Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Nano-Antibiotics against Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Bacterial Isolates
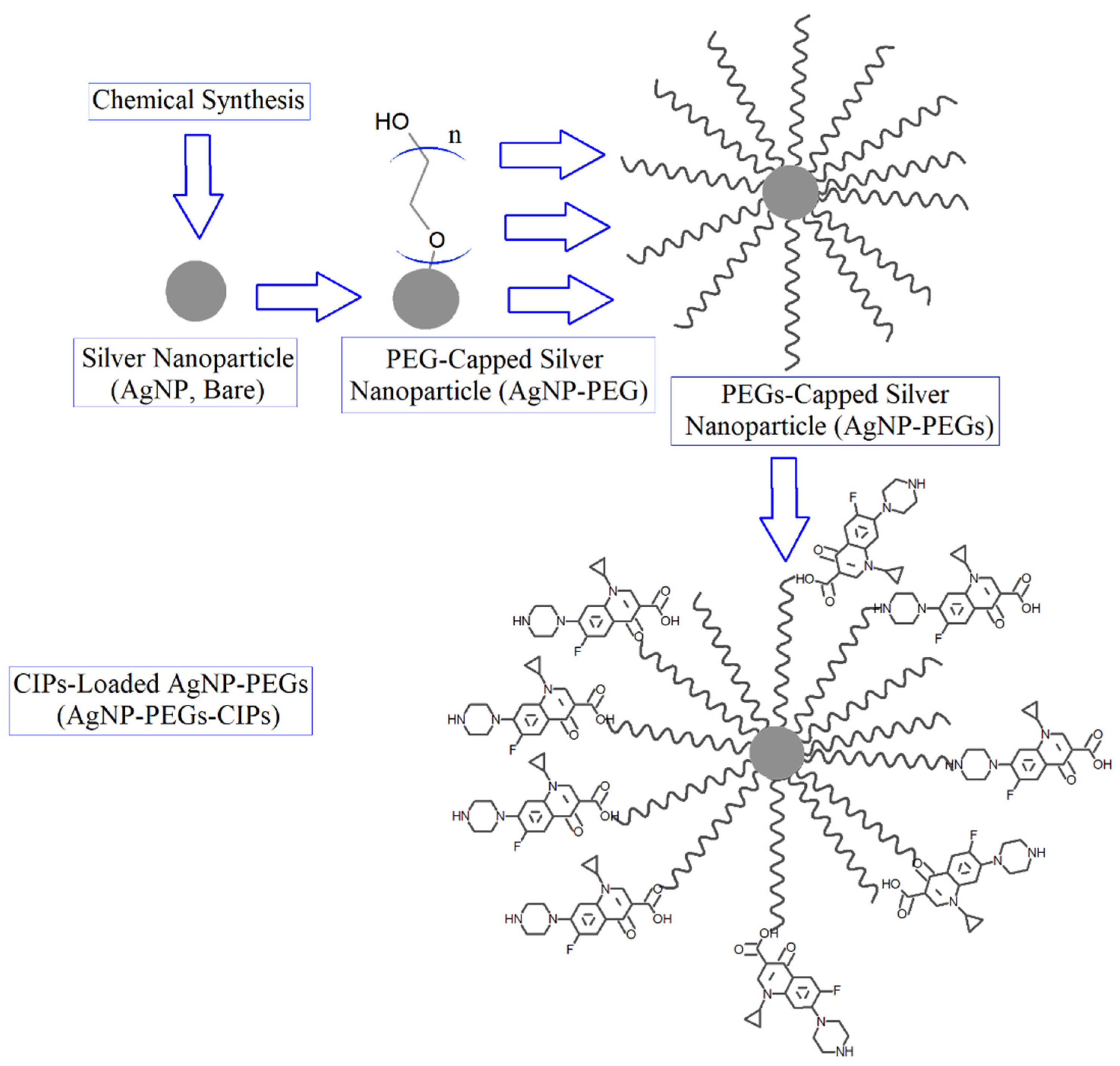
2.3. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Combinations
2.3.1. Synthesis of Bare AgNPs and Coated AgNPs-PEG
2.3.2. Preparation of AgNPs-CIP and AgNPs-PEG-CIP
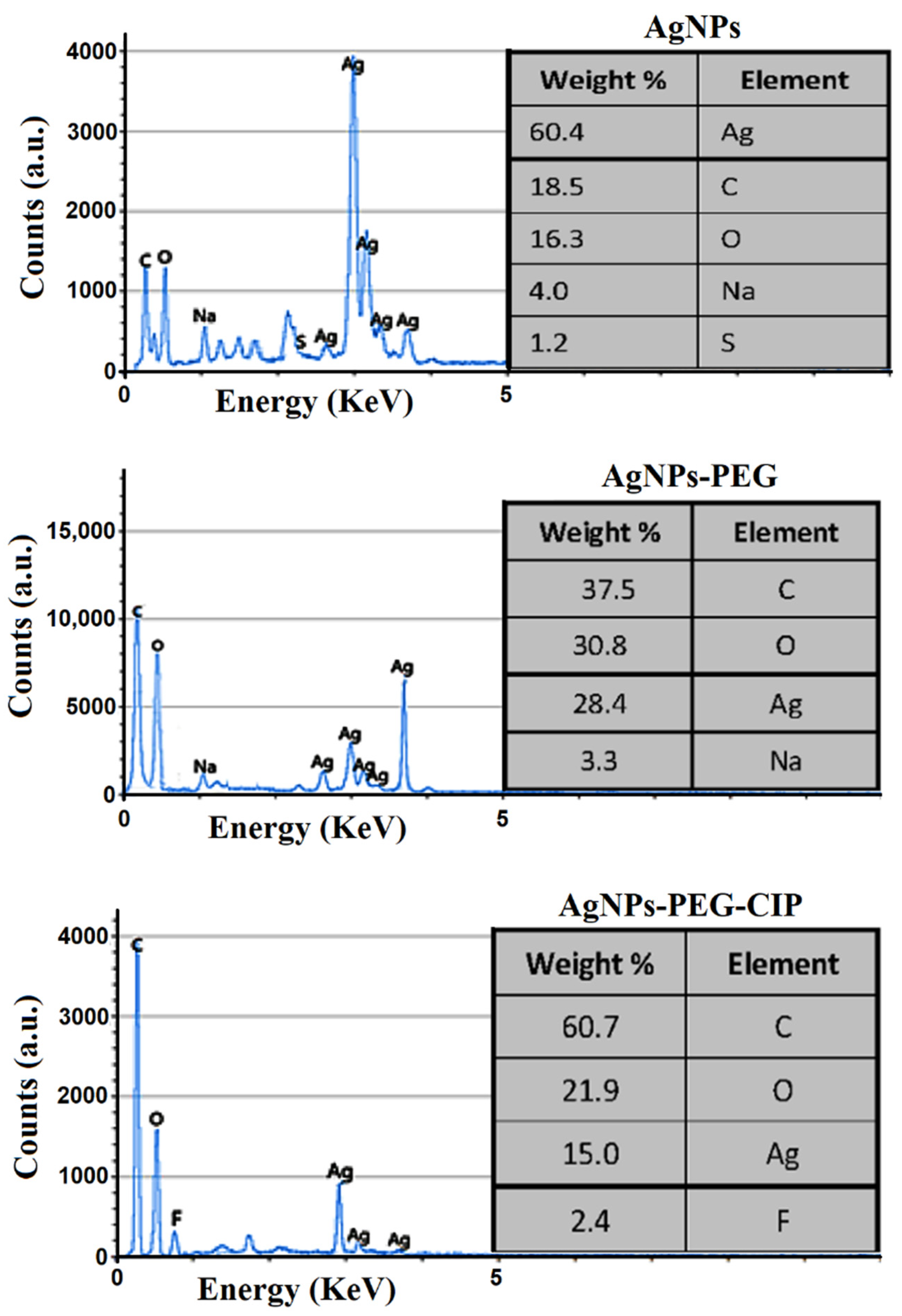
2.4. Characterization of AgNPs and Their Conjugates
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
2.7. Antibiofilm Effect
2.8. Determination of MIC and MBC
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
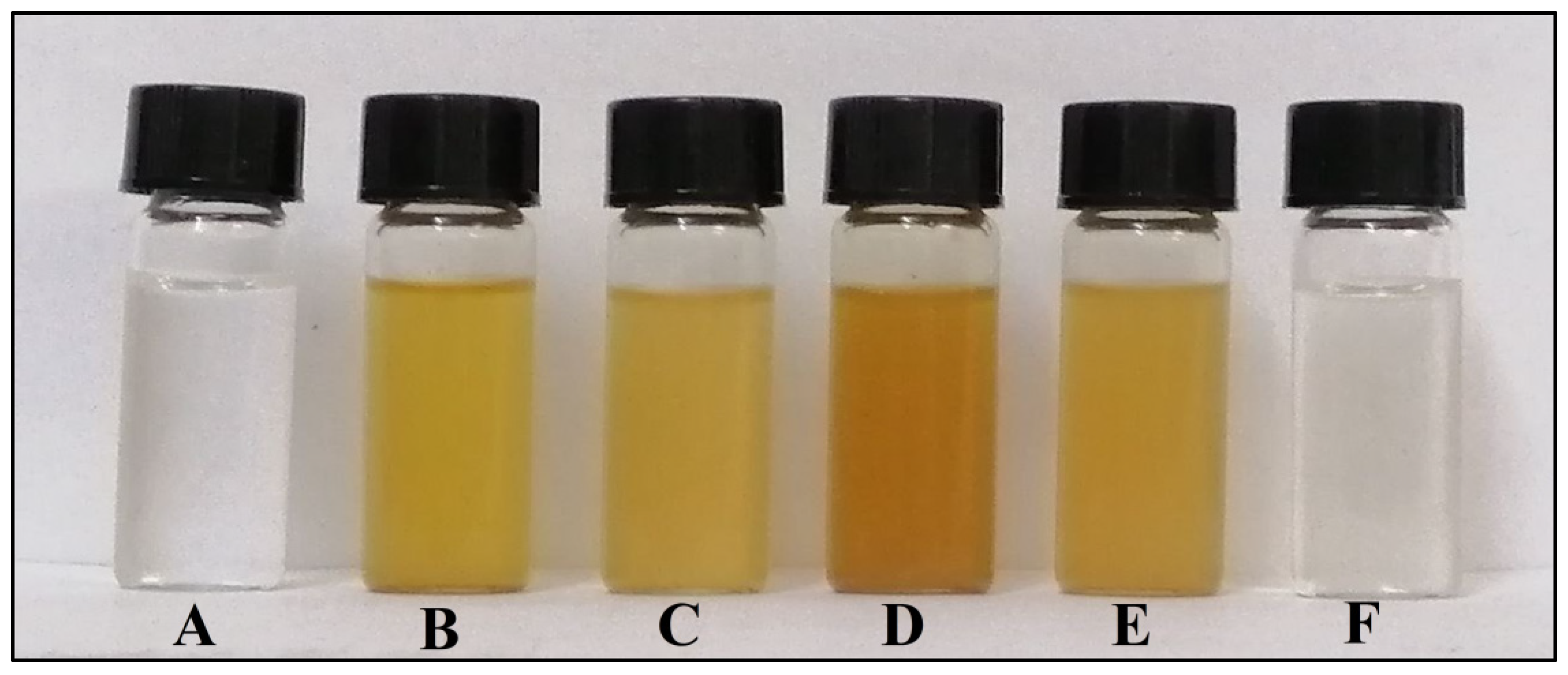
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AgNPs, AgNPs-PEG, AgNPs-CIP, and AgNPs-PEG-CIP
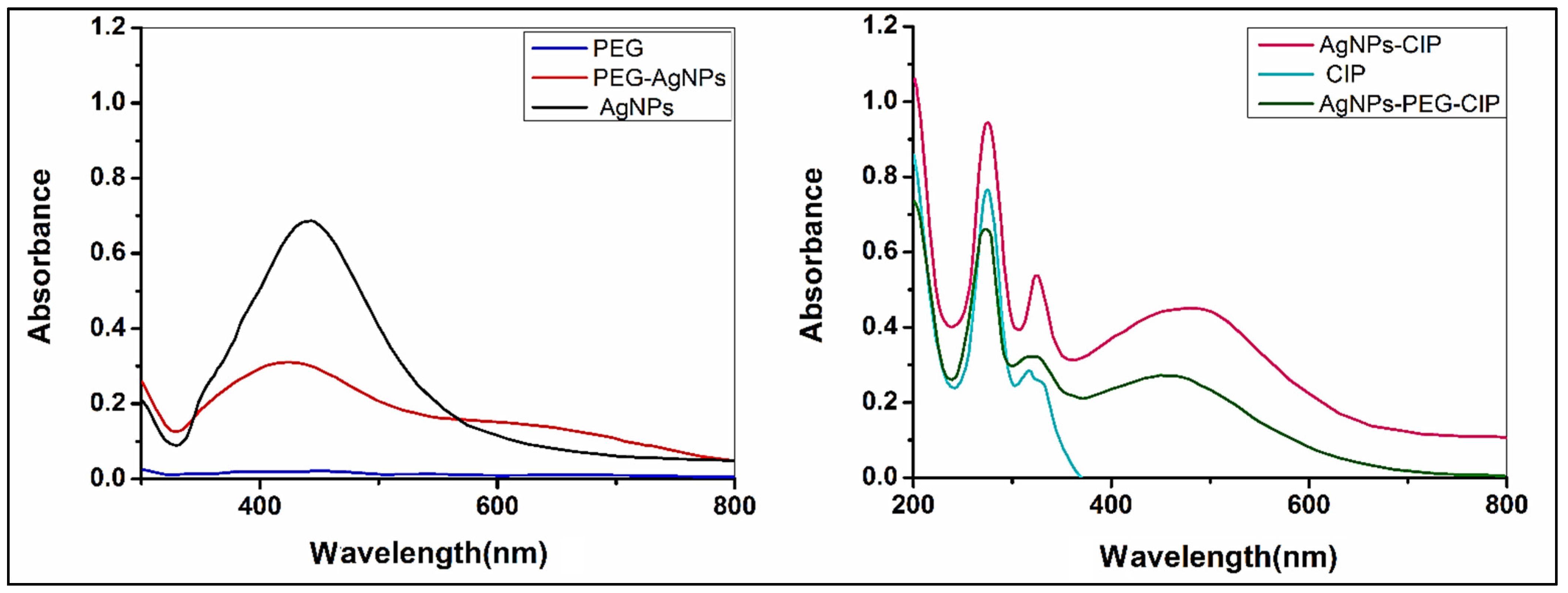
3.1.1. Characterization by UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
3.1.2. FT-IR Analysis
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
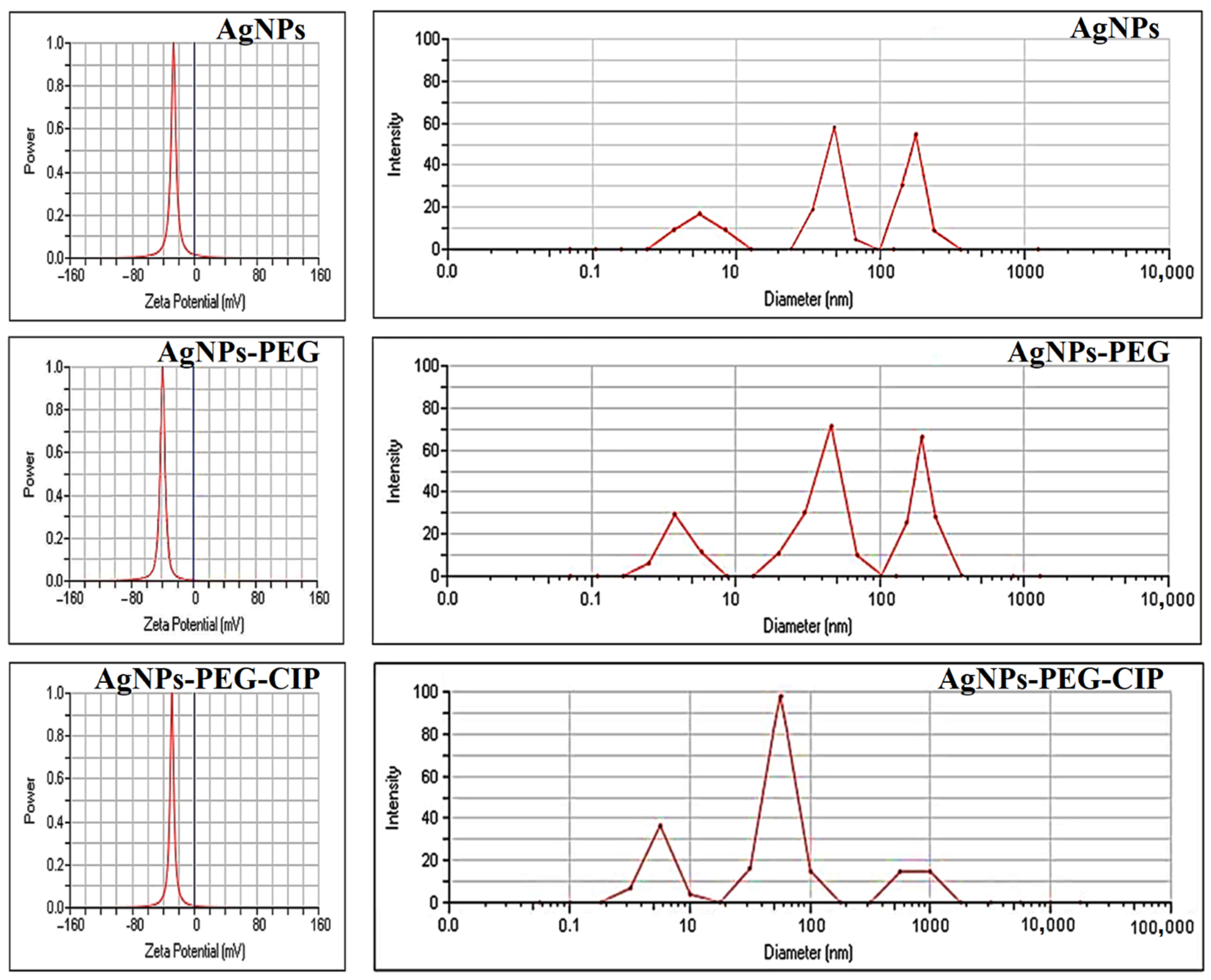
3.1.4. Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
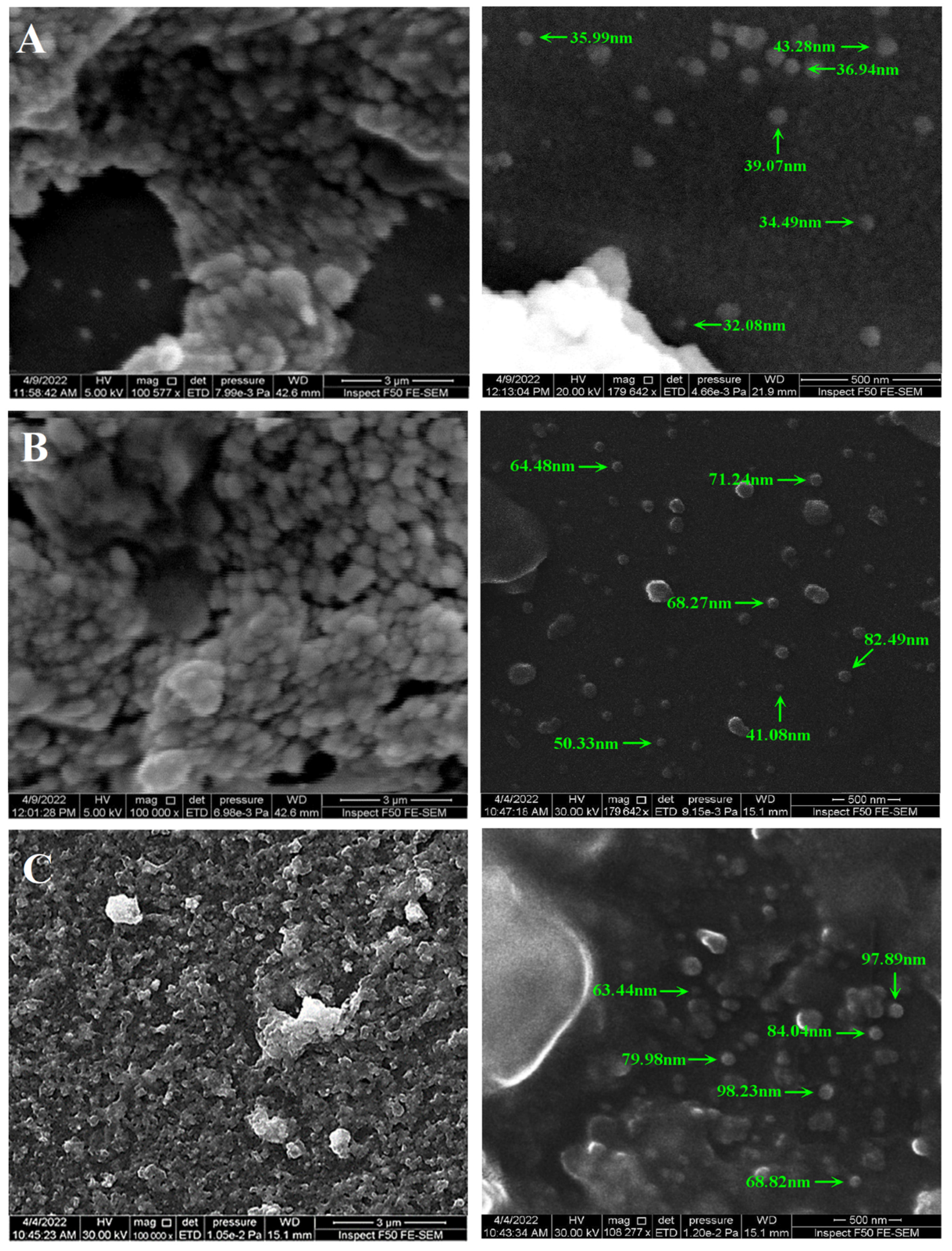
3.1.5. FE-SEM Analysis
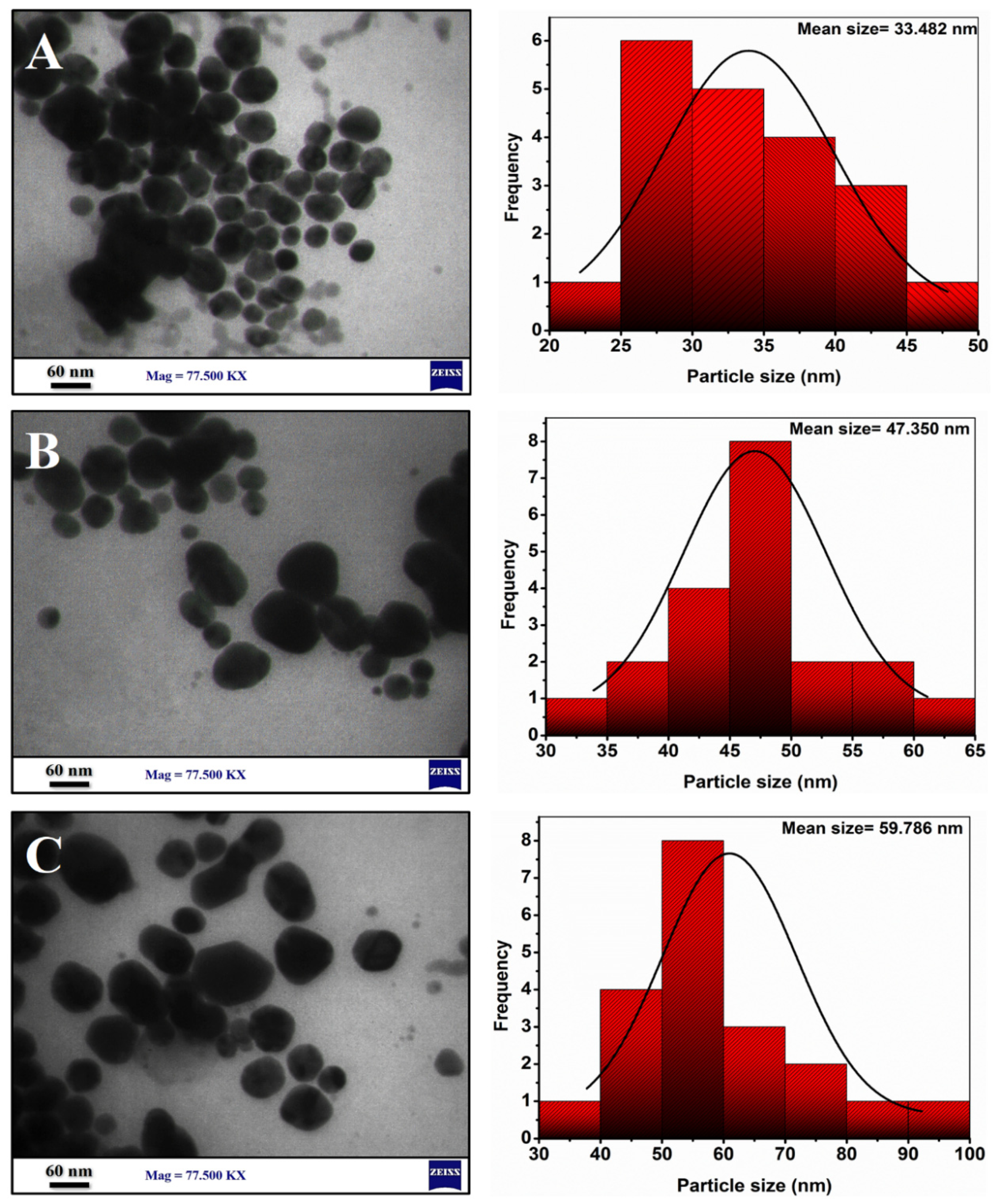
3.1.6. TEM Analysis
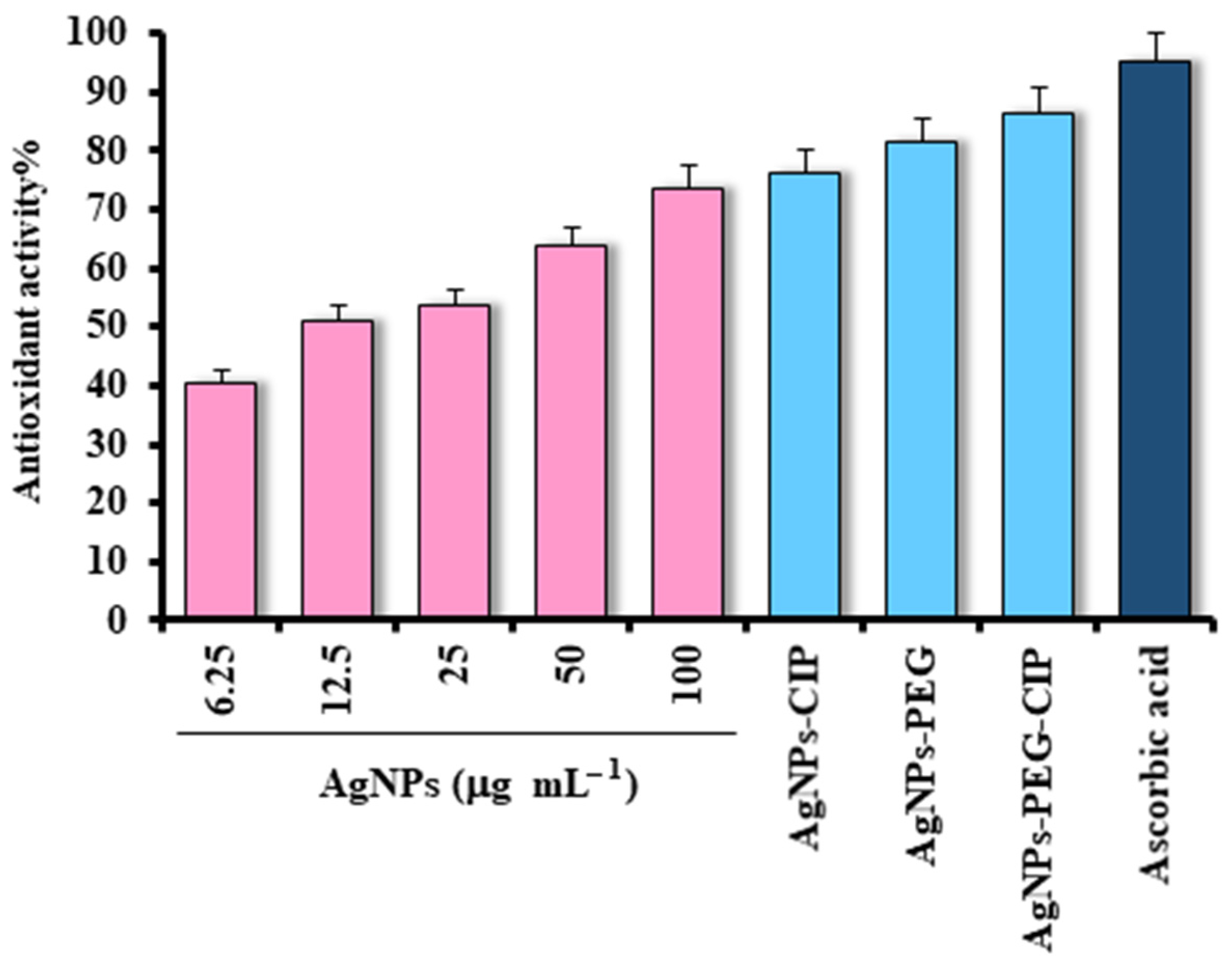
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
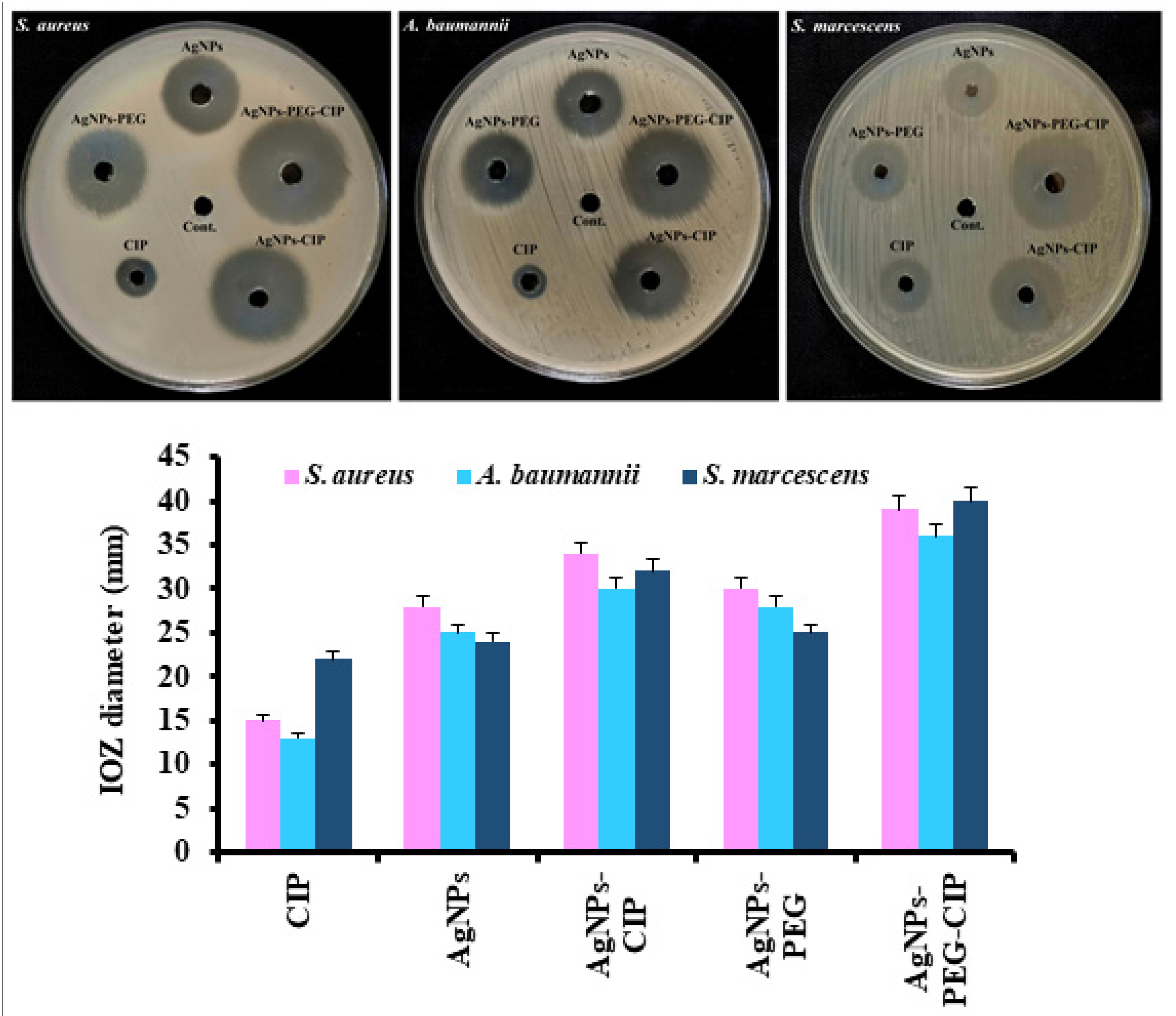
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
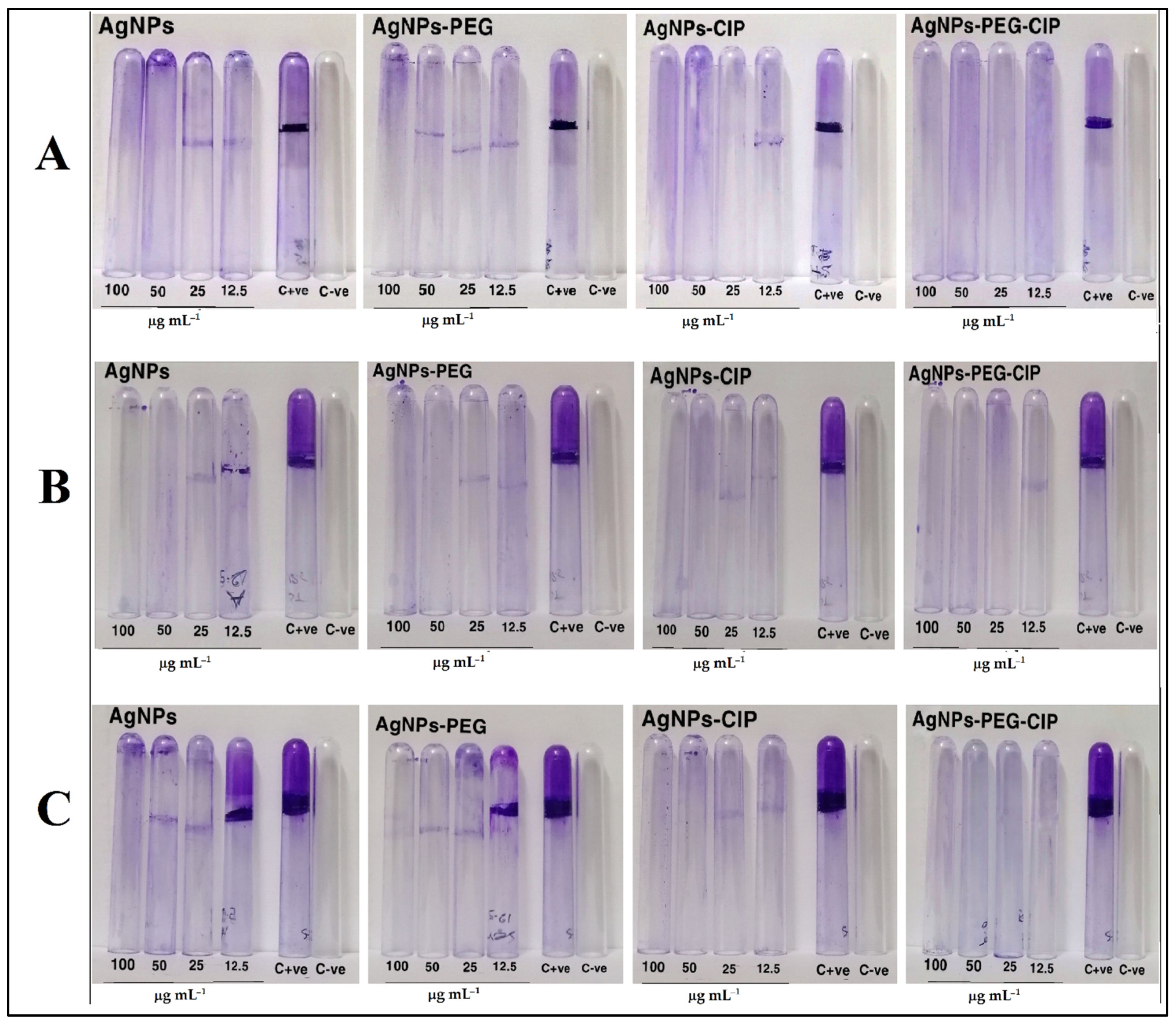
3.4. Antibiofilm Activity
3.5. Determination of MIC and MBC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver Nanoparticles |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| CV | Crystal Violet Stain |
| DPPH | 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl |
| MBC | Minimum Bactericidal Concentration |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffer Saline |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| TSB | Tryptic Soy Broth |
References
- Banin, E.; Hughes, D.; Kuipers, O.P. Bacterial pathogens, antibiotics and antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Patel, S.; Pargaien, K.C. Synthesis, characterization and properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Preet, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R. Synergetic effect of vancomycin-loaded silver nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; McShan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sinha, S.S.; Arslan, Z.