Band Polarization Effect on the Kondo State in a Zigzag Silicene Nanoribbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
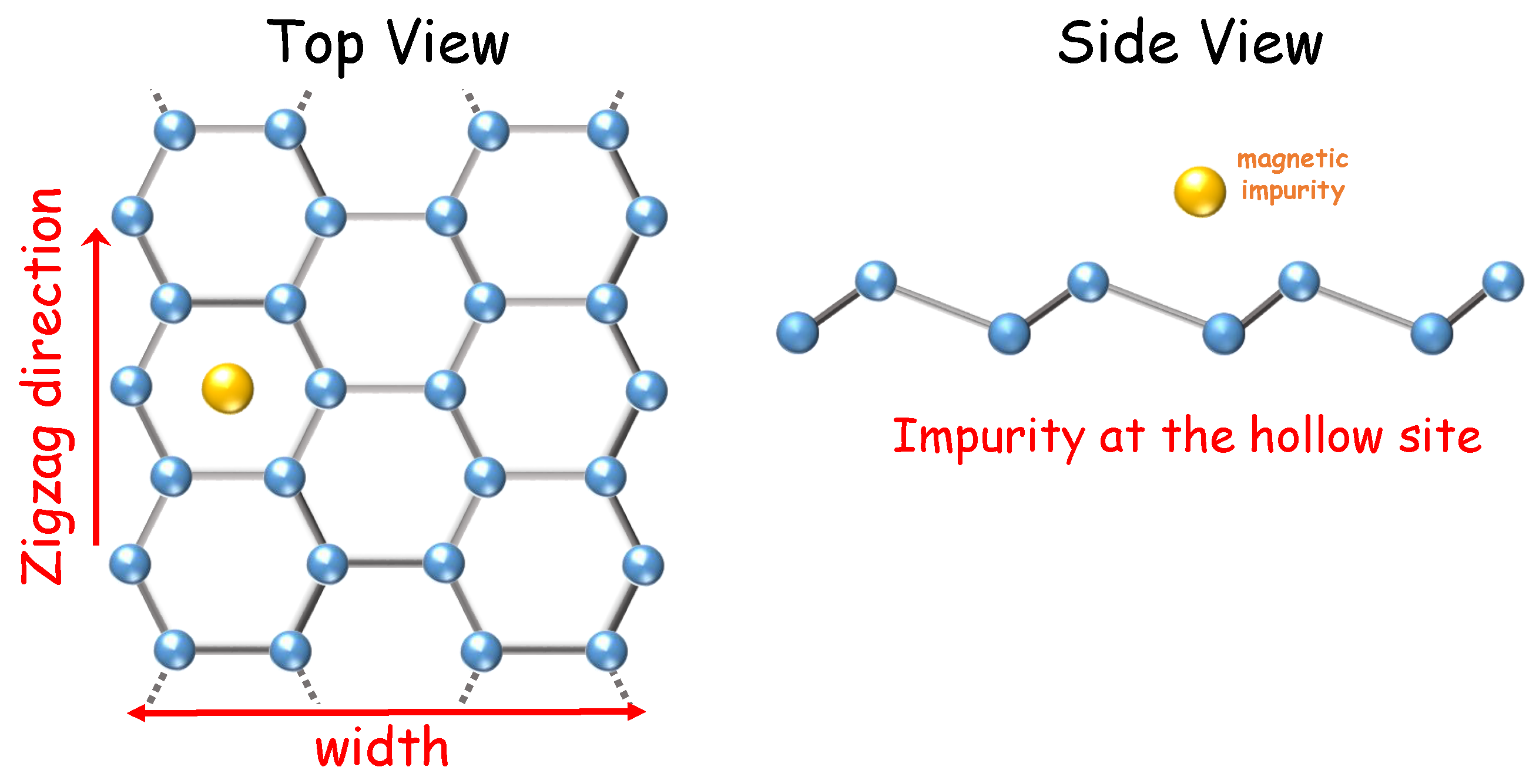
2.1. Model Hamiltonian
2.2. Tight-Binding Bands
2.3. Hybridization Function
2.4. Results and Discussion
3. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GF | Green’s function |
| LDOS | Local density of states |
| NRG | Numerical Renormalization Group |
| SOC | Spin orbit coupling |
| ZNR | Zigzag nanoribbon |
Appendix A. Appendix Calculations for Finite

Appendix B. Appendix Hamiltonian for Bulk Silicene
References
- Kane, C.L.; Mele, E.J. Quantum Spin Hall Effect in Graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 226801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kane, C.L.; Mele, E.J. Z2 Topological Order and the Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 146802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haldane, F.D.M. Model for a Quantum Hall Effect without Landau Levels: Condensed-Matter Realization of the “Parity Anomaly”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, M.; Wiedmann, S.; Brüne, C.; Roth, A.; Buhmann, H.; Molenkamp, L.W.; Qi, X.L.; Zhang, S.C. Quantum spin hall insulator state in HgTe quantum wells. Science 2007, 318, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, M.; Buhmann, H.; Molenkamp, L.W.; Hughes, T.; Liu, C.X.; Qi, X.L.; Zhang, S.C. The quantum spin Hall effect: Theory and experiment. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 77, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Y. Low-energy effective Hamiltonian involving spin-orbit coupling in silicene and two-dimensional germanium and tin. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 195430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molle, A.; Goldberger, J.; Houssa, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.C.; Akinwande, D. Buckled two-dimensional Xene sheets. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Tang, X.; Liao, X.; Ge, Y.; Jin, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y. Recent progress of spintronics based on emerging 2D materials: Crl(3) and Xenes. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, I.S.; Randhawa, D.K.K. Something more than graphene - futuristic two-dimensional nanomaterials. Curr. Sci. 2020, 118, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, T.; Yu, Z.; Dai, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Pan, R.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; et al. Recent Advances in Hybridization, Doping, and Functionalization of 2D Xenes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendhran, S.; Walia, S.; Nili, H.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M. Elemental Analogues of Graphene: Silicene, Germanene, Stanene, and Phosphorene. Small 2015, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molle, A.; Grazianetti, C.; Tao, L.; Taneja, D.; Alam, M.H.; Akinwande, D. Silicene, silicene derivatives, and their device applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.K.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, C.W.; Wang, P.J. Stanene: A Promising Material for New Electronic and Spintronic Applications. Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 2019, 531, 1900017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, M.; Motta, N.; De Crescenzi, M.; Camilli, L. Group-IV 2D materials beyond graphene on nonmetal substrates: Challenges, recent progress, and future perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 041310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, T.; Sofer, Z. Beyond Graphene: Chemistry of Group 14 Graphene Analogues: Silicene, Germanene, and Stanene. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezawa, M. A topological insulator and helical zero mode in silicene under an inhomogeneous electric field. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezawa, M. Monolayer Topological Insulators: Silicene, Germanene, and Stanene. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 84, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaroshevich, A.S.; Kvon, Z.D.; Gusev, G.M.; Mikhailov, N.N. Microwave Photoresistance of a Two-Dimensional Topological Insulator in a HgTe Quantum Well. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 2020, 111, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvon, Z.D.; Kozlov, D.A.; Olshanetsky, E.B.; Gusev, G.M.; Mikhailov, N.N.; Dvoretsky, S.A. Topological insulators based on HgTe. Physics-Uspekhi 2020, 63, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, M. Spin-Related Transport Phenomena in HgTe-Based Quantum Well Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.W. Localized Magnetic States in Metals. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, A.C. The Kondo Problem to Heavy Fermions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Stano, P.; Klinovaja, J.; Loss, D. Helical liquids in semiconductors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goth, F.; Luitz, D.J.; Assaad, F.F. Magnetic impurities in the Kane-Mele model. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 075110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allerdt, A.; Feiguin, A.E.; Martins, G.B. Spatial structure of correlations around a quantum impurity at the edge of a two-dimensional topological insulator. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 035109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allerdt, A.; Feiguin, A.; Martins, G. Kondo effect in a two-dimensional topological insulator: Exact results for adatom impurities. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 128, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büsser, C.A.; Martins, G.B.; Feiguin, A.E. Lanczos transformation for quantum impurity problems in d -dimensional lattices: Application to graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 245113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allerdt, A.; Büsser, C.A.; Martins, G.B.; Feiguin, A.E. Kondo versus indirect exchange: Role of lattice and actual range of RKKY interactions in real materials. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 085101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weymann, I.; Zwierzycki, M.; Krompiewski, S. Spectral properties and the Kondo effect of cobalt adatoms on silicene. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernek, E.; Martins, G.B.; Žitko, R. Anisotropic Kondo screening induced by spin-orbit coupling in quantum wires. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 155114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, G.S.; Luiz, G.I.; Latgé, A.; Vernek, E. From Kondo to local singlet state in graphene nanoribbons with magnetic impurities. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 115444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakada, K.; Fujita, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Edge state in graphene ribbons: Nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 17954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.G.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.H. Quantum impurities in channel mixing baths. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 035102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osolin, V.; Žitko, R. Fine structure of the spectra of the Kondo lattice model: Two-site cellular dynamical mean-field theory study. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 035107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demchenko, D.O.; Joura, A.V.; Freericks, J.K. Effect of Particle-Hole Asymmetry on the Mott-Hubbard Metal-Insulator Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 216401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zitko, R. NRG Ljubljana. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4841076#.Yl1EmOFByUk (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- Campo, V.L.; Oliveira, L.N. Alternative discretization in the numerical renormalization-group method. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 104432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias da Silva, L.G.G.V.; Sandler, N.P.; Ingersent, K.; Ulloa, S.E. Zero-Field Kondo Splitting and Quantum-Critical Transition in Double Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 096603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, G.S.; Vernek, E.; Martins, G.B. Band Polarization Effect on the Kondo State in a Zigzag Silicene Nanoribbon. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091480
Diniz GS, Vernek E, Martins GB. Band Polarization Effect on the Kondo State in a Zigzag Silicene Nanoribbon. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091480
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Ginetom S., Edson Vernek, and George B. Martins. 2022. "Band Polarization Effect on the Kondo State in a Zigzag Silicene Nanoribbon" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091480
APA StyleDiniz, G. S., Vernek, E., & Martins, G. B. (2022). Band Polarization Effect on the Kondo State in a Zigzag Silicene Nanoribbon. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091480





