Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Sensing and Bending Actuator Response of Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials with Magnetic Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Materials Processing
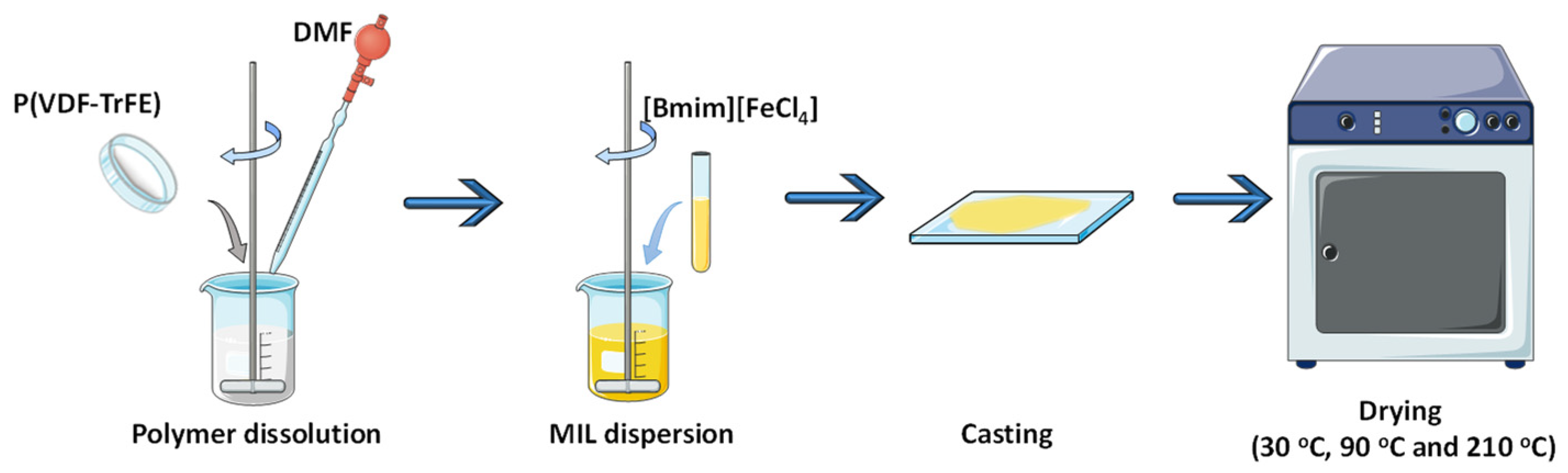
2.2.1. Preparation of the Composite Films
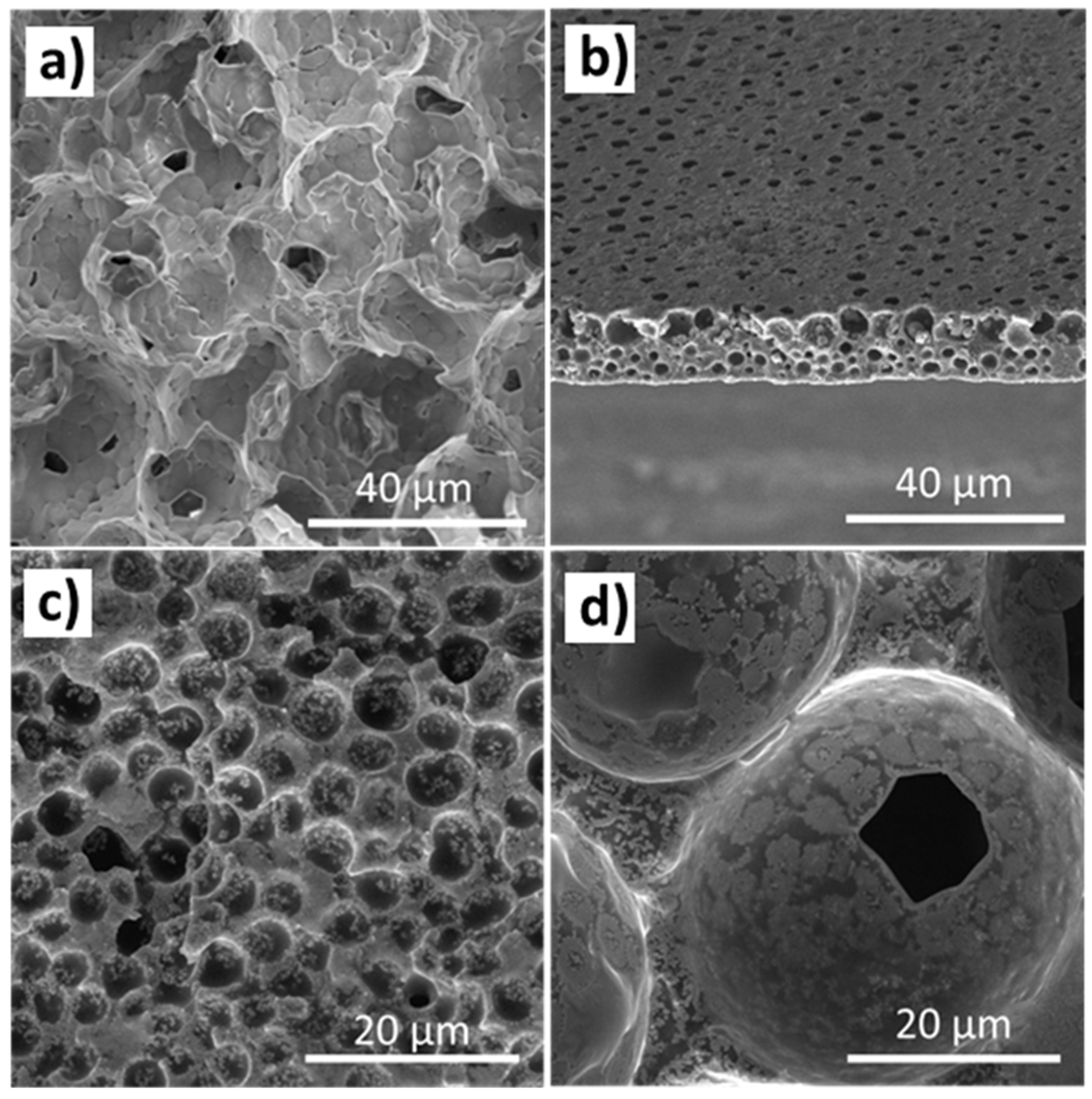
2.2.2. Morphological and Functional Characterization
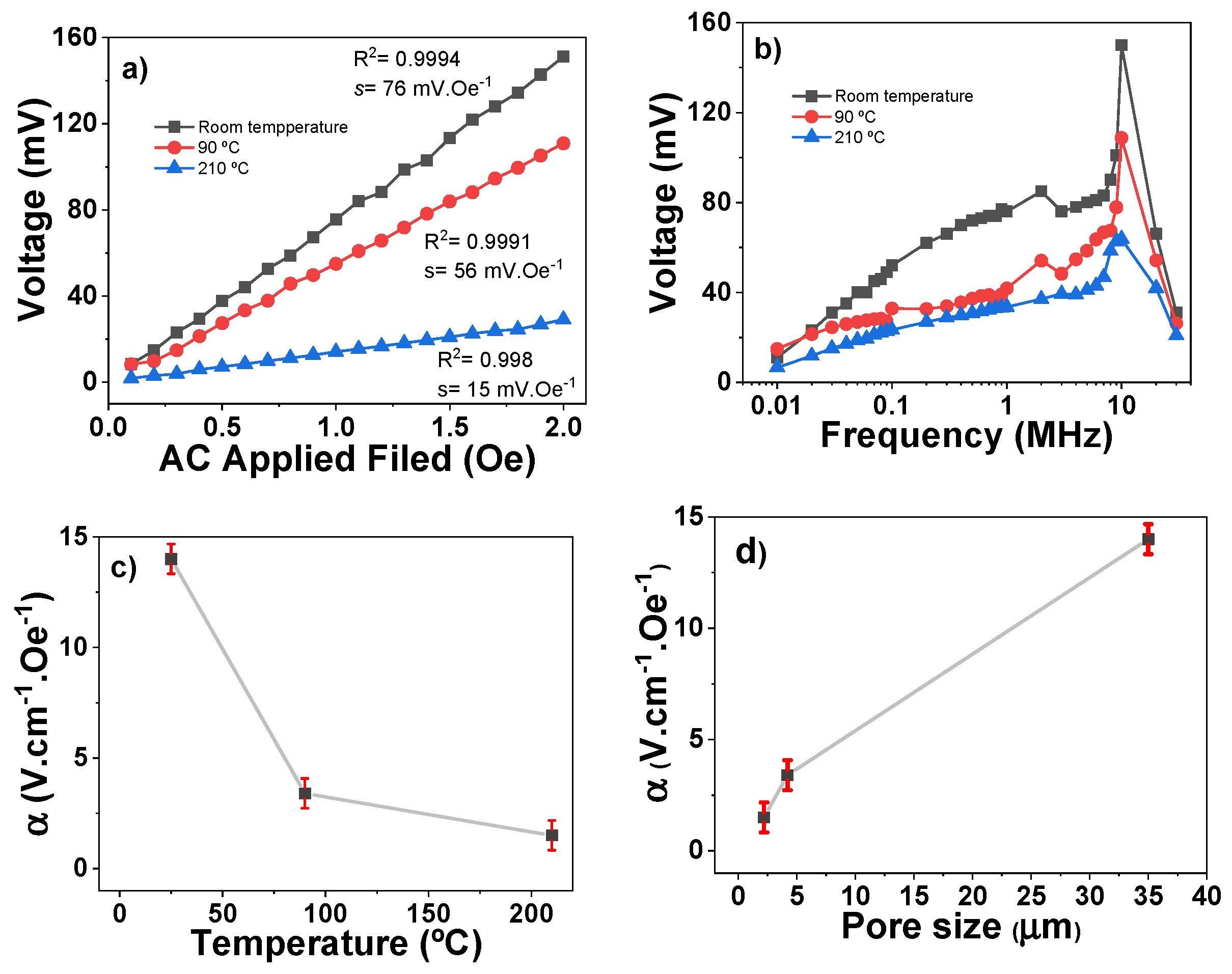
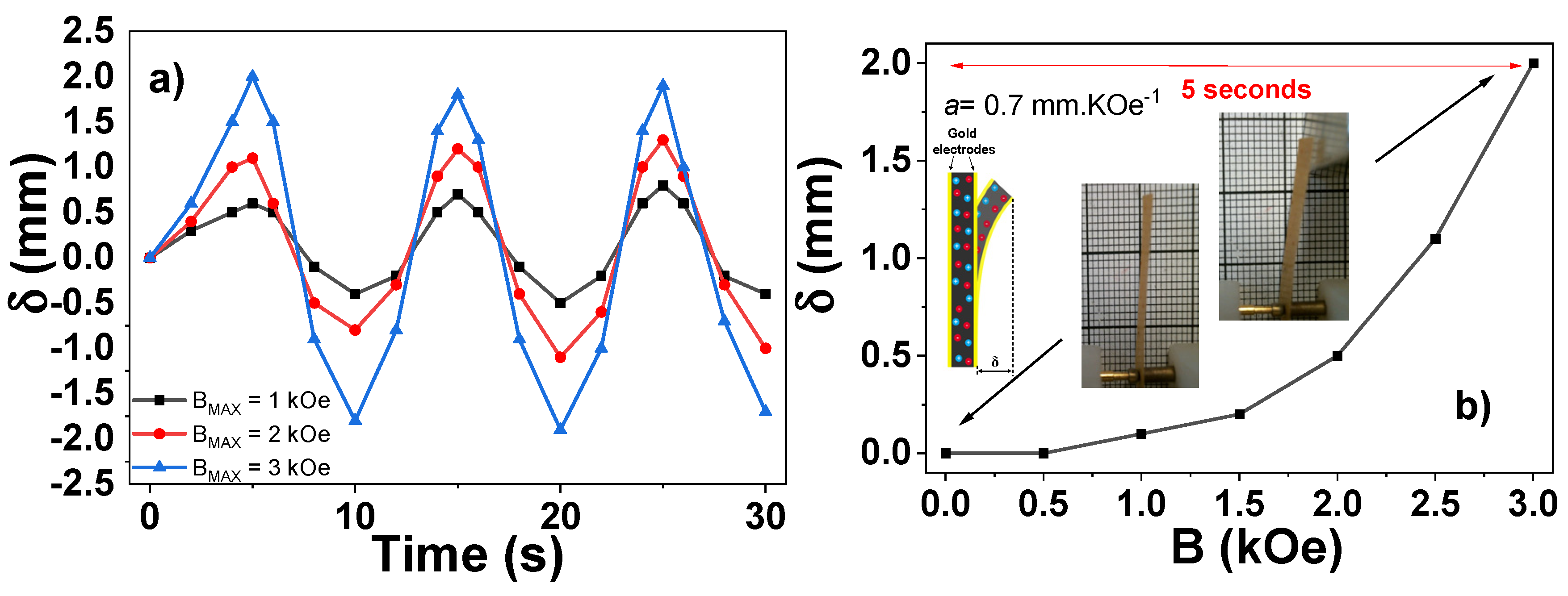
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garbie, I.; Garbie, A. Outlook of Requirements of Manufacturing Systems for Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2020 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4 February–9 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, C.; Pierangelini, L.; Vollero, L. IoT Gateways for Industrial and Medical Applications: Architecture and Performance Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Roma, Italy, 3–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Drossel, W.G.; Meinel, F.; Bucht, A.; Kunze, H. Smart Materials for Smart Production—A Cross-Disciplinary Innovation Network in the Field of Smart Materials. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Correia, V.; Castro, H.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polymer-based smart materials by printing technologies: Improving application and integration. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Martins, P.; Tariq, M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Low-field giant magneto-ionic response in polymer-based nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15747–15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.C.; Martins, M.S.; Ribeiro, S.; Silva, M.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Botelho, G.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electromechanical actuators based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) with [N1112(OH)][NTf2] and [C2mim] [C2SO4]. