Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Pesticides on Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Materials
2.3. Larval Toxicity Bioassay
2.4. Preparation of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
2.5. HPLC Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
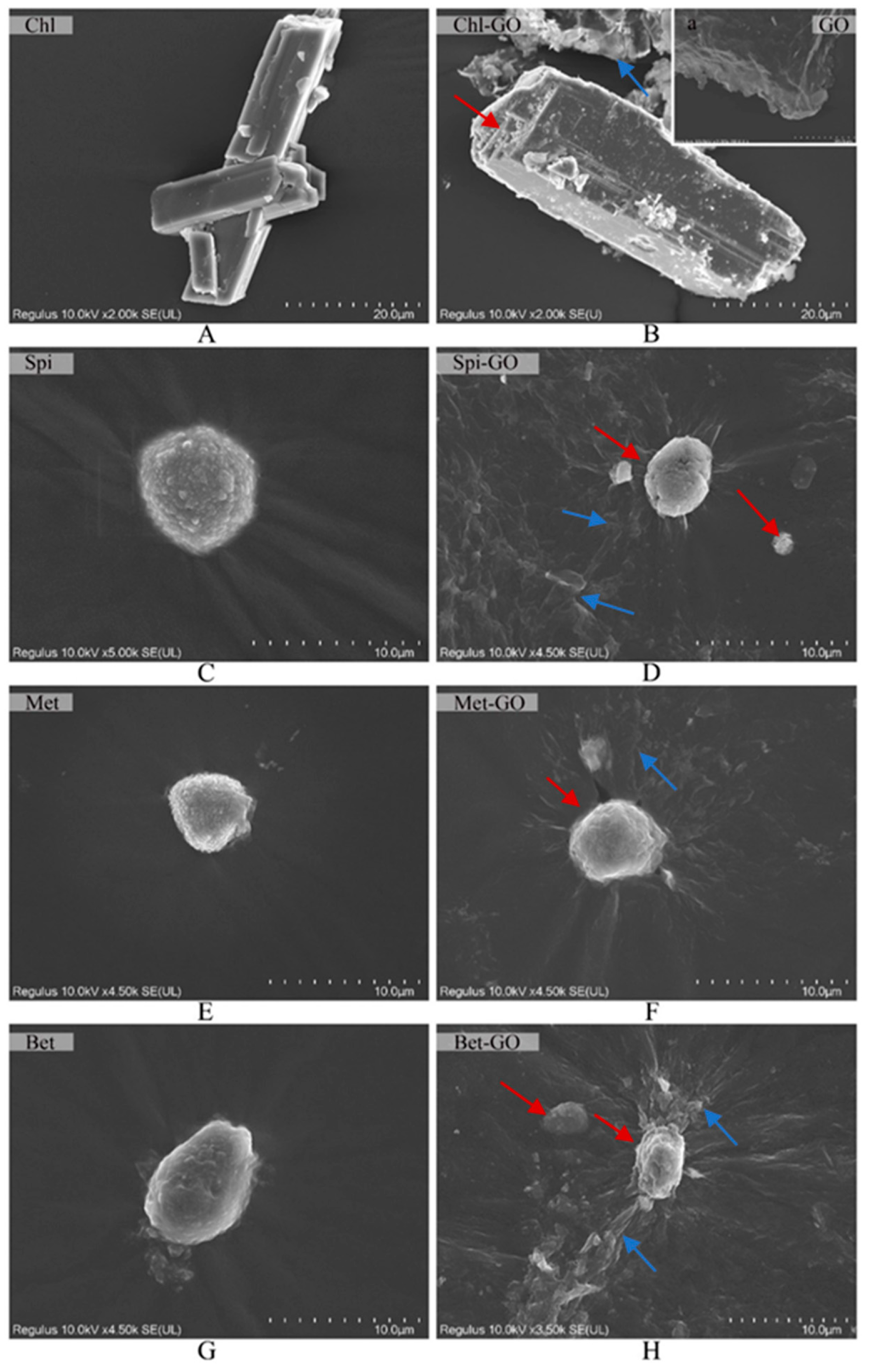
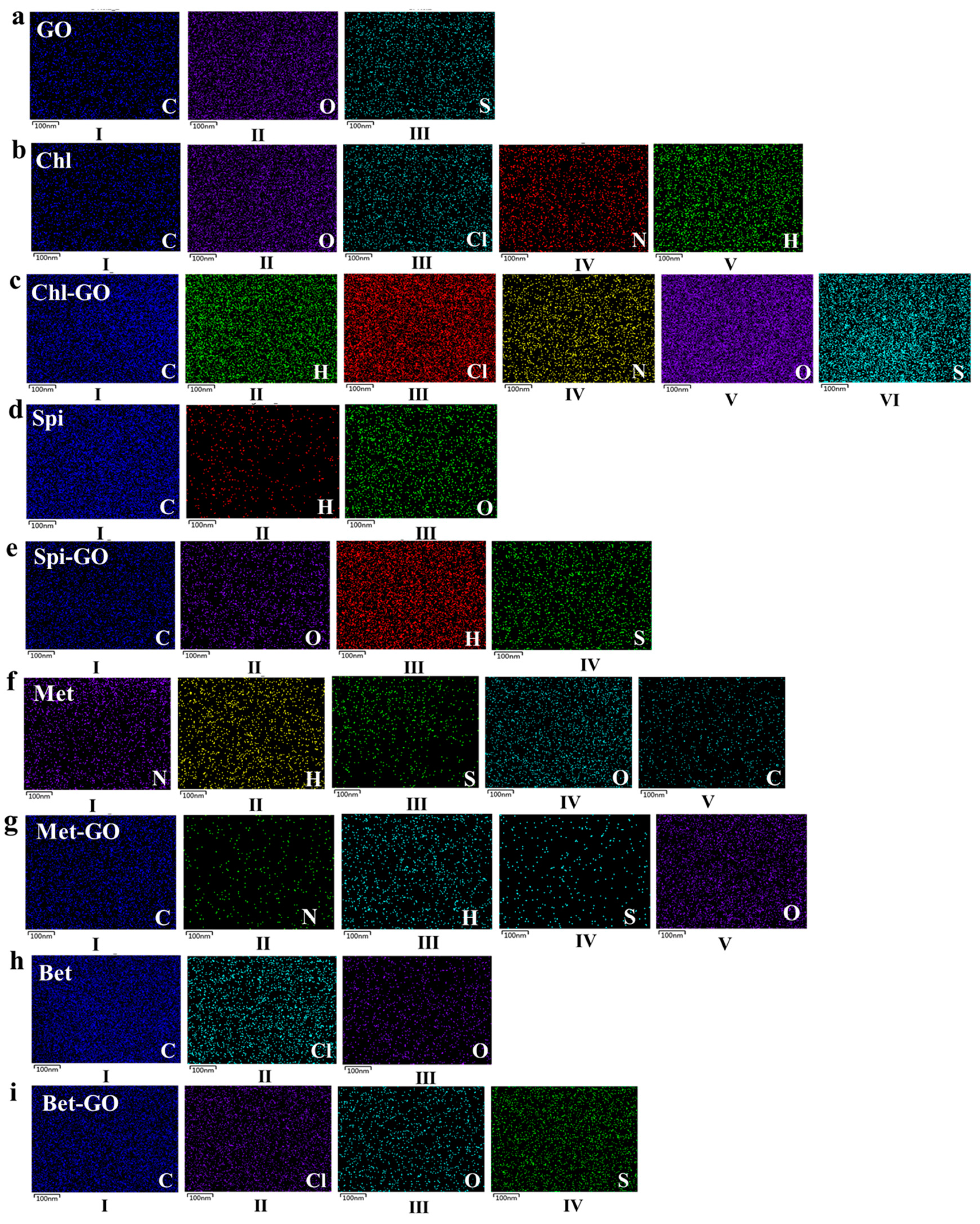
3.1. SEM and EDS Analysis
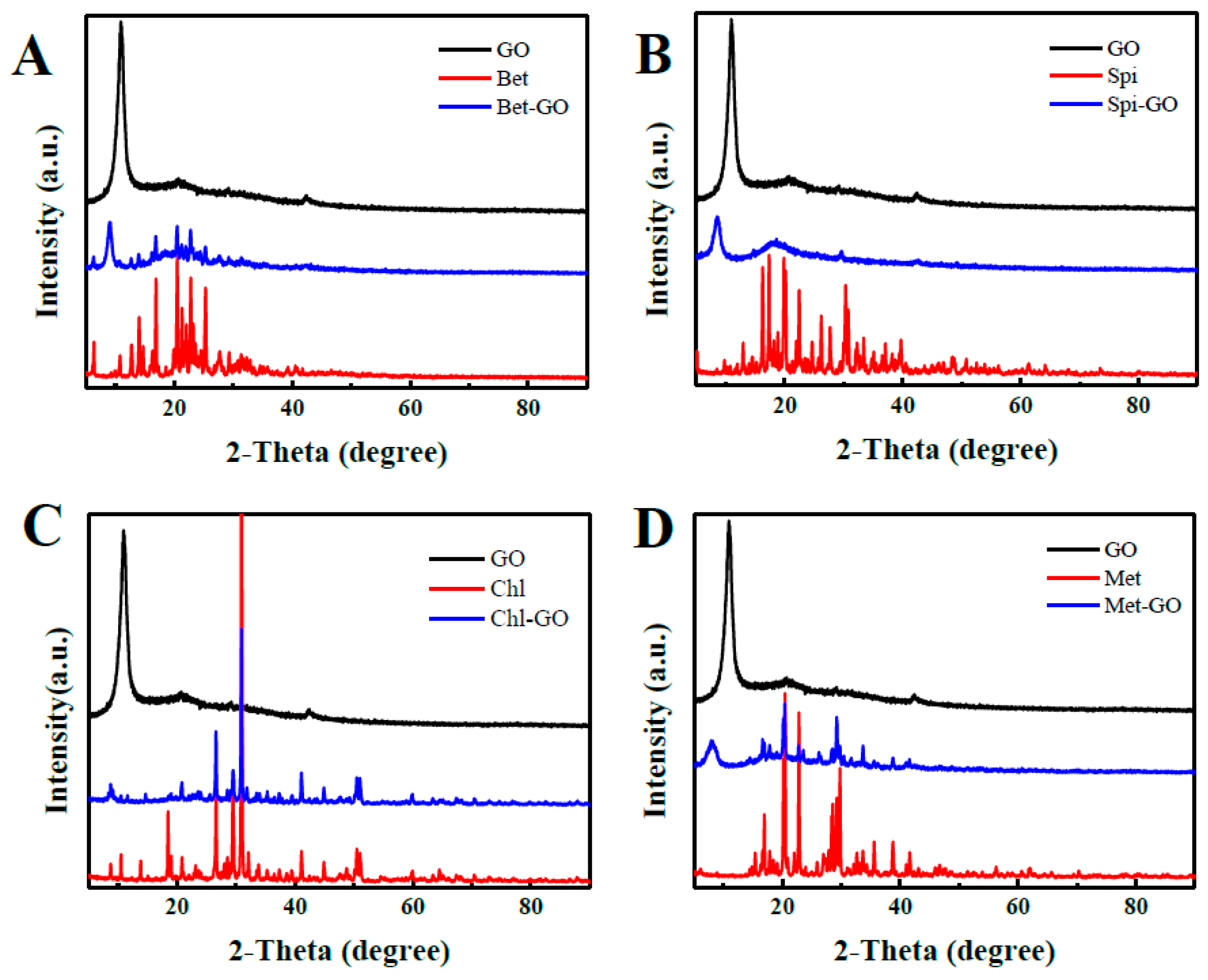
3.2. XRD of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
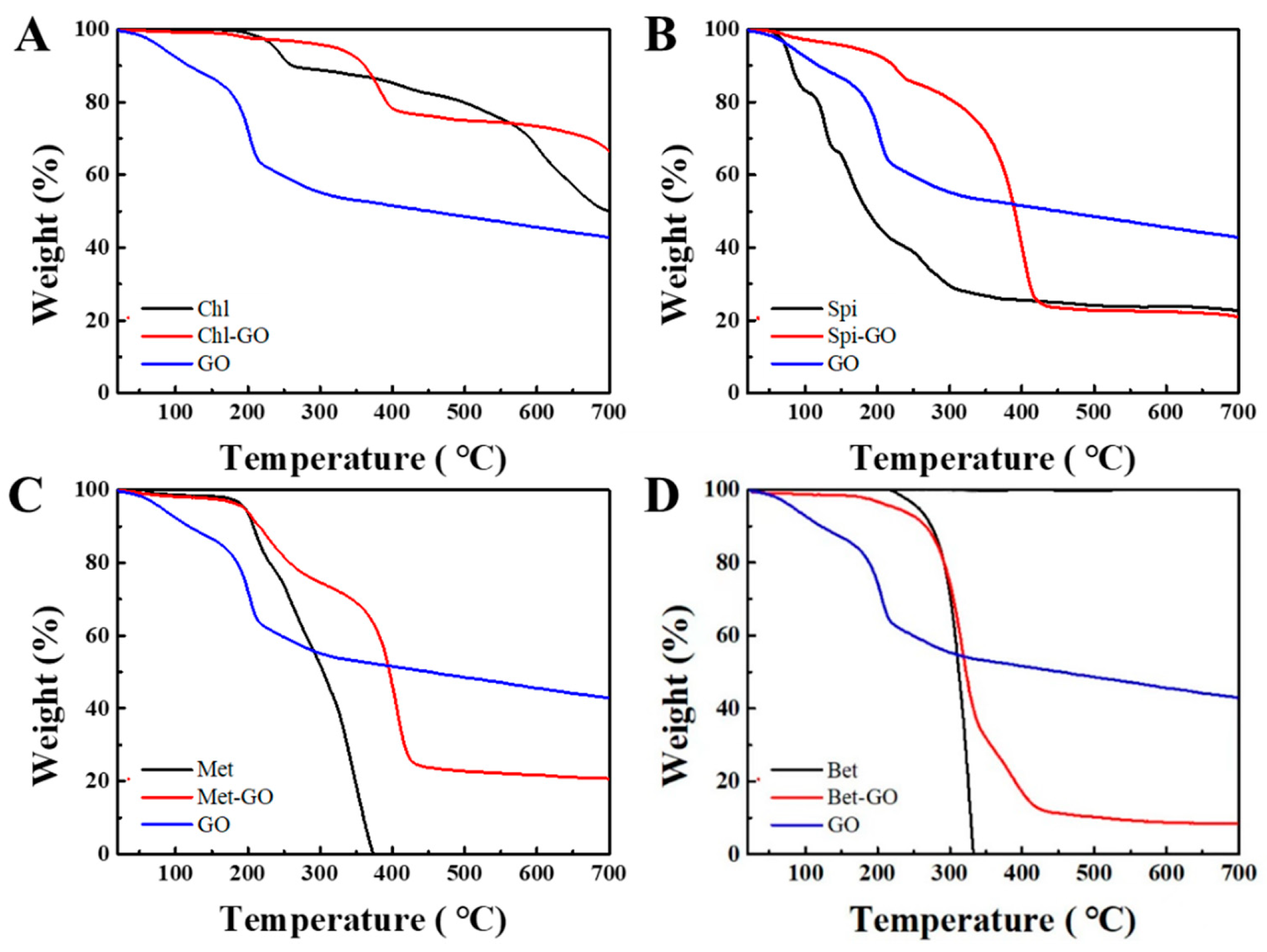
3.3. Thermal Stability Analysis of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
3.4. FT-IR Spectra of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
3.5. HPLC Analysis of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
3.6. Larval Toxicity Bioassay with Pesticides
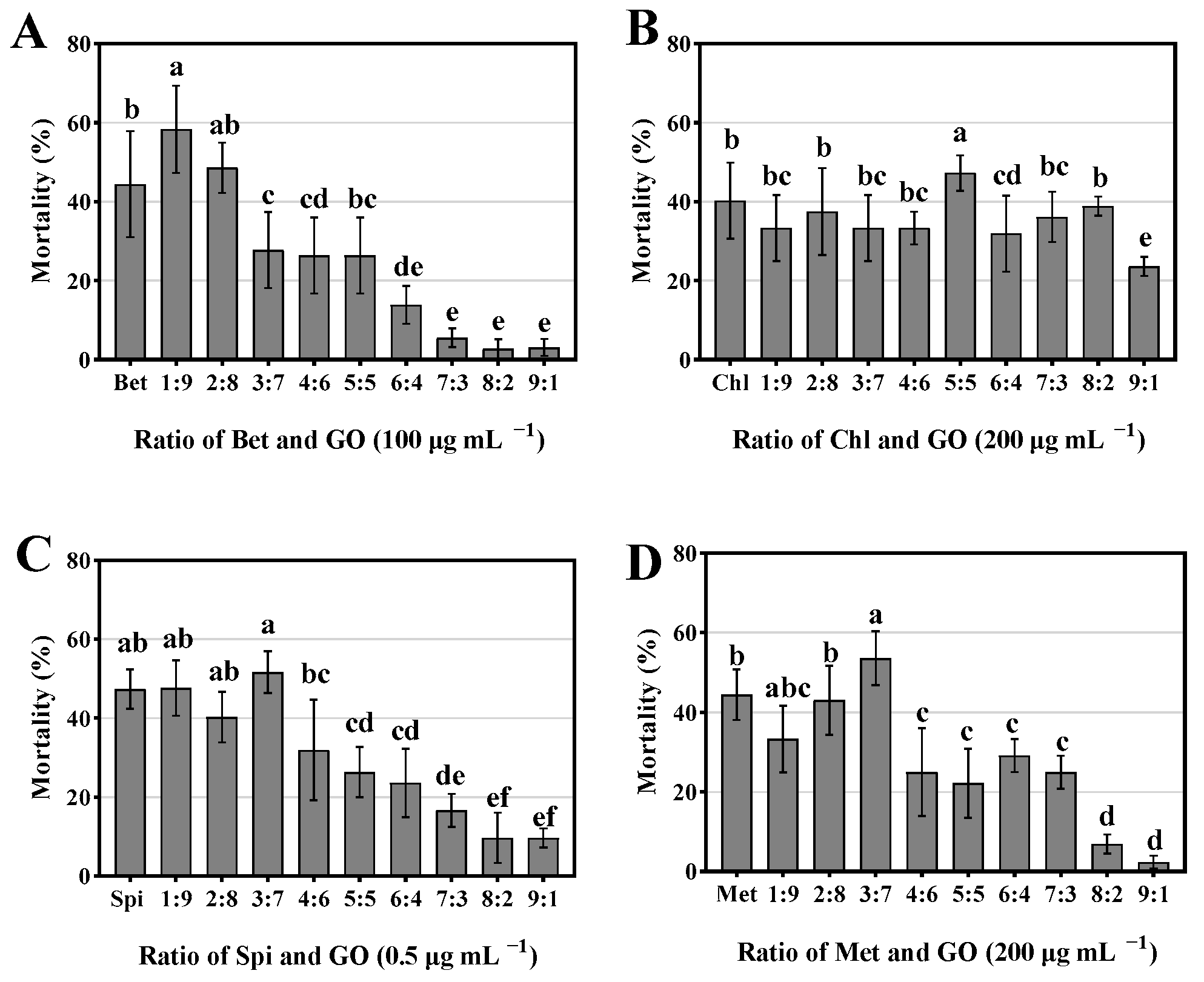
3.7. Optimal Ratio of GO and Pesticides
3.8. Bioassay of GO-Pesticide Nanocomposites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.F.; Zhao, J.Q.; He, K.L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.Y. Potential invasion of the crop-devastating insect pest fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda to China. Plant Protect. 2018, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.J. Migration and the life history strategy of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda in the western hemisphere. J. Trop. Insect. Sci. 1987, 8, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Biological characteristics, trend of fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda, and the strategy for management of the pest. Chin. J. App. Entomol. 2019, 56, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, K.W.; Zhong, G.H.; Xian, J.D.; He, X.F.; Lu, Q.Y. Progress for occurrence and management and the strategy of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith). J. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, L.F.; Wang, H.H.; Li, X.; Sun, G.; Gu, S.H. Genotype and mutation frequency of ace-1, the target gene of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides, in field populations of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in China. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 574–581. [Google Scholar]
- Montezano, D.G.; Specht, A.; Sosa-Gómez, D.R.; Sosa-Gómez, V.F.; Roque-Specht, J.C.; Sousa-Silva, S.V.; Paula-Moraes, S.D.; Peterson, J.A.; Hunt, T.E. Host plants of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas. Afr. Entomol. 2018, 26, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.H.; Tai, H.K.; Wang, Z.Y. A preliminary report on the damage to sugarcane by Spodoptera frugiperda. China Plant Protect. 2019, 39, 35–36+66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, M.H.; Zhang, D.D.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, K.M. Molecular identification of invasive fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda in Yunnan Province. Plant Protect. 2019, 45, 19–24+56. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.M. Analysis on the occurrence dynamics and future trend of the invasion of Spodoptera frugiperda in China. China Plant Protect. 2019, 39, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, H.K.; Guo, J.F.; Yang, S.C.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.Q. Biological characteristics and damage symptoms of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, on sugarcane in Dehong prefecture of Yunnan Province. Plant Protect. 2019, 45, 75–79+89. [Google Scholar]