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanistic study of the synergistic antibacterial activity of combined silver nanoparticles and common antibiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8840–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisida, S.O.; Ugwu, K.; Akpa, P.A.; Nwanya, A.C.; Nwankwo, U.; Botha, S.S.; Ezema, F.I. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using bitter leave (Veronica amygdalina) for antibacterial activities. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 17, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsova, T.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Donchak, V.; Harhay, K.; Korolko, S.; Budkowski, A.; Stetsyshyn, Y. Temperature-responsive hybrid nanomaterials based on modified halloysite nanotubes uploaded with silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 641, 128525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Jishma, P.; Snigdha, S.; Soumya, K.R.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Enhanced antimicrobial efficacy of biosynthesized silver nanoparticle-based antibiotic conjugates. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 117, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, D. Antioxidants and cardiovascular risk factors. Diseases 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Nayak, D.; Biswas, K.; Singdevsachan, S.K.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Hashem, A.; Mohanta, T.K. Silver nanoparticles synthesized using wild mushroom show potential antimicrobial activities against food borne pathogens. Molecules 2018, 23, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: A critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials 2013, 6, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, N.; Sadaf, M.; Salomi, A.; Daniel, E.C. Cytotoxicity of functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles coated with rifampicin and tetracycline hydrochloride on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbara, W.K.; Ramadan, W.H.; Rahbany, P.; Al-Natour, S. Evaluation of the appropriate use of commonly prescribed fluoroquinolones and the risk of dysglycemia. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvanian, M.; Tan, C.K.; Ng, S.F. Simvastatin-loaded lyophilized wafers as a potential dressing for chronic wounds. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giguère, S.; Dowling, P.M. Fluoroquinolones. In Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.Z.H.; Kiran, U.; Ali, M.I.; Jamal, A.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, N. Combined efficacy of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles and different antibiotics against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Huang, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Recent advances and progress on melanin-like materials and their biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskov, A.N.; Kulikov, P.P.; Goryachaya, A.V.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Docea, A.O.; Velonia, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Amphiphilic poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles as carriers for non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs: In vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo acute toxicity study. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Meda, V.; Zhang, W.J.; Farhan, K.M.; Gnanamani, A. Synthesis, characterization and comparison of antimicrobial activity of PEG/TritonX-100 capped silver nanoparticles on collagen scaffold. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckiewicz, K.P.; Cieciórski, P.; Barcińska, E.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Narajczyk, M.; Bauer, M.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Silver nanoparticles as chlorhexidine and metronidazole drug delivery platforms: Their potential use in treating periodontitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzaru, I.; Coricovac, D.; Dehelean, C.; Moacă, E.A.; Mioc, M.; Baderca, F.; Şoica, C. Stable PEG-coated silver nanoparticles—A comprehensive toxicological profile. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, N.; Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Masoud, M.S.; Ali, I.; Hasan, A. Silver nanoparticle impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel enhances wound healing in diabetes induced rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, E.; El-Borady, O.M.; Mohamed, M.B.; Fahim, I.S. Synthesis and characterization of ciprofloxacin-loaded silver nanoparticles and investigation of their antibacterial effect. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2020, 13, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khane, Y.; Benouis, K.; Albukhaty, S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Al Ali, A.; Aouf, D.; Fenniche, F.; Khane, S.; Chaibi, W.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous Citrus limon zest extract: Characterization and evaluation of their antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawar, S.N.; Al-Shmgani, H.S.; Al-Kubaisi, Z.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Dewir, Y.H.; Rikisahedew, J.J. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Alhagi graecorum leaf extract and evaluation of their cytotoxicity and antifungal activity. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1058119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, N. Comparison of tissue culture plate method, tube method and Congo-red agar method for the detection of biofilm formation by coagulase negative Staphylococcus isolated from non-clinical isolates. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, N.N.; Muslim, A.H. Detection of the antibacterial activity of AgNPs biosynthesized by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 50, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, S.; Agarwala, A.; Shrivastava, V.; Shrivastava, R. Poly (ethylene glycol)-400 crowned silver nanoparticles: A rapid, efficient, selective, colorimetric nano-sensor for fluoride sensing in an aqueous medium. J. Chem. Sci. 2022, 134, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, W.R.; Pieretti, J.C.; Renó, D.L.; Lima, B.A.; Nascimento, M.H.; Ambrosio, F.N.; Seabra, A.B. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity to tumor cells of nitric oxide donor and silver nanoparticles containing PVA/PEG films for topical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6589–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, H.; Culha, M. A Drug Stability Study Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering on Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laponogov, I.; Sohi, M.K.; Veselkov, D.A.; Pan, X.S.; Sawhney, R.; Thompson, A.W.; McAuley, K.E.; Fisher, L.M.; Sanderson, M.R. Structural insight into the quinolone-DNA cleavage complex of type IIA topoisomerases. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal Roy, S.; Sharma, B.K.; Roy, D.R. Synthesis of ciprofloxacin drug capped silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity: A joint spectrophotometric and density functional investigation. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawani, E.M.; Hassan, A.M.; El-Rab, S.M.G. Nanoformulation of biogenic cefotaxime-conjugated-silver nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria and anticancer studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzamil, M.; Khalid, N.; Aziz, M.D.; Abbas, S.A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by silver salt reduction and its characterization. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 60, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadkasim, A.S.; Ariff, A.B.; Mohamad, R.; Wong, F.W.F. Interrelations of synthesis method, polyethylene glycol coating, physico-chemical characteristics, and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiuddin, M.; Saha, P.; Ochiai, B. Green synthesis and catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles based on Piper chaba stem extracts. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; Abudoleh, S.M.; Abualassal, Q.I.A.; Abudayeh, Z.; Aldalahmah, Y.; Hussein, M.Z. Preparation and characterisation of ciprofloxacin-loaded silver nanoparticles for drug delivery. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Peterka, F.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, X. Synthesis and comparative biological properties of Ag-PEG nanoparticles with tunable morphologies from janus to multi-core shell structure. Materials 2018, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Mohammad, A.A.; Abdul-Wahed, H.E.; Ismail, M.M. Biosynthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles using Rosmarinus officinalis extract. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2013, 8, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Alturki, H.N.; Tawfeek, H.M. Different cellulosic polymers for synthesizing silver nanoparticles with antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derman, S. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Effect of various process parameters on reaction yield, encapsulation efficiency, and particle size. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 341848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepu, S.; Khandelwal, M. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of bacterial cellulose silver nanocomposites with sustained release. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1596–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paosen, S.; Saising, J.; Septama, A.W.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plants from Myrtaceae family and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.; Tai, J.T.; Wang, H.F.; Ho, R.M.; Hsiao, T.C.; Tsai, D.H. Surface PEGylation of silver nanoparticles: Kinetics of simultaneous surface dissolution and molecular desorption. Langmuir 2016, 32, 9807–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfeek, H.M.; Abdellatif, A.A.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A.; Hassan, Y.A.; Fathalla, D. Transfersomal gel nanocarriers for enhancement the permeation of lornoxicam. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissan, H.; Ristig, S.; Kaminski, H.; Asbach, C.; Epple, M. Comparison of different characterization methods for nanoparticle dispersions before and after aerosolization. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7324–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, S.H.; Adi, W.A. Synthesis and characterization of high purity Fe3O4 and α-Fe2O3 from local iron sand. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1091, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y. The role of poly(ethylene) glycol in the formation of silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokerst, J.V.; Lobovkina, T.; Zare, R.N.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanoparticle PEGylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sushma, V.; Patra, S.; Barui, A.K.; Bhadra, M.P.; Sreedhar, B.; Patra, C.R. Green chemistry approach for the synthesis and stabilization of biocompatible gold nanoparticles and their potential applications in cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 455103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jubori, A.