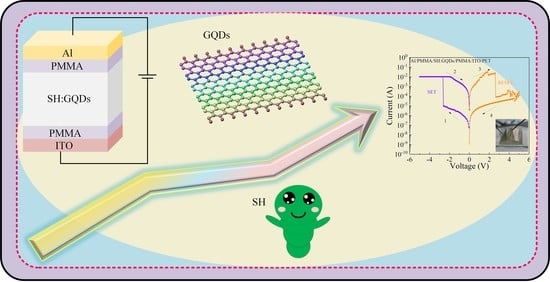
Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Device Fabrication
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Xuan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Smith, C.G.; Luo, J. Transient Resistive Switching Devices Made from Egg Albumen Dielectrics and Dissolvable Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10954–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgunde, B.K.; Rabinal, M.K. Solution processed bilayer junction of silk fibroin and semiconductor quantum dots as multilevel memristor devices. Org. Electron. 2017, 48, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Elshekh, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Hou, W.; Zhao, Y. The pH-controlled memristive effect in a sustainable bioelectronic device prepared using lotus root. Mater. Today Sustain. 2020, 7–8, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; Dugasani, S.R.; Raza, M.T.; Jeon, Y.R.; Park, S.H.; Choi, C. The observation of resistive switching characteristics using transparent and biocompatible Cu2+-doped salmon DNA composite thin film. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 335203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Sun, B.; Fu, G.; Li, T.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, L.; Mao, S.; Kan, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y. A nonvolatile organic resistive switching memory based on lotus leaves. Chem. Phys. 2019, 516, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, W. From natural biomaterials to environmentally friendly and sustainable nonvolatile memory device. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, M.; Guerrini, A.; Ballestri, M.; Aluigi, A.; Zamboni, R.; Sotgiu, G.; Posati, T. Bioactive Keratin and Fibroin Nanoparticles: An Overview of Their Preparation Strategies. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Lan, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, S.; Stegmann, A.E.; Yu, R.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.Y. Flexible and Insoluble Artificial Synapses Based on Chemical Cross-Linked Wool Keratin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Sushko, M.L.; Qiu, W.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.Y. Silk Flexible Electronics: From Bombyx mori Silk Ag Nanoclusters Hybrid Materials to Mesoscopic Memristors and Synaptic Emulators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, C.; Hota, M.K.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. Resistive switching in natural silk fibroin protein-based biomemristors. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2013, 210, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, M.K.; Bera, M.K.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. A Natural Silk Fibroin Protein-Based Transparent Bio-Memristor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, J.S. Artificial Synapses with Short- and Long-Term Memory for Spiking Neural Networks Based on Renewable Materials. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8962–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Cheong, K.Y. Effects of drying temperature and ethanol concentration on bipolar switching characteristics of natural Aloe vera-based memory devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 26833–26853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Sreenivasan, S.; Wong, Y.H.; Zhao, F.; Cheong, K.Y. Effects of Electrode Materials on Charge Conduction Mechanisms of Memory Device Based on Natural Aloe Vera. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.Y.; Cho, W.J. High-Performance Resistive Switching in Solution-Derived IGZO: N Memristors by Microwave-Assisted Nitridation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoman, M.; Aldrigo, M.; Dragoman, D. Perspectives on Atomic-Scale Switches for High-Frequency Applications Based on Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tan, L.; Sun, B.; Lei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Memristive effect with nonzero-crossing current-voltage hysteresis behavior based on Ag doped Lophatherum gracile Brongn. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogurla, N.; Mondal, S.P.; Sinha, A.K.; Katiyar, A.K.; Banerjee, W.; Kundu, S.C.; Ray, S.K. Transparent and flexible resistive switching memory devices with a very high ON/OFF ratio using gold nanoparticles embedded in a silk protein matrix. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 345202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Lee, J.-S. Controlling the Resistive Switching Behavior in Starch-Based Flexible Biomemristors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Sun, F.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Hao, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Bioinspired flexible artificial synapses for pain perception and nerve injuries. Npj Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yarimaga, O.; Choi, S.-J.; Choi, Y.-K. Highly durable and flexible memory based on resistance switching. Solid·State Electron. 2010, 54, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.; Bocchini, S.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Perrone, D.; Bejtka, K.; Ricciardi, C.; Pirri, C.F.; Chiolerio, A. Spin-coated silver nanocomposite resistive switching devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 168, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Jang, J.; Park, S.; Ji, G.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-B.; Yoon, K.-H.; Chung, C.-M.; Cho, S. Flexible and transparent electrode based on Ag-nanowire embedded colorless poly (amide-imide). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Tay, R.Y.; Nguyen, V.C.; Wang, J.; Cai, G.; Chen, T.; Teo, E.H.T.; Lee, P.S. Hexagonal Boron Nitride Thin Film for Flexible Resistive Memory Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.-S. Flexible Artificial Synaptic Devices Based on Collagen from Fish Protein with Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Rho, J. Solution-Processed Flexible Biomemristor Based on Gold-Decorated Chitosan. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5445–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wen, D. Nonvolatile Bio-Memristor Based on Silkworm Hemolymph Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X. Enhanced memory characteristics of charge trapping memory by employing graphene oxide quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J. Highly improved performance in Zr0.5Hf0.5O2 films inserted with graphene oxide quantum dots layer for resistive switching nonvolatile memory. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11046–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Large magnetization modulation in ZnO-based memory devices with embedded graphene quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 16047–16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-rectifying resistive switching and short-term memory characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN artificial synaptic device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Meng, F.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Sericin for resistance switching device with multilevel nonvolatile memory. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5498–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Baeg, K.-J.; Khim, D.; Noh, Y.-Y.; Kim, D.-Y. Printed, Flexible, Organic Nano-Floating-Gate Memory: Effects of Metal Nanoparticles and Blocking Dielectrics on Memory Characteristics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3503–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Wen, D. Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
Wang L, Yang J, Zhu H, Li W, Wen D. Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Jing Yang, Hongyu Zhu, Wenhao Li, and Dianzhong Wen. 2022. "Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
APA StyleWang, L., Yang, J., Zhu, H., Li, W., & Wen, D. (2022). Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709