In-Situ Hydrothermal Fabrication of ZnO-Loaded GAC Nanocomposite for Efficient Rhodamine B Dye Removal via Synergistic Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO-Loaded Activated Carbon (ZnO@GAC)
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Photocatalytic Degradation Test
2.5. Batch Adsorption Test
2.6. Stability Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
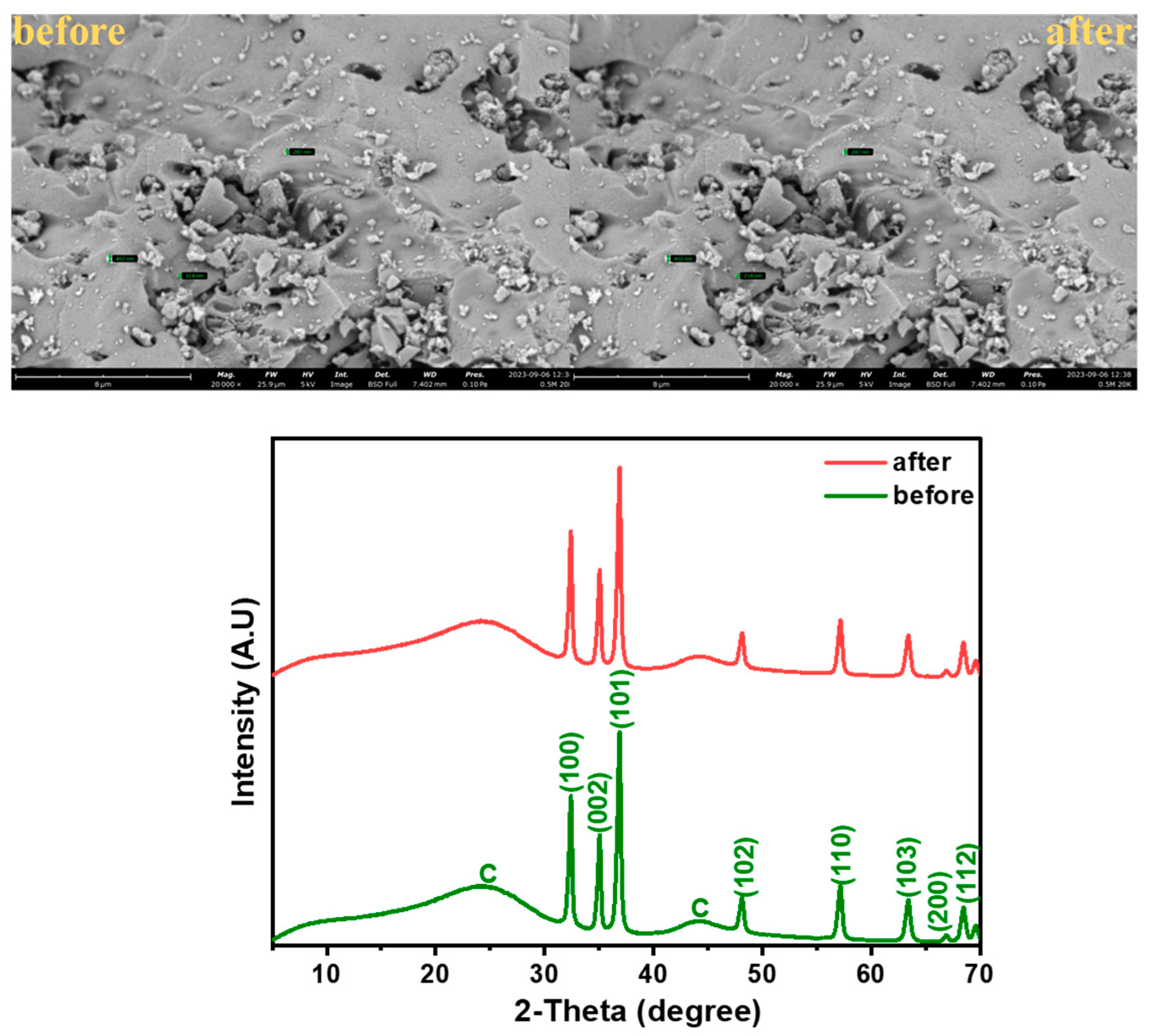
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
3.1.2. BET Measurement
3.1.3. SEM/EDX Analysis
3.1.4. TGA/DTG Analysis
3.2. Photocatalytic Performance
3.3. Stability Test and TOC Removal
3.4. Adsorptive Performance
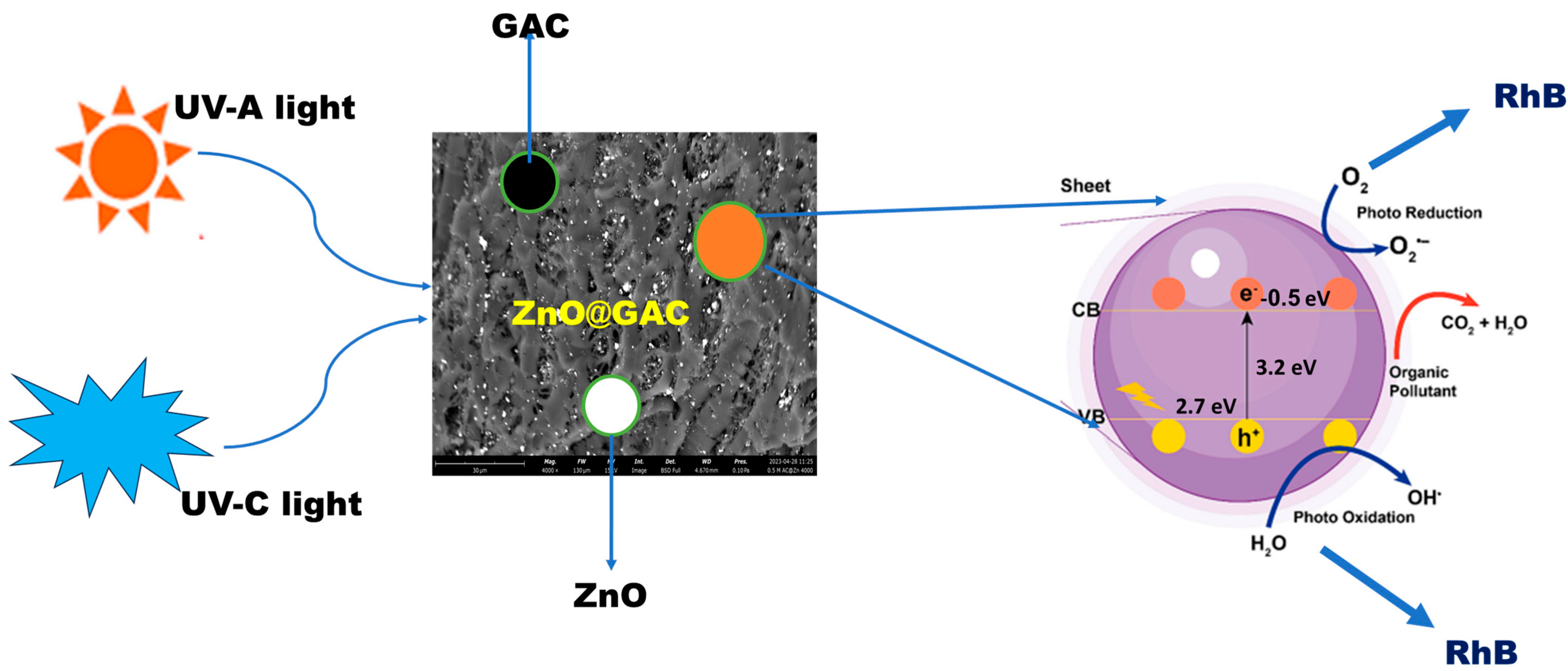
3.5. Plausible Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanism
| Catalyst | Irradiation Time (min) | Light Source | PDE (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTh/Ag3PO4/BiOI/Ti– Cu2O/Cu | 120 | Visible light | 96 | [75] |
| MTiO3@EDFG | 120 | Visible light | 91 | [53] |
| SnFe2O4/Bi2WO6 | 120 | 350-W xenon lamp | 96 | [54] |
| H [K2Ag9(DPT)7 (u-2-O)2(H2O)4][SiW12O40]2 | 300 | UV light radiation | 76 | [76] |
| AgNPs@ZnO | 180 | 500 W Xe lamp | 95 | [77] |
| Zn0.5Mn0.5Ce0.08Fe1.92O4 | 180 | Visible light | 97 | [78] |
| TiO2/rGO (5%) | 120 | Visible light | 95 | [79] |
| Co3O4/ZnFe2O4 | 240 | UV light | 93 | [80] |
| ZnO: Mo/rGO films | 120 | Sunlight | 68 | [81] |
| MoS2/PMS | 120 | Visible light | 90 | [66] |
| 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 120 | UV-A light | 82 | This study |
| 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 120 | UV-C light | 97 | This study |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nasr, R.A.; Ali, E.A. Polyethersulfone/gelatin nano-membranes for the Rhodamine B dye removal and textile industry effluents treatment under cost effective condition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Renteria, E.; Oliva, J.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V. A sustainable and green chlorophyll/TiO2:W composite supported on recycled plastic bottle caps for the complete removal of Rhodamine B contaminant from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivio, R.K.O.; Go, A.W.; Angkawijaya, A.E.; Santoso, S.P.; Gunarto, C.; Soetaredjo, F.E. Extractives-free sugarcane bagasse as adsorbent for the removal of Rhodamine B (Basic Violet 10) with high capacity and reusability. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 124, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.S.; Aziz KH, H. Heterogeneous catalytic activation of persulfate for the removal of rhodamine B and di-clofenac pollutants from water using iron-impregnated biochar derived from the waste of black seed pomace. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Adegoke, O.R.; Araoye, A.O.; Ogunmodede, J.; Agboola, O.S.; Bello, O.S. Engineered raw, carbonaceous, and modified biomass-based adsorbents for Rhodamine B dye removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, U.; Banerjee, D.; Das, D.; Sarkar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Photo-induced catalytic removal of rhodamine-B by aligned silicon nanowires developed through metal assisted chemical etching. Mater. Charact. 2022, 188, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-N.; Kim, S.; Her, N.; Choong, C.E.