Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model, Methods, and Observables
Numerical Renormalization Group
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview and Phase Diagram
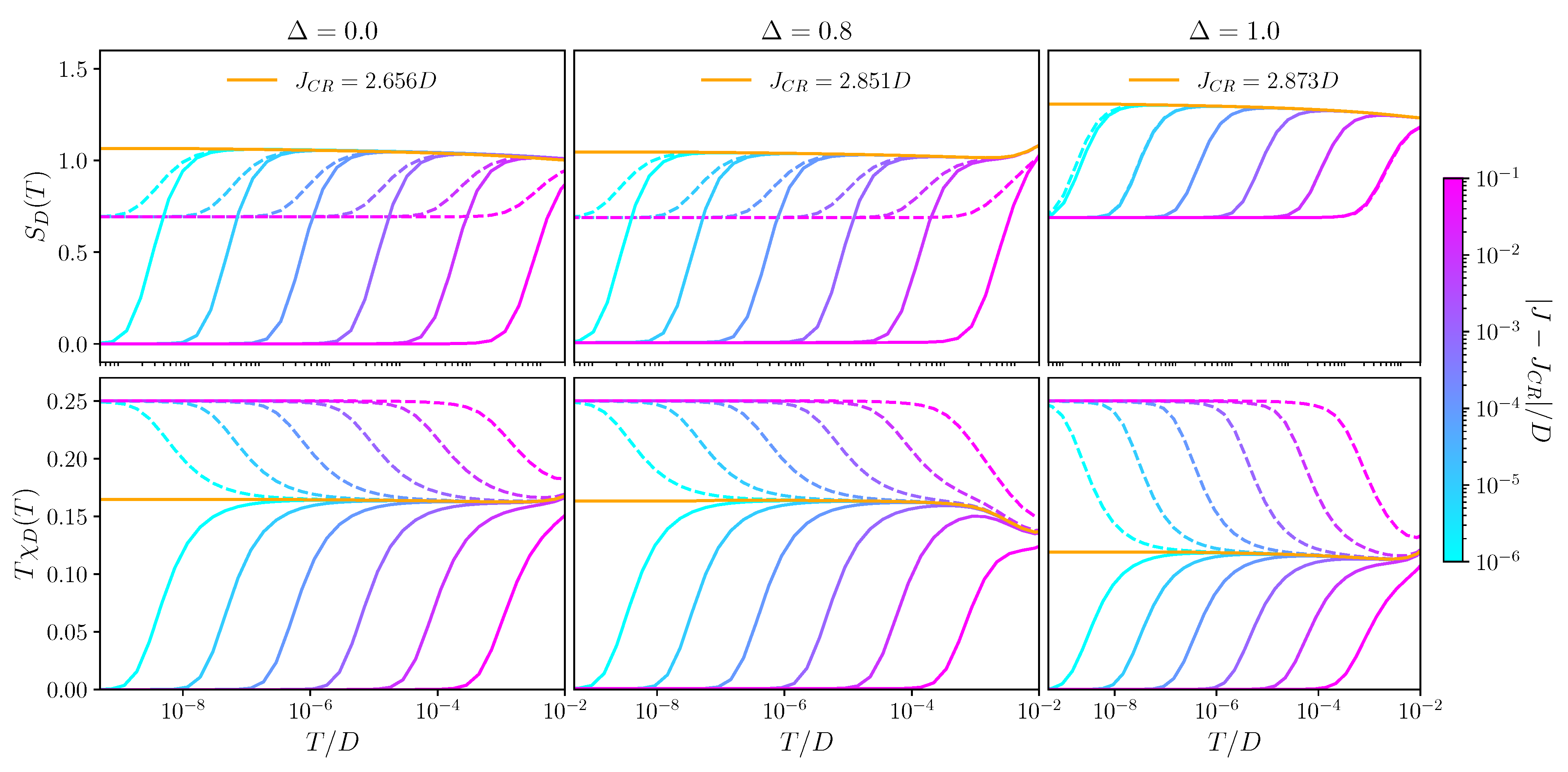
3.2. Thermodynamics and Fixed Points
3.2.1. Frozen Channel Degree of Freedom:
3.2.2. Frustrated Channel Degree of Freedom:
3.3. Dynamics and Transport
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QD | quantum dot |
| QPC | quantum point contact |
| QPT | quantum phase transition |
| QCP | quantum critical point |
| 2CK | two-channel Kondo |
| NRG | Numerical Renormalization Group |
| FL | Fermi liquid |
| NFL | non-Fermi liquid |
| DoS | density of states |
| RG | renormalization group |
| FP | fixed point |
| LM | local moment |
| (F)ALM | (frustrated) asymmetric local moment |
| (F)ASC | (frustrated) asymmetric strong coupling |
| (F)SSC | (frustrated) symmetric strong coupling |
| (F)ACR | (frustrated) asymmetric critical |
References
- Kondo, J. Resistance minimum in dilute magnetic alloys. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1964, 32, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, A.C. The Kondo Problem to Heavy Fermions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.G. The renormalization group: Critical phenomena and the Kondo problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1975, 47, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, J.; Utsumi, Y.; Imamura, H.; Barnaś, J.; Maekawa, S.; König, J.; Schön, G. Kondo effect in quantum dots coupled to ferromagnetic leads. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 127203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Schulze, G.; Pascual, J. Competition of superconducting phenomena and Kondo screening at the nanoscale. Science 2011, 332, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Schuricht, D.; Vojta, M.; Fritz, L. Kondo effect on the surface of three-dimensional topological insulators: Signatures in scanning tunnelling spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 075430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Fritz, L. Kondo effect in three-dimensional Dirac and Weyl systems. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 121109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, L.; Cullen, W.G.; Williams, E.D.; Fuhrer, M.S. Tunable Kondo effect in graphene with defects. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, L.; Vojta, M. The physics of Kondo impurities in graphene. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 032501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.C.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, A.J.; Oliver, W.D.; Vandersypen, L.M.; Ardavan, A.; Sessoli, R.; Loss, D.; Jayich, A.B.; Fernandez-Rossier, J.; Laucht, A.; Morello, A. Quantum-coherent nanoscience. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, P.; Vandersypen, L.M. Quantum dot systems: A versatile platform for quantum simulations. Ann. Phys. 2013, 525, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, M.A.; Klein, O.; Lyszczarz, T.M.; Mankiewich, P.M.; Shaver, D.C.; Wind, S.; Abusch-Magder, D.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D.J.; Morgan, N.Y. Artificial Atoms; Technical Report; Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT): Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhaber-Gordon, D.; Shtrikman, H.; Mahalu, D.; Abusch-Magder, D.; Meirav, U.; Kastner, M.A. Kondo effect in a single-electron transistor. Nature 1998, 391, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronenwett, S.M.; Oosterkamp, T.H.; Kouwenhoven, L.P. A tunable Kondo effect in quantum dots. Science 1998, 281, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Wiel, W.; Franceschi, S.D.; Fujisawa, T.; Elzerman, J.; Tarucha, S.; Kouwenhoven, L. The Kondo effect in the unitary limit. Science 2000, 289, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Becker, M.; Bulla, R. Real-space renormalization group flow in quantum impurity systems: Local moment formation and the Kondo screening cloud. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 115120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.; Lee, S.S.; Sim, H.S. Detecting Kondo entanglement by electron conductance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 146801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustilnik, M.; Glazman, L. Kondo effect in quantum dots. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojta, M. Impurity quantum phase transitions. Philos. Mag. 2006, 86, 1807–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Jarrold, T.F.; Logan, D.E. Quantum phase transition in quantum dot trimers. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 085124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Amasha, S.; Weymann, I.; Moca, C.; Rau, I.; Katine, J.; Shtrikman, H.; Zaránd, G.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Emergent SU (4) Kondo physics in a spin–charge-entangled double quantum dot. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Liberman, A.; Sela, E.; Affleck, I. SO (5) non-Fermi liquid in a Coulomb box device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 147702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potok, R.; Rau, I.; Shtrikman, H.; Oreg, Y.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Observation of the two-channel Kondo effect. Nature 2007, 446, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.; Peeters, L.; Moca, C.; Weymann, I.; Mahalu, D.; Umansky, V.; Zaránd, G.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system. Nature 2015, 526, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E. Universal low-temperature crossover in two-channel Kondo models. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 235127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E.; Logan, D.E. Two-channel Kondo physics in two-impurity Kondo models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 086405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozieres, P.; Blandin, A. Kondo effect in real metals. J. Phys. 1980, 41, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affleck, I.; Ludwig, A.W. Critical theory of overscreened Kondo fixed points. Nucl. Phys. B 1991, 360, 641–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, Z.; Jezouin, S.; Anthore, A.; Gennser, U.; Parmentier, F.; Cavanna, A.; Pierre, F. Two-channel Kondo effect and renormalization flow with macroscopic quantum charge states. Nature 2015, 526, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Landau, L.; Fritz, L.; Sela, E. Universality and scaling in a charge two-channel Kondo device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 157202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, Z.; Anthore, A.; Mitchell, A.; Parmentier, F.; Gennser, U.; Ouerghi, A.; Cavanna, A.; Mora, C.; Simon, P.; Pierre, F. Tunable quantum criticality and super-ballistic transport in a “charge” Kondo circuit. Science 2018, 360, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Iftikhar, Z.; Kleeorin, Y.; Anthore, A.; Pierre, F.; Meir, Y.; Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E. Fractional entropy of multichannel Kondo systems from conductance-charge relations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouse, W.; Peeters, L.; Hsueh, C.L.; Gennser, U.; Cavanna, A.; Kastner, M.A.; Mitchell, A.K.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12691. [Google Scholar]
- Matveev, K. Coulomb blockade at almost perfect transmission. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusaki, A.; Matveev, K. Theory of strong inelastic cotunnelling. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 16676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, I.; Fritz, L.; Anders, F.B.; Benlagra, A.; Vojta, M. Two-channel pseudogap Kondo and Anderson models: Quantum phase transitions and non-Fermi liquids. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 125139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, M.; Bradley, S.J.; Nann, T. Graphene quantum dots. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; Pu, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Recent advances on graphene quantum dots: From chemistry and physics to applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S.; Fu, J. An eco-friendly imprinted polymer based on graphene quantum dots for fluorescent detection of p-nitroaniline. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41383–41391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebanon, E.; Schiller, A.; Anders, F.B. Coulomb blockade in quantum boxes. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 041311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, E. Poor man’s scaling: Anisotropic Kondo and Coqblin–Schrieffer models. J. Phys. Commun. 2018, 2, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, L.; Vojta, M. Phase transitions in the pseudogap Anderson and Kondo models: Critical dimensions, renormalization group, and local-moment criticality. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 214427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumida, W.; Sakai, O.; Shimizu, Y. Many body effects on electron tunnelling through quantum dots in an Aharonov-Bohm circuit. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 66, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minarelli, E.L.; Rigo, J.B.; Mitchell, A.K. Linear response quantum transport through interacting multi-orbital nanostructures. 2022; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Meir, Y.; Wingreen, N.S. Landauer formula for the current through an interacting electron region. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, T.; Sheekey, O.; Lüscher, S.; Fallahi, S.; Gardner, G.C.; Manfra, M.; Kleeorin, Y.; Meir, Y.; Folk, J. Entropy measurement of a strongly correlated quantum dot. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.14158. [Google Scholar]
- Bulla, R.; Costi, T.A.; Pruschke, T. Numerical renormalization group method for quantum impurity systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 395–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, A.; Von Delft, J. Sum-rule conserving spectral functions from the numerical renormalization group. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 076402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, R.; Pruschke, T.; Hewson, A. Anderson impurity in pseudo-gap Fermi systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Pruschke, T.; Anders, F.B. Numerical renormalization group approach to Greenâ’s functions for quantum impurity models. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 245114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, F.B.; Schiller, A. Real-time dynamics in quantum-impurity systems: A time-dependent numerical renormalization-group approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 196801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Buxton, C.; Ingersent, K. Renormalization-group study of Anderson and Kondo impurities in gapless Fermi systems. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, D.E.; Glossop, M.T. A local moment approach to magnetic impurities in gapless Fermi systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vojta, M.; Fritz, L. Upper critical dimension in a quantum impurity model: Critical theory of the asymmetric pseudogap Kondo problem. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 094502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojta, M.; Fritz, L.; Bulla, R. Gate-controlled Kondo screening in graphene: Quantum criticality and electron-hole asymmetry. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2010, 90, 27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Vojta, M.; Bulla, R.; Fritz, L. Quantum phase transitions and thermodynamics of the power-law Kondo model. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 195119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojta, M.; Bulla, R. Kondo effect of impurity moments in d-wave superconductors: Quantum phase transition and spectral properties. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 014511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Asymmetry | Fixed Point | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM line | 0 | |||||
| ASC | 0 | 0 | ||||
| ACR * | 0 | |||||
| FASC * | 0 | |||||
| FACR * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minarelli, E.L.; Rigo, J.B.; Mitchell, A.K. Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
Minarelli EL, Rigo JB, Mitchell AK. Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinarelli, Emma L., Jonas B. Rigo, and Andrew K. Mitchell. 2022. "Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
APA StyleMinarelli, E. L., Rigo, J. B., & Mitchell, A. K. (2022). Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513