- Okuma, D.M.; Bernardi, D.; Horikoshi, R.J.; Bernardi, O.; Silva, A.P.; Omoto, C. Inheritance and fitness costs of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) resistance to spinosad in Brazil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togola, A.; Meseka, S.; Menkir, A.; Badu-Apraku, B.; Boukar, O.; Tamò, M.; Djouaka, R. Measurement of pesticide residues from chemical control of the invasive Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in a maize experimental field in Mokwa, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Tai, H.K.; Gu, R.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, S.; Mi, Q. Economic loss assessment of maize production caused by the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and investigation of control strategies in Dehong prefecture of Yunnan province. Plant Protect. 2022, 48, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yu, K.; Zhou, J.R.; Cao, H.L.; Lv, J. Porous craphitic biomass carbons as sustainable adsorption and controlled release carriers for atrazine fixation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 20180–20189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Nawaz, M.; Yasin, T.; Riaz, M. Chitosan/CNTs nanocomposite as green carrier material for pesticides controlled release. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; He, K. Graphene oxide as a pesticide delivery vector for enhancing acaricidal activity against spider mites. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Abbaszadeh, M. Synthesis and characterization of MgO/PEG/GO Nanocomposite and its application for removal of Copper (II) from aquatic media. ACS Nano 2017, 86, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernat, A.; Györfi, S.J.; Irimes, M.; Tertiș, M.; Bodoki, A.; Pralea, I.; Suciu, M.; Cristea, C. Click chemistry on azide-functionalized graphene oxide. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 98, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y.; Chu, X.; Xie, J.; Zhou, N. Biomedical application of graphene: From drug delivery, tumor therapy, to theranostics. Colloid Surf. B 2020, 185, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, A.; Che Man, S.H.; Agarwal, V.; Yao, Y.; Thickett, S.C.; Zetterlund, P.B. Structural Complexity of Graphene Oxide: The Kirigami Model. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18255–18263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jiang, X.; Shen, H.; Wu, W.; Shi, Q.; Wan, M. MXene (Ti3C2) based pesticide delivery system for sustained release and enhanced pest control. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6912–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Feng, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; He, K.; Jing, D. Graphene oxide as a multifunctional synergist of insecticides against lepidopteran insect. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Mao, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Thermoresponsive polymer-encapsulated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in insecticide delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.D.; Shi, F.; Peng, F.; Shi, X.; Cheng, C.; Hou, W. Formulation of nanopesticide with graphene oxide as the nanocarrier of pyrethroid pesticide and its application in spider mite control. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3689–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wan, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Mo, H.; Jiang, X. Graphene oxide as the potential vector of hydrophobic pesticides: Ultrahigh pesticide loading capacity and improved antipest activity. ACS Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muda, M.S.; Kamari, A.; Bakar, S.A.; Yusoff, S.N.M.; Fatimah, I.; Phillip, E. Chitosan-graphene oxide nanocomposites as water-solubilising agents for rotenone pesticide. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2020. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2020/202003/202004/t20200416_6341680.htm (accessed on 25 December 2021).
- Gao, Z.P.; Guo, J.F.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Toxicity of spinetoram and its effects on the detoxifying enzyme and acetyl cholinesterase activities in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ywa, B.; Ssa, B.; Xca, B.; Wfa, B.; Jie, L.; Xha, B. A new temperature-responsive controlled-release pesticide formulation—Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) modified graphene oxide as the nanocarrier for lambda-cyhalothrin delivery and their application in pesticide transportation. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 612, 125987. [Google Scholar]
- Ganya, E.S.; Moli, S.J.; Ray, S.C.; Pong, W.F. Tuning the electronic and magnetic properties of PEDOT-PSS-coated graphene oxide nanocomposites for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, N.; Shi, Z.; Ge, Z. Fabrication, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility of graphene-reinforced chitosan composites. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, N.; El-Daly, H.; El Sharkawy, R.G.; Nasr, B.T. Synthesis and efficacy of PPy/CS/GO nanocomposites for adsorption of ponceau 4R dye. Polymer 2018, 146, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.Y.; Napiwocki, B.N.; Peng, X.F.; Turng, L.S. Mussel-inspired electroactive chitosan/graphene oxide composite hydrogel with rapid self-healing and recovery behavior for tissue engineering. Carbon 2017, 125, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Ren, N. Graphene oxide-reinforced biodegradable genipin-cross-linked chi-tosan fluorescent biocomposite film and its cytocompatibility. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3415–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y. Graphene oxide cross-linked chitosan nanocomposite membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 989–992. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S. Production of Pt nanoparticles-supported chelating group-modified graphene for direct methanol fuel cells. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajula, J.; Rahman, A.; Krutmuang, P. Entomopathogenic fungi in Southeast Asia and Africa and their possible adoption in biological control. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.; Samih, M.A.; Kalantari, S. Insecticied effect of silver and zinc nanoparticles against Aphis nerii Boyer of fonscolombe (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 72, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.J.; Cheng, C.H.; Peng, F.; Hou, W.L.; Lin, X.H.; Wang, X.P. Adsorption properties of graphene materials for pesticides: Structure effect. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaj, G.; Roopa, R.S.; Drashya, G.; Sunita, H.; Sarita, K. Multifunctional activity of graphene oxide-based nanoformulation against the disease vector, Aedes aegypti. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2021, 13, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Shao, L.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Sun, H.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X. Adhesive and stimulus-responsive polydopamine-coated Graphene Oxide system for pesticide-loss control. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2616–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Kedia, A.; Das, S.; Dubey, N.K. Essential oils and their bioactive compounds as eco-friendly novel green pesticides for management of storage insect pests: Prospects and retrospects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18918–18940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Ke, Q.; Kou, X. Cyclodextrins as carriers for volatile aroma compounds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Ganguli, A.K.; Shanmugam, V. Anti-drift nano-stickers made of graphene oxide for targeted pesticide delivery and crop pest control. Carbon 2017, 115, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhu, F. Structural characterization of nanoparticles loaded with garlic essential oil and their insecticidal activity against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10156–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, P.U.; Madhusudhanamurthy, J.; Sreedhar, B. Dynamic adsorption of α-pinene and linalool on silica nanoparticles for enhanced antifeedant activity against agricultural pests. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Concentrations (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| CK | 2%DMSO, 0.1% Tween 80 and water solution |
| Chl, GO, Chl-GO | 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 |
| Bet, GO, Bet-GO | 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 |
| Spi, GO, Spi-GO | 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 |
| Met, GO, Met-GO | 31.25, 62.5, 125, 250, 500 |
| Treatment | Instar | Slope ± SE a | χ2 | LC50 (95%FL) b | LC90 (95%FL) | df |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinetoram | 3rd instar | 1.81 ± 0.20 | 3.47 | 0.49 | 3.96 | 12 |
| (0.41–0.60) | (2.61–7.44) | |||||
| Methoxyfenozide | 3rd instar | 1.40 ± 0.15 | 7.22 | 159.88 | 1746.32 | 15 |
| (126.46–208.20) | (1023.91–3928) | |||||
