Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Synthesis
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound and Microwave Irradiation on the Characteristics of Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica
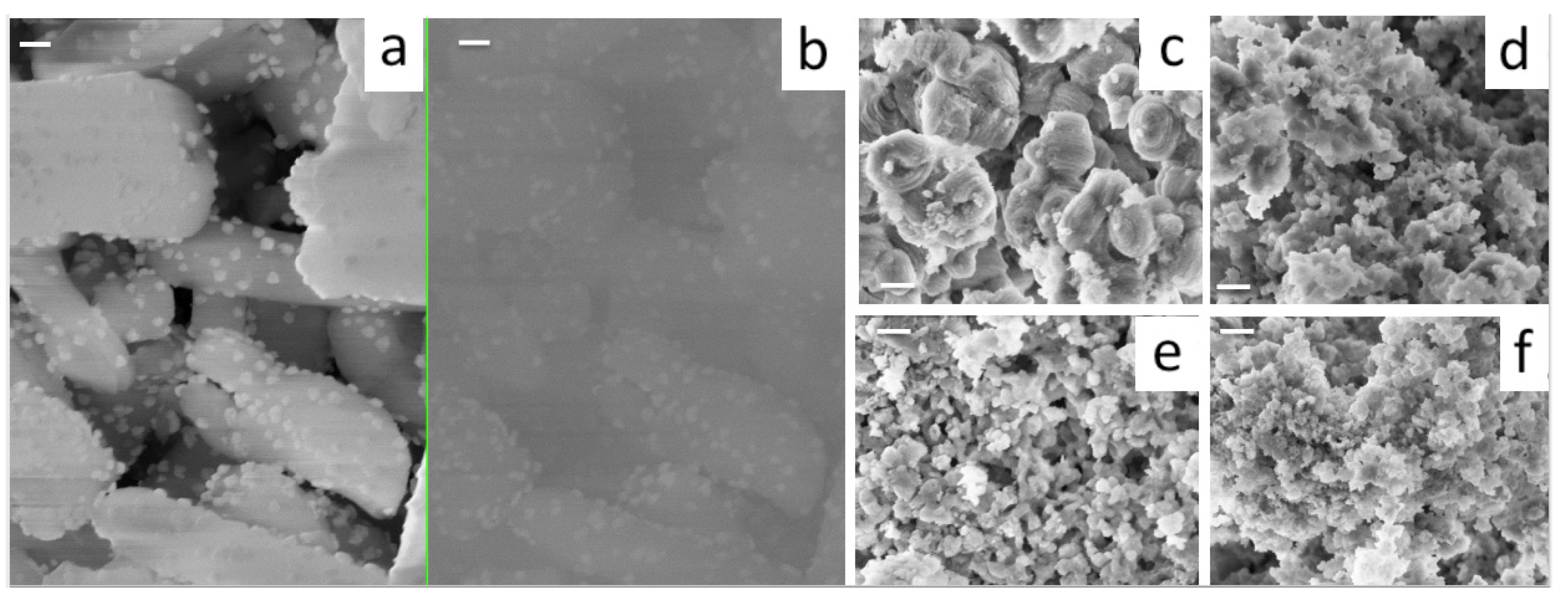
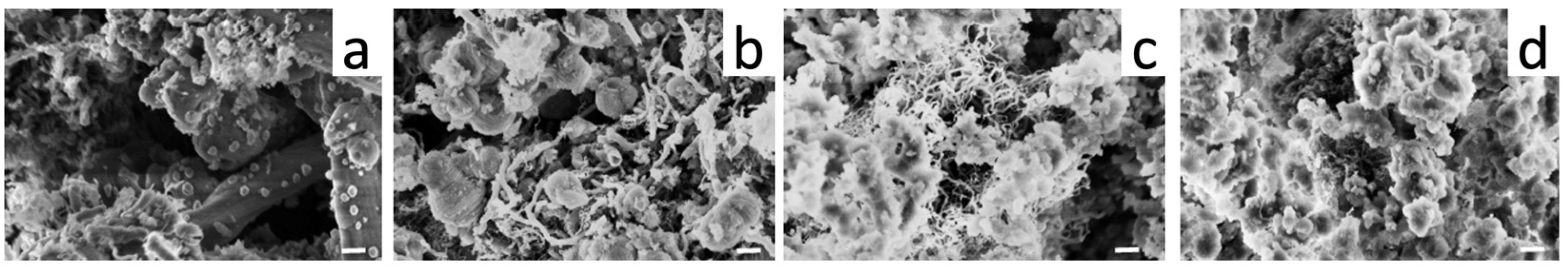
3.2. Ce-Modified Hexagonal Silica as Catalytic Supports for Nickel
3.3. Catalytic Evaluation of Ni/Ce-Promoted Silica in the Ethanol Steam Reforming Reaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, N.; Cho, E.-B.; Patra, A.K.; Kim, D. Ceria-Containing Ordered Mesoporous Silica: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.S.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y. Pore Size Effect on Methane Adsorption in Mesoporous Silica Materials Studied by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, W.S.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Georgi, D.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y. Methane Adsorption in Model Mesoporous Material, SBA-15, Studied by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4354–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Dutta, S.; Wu, K.C.W. Integrated, Cascading Enzyme-/Chemocatalytic Cellulose Conversion Using Catalysts Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3241–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Fuku, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kamegawa, T.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Design and Functionalization of Photocatalytic Systems within Mesoporous Silica. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J. The Discovery of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves from the Twenty Year Perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Xia, K.; Gan, N.; Lu, X.; Nie, R.; Xia, Q. Construction of Solely Lewis Acidic Sites on Zr-MCM-41 and