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Performance assessment and opti-mization of forward osmosis–low pressure ultrafiltration hybrid system using machine learning for rhodamine B removal. Desalination 2022, 543, 116102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbani, P.; Mehrizad, A. Preparation and characterization of graphitic carbon nitrides/polyvinylidene fluoride ad-sorptive membrane modified with chitosan for Rhodamine B dye removal from water: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Park, C.M.; Meenakshi, S. Designed fabrication of sulfide-rich bi-metallic-assembled MXene layered sheets with dramatically enhanced photocatalytic performance for Rhodamine B removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lu, B.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Q. Fe-Mo-O doping g-C3N4 exfoliated composite for removal of rhodamine B by advanced oxidation and photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, F.; Razak, A.S.A.; Krishnan, S.; Zularisam, A.; Nasrullah, M. A review of eco-sustainable techniques for the removal of Rhodamine B dye utilizing biomass residue adsorbents. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 128, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. C, F co-doping Ag/TiO2 with UV-light photocatalytic performance toward degrading Rhodamine B. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Q. Two polyoxometalates based on (P2Mo5) catalysts: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation of RhB. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, O.; Obayomi, K.S.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Folarin, O. Bioremediation of artificially contaminated soil with petroleum using animal waste: Cow and poultry dung. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1721409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of graphene oxide/4A molecular sieve composite and evaluation of adsorption performance for Rhodamine B. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Gu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, G. Review on multi-dimensional assembled S-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 160, 214–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haounati, R.; Ighnih, H.; Malekshah, R.E.; Alahiane, S.; Alakhras, F.; Alabbad, E.; Alghamdi, H.; Ouachtak, H.; Addi, A.A.; Jada, A. Exploring ZnO/Montmorillonite photocatalysts for the removal of hazardous RhB Dye: A combined study using molecular dynamics simulations and experiments. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noukelag, S.K.; Razanamahandry, L.C.; Ntwampe, S.K.; Arendse, C.J.; Maaza, M. Industrial dye removal using bio-synthesized Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asjadi, F.; Yaghoobi, M. Characterization and dye removal capacity of green hydrothermal synthesized ZnO nanopar-ticles. Ceram. Int. 2023, 48, 27027–27038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Bimetallic CuPd alloy nanoparticles decorated ZnO nanosheets with enhanced photocata-lytic degradation of methyl orange dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, R.; Sethuraman, M.G. Pd-ZnO nanoparticles decorated acid activated montmorillonite for the efficient removal of cationic dyes from water. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1278, 134910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazazi, S.; Jodeyri, S.; Hosseini, S.P.; Arsalani, N.; Rashidzadeh, B.; Fathalipour, S.; Seidi, F.; Hashemi, E. Ball mill-hydrothermal method for one-step synthesis of zinc oxide/carbon quantum dot (ZnO-CQD) nanocomposites as photo-catalyst for degradation of organic pollutants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 445, 115096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohzadi, S.; Maleki, A.; Bundschuh, M.; Vahabzadeh, Z.; Johari, S.A.; Rezaee, R.; Shahmoradi, B.; Marzban, N.; Amini, N. Doping zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles with molybdenum boosts photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine b (RhB): Particle characterization, degradation kinetics and aquatic toxicity testing. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Cai, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, L.; Su, P. Constructing BiOCl/ZnO heterojunction from Bi-MOF for efficient photocatalytic degradation performance. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 140, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yu, M. Green and facile fabrication of nano-ZnO coated cellulose/starch/activated carbon hydrogel for enhanced dyes adsorption and antibacterial activity. Mater. Commun. 2022, 33, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packialakshmi, J.S.; Albeshr, M.F.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Selvankumar, T.; Mythili, R. Development of ZnO/SnO2/rGO hybrid nanocomposites for effective photocatalytic degradation of toxic dye pollutants from aquatic ecosys-tems. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machrouhi, A.; Khiar, H.; Elhalil, A.; Sadiq, M.; Abdennouri, M.; Barka, N. Synthesis, characterization, and photo-catalytic degradation of anionic dyes using a novel ZnO/activated carbon composite. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Azizah, D.A.; Kumoro, A.C.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman MH, D. Fabrication, characterization, and application of PSf/Ni@ZnO amalgamated membrane for photocatalytic degradation of dyeing wastewater from batik industry. Mater. Chem. 2023, 30, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwasogo, D.A.; Varangane, S.; Prabhu, Y.T.; Abraham, B.M.; Perupogu, V.; Pal, U. Biosynthetic modulation of carbon-doped ZnO for rapid photocatalytic endocrine disruptive remediation and hydrogen evolution. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 394, 136393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Altuner, E.E.; Gulbagca, F.; Tiri RN, E.; Sen, F.; Javadi, A.; Dragoi, E.N. Facile bio-fabrication of ZnO@AC nanoparticles from chitosan: Characterization, hydrogen generation, and photocatalytic properties. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, W.; Dilbaghi, N.; Kumar, R.; Singhal, N.K.; Kaushik, A.; Kumar, S. Adsorption of harmful dyes and antimi-crobial studies utilizing recyclable ZnO, its composites with conventionally used activated carbon, and waste orange peel as a greener approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayomi, K.S.; Lau, S.Y.; Mayowa, I.E.; Danquah, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Chiong, T.; Meunier, L.; Rahman, M.M. Recent advances in graphene-derived materials for biomedical waste treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 51, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Tian, F.; Zou, H.; Ye, Z.; Peng, C.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; et al. ZnO/biochar nanocom-posites via solvent free ball milling for enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-M.; Li, B.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Yang, J.-C.E.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.-B.; Zheng, Y.