Water-Soluble Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles: Direct Synthesis and Ligand Exchange Routes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PVP-Coated PbS Nano-Cubes
2.2. Ligand Exchange from ODA to PVP in PbS Truncated Nano-Cubes
2.2.1. Synthesis of ODA Coated PbS Truncated Nano-Cubes
2.2.2. Ligand Exchange from ODA to PVP
2.3. Characterization Methods
- X-ray diffraction
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy
- Thermal gravimetric analysis
3. Results and Discussion
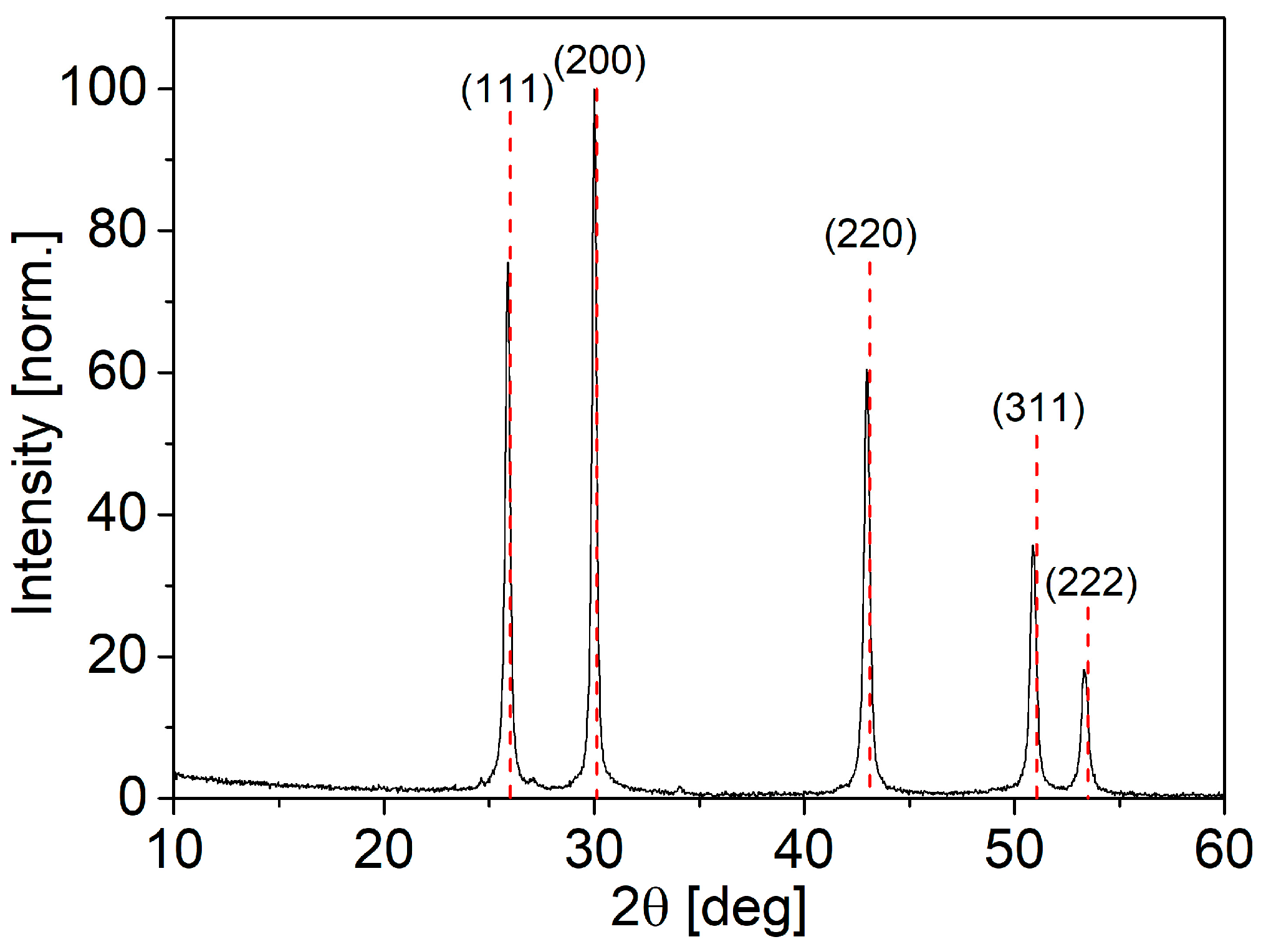
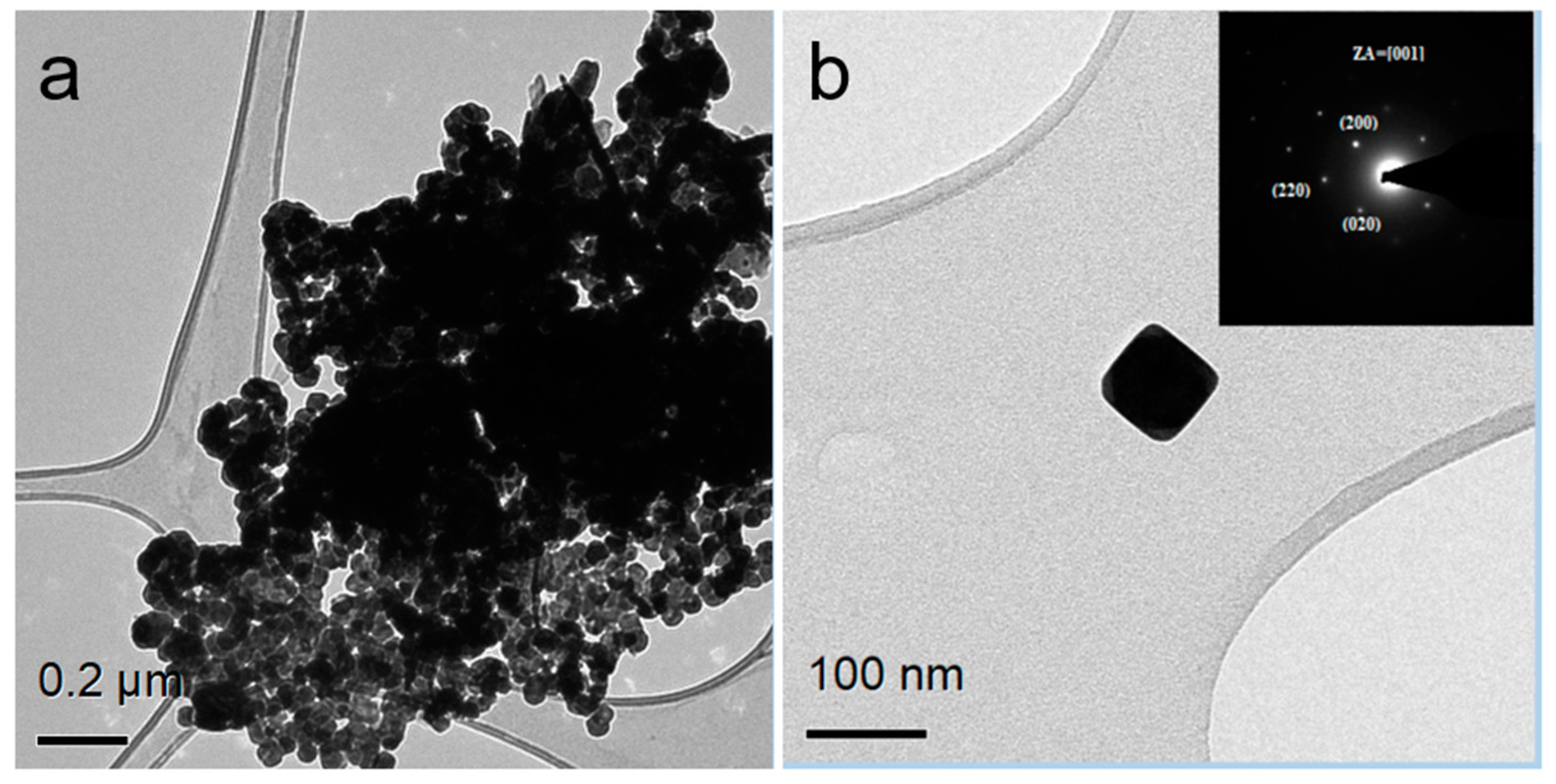
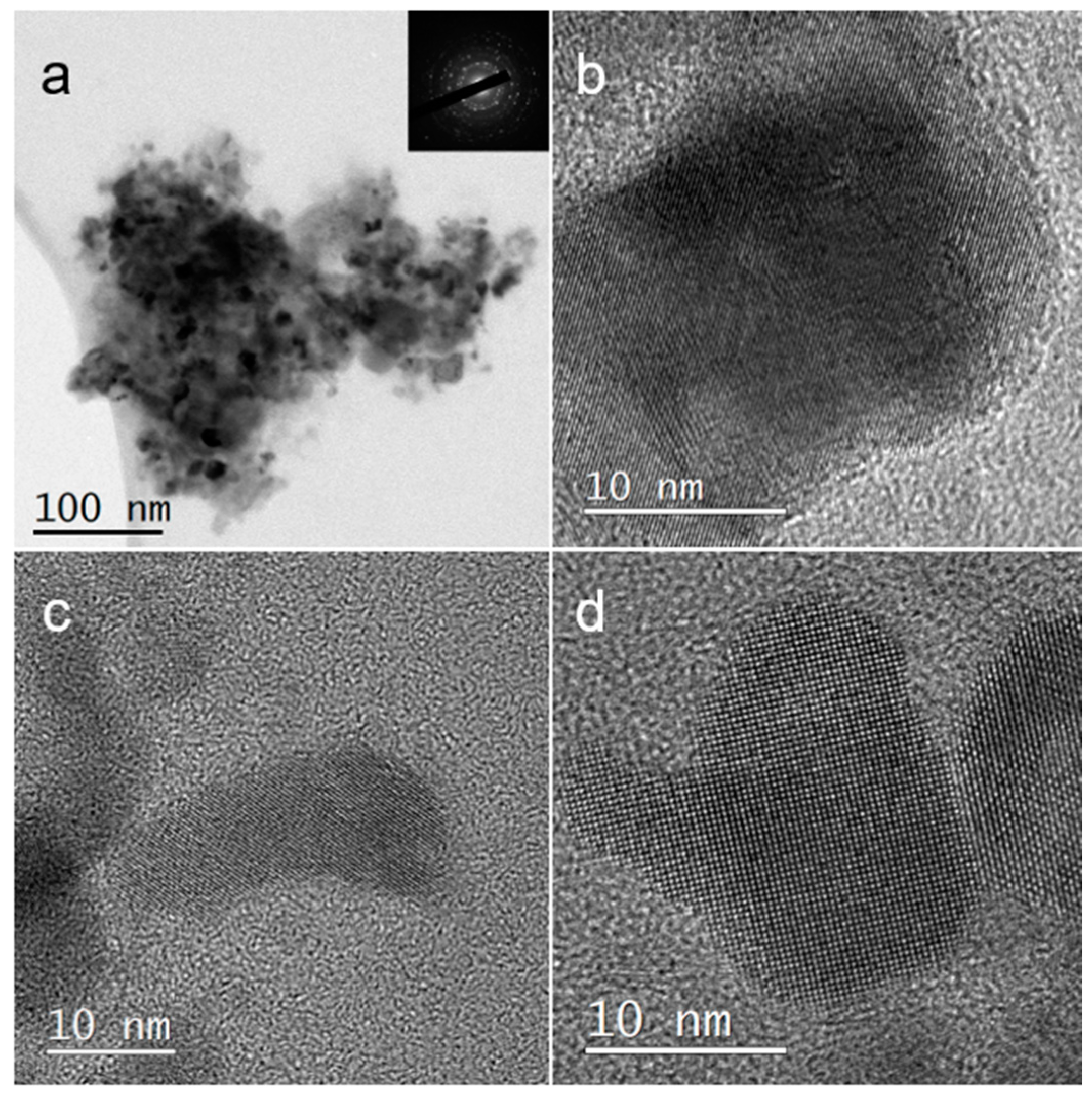
3.1. PVP-Coated PbS Nano-Cubes
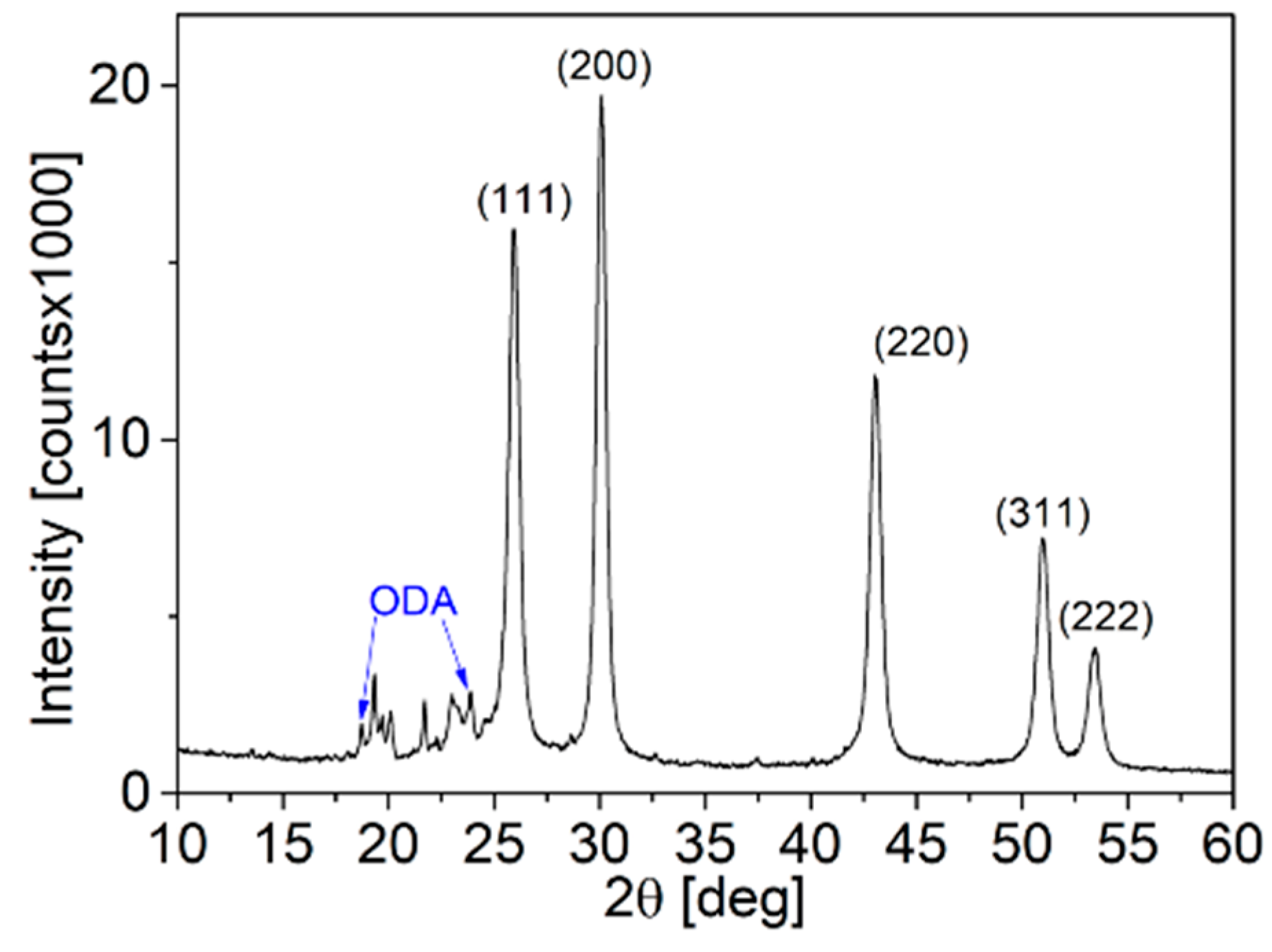
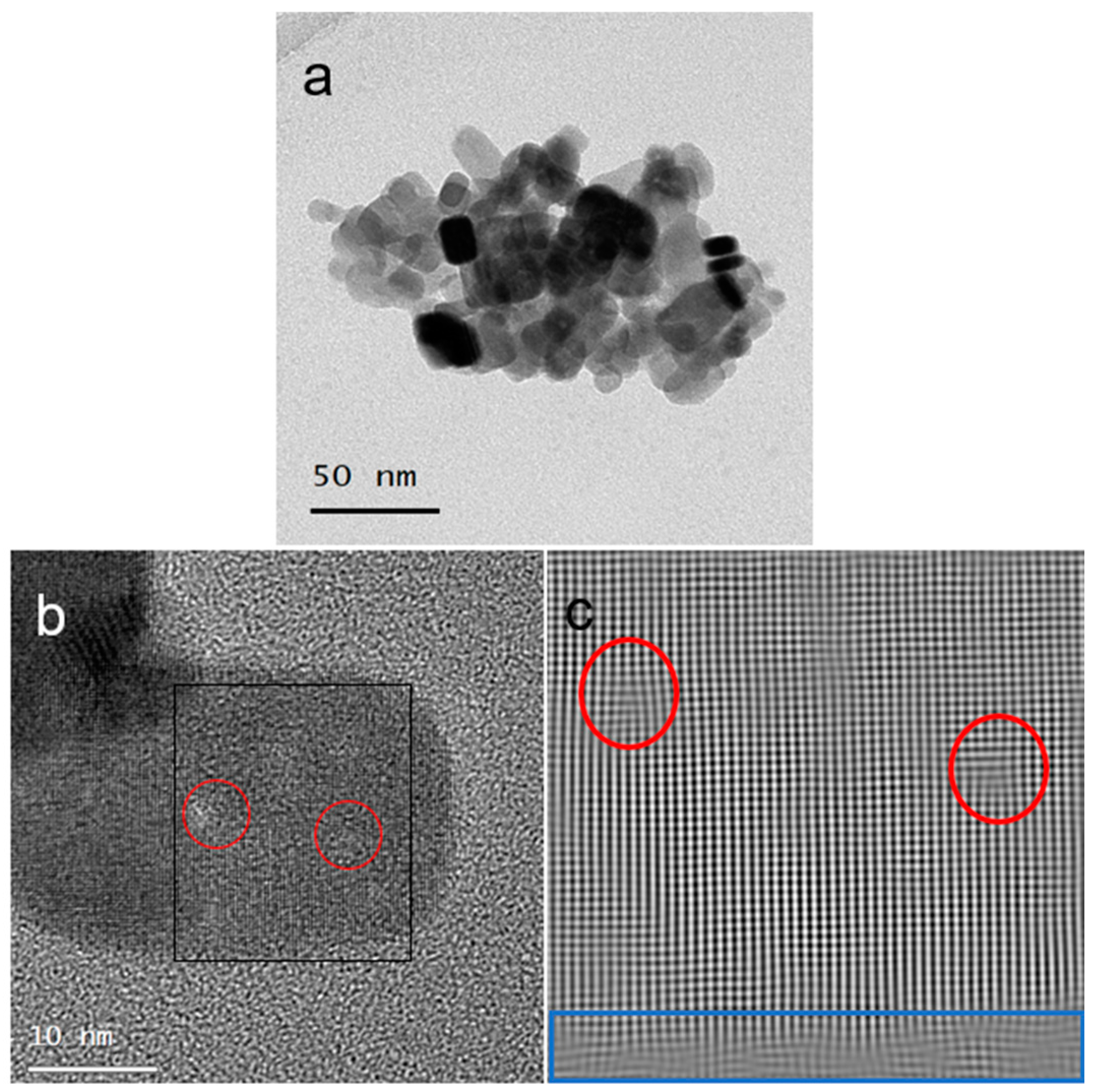
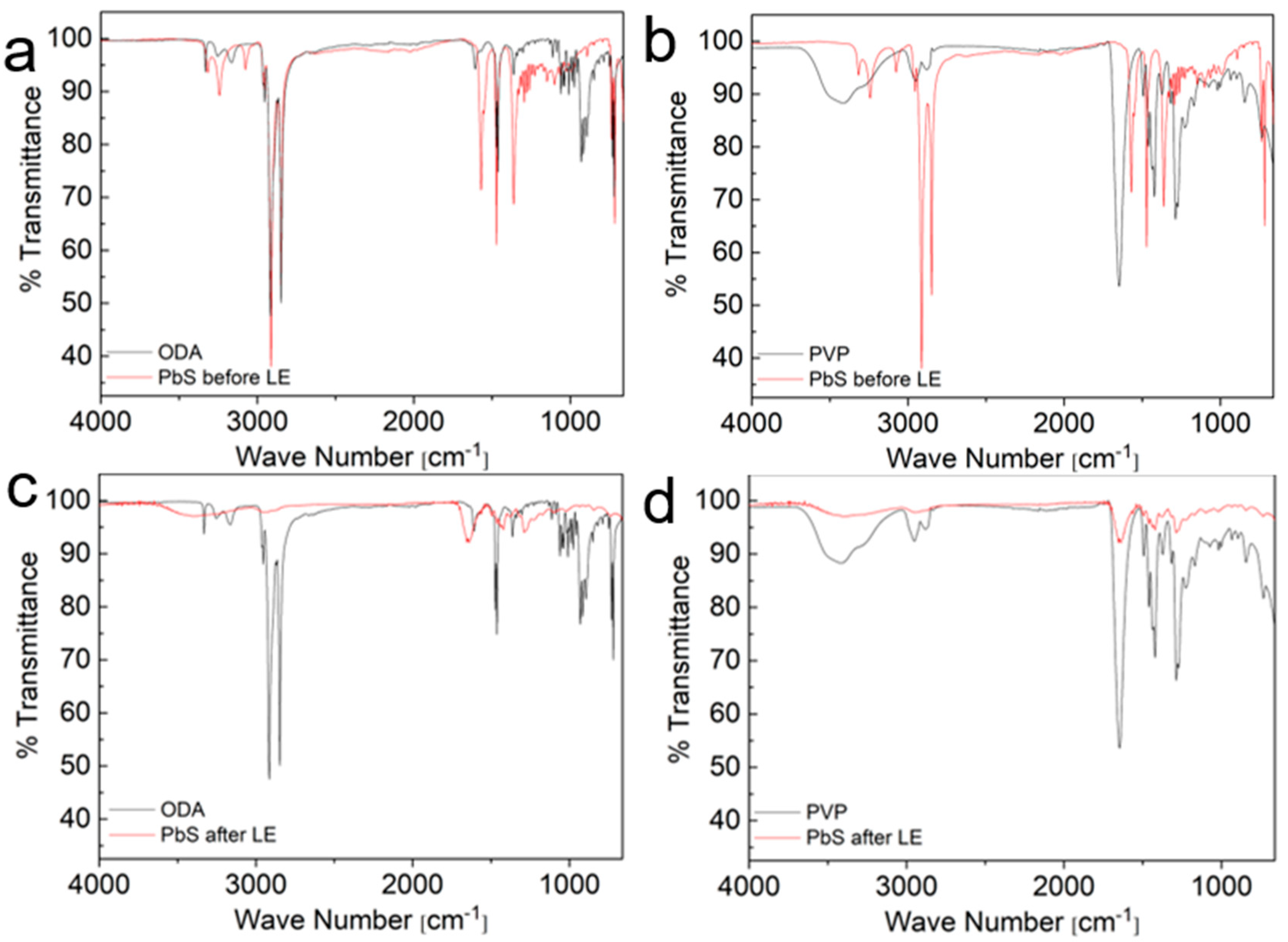
3.2. Ligand Exchange from ODA to PVP in PbS Truncated Nano-Cubes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reiss, P.; Protière, M.; Li, L. Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanocrystals. Small 2009, 5, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mélinon, P.; Begin-Colin, S.; Duvail, J.L.; Gauffre, F.; Boime, N.H.; Ledoux, G.; Plain, J.; Reiss, P.; Silly, F.; Warot-Fonrose, B. Engineered Inorganic Core/Shell Nanoparticles. Phys. Rep. 2014, 543, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, F.; Mahler, B.; Dubertret, B.; Doris, E.; Mioskowski, C. A Versatile Strategy for Quantum Dot Ligand Exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 482–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, M.A.; Ling, D.; Hyeon, T.; Talapin, D.V. The Surface Science of Nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutbul, R.E.; Golan, Y. “Beneficial Impurities” in Colloidal Synthesis of Surfactant Coated Inorganic Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, A.