Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Vascularization of Nanostructured Scaffold Transplanted into Nude Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. hASC Isolation and Culture
2.3. hASC Characterization
2.4. hASC-Conditioned Medium and Protein Extract Preparation
2.5. hASC-Conditioned Medium and Protein Extract Characterization
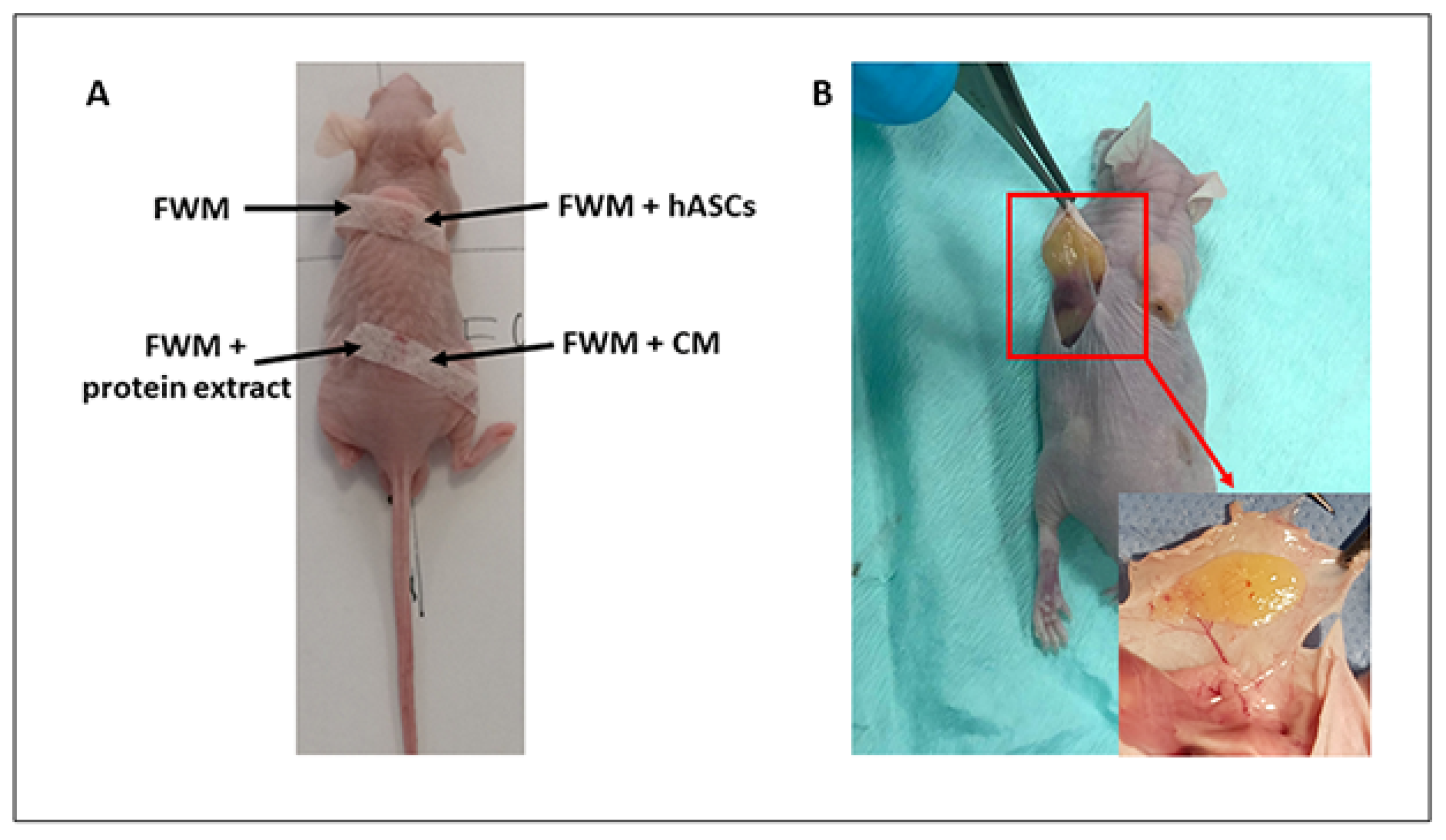
2.6. Xenogenic Grafting
2.7. Gross Examination of Scaffold
2.8. Sample Collection
2.9. Optical Microscopy
2.10. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
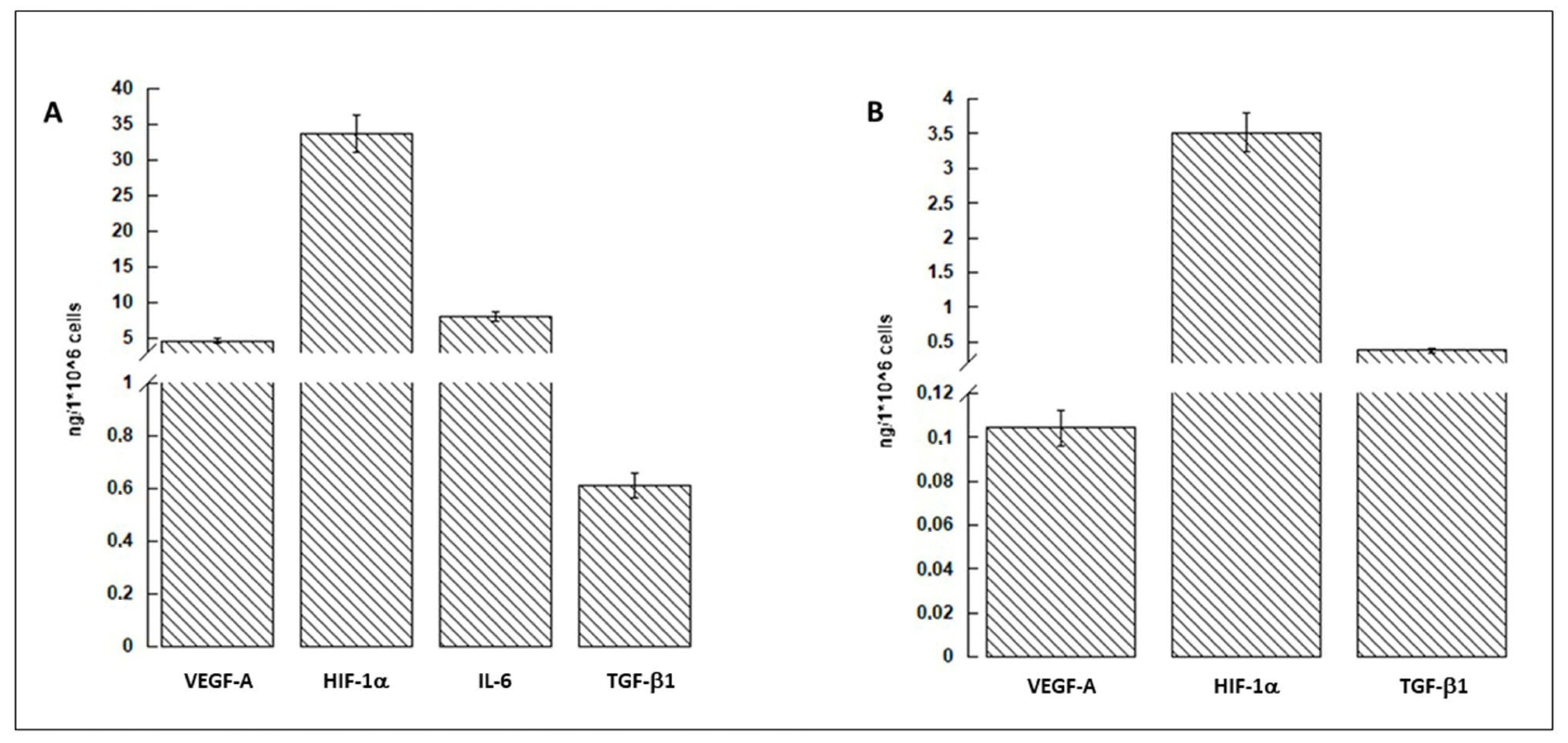
3.1. hASCs and Conditioned Medium Characterization
3.2. Scaffold Evaluation and Gross Examination
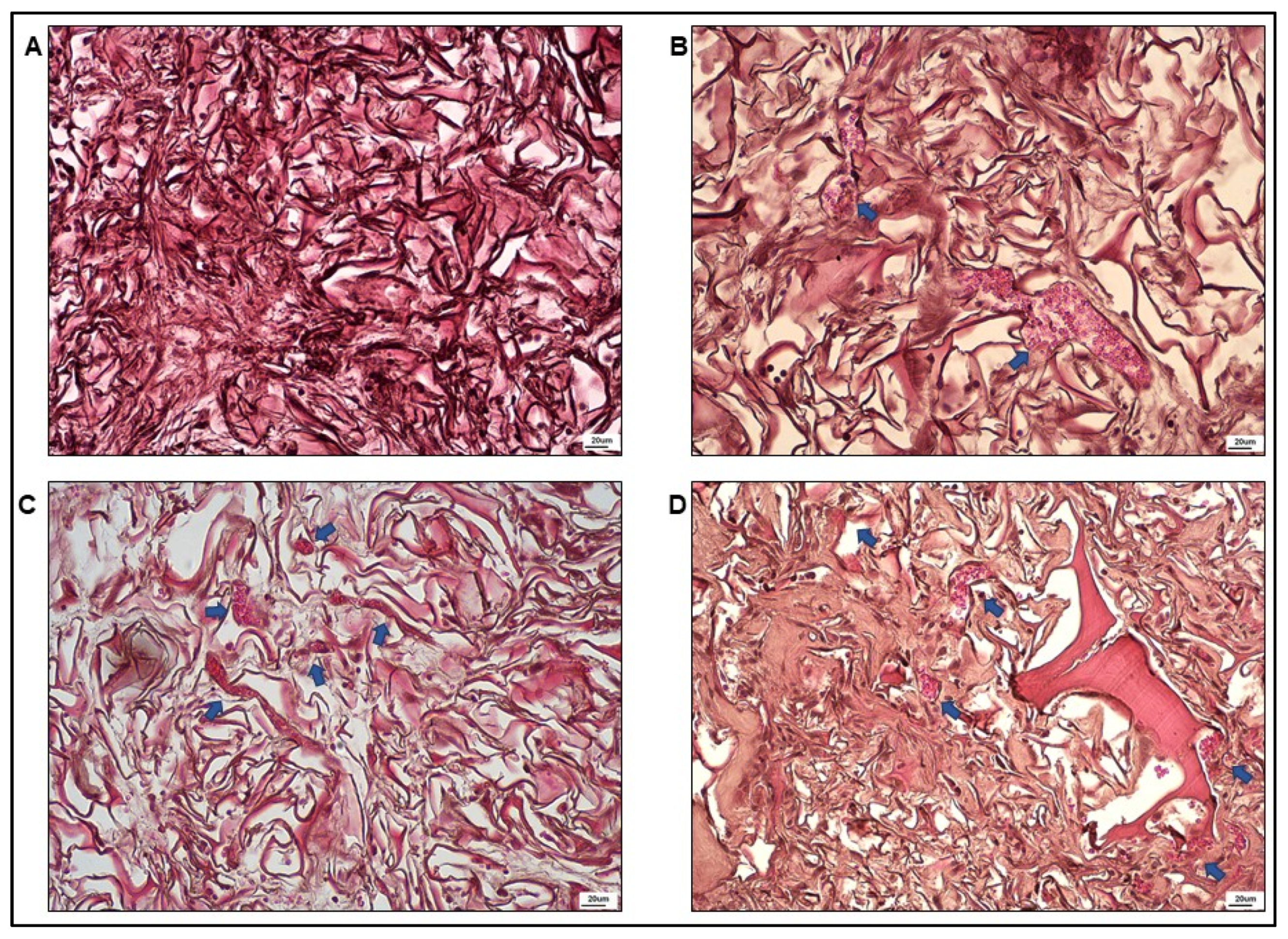
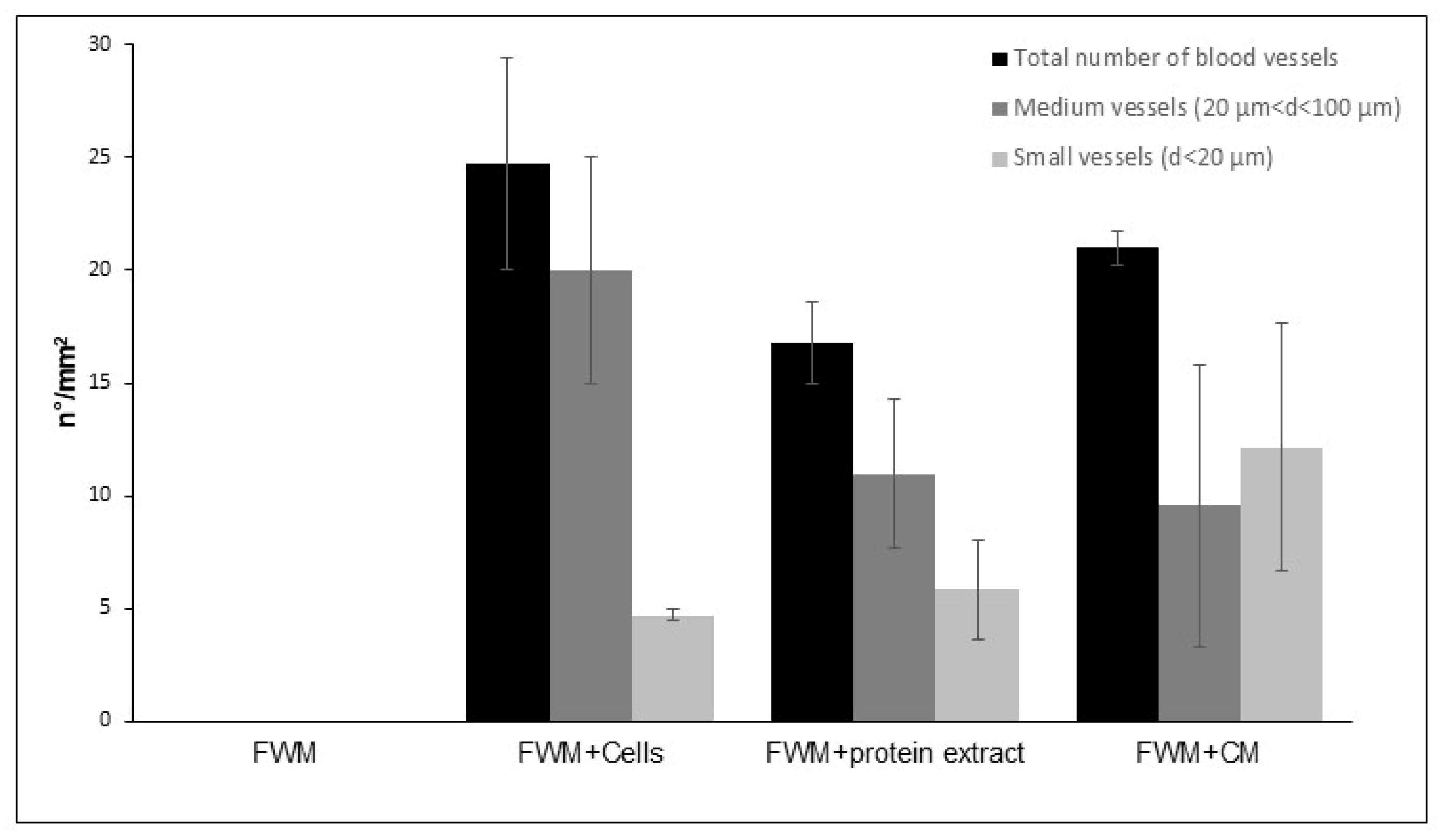
3.3. Optical Microscopy
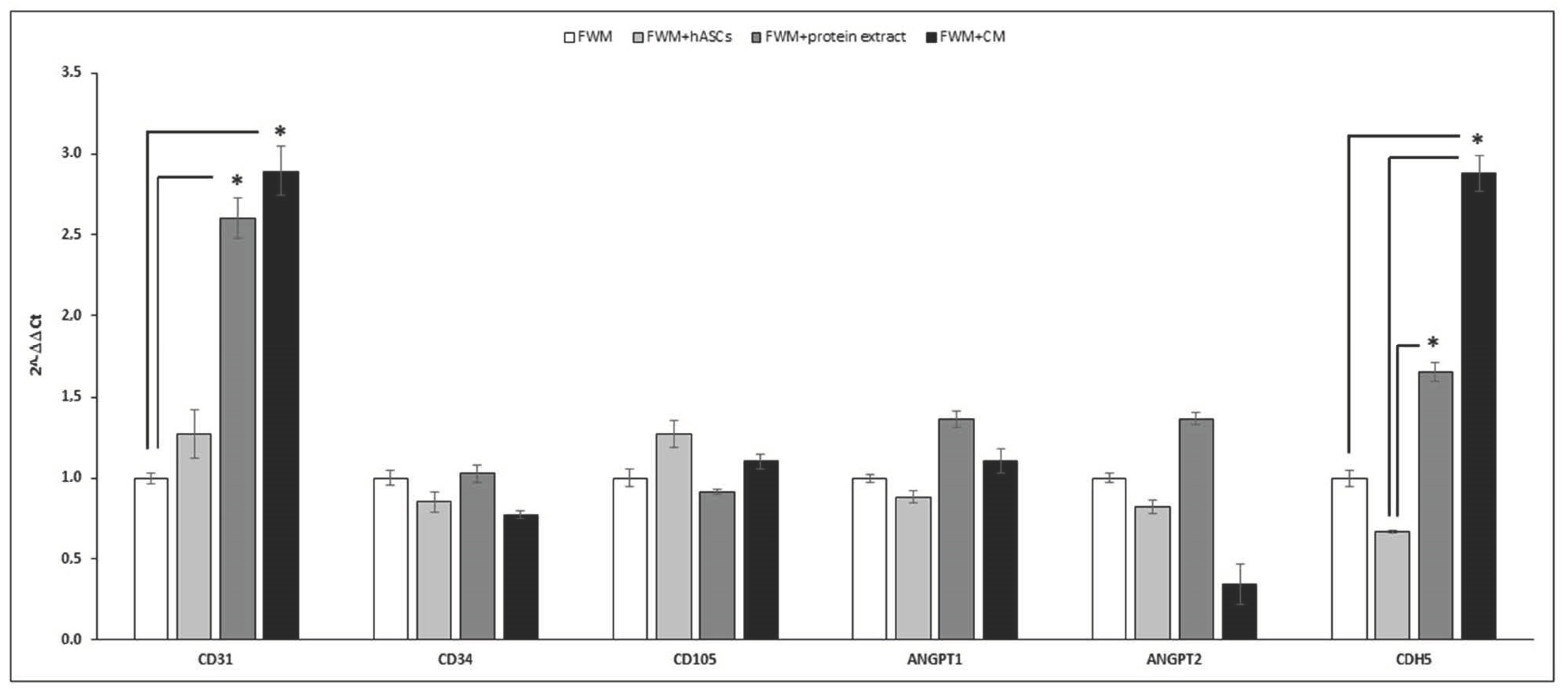
3.4. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, F.; Tanaka, M. Designing Smart Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, M.N.P.T.; Brunger, J.M.; Gloss, M.C.C.; Moutos, F.T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Guilak, F. Genetic Engineering of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Differential Matrix Deposition on 3D Woven Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2018, 24, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; MacQueen, L.A.; Usprech, J.F.; Maleki, H.; Sider, K.L.; Matthew, G.; Doyle, M.; Sun, Y.; Simmons, C.A. Microdevice arrays with strain sensors for 3D mechanical stimulation and monitoring of engineered tissues. Biomaterials 2018, 172, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Palugan, L.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. A Graphical Review on the Escalation of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing in the Pharmaceutical Field. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2943–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List of FDA Approved Stem Cell Therapies. Available online: https://ipscell.com/2021/03/list-of-fda-approved-stem-cell-therapies (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Talib, S.; Shepard, K.A. Unleashing the cure: Overcoming persistent obstacles in the translation and expanded use of hematopoietic stem cell-based therapies. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherubino, M.; Valdatta, L.; Balzaretti, R.; Pellegatta, I.; Rossi, F.; Protasoni, M.; Tedeschi, A.; Accolla, R.S.; Bernardini, G.; Gornati, R. Human adipose-derived stem cells promote vascularization of collagen-based scaffolds transplanted into nude mice. Regen. Med. 2016, 11, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovett, M.; Lee, K.; Edwards, A.; Kaplan, D.L. Vascularization Strategies for Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelps, E.A.; García, A.J. Engineering more than a cell: Vascularization strategies in tissue engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folkman, J.; Shing, Y. Angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10931–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, M.S.; Lee, H.J.; Ko, J.H.; Wee, W.R.; Lee, J.H. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Angiogenic Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Corneal Wound Healing Following Chemical Injury. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, K.; Das, S.; Houser, S.D.; Quadri, S.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Concentration-dependent inhibition of angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood 2009, 113, 4197–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Péault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcozzi, C.; Frattini, A.; Borgese, M.; Rossi, F.; Barone, L.; Solari, E.; Valli, R.; Gornati, R. Paracrine effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on lymphatic endothelial cells. Regen. Med. 2020, 15, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Sharma, S.; Korutla, L.; Datla, S.R.; Shoja-Taheri, F.; Mishra, R.; Bigham, G.E.; Sarkar, M.; Morales, D.; Bittle, G.; et al. Circulating exosomes derived from transplanted progenitor cells aid the functional recovery of ischemic myocardium. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spees, J.L.; Lee, R.H.; Gregory, C.A. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litowczenko, J.; Woźniak-Budych, M.J.; Staszak, K.; Wieszczycka, K.; Jurga, S.; Tylkowski, B. Milestones and current achievements in development of multifunctional bioscaffolds for medical application. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2412–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgese, M.; Barone, L.; Rossi, F.; Raspanti, M.; Papait, R.; Valdatta, L.; Bernardini, G.; Gornati, R. Effect of Nanostructured Scaffold on Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Outcome of In Vitro Experiments. Nanomater. 2020, 10, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.K.; Ioanas, H.-I.; Xandry, J.; Rudin, M. An in vivo wound healing model for the characterization of the angiogenic process and its modulation by pharmacological interventions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.L.; Hammer, D.A. Assembly of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells on Compliant Hydrogels. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2010, 3, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Davis, G.E. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Vascular Lumen Formation. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, F.; Perestrelo, A.R.; Vinarsky, V.; Pagliari, S.; Forte, G. Cellular Mechanotransduction: From Tension to Function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Cooper-White, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Shenoy, V.B. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature 2020, 584, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Später, T.; Frueh, F.S.; Metzger, W.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. In vivo biocompatibility, vascularization, and incorporation of Integra® dermal regenerative template and flowable wound matrix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 106, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integra. Available online: www.integralife.com (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Borgese, M.; Rossi, F.; Bonfanti, P.; Colombo, A.; Mantecca, P.; Valdatta, L.; Bernardini, G.; Gornati, R. Recovery ability of human adipose stem cells exposed to cobalt nanoparticles: Outcome of dissolution. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratushnyy, A.; Ezdakova, M.; Buravkova, L. Secretome of Senescent Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Negatively Regulates Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palombella, S.; Pirrone, C.; Cherubino, M.; Valdatta, L.; Bernardini, G.; Gornati, R. Identification of reference genes for qPCR analysis during hASC long culture maintenance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, F.; Bernardini, G.; Bonfanti, P.; Colombo, A.; Prati, M.; Gornati, R. Effects of TCDD on Spermatogenesis Related Factor-2 (SRF-2): Gene expression in Xenopus. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, N.; Del Bakhshayesh, A.R.; Davaran, S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Common biocompatible polymeric materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Conducting Polymers for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.; Lv, Y. Application of Collagen Scaffold in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and New Perspectives. Polymers 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chicharro-Alcántara, D.; Rubio-Zaragoza, M.; Damiá-Giménez, E.; Carrillo-Poveda, J.M.; Cuervo-Serrato, B.; Peláez-Gorrea, P.; Sopena-Juncosa, J.J. Platelet Rich Plasma: New Insights for Cutaneous Wound Healing Management. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Pascale, M.R.; Sommese, L.; Casamassimi, A.; Napoli, C. Platelet Derivatives in Regenerative Medicine: An Update. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J. Platelets in wound healing and regenerative medicine. Platelets 2018, 29, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.L.; Kandoi, S.; Misra, R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Verma, R.S. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Parthiban, P.; Jin, G.-Z.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.-W. Materials roles for promoting angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.E.; Smith, P.C.; Palma Alvarado, V. The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: A concise update. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrientos, S.; Stojadinovic, O.; Golinko, M.S.; Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. PERSPECTIVE ARTICLE: Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Wolf, L.; Deckenback, J.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Human Platelet-Rich Plasma- and Extracellular Matrix-Derived Peptides Promote Impaired Cutaneous Wound Healing In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, M.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A.; Minutoli, L.; Calò, M.; Cascio, P.L.; Polito, F.; Giugliano, G.; Squadrito, G.; Mioni, C.; et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin improves angiogenesis and wound healing in experimental burn wounds*. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.R.; Teixeira, G.Q.; Santos, S.G.; Barbosa, M.A.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Gonçalves, R.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome: Influencing Therapeutic Potential by Cellular Pre-conditioning. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Katagiri, W.; Osugi, M.; Sugimura, Y.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M. Secretomes from bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells enhance periodontal tissue regeneration. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, A.; Dzau, V.J. Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 1204–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonsatti, E.; Sigalotti, L.; Arslan, P.; Altomonte, M.; Maio, M. Emerging Role of Endoglin (CD105) as a Marker of Angiogenesis with Clinical Potential in Human Malignancies. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2003, 3, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Anand, V.; Roy, S. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling in Hypoxia and Inflammation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, G.; Liu, D.; He, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, X.; Chen, B.; OuYang, W.; Dai, J.; Li, X. A dual functional collagen scaffold coordinates angiogenesis and inflammation for diabetic wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6337–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestweber, D. VE-Cadherin. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmeliet, P.; Collen, D. Molecular Basis of Angiogenesis: Role of VEGF and VE-Cadherin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 902, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrhan, F.; Stockmann, P.; Nkenke, E.; Schlegel, K.A.; Guentsch, A.; Wehrhan, T.; Neukam, F.W.; Amann, K. Differential impairment of vascularization and angiogenesis in bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw-related mucoperiosteal tissue. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, S.; Monnot, C.; Muller, L.; Eichmann, A. Hypoxia-driven angiogenesis: Role of tip cells and extracellular matrix scaffolding. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2010, 17, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellström, M.; Phng, L.-K.; Hofmann, J.J.; Wallgard, E.; Coultas, L.; Lindblom, P.; Alva, J.; Nilsson, A.-K.; Karlsson, L.; Gaiano, N.; et al. Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature 2007, 445, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.K.; Bourdeau, A.; Letarte, M.; Zúñiga-Pflücker, J.C. Expression and function of CD105 during the onset of hematopoiesis from Flk1+ precursors. Blood 2001, 98, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, F.; Cusimano, M.D.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Rotondo, F.; Fazio, A.; Yousef, G.M.; Syro, L.V.; Kovacs, K.; Lloyd, R.V. Endoglin (CD105): A review of its role in angiogenesis and tumor diagnosis, progression and therapy. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2283–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, N.A.; Mahsuni, P.; Taheri, D. Evaluation of Endoglin as an Angiogenesis Marker in Glioblastoma. Iran. J. Pathol. 2015, 10, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brindle, N.P.J.; Saharinen, P.; Alitalo, K. Signaling and Functions of Angiopoietin-1 in Vascular Protection. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, G.Y. Orchestral actions of angiopoietin-1 in vascular regeneration. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Sequence 5′–3′ | Tm (°C) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mm_βActin | Fw GCCCAGAGCAAGAGAGGTA Rv TAGAAGGTGTGGTGCCAGAT | 65 | NM_007393.5 |
| 64.9 | |||
| Mm_GAPDH | Fw ACCTGCCAAGTATGATGAC Rv GGAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTC | 64 | NM_008084.3 |
| 59.7 | |||
| Mm_CD31 | Fw AACAGAGCCAGCAGTATGA Rv ATGACAACCACCGCAATG | 62.6 | NM_001305157.1 |
| 62.5 | |||
| Mm_CD34 | Fw CTGCTCCGAGTGCCATTA Rv CTCCTCACAACTAGATGCTTCA | 63.3 | NM_001111059.1 |
| 63.7 | |||
| Mm_ANGPT1 | Fw GGAAGATGGAAGCCTGGATT Rv ACTGCCTCTGACTGGTTATTG | 65.1 | NM_009640.4 |
| 64.2 | |||
| Mm_ANGPT2 | Fw CGACTACGACGACTCAGT Rv TCTCCACCATCTCCTTCTTC | 63.7 | NM_007426.4 |
| 63.8 | |||
| Mm_CDH5 | Fw CAGAGTCCATCGCAGAGT Rv AGCCAGCATCTTGAACCT | 64.1 | NM_009868.4 |
| 64.4 | |||
| Mm_CD105 | Fw CGATAGCAGCACTGGATGAC Rv TGGCAAGCACAAGAATGGT | 64.7 | NM_001146350.1 |
| 64.5 | |||
| Hs_CD90 | Fw CTCTACTTATCCGCCTTCACT Rv CGTTCTGGGAGGAGATGG | 62.9 | NM_006288.5 |
| 63 | |||
| Hs_FABP4 | Fw AAGTCAAGAGCACCATAACCT Rv GCATTCCACCACCAGTTTATC | 63.3 | NM_001442.3 |
| 63.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barone, L.; Rossi, F.; Valdatta, L.; Cherubino, M.; Papait, R.; Binelli, G.; Romano, N.; Bernardini, G.; Gornati, R. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Vascularization of Nanostructured Scaffold Transplanted into Nude Mice. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091521
Barone L, Rossi F, Valdatta L, Cherubino M, Papait R, Binelli G, Romano N, Bernardini G, Gornati R. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Vascularization of Nanostructured Scaffold Transplanted into Nude Mice. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091521
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarone, Ludovica, Federica Rossi, Luigi Valdatta, Mario Cherubino, Roberto Papait, Giorgio Binelli, Nicla Romano, Giovanni Bernardini, and Rosalba Gornati. 2022. "Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Vascularization of Nanostructured Scaffold Transplanted into Nude Mice" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091521
APA StyleBarone, L., Rossi, F., Valdatta, L., Cherubino, M., Papait, R., Binelli, G., Romano, N., Bernardini, G., & Gornati, R. (2022). Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Vascularization of Nanostructured Scaffold Transplanted into Nude Mice. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091521







