Effect of Conducting, Semi-Conducting and Insulating Nanoparticles on AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity of Synthetic Ester: A Statistical Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
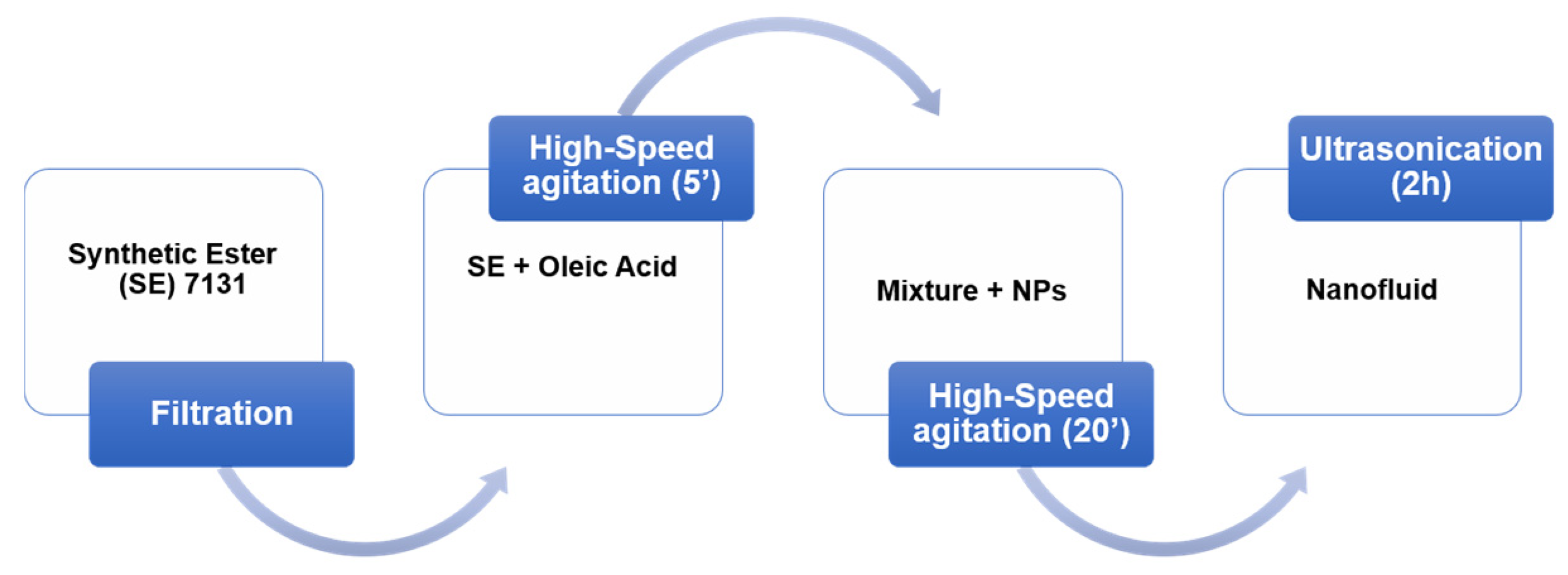
2.2. Samples Preparation
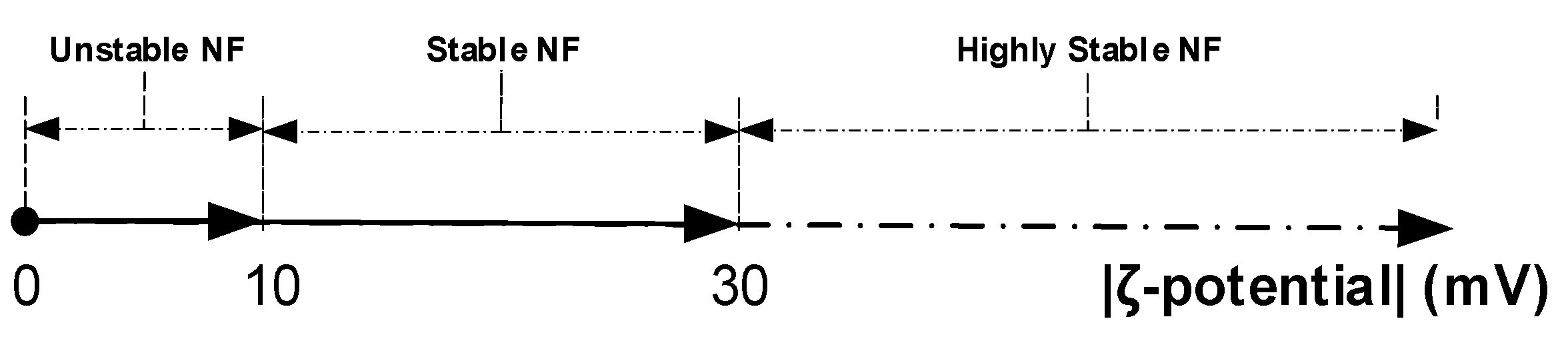
2.3. Stability of Nanofluids
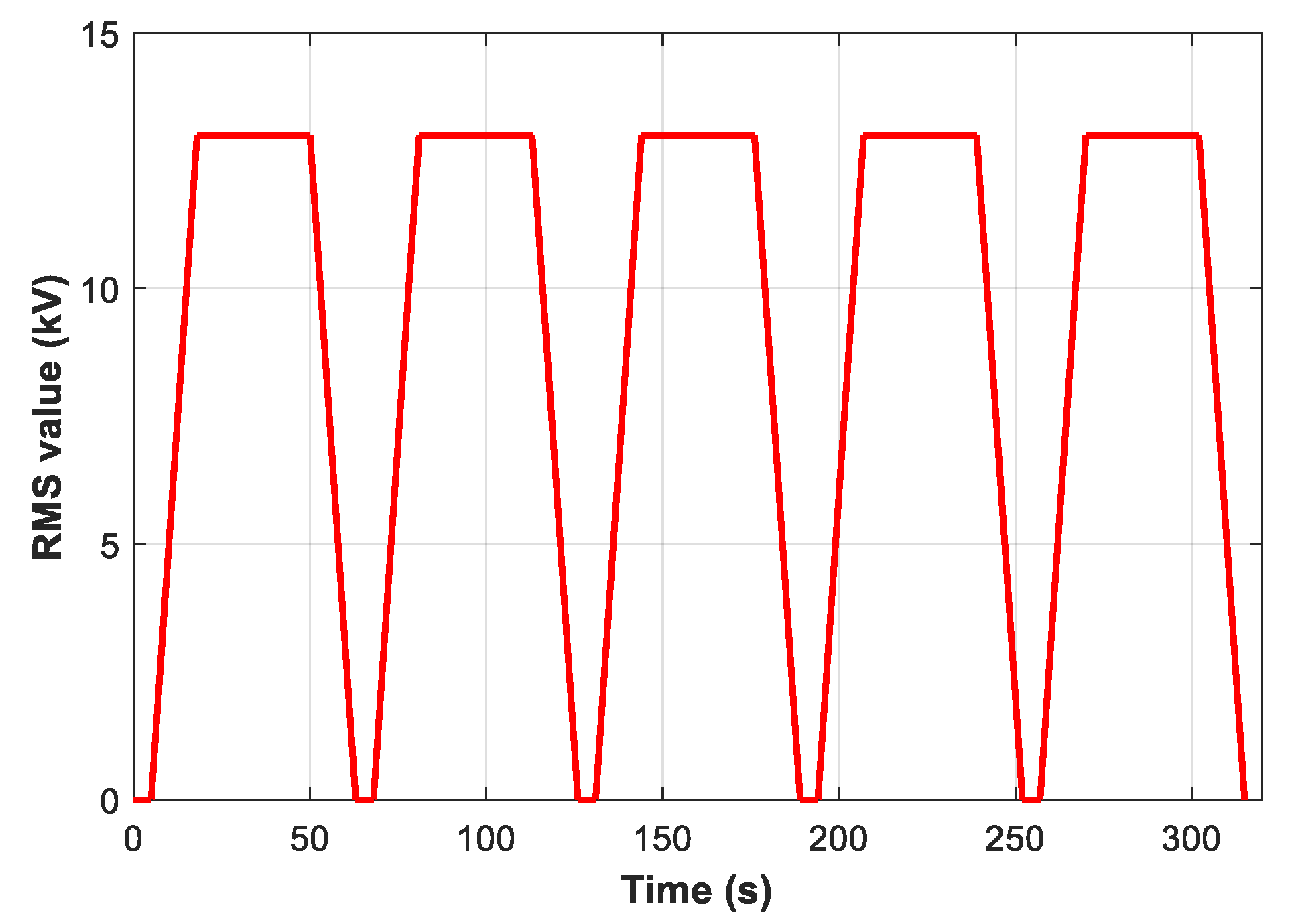
2.4. Procedure for Breakdown Voltage Measurement
2.5. Partial Discharges Measurement under AC 50 Hz Stress
3. Results
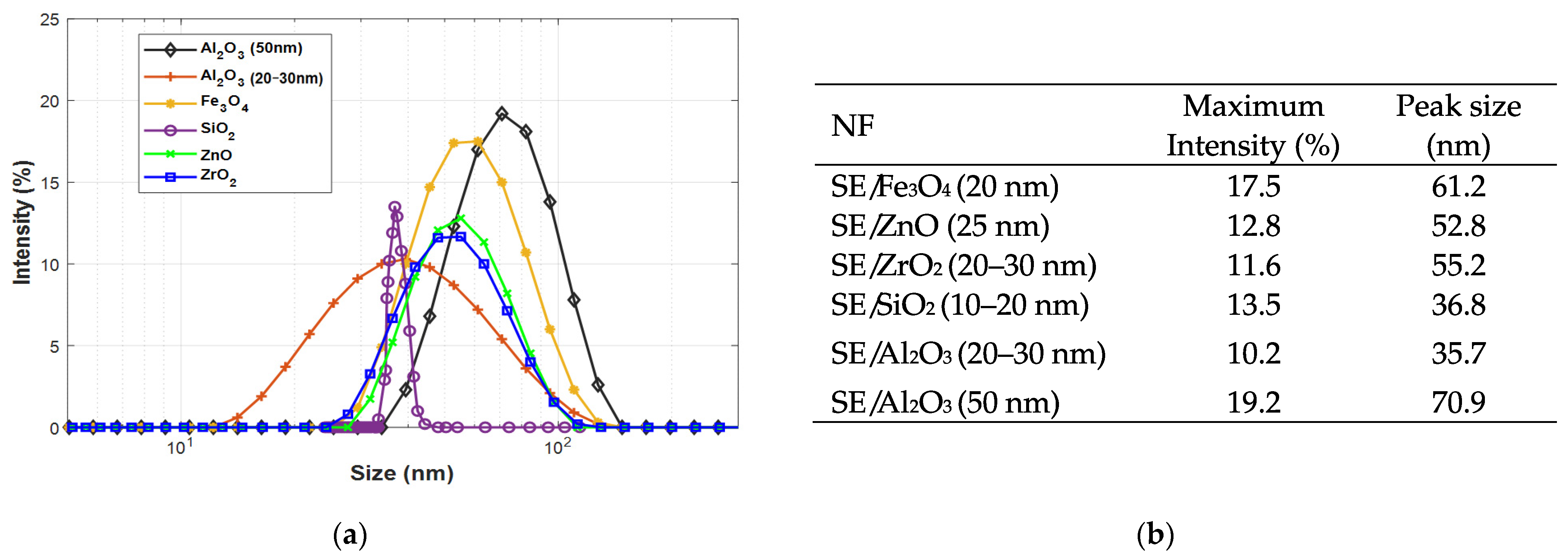
3.1. Stability of Nanofluids
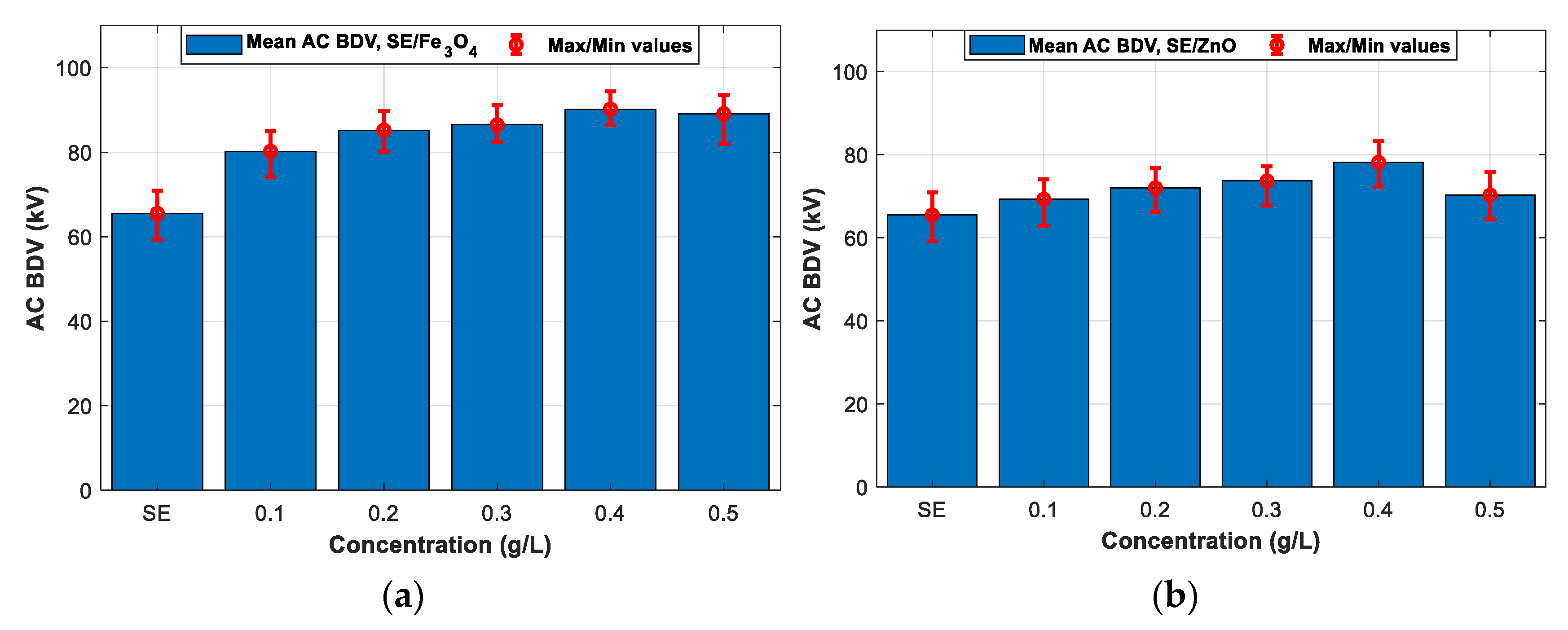
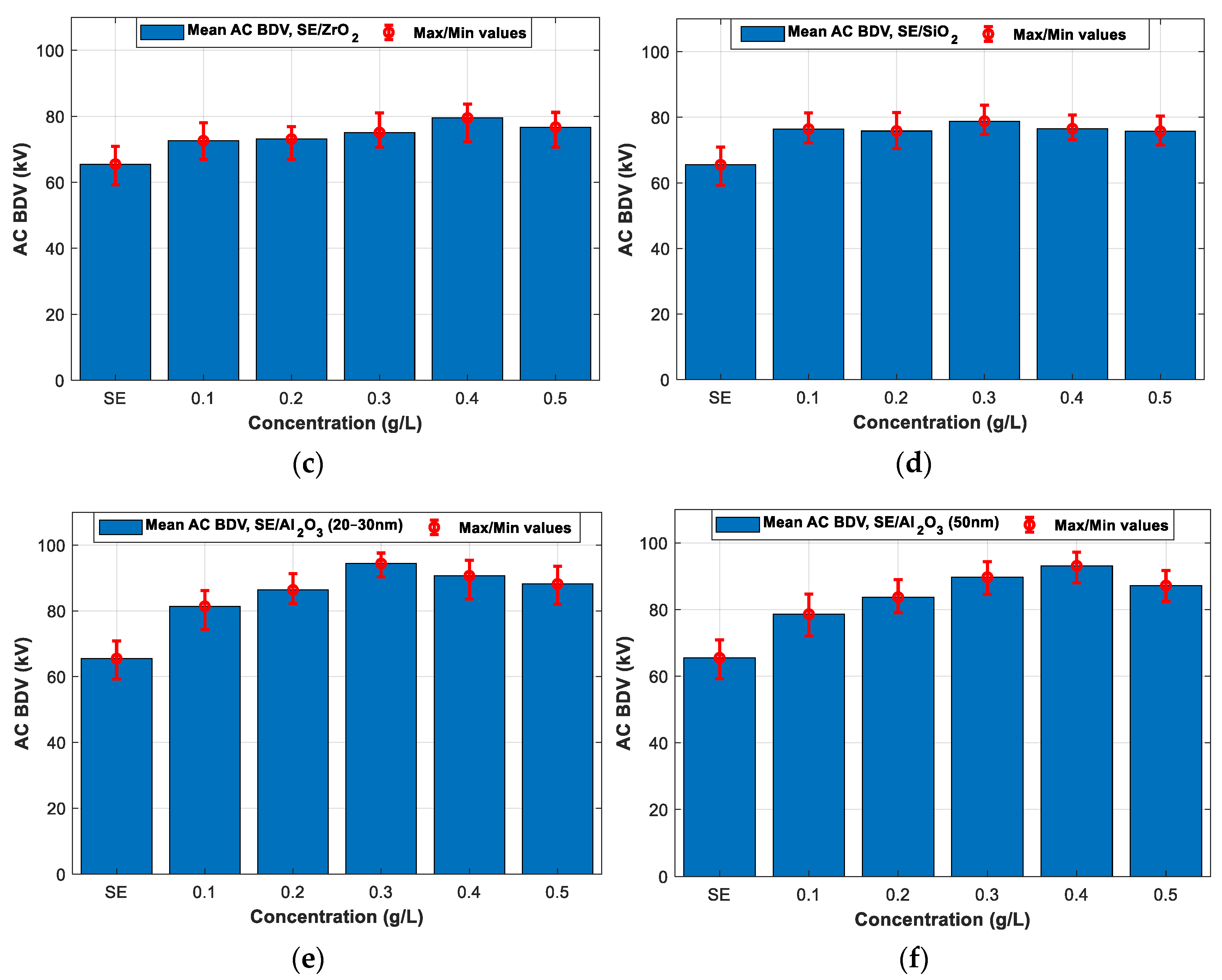
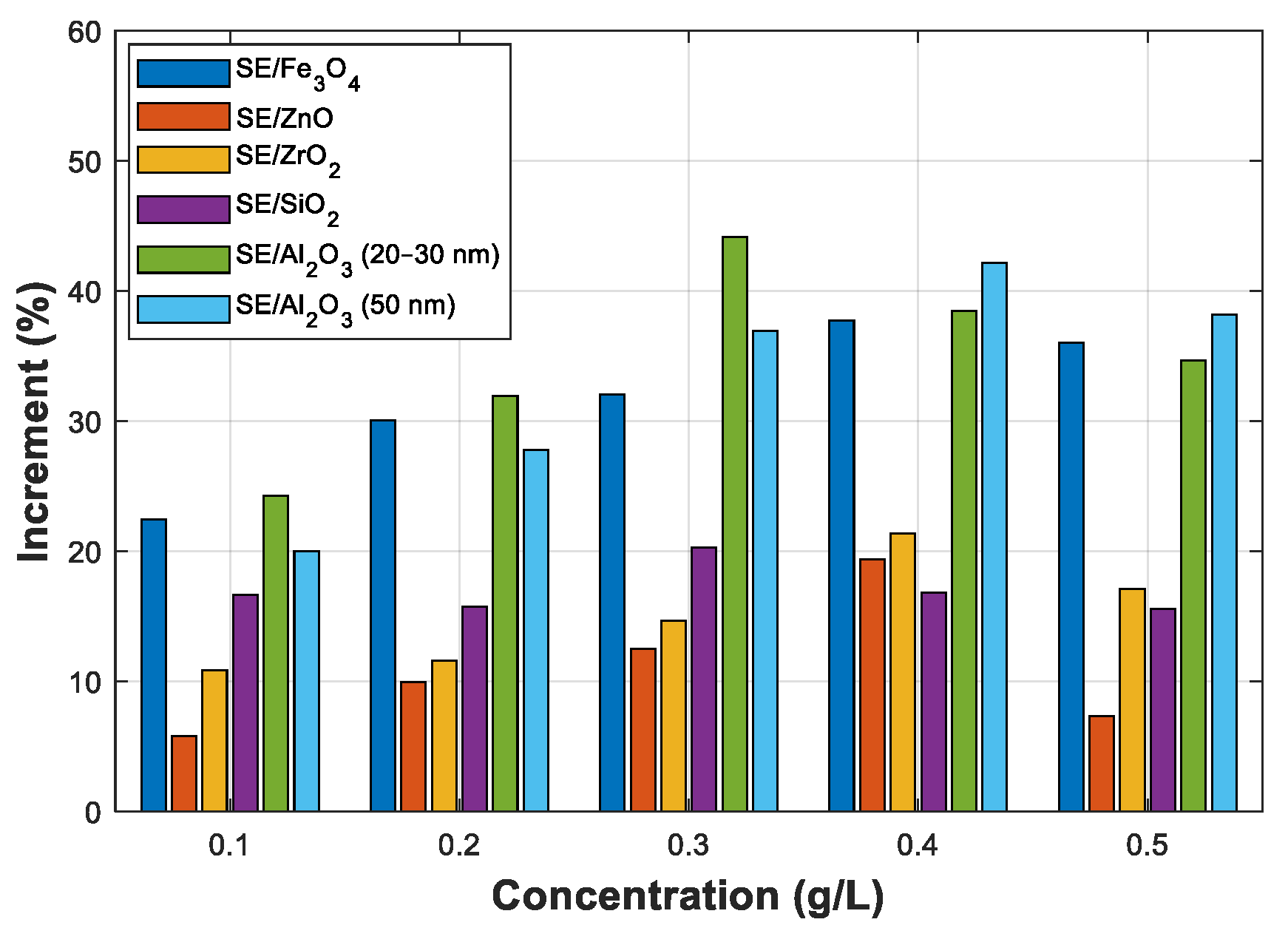
3.2. AC Breakdown Voltage Test for 2 mm Electrodes Gap
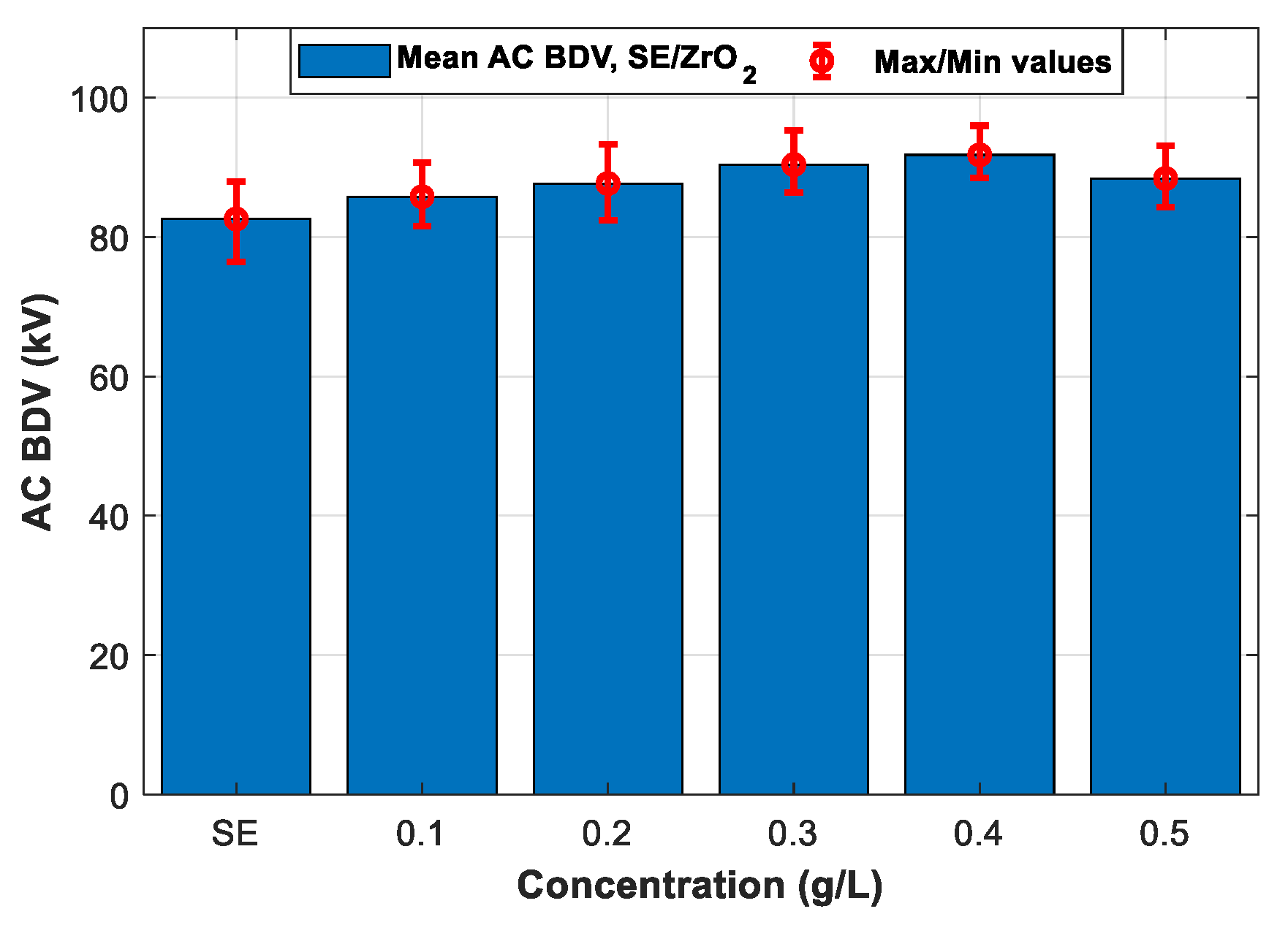
3.3. AC Breakdown Voltage Test for 2.5 mm Electrode Gap (IEC 60156)
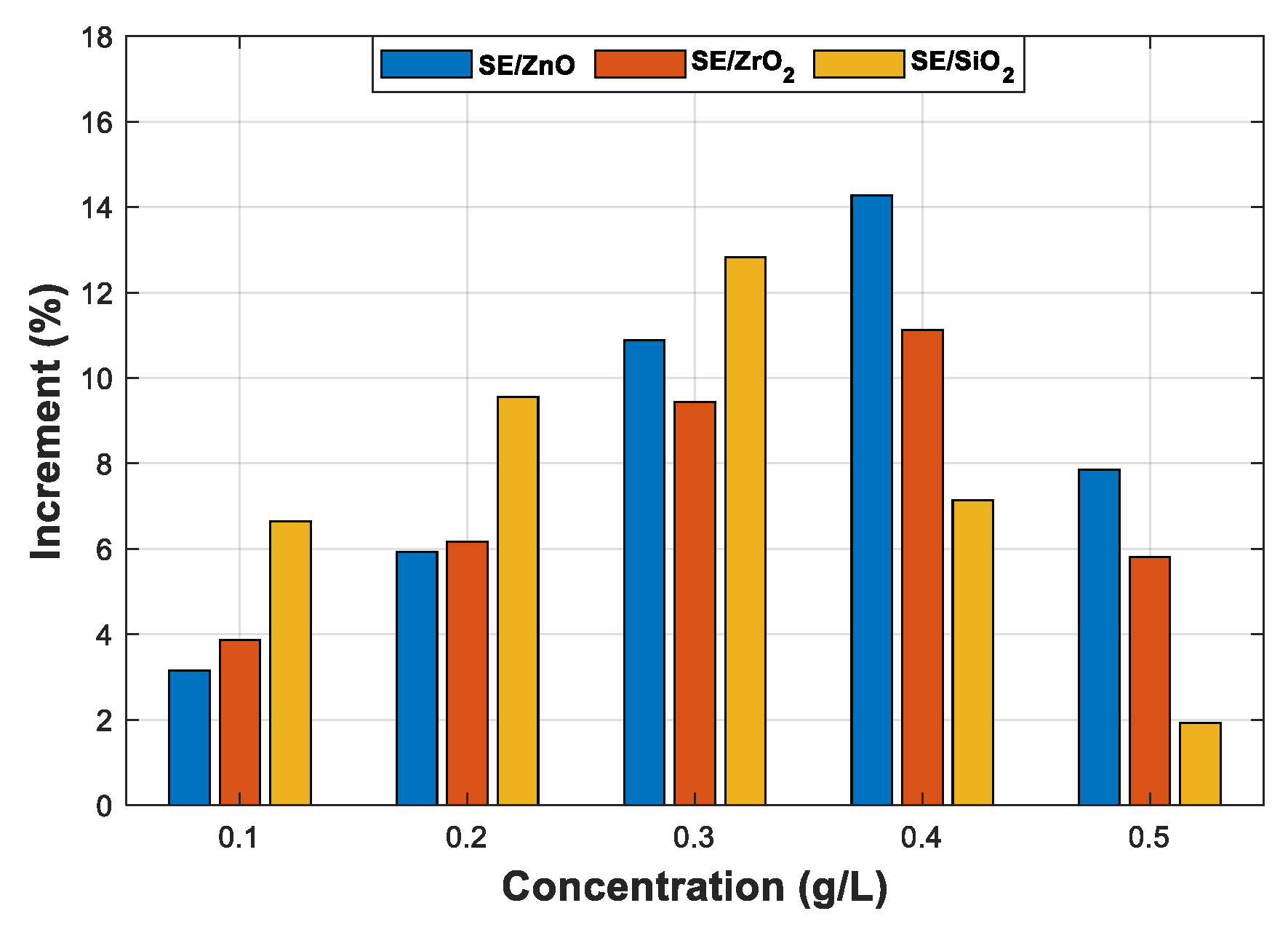
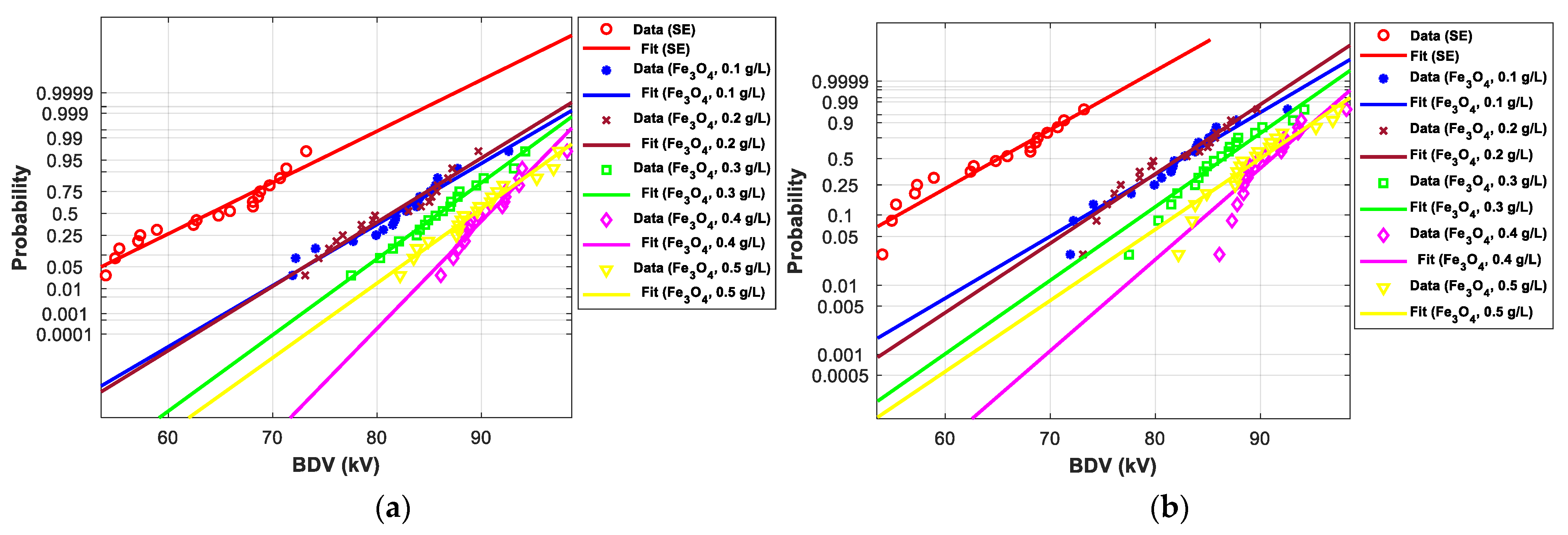
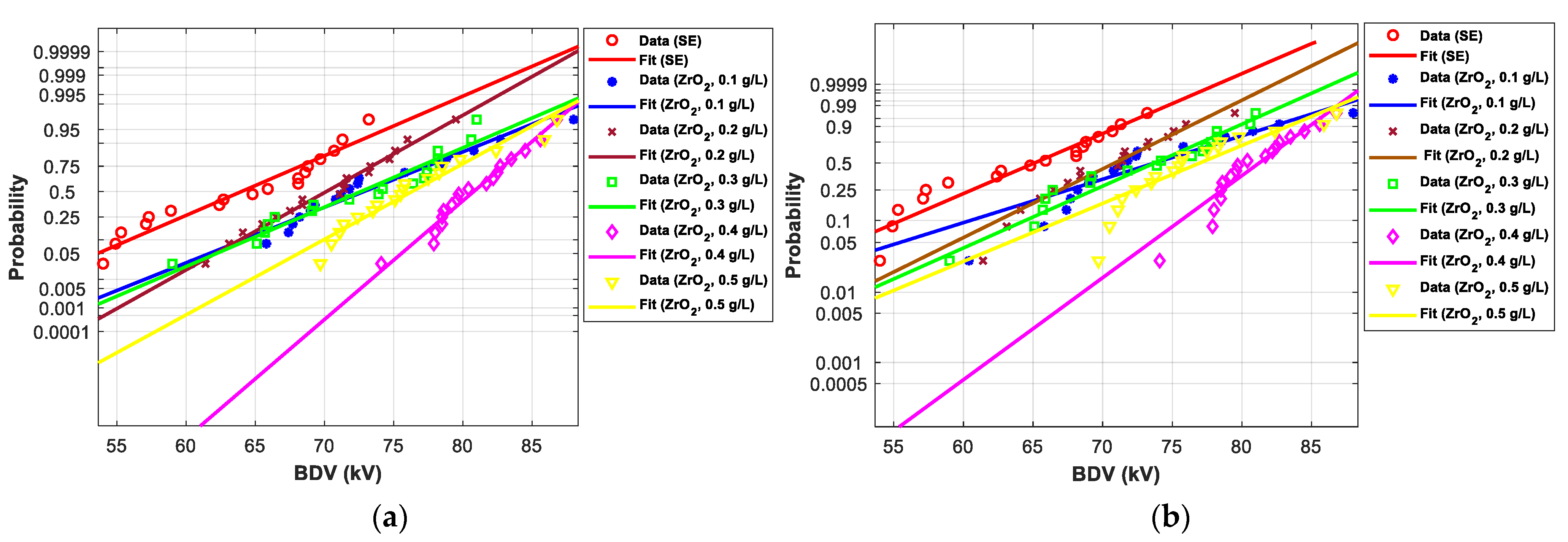
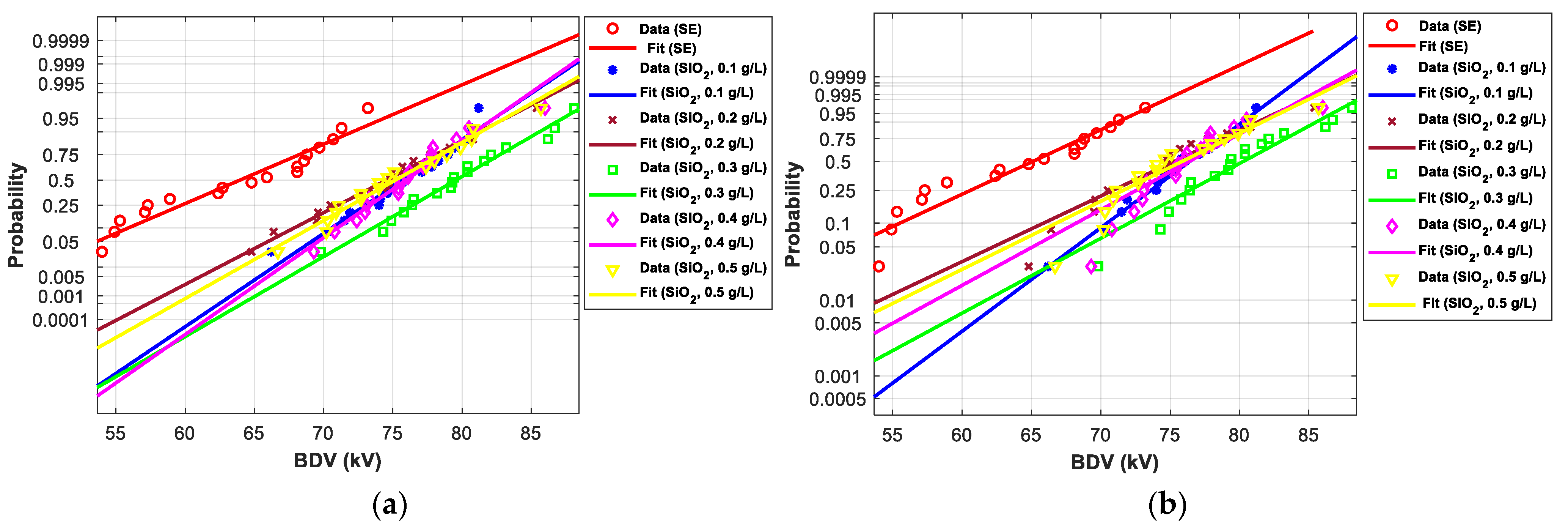
3.4. Statistical Analysis of AC Breakdown Voltage Data
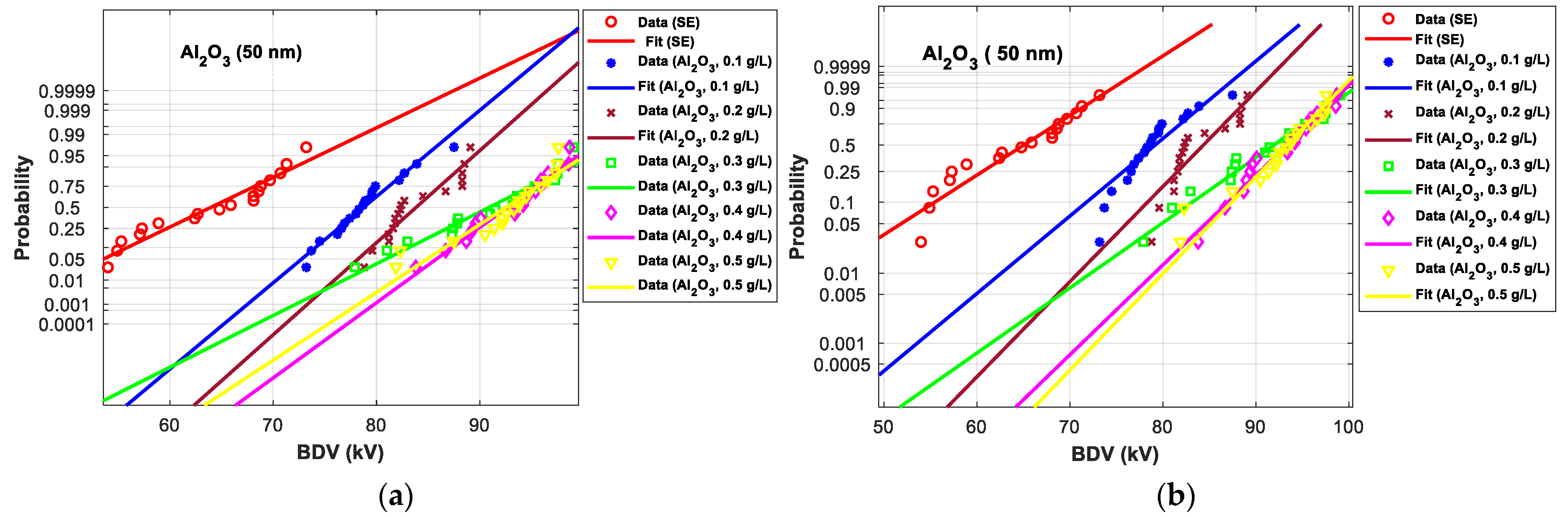
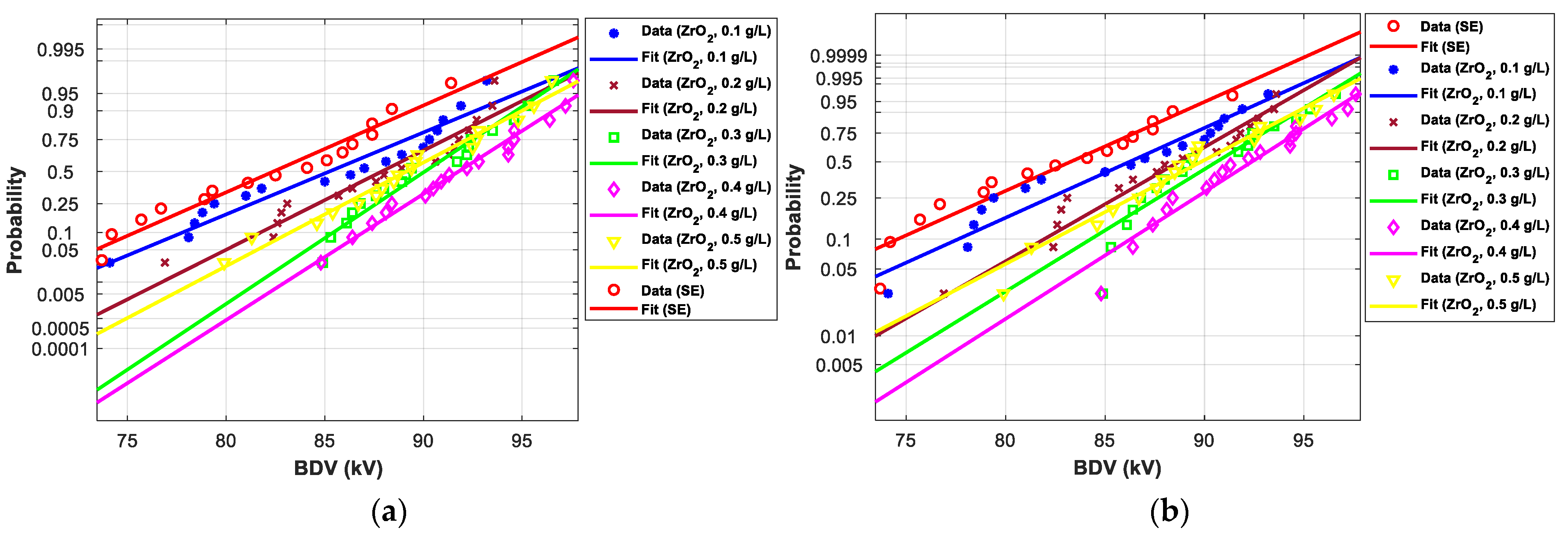
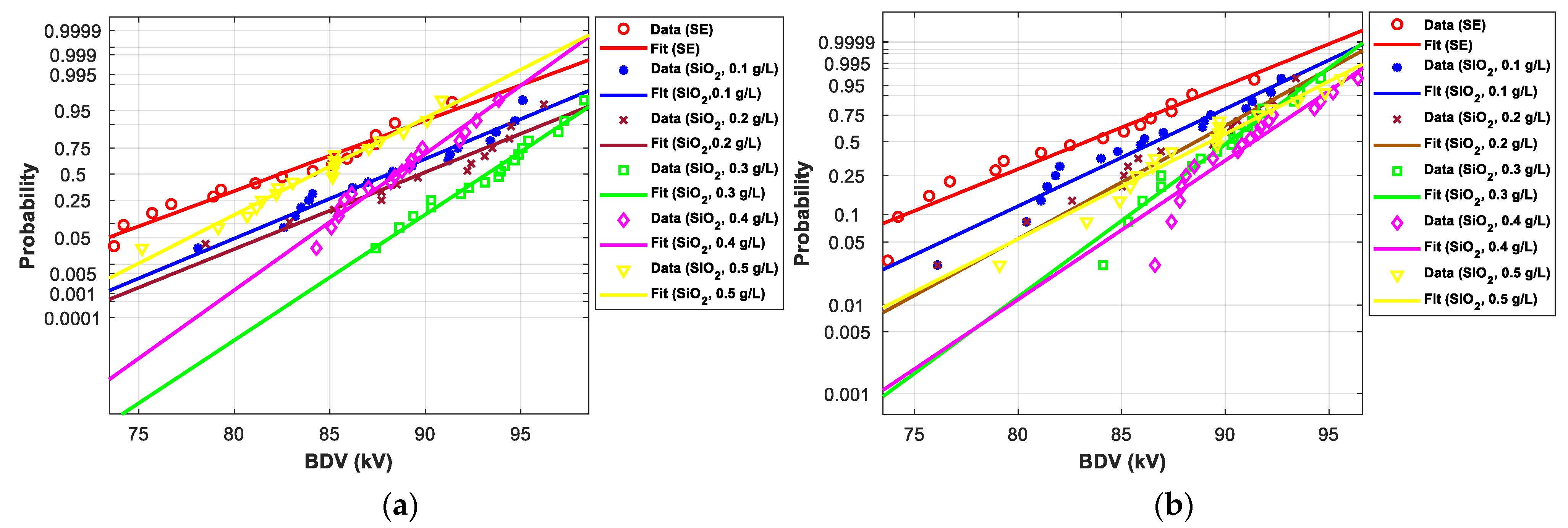
3.4.1. Statistical Analysis of AC Breakdown Voltage Outcomes for 2 mm Electrodes Gap