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Kang, Y.; Gordon, T.; Kikkawa, J.M.; Murray, C.B. A Generalized Ligand-Exchange Strategy Enabling Sequential Surface Functionalization of Colloidal Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Batmunkh, M.; Tricoli, A.; Qiao, S.Z.; Dai, S. Near-Infrared Active Lead Chalcogenide Quantum Dots: Preparation, Post-synthesis Ligand Exchange, and Applications in Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 5256–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, D.M.; Vörös, M.; Brawand, N.P.; McNichols, B.W.; Miller, E.M.; Gu, J.; Nozik, A.J.; Sellinger, A.; Galli, G.; Beard, M.C. Tuning Colloidal Quantum Dot Band Edge Positions through Solution-Phase Surface Chemistry Modification. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Trizio, L.; Manna, L. Forging Colloidal Nanostructures via Cation Exchange Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10852–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, B.L.; Urbano, B.F.; Sánchez, J. Water-Soluble and Insoluble Polymers, Nanoparticles, Nanocomposites and Hybrids with Ability to Remove Hazardous Inorganic Pollutants in Water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, F.Y.; Zhilenkov, A.V.; Voronov, I.I.; Khakina, E.A.; Mischenko, D.V.; Troshin, P.A.; Hsu, S.H. Water-Soluble Fullerene Derivatives as Brain Medicine: Surface Chemistry Determines If They Are Neuroprotective and Antitumor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11482–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnorr, J.M.; Swager, T.M. Emerging Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabkin, A.; Belman, N.; Israelachvili, J.; Golan, Y. Directed Coassembly of Oriented PbS Nanoparticles and Monocrystalline Sheets of Alkylamine Surfactant. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15119–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiyev, Z.Q.; Balayeva, N.O. Preparation and optical studies of PbS nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2015, 46, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, W.; Peng, J.; Cao, Y. Size-Tunable near-Infrared PbS Nanoparticles Synthesized from Lead Carboxylate and Sulfur with Oleylamine as Stabilizer. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 345602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.T.; Chung, W.J.; Lim, J.; Johe, P.; Glass, R.S.; Pyun, J.; Char, K. One-Pot Synthesis of PbS NP/Sulfur-Oleylamine Copolymer Nanocomposites via the Copolymerization of Elemental Sulfur with Oleylamine. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3617–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, W. Oleic Acid Capped PbS Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 98, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evstropiev, S.K.; Kislyakov, I.M.; Bagrov, I.V.; Belousova, I.M. Stabilization of PbS Quantum Dots by High Molecular Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrov, I.A.; Danilov, V.V.; Evstrop’ev, S.K.; Kiselev, V.M.; Kislyakov, I.M.; Panfutova, A.S.; Khrebtov, A.I. Photoinduced Variation of the Luminescent Properties of PbS Nanoparticle Suspensions Stabilized by Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2015, 41, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Gautam, U.K.; Sasaki, T.; Bandog, Y.; Golan, Y.; Ariga, K. Ultra Narrow PbS Nanorods with Intense Fluorescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4594–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashouti, M.; Lifshitz, E. PbS Sub-Micrometer Structures with Anisotropic Shape: Ribbons, Wires, Octapods, and Hollowed Cubes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salavati-Niasari, M.; Sobhani, A.; Davar, F. Synthesis of Star-Shaped PbS Nanocrystals Using Single-Source Precursor. J. Alloys. Compd. 2010, 507, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Curry, R.J. Lead Sulphide Nanocrystal Photodetector Technologies. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.R.; Kim, D.; Lunt, R.R.; Zhao, N.; Bawendi, M.G.; Grossman, J.C.; Bulović, V. Energy Level Modification in Lead Sulfide Quantum Dot Thin Films through Ligand Exchange. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5863–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamiyev, Z.; Balayeva, N.O. PbS nanostructures: A review of recent advances. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 21, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Chen, C.; Krishnan, R.; Krauss, T.D.; Harbold, J.M.; Wise, F.W.; Thomas, M.G.; Silcox, J. Optical Properties of Colloidal PbSe Nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, S.A.; Konstantatos, G.; Zhang, S.; Cyr, P.W.; Klem, E.J.D.; Levina, L.; Sargent, E.H. Solution-Processed PbS Quantum Dot Infrared Photodetectors and Photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakueva, L.; Gorelikov, I.; Musikhin, S.; Zhao, X.S.; Sargent, E.H.; Kumacheva, E. PbS Quantum Dots with Stable Efficient Luminescence in the Near-IR Spectral Range. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalapathi, U.; Jayasree, Y.; Park, S.H. Lead-Doped Cubic Tin Sulfide Thin Films for Solar Cell Applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 150, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuklov, I.A.; Toknova, V.F.; Lizunova, A.A.; Razumov, V.F. Controlled aging of PbS colloidal quantum dots under mild conditions. Mater Today Chem. 2020, 18, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Fritzs, K.; Guerin, G.; Bardajee, G.R.; Hinds, S.; Sukhovatkin, V.; Sargent, E.H.; Scholes, G.D.; Winnik, M.A. Highly luminescent lead sulfide nanocrystals in organic solvents and water through ligand exchange with poly(acrylic acid). Langmuir 2008, 24, 8215–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, C.C.; Johansson, E. Colloidally Prepared 3-Mercaptopropionic Acid Capped Lead Sulfide Quantum Dots. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7313–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, I.S.; Stonas, A.R.; Lonergan, M.C. PbS nanocrystals functionalized with a short-chain, ionic, dithiol ligand. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19383–19389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichaandi, J.; Abel, K.A.; Johnson, N.J.J.; Van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Long-term colloidal stability and photoluminescence retention of lead-based quantum dots in saline buffers and biological media through surface modification. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.J.J.; Sangeetha, N.M.; Boyer, J.C.; Van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Facile Ligand-Exchange with Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Subsequent Silica Coating of Hydrophobic Upconverting β-NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontidis, E.; Orphanou, M.; Kyprianidou-Leodidou, T.; Krumeich, F.; Caseri, W. Composite