-M. Zinc oxide nanosheet decorated self-supporting hierarchical porous wood carbon electrode for efficient capacitive deionization defluorination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared-Hajishirkiaee, R.; Ehtesabi, H.; Najafinobar, S.; Masoumian, Z. Multifunctional chitosan/carbon dots/sodium alginate/zinc oxide double-layer sponge hydrogel with high antibacterial, mechanical and hemostatic properties. OpenNano 2023, 12, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, W.; Erk, N.; Özalp; Soylak, M. Construction of a novel sensor based on activated nanodiamonds, zinc oxide, and silver nanoparticles for the determination of a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate in real biological and food samples. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 137, 110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, L.M.; Cong, C.Q.; Hai, N.D.; Nam, N.T.H.; An, H.; Tai, L.T.; Dat, T.D.; Dat, N.T.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Green synthesis of carbon-doped zinc oxide using Garcinia mangostana peel extract: Characterization, photocatalytic degradation, and hydrogen peroxide production. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 392, 136269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Gan, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B. Rational design of activated graphitic carbon spheres with optimized ion and electron transfer channels for zinc-ion hybrid capacitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 651, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Moradi, H.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-K. Highly porous biobased graphene-like carbon adsorbent for dye removal: Preparation, adsorption mechanisms and optimization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, M.; Escarabajal, J.C.G.; Palomino, G.T.; Cabello, C.P. Zinc/Iron mixed-metal MOF-74 derived magnetic carbon nanorods for the enhanced removal of organic pollutants from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 428, 131147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Saber, S.E.M.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Reghioua, A.; Alothman, Z.A.; Wilson, L.D. Mesoporous activated carbon from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) peels by H3PO4 assisted microwave: Optimization, characterization, and adsorption mechanism for methylene blue dye removal. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 129, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayomi, K.S.; Oluwadiya, A.E.; Lau, S.Y.; Dada, A.O.; Akubuo-Casmir, D.; Adelani-Akande, T.A.; Bari, A.F.; Temidayo, S.O.; Rahman, M.M. Biosynthesis of Tithonia diversifolia leaf mediated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles loaded with flamboyant pods (Delonix regia) for the treatment of Methylene Blue Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiraja, N.; Prabhahar, R.S.S.; Joshua, A. Preparation and Physio–Chemical characterisation of activated carbon derived from prosopis juliflora stem for the removal of methylene blue dye and heavy metal containing textile industry effluent. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.S.; Li, X.B.; Arif, U.; Ali, F.; Ali, A.; Raziq, F.; Ali, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Development and characterization of silver modified novel graphitic-carbon nitride (Ag-ZnO/C3N4) coupled with metal oxide photocatalysts for accelerated deg-radation of dye-based emerging pollutants. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 39, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; He, Y.; Xue, G. Achieving multi-cycle regeneration of activated carbon and Cr(VI) removal over a wide pH range by hydrothermal converting quinonimine dye into difunctional pyrrolic-N: Implication for carbon capture in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, A.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Tokula, B.E.; Bayode, A.A.; Obayomi, K.S.; Ajanaku, C.O.; Adekola, F.A.; Ajanaku, K.O.; Pal, U. Zinc oxide decorated plantain peel activated carbon for adsorption of cationic malachite green dye: Mecha-nistic, kinetics and thermodynamics modeling. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Liu, N.; Kang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. A covalent organic skeleton based on pyridinyl benzene embedded into BiVO4 sites for visible-driven photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 445, 115046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Singh, S. Corona-poling enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl-violet and rhodamine B pollutants using ferroelectric nanoparticles. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2023, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Dong, C.; Mu, W.; Han, X. Degradation of Rhodamine B in the photocatalytic reactor containing TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with nanobubbles. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2023, 2, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Guzmán, G.; Seguel, M.; Fernández, L.; Caro, C.; Suarez, C.; Matus, M.; Cifuentes, C.; Bustos, F.; Ariz, K. A photochemical approach to the synthesis of ZnO/CuO films and their application to the photocatalytic degradation of rho-damines (Rh-B and Rh-6G) under UV–Vis light irradiation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 152, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongamwong, T.; Barrabés, N.; Donphai, W.; Witoon, T.; Rupprechter, G.; Chareonpanich, M. Chlorophyll-modified Au25(SR)18-functionalized TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 325, 122336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayomi, K.S.; Lau, S.Y.; Danquah, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Chiong, T.; Meunier, L.; Gray, S.R.; Rahman, M.M. Green synthesis of graphene-oxide based nanocomposites for efficient removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater. Desalination 2023, 564, 116749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiroosi, A.; Mahjoub, A.R.; Khavar, A.H.C.; Boukherroub, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Kaur, P. Effects of functionalized magnetic graphene oxide on the visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity of perovskite-type MTiO3 (M = Zn and Mn) for the degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1284, 135298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Shao, N.; Jiang, P.; Yang, H.; Li, B. Rational design of a novel magnetically recoverable and environ-ment-friendly Z-scheme SnFe2O4/Bi2WO6 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic performance for rhodamine B degra-dation and toxicity elimination. Mater. Chem. 2023, 30, 101538. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, R.W.; Lima, A.E.B.; de Souza, L.K.; Santos, E.C.; Santos, C.C.; De Menezes, A.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Cavalcante, L.S.; da Costa, M.E.M.; Sales, T.O.; et al. BiOBr/ZnWO4 heterostructures: An important key player for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye and antibiotic ciprofloxacin. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2023, 173, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathy, S.; Priyadharsan, A.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Guganathan, L.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Kim, S. Effect of doping and loading Parameters on photocatalytic degradation of brilliant green using Sn doped ZnO loaded CSAC. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Guan, J.; Guo, Y.; Yu, W. 3D chitosan/GO/ZnO hydrogel with enhanced photocorro-sion-resistance and adsorption for efficient removal of typical water-soluble pollutants. Catal. Commun. 2023, 176, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, H. Degradation of rhodamine B in water by ultrasound-assisted TiO2 photocatalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenbach, T.; Benitez, M.J.; Tirado, S.A.; Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K. Adsorption enhanced photo-catalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using GdxBi1-xFeO3@SBA-15 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15) nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29139–29148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, W.; Liang, C.; Shi, X.; Wang, C. Ultrasound-assisted photocatalytic degradation of RhB by Bi-doped AgNbO3 under internal electric field control. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Lai, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Ren, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, R.; Ma, G.; et al. Multi-shelled hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6749–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighnih, H.; Haounati, R.; Malekshah, R.E.; Ouachtak, H.; Jada, A.; Addi, A.A. Photocatalytic degradation of RhB dye using hybrid nanocomposite BiOCl@Kaol under sunlight irradiation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 103925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, E.H.; Kianfar, A.H.; Dinari, M.; Rezaei, B.; Saeidi, S. Photocatalytic activity of the novel triazine-based magnetic core–shell Cu nanocomposite for degradation of RhB and MB via air oxidation and Cr(VI) reduction. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wan, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J. Construction of hier-archical porous carbon with mesopores-enriched from sodium lignosulfonate by dual template strategy and their diversified applications for CO2 capture, radioactive iodine adsorption, and RhB removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, N.; Diery, W.A.; Moujaes, E.A.; Tahir, M.; Singh, P. Co+2, Ni+2 and Cu+2 incorporated Bi2O3 nano photocatalysts: Synthesis, DFT analysis of band gap modification, adsorption and photodegradation analysis of rhodamine B and Triclopy. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinithi, S.; Balakumar, V.; Chen, T.-W.; Chen, S.-M.; Akilarasan, M.; Lou, B.-S.; Yu, J. In-situ fabrication of TiO2-MWCNT composite for an efficient electron transfer photocatalytic rhodamine B dye degradation under UV–visible light. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 138, 110245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, X. Main factors for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B by MoS2 activated PMS. Mater. Lett. 2023, 341, 134191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yu, R.; Tang, Z. Multi-shelled CeO2 hollow microspheres as superior photocatalysts for water oxidation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4072–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, K.M.; Benitto, J.J.; Vijaya, J.J.; Bououdina, M. Recent Advances in ZnO-Based Nanostructures for the Photo-catalytic Degradation of Hazardous, Non-Biodegradable Medicines. Crystals 2023, 13, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Maivizhikannan, V.; Rao, V.N.