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Tawfeeq, A.T.; Mohammed, H.A.; Khan, R.A.; Mohammed, S.A. Layer-by-layer nanoparticles of tamoxifen and resveratrol for dual drug delivery system and potential triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligiannakis, Y.; Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antioxidant and antiradical SiO2 nanoparticles covalently functionalized with gallic acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6609–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasson, B.A.; Mahdi, L.H.; Essa, R.H. Evidence of antioxidant activity of novel L-glutaminase purified from L. gasseri BRLHM. J. Appl. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 1, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala, R.; Arunachalam, P.; Sivasankari, M. Synergistic bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles and ciprofloxacin against phytopathogens. J. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 12, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikparast, Y.; Saliani, M. Synergistic effect between phyto-syntesized silver nanoparticles and ciprofloxacin antibiotic on some pathogenic bacterial strains. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2018, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Wei, D.X.; Ye, H.M.; Zhang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Development of poly (vinyl alcohol) porous scaffold with high strength and well ciprofloxacin release efficiency. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.K.; Hawar, S.N.; Sulaiman, G.M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Penicillium italicum and its antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity activities. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Nawaz, M.; Hussain, R.; Price, G.J.; Warsi, M.F.; Waseem, M. Enhanced antibacterial activity of size-controlled silver and polyethylene glycol functionalized silver nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Prior, R.L. The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, J.J.; Neveling, D.P.; Hattingh, M.; Dicks, L.M. Ciprofloxacin-eluting nanofibers inhibits biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Allori, M.C.G.; Jure, M.A.; Romero, C.; and de Castillo, M.E.C. Antimicrobial resistance and production of biofilms in clinical isolates of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus strains. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