3.4.2. Statistical Analysis of AC Breakdown Voltage Outcomes for 2.5 mm Gap Distance
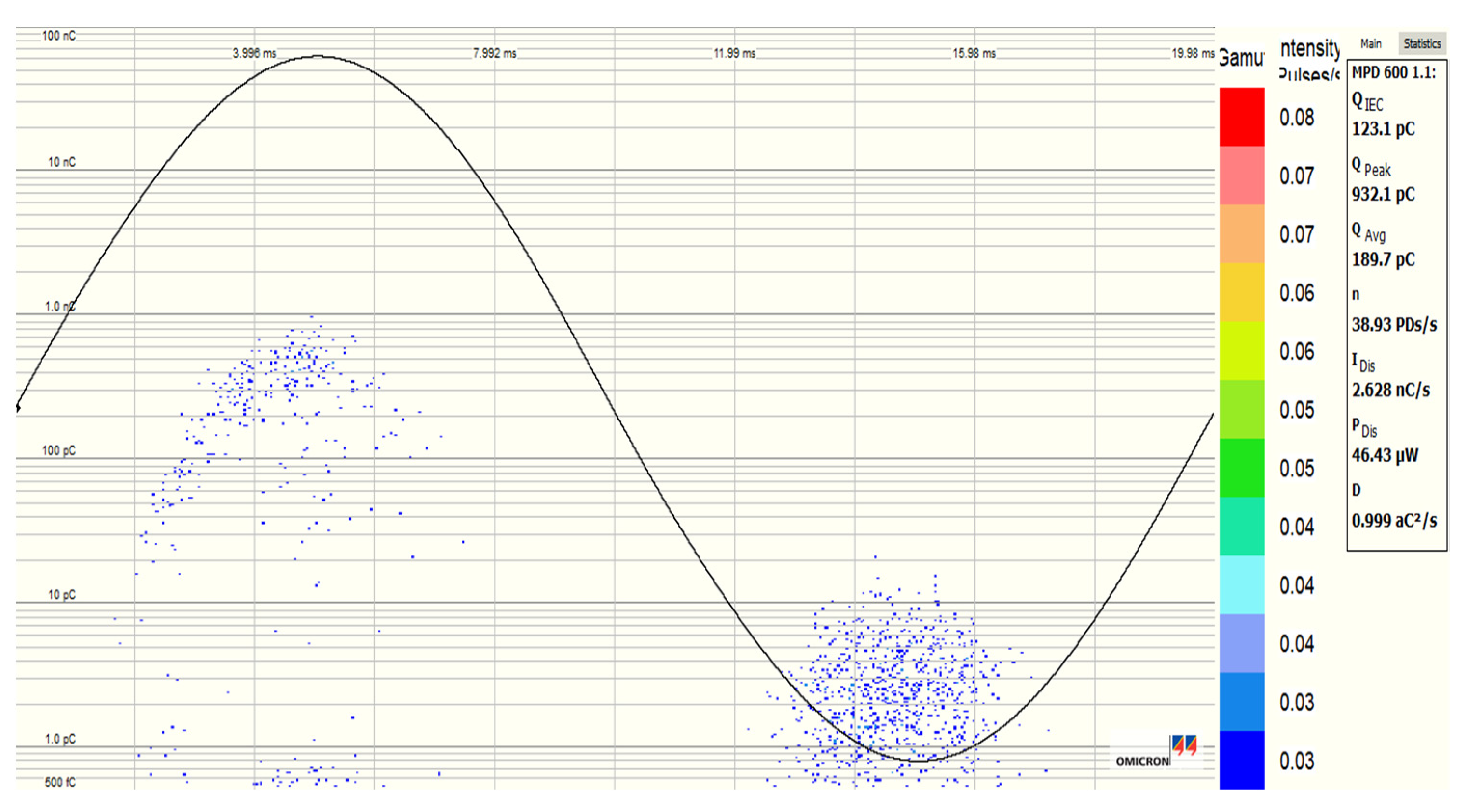
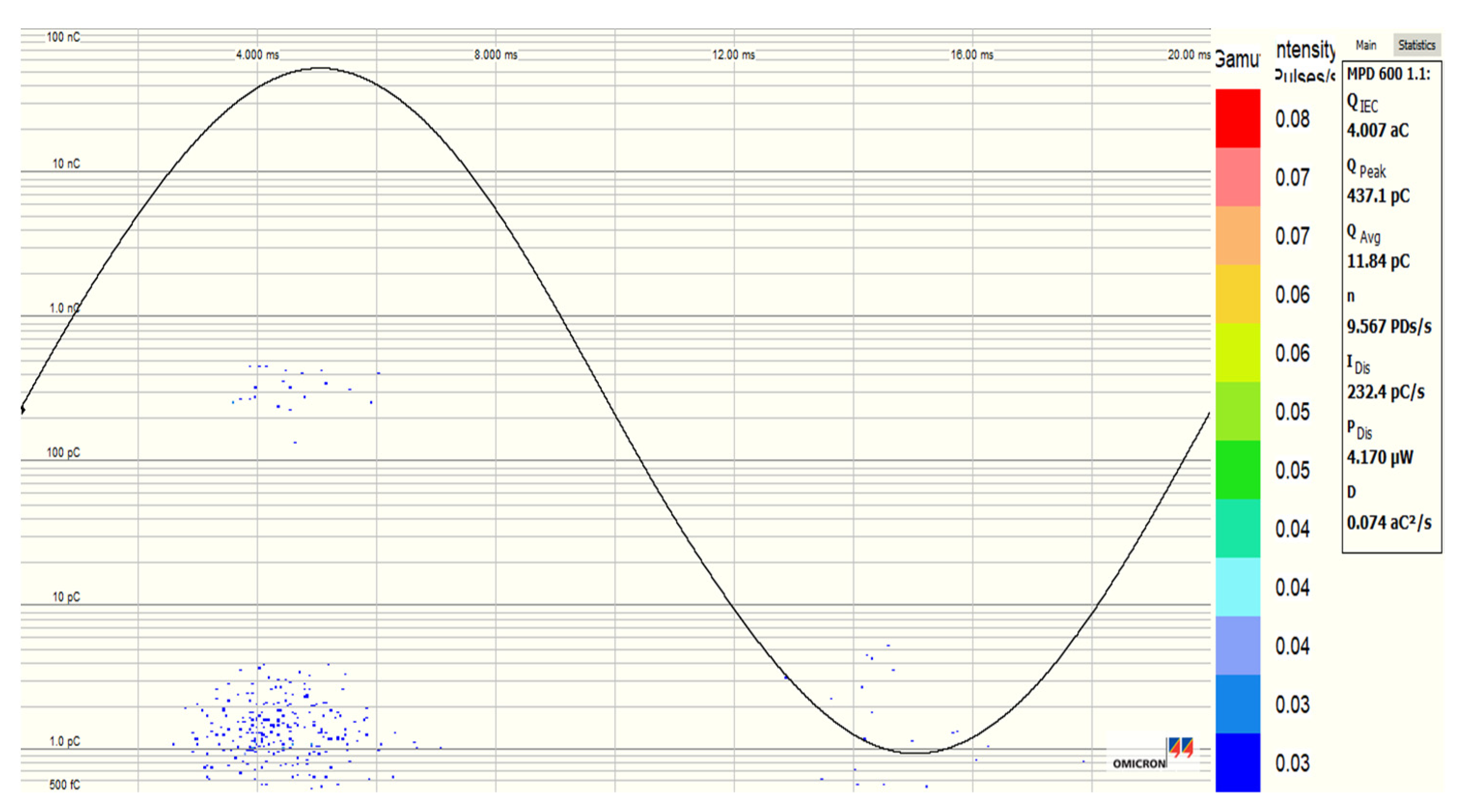
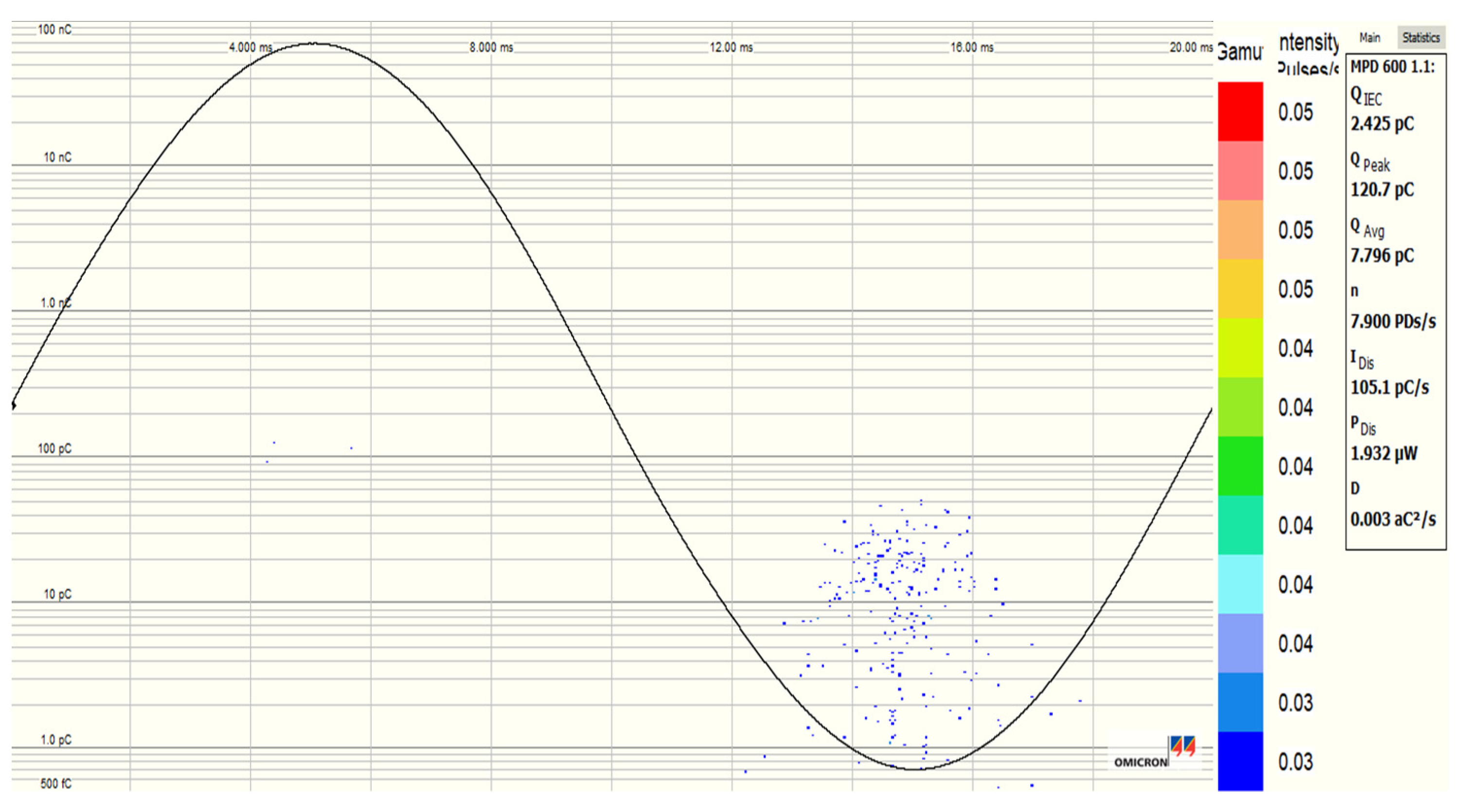
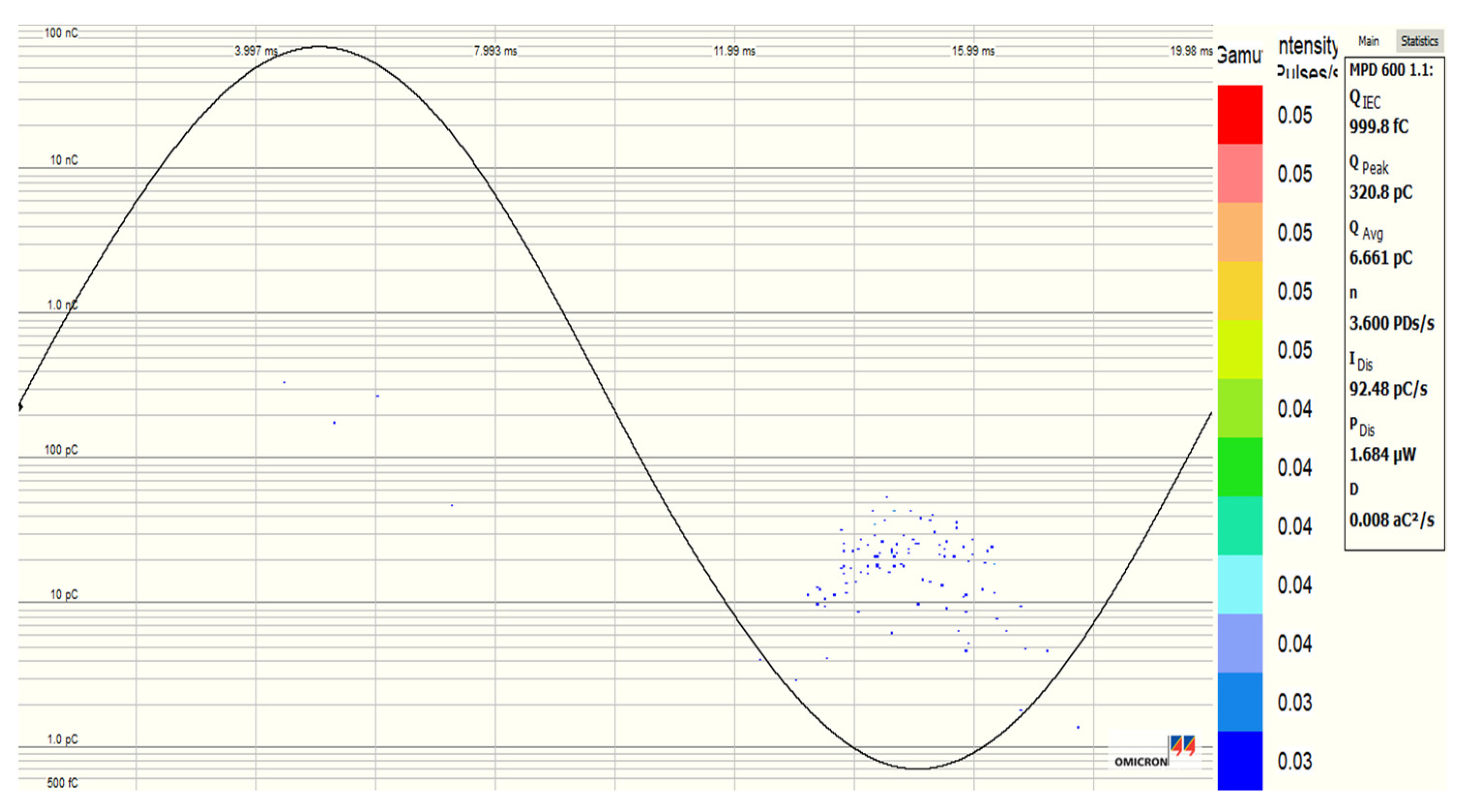
3.5. Partial Discharge Activity of Al2O3 and Fe3O4 NFs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riehemann, K.; Schneider, S.W.; Luger, T.A.; Godin, B.; Ferrari, M.; Fuchs, H. Nanomedicine—Challenge and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 872–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Webster, T.J. Nanobiotechnology: Microbes and Plant Assisted Synthesis of Nanoparticles, Mechanisms and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Nakamura, M. Nanomedicine for Drug Delivery and Imaging: A Promising Avenue for Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis Using Targeted Functional Nanoparticles. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, L.; Tratnyek, P.; Jacobs, P.; Doolittle, N.; Christoforidis, G.; Frank, J.; Lindau, M.; Lockman, P.; Manninger, S.; Qiang, Y.; et al. Imaging and Nanomedicine for Diagnosis and Therapy in the Central Nervous System: Report of the Eleventh Annual Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Consortium Meeting. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nanotechnology for Electronics, Photonics, and Renewable Energy; Korkin, A.; Krstić, P.S.; Wells, J.C. (Eds.) Nanostructure Science and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-7234-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kamat, P.V.; Schatz, G.C. Nanotechnology for next Generation Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 15473–15475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, P.; Sima, W.; Shao, Q.; Ye, L.; Li, C. A Promising Nano-Insulating-Oil for Industrial Application: Electrical Properties and Modification Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.R.; Khan, Q.; Khan, A.A.; Refaat, S.S.; Abu-Rub, H. Dielectric Performance of Magneto-Nanofluids for Advancing Oil-Immersed Power Transformer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 163316–163328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.E.; Abd-Elhady, A.M.; Izzularab, M.A. Effect of Nanoparticles on Transformer Oil Breakdown Strength: Experiment and Theory. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2016, 10, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, W.; Shi, J.; Yang, Q.; Huang, S.; Cao, X. Effects of Conductivity and Permittivity of Nanoparticle on Transformer Oil Insulation Performance: Experiment and Theory. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.G.; Zahn, M.; O’Sullivan, F.M.; Pettersson, L.A.A.; Hjortstam, O.; Liu, R. Effects of Nanoparticle Charging on Streamer Development in Transformer Oil-Based Nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 014310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, W.; Wang, F.; Wan, F.; Tan, Y.; Mehmood, M.A. Electrical and Thermal Properties of Insulating Oil-based Nanofluids: A Comprehensive Overview. IET Nanodielectrics 2019, 2, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, G.D.; Charalampakos, V.P.; Pyrgioti, E.C.; Danikas, M.G.; Bakandritsos, A.; Gonos, I.F. Statistical Investigation of AC Breakdown Voltage of Nanofluids Compared with Mineral and Natural Ester Oil. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2016, 10, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhen Lv; Muhammad Rafiq; Chengrong Li; Bingliang Shan Study of Dielectric Breakdown Performance of Transformer Oil Based Magnetic Nanofluids. Energies 2017, 10, 1025. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaled, U.; Beroual, A. AC Dielectric Strength of Mineral Oil-Based Fe3O4 and Al2O3 Nanofluids. Energies 2018, 11, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaled, U.; Beroual, A. AC Dielectric Strength of Synthetic Ester-Based Fe3O4, Al2O3 and SiO2 Nanofluids—Conformity with Normal and Weibull Distributions. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2019, 26, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, C.; Méndez, C.; Ortiz, F.; Delgado, F.; Ortiz, A. Titania Nanofluids Based on Natural Ester: Cooling and Insulation Properties Assessment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiesa, M.; Das, S.K. Experimental Investigation of the Dielectric and Cooling Performance of Colloidal Suspensions in Insulating Media. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 335, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Duzkaya, H. AC and Lightning Impulse Breakdown Voltages of Natural Ester Based Fullerene Nanofluids. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifa, H.; Vagnon, E.; Beroual, A. AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity in Synthetic Ester—Based Fullerene and Graphene Nanofluids. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 5620–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Morshuis, P.; Mor, A.R.; Smit, J.J.; Andritsch, T. Partial Discharge Behavior of Mineral Oil Based Nanofluids. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huifei, J.; Morshuis, P.H.F.; Mor, A.R.; Andritsch, T. An Investigation into the Dynamics of Partial Discharge Propagation in Mineral Oil Based Nanofluids. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 18th International Conference on Dielectric Liquids (ICDL), Bled, Slovenia, 29 June–3 July 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Atiya, E.G.; Mansour, D.-E.A.; Izzularab, M.A. Partial Discharge Activity of Al2O3 Nanofluid Impregnated Paper Insulation System. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM), Tokyo, Japan, 13–17 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Atiya, E.G.; Mansour, D.-E.A.; Izzularab, M.A. Partial Discharge Development in Oil-Based Nanofluids: Inception, Propagation and Time Transition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 181028–181035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, K.N.; Tegopoulos, S.N.; Charalampakos, V.P.; Kyritsis, A.; Gonos, I.F.; Pyrgioti, E.C. Breakdown Performance and Partial Discharge Development in Transformer Oil-Based Metal Carbide Nanofluids. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M&I Materials. MIDEL 7131, Synthetic Ester Transformer Fluid Fire Safe and Biodegradable; M&I Materials: Manchester, UK, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H. A Review on Nanofluids: Preparation, Stability Mechanisms, and Applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dukhin, A.S.; Goetz, P.J. Ultrasound for Characterizing Colloids: Particle Sizing, Zeta Potential, Rheology, 1st ed.; Studies in interface science; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-444-51164-5. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 60156; Insulating Liquids—Determination of the Breakdown Voltage at Power Frequency—Test Method. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Koutras, K.N.; Naxakis, I.A.; Antonelou, A.E.; Charalampakos, V.P.; Pyrgioti, E.C.; Yannopoulos, S.N. Dielectric Strength and Stability of Natural Ester Oil Based TiO2 Nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 316, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzkaya, H.; Beroual, A. Statistical Analysis of AC Dielectric Strength of Natural Ester-Based ZnO Nanofluids. Energies 2020, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsaglia, G.; Marsaglia, J. Evaluating the Anderson-Darling Distribution. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, M.A. EDF Statistics for Goodness of Fit and Some Comparisons. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, U.; Beroual, A. Influence of Conductive Nanoparticles on the Breakdown Voltage of Mineral Oil, Synthetic and Natural Ester Oil-Based Nanofluids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 20th International Conference on Dielectric Liquids (ICDL), Roma, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Microtechnologies and Microsystems Series; Research Studies Press: Hertfordshire, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-0-86380-255-3. [Google Scholar]
- Makmud, M.; Illias, H.; Chee, C.; Dabbak, S. Partial Discharge in Nanofluid Insulation Material with Conductive and Semiconductive Nanoparticles. Materials 2019, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Property | MIDEL 7131 |
|---|---|
| Density at 20 °C (kg/L) | 0.97 |
| Kinematic Viscosity (mm2/s) | |
| at 40 °C | 29 |
| at −20 °C | 1440 |
| Pour point (°C) | −56 |
| Flash point (°C) | 260 |
| Fire point (°C) | 316 |
| Water content (ppm) | 50 |
| AC BDV “60Hz” (kV) | >75 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.2 |
| Power Factor at 90 °C | <0.008 |
| DC Resistivity at 90 °C (GΩ·m) | >20 |
| NPs | Fe