Research on Electric Field Homogenization in Radial Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Discussion
2.1. Establishing the Model of the Electrospinning System with Solidworks
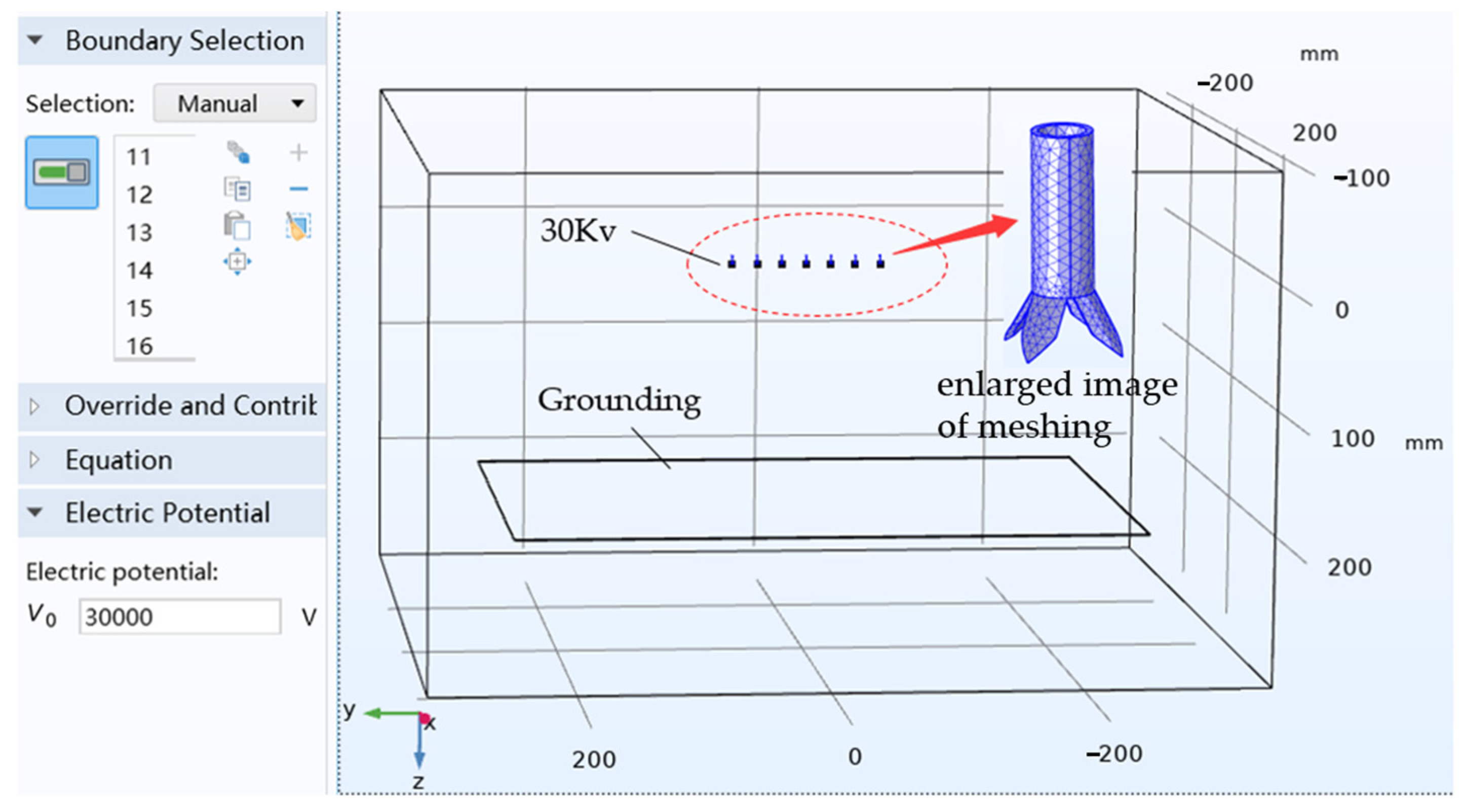
2.2. Electric Field Simulation of the Electrospinning System with COMSOL
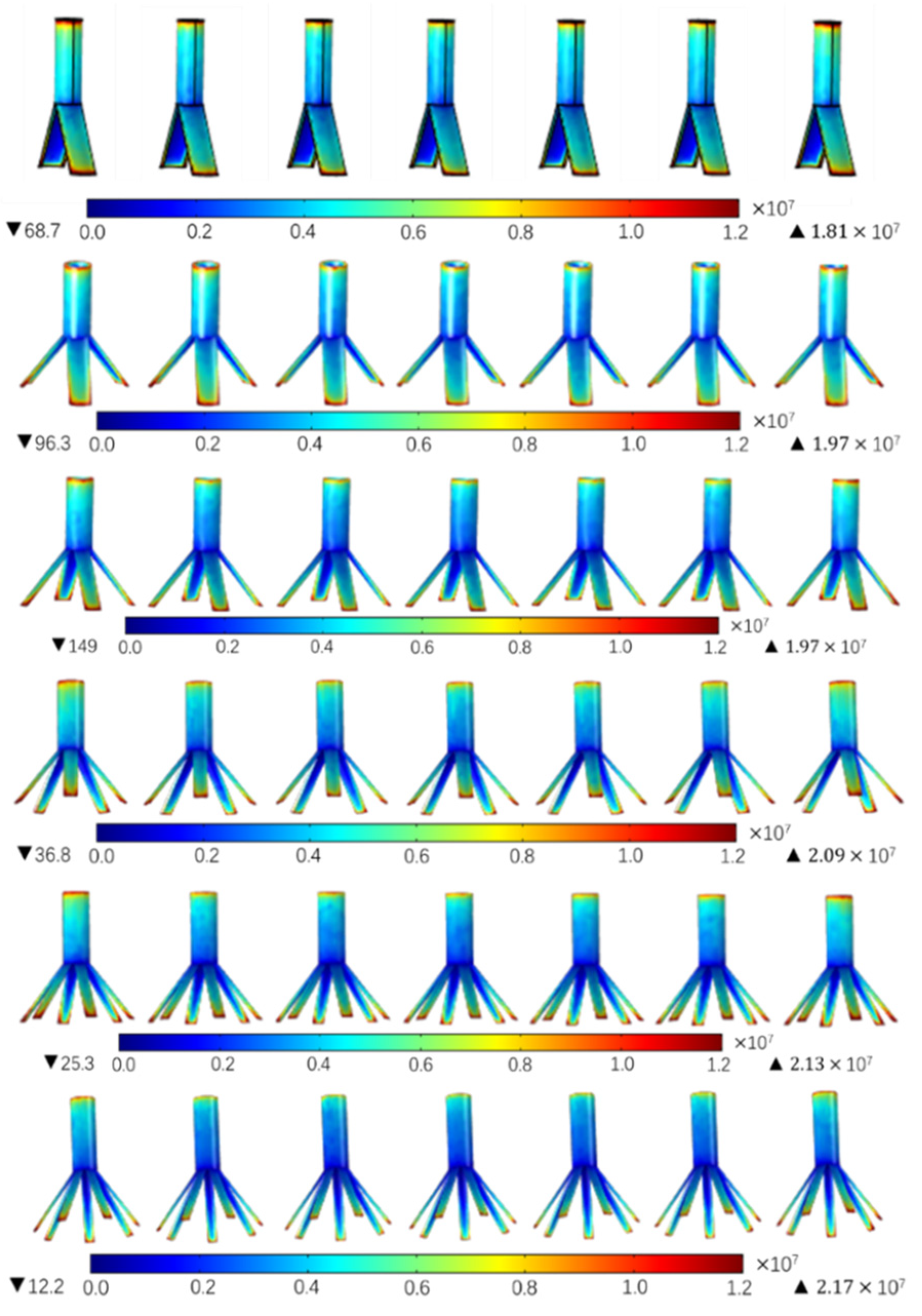
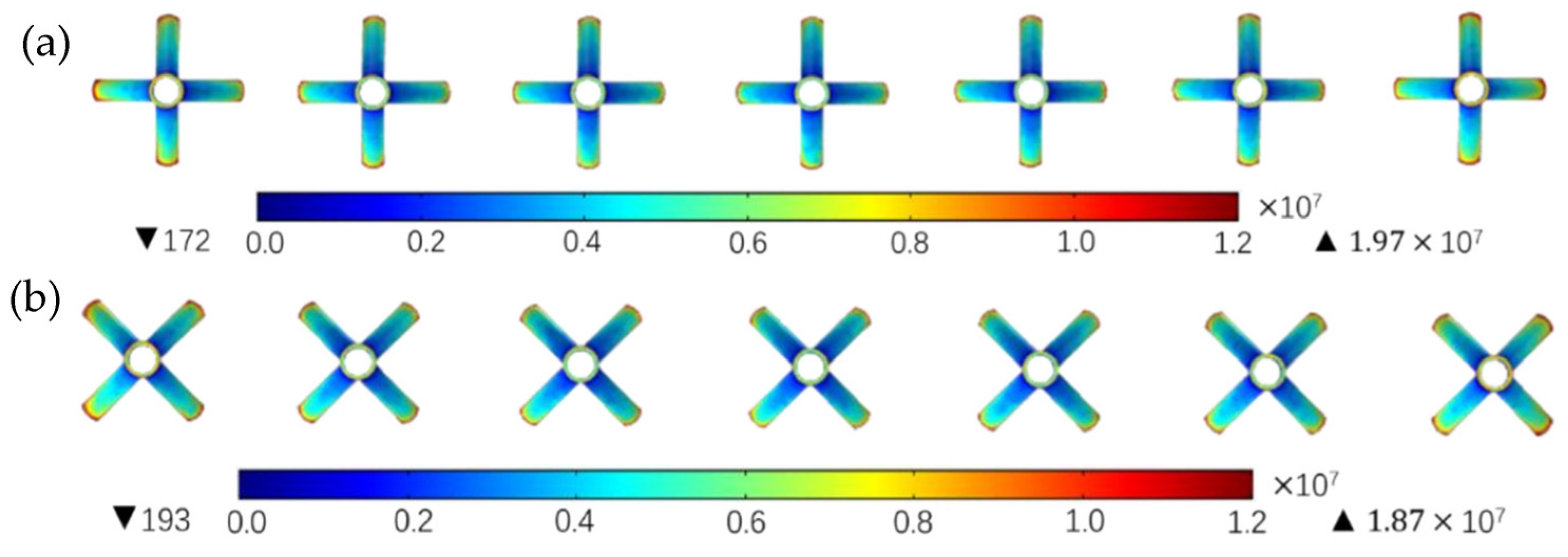
2.2.1. Effects of the Number of Vanes on the Electric Field
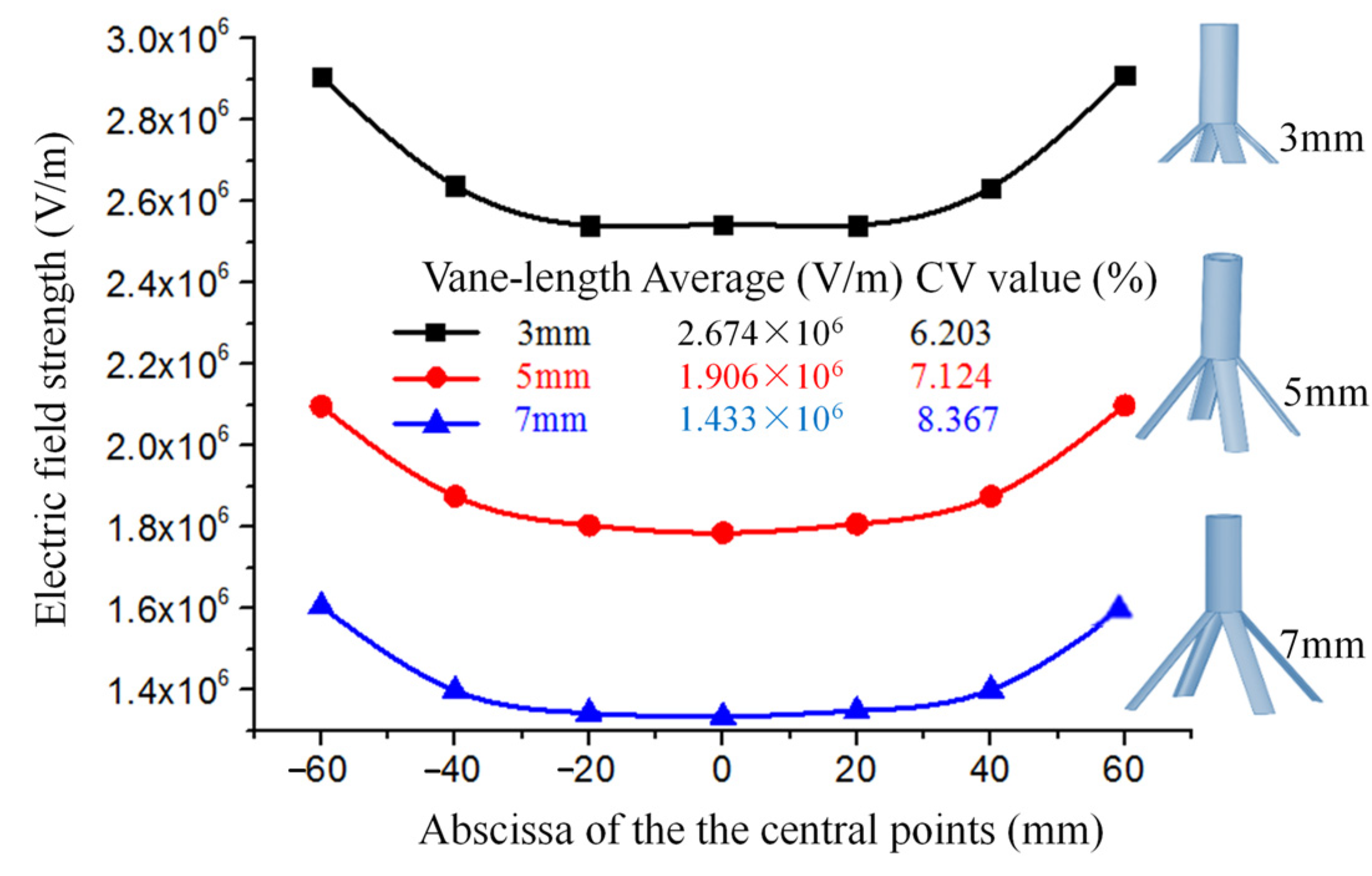
2.2.2. Effects of the Length of the Vanes on the Electric Field
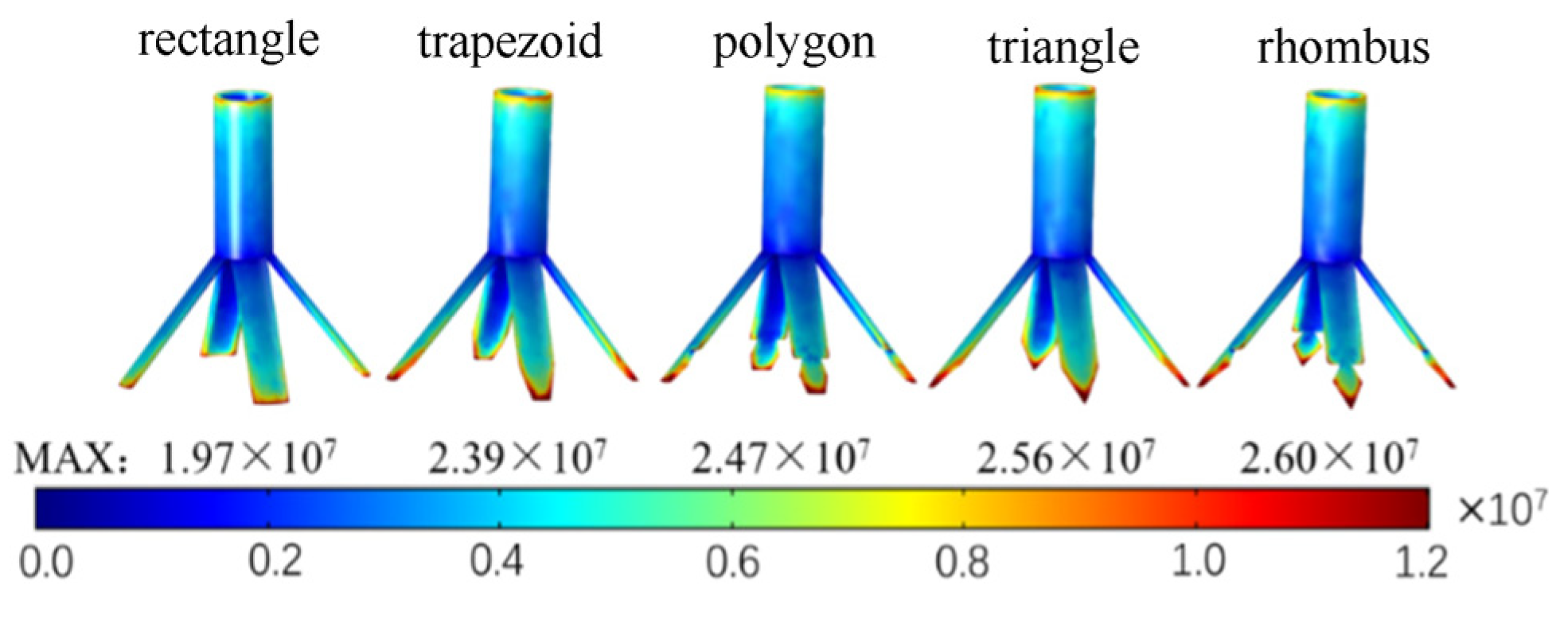
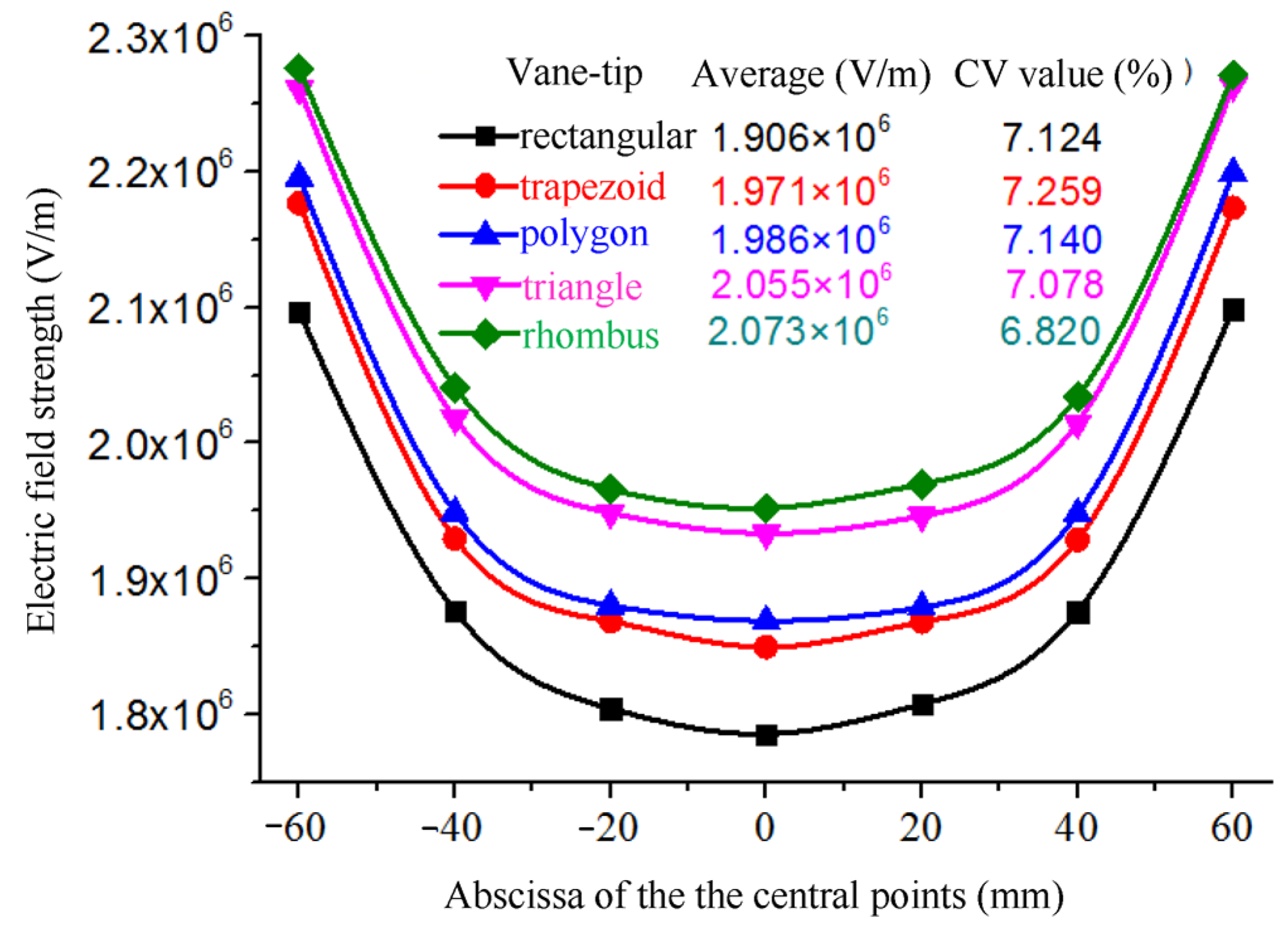
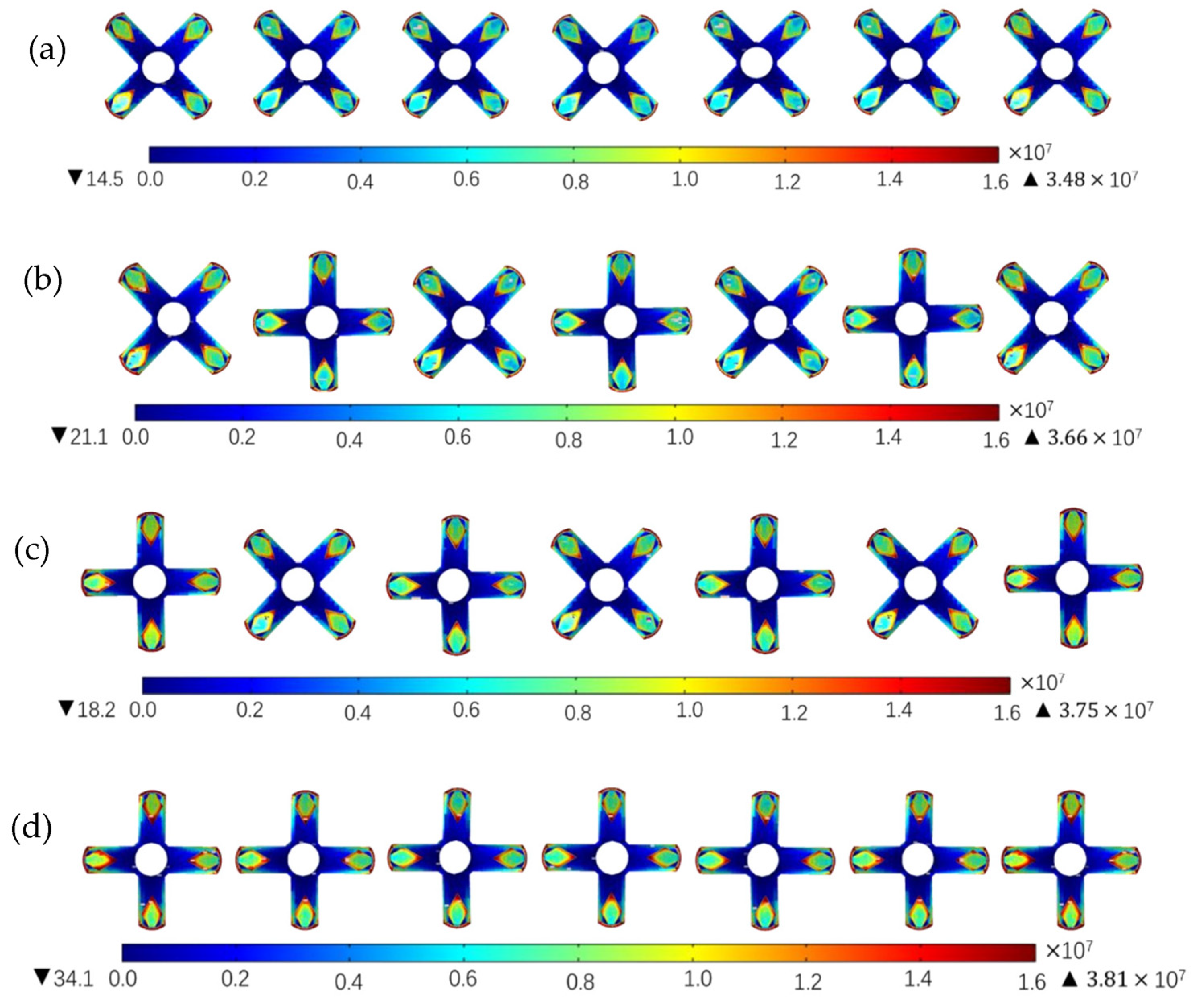
2.2.3. Effects of the Tip Shape of the Vanes on the Electric Field
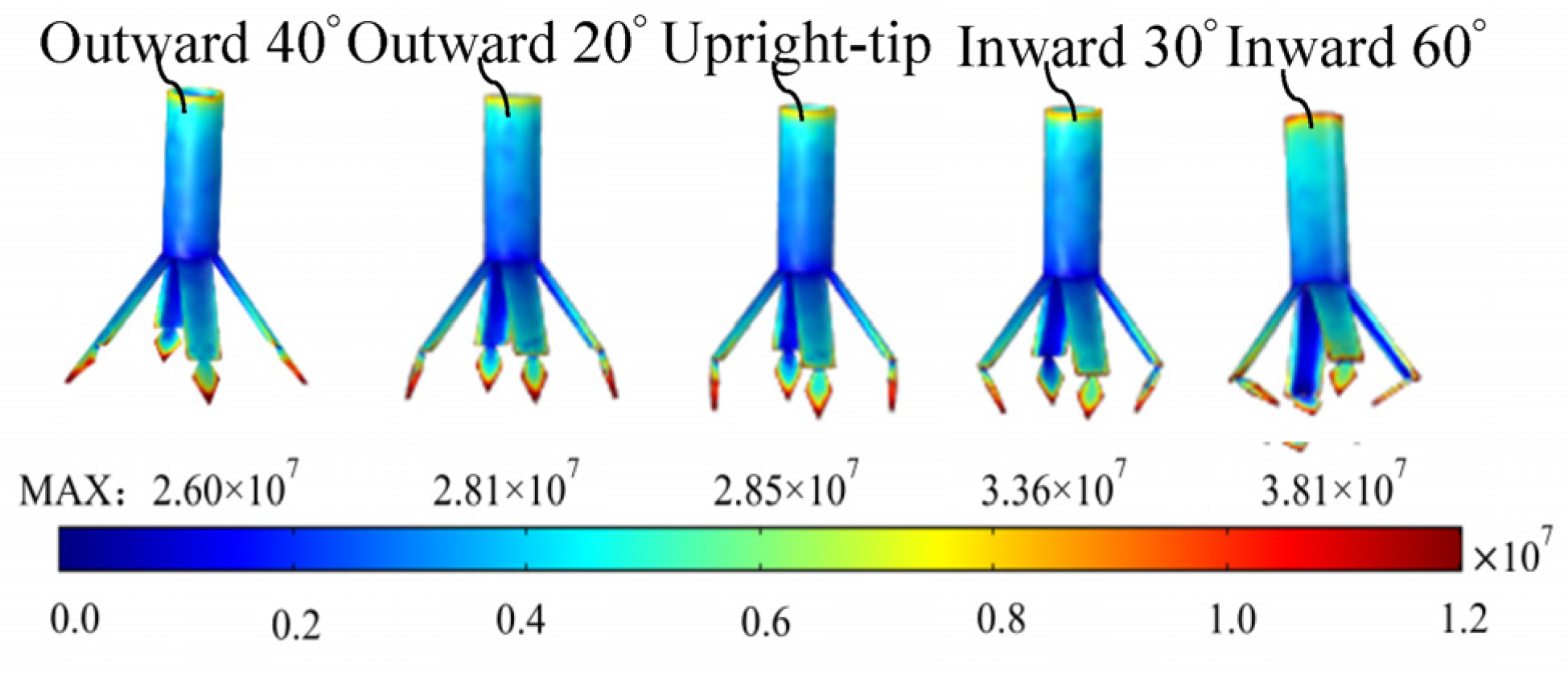
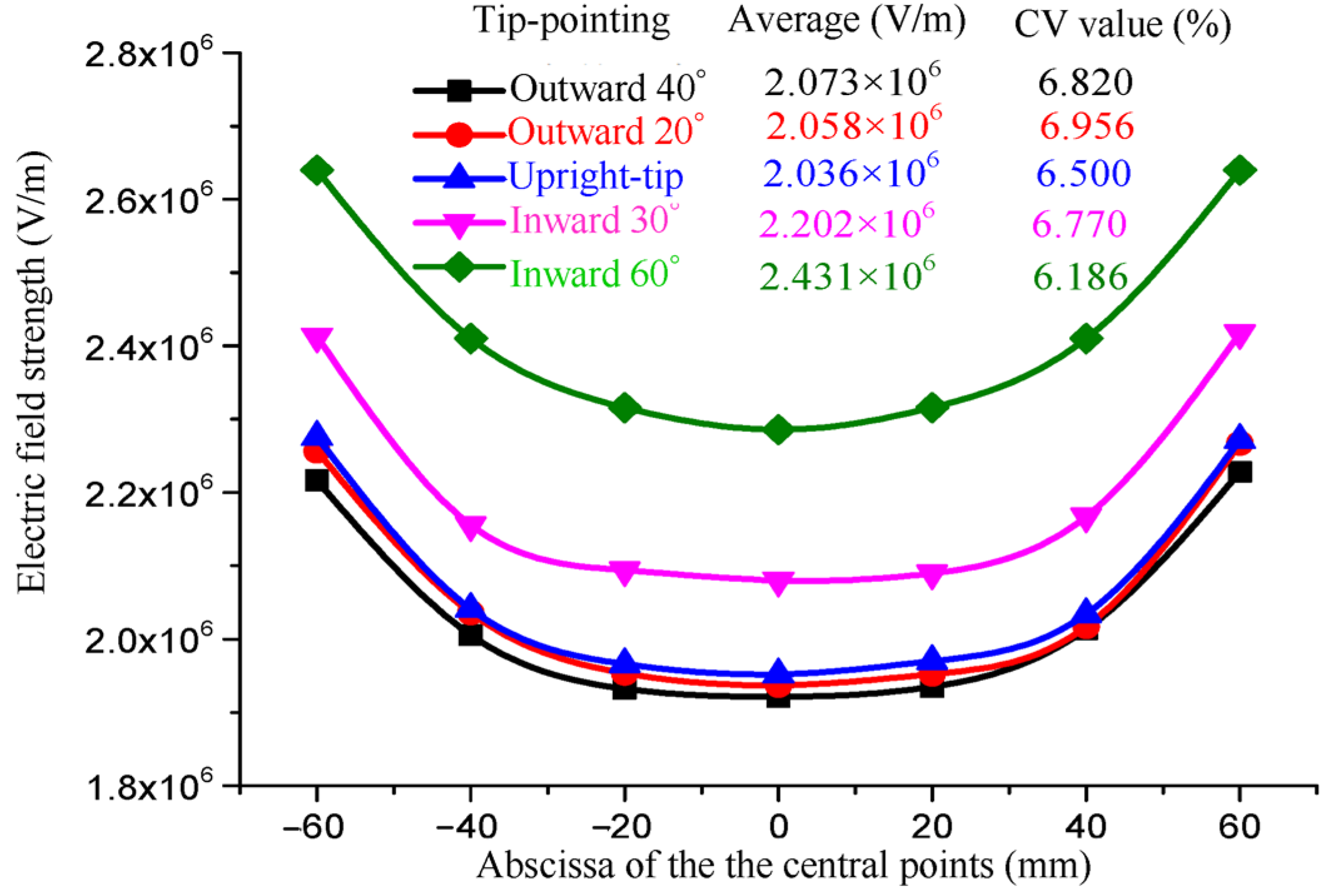
2.2.4. Effects of the Tip-Pointing Direction of the Vanes on the Electric Field
2.2.5. Effect of Relative Orientation of the Vanes between the Neighboring Radial Nozzles on the Electric Field
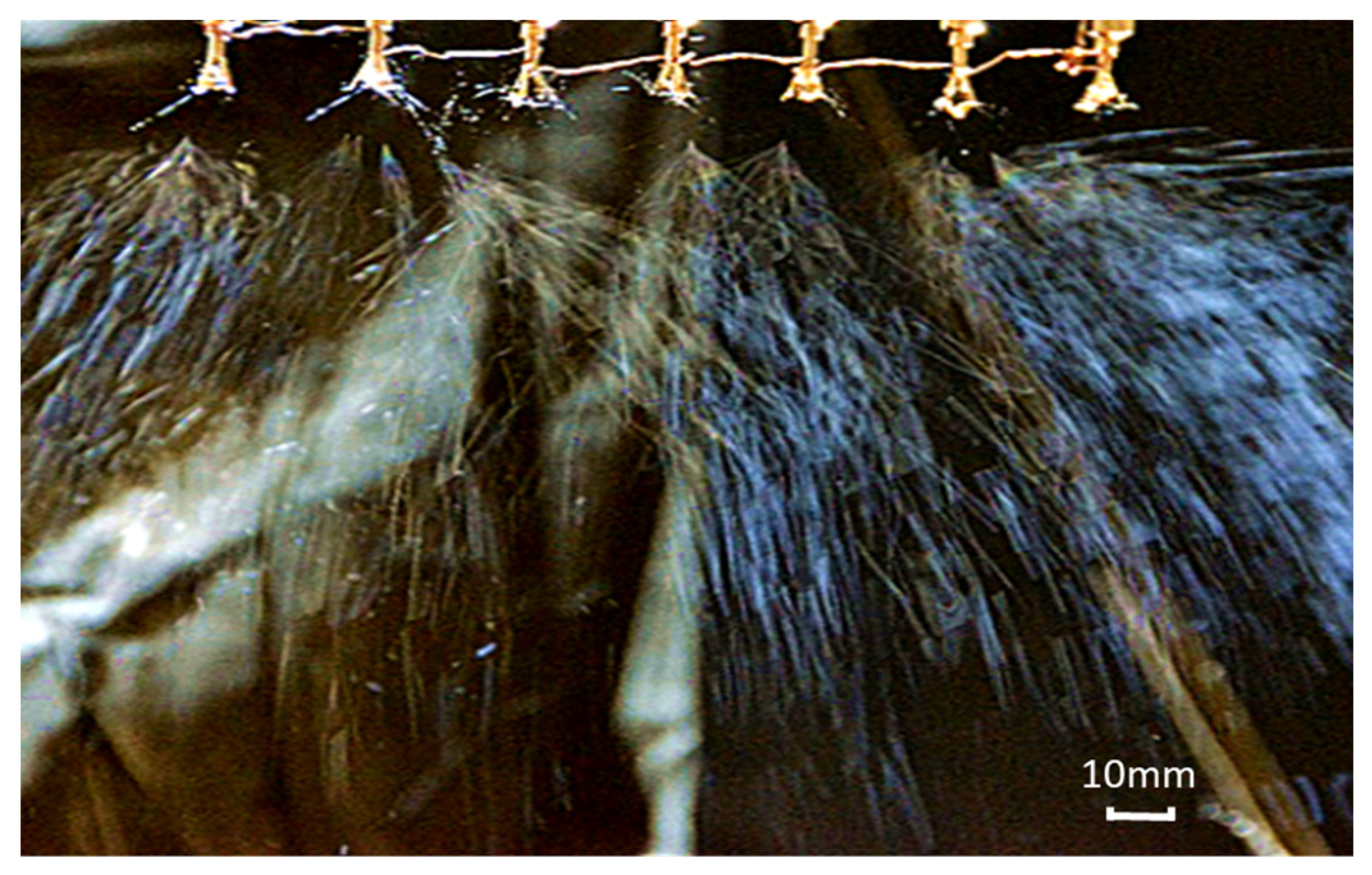
3. Materials and Experiments
