UV-Nanoimprint Lithography for Predefined SERS Nanopatterns Which Are Reproducible at Low Cost and High Throughput
Abstract
1. Introduction
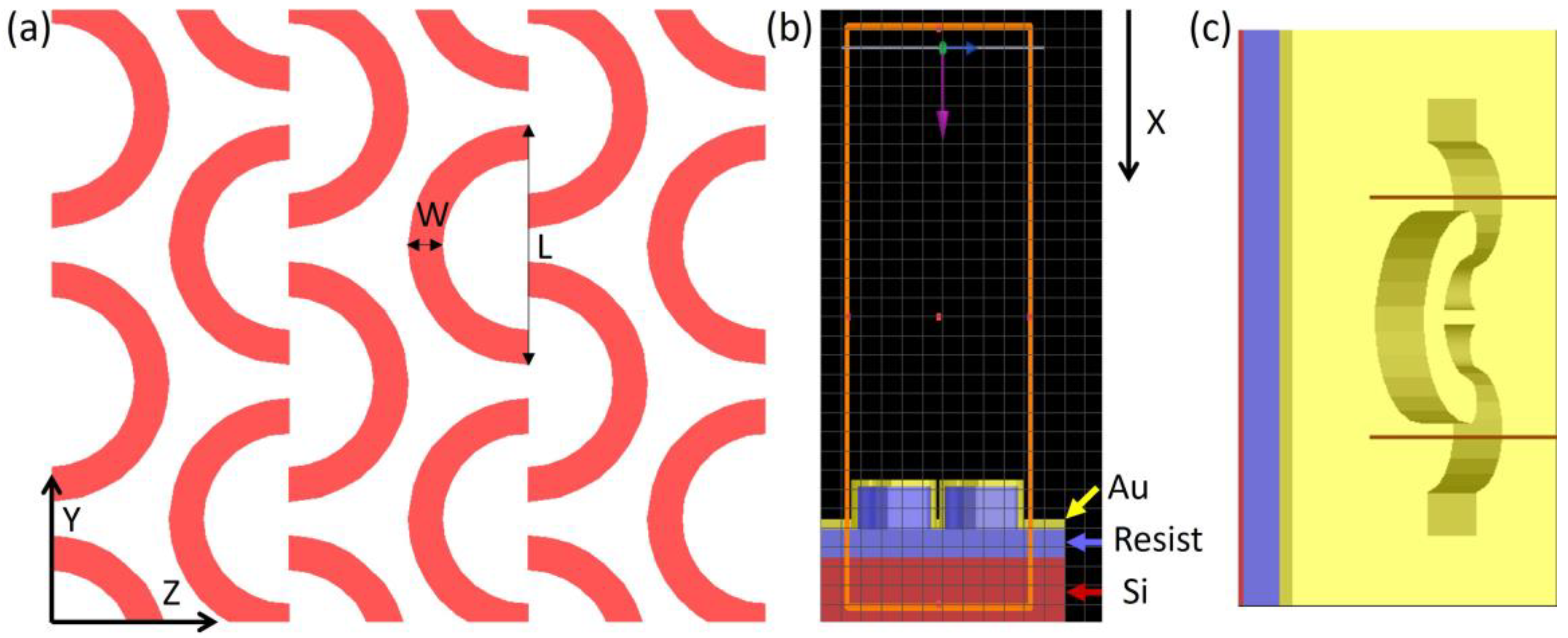
2. Design
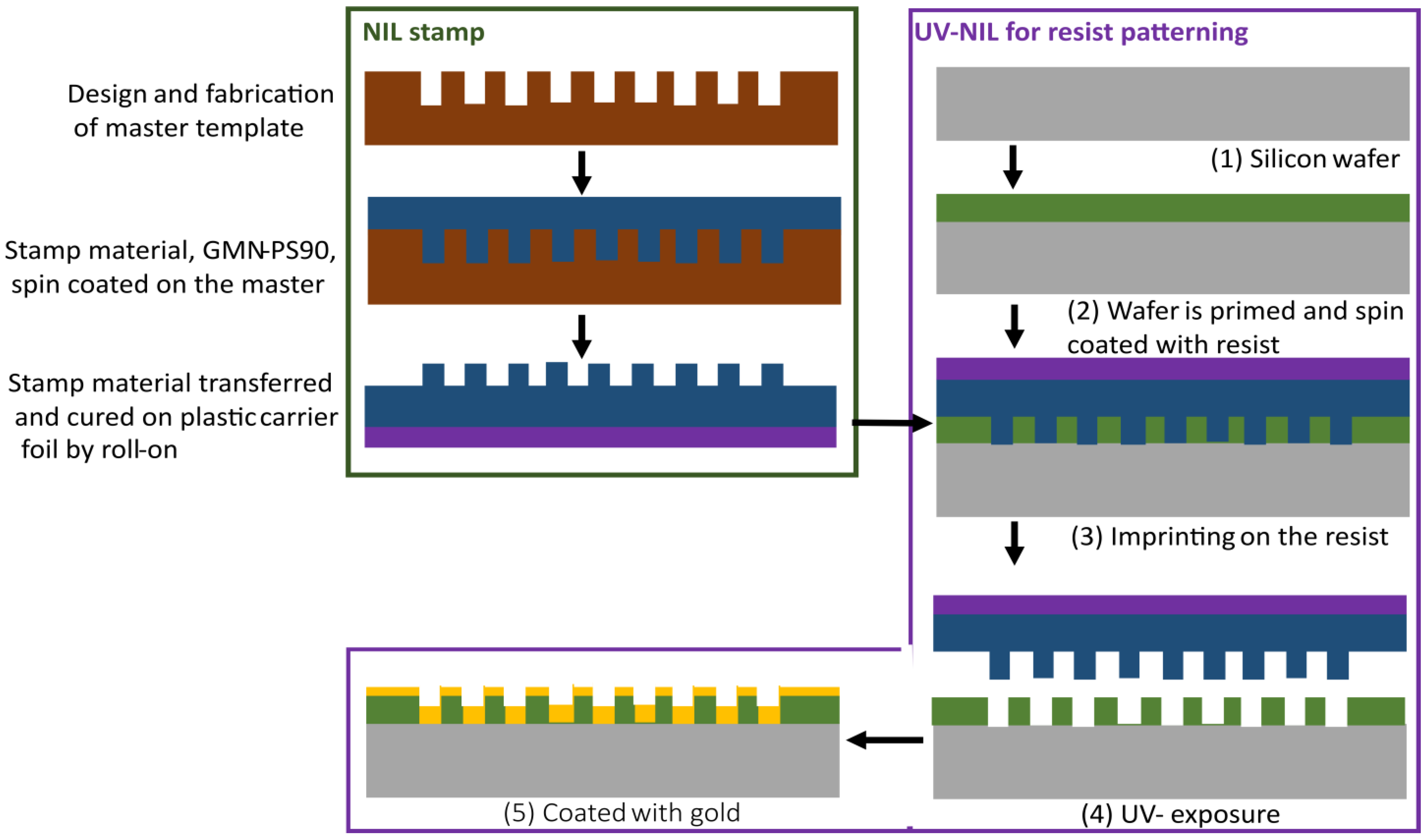
3. Fabrication
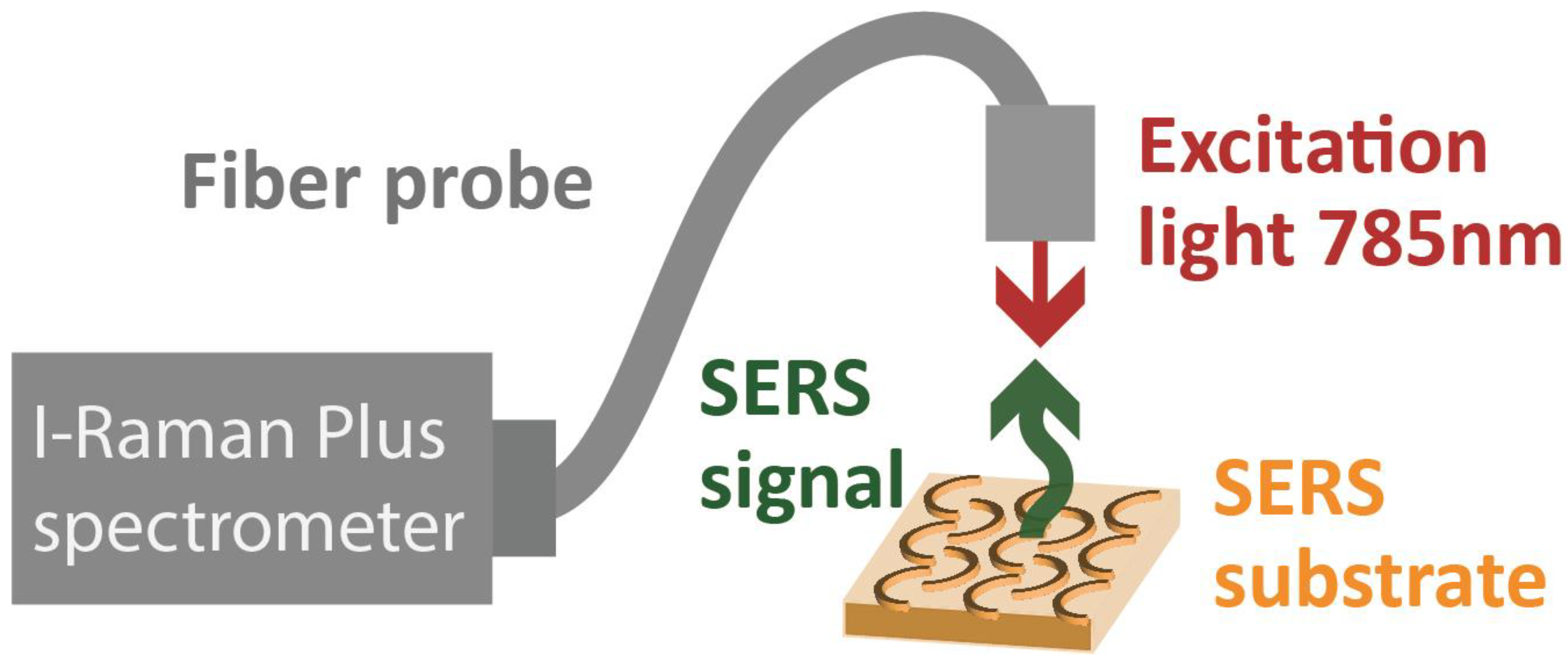
4. Experimental Setup
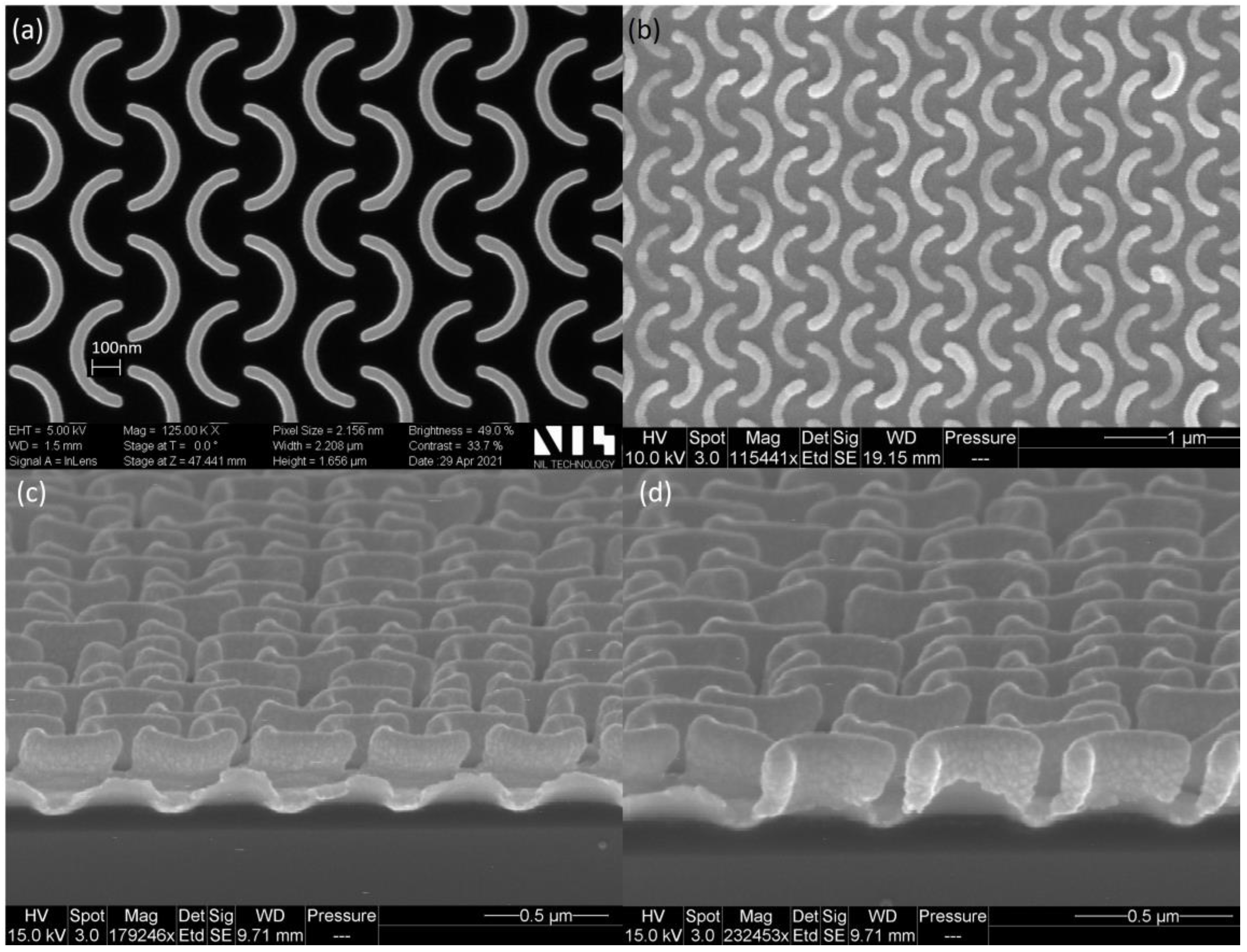
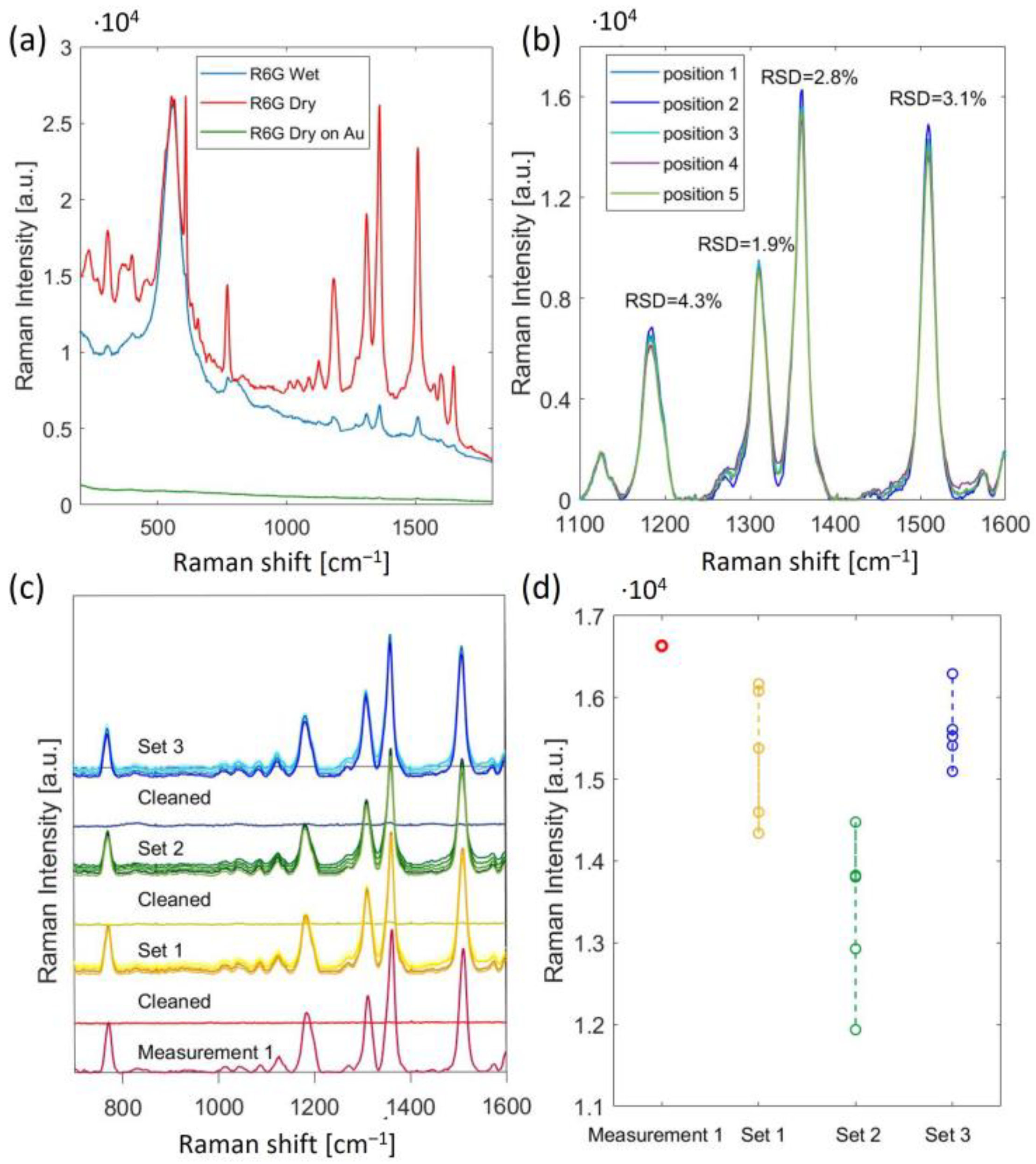
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langer, J.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and future of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chen, W.; Ju, H. Rapid detection of pesticide residues using a silver nanoparticles coated glass bead as nonplanar substrate for SERS sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, R.; Milenko, K.; Vereshchagina, E.; Iacob, B.C.; Schneider, K.; Farcău, C.; Bodoki, E. EC-SERS detection of thiabendazole in apple juice using activated screen-printed electrodes. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisanga, M.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Enhancing disease diagnosis: Biomedical applications of surface-enhanced raman scattering. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Yang, T.; He, L. Review of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) detection of synthetic chemical pesticides. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, A.I.; Lyu, D.; Lu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ren, B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Benefits, trade-offs and future developments. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4563–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liu, X.; Ying, Y. Facing Challenges in Real-Life Application of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: Design and Nanofabrication of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates for Rapid Field Test of Food Contaminants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6525–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.E.J.; Charron, G.; Cortés, E.; Kneipp, J.; Lamy, M.; Chapelle, D.; Langer, J.; Proch, M.; Tran, V.; Schl, S. Towards Reliable and Quantitative Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS): From Key Parameters to Good Analytical Practice Angewandte. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 5454–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grys, D.; Baumberg, J.J. Eliminating irreproducibility in SERS substrates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2020, 52, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tardivel, M.; Lequeux, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, G.; et al. Evaluation of the Reliability of Six Commercial SERS Substrates. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Shao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, A.; Zhang, C.; Xiu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Z. Elevating the density and intensity of hot spots by repeated annealing for high-efficiency SERS. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 29357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziuk, D.; Moehwald, H. Prospects for plasmonic hot spots in single molecule SERS towards the chemical imaging of live cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21072–21093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvalya, V.; Filipič, G.; Zavašnik, J.; Abdulhalim, I.; Cvelbar, U. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for chemical and biological sensing using nanoplasmonics: The relevance of interparticle spacing and surface morphology. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 031307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Gong, T.; Long, X.; Kravets, V.; Gao, P.; Pu, M.; Wang, C. Sensitive and reproducible surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) with arrays of dimer-nanopillars. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuytens, P.C.; Skirtach, A.G.; Baets, R. On-chip surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using nanosphere-lithography patterned antennas on silicon nitride waveguides. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Mancini, A.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Maier, S.A.; De Mello, J.C. High-Throughput Fabrication of Triangular Nanogap Arrays for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 7438–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvill, D.; Iarossi, M.; Abraham Ekeroth, R.M.; Hubarevich, A.; Huang, J.A.; De Angelis, F. Breaking the symmetry of nanosphere lithography with anisotropic plasma etching induced by temperature gradients. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottat, M.; Lidgi-Guigui, N.; Tijunelyte, I.; Barbillon, G.; Hamouda, F.; Gogol, P.; Aassime, A.; Lourtioz, J.M.; Bartenlian, B.; de la Chapelle, M.L. Soft UV nanoimprint lithography-designed highly sensitive substrates for SERS detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Hu, M.; Ou, F.S.; Li, Z.; Williams, R.S. Cones fabricated by 3D nanoimprint lithography for highly sensitive surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 255502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo, S.J.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Williams, R.S. Nanoimprint lithography of plasmonic platforms for SERS applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2015, 121, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Cui, B.; Bravo-Vasquez, J.-P.; Veres, T.; Fenniri, H. Nanoimprinted SERS-Active Substrates with Tunable Surface Plasmon Resonances. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6720–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcau, C.; Marconi, D.; Colniță, A.; Brezeștean, I.; Barbu-Tudoran, L. Gold nanopost-shell arrays fabricated by nanoimprint lithography as a flexible plasmonic sensing platform. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Espulgar, W.V.; Luo, X.; Saito, M.; Yoshikawa, H.; Tamiya, E. SERS active hierarchical nanopillar-huddle array fabricated via the combination of nanoimprint lithography and anodization. Electrochemistry 2020, 88, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, R.; Jia, S.; Feng, Z.; Lin, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. SERS hotspots distribution of the highly ordered noble metal arrays on flexible substrates. Opt. Mater. 2021, 122, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Czolkos, I.; Johansson, A.; Nielsen, T.; Kristensen, A. Master origination by 248 nm DUV lithography for plasmonic color generation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 141103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palik, E.D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, C.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Plasmon-sampled surface-enhanced Raman excitation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7426–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, D.A.; Yonzon, C.R.; Zhang, X.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N.C.; Glucksberg, M.R.; Walsh, J.T.; Van Duyne, R.P. Glucose sensing using near-infrared surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy: Gold surfaces, 10-day stability, and improved accuracy. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4013–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikac, L.; Kovačević, E.; Ukić, Š.; Raić, M.; Jurkin, T.; Marić, I.; Gotić, M.; Ivanda, M. Detection of multi-class pesticide residues with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 252, 119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoint, P.G. Surface