nanotubes formed by self-assembly of PbS nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.D.; Chaudhuri, T.K. Synthesis of PbS/Poly (Vinyl-Pyrrolidone) Nanocomposite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.H.; Chaudhuri, T.K.; Shripathi, T.; Deshpande, U.; Patel, V.K. Influence of Pb+2-Thiourea Complex Concentration on the Structural, Optical, Thermal and Electrical Properties of PbS/PVP-PVA Nanocomposite Films. J. Poly. Res. 2018, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Patel, N.; Panjabi, S.; Patel, V. Structural, Morphological, Optical, and Thermal Properties of Electrospun PbS/PVP-PEO Nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 8839–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.H.; Chaudhuri, T.K.; Patel, V.K.; Shripathi, T.; Deshpande, U.; Lalla, N.P. Dip-Coated PbS/PVP Nanocomposite Films with Tunable Band Gap. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4422–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.H.; Chaudhuri, T.K.; Patel, V.K. Solid State in Situ Thermolysis Approach for Synthesis of PbS/PEO/PVP Nanocomposite Films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.A.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.Z.; Torres-Martinez, C.L.; Mehra, R.K.; Yang, Y.; Risbud, S.H. Synthesis, Optical Spectroscopy and Ultrafast Electron Dynamics of PbS Nanoparticles with Different Surface Capping. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 11598–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, N.; Rusen, E.; Enculescu, M.; Matei, E.; Marculescu, B.; Enculescu, I. Polymer-Assisted Crystallization of Low-Dimensional Lead Sulfide Particles. Physica. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 43, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.S.; Honma, I.; Komiyama, H.; Haus, J.W. Coated Semiconductor Nanoparticles: The CdS/PbS System’s Synthesis and Properties. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, H.; Barsheshet, N.; Kolusheva, S.; Mokari, T.; Hayun, S.; Golan, Y. Real-Time Monitoring of Phase Transitions in π-SnS Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 8881–8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Gao, N.; Zhang, J.; Yi, F.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Liu, H. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of SnO2 Quantum Dot Films Employing Atomic Ligand-Exchange Strategy for Fast Response H2S Gas Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 271, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, J.J.; San-Miguel, M.A.; Domínguez-Meister, S.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Salmeron, M. Structure and Chemical State of Octadecylamine Self-Assembled Monolayers on Mica. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 19716–19723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann Liebert, M.; Biswas, P. Lead Species Aerosol Formation and Growth in Multicomponent High-Temperature Environments. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2000, 17, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmsen, G.J. Characterization of Fugitive Material within a Primary Lead Smelter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

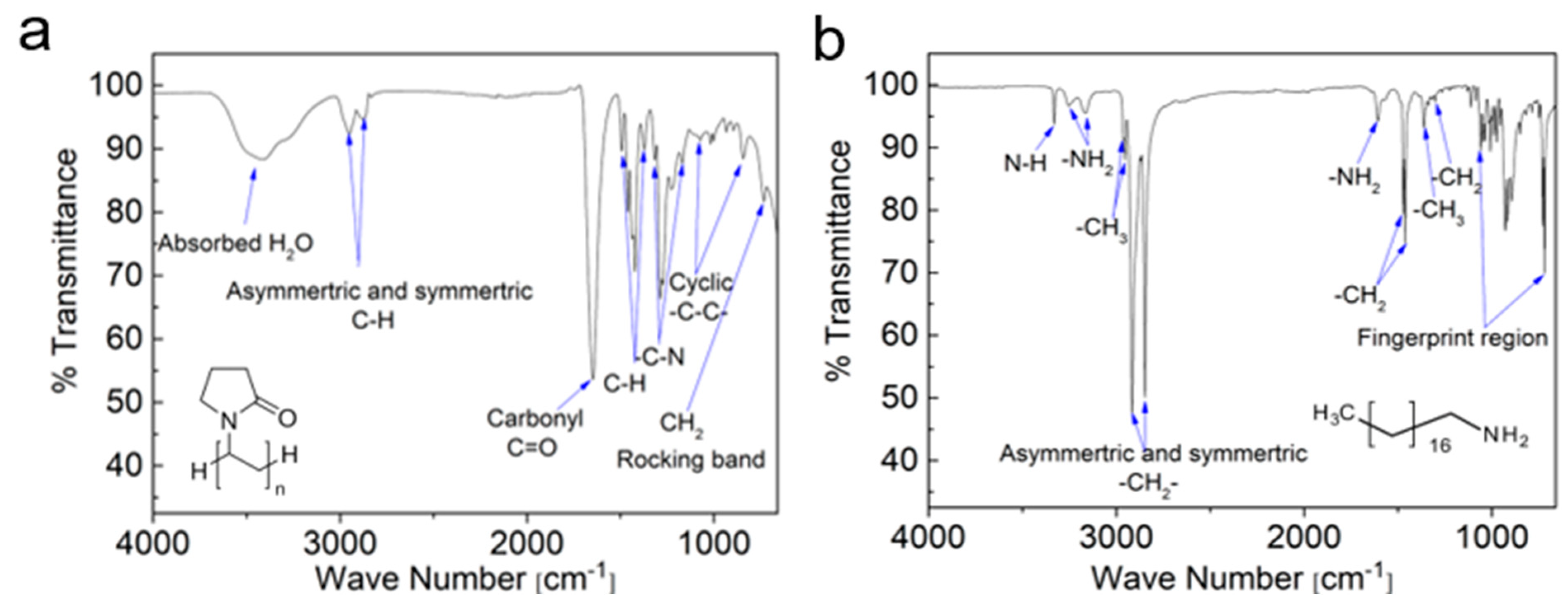

| ODA | PVP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance Band cm−1 | Functional Group | Absorbance Band cm−1 | Functional Group |
| 3330 | N–H crystalline | 3400 | Absorbed H2O |