3.1. Materials and the Solution
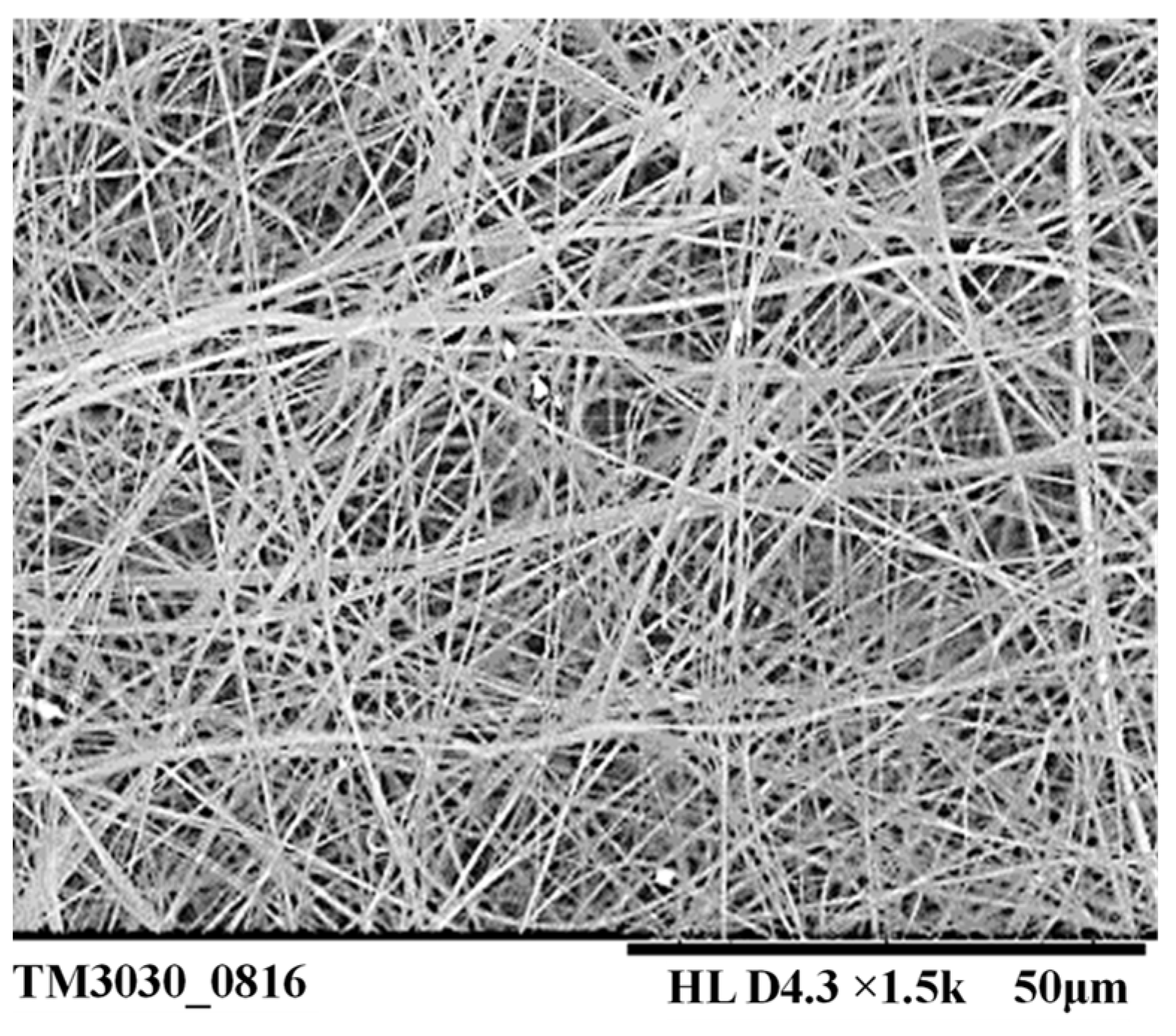
3.2. Electrospinning Experiment
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of advanced electrospinning techniques: A critical review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Pan, F.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Cai, L.; Xiu, Z.; Chen, L.F.; Batalu, D.; et al. Electrospinning technology on one dimensional microwave absorbers: Fundamentals, current progress, and perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Wang, Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Nagy, Z.K.; Vass, P.; Buzgo, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Radacsi, N. The history of electrospinning: Past, present, and future developments. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Awuye, D.E.; Guan, M.; Zhu, Y. Electrospinning-based biosensors for health monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, M.Z.A.; Nordin, D.; Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K. Overview of electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Fong, H. Electrospun