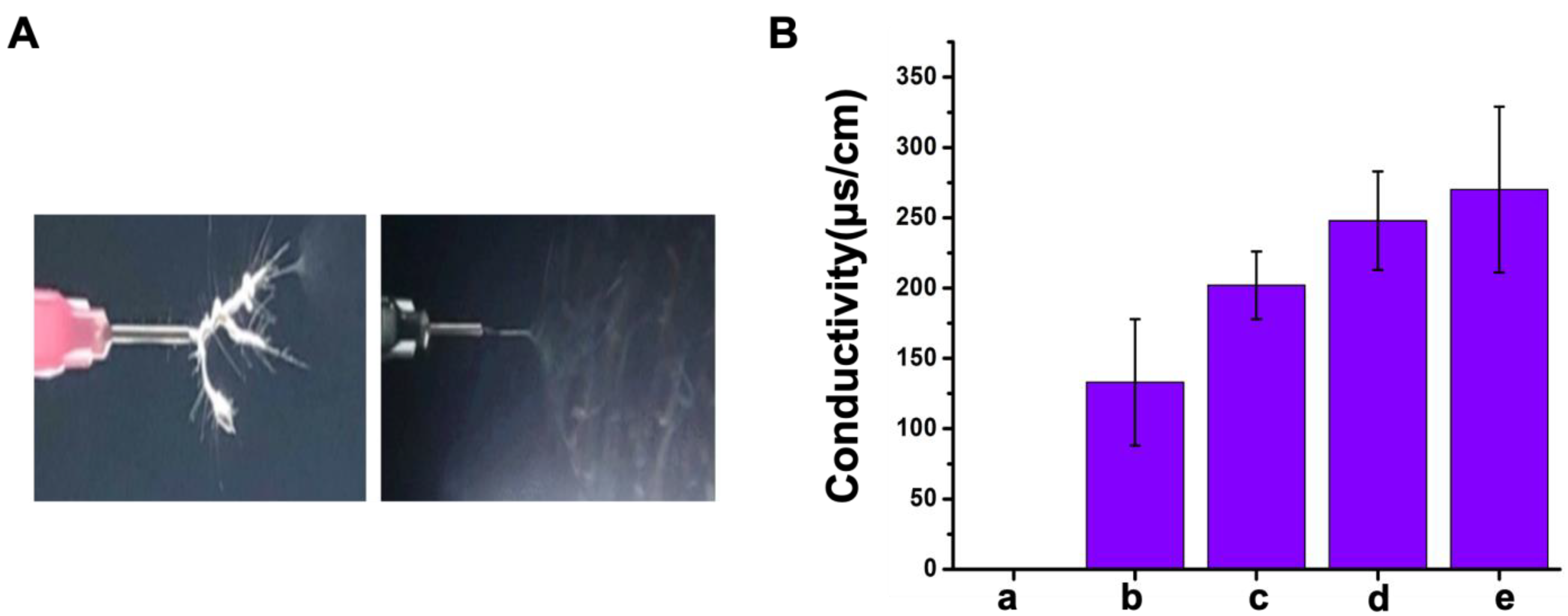
2.2.2. Viscosity and Conductivity of Polymer Emulsion
2.2.3. Morphological Structures
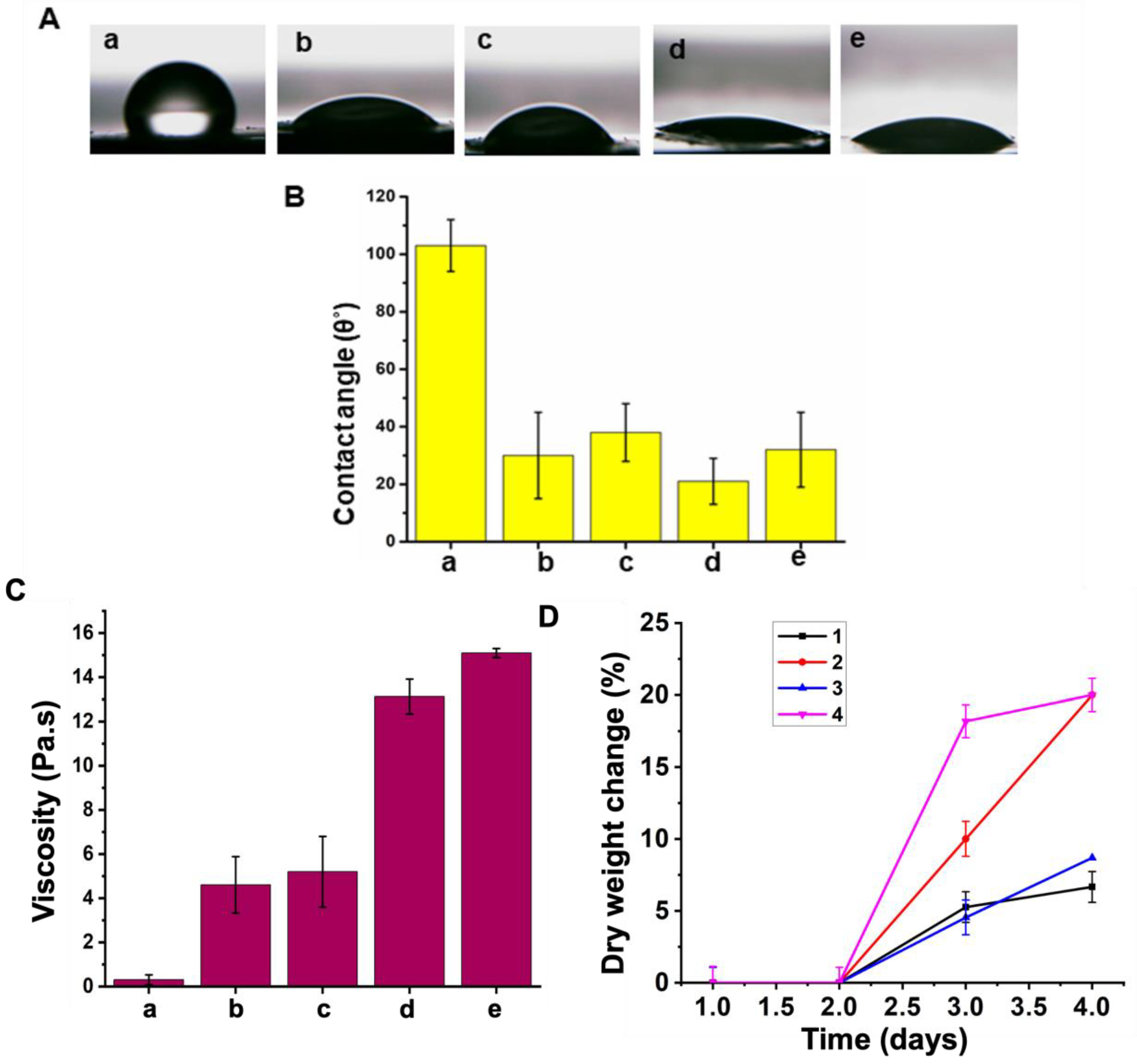
2.2.4. Wettability Analysis
2.2.5. Mass Loss Study
2.2.6. Antibacterial Assays
2.2.7. Cell Culture
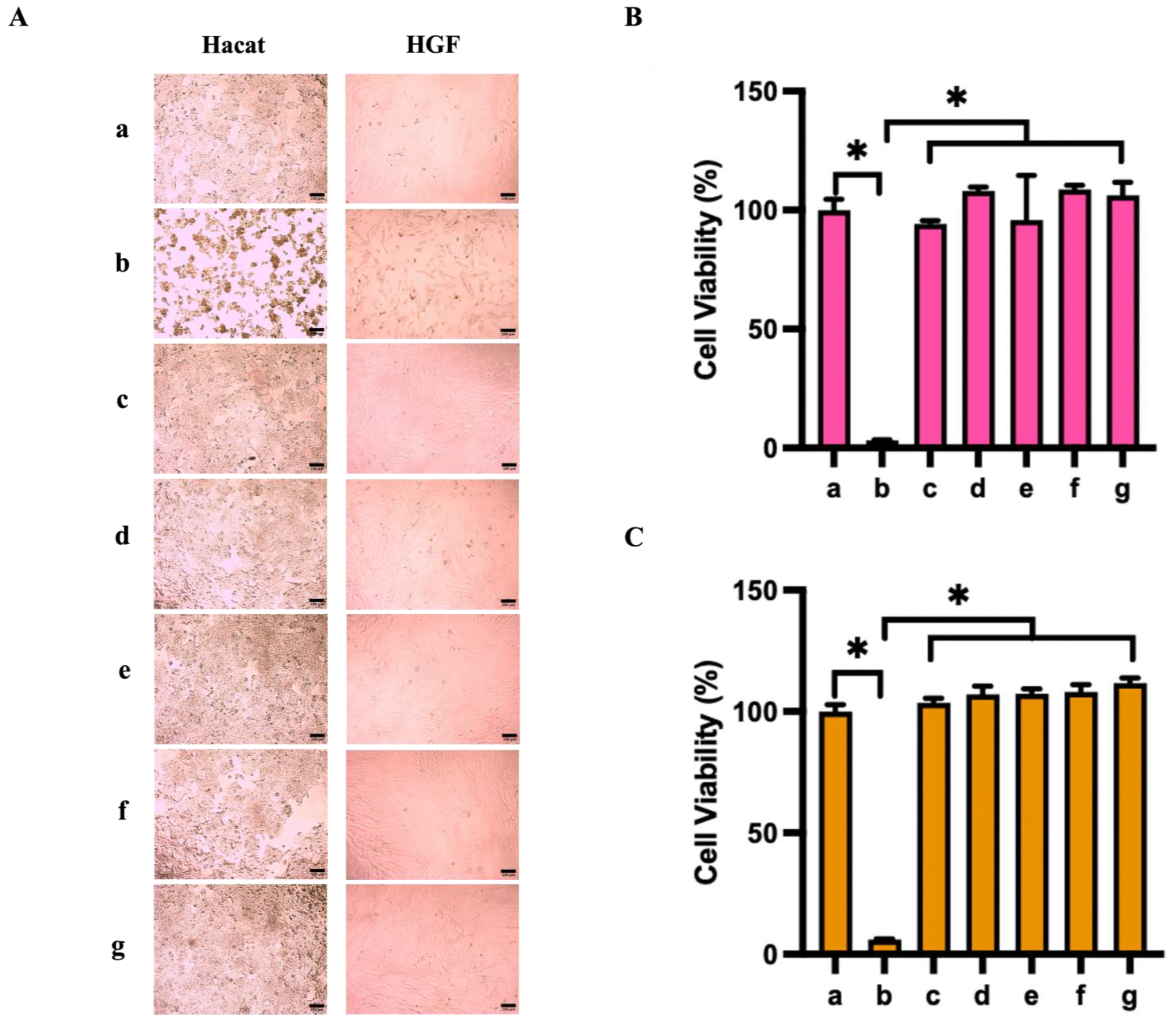
2.2.8. Cell Viability and Proliferation
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimal Parameters for Electrospinning
3.2. Fiber Morphology
3.3. Hydrophilicity
3.4. Mass Loss
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
3.6. Cytocompatibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; Rajeev, M.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Rice, B.L.; Takahashi, S.; Tatem, A.J.; Wagner, C.E.; Wang, L.-F. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arqué, X.; Torres, M.D.T.; Patiño, T.; Boaro, A.; Sánchez, S.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Autonomous Treatment of Bacterial Infections in Vivo Using Antimicrobial Micro- and Nanomotors. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7547–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Thambi, T.; Joe, A.; Han, H.-W.; Seo, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Conde, J.; Jang, E.-S. Progress in nanomaterial-based synergistic photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic therapy in combating bacterial infections. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, K.; Lu, X.; Zhai, X.; Wan, Z.; Gao, J. Highly active probiotic hydrogels matrixed on bacterial EPS accelerate wound healing via maintaining stable skin microbiota and reducing inflammation. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, G.; Xia, X.; Chen, H.; Feng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; et al. Guard against internal and external: An antibacterial, anti-inflammation and healing-promoting spray gel based on lyotropic liquid crystals for the treatment of diabetic wound. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 646, 123442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, W. A bioactive composite hydrogel dressing that promotes healing of both acute and chronic diabetic skin wounds. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 34, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, P.; Shen, X.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Nano-oxygenated hydrogels for locally and permeably hypoxia relieving to heal chronic wounds. Biomaterials 2022, 282, 121401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninan, N.; Forget, A.; Shastri, V.P.; Voelcker, N.H.; Blencowe, A. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory pH-Responsive Tannic Acid-Carboxylated Agarose Composite Hydrogels for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28511–28521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.; Ninan, N.; Nguyen, N.H.; Wang, J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Vasilev, K.; Truong, V.K.; Tang, Y. Antibacterial Plasma Coating with Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers to Prevent Surgical Site Infections. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2400053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkeren, E.; Diard, M.; Hardt, W.-D. Evolutionary causes and consequences of bacterial antibiotic persistence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, S.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, L.; Yang, L. Nanofiber scaffolds as drug delivery systems promoting wound healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, N.A.M.; Lin, W.