the Catalytic Activity for the Prins Condensation of β-pinene and Paraformaldehyde to Nopol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 230, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.; Pradhan, A.C.; Parida, K. A Comparative Study on Adsorption and Photocatalytic Dye Degradation under Visible Light Irradiation by Mesoporous MnO 2 Modified MCM-41 Nanocomposite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, O.G.; Heredia, J.D.L.R.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Castellanos, A.M.; Llanos, M. Hydrogen Production over Rh/Ce-MCM-41 catalysts via Ethanol Steam Reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 13914–13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, C.; Reboul, J.; Bonne, M.; Lebeau, B. Ecodesign of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4217–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook of Ultrasonics and Sonochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 978-981-287-277-7.
- Askari, S.; Alipour, S.M.; Halladj, R.; Farahani, M.H.D.A. Effects of Ultrasound on the Synthesis of Zeolites: A review. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompsett, G.A.; Conner, W.C.; Yngvesson, K.S. Microwave Synthesis of Nanoporous Materials. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 296–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, I.; Ricci, A.S. Chemical Activation Using an Open-End Coaxial Applicator. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2006, 41, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.T.; Peden, C.H.F. Oxygen Vacancies and Catalysis on Ceria Surfaces. Science 2005, 309, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, L.; Duprez, D. Ceria-Based Solid Catalysts for Organic Chemistry. Chemsuschem 2010, 3, 654–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akondi, A.M.; Trivedi, R.; Sreedhar, B.; Kantam, M.L.; Bhargava, S. Cerium-Containing