polyimide nanofibers and their applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 61, 67–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tian, F.; Shang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z. Co-axial electrospun polystyrene/polyurethane fibres for oil collection from water surface. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.M.; Teoh, X.Y.; Le Hwang, J.; Khong, Z.P.; Sejare, R.; Almashhadani, A.Q.; Abou Assi, R.; Chan, S.Y. Electrospinning and its potential in fabricating pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, W.; Szadkowski, M. Investigation of electrospinning with the use of a multi-jet electrospinning head. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2005, 13, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Theron, S.A.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Kroll, E. Multiple jets in electrospinning: Experiment and modeling. Polymer 2005, 46, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosunmu, O.O.; Chase, G.G.; Kataphinan, W.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibres from multiple jets on a porous tubular surface. J. Nanotechnol. 2006, 17, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varabhas, J.S.; Chase, G.G.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospun nanofibers from a porous hollow tube. Polymer 2008, 49, 4226–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Moon, S.; Lahann, J.; Lee, K.J. Recent progress in preparing nonwoven nanofibers via needleless electrospinning. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppey, N.M.; Gorga, R.E.; Bochinski, J.R.; Clarke, L.I. Effect of solution parameters on spontaneous jet formation and throughput in edge electrospinning from a fluid-filled bowl. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Qin, X. High throughput of quality nanofibers via one stepped pyramid-shaped spinneret. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wu, S.; Shi, W.; Aldrich, A.L.; Kielian, T.; Carlson, M.A. Large-scale and rapid preparation of nanofibrous meshes and their application for drug-loaded multilayer mucoadhesive patch fabrication