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Shankar, M.V.; Krishnan, V. Sea urchin shaped ZnO coupled with MoS2 and polyaniline as highly efficient photocatalysts for organic pollutant decomposition and hydrogen evolution. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 10301–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwadai, N.; Shakil, M.; Inayat, U.; Tanveer, M.; Ashraf, M.; Gillani SS, A.; Al-Buriahi, M.S.; Alrowaili, Z.A. Unlocking the synergistic potential of peanut shell derived activated carbon-doped TiO2 for highly efficient photocatalytic removal of organic dye under UV-light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 296, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zi, G.; Zhou, C.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. One-step supramolecular preorgani-zation constructed crinkly graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Feng, W. Two-dimensional gersiloxenes with tunable bandgap for photocatalytic H2 evolution and CO2 photoreduction to CO. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Germanium-based monoelemental and binary two-dimensional materials: Theoretical and experimental investigations and promising applications. InfoMat 2022, 4, e12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, D.; Mou, J.; Yao, H.; Zhong, N. Visible-light responsive photocatalytic fuel cell with double Z-scheme heterojunction PTh/Ag3PO4/BiOI/Ti photoanode for efficient rhodamine B degradation and stable electricity generation. Opt. Mater. 2022, 134, 113103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xiao, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Bu, M.; Sun, J. Self-organization towards complex meso-helix in the structures of keggin-type polyoxometalate-based metal-organic frameworks for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. J. Solid State Chem. 2023, 324, 124109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaicham, C.; Rizki, I.N.; Sekar, K.; Shenoy, S.; Srikhaow, A.; Trakulmututa, J.; Sasaki, K. Bio-reduced Ag nanopar-ticle decorated on ZnO for enhancement of photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium and photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 939, 168797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, M.; Al-Wafi, R.; AlHammad, M. Highly efficient visible light driven photocatalytic activity of rare earth cerium doped zinc-manganese ferrite: Rhodamine B degradation and stability assessment. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 29245–29258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, S.H.; Salem, K.H.; Alshamsi, H.A. Visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye onto TiO2/rGO nanocomposites. Mater. Commun. 2023, 33, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, T.; Ramesh, K.; Ashok, B.; Jyothi, L.; Kumar, B.V.; Upender, G. Insights into charge transfer via Z-scheme for Rhodamine B degradation over novel Co3O4/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposites. Opt. Mater. 2023, 143, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ma, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Hua, Y.; Wang, C. Adsorption of BiOBr microspheres to rhodamine B and its influence on photocatalytic reaction. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