enhanced raman scattering enhancement factors: A comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzortey, A.A.; Anderson, B.; Owusu, A. Raman spectra recovery using a second derivative technique and range independent baseline correction algorithm. OSA Contin. 2021, 4, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milenko, K.; Dullo, F.T.; Thrane, P.C.V.; Skokic, Z.; Dirdal, C.A. UV-Nanoimprint Lithography for Predefined SERS Nanopatterns Which Are Reproducible at Low Cost and High Throughput. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13101598
Milenko K, Dullo FT, Thrane PCV, Skokic Z, Dirdal CA. UV-Nanoimprint Lithography for Predefined SERS Nanopatterns Which Are Reproducible at Low Cost and High Throughput. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(10):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13101598
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilenko, Karolina, Firehun Tsige Dullo, Paul C. V. Thrane, Zeljko Skokic, and Christopher A. Dirdal. 2023. "UV-Nanoimprint Lithography for Predefined SERS Nanopatterns Which Are Reproducible at Low Cost and High Throughput" Nanomaterials 13, no. 10: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13101598
APA StyleMilenko, K., Dullo, F. T., Thrane, P. C. V., Skokic, Z., & Dirdal, C. A. (2023). UV-Nanoimprint Lithography for Predefined SERS Nanopatterns Which Are Reproducible at Low Cost and High Throughput. Nanomaterials, 13(10), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13101598