-C. Accelerating the excisional wound closure by using the patterned microstructural nanofibrous mats/gentamicin-loaded hydrogel composite scaffold. Mater. Today Bio. 2022, 16, 100347. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, N.; Jha, D.; Roy, I.; Kumar, P.; Gaurav, S.S.; Marimuthu, K.; Ng, O.-T.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Verma, N.K.; Gautam, H.K. Nanobiotics against antimicrobial resistance: Harnessing the power of nanoscale materials and technologies. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Handy, R.D.; Upton, M.; Besinis, A. Review of antimicrobial nanocoatings in medicine and dentistry: Mechanisms of action, biocompatibility performance, safety, and benefits compared to antibiotics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7064–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, N.; Venugopal, D.; Gopinath, A.M.; Samavedi, S. Connecting in situ cone/jet length in electrospinning to fiber diameter and drug release for the rational design of electrospun drug carriers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 295, 120168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungenast, L.; Nieminen, R.; Gaiser, C.; Faia-Torres, A.B.; Rühe, J.; Suter-Dick, L. Electrospun decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds promote the regeneration of injured neurons. Biomater. Biosyst. 2023, 11, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Si, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ke, Q.; Hu, J. Electrospun textile strategies in tendon to bone junction reconstruction. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 764–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Lamprou, D.; Zhao, M. Electrospinning technologies for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals: Current status and future trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 651, 123641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, N.; Xing, D. Multi-material electrospinning: From methods to biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 21, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.S.; Mondal, J.; Hasan, M.N.; Revuri, V.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, Y.-K. Electrospinning nanofibers for therapeutics delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, G.; Carvajal Berrio, D.; Laurita, A.; Pepe, A.; Bochicchio, B.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Hinderer, S. Controlled and tuneable drug release from electrospun fibers and a non-invasive approach for cytotoxicity testing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.-F.; Carson, D.; Woodrow, K.A. Current strategies for sustaining drug release from electrospun nanofibers. J. Control Release 2015, 220, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Si, Y.; Guo, C.; Hu, J. Recent advances of electrospun strategies in topical products encompassing skincare and dermatological treatments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 331, 103236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Bedir, T.; Kalkandelen, C.; Başar, A.O.; Şaşmazel, H.T.; Ustundag, C.B.; Sengor, M.; Gunduz, O. Coaxial and emulsion electrospinning of extracted hyaluronic acid and keratin based nanofibers for wound healing applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 142, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M. Three-dimensional endothelial cell incorporation within bioactive nanofibrous scaffolds through concurrent emulsion electrospinning and coaxial cell electrospraying. Acta Biomater. 2021, 123, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Zhang, H.; Gao, B.; Shiu, B.-C.; Ren, H.-T.; Peng, H.-K.