A Durable Magnetic Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge: For Solving Complex Marine Oil Spills
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
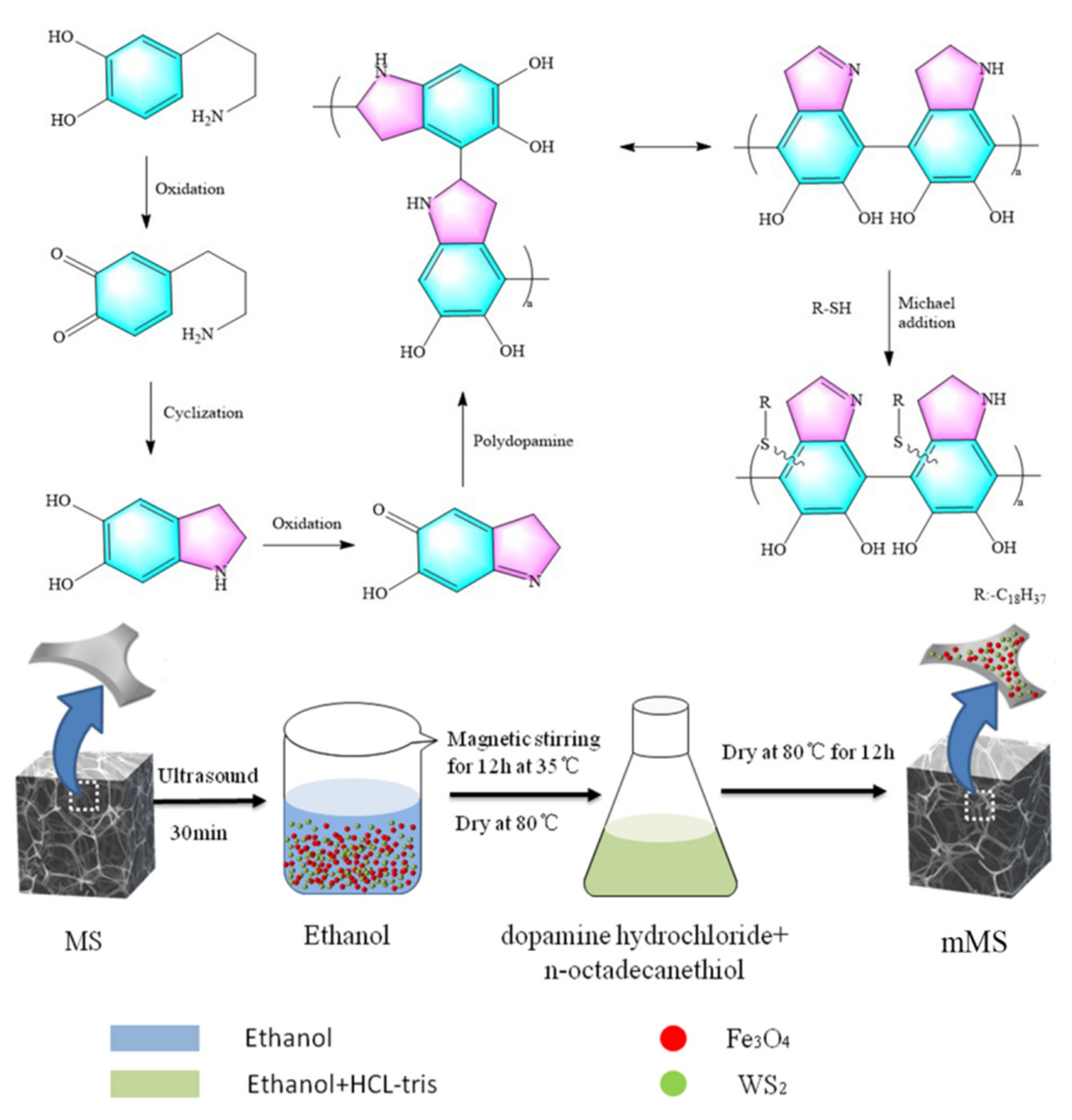
2.2. Preparation of mMS
2.3. Contact Angle Test
2.4. Oil Adsorption and Recycling Performance Test
2.5. Oil–Water Separation Performance Test
2.6. Stability and Durability Test
2.7. Magnetic Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Characterization Analysis
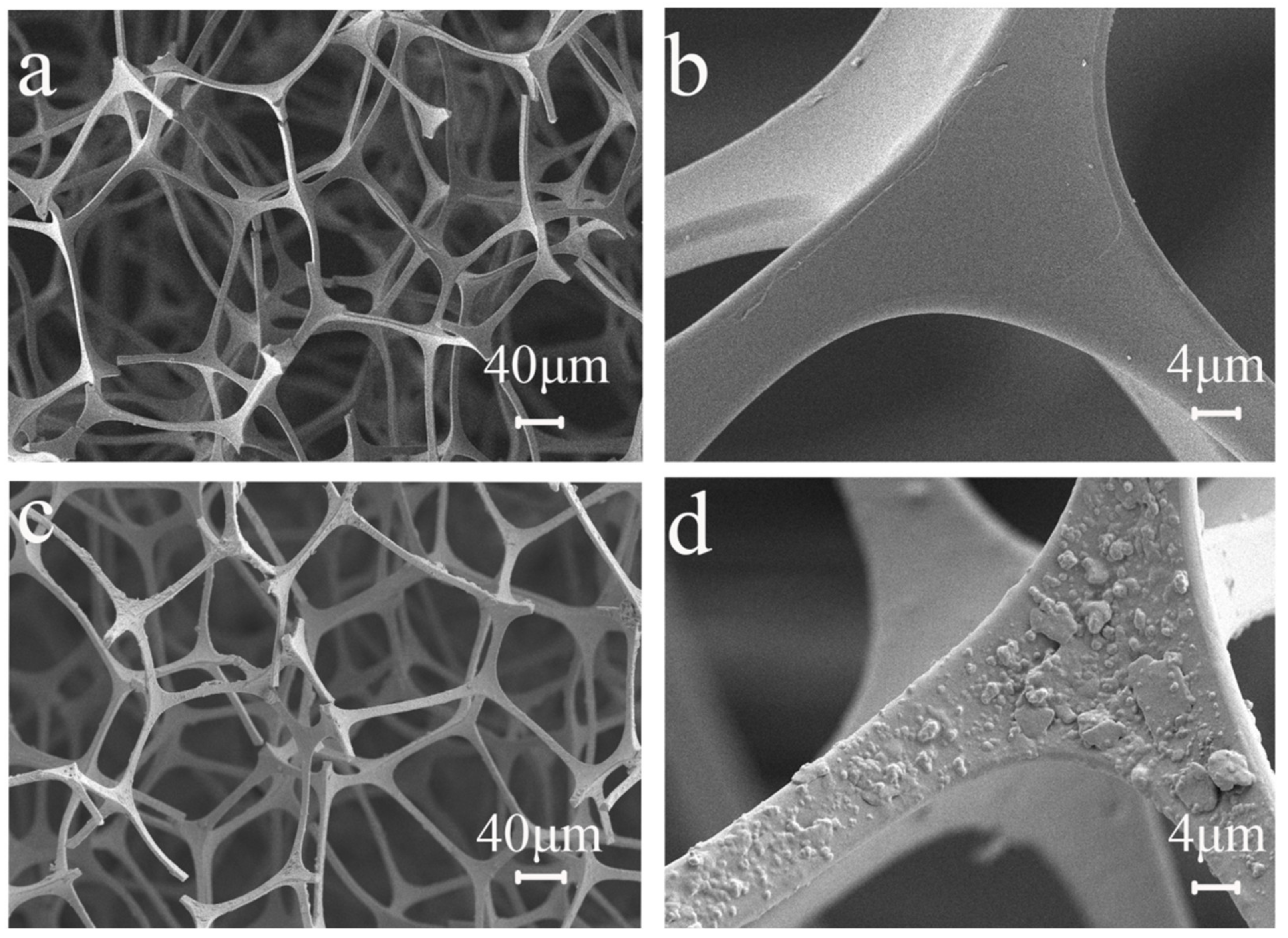
3.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
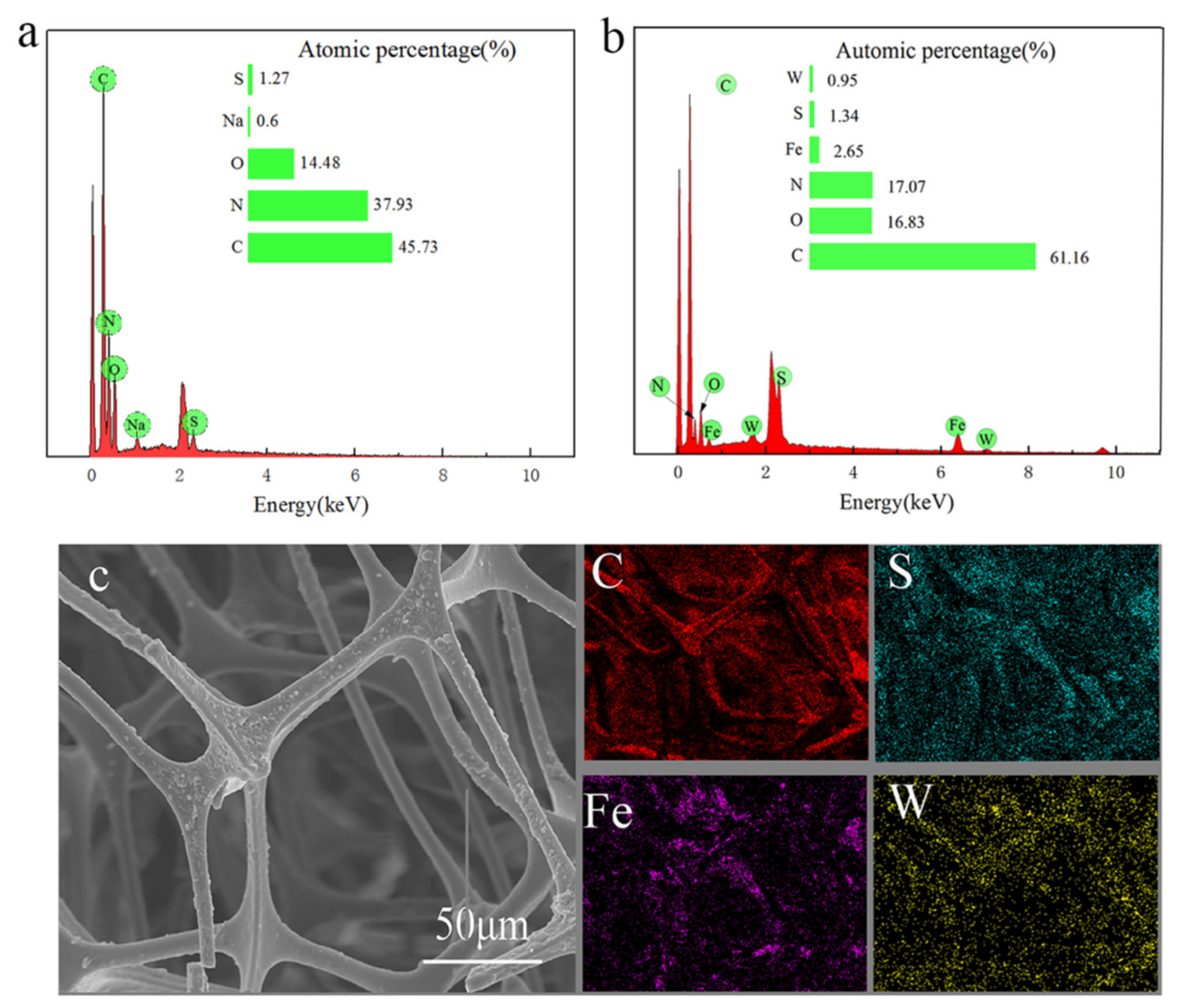
3.1.2. EDS Analysis
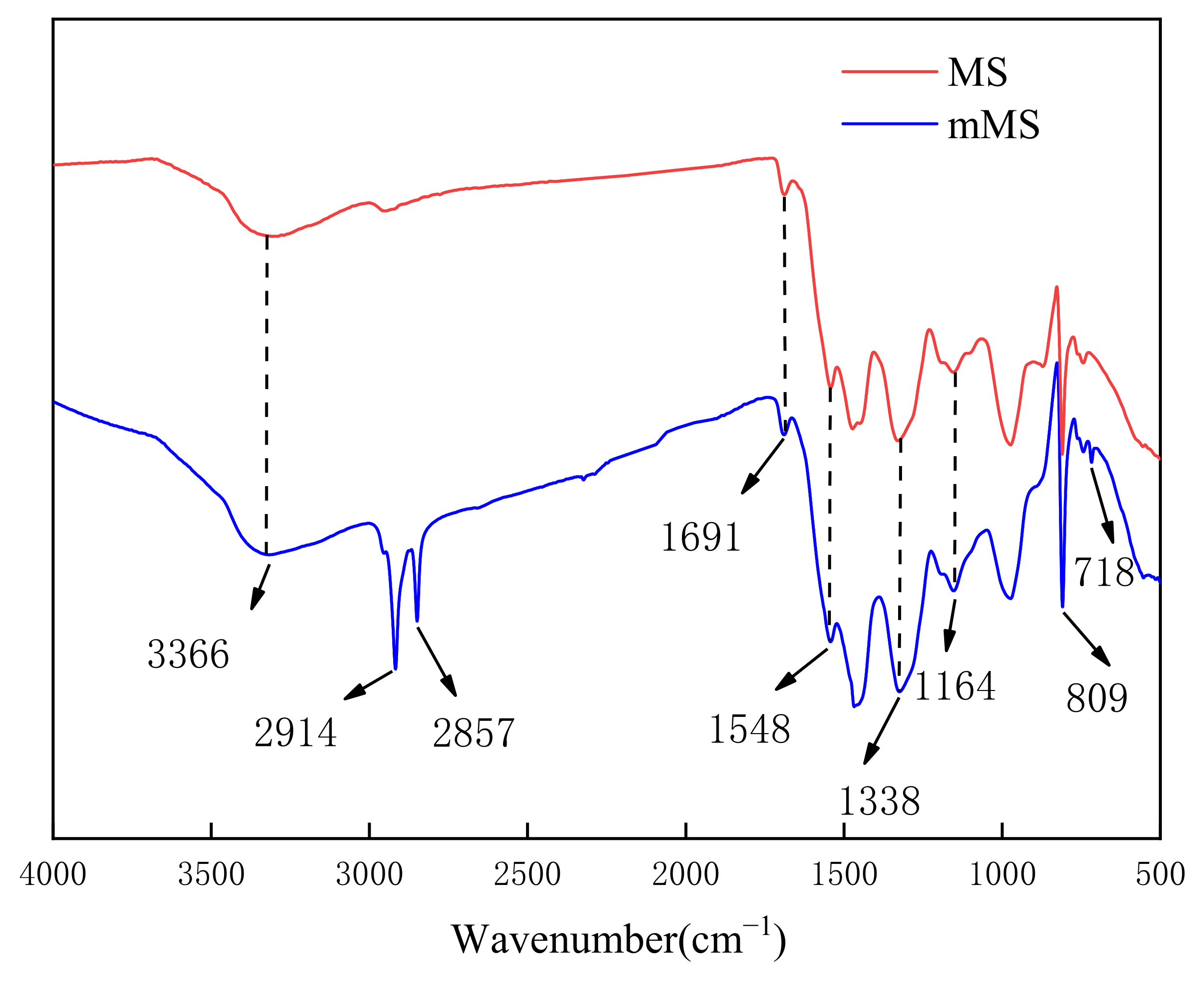
3.1.3. FTIR Analysis
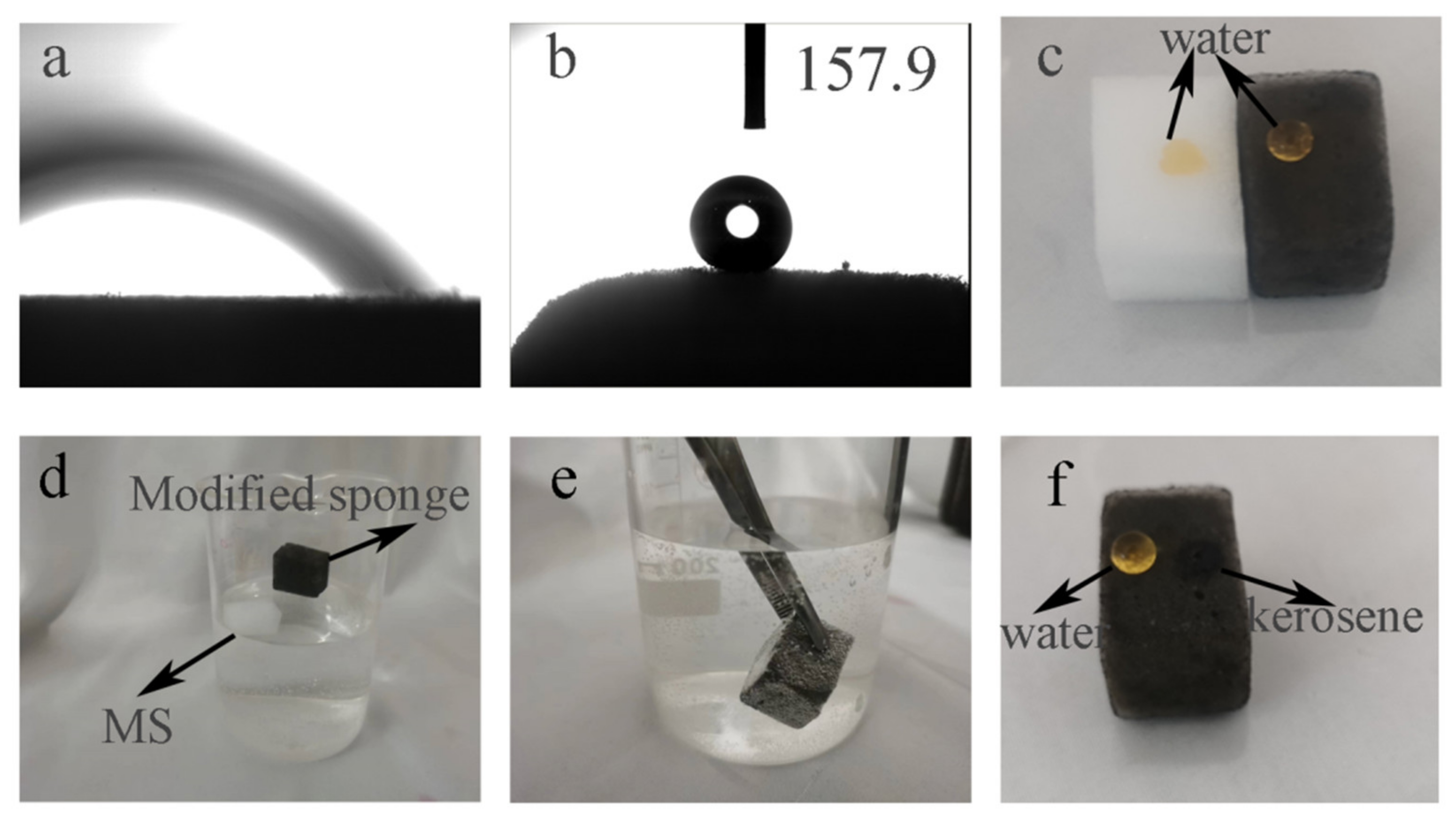
3.2. Wettability Analysis
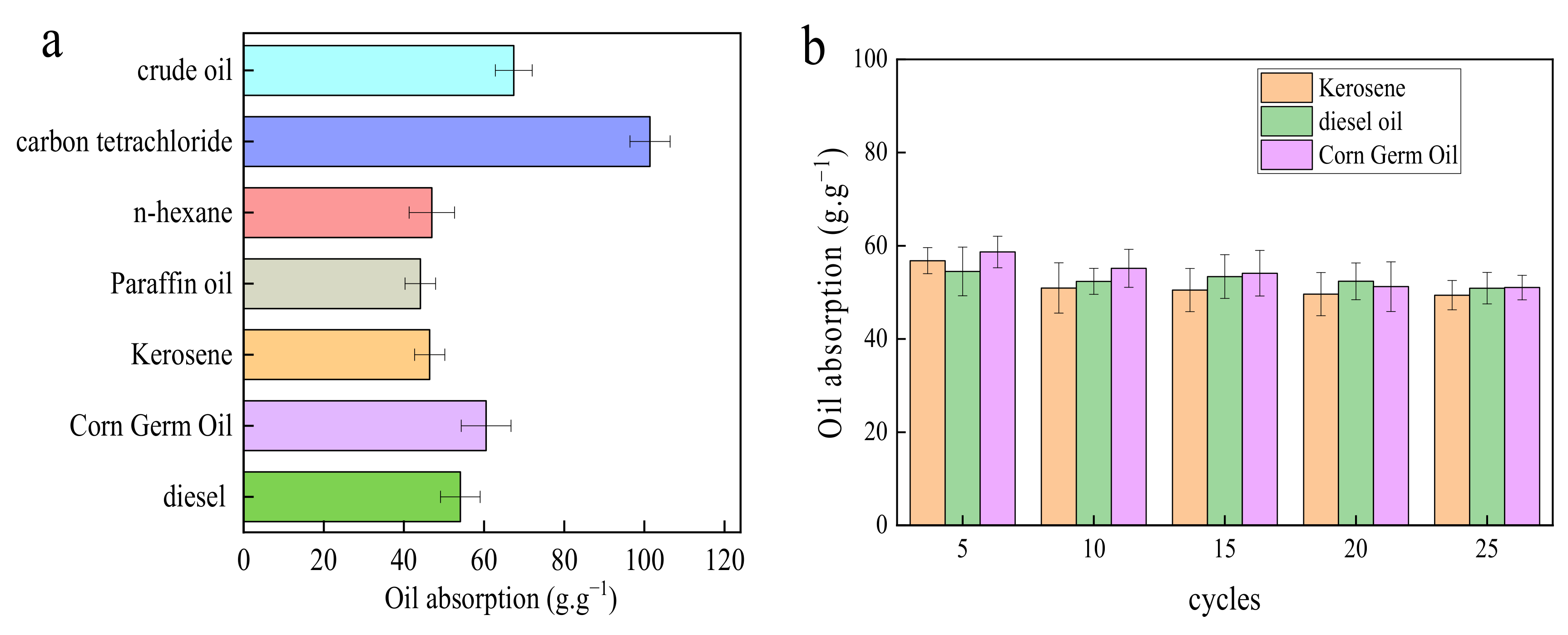
3.3. Adsorption Performance Analysis and Recycling Performance Analysis
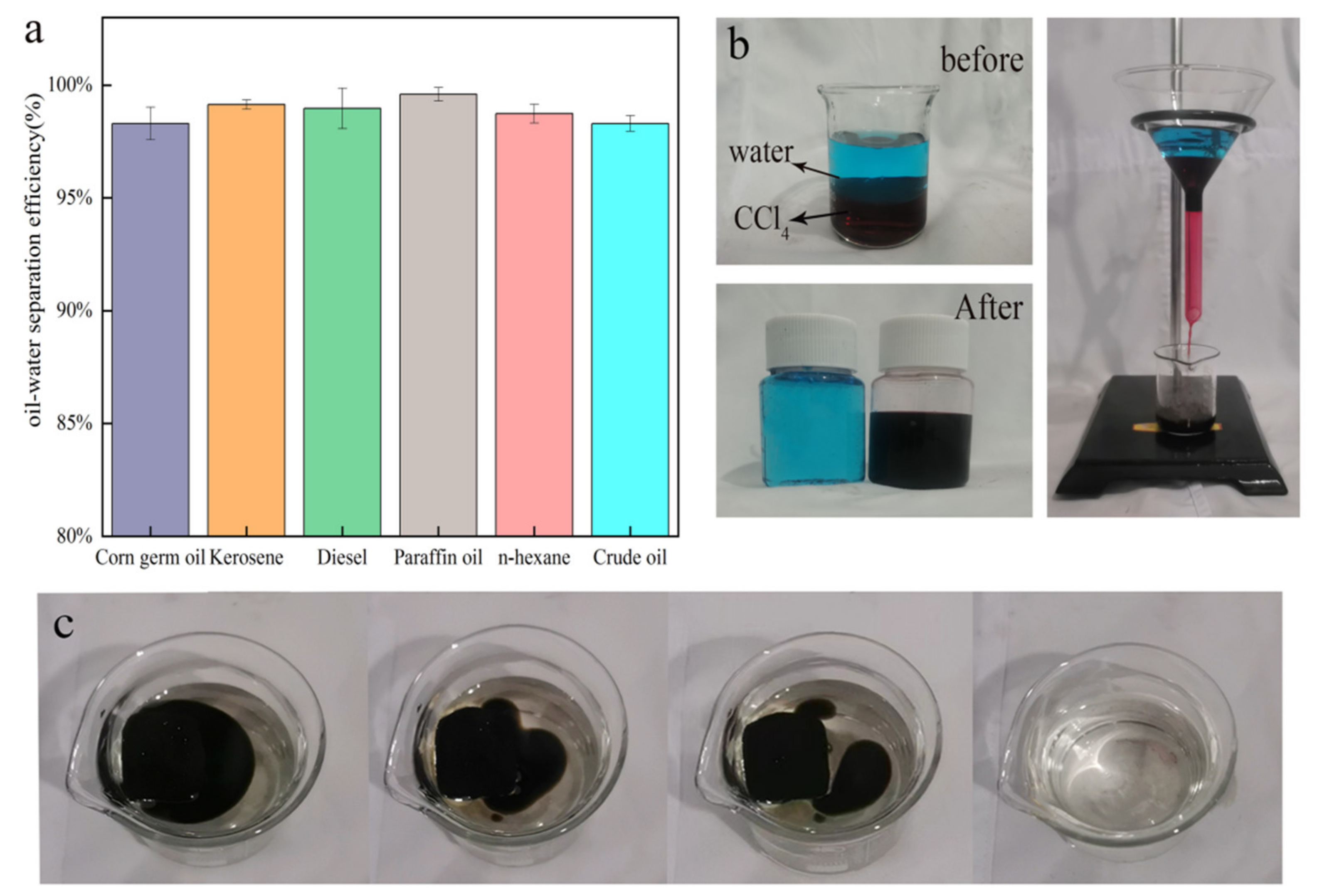
3.4. Oil–Water Separation Performance Analysis
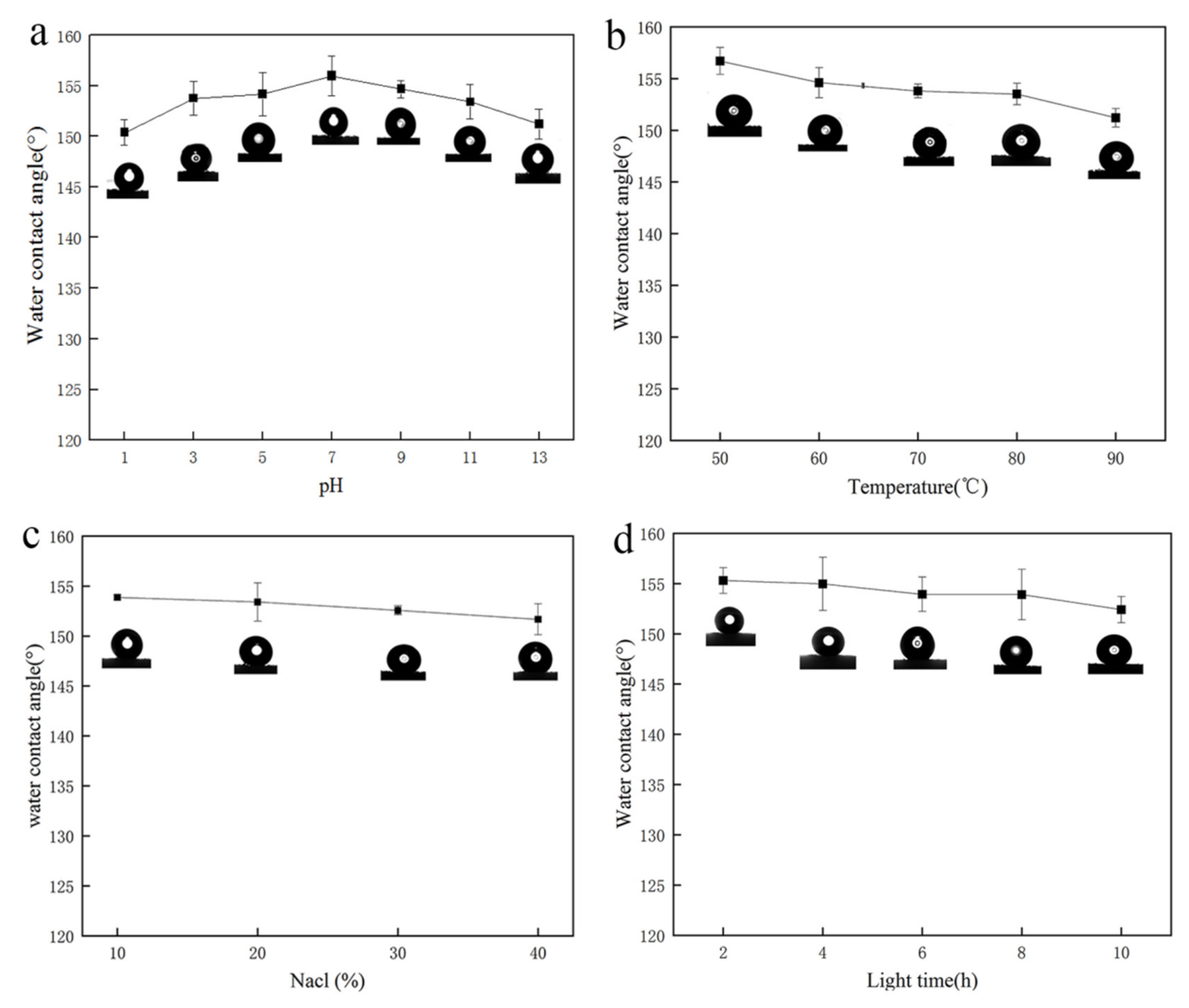
