Mechanism of Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Transport of Thermally Radiative Williamson Nanomaterials with Slip Boundaries and Induced Magnetic Field: A Bio-Nanoengineering Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
2.1. Williamson Nanofluid Model
2.2. Formulation
- (a)
- The equation of continuity is defined as
- (b)
- (c)
- The thermal energy, which includes viscous dissipation, thermal radiation effects, nanoparticle fraction, and solute concentration, is defined as [50]
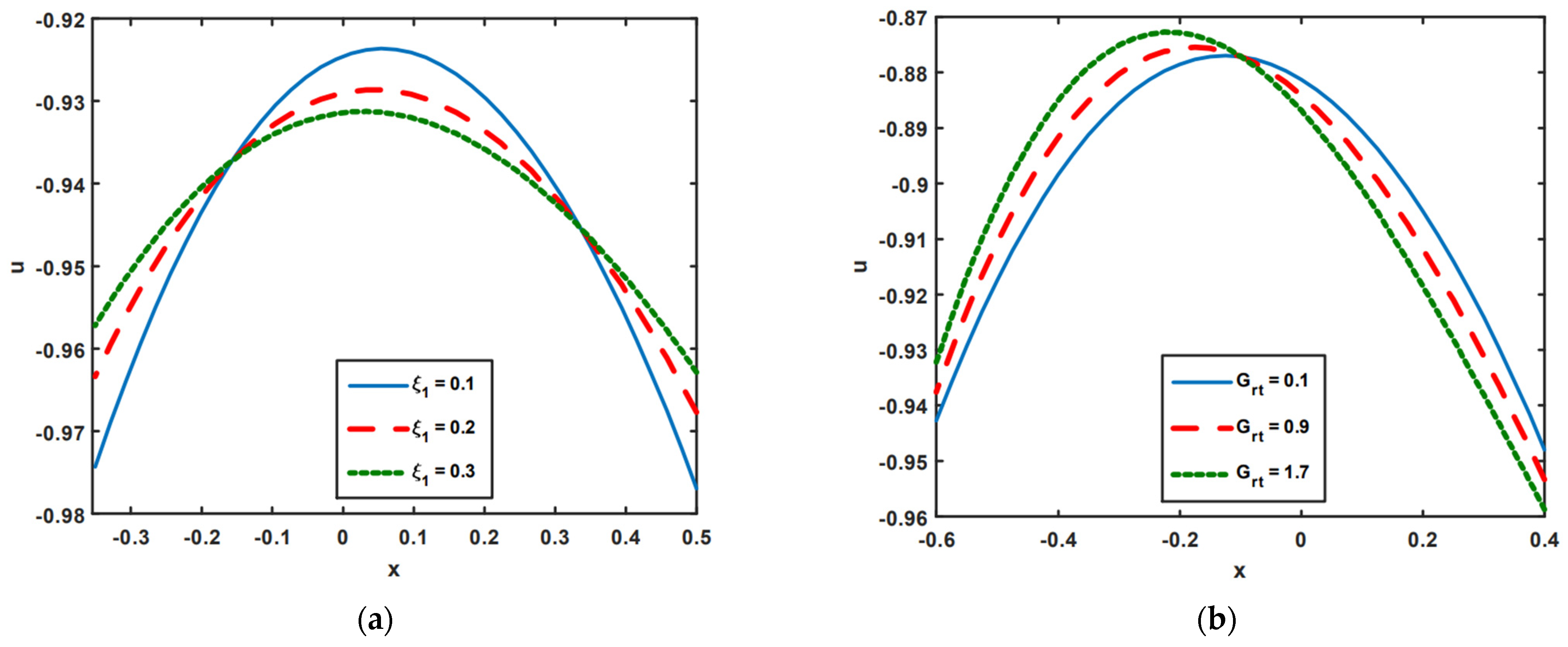
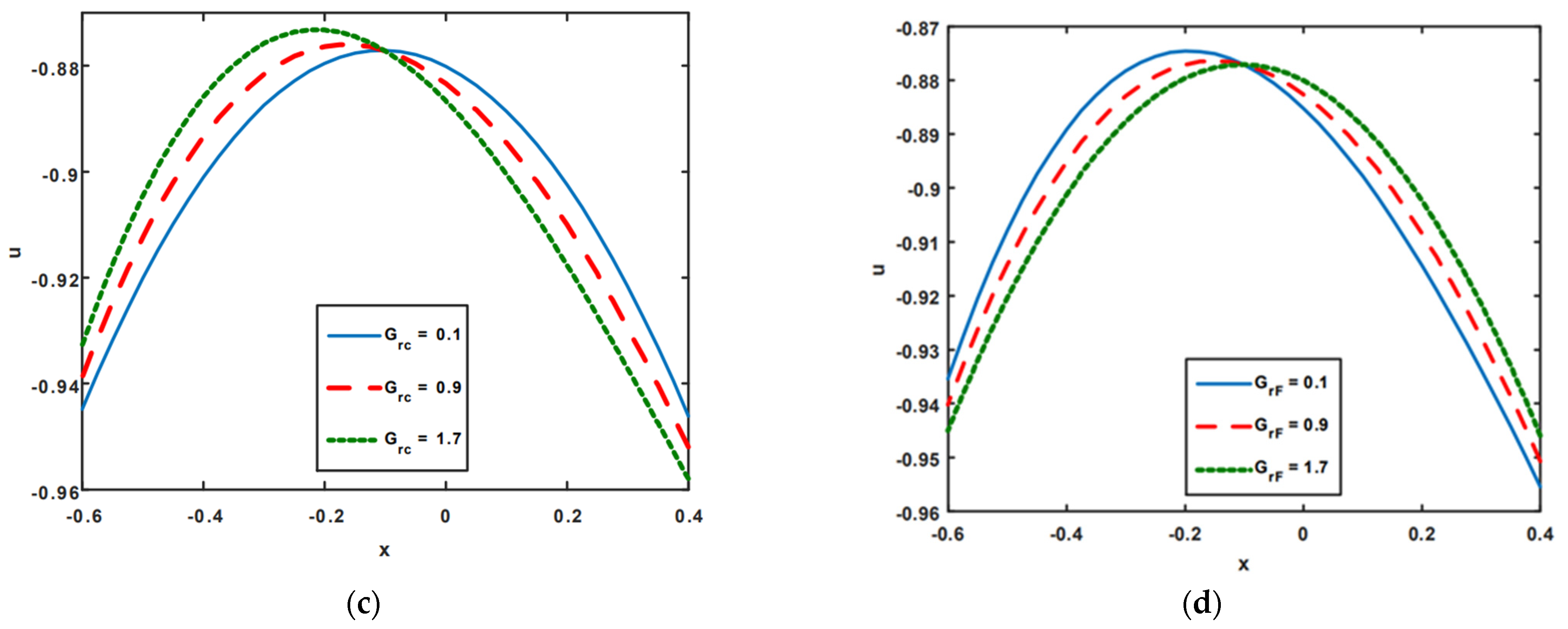
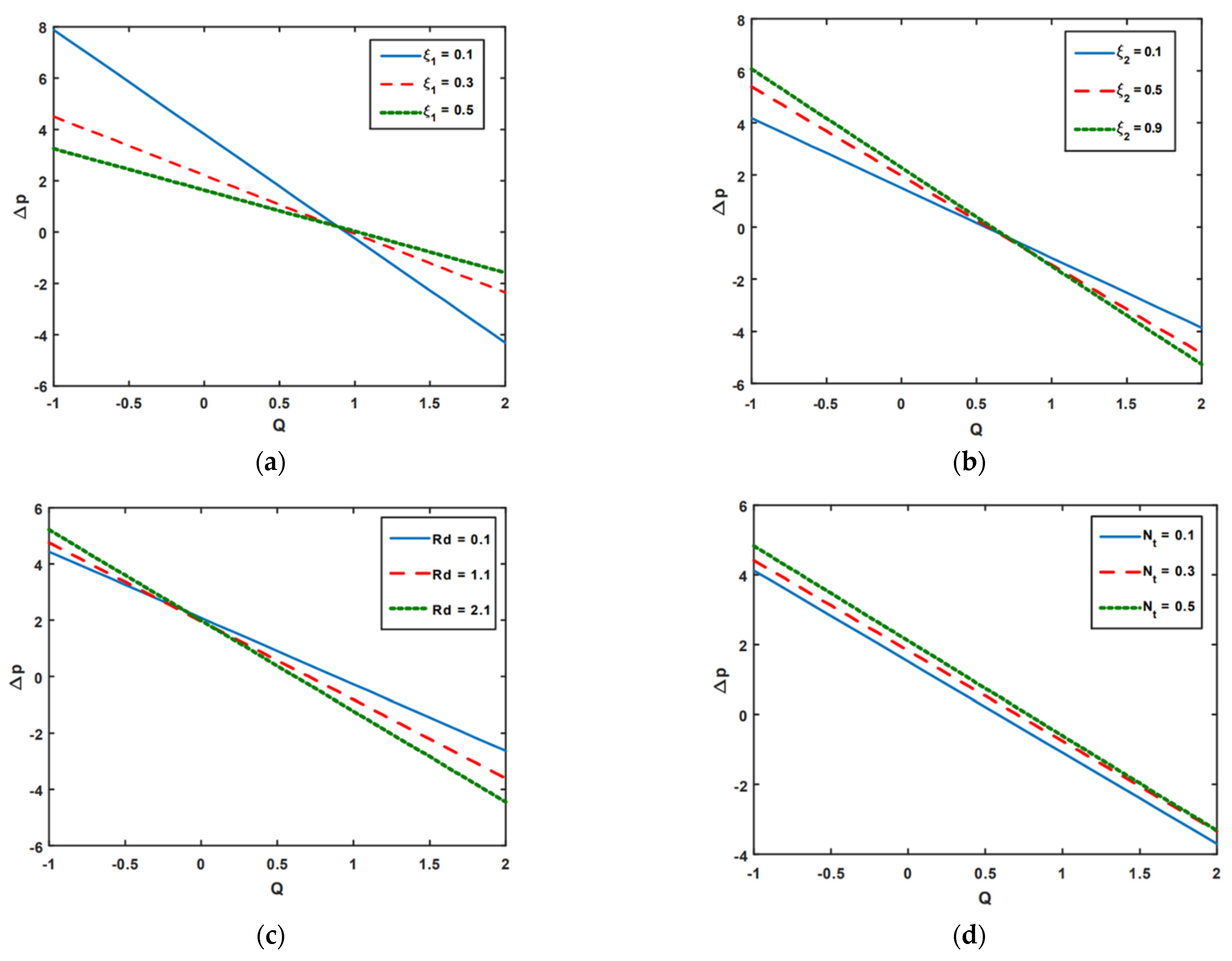