| 3255 | Asymmetric and symmetric –NH2 stretching mode | 2950 | Asymmetric and symmetric C–H stretching mode |
| 3163 | 2873 | ||
| 2962 | Asymmetric and symmetric methyl –CH3 stretching mode | 1647 | Carbonyl C=O stretching mode |
| 2953 | |||
| 2915 | Asymmetric and symmetric –CH2– stretching | 1493 | In plane C–H bending of different –CH2 and C–H |
| 1460 | |||
| 2847 | 1435 | ||
| 1421 | |||
| 1373 | |||
| 1607 | –NH2 | 1316 | –C–N stretching mode |
| 1286 | |||
| 1471 | –CH2 splitting | 1226 | –C–N stretching mode |
| 1461 | 1170 | ||
| 1364 | –CH3 “umbrella” | 1074 | Cyclic –C–C– stretching mode |
| 1017 | |||
| 1338 | 933 | ||
| 844 | |||
| 1320 | Twisting–rocking and wagging –CH2– | 731 | Amide or CH2 rocking band |
| 1303 | |||
| 719–1060 | Fingerprint region | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfeffer, S.; Ezersky, V.; Kolusheva, S.; Golan, Y. Water-Soluble Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles: Direct Synthesis and Ligand Exchange Routes. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141235
Pfeffer S, Ezersky V, Kolusheva S, Golan Y. Water-Soluble Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles: Direct Synthesis and Ligand Exchange Routes. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141235
Chicago/Turabian StylePfeffer, Saar, Vladimir Ezersky, Sofiya Kolusheva, and Yuval Golan. 2024. "Water-Soluble Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles: Direct Synthesis and Ligand Exchange Routes" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141235
APA StylePfeffer, S., Ezersky, V., Kolusheva, S., & Golan, Y. (2024). Water-Soluble Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles: Direct Synthesis and Ligand Exchange Routes. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141235