for mouth ulcer treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28740–28751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, W.; Guo, S. Self-cleaning threaded rod spinneret for high-efficiency needleless electrospinning. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2018, 124, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Hao, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, B. Numerical simulation for electric field intensity and jet space of the quadratic spiral spinneret with auxiliary electrode. Text. Res. J. 2024, 94, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Huang, D.W. Multi-jet electrospinning via auxiliary electrode. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zeng, Y. Effects of electric field on multineedle electrospinning: Experiment and simulation study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5336–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Ali, U.; Shahzad, A.; Qadir, M.B.; Khaliq, Z.; Nazir, A.; Abid, S.; Khan, M.Q.; Hussain, T. Bullet-Spinneret based needleless electrospinning; a versatile way to fabricate continuous nanowebs at low voltage. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 025053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partheniadis, I.; Nikolakakis, I.; Laidmäe, I.; Heinämäki, J. A mini-review: Needleless electrospinning of nanofibers for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Processes 2020, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeau, Y. Surface Tension: From Fundamental Principles to Applications in Liquids and in Solids. Ph.D. Thesis, Warsaw School of Statistical Physics, Warsaw, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Varesano, A.; Carletto, R.A.; Mazzuchetti, G. Experimental investigations on the multi-jet electrospinning process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5178–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Electrically driven jets. J. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Taylor cone and jetting from liquid droplets in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, L. Homogeneous field intensity control during multi-needle