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Daylight-driven rechargeable, antibacterial, filtrating micro/nanofibrous composite membranes with bead-on-string structure for medical protection. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, J.G.; Harrison, S.; Hatton, P.V.; Murdoch, C.; Spain, S.G.; Colley, H.E. Electrospinning polymersomes into bead-on-string polyethylene oxide fibres for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals to mucosal epithelia. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 157, 213734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Electrospun core-shell bead-on-string nanofibers for sustained release of simvastatin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 678, 132516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombin, A.D.J.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Electrospinning of natural polymers for the production of nanofibres for wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, A.S.; Sood, M.; Deol, P.K.; Kaur, I.P. Synthetic polymer based electrospun scaffolds for wound healing applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, N.; Del Bakhshayesh, A.R.; Davaran, S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Common biocompatible polymeric materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Zamboulis, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Michailidou, G.; Noordam, M.J.; Bikiaris, D.N. Biocompatible synthetic polymers for tissue engineering purposes. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1841–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phutane, P.; Telange, D.; Agrawal, S.; Gunde, M.; Kotkar, K.; Pethe, A. Biofunctionalization and Applications of Polymeric Nanofibers in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Polymers 2023, 15, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakabad, F.S.T.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Zeighamian, V.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Ghanbarian, H.; Ranjbari, J.; Kazemi, B. Optimization of topography and surface properties of polyacrylonitrile-based electrospun scaffolds via nonoclay concentrations and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2021, 20, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.-J.; Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Silk Sericin Protein Materials: Characteristics and Applications in Food-Sector Industries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Reis, S.; Spencer, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Barros, L.; Vaz, J.A.; Coutinho, P. Silk sericin: A promising sustainable biomaterial for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilotra, S.; Chouhan, D.; Bhardwaj, N.; Nandi, S.K.; Mandal, B.B. Potential of silk sericin based nanofibrous mats for wound dressing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista-Silva, S.; Borges, S.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Costa, R.; Amorim, M.; Dias, J.R.; Ramos, O.; Alves, P.; Granja, P.L.; Soares, R. In situ forming silk sericin-based hydrogel: A novel wound healing biomaterial. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, B.; Hemavathi, A.; Panda, P. Poly (ε-caprolactone)-based electrospun nano-featured substrate for tissue engineering applications: A review. Prog. Biomater. 2021, 10, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qian, Y.; Lin, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, C.