MCM-41 Catalyst for Selective Oxidative Arene Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reactions. Catal. Today 2012, 198, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chen, Y.; Min, L.; Fang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Liquid Oxidation of Cyclohexane to Cyclohexanol over Cerium-Doped MCM-41. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 246, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Valenzuela, M.; Salas, P.; García-Ruiz, A.; Toledo, J.; Cortes-Jácome, M.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; Novaro, O. Ni/Ce-MCM-41 Mesostructured Catalysts for Simultaneous Production of Hydrogen and Nanocarbon via Methane Decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3509–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Gong, J. Ceria-promoted Ni/SBA-15 Catalysts for Ethanol Steam Reforming with Enhanced Activity and Resistance to Deactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, W.; Yue, B.; He, H. Promotional Effect of Cerium on Nickel-Containing Mesoporous Silica for Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Castaldo, F.; Ciambelli, P.; Iaquaniello, G. CeO2-supported Pt/Ni Catalyst for the Renewable and Clean H2 Production via Ethanol Steam Reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 145, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, I.A.C.; Montini, T.; Lorenzut, B.; Troiani, H.; Gennari, F.C.; Graziani, M.; Fornasiero, P. Hydrogen Production from Ethanol Steam Reforming on M/CeO2/YSZ (M=Ru, Pd, Ag) Nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2012, 180, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles, J.; Carrero, A.; Vizcaíno, A. Ce and La Modification of Mesoporous Cu–Ni/SBA-15 Catalysts for Hydrogen Production Through Ethanol Steam Reforming. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 119, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Ereña, J.; Montero, C.; Azkoiti, M.J.; Bilbao, J.; Gayubo, A.G. Reaction Pathway for Ethanol Steam Reforming on A Ni/SiO 2 Catalyst Including coke Formation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18820–18834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R.; Onor, M.; Bramanti, E.; Longo, I.; Ferrari, C. Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction of Microcrystalline Cellulose in Hydrothermal Microwave-Assisted Decomposition: Effect of Modified Zeolite Beta. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, T.N.; Huang, T.C.; Toraya, H.; Hubbard, C.R.; Robie, S.B.; Louër, D.; Göbel, H.E.; Will, G.; Gilles, R.; Raftery, T. JCPDS—International Centre for Diffraction Data Round Robin Study of Silver Behenate. A Possible Low-Angle X-Ray Diffraction Calibration Standard. Powder Diffr. 1995, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Tovar-Rodríguez, J.; Bramanti, E.; Duce, C.; Longo, I.; Fratini, E.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R.; Ferrari, C. Surfactant Recovery from Mesoporous Metal-modified Materials (Sn–, Y–, Ce–, Si–MCM-41), by Ultrasound Assisted Ion-Exchange Extraction and Its Re-Use for a Microwave in Situ Cheap and Eco-Friendly MCM-41 Synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7020–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.; Gómez, V.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Revés, M.; Echeverría, J.; Cremades, E.; Barragán, F.; Alvarez, S. Covalent Radii Revisited. Dalton Trans. 2008, 21, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleitz, F.; Schmidt, W.; Schüth, F. Evolution of Mesoporous Materials during the Calcination Process: Structural and Chemical Behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 44, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H. Small Angle Neutron Scattering Studies of the Structure and Interaction in Micellar and Microemulsion Systems. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1986, 37, 351–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Song, B.Y.; Lee, T.G. Effects of Surfactant/Silica and Silica/Cerium Ratios on the Characteristics of Mesoporous Ce-MCM-41. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, C.; Yin, H. Effect of the Si/Ce Molar Ratio on the Textural Properties of Rare Earth Element Cerium Incorporated Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Obtained Room Temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9425–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, C.-S.; Yin, H. Characterization and Synthesis of Ce-Incorporated Mesoporous Molecular Sieves under Microwave Irradiation Condition. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.M.; Zholobenko, V.L.; Thursfield, A.; Plaisted, R.J.; Cundy, C.S.; Dwyer, J. In situ FTIR Study of the Formation of MCM-41. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Sainkar, S.; Kumar, R. Cerium Containing MCM-41-Type Mesoporous Materials and their Acidic and Redox Catalytic Properties. J. Catal. 2002, 207, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulková, D.; Vít, Z. Silica-Ceria as Support for the Preparation of NiMo(P) Hydrodesulfurization and Hydrodenitrogenation Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1995, 125, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Low-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction over Cu- and Ni-Loaded Cerium Oxide Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 27, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Han, C. Nickel Nanoparticles Highly Dispersed with An Ordered Distribution in MCM-41 Matrix as An Efficient Catalyst for Hydrodechlorination of Chlorobenzene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 185, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L. A Simple Method to Prepare Highly Active and Dispersed Ni/MCM-41 Catalysts by Co-Impregnation. Catal. Commun. 2013, 42, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryanto, A.; Fernando, S.; Murali, N.; Adhikari, S. Current Status of Hydrogen Production Techniques by Steam Reforming of Ethanol: A Review. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlett, C.M.A.; Aydin, A.; Durndell, L.J.; Frattini, L.; Isaacs, M.A.; Lee, A.F.; Liu, X.; Olivi, L.; Trofimovaite, R.; Wilson, K.; et al. Tailored Mesoporous Silica Supports for Ni Catalysed Hydrogen Production from Ethanol Steam Reforming. Catal Commun 2017, 91, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Senanayake, S.D.; Zhou, G.; Stacchiola, D.; Stach, E.A.; Rodriguez, J.A. Steam Reforming of Ethanol on Ni/CeO2: Reaction Pathway and Interaction between Ni and the CeO2 Support. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankhah, S.; Abatzoglou, N.; Gitzhofer, F.; Blanchard, J.; Oudghiri-Hassani, H. Catalytic Properties of Carbon Nano-Filaments Produced by Iron-Catalysed Reforming of Ethanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
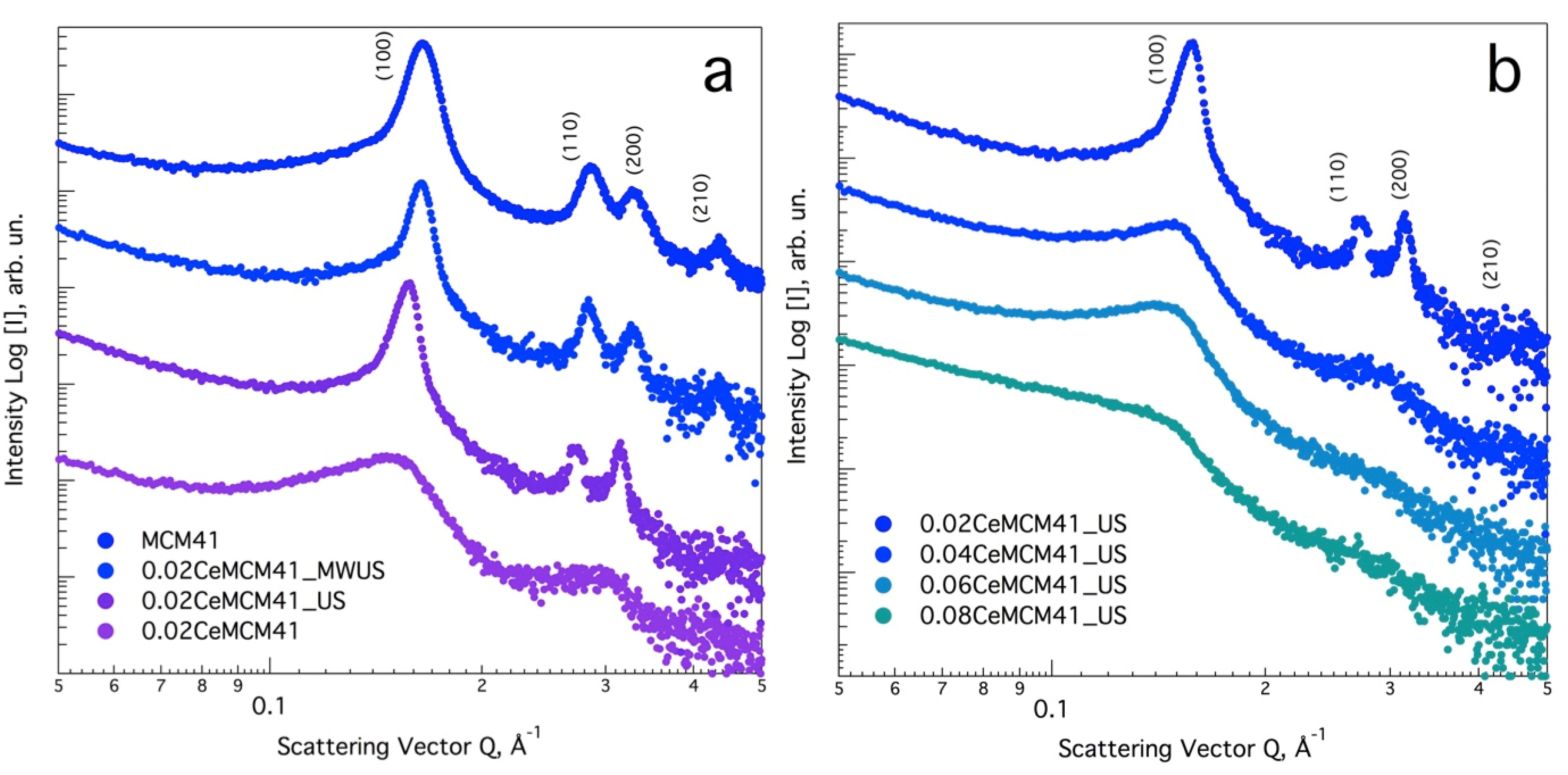


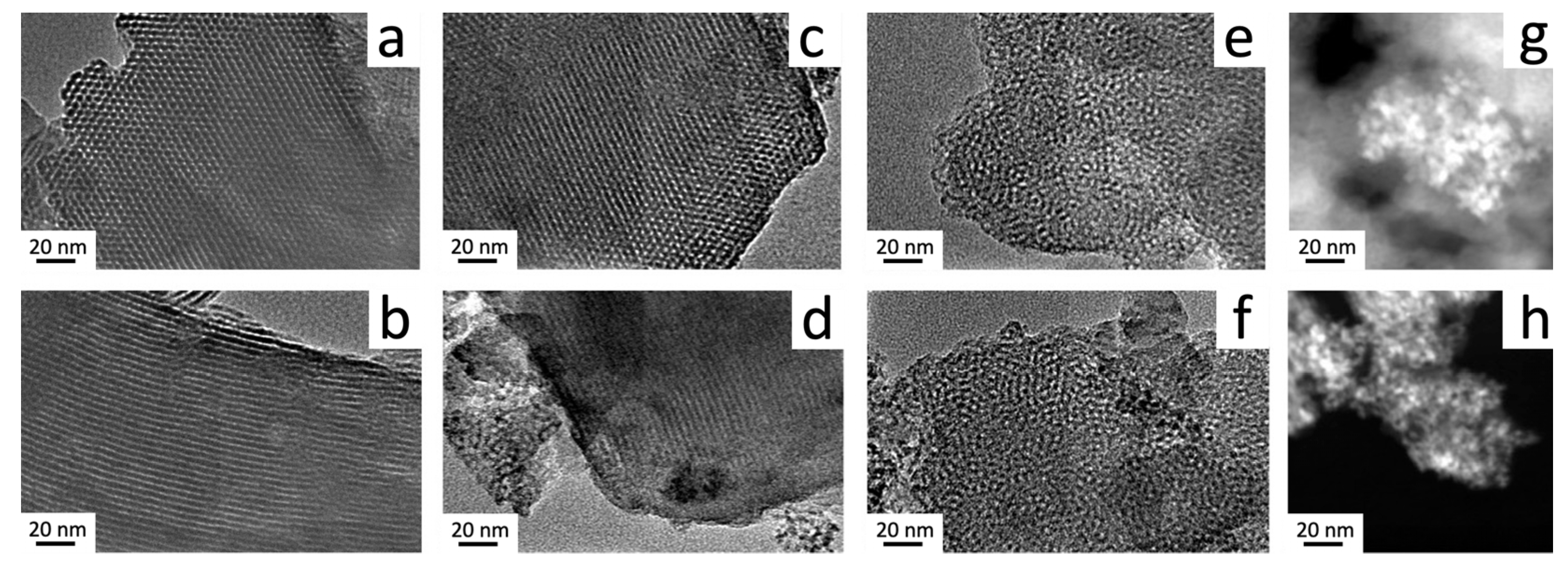
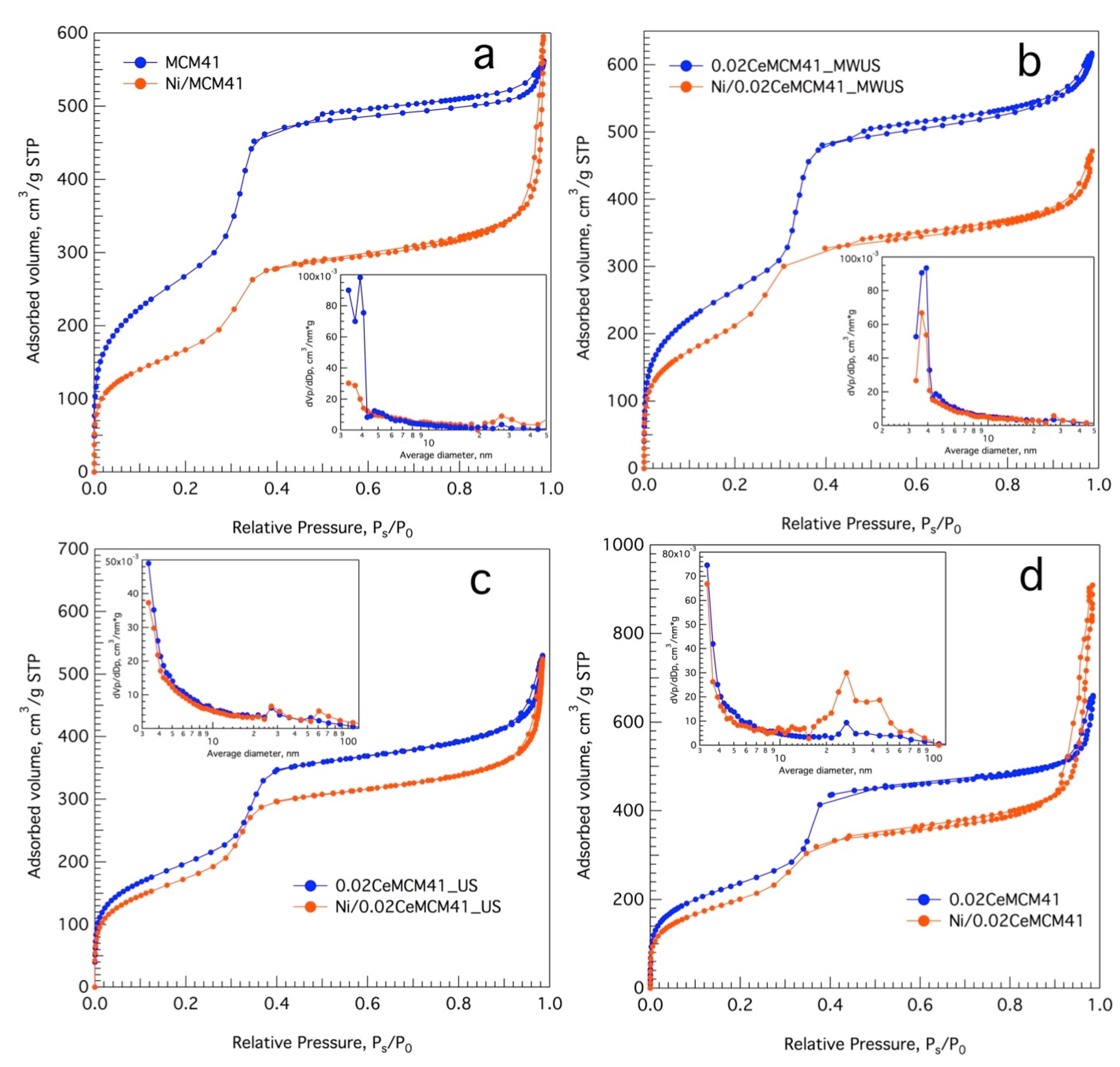

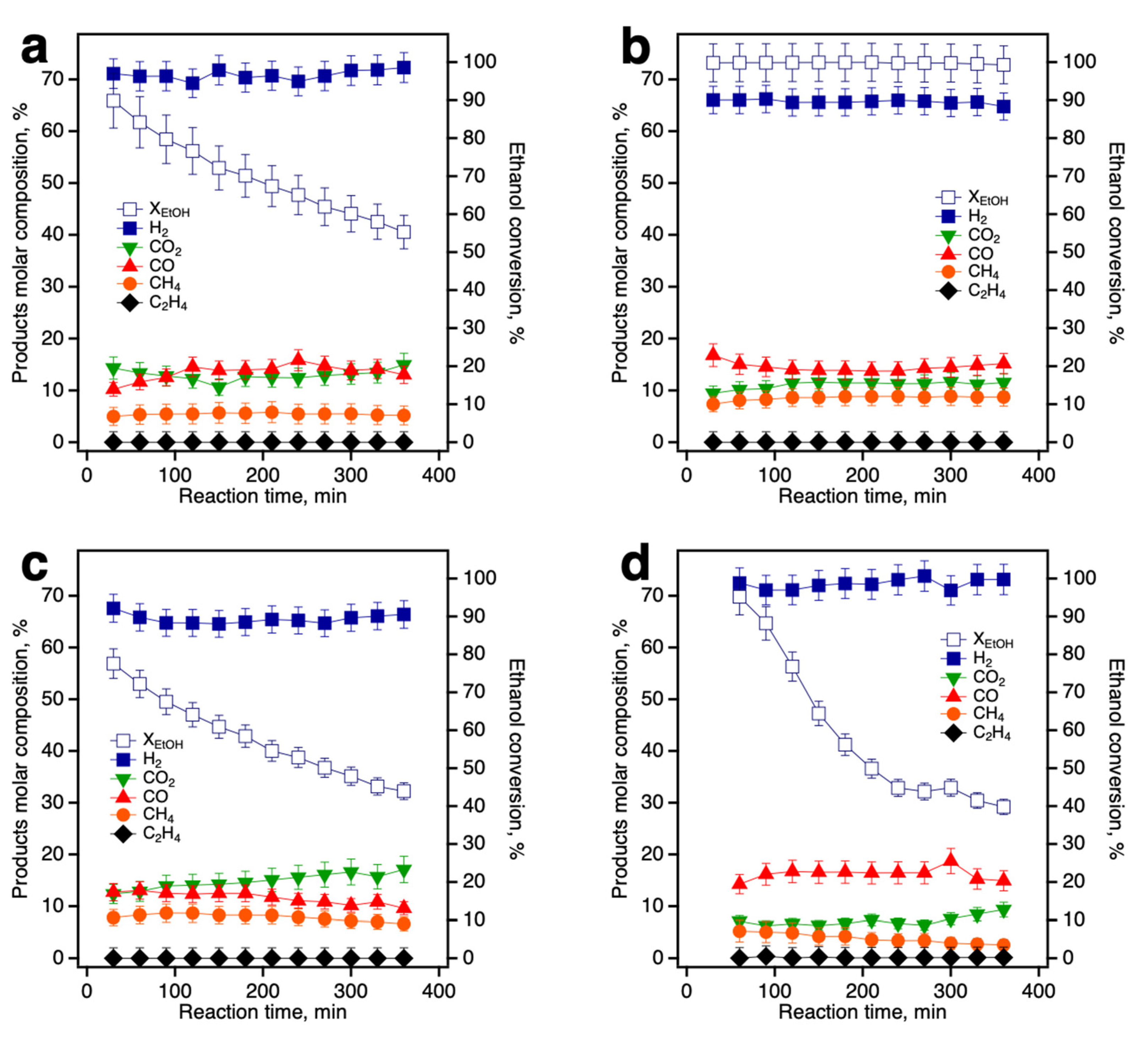
| Sample Name | Ce/Si Ratio | d100, nm [a] | a0, nm [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 0 | 4.42 | 5.10 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_MWUS [c] | 0.02 | 4.46 | 5.15 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41 [d] | 0.02 | 4.78 | 5.52 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.02 | 4.63 | 5.35 |
| 0.04Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.04 | 4.88 | 5.63 |