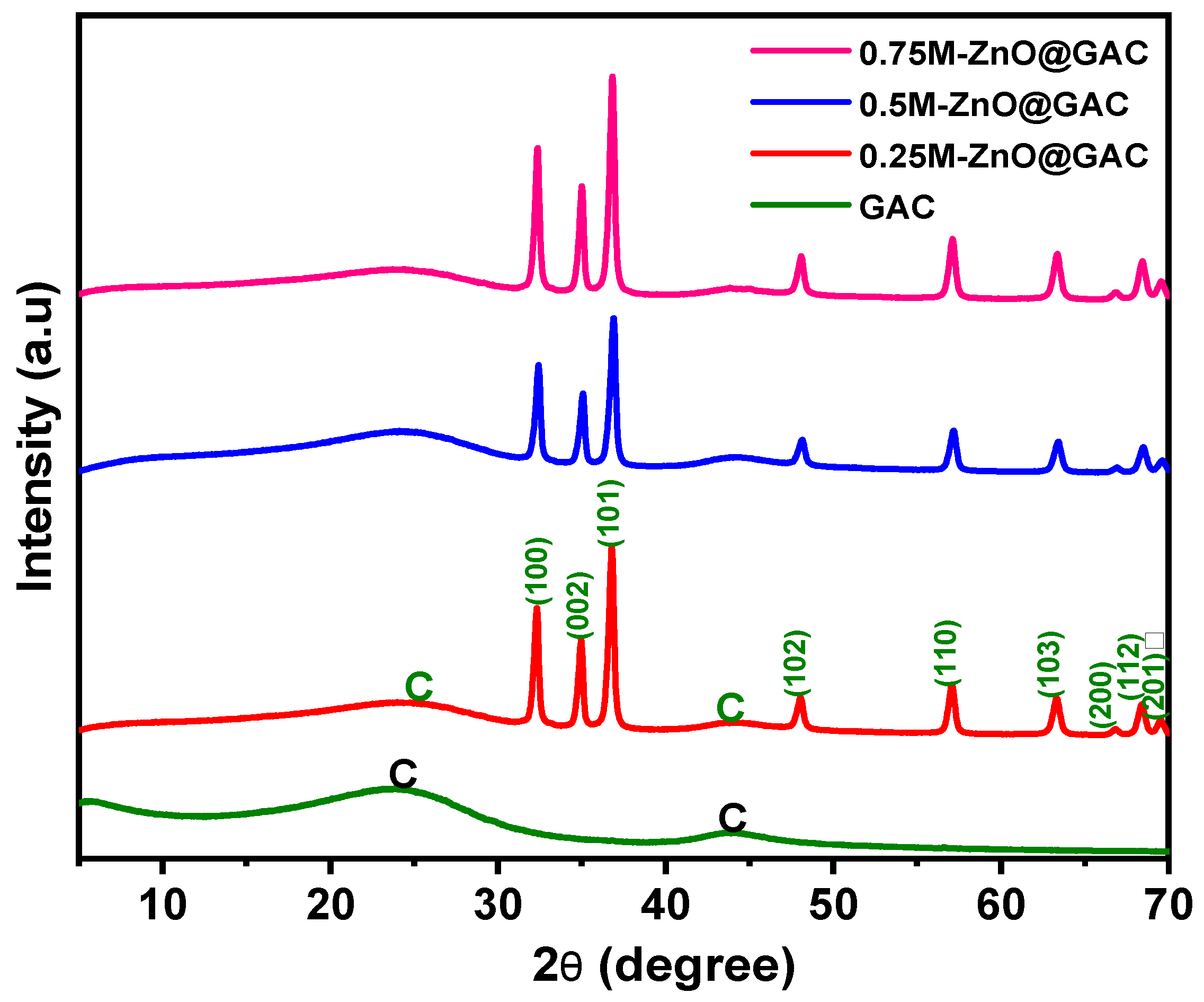

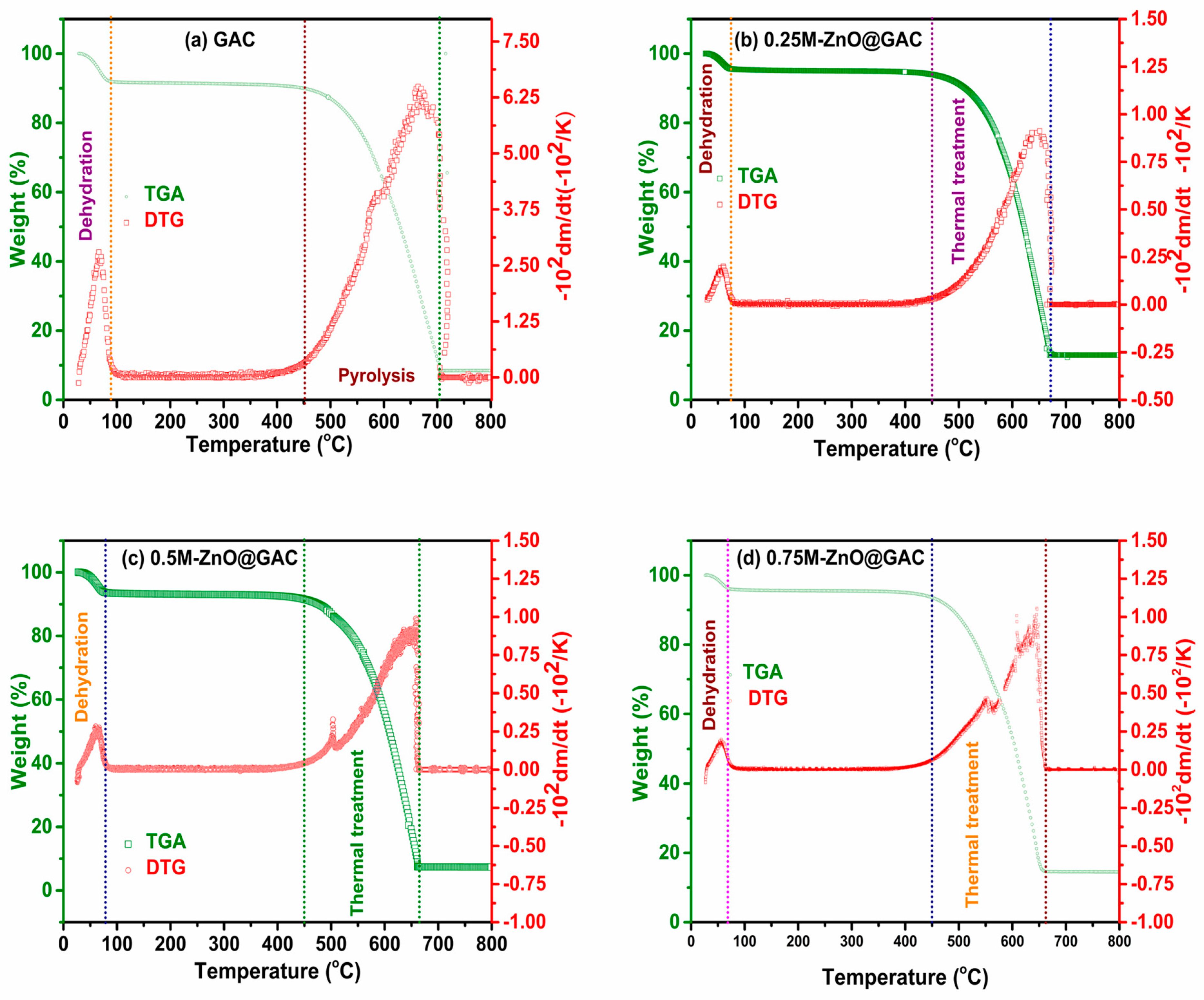
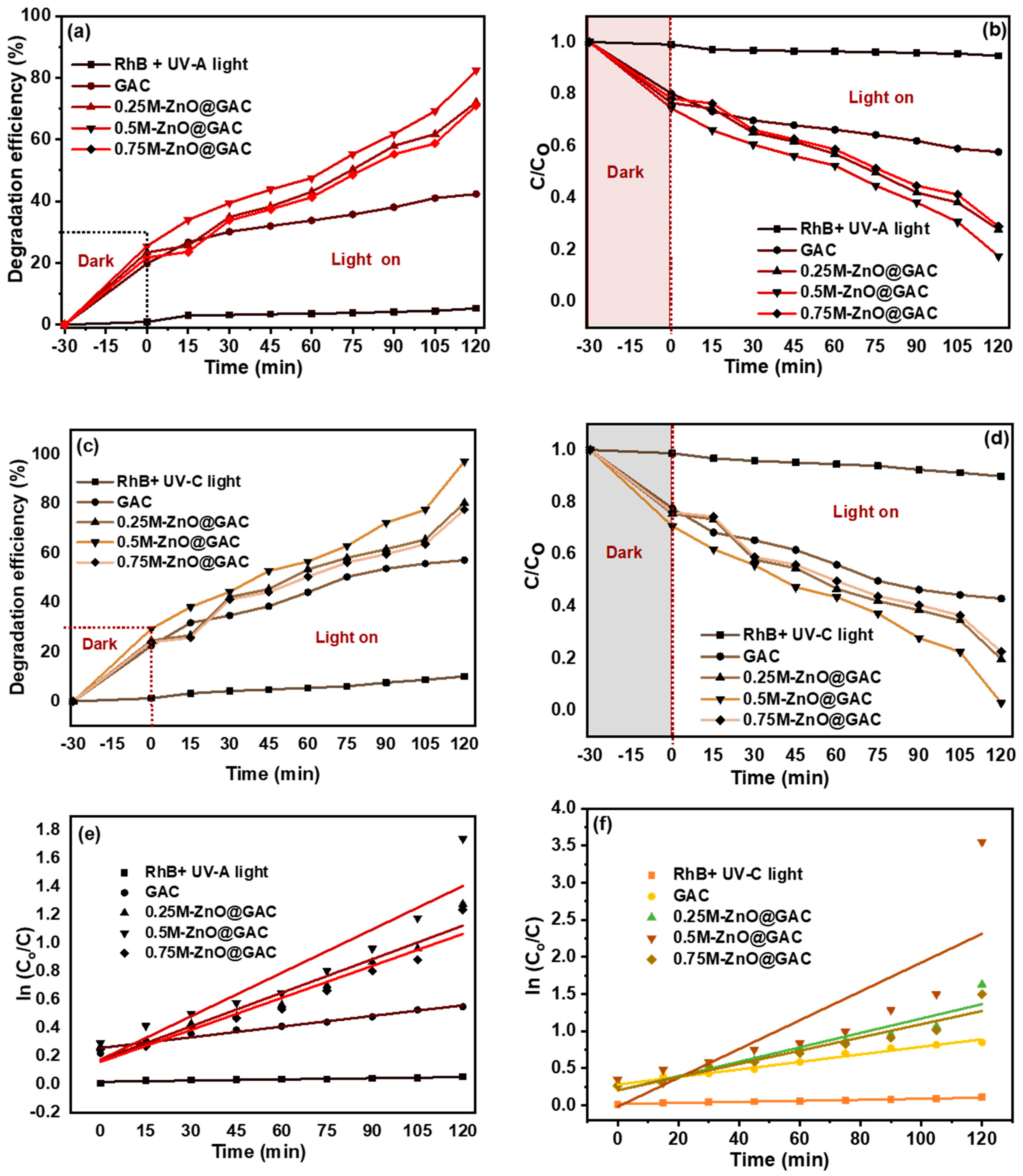
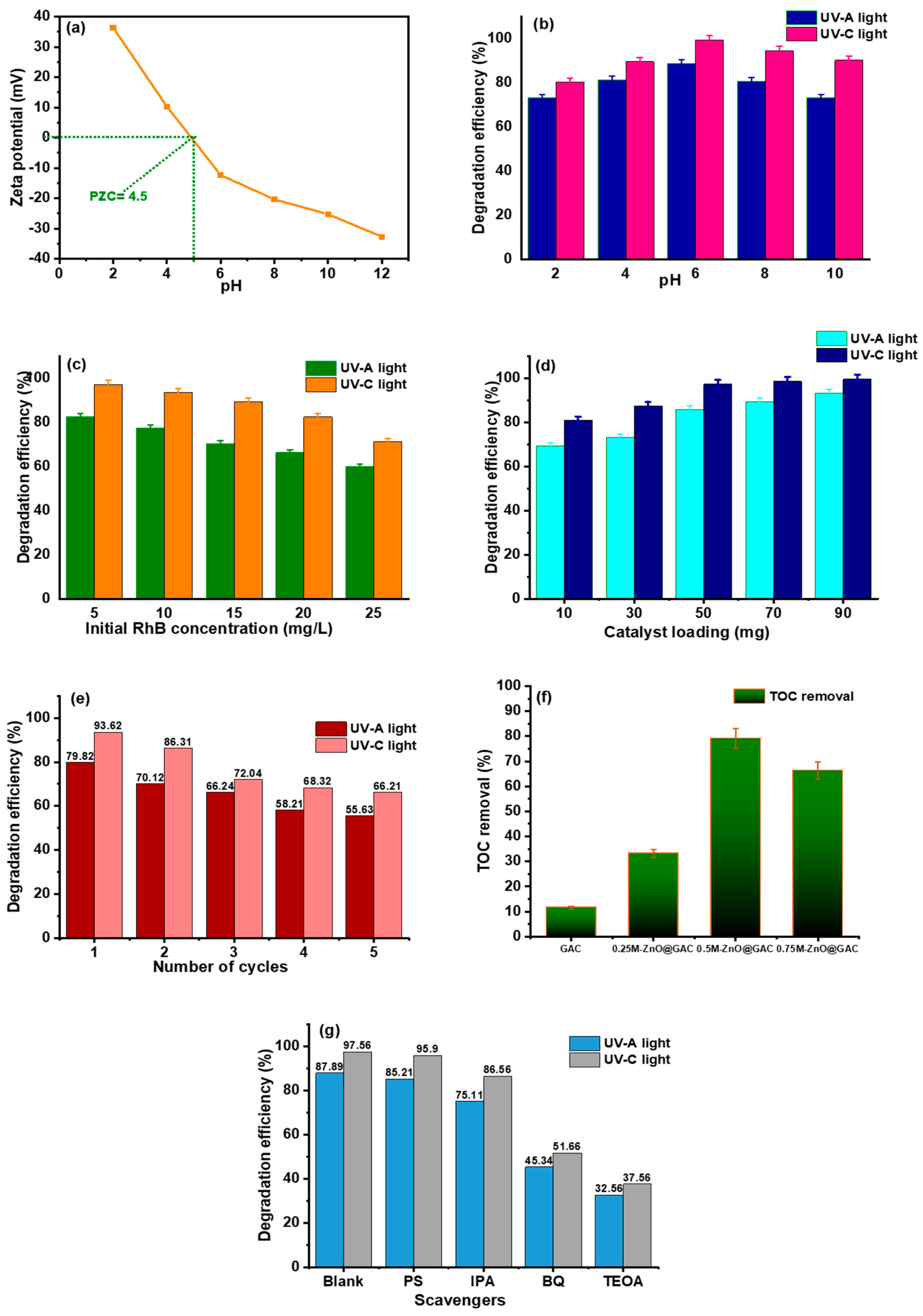
| Properties | Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAC | 0.25M-ZnO@GAC | 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 0.75M-ZnO@GAC | |
| SBET (m2/g) | 474 | 450 | 453 | 421 |
| SLang (m2/g) | 707 | 675 | 679 | 632 |
| Smic (m2/g) | 325 | 288 | 298 | 245 |
| Smic/SBET (%) | 68.57 | 64.0 | 65.78 | 58.19 |
| Sext (m2/g) | 149 | 162 | 155 | 176 |
| Sext/SBET (%) | 31.43 | 36.0 | 34.22 | 41.81 |
| Vtot (cm3/g) | 0.2683 | 0.2727 | 0.2659 | 0.2620 |
| Vmeso (cm3/g) | 0.1931 | 0.1618 | 0.1670 | 0.1217 |
| Vmic (cm3/g) | 0.0752 | 0.1109 | 0.0989 | 0.1403 |
| Vmeso/Vtot (%) | 71.97 | 59.33 | 62.81 | 46.45 |
| Vmic/Vtot (%) | 28.03 | 40.67 | 37.19 | 53.55 |
| Dp (nm) | 2.26 | 2.42 | 2.35 | 2.49 |
| Sample | Particle 1 | Particle 2 | Particle 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | Weight (%) | Weight (%) | |||||||
| C | O | Zn | C | O | Zn | C | O | Zn | |
| GAC | 92.6 | 7.2 | - | 92.0 | 9.1 | - | 86.4 | 10.4 | - |
| 0.25M-ZnO@GAC | 43.0 | 5.9 | 17.3 | 51.5 | 8.6 | 3.2 | 68.6 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 23.5 | 15.5 | 12.5 | 47.1 | 7.5 | 15.9 | 42.0 | 7.2 | 8.9 |
| 0.75M-ZnO@GAC | 22.7 | 11.6 | 30.6 | 21.8 | 12.2 | 29.2 | 39.5 | 10.0 | 20.2 |
| Materials | UV-A Light | UV-C Light | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE (%) | k1 (min−1) | PDE (%) | k1 (min−1) | |
| RhB | 5.30 | 0.00028 | 10.12 | 0.00071 |
| GAC | 42.33 | 0.0025 | 57.12 | 0.0051 |
| 0.25M-ZnO@GAC | 72.09 | 0.0079 | 80.37 | 0.097 |
| 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 82.42 | 0.010 | 97.11 | 0.019 |
| 0.75M-ZnO@GAC | 70.98 | 0.0078 | 78.58 | 0.0089 |
| Sample | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/(mg.min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| GAC | 0.010 | 668.70 | 0.992 | 0.0000053 | 490.67 | 0.999 |
| 0.25M-ZnO@GAC | 0.021 | 549.77 | 0.984 | 0.000024 | 459.72 | 0.999 |
| 0.5M-ZnO@GAC | 0.013 | 617.28 | 0.994 | 0.0000086 | 478.91 | 0.999 |
| 0.75M-ZnO@GAC | 0.0085 | 730.55 | 0.990 | 0.0000045 | 449.88 | 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obayomi, K.S.; Lau, S.Y.; Xie, Z.; Gray, S.R.; Zhang, J. In-Situ Hydrothermal Fabrication of ZnO-Loaded GAC Nanocomposite for Efficient Rhodamine B Dye Removal via Synergistic Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Performance. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141234
Obayomi KS, Lau SY, Xie Z, Gray SR, Zhang J. In-Situ Hydrothermal Fabrication of ZnO-Loaded GAC Nanocomposite for Efficient Rhodamine B Dye Removal via Synergistic Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Performance. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141234
Chicago/Turabian StyleObayomi, Kehinde Shola, Sie Yon Lau, Zongli Xie, Stephen R. Gray, and Jianhua Zhang. 2024. "In-Situ Hydrothermal Fabrication of ZnO-Loaded GAC Nanocomposite for Efficient Rhodamine B Dye Removal via Synergistic Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Performance" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141234
APA StyleObayomi, K. S., Lau, S. Y., Xie, Z., Gray, S. R., & Zhang, J. (2024). In-Situ Hydrothermal Fabrication of ZnO-Loaded GAC Nanocomposite for Efficient Rhodamine B Dye Removal via Synergistic Photocatalytic and Adsorptive Performance. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141234