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W.; Cai, K.; Germershaus, O.; Yang, L. The effect of silk gland sericin protein incorporation into electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers on in vitro and in vivo characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnthip, N.; Teeka, J.; Kantha, P.; Teepoo, S.; Damjuti, W. Fabrication and characterization of polycaprolactone/cellulose acetate blended nanofiber mats containing sericin and fibroin for biomedical application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, M.C.; Montoya, Y.; Peresin, M.S.; Bustamante, J.; Álvarez-López, C. Silk sericin as a biomaterial for tissue engineering: A review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.; Zou, M.; Cai, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Silk sericin-based materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoolaert, E.; Cossu, L.; Becelaere, J.; Van Guyse, J.F.; Tigrine, A.; Vergaelen, M.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Clerck, K. Nanofibers with a tunable wettability by electrospinning and physical crosslinking of poly (2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline). Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi, H.; Fazilati, M.; Hashemi, M.; Noshirvani, N. Novel carboxymethyl cellulose-polyvinyl alcohol blend films stabilized by Pickering emulsion incorporation method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Jahng, K.Y. An improved hydrophilicity via electrospinning for enhanced cell attachment and proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2006, 78, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlen, M.; Lavrič, Z.; Prestidge, C.; Dreu, R. Preparation, physicochemical characterisation and DoE optimisation of a spray-dried dry emulsion platform for delivery of a poorly soluble drug, simvastatin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C. Surface modification and property analysis of biomedical polymers used for tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 60, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, S.; Honaker, L.W.; Frey, M.W.; Basoli, F.; Lagerwall, J.P. Electrospinning ethanol–water solutions of poly (acrylic acid): Nonlinear viscosity variations and dynamic Taylor cone behavior. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; Teoh, X.Y.; Le Hwang, J.; Khong, Z.P.; Sejare, R.; Almashhadani, A.Q.; Abou Assi, R.; Chan, S.Y. Electrospinning and its potential in fabricating pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramariuc, B.; Cramariuc, R.; Scarlet, R.; Manea, L.R.; Lupu, I.G.; Cramariuc, O. Fiber diameter in electrospinning process. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Ju, J.E.; Shin, M.; Holland, C.; Lee, K.H. Sericin promotes fibroin silk I stabilization across a phase-separation. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Conductive electrospun nanofiber mats. Materials 2019, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, W. Nanofiber spraying method using a supplementary electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 013111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleyas, A.; Bakar, S.; Halif, N.; Yahud, S. The effect of flow rate, concentration, and voltage on diameter of pan precursor fiber by electrospinning technique. J. Built Environ. Technol. Eng 2017, 2, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Amariei, N.; Manea, L.; Bertea, A.; Bertea, A.; Popa, A. The influence of polymer solution on the properties of electrospun 3D nanostructures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla-Botero, J.; Alvarez-Lainez, M.; Lagaron, J. The influence of electrospinning parameters and solvent selection on the morphology and diameter of polyimide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodana, M.; Nistor, C.