| 0.06Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.06 | 4.98 | 5.75 |
| 0.08Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.08 | 5.04 | 5.82 |
| Sample Name | SBET [a], m2g−1 | Vpore [b], cm3g−1 | Vmonolayer [c], cm3g−1 | Dpore [d], nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 980 | 0.86 | 225 | 3.49 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_MWUS | 967 | 0.94 | 222 | 3.88 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41 | 865 | 0.96 | 199 | 4.45 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_US | 806 | 0.77 | 185 | 3.84 |
| 0.04Ce-MCM-41_US | 711 | 0.68 | 163 | 3.84 |
| 0.06Ce-MCM-41_US | 629 | 0.65 | 145 | 4.14 |
| 0.08Ce-MCM-41_US | 546 | 0.60 | 125 | 4.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tovar-Rodriguez, J.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Ferrari, C.; de los Reyes-Heredia, J.A.; Ramírez-Hernández, Y.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R. Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
Tovar-Rodriguez J, Fratini E, Baglioni P, Ferrari C, de los Reyes-Heredia JA, Ramírez-Hernández Y, Galindo-Esquivel IR. Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(6):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
Chicago/Turabian StyleTovar-Rodriguez, Jorge, Emiliano Fratini, Piero Baglioni, Carlo Ferrari, José Antonio de los Reyes-Heredia, Yonatan Ramírez-Hernández, and Ignacio René Galindo-Esquivel. 2023. "Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming" Nanomaterials 13, no. 6: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
APA StyleTovar-Rodriguez, J., Fratini, E., Baglioni, P., Ferrari, C., de los Reyes-Heredia, J. A., Ramírez-Hernández, Y., & Galindo-Esquivel, I. R. (2023). Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials, 13(6), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997