| Chlorantraniliprole | 3rd instar | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 4.96 | 14.12 | 199.5 | 13 |
| (11.17–18.66) | (113.02–458.75) | |||||
| Beta cypermethrin | 3rd instar | 2.20 ± 0.21 | 8.25 | 103.69 | 578.64 | 13 |
| (84.04–128.07) | (395.41–1042.74) |
| Treatment | Slope ± SE a | χ2 b | df | N c | LC50 (95% FL) d | SR e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 4.96 | 13 | 360 | 14.12 (11.17–18.66) | - |
| Chl-GO | 1.32 ± 0.17 | 7.16 | 13 | 360 | 9.00 (8.32–13.98) | 1.56 |
| Bet | 2.20 ± 0.20 | 8.25 | 13 | 360 | 104.70 (84.04–128.07) | - |
| Bet-GO | 2.38 ± 0.22 | 6.63 | 13 | 360 | 68.00 (64.11–94.08) | 1.54 |
| Met | 1.40 ± 0.15 | 7.22 | 15 | 360 | 159.88 (126.46–208.20) 63.14 | - |
| Met-GO | 1.59 ± 0.21 | 9.30 | 13 | 360 | (49.84–77.56) | 2.53 |
| Spi | 3.80 ± 0.48 | 3.47 | 12 | 360 | 0.49 (0.41–0.60) | - |
| Spi-GO | 2.12 ± 0.20 | 8.61 | 13 | 360 | 0.28 (0.24–0.33) | 1.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Pesticides on Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223985
Li X, Wang Q, Wang X, Wang Z. Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Pesticides on Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(22):3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223985
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xue, Qinying Wang, Xiuping Wang, and Zhenying Wang. 2022. "Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Pesticides on Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda" Nanomaterials 12, no. 22: 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223985
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, Q., Wang, X., & Wang, Z. (2022). Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Pesticides on Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Nanomaterials, 12(22), 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223985