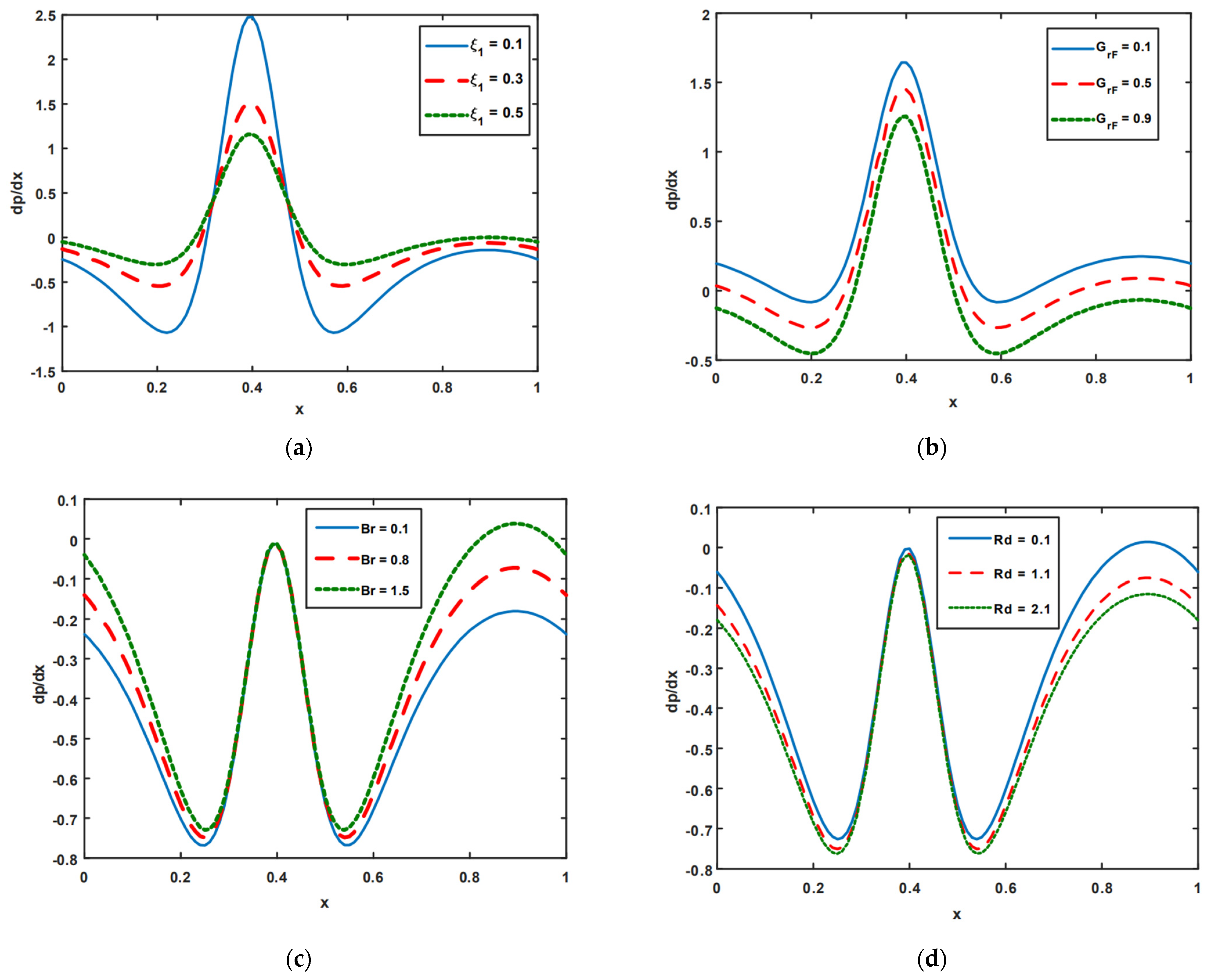
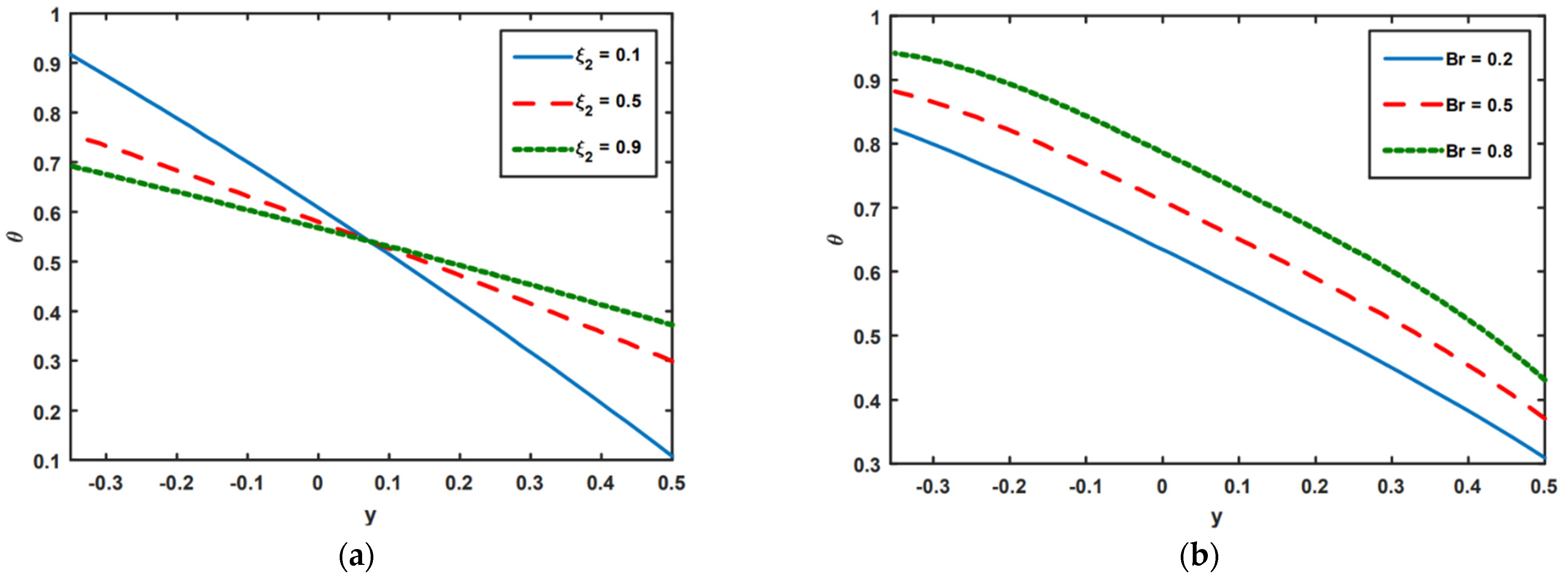
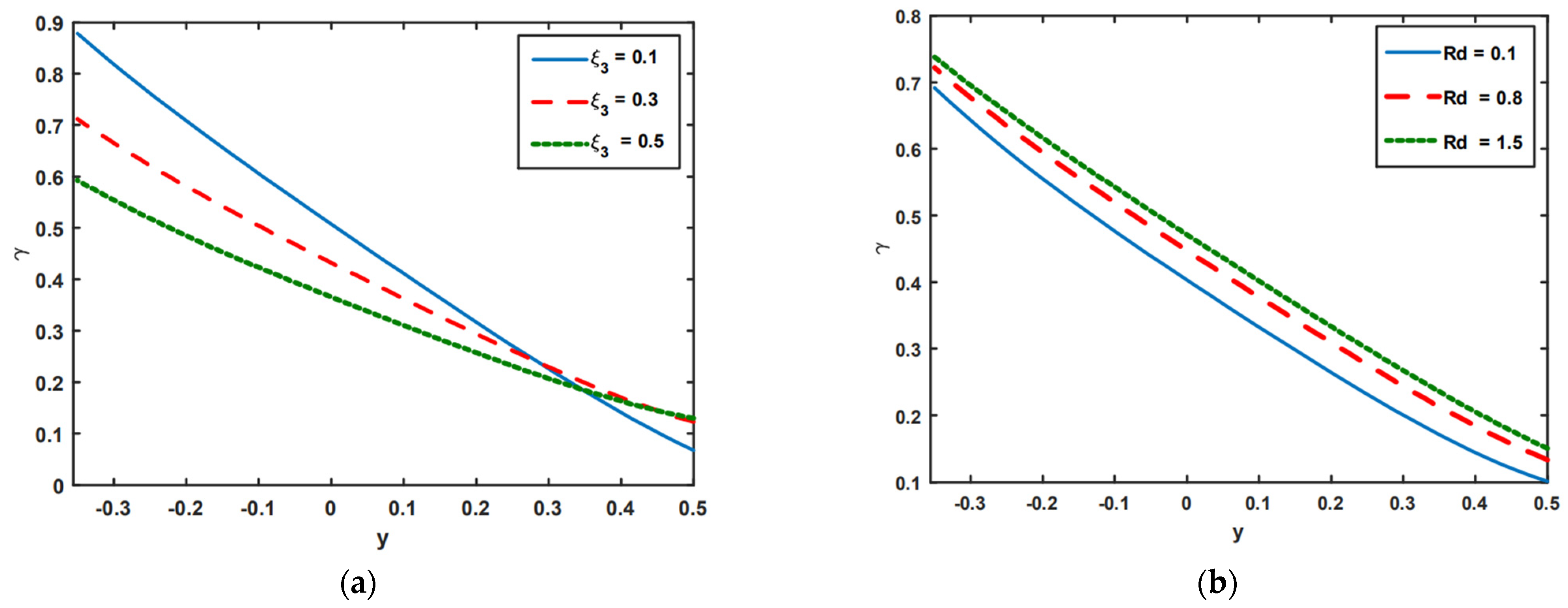
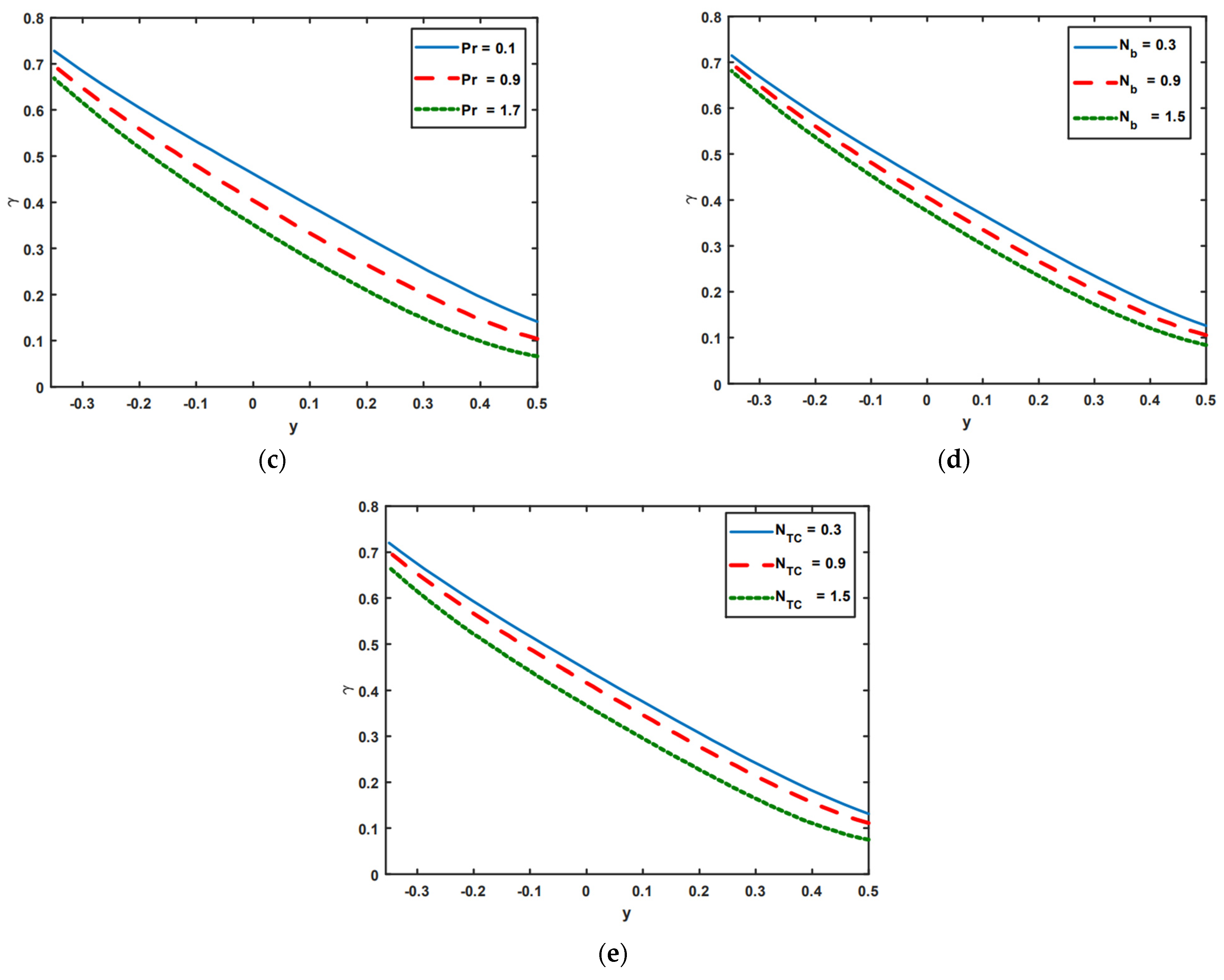
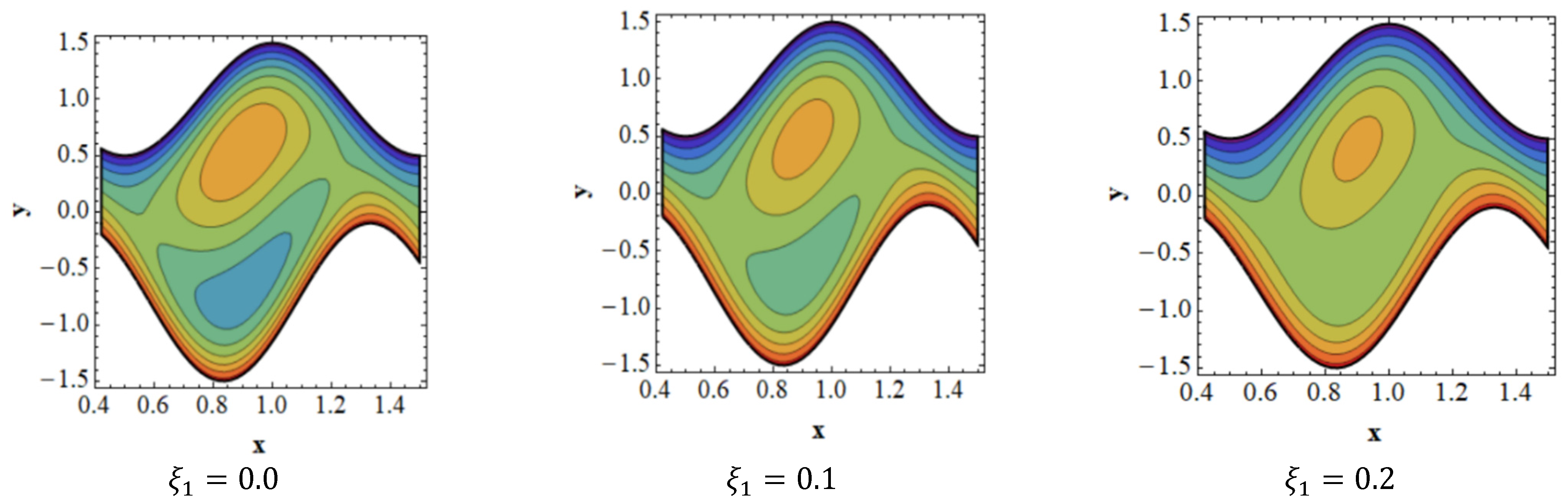
3. Numerical Simulation and Graphical Solutions
4. Conclusions
- The rising impact of velocity slip results in a reduction in resistance that increases fluid velocity at the channel’s center.
