Physical Transient Photoresistive Variable Memory Based on Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
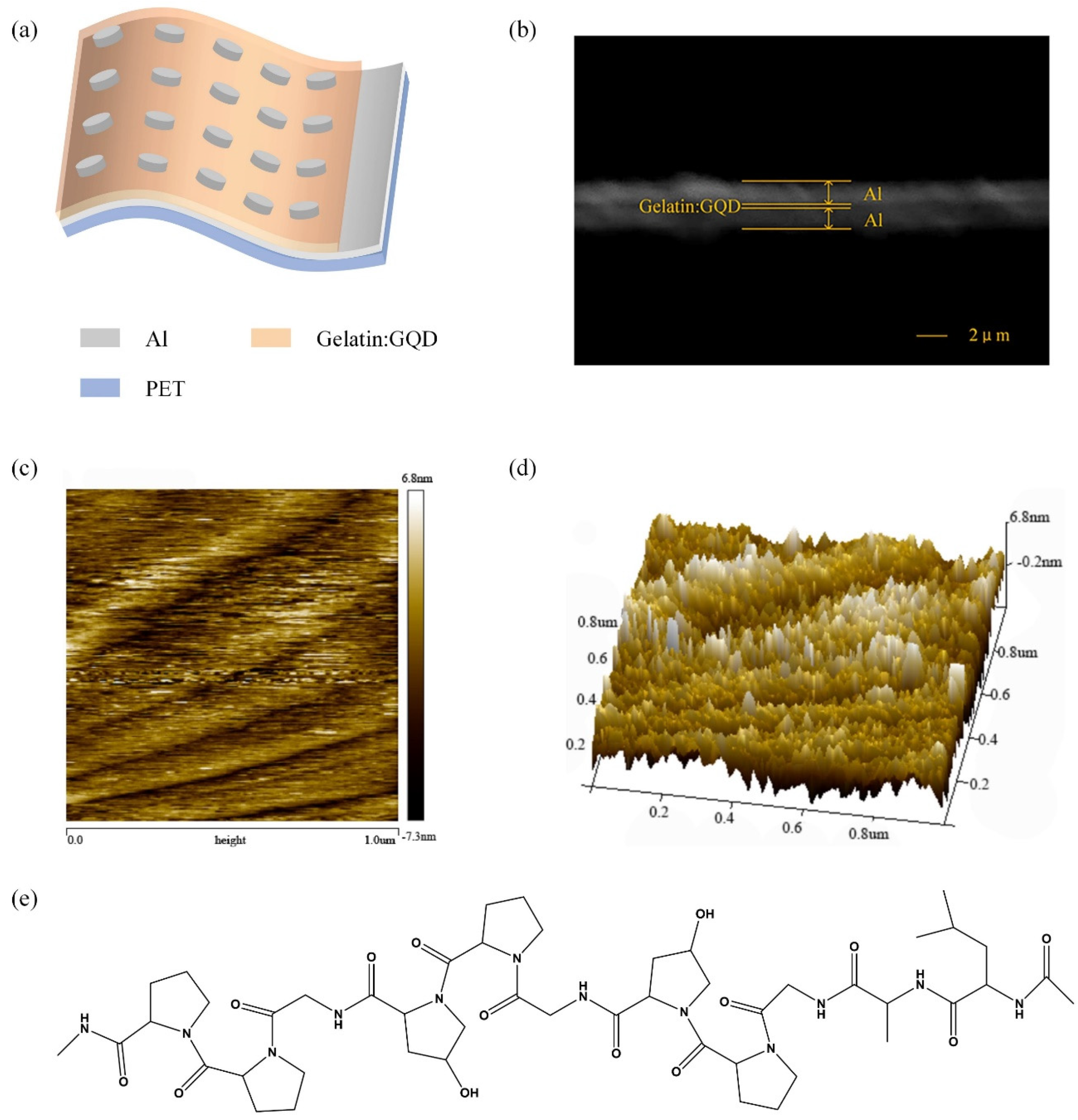
2.1. Preparation of the Device
2.2. Feature Description
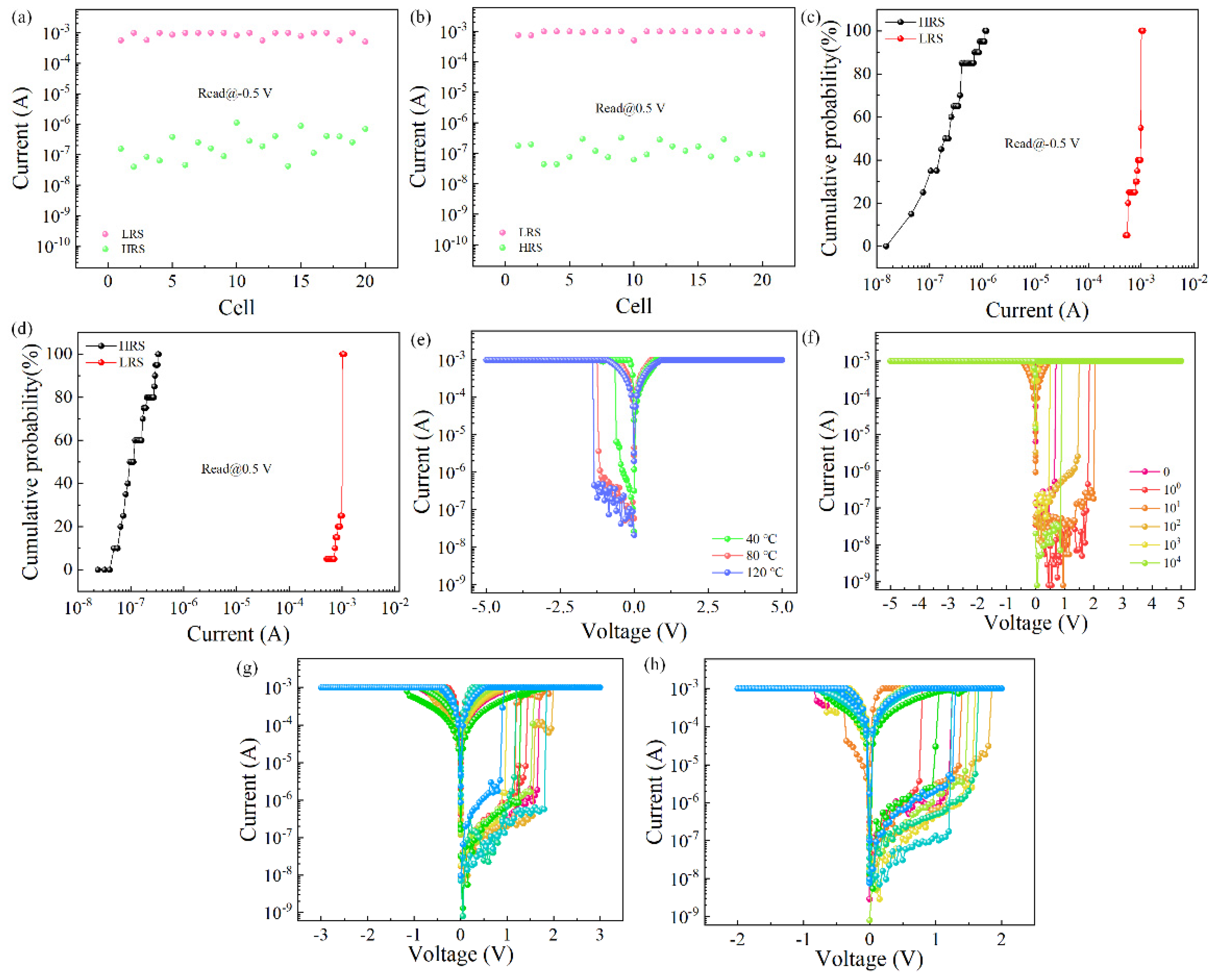
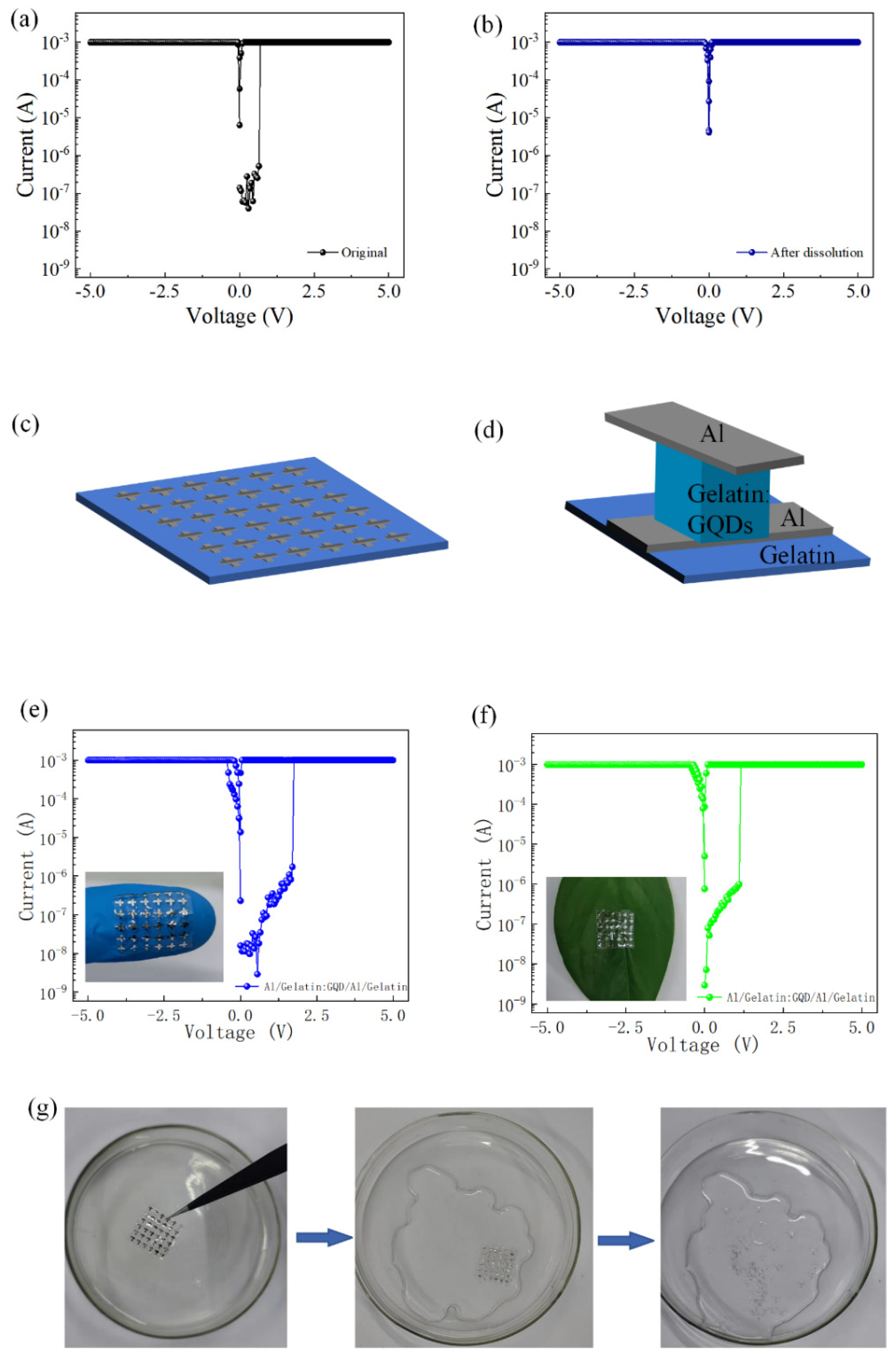
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, D.; Mukherjee, A. Biomaterial film for soluble organic sorption and anti-microbial activity in water environment. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Viventi, J.; Amsden, J.J.; Xiao, J.L.; Vigeland, L.; Kim, Y.S.; Blanco, J.A.; Panilaitis, B.; Frechette, E.S.; Contreras, D.; et al. Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Talukdar, B.; Bharali, R.; Rajkhowa, R.; Devi, D. Fabrication and characterization of biomaterial film from gland silk of muga and eri silkworms. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Lee, J.S. Controlling the Resistive Switching Behavior in Starch-Based Flexible Biomemristors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, C.H.; Woo, S.J.; Wu, C.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.W. Flexible bio-memristive devices based on chicken egg albumen: Au@SiO(2)core-shell nanoparticle nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Y.; Dugasani, S.R.; Raza, M.T.; Jeon, Y.R.; Park, S.H.; Choi, C. The observation of resistive switching characteristics using transparent and biocompatible Cu2+-doped salmon DNA composite thin film. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 335203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.L.; Dong, R.X. Organic memristive devices based on silver nanoparticles and DNA. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 3476–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.R.; Lee, J.S. Resistive Switching Memory Based on Bioinspired Natural Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Acs Nano 2015, 9, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.R.; Lee, J.S. Biocompatible and Flexible Chitosan-Based Resistive Switching Memory with Magnesium Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5586–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yu, H.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Chung, W.L.; Wu, S.L.; Su, Y.K. Nonvolatile Bio-Memristor Fabricated with Egg Albumen Film. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Sushko, M.R.A.; Qiu, W.; Yan, X.B.; Liu, X.Y. Silk Flexible Electronics: From Bombyx mori Silk Ag Nanoclusters Hybrid Materials to Mesoscopic Memristors and Synaptic Emulators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.Q.; Hao, S.L.; Hu, W.; Wang, M.; Zang, Z.G.; Zhu, L.N.; Du, J.; Tang, X.S. Human hair keratin for physically transient resistive switching memory devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Jian, J.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Young, S.J. A Green Strategy for Developing a Self-Healing Gelatin Resistive Memory Device. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5318–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H. Solution-processed Al-chelated gelatin for highly transparent non-volatile memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 123302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H. Resistive Switching Behavior in Gelatin Thin Films for Nonvolatile Memory Application. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5413–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.B.; Hu, F.; Sun, Y.L.; Wu, C.X.; Xu, H.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Construction of White-Light-Emitting Silk Protein Hybrid Films by Molecular Recognized Assembly among Hierarchical Structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5284–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.W.; Song, J.K.; Huang, X.; Cheng, H.Y.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, S.; Huang, Y.G.; Rogers, J.A. High-Performance Biodegradable/Transient Electronics on Biodegradable Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Q.; Zhao, X.N.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Hu, J.L.; Ma, J.G.; Liu, Y.C. Biodegradable Natural Pectin-Based Flexible Multilevel Resistive Switching Memory for Transient Electronics. Small 2019, 15, 1803970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominov, R.V.; Vakulov, Z.E.; Avilov, V.I.; Khakhulin, D.A.; Fedotov, A.A.; Zamburg, E.G.; Smirnov, V.A.; Ageev, O.A. Synthesis and Memristor Effect of a Forming-Free ZnO Nanocrystalline Films. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Hu, W.; Zeng, F.J.; Zhang, C.G.; Peng, Y.; Guo, Y.C. Ultrafast degradable resistive switching memory based on?—Lactose thin films. Org. Electron. 2020, 83, 105750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Hassan, B.; Liang, Y.; Ganesan, K.; Rajasekharan, R.; Evans, R.; Egan, G.; Kavehei, O.; Li, J.L.; Chana, G.; et al. A Silk Fibroin Bio-Transient Solution Processable Memristor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.P.; Tak, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Kim, H.J. Analysis of the Bipolar Resistive Switching Behavior of a Biocompatible Glucose Film for Resistive Random Access Memory. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Costa, V.; Makila, E.; Granroth, S.; Kukk, E.; Salonen, J. Synaptic and Fast Switching Memristance in Porous Silicon-Based Structures. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zrinski, I.; Loeefler, M.; Zavasnik, J.; Cancellieri, C.; Jeurgens, L.P.H.; Hassel, A.W.; Mardare, A.I. Impact of Electrolyte Incorporation in Anodized Niobium on Its Resistive Switching. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawa, A. Resistive switching in transition metal oxides. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Chang, M.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, C.J.; Seo, D.H.; Seo, S.; et al. A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5−x/TaO2−x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories-Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, C.; Kang, M.; Kim, S. Multi-Level Analog Resistive Switching Characteristics in Tri-Layer HfO2/Al2O3/HfO2 Based Memristor on ITO Electrode. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, K.; Otsus, M.; Kozlova, J.; Tarre, A.; Kasikov, A.; Rammula, R.; Link, J.; Stern, R.; Vinuesa, G.; Lendinez, J.M.; et al. Memory Effects in Nanolaminates of Hafnium and Iron Oxide Films Structured by Atomic Layer Deposition. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Song, L.; Zhong, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lim, K.G.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R. Biodegradable and Flexible Resistive Memory for Transient Electronics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 16909–16915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.S.; Yan, X. Colloidal Graphene Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Qiao, C.Y.; Tang, S.J.; Li, Y.F.; Yuan, W.J.