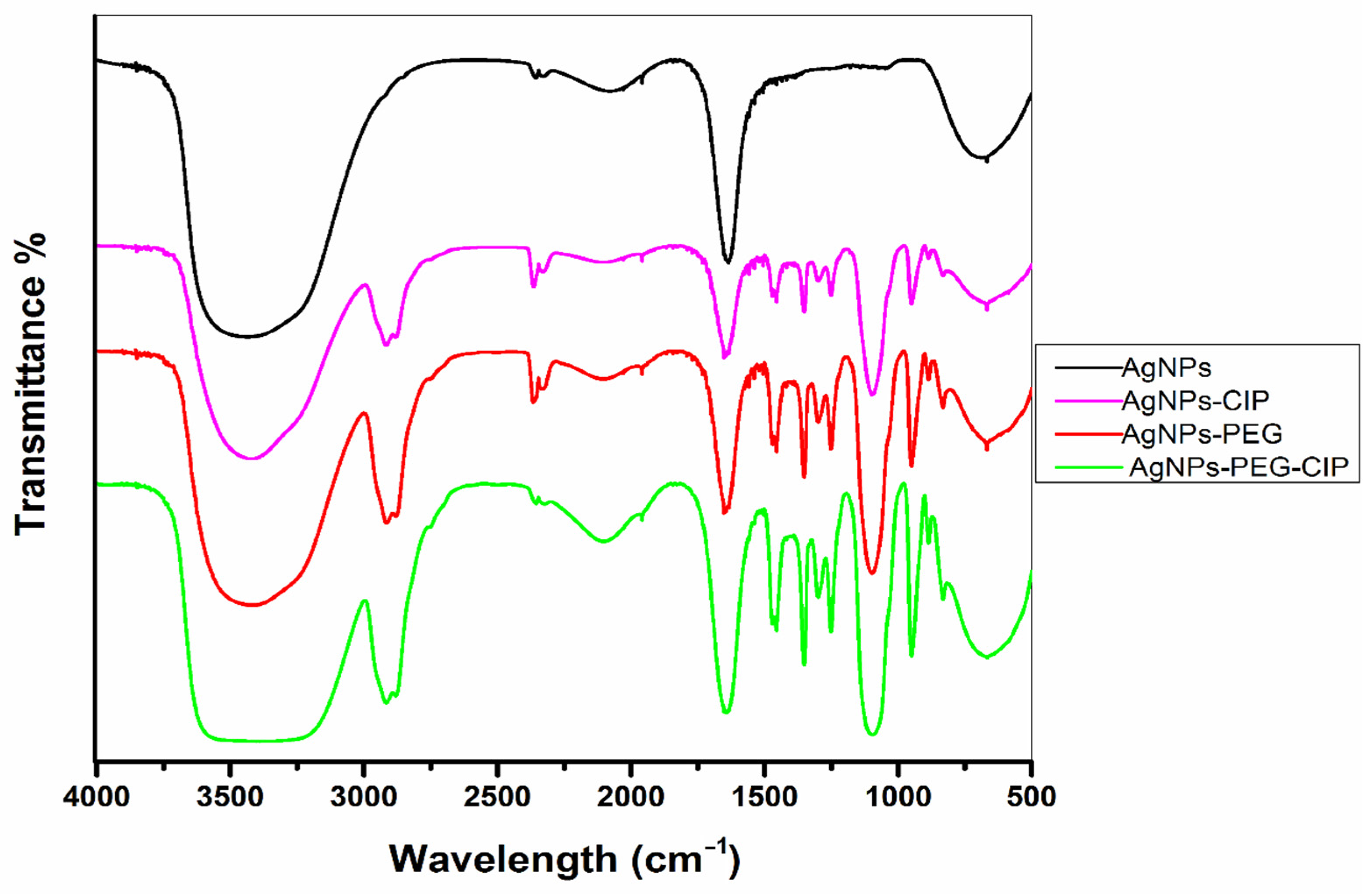


| Bonding Types | Functional Groups | Products and Wavelengths (cm−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | AgNPs-PEG | AgNPs-CIP | AgNPs-PEG-CIP | ||
| O-H | Hydroxyl | 3455.56 | 3428.65 | 3434.62 | 3413.61 |
| C-H | Aryl | - | - | 2919.39 | 2914.81 |
| C=O | Carbonyl | 1635.80 | 1634.21 | 1635.59 | 1634.15 |
| N-H | Amine | 1046.57 | 1096.94 | 1094.57 | 1098.04 |
| C=C | Alkene | 667.44 | 667.27 | 667.56 | 667.37 |
| Bacteria | Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles (μg mL−1) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | AgNPs-PEG | AgNPs-CIP | AgNPs-PEG-CIP | |||||||||||||
| 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 | |
| S. aureus | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| A. baumannii | ++ | + | − | − | ++ | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| S. marcescens | +++ | ++ | + | − | +++ | ++ | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibraheem, D.R.; Hussein, N.N.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Khan, R.A.; Al Rugaie, O. Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Nano-Antibiotics against Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162808
Ibraheem DR, Hussein NN, Sulaiman GM, Mohammed HA, Khan RA, Al Rugaie O. Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Nano-Antibiotics against Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162808
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbraheem, Duaa R., Nehia N. Hussein, Ghassan M. Sulaiman, Hamdoon A. Mohammed, Riaz A. Khan, and Osamah Al Rugaie. 2022. "Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Nano-Antibiotics against Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162808
APA StyleIbraheem, D. R., Hussein, N. N., Sulaiman, G. M., Mohammed, H. A., Khan, R. A., & Al Rugaie, O. (2022). Ciprofloxacin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Nano-Antibiotics against Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162808