- Thanks to the increasing impact of thermal radiation, the pressure rising increases in retrograde regions, while in the augmented region, peristaltic region, and free pumping zones, the pressure rising decreases.
- As heat radiation increases, temperatures tend to drop because heat radiation and thermal conduction are inversely related.
- A significant nanoparticle transition from a hot to a cold region causes a decrease in concentration distribution.
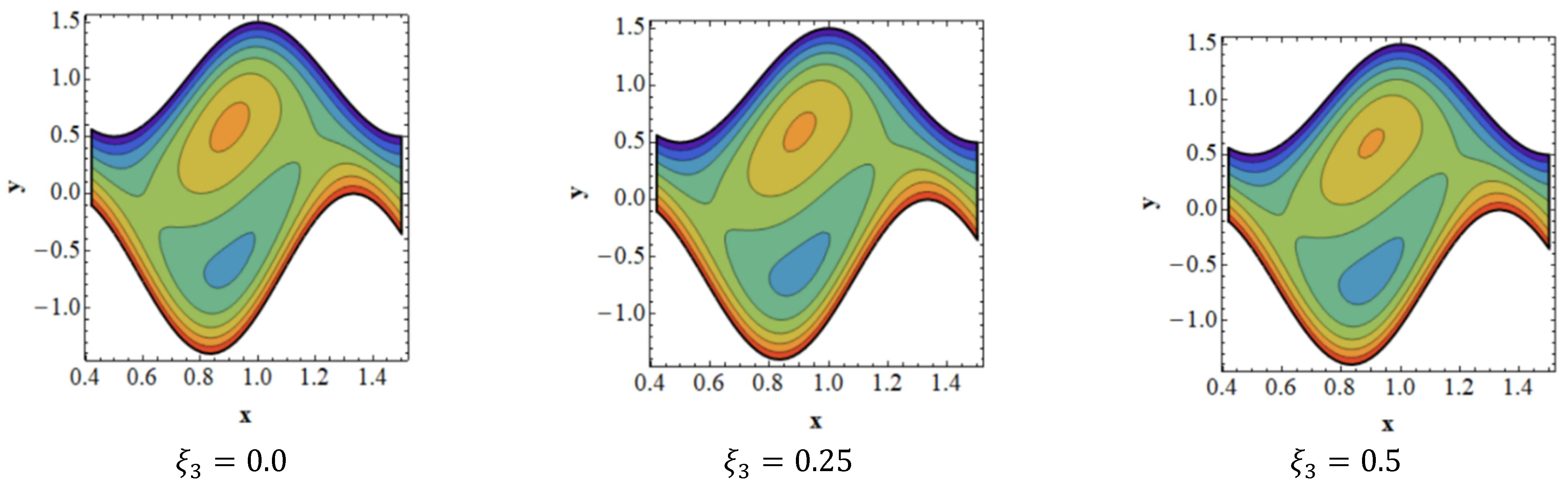
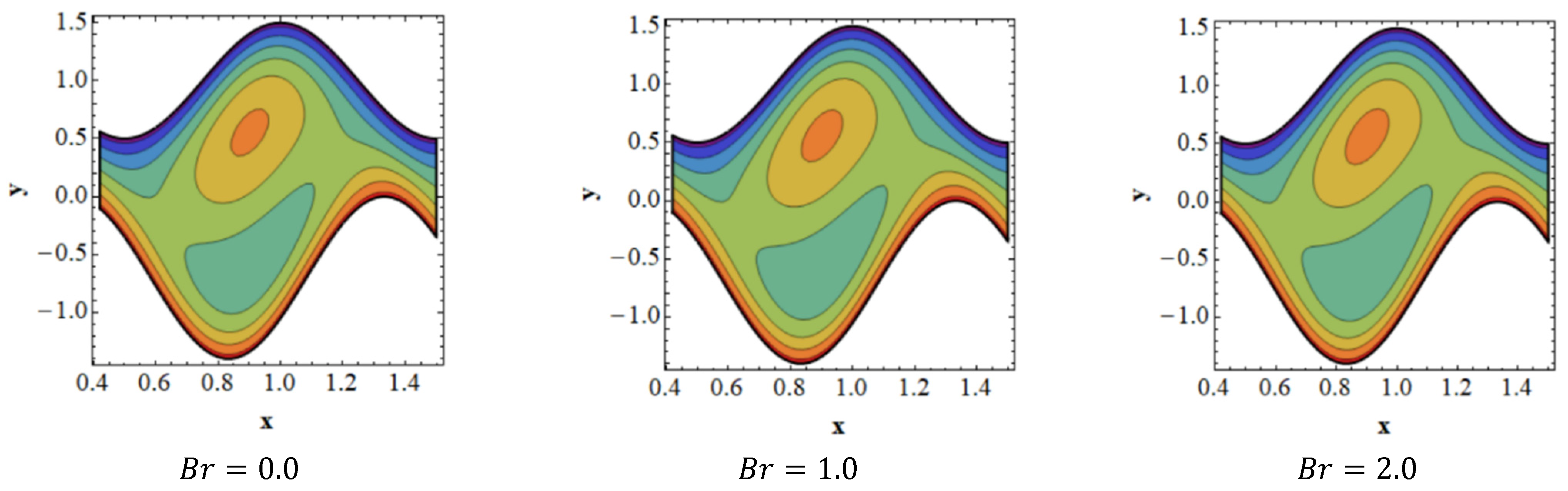
- The size of the trapping bolus decreases in the upper portion of the channel, while the quantity of trapped boluses in the lower portion falls as the influence of velocity slip grows.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamkha, A.J.; Abbasbandy, S.; Rashad, A.M.; Vajravelu, K. Radiation Effects on Mixed Convection over a Wedge Embedded in a Porous Medium Filled with a Nanofluid. Transp. Porous Media 2012, 91, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.G.; Padma, P.; Shankar, B.; Gireesha, B.J. Thermal Radiation Effects on MHD Stagnation Point Flow of Nanofluid Over a Stretching Sheet in a Porous Medium. J. Nanofluids 2016, 5, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyari, E.; Pantokratoras, A. Note on the effect of thermal radiation in the linearized Rosseland approximation on the heat transfer characteristics of various boundary layer flows. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Alsaedi, A.; Shafiq, A. Inclined magnetic field and heat source/sink aspects in flow of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 103, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Irfan, M.; Khan, W. Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation and gyrotactic microorganisms on the Magneto-Burgers nanofluid. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 130, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshizi, S.A.; Malvandi, A. Different modes of nanoparticle migration at mixed convection of Al2O3–water nanofluid inside a vertical microannulus in the presence of heat generation/absorption. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1947–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, T.W. Fluid Motions in a Peristaltic Pump. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Sucharitha, G.; Sreenadh, S.; Lakshminarayana, P. Nonlinear peristaltic transport of a conducting prandtl fluid in a porous asymmetric channel. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, V.P.; Saxena, M. A two-fluid model of non-Newtonian blood flow induced by peristaltic waves. Rheol. Acta 1995, 34, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stud, V.K.; Sekhon, G.S.; Mishra, R.K. Pumping action on blood flow by a magnetic field. Bull. Math. Biol. 1977, 39, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, H.L.; Anwaruddin, B. Peristaltic flow of blood in a branch. Ranchi Univ. Math. J. 1984, 15, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pukhnachev, V.V.; Zhuravleva, E.N. Viscous flows with flat free boundaries. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.M.; Zeeshan, A. Study of variable magnetic field and endoscope on peristaltic blood flow of particle-fluid suspension through an annulus. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2016, 6, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershkov, S.V. Non-stationary creeping flows for incompressible 3D Navier-Stokes equations. Eur. J. Mech.—B/Fluids 2017, 61, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Ijaz, N.; Zeeshan, A.; Li, Y.-Z. Magneto-hydrodynamics of a solid-liquid two-phase fluid in rotating channel due to peristaltic wavy movement. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 30, 2501–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Zeeshan, A.; Ahmad, S.; Razaq, A.; Zubair, M. Effects of External Magnetic Field on non-Newtonian Two Phase Fluid in an Annulus with Peristaltic Pumping. J. Magn. 2019, 24, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekheimer, K. Effect of the induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a couple stress fluid. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 372, 4271–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.K.H.; Fang, J. Peristaltic transport in a slip flow. Eur. Phys. J. B 2000, 16, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, S.I.; Bhatti, M.M. The study of non-Newtonian nanofluid with hall and ion slip effects on peristaltically induced motion in a non-uniform channel. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7904–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Mekheimer, K.; Elmaboud, Y.A. Particulate suspension slip flow induced by peristaltic waves in a rectangular duct: Effect of lateral walls. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandviwalla, X.; Archer, R. The Influence of Slip Boundary Conditions on Peristaltic Pumping in a Rectangular Channel. J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Razia, A.; Afzal, F. Effects of velocity second slip model and induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in the presence of double-diffusivity convection in nanofluids. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2020, 90, 1583–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Siva, E.P.; Tripathi, D.; Bég, O.A. Thermal slip and radiative heat transfer effects on electroosmotic magneto nanoliquid peristaltic propulsion through a microchannel. Heat Transf.—Asian Res. 2019, 48, 2882–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahi, R.; Hussain, F.; Ishtiaq, F.; Hussain, A. Peristaltic transport of Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct through a porous medium under the effect of partial slip: An application to upgrade industrial sieves/filters. Pramana 2019, 93, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.; Obaidat, S. Peristaltic flow of a Williamson fluid in an inclined asymmetric channel with partial slip and heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 1995; Volume 66, pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.U.-S.; Li, S.; Eastman, J.A. Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Fluids Containing Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Heat Transf. 1999, 121, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.A.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; Thompson, L.J. Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, W.; Nakayama, A. Convective heat transfer of nanofluids in a concentric annulus. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 71, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Bég, O.A. A study on peristaltic flow of nanofluids: Application in drug delivery systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 70, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Shah, Z.; Parveen, N.; Ali, A.; Kumam, P.; Rehman, H.; Thounthong, P. MHD Effects on Ciliary-Induced Peristaltic Flow Coatings with Rheological Hybrid Nanofluid. Coatings 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Xu, H. Peristaltic channel flow and heat transfer of Carreau magneto hybrid nanofluid in the presence of homogeneous/heterogeneous reactions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Numerical simulation for forced convection flow of MHD CuO-H2O nanofluid inside a cavity by means of LBM. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Tripathi, D.; Triwari, A.K.; Sait, S.M.; Ellahi, R. Peristaltic Pumping of Nanofluids through a Tapered Channel in a Porous Environment: Applications in Blood Flow. Symmetry 2019, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, S.; Saleem, N. Mixed convective cilia triggered stream of magneto ternary nanofluid through elastic electroosmotic pump: A comparative entropic analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 352, 118662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, S.; Hosseini, R.; Pop, I. Axisymmetric mixed convective stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid over a vertical permeable cylinder by Tiwari-Das nanofluid model. Powder Technol. 2017, 311, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M. Comparison of the pseudo-single-phase continuum model and the homogeneous single-phase model of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 120, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Nadeem, S. Significance of nanofluid and partial slip on the peristaltic transport of a Jeffrey fluid model in an asymmetric channel with different wave forms. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2014, 13, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, D.A.; Kuznetsov, A.V. The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 5792–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.S.; Nadeem, S. Endoscopic Effects on Peristaltic Flow of a Nanofluid. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2011, 56, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojtabi, A.; Charrier-Mojtabi, M.C. Double diffusive convection in porous media. In Handbook of Porous Media; Vafai, K., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 269–320. [Google Scholar]
- Narayana, M.; Sibanda, P.; Motsa, S.; Siddheshwar, P. On double-diffusive convection and cross diffusion effects on a horizontal wavy surface in a porous medium. Bound. Value Probl. 2012, 2012, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqa, S.; Abrar, M.; Hossain, M.; Gorla, R.S.R. Double Diffusive Natural Convection Flow Over a Wavy Surface Situated in a Non-absorbing Medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 109, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.A.; Marin, M. Analytical solution of thermoelastic interaction in a half-space by pulsed laser heating. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 87, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.V.K.; Chaitanya, G.S.K.; Raju, R.S. Double diffusive effects on mixed convection Casson fluid flow past a wavy inclined plate in presence of Darcian porous medium. Results Eng. 2019, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Afzal, Q.; Aly, E.H. Half-breed effects of thermal and concentration convection of peristaltic pseudoplastic nanofluid in a tapered channel with induced magnetic field. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 22, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bég, O.A.; Tripathi, D. Mathematica simulation of peristaltic pumping with double-diffusive convection in nanofluids a bio-nanoengineering model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2012, 225, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, S.; Afzal, Q. Effects of thermal and concentration convection and induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of Williamson nanofluid in inclined uniform channel. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolaiyan, H.; Riaz, A.; Razaq, A.; Saleem, N.; Zeeshan, A.; Bhatti, M.M. Effects of Double Diffusion Convection on Third Grade Nanofluid through a Curved Compliant Peristaltic Channel. Coatings 2020, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tripathi, D.; Sharma, R.; Tiwari, A. Analysis of double diffusive convection in electroosmosis regulated peristaltic transport of nanofluids. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 535, 122148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.P.; Srinivasan, J. Effect of Rayleigh numbers on the evolution of double-diffusive salt fingers. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 062104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, D.; Kuznetsov, A. The onset of double-diffusive convection in a nanofluid layer. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akram, S.; Athar, M.; Saeed, K.; Razia, A.; Muhammad, T.; Alghamdi, H.A. Mechanism of Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Transport of Thermally Radiative Williamson Nanomaterials with Slip Boundaries and Induced Magnetic Field: A Bio-Nanoengineering Model. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050941
Akram S, Athar M, Saeed K, Razia A, Muhammad T, Alghamdi HA. Mechanism of Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Transport of Thermally Radiative Williamson Nanomaterials with Slip Boundaries and Induced Magnetic Field: A Bio-Nanoengineering Model. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050941
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkram, Safia, Maria Athar, Khalid Saeed, Alia Razia, Taseer Muhammad, and Huda Ahmed Alghamdi. 2023. "Mechanism of Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Transport of Thermally Radiative Williamson Nanomaterials with Slip Boundaries and Induced Magnetic Field: A Bio-Nanoengineering Model" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050941
APA StyleAkram, S., Athar, M., Saeed, K., Razia, A., Muhammad, T., & Alghamdi, H. A. (2023). Mechanism of Double-Diffusive Convection on Peristaltic Transport of Thermally Radiative Williamson Nanomaterials with Slip Boundaries and Induced Magnetic Field: A Bio-Nanoengineering Model. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050941