-E.; Stoian, A.B.; Ionita, D.; Burnei, C. Dual nanofibrous bioactive coatings on TiZr implants. Coatings 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.; Gomes, V.G. Interactions at scaffold interfaces: Effect of surface chemistry, structural attributes and bioaffinity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.; Oliver, S.; Wong, E.H.; Boyer, C. Effect of hydrophilic groups on the bioactivity of antimicrobial polymers. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 5689–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Liang, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, L. Recent advance in surface modification for regulating cell adhesion and behaviors. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, D.P.; Miller, I.S.; Ardhaoui, M.; Gallagher, W.M. Effect of surface wettability and topography on the adhesion of osteosarcoma cells on plasma-modified polystyrene. J. Biomater. Appl. 2011, 26, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yoshinari, M.; Takemoto, S.; Hattori, M.; Kawada, E.; Liu, B.; Oda, Y. Adhesion of mouse fibroblasts on hexamethyldisiloxane surfaces with wide range of wettability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2007, 81, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, Y.; Ikada, Y. Effect of preadsorbed proteins on cell adhesion to polymer surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 155, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Campos, E.V.R.; Fraceto, L.F.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Mariano, K.C.F.; de Araujo, D.R.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Grillo, R.; Patra, J.K. Sericin based nanoformulations: A comprehensive review on molecular mechanisms of interaction with organisms to biological applications. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, S.; Qu, Y.; Waddington, L.J.; Easton, C.D.; Glattauer, V.; Lithgow, T.J.; McLean, K.M.; Forsythe, J.S.; Hartley, P.G. Self-assembly of ciprofloxacin and a tripeptide into an antimicrobial nanostructured hydrogel. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yao, T.; Ren, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Antibacterial PCL electrospun membranes containing synthetic polypeptides for biomedical purposes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, N.H.; Jadhav, N.R.; More, H.N.; Jadhav, A.D. Screening of drug-sericin solid dispersions for improved solubility and dissolution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamboni, L.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q. Silk sericin: A versatile material for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Qin, S.; Liu, J.; Lv, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.s.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Development and Application of an Advanced Biomedical Material-Silk Sericin. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2311593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Duan, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, M.; Liang, H.; Peng, G.; Yang, X.; Si, Y.; Yi, S. Multifunctional and Sprayable 2D MoS2/Silk Sericin Bio-Nanocomposite Dressings with Enhanced Photothermal Effect for Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X. Enhanced biocompatibility of silk sericin/caffeic acid nanoparticles by red blood cell membranes cloaking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.; Talukdar, S.; Kundu, S.C. Potential of 2D crosslinked sericin membranes with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badmus, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Radacsi, N.; Zhao, Y. Hierarchically electrospun nanofibers and their applications: A review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 3, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of Humidity and Solution Viscosity on Electrospun Fiber Morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.-Y. Effect of needle length, electrospinning distance, and solution concentration on morphological properties of polyamide-6 electrospun nanowebs. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Sari, T.I.; Anggoro, D. Effect of Concentration and Nozzle-Collector Distance on the Morphology of Nanofibers. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 860, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Fang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Jin, G.; Diao, G. Electrospinning of Calixarene-Functionalized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Membranes and Application as an Adsorbent and Catalyst Support. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11858–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lee, I.-H. Controlled release of ketoprofen from electrospun porous polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibers. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 18, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.-H.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.-J.; Lou, W.-Y.; Li, N.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid nanofilm incorporating cinnamon essential oil/ β -cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antimicrobial packaging. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hazeem, N.Z. Effect of the Distance between the Needle Tip and the Collector on Nanofibers Morphology. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Open Access 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Initial Concentration (μg/mL) | Final Concentration (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 140 | 3.0 |
| 3 | 320 | 7.0 |
| Viscosity | Conductivity | Environmental Condition | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–15 Pa·s | >100 μS/cm | T: 23 °C | 12.5 cm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fong, Y.X.; Pakrath, C.; Kadavan, F.S.P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Luu, T.Q.; Stoilov, B.; Bright, R.; Nguyen, M.T.; Ninan, N.; Tang, Y.; et al. Antibacterial Electrospun Membrane with Hierarchical Bead-on-String Structured Fibres for Wound Infections. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171429
Fong YX, Pakrath C, Kadavan FSP, Nguyen TT, Luu TQ, Stoilov B, Bright R, Nguyen MT, Ninan N, Tang Y, et al. Antibacterial Electrospun Membrane with Hierarchical Bead-on-String Structured Fibres for Wound Infections. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(17):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171429
Chicago/Turabian StyleFong, Yu Xuan, Catherine Pakrath, Fathima Shana Pattar Kadavan, Tien Thanh Nguyen, Trong Quan Luu, Borislav Stoilov, Richard Bright, Manh Tuong Nguyen, Neethu Ninan, Youhong Tang, and et al. 2024. "Antibacterial Electrospun Membrane with Hierarchical Bead-on-String Structured Fibres for Wound Infections" Nanomaterials 14, no. 17: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171429
APA StyleFong, Y. X., Pakrath, C., Kadavan, F. S. P., Nguyen, T. T., Luu, T. Q., Stoilov, B., Bright, R., Nguyen, M. T., Ninan, N., Tang, Y., Vasilev, K., & Truong, V. K. (2024). Antibacterial Electrospun Membrane with Hierarchical Bead-on-String Structured Fibres for Wound Infections. Nanomaterials, 14(17), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171429












