Novel Sol-Gel Route to Prepare Eu3+-Doped 80SiO2-20NaGdF4 Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramic for Photonic Device Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of 1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4 Aqueous Suspensions
2.2. Synthesis of OxGCs with Composition 80SiO2-20(1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4)
2.3. Characterisation of 1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4 Aqueous Suspensions
2.4. Characterisation of OxGCs with Composition 80SiO2-20(1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4)
2.5. Optical Characterisation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterisation of 1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4 NPs
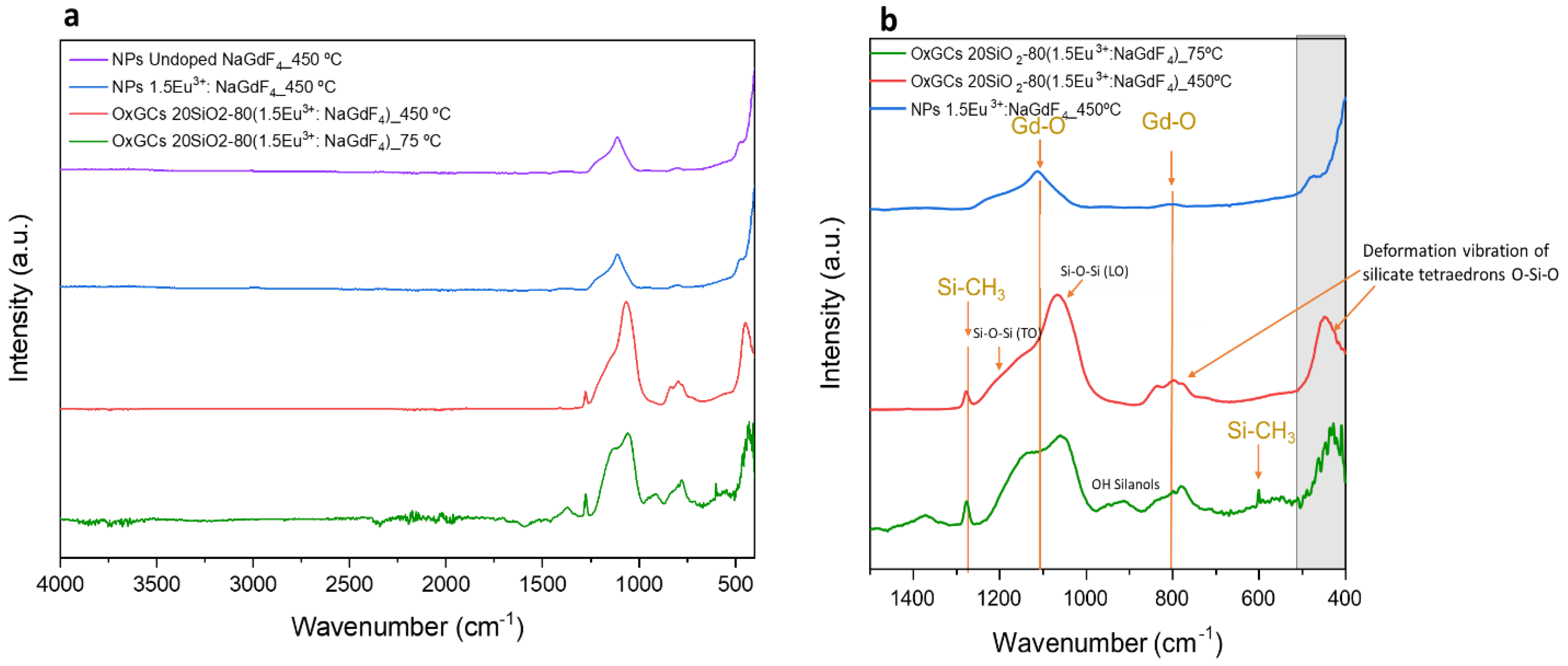
3.2. Structural Characterisation of 80SiO2-20(1.5 Eu3+: NaGdF4) OxGCs Powders
3.3. Luminescence Properties of 1.5Eu3+: NaGdF4 NPs
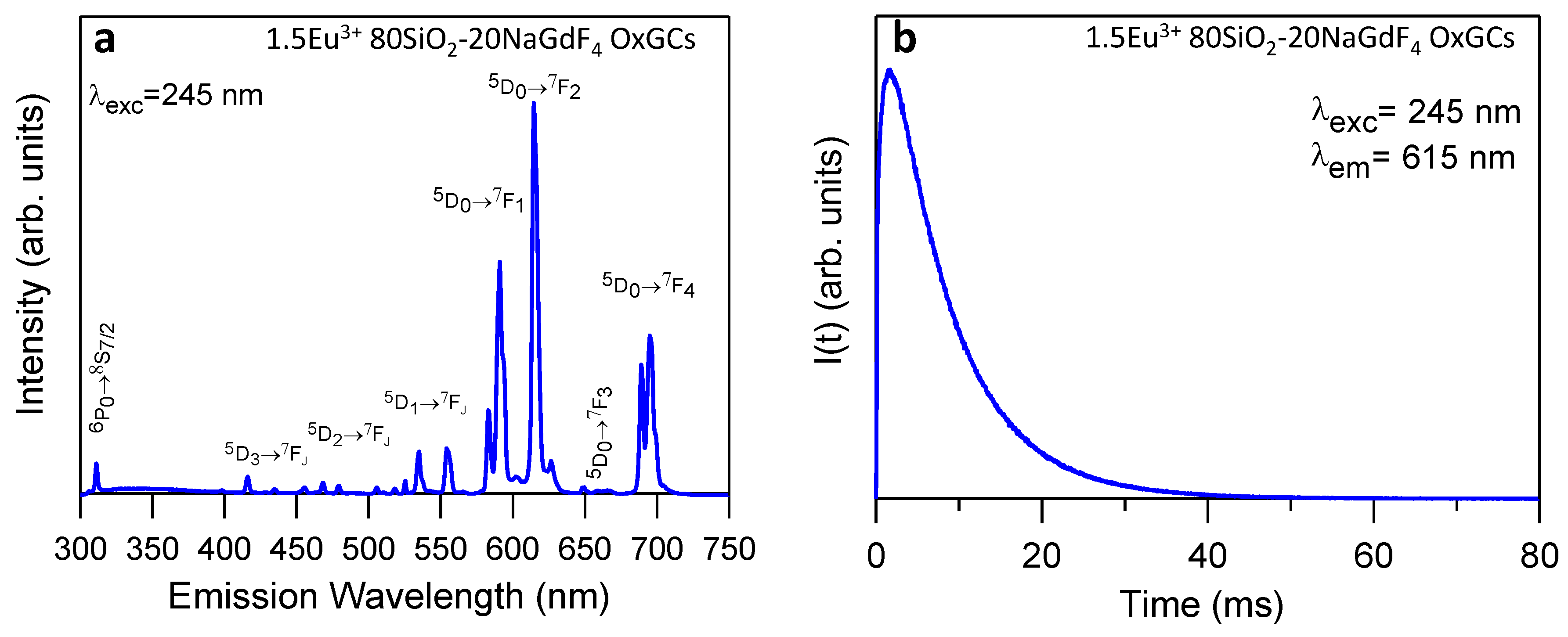
3.4. Luminescence Properties of 80SiO2-20(1.5Eu3+NaGdF4) OxGCs
| Observed Transitions | Wavelength (Figure 5b and Figure 7a) | NaGdF4 [63] | NaLaF4 [64,65] | EuF3 [66] | GdF3 [67] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6P0→8S7/2 | 311 nm | ||||
| 5D3→7F1 | 415.5 nm | ||||
| 5D3→7F2 | 429 nm | ||||
| 5D3→7F3 | 434.5 nm | ||||
| 5D3→7F4 | 468 nm | ||||
| 5D2→7F2 | 478.5 nm | ||||
| 5D2→7F3 | 505.5 | ||||
| 5D1→7F0 | 525 nm | ||||
| 5D1→7F1 | 534.5 nm | ||||
| 5D1→7F2 | 554 nm | ||||
| 5D0→7F1 | 583 nm, 591 nm | 592 mm | 592 mm | 590 nm | 591 nm |
| 5D0→7F2 | 614.5 nm | 613 nm | 615 nm | 612/617 nm | 615 nm |
| 5D0→7F3 | 649 nm | 653 nm | 650 nm | 652 nm | |
| 5D0→7F4 | 689 nm, 695.5 nm | 695 nm | 695 nm |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boulard, B.; Dieudonné, B.; Gao, Y.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M. Up-conversion visible emission in rare-earth doped fluoride glass waveguides. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 071814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.; Castro, Y.; Durán, A. Glasses and Glass-Ceramics Prepared by Sol–Gel. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2020, 2, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Mudring, A.V.; Ghosh, P. Recent trends in binary and ternary rare-earth fluoride nanophosphors: How structural and physical properties influence optical behavior. J. Lumin. 2017, 189, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablos-Martin, A.; Ferrari, M.; Pascual, M.J.; Righini, G.C. Glass-ceramics: A class of nanostructured materials for photonics. Riv. Del Nuovo Cim. 2015, 38, 311–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Durán, A.; Castro, Y. Transparent glass-ceramics produced by Sol-Gel: A suitable alternative for photonic materials. Materials 2018, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Ghosh, P. Lanthanide-Doped Luminescent Nanophosphors via Ionic Liquids. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 715531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, P.P.; Luginina, A.A.; Popov, A.I. Transparent oxyfluoride glass ceramics. J. Fluor. Chem. 2015, 172, 22–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alombert-Goget, G.; Armellini, C.; Berneschi, S.; Chiappini, A.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M.; Guddala, S.; Moser, E.; Pelli, S.; Rao, D.N.; et al. Tb3+/Yb3+ co-activated Silica-Hafnia glass ceramic waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2010, 33, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezhnina, M.M.; Jüstel, T.; Kätker, H.; Wiechert, D.U.; Kynast, U.H. Efficient luminescence from rare-earth fluoride nanoparticles with optically functional shells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Sontakke, A.D.; Ghosh, J.; Annapurna, K. Enhanced blue emission from transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics containing Pr3+: BaF2 nanocrystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Pichaandi, J.; Regier, T.; Van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Nonstatistical dopant distribution of Ln3+-doped NaGdF 4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15950–15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissue, B.M. Synthesis and luminescence of lanthanide ions in nanoscale insulating hosts. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Gorni, G.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Durán, A.; Castro, Y. Novel sol-gel SiO2-NaGdF4 transparent nano-glass-ceramics. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2019, 520, 119447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, B.R.E.; Insley, H. The Sodium Fluoride-Lanthanide. Inorg. Chem. 1964, 1005, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar]
- You, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tao, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescence properties of NaGdF4:Eu. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 343, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Shi, S.; Geng, H.; Huang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, L.; Grimes, C.A.; Feng, X.; Cai, Q. NaGdF4:Nd@NaGdF4 Core-Shell Down-Conversion Nanoparticles as NIR-II Fluorescent Probes for Targeted Imaging of Bacteria. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11231–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, C. Nanophotonics and Nanochemistry: Controlling the Excitation Dynamics for Frequency Up- and Down-Conversion in Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Chandra, P.; Rhee, S.W.; Kim, J. Enhanced upconversion luminescence in NaGdF4:Yb,Er nanocrystals by Fe3+ doping and their application in bioimaging. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8711–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Zhao, S.; Huang, L.; Deng, D.; Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Xu, S. Up-conversion luminescence of Er3+ - doped glass ceramics containing β-NaGdF4 nanocrystals for silicon solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2012, 78, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Tylkowski, M.; Bocker, C.; Rüssel, C. Cubic and hexagonal NaGdF4 crystals precipitated from an aluminosilicate glass: Preparation and luminescence properties. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Chi, X.; Guo, H. Enhanced green upconversion in Tb3+–Yb3+ co-doped oxyfluoride glass ceramics containing LaF3 nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2013, 137, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakovskis, A.; Krieke, G. Upconversion luminescence in erbium doped transparent oxyfluoride glass ceramics containing hexagonal NaYF4 nanocrystals. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 3665–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, W.; Xu, D.; Hu, F.; Chen, L.P.; Guo, H. Wide-range thermometry based on green up-conversion of Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped KLu2F7 transparent bulk oxyfluoride glass ceramics. J. Lumin. 2018, 194, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, E.; Cao, S.P.O.; Na, M.; Migneco, C.; Vern, E. Comparison between Bioactive Sol-Gel and Melt-Derived Glasses/Glass-Ceramics Based on the Multicomponent SiO2–P2O5–CaO–MgO–Na2O–K2O System. Materials 2020, 13, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, M.E.; Sedano, M.; Castro, Y.; Pascual, M.J.; Fernández, J.; Balda, R.; Durán, A. Rare-earth doped transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics: Processing is the key [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C. The Sol-Gel Chemistry of Oxides from Alkoxides. In Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783030381431. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science—The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; p. 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R. Ceramics by the solution-sol-gel route. Science 1987, 238, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L.; West, J.K. The Sol-Gel Process. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.; Castro, Y.; Durán, A. Transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics obtained by different sol-gel routes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorni, G.; Velázquez, J.J.; Mosa, J.; Mather, G.C.; Serrano, A.; Vila, M.; Castro, G.R.; Bravo, D.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; et al. Transparent sol-gel oxyfluoride glass-ceramics with high crystalline fraction and study of re incorporation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.; Durán, A.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Mather, G.C.; Castro, Y. A new sol–gel route towards Nd3+ -doped SiO2 –LaF3 glass-ceramics for photonic applications. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 3589–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.; Fernandez, J.; Durán, A.; Balda, R.; Castro, Y. Optically active nano-glass-ceramic coatings of Nd3+ doped-80SiO2-20LaF3 prepared by the pre-crystallized nanoparticles sol-gel route. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2023, 601, 122050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; Xiong, Q.; Xiong, J. Synthesis of Rare-Earth Nanomaterials Ag-Doped NaYF4: Yb3+/Er3+ @ NaYF 4: Nd 3 + @ NaGdF 4 for In Vivo Imaging. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, M.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Rajamanthrilage, A.C.; Willoughby, W.R.; Dickey, A.; McMillen, C.; Kolis, J.W.; Bolding, M.; Anker, J.N. X-ray excited luminescence spectroscopy and imaging with NaGdF4:Eu and Tb. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 31717–31726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Feng, G.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, S. Core-mediated synthesis, growth mechanism and near-infrared luminescence enhancement of α-NaGdF4@β-NaLuF4:Nd3+ core-shell nanocrystals. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, P.; Green, M. The synthesis of rare earth fluoride based nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mech, A.; Karbowiak, M.; Kȩpiński, L.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Strȩk, W. Structural and luminescent properties of nano-sized NaGdF4:Eu3+ synthesised by wet-chemistry route. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 380, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowiak, M.; Mech, A.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Strȩk, W. Structural and luminescent properties of nanostructured KGdF4:Eu3+ synthesised by coprecipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 380, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheendra, L.; Das, G.K.; Li, C.; Stark, D.; Cena, J.; Cherry, S.; Kennedy, I.M. NaGdF4:Eu3+ nanoparticles for enhanced X-ray excited optical imaging. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.K.; Yang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.L. Down-converted luminescence and energy transfer of α -KGd 1−x Eu x F 4 nanophosphors with selective excitation. J. Lumin. 2013, 143, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Khan, Z.U.; Rodrigues, R.V.; da Costa, L.S.; Gidlund, M.; Brito, H.F. Synthesis and characterization of tunable color upconversion luminescence β-NaGdF4:Yb3+,Er3+ nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 16856–16863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Adam, J. Time-resolved fluorescence-line narrowing and energy-transfer studies in a-doped fluorophosphate glass. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1996, 54, 12076–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamuah, A.; Ojha, S.; Bhattacharya, K.; Ghosh, C.K.; Bhattacharya, S. AC conductivity and electrical relaxation of a promising Ag2S-Ge-Te-Se chalcogenide glassy system. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 166, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.L.; de Oliveira, A.H.; Fernandes, M.L.S. Influence of preferred orientation of minerals in the mineralogical identification process by X-ray diffraction. In Proceedings of the INAC 2011: International Nuclear Atlantic Conference, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil, 24–25 October 2011; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Yang, P.; Wang, D.; Niu, N.; Gai, S.; Li, X. Self-assembled β-NaGdF4 microcrystals: Hydrothermal synthesis, morphology evolution, and luminescence properties. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4116–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogachev, N.A.; Betina, A.A.; Bulatova, T.S.; Nosov, V.G.; Kolesnik, S.S.; Tumkin, I.I.; Ryazantsev, M.N.; Skripkin, M.Y.; Mereshchenko, A.S. Lanthanide-Ion-Doping Effect on the Morphology and the Structure of NaYF4:Ln3+ Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, D.; Lin, J. Rare earth β-NaGdF4 fluorides with multiform morphologies: Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescent properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Liang, X.; Maksimuk, S.; Yang, H. Synthesis of porous platinum nanoparticles. Small 2006, 2, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L. Controlling the final phase of multiphase KGdF4 materials via chemical synthesis and structural phase transition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 18096–18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.E.; Li, J.; Gorni, G.; Durán, A.; Mather, G.C.; Balda, R.; Fernández, J.; Castro, Y. Nd3+doped- SiO2–KLaF4 oxyfluoride glass-ceramics prepared by sol-gel. J. Lumin. 2021, 235, 118035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaprasath, G.; Murugan, R.; Hayakawa, Y.; Ravi, G. Optical and magnetic studies on Gd doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Lumin. 2016, 178, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passuello, T.; Pedroni, M.; Piccinelli, F.; Polizzi, S.; Marzola, P.; Tambalo, S.; Conti, G.; Benati, D.; Vetrone, F.; Bettinelli, M.; et al. PEG-capped, lanthanide doped GdF3 nanoparticles: Luminescent and T2 contrast agents for optical MRI multimodal imaging. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7682–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, P.; Schäfer, H.; Kömpe, K.; Haase, M. Crystal phase control of luminescing NaGdF4:Eu3+ nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3843–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisfeld, R.; Zigansky, E.; Gaft, M. Europium probe for estimation of site symmetry in glass films, glasses and crystals. Mol. Phys. 2004, 102, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Tang, S.; Mudring, A.V. Efficient quantum cutting in hexagonal NaGdF4:Eu3+ nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 8640–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegh, R.; Donker, H.; Meijerink, A.; Lamminmäki, R.; Hölsä, J. Vacuum-ultraviolet spectroscopy and quantum cutting for Gd3+ in LYF4. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1997, 56, 13841–13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoutre, S.; Boyer, D.; Mahiou, R. Quantum cutting abilities of sol-gel derived LiGdF4:Eu3+ powders. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabouw, F.T.; Prins, P.T.; Norris, D.J. Europium-Doped NaYF4 Nanocrystals as Probes for the Electric and Magnetic Local Density of Optical States throughout the Visible Spectral Range. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7254–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, T.K.; Kumar, A.; Swart, H.C.; Kroon, R.E. Effect of annealing on structural and luminescence properties of Eu3+ doped NaYF4 phosphor. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 535, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, D.; Zhu, H.; Li, R.; Luo, W.; Chen, X. A strategy to achieve efficient dual-mode luminescence of Eu3+ in Lanthanides doped multifuncional NaGdF4 nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3266–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowiak, M.; Mech, A.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Strȩk, W.; Kȩpiński, L. Comparison of different NaGdF4:Eu3+ synthesis routes and their influence on its structural and luminescent properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2005, 66, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Liu, M.; Gao, P.; Pu, H.; Fan, L.; Jiang, R.; Liu, Z.; Shi, F.; Lu, H. Sub-10 nm Water-Dispersible β-NaGdF4:X% Eu3+ Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility for in Vivo X-ray Luminescence Computed Tomography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39985–39993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuomela, A.; Pankratov, V.; Sarakovskis, A.; Doke, G.; Grinberga, L.; Vielhauer, S.; Huttula, M. Oxygen influence on luminescence properties of rare-earth doped NaLaF4. J. Lumin. 2016, 179, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladol, J.; Khajuria, H.; Khajuria, S.; Sheikh, H.N. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and luminescent properties of lanthanide-doped NaLaF4 nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Cao, X. Facile sonochemical synthesis of single-crystalline europium fluorine with novel nanostructure. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasturi, S.; Sivakumar, V.; Jeon, D.Y. Europium-activated rare earth fluoride (LnF3:Eu3+–Ln = La, Gd) nanocrystals prepared by using ionic liquid/NH4F as a fluorine source via hydrothermal synthesis. Luminescence 2016, 31, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Interpretation of europium(III) spectra. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 295, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, P.H. Point Group Symmetry Application: Method and Tables; in Plenum 5; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz, M.E.; Ngoc Lam Tran, T.; Chiasera, A.; Durán, A.; Fernandez, J.; Balda, R.; Castro, Y. Novel Sol-Gel Route to Prepare Eu3+-Doped 80SiO2-20NaGdF4 Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramic for Photonic Device Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050940
Cruz ME, Ngoc Lam Tran T, Chiasera A, Durán A, Fernandez J, Balda R, Castro Y. Novel Sol-Gel Route to Prepare Eu3+-Doped 80SiO2-20NaGdF4 Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramic for Photonic Device Applications. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050940
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz, María Eugenia, Thi Ngoc Lam Tran, Alessandro Chiasera, Alicia Durán, Joaquín Fernandez, Rolindes Balda, and Yolanda Castro. 2023. "Novel Sol-Gel Route to Prepare Eu3+-Doped 80SiO2-20NaGdF4 Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramic for Photonic Device Applications" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050940
APA StyleCruz, M. E., Ngoc Lam Tran, T., Chiasera, A., Durán, A., Fernandez, J., Balda, R., & Castro, Y. (2023). Novel Sol-Gel Route to Prepare Eu3+-Doped 80SiO2-20NaGdF4 Oxyfluoride Glass-Ceramic for Photonic Device Applications. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050940