electrospinning via finite element analysis and simulation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjo, J.; Umemura, A. Detailed simulation of primary atomization mechanisms in diesel jet sprays (isolated identification of liquid jet tip effects). Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
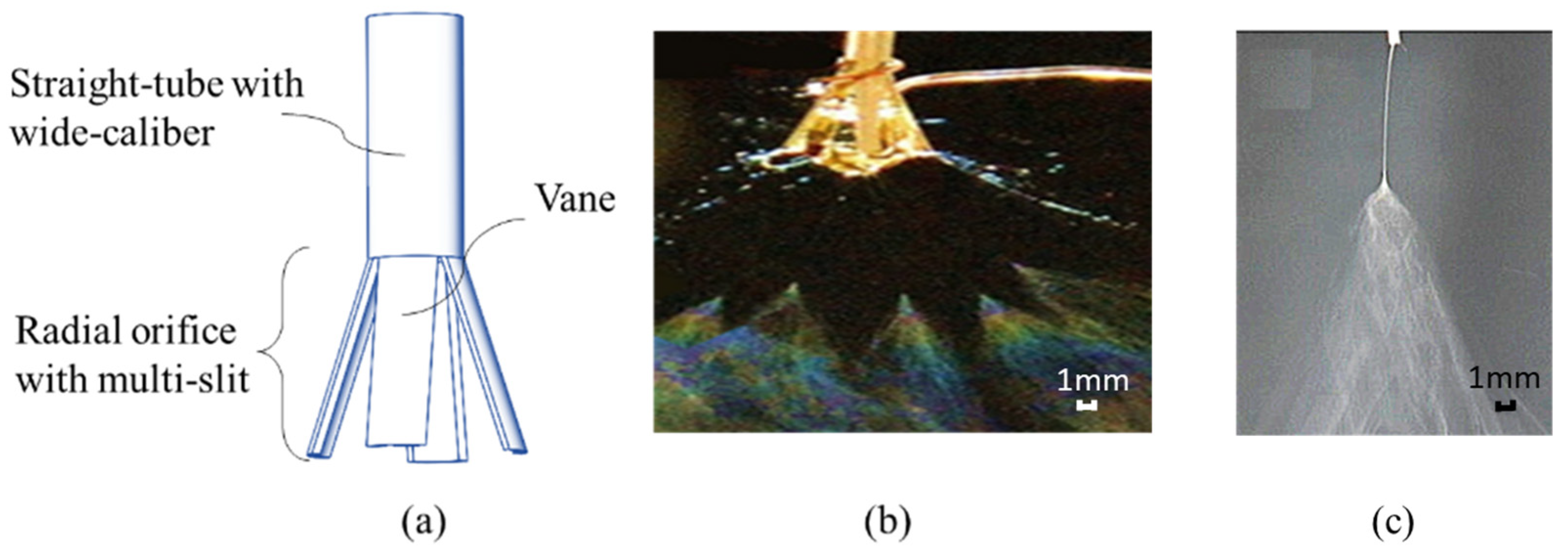
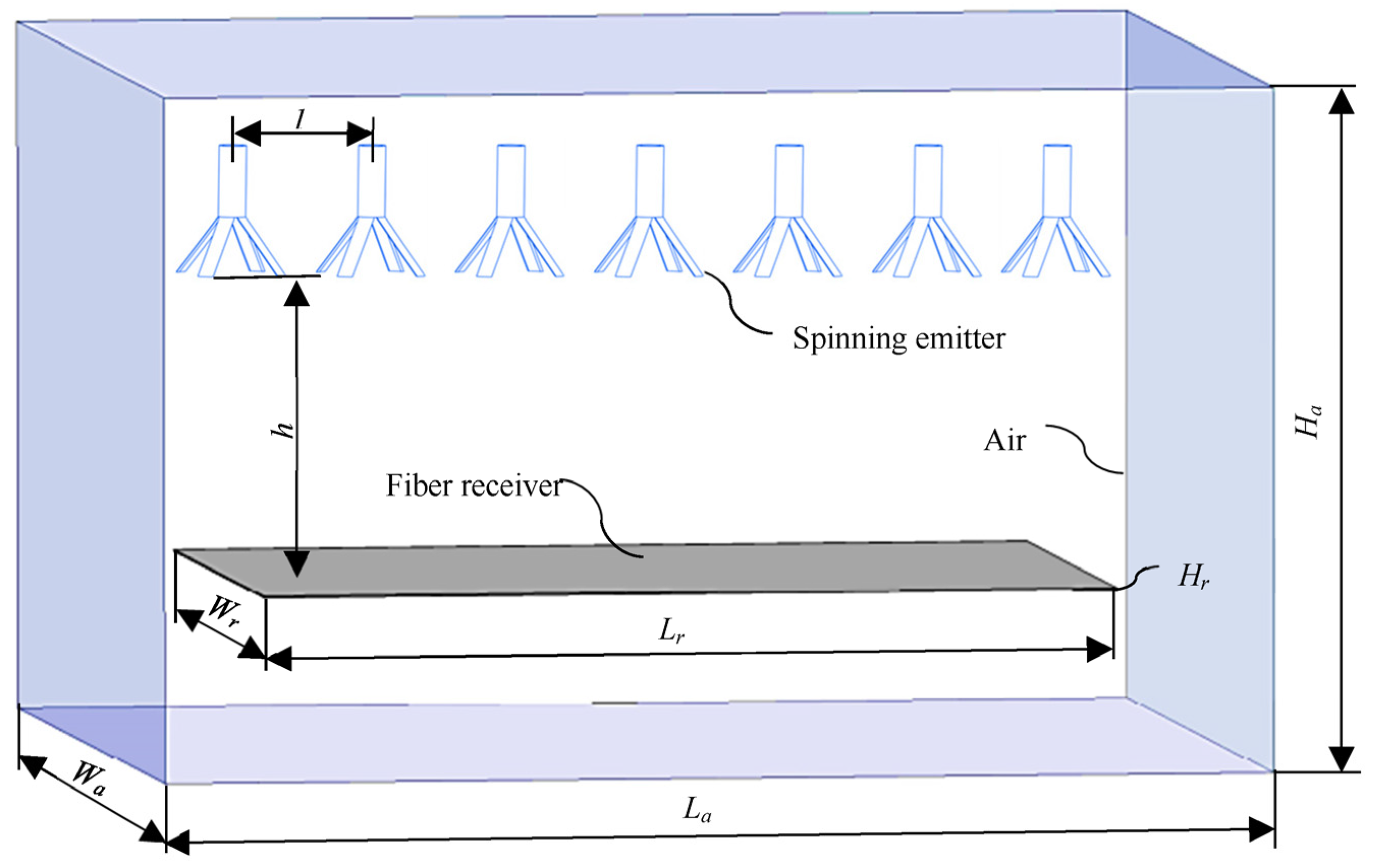

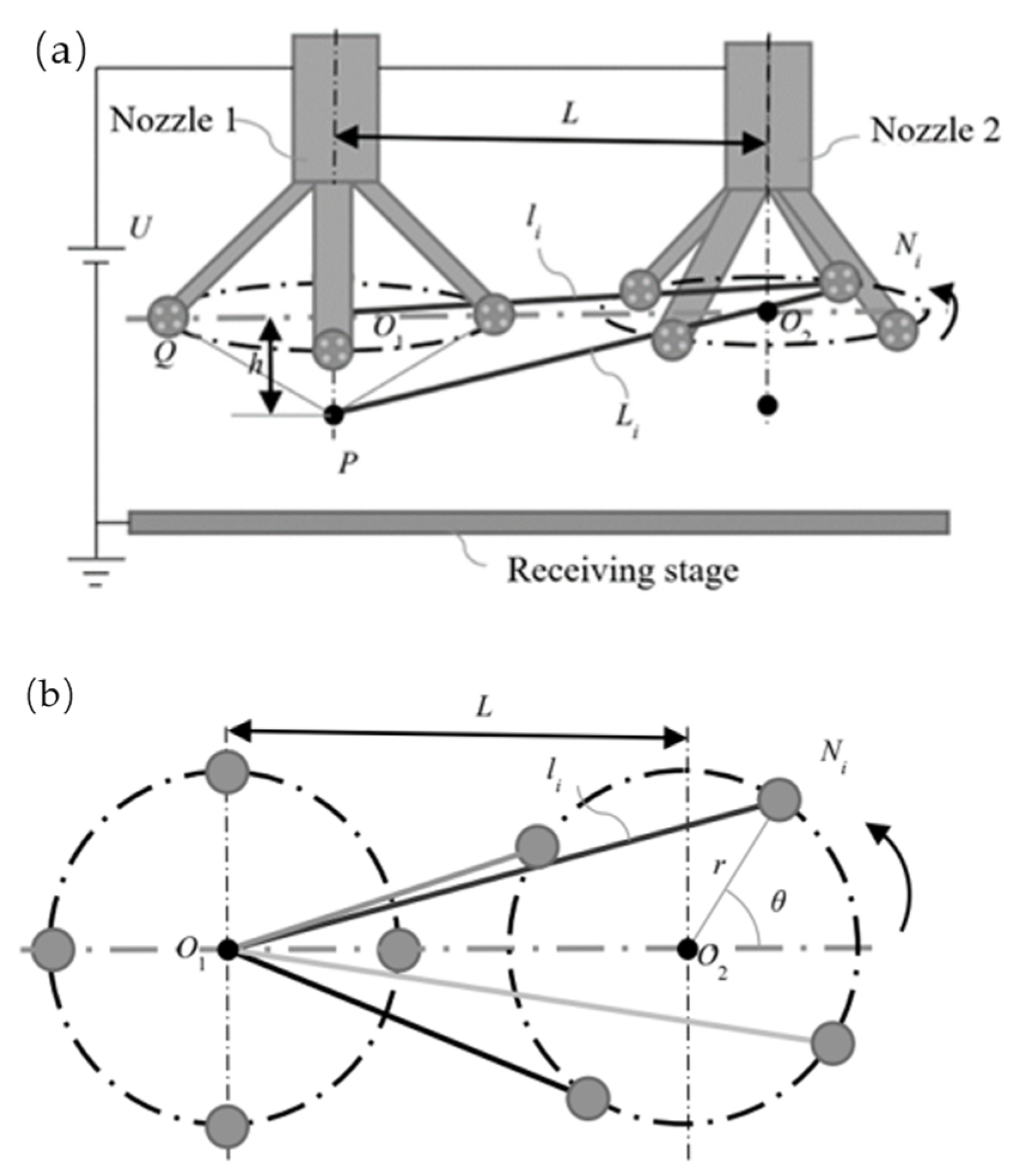




| l (mm) | h (mm) | Receiver Lr × Wr × Hr (mm) | Air La × Wa × Ha (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 200 | 500 × 400 × 1 | 650 × 650 × 400 |
| Instruments | Type | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Spinning device | Seven radial nozzles | In-house |
| DC high-voltage power supply | DW-P/N603 | Tianjin Dongwen High Voltage Power Supply, Ltd., Tianjin, China |
| Metal halide lamp | 70W | Xincheng Lighting, Ltd., Huzhou, China |
| Motor agitator | DF-101S | Gongyi Yuhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou, China |
| Thermostat water bath | HH-4 | Kexi Instrument, Ltd., Changzhou, China |
| Camera | Sony DSC-TX9 | Sony, Beijing, China |
| Electron microscope | TM3030 | Techcomp (China) Ltd., Beijing, China |
| Film-thickness-measuring instrument | CHY-C2 | Jinan Labthink Mechatronics Technology Co., Ltd., Jinan, China |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.1046 | 0.1072 | 0.1261 | 0.1205 | 0.1252 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Pan, S.; Yin, Z. Research on Electric Field Homogenization in Radial Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141199
Liu J, Dong S, Wang C, Liu Y, Pan S, Yin Z. Research on Electric Field Homogenization in Radial Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jian, Shoujun Dong, Chenghao Wang, Yanbo Liu, Shanshan Pan, and Zhaosong Yin. 2024. "Research on Electric Field Homogenization in Radial Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141199
APA StyleLiu, J., Dong, S., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Pan, S., & Yin, Z. (2024). Research on Electric Field Homogenization in Radial Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141199