3.5. Stability and Durability Analysis
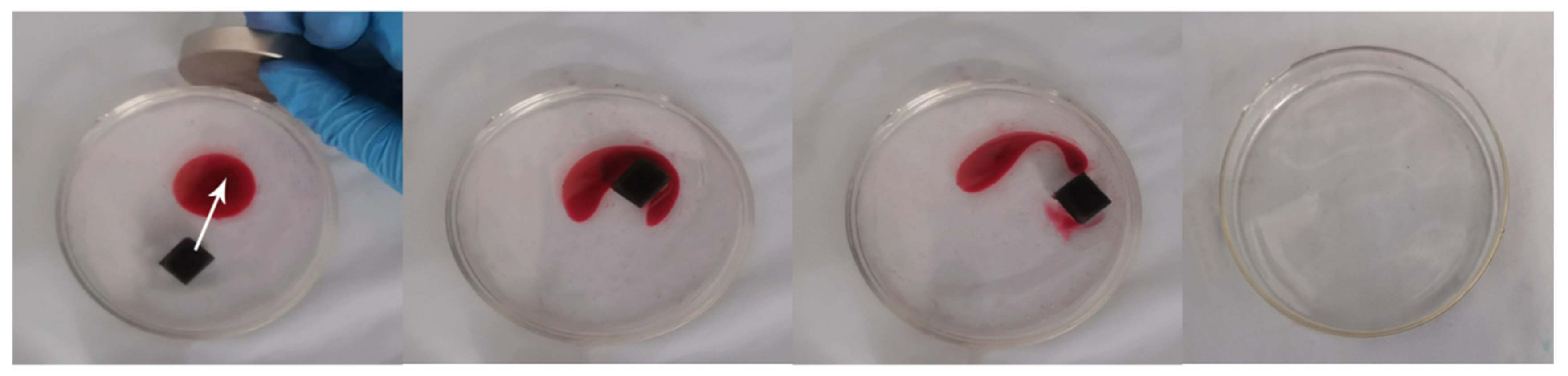
3.6. Magnetic Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, L. Hazards of offshore oil spills and their emergency response. Inf. Rec. Mater. 2018, 19, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.F.; Mather, R.R.; Fotheringham, A.F.; Yang, R.D. Evaluation of nonwoven polypropylene oil sorbents in marine oil-spill recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhardwaj, N.; Arya, S.K.; Khatri, M. Environmental impacts of oil spills and their remediation by magnetic nanomaterials. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.; Udofia, E.A.; Ekong, I.; Ebuk, G. Health Risks Associated with Oil Pollution in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelova, D.; Uzunov, I.; Uzunova, S.; Gigova, A.; Minchev, L. Kinetics of oil and oil products adsorption by carbonized rice husks. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H. Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Jalali, M.L.; Fard, G.C.; Maleknia, L. Surfactant Grafted PDA-PAN Nanofiber: Optimization of Synthesis, Characterization and Oil Absorption Property. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, D. Coherent-Interface-Assembled Ag2O-Anchored Nanofibrillated Cellulose Porous Aerogels for Radioactive Iodine Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29179–29185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S. Approach of Cost-Effective Adsorbents for Oil Removal from Oily Water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1916–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radetic, M.; Ilic, V.; Radojevic, D.; Miladinovic, R.; Jocic, D.; Jovancic, P. Efficiency of recycled wool-based nonwoven material for the removal of oils from water. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Qiu, F. Recent progress and future prospects of oil-absorbing materials. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. Superwetting Porous Materials for Wastewater Treatment: From Immiscible Oil/Water Mixture to Emulsion Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Huang, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Advanced Sorbents for Oil-Spill Cleanup: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Koch, K. Micro-, nano- and hierarchical structures for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and low adhesion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. 2009, 367, 1631–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshian, S.; Jokinen, V.; Somerkivi, V.; Lokanathan, A.R.; Franssila, S. Robust Superhydrophobic Silicon without a Low Surface-Energy Hydrophobic Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A Superhydrophobic Sponge with Excellent Absorbency and Flame Retardancy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 5556–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, D.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Zeng, X. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic, flame-retardant and conductive polyurethane sponge via dip-coating. Mater. Lett. 2021, 287, 129307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Mi, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Li, N. A facile method to fabricate the superhydrophobic magnetic sponge for oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Bao, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Y. An environmentally benign approach to prepare superhydrophobic magnetic melamine sponge for effective oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Wu, H.T.; Chen, W.Y.; He, F.A.; Li, D.H. Preparation of magnetic superhydrophobic melamine sponges for effective oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 212, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces: Multiscale approach. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2633–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Dickerson, J.H. Superhydrophobic silanized melamine sponges as high efficiency oil absorbent materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14181–14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merline, D.J.; Vukusic, S.; Abdala, A.A. Melamine formaldehyde: Curing studies and reaction mechanism. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniak, S.; Szymański, G.; Siedlewski, J.; Świątkowski, A. The characterization of activated carbons with oxygen and nitrogen surface groups. Carbon 1997, 35, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, X. Study on the structure of polyethyleneimine by infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2016, 36 (Suppl. 1), 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Cai, C.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, H.; Zha, F.; Guo, J.; Feng, B.; He, T.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Low-cost mussel inspired poly(catechol/polyamine) coating with superior anti-corrosion capability on copper. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 463, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yu, Z.; Luo, M.; Sun, X. Research Progress in Wetting Theory of Superhydrophobic Surface. J. Mater. Rev. 2012, 26, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, P.; Vanaki, S.M.; Thoo, K.K.; Chin, W.M. Air-side heat transfer characteristics of hydrophobic and super-hydrophobic fin surfaces in heat exchangers: A review. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 74, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1994, 40, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Lin, S.J. Robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge for effective continuous absorption and expulsion of oil pollutants from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8861–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, H.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Z.; Wang, B.; Tong, Q.; Lin, M. A Durable Magnetic Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge: For Solving Complex Marine Oil Spills. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142488
Si H, Liu Q, Fan Z, Wang B, Tong Q, Lin M. A Durable Magnetic Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge: For Solving Complex Marine Oil Spills. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(14):2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142488
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Hanmo, Qingwang Liu, Zhenzhong Fan, Biao Wang, Qilei Tong, and Mengqi Lin. 2022. "A Durable Magnetic Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge: For Solving Complex Marine Oil Spills" Nanomaterials 12, no. 14: 2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142488
APA StyleSi, H., Liu, Q., Fan, Z., Wang, B., Tong, Q., & Lin, M. (2022). A Durable Magnetic Superhydrophobic Melamine Sponge: For Solving Complex Marine Oil Spills. Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142488