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 9490–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Farajollahi, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Lin, I.-T.; Marshall, J.E.; Thompson, N.M.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Madden, J.D.W.; Smoukov, S.K. Electroactive polymers for sensing. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20160026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaal, W.; Herold, S. Electroactive Polymer Actuators in Dynamic Applications. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.C.; Correia, D.M.; Fernández, E.; Tariq, M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Design of Ionic-Liquid-Based Hybrid Polymer Materials with a Magnetoactive and Electroactive Multifunctional Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 42089–42098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Smela, E. Biomedical Applications of Electroactive Polymer Actuators; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Palza, H.; Zapata, P.A.; Angulo-Pineda, C. Electroactive Smart Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, T.G.; Rosset, S.; Anderson, I.A.; Shea, H. An electroactive polymer energy harvester for wireless sensor networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 476, 012117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernould, B.; Bertrand, O.; Minoia, A.; Lazzaroni, R.; Vlad, A.; Gohy, J.-F. Electroactive polymer/carbon nanotube hybrid materials for energy storage synthesized via a “grafting to” approach. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17301–17310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Costa, C.M.; Correia, D.M.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Martins, P.; Gonçalves, R.; Cardoso, V.F.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based structures for advanced applications. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 681–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; Martins, P.M.; García-Astrain, C.; Costa, C.M.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Ionic Liquid–Polymer Composites: A New Platform for Multifunctional Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yan, F.; Texter, J. Advanced applications of ionic liquids in polymer science. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.J.L.; Soromenho, M.R.C.; Shimizu, K.; Marrucho, I.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Density, Thermal Expansion and Viscosity of Cholinium-Derived Ionic Liquids. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Sanchez, C.; Erdmenger, T.; Lara-Ceniceros, T.E.; Jimenez-Regalado, E.; Schubert, U.S. Smart Materials Based on Ionic Liquids: The Magnetorheological Fluid Case. In Ionic Liquids: From Knowledge to Application; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Watanabe, M.; Deng, Y. Beyond solvents and electrolytes: Ionic liquids-based advanced functional materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 80–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Magnetic ionic liquids: Synthesis, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40008–40018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosub, T.; Kopte, M.; Hühne, R.; Appel, P.; Shields, B.; Maletinsky, P.; Hübner, R.; Liedke, M.O.; Fassbender, J.; Schmidt, O.G.; et al. Purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, M. Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R123–R152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Lu, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids for energy, materials, and medicine. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9228–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, R.; Dias, J.; Hentati, S.B.; Martins, M.; Costa, C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Effect of anion type in the performance of ionic liquid/poly(vinylidene fluoride) electromechanical actuators. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 453, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.; Borges, R.; Godinho, M.; Marques, C.; Langa, E.; Ribeiro, A.; Lourenço, M.; Santos, F.; de Castro, C.N.; Macatrão, M.; et al. Thermophysical and magnetic studies of two paramagnetic liquid salts: [C4mim][FeCl4] and [P66614][FeCl4]. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2013, 350, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Pereira, J.; Ribeiro, S.; Ribeiro, C.; Gombek, C.J.; Gama, F.M.; Gomes, A.C.; Patterson, D.A.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and copolymers as porous membranes for tissue engineering applications. Polym. Test. 2015, 44, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Cardoso, V.F.; Pereira, N.; Oliveira, J.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties and Active Response of Piezoelectric Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) as a Function of Its Microstructure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 11433–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadewald, U.; Halbedel, B.; Ziolkowski, M.; Brauer, H. The Manipulation of Paramagnetic Ions by Magnetic Field Gradient Forces. In Modelling for Material Processing; Cambridge University Press: Riga, Latvia, 2010; pp. 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczuk, J.; Bielejewski, M.; Tritt-Goc, J. Ionic liquid dynamics and electrical conductivity under confinement within micro and nanocellulose ionogels. Cellulose 2023, 30, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, J.; Singh, R.; Hung, F.R. Effects of pore size and pore loading on the properties of ionic liquids confined inside nanoporous CMK-3 carbon materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.C.; Pereira, N.; Ribeiro, C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Martins, P. Greener Solvent-Based Processing of Magnetoelectric Nanocomposites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 4122–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.; Silva, M.P.; Castro, N.; Correia, V.; Rocha, J.G.; Martins, P.; Lasheras, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electronic optimization for an energy harvesting system based on magnetoelectric Metglas/poly(vinylidene fluoride)/Metglas composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, L.C.; Correia, D.M.; Tariq, M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Sensing and Bending Actuator Response of Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials with Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152186
Fernandes LC, Correia DM, Tariq M, Esperança JMSS, Martins P, Lanceros-Méndez S. Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Sensing and Bending Actuator Response of Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials with Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(15):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152186
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Liliana C., Daniela M. Correia, Mohammad Tariq, José M. S. S. Esperança, Pedro Martins, and Senentxu Lanceros-Méndez. 2023. "Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Sensing and Bending Actuator Response of Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials with Magnetic Ionic Liquids" Nanomaterials 13, no. 15: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152186
APA StyleFernandes, L. C., Correia, D. M., Tariq, M., Esperança, J. M. S. S., Martins, P., & Lanceros-Méndez, S. (2023). Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Sensing and Bending Actuator Response of Polymer-Based Hybrid Materials with Magnetic Ionic Liquids. Nanomaterials, 13(15), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152186