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Wu, G.H.; Yang, G.H.; Peng, J.; Zhao, J.W.; Zhu, J.J. Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: Current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4015–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, N.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Wu, C.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Chen, I.W.P. One-Pot Synthesis of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots via Exfoliating and Disintegrating Graphite Flakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Wu, C.; Bok, C.H.; Kim, T.W. Organic electronic synapses with pinched hystereses based on graphene quantum-dot nanocomposites. Npg Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, T.; Bai, L.; Kang, Z.H.; Wang, C.H.; Zhao, X.N.; Xu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.C. Photoreduced nanocomposites of graphene oxide/N-doped carbon dots toward all-carbon memristive synapses. Npg Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Input | Output | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Opt. | Ele. | Current (A) | Logic |
| 0 | 0 | 1.06 × 10−6 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 7.28 × 10−4 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wen, D. Physical Transient Photoresistive Variable Memory Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223976
Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Wen D. Physical Transient Photoresistive Variable Memory Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(22):3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223976
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Yukai Zhang, Peng Zhang, and Dianzhong Wen. 2022. "Physical Transient Photoresistive Variable Memory Based on Graphene Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 12, no. 22: 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223976
APA StyleWang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, P., & Wen, D. (2022). Physical Transient Photoresistive Variable Memory Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 12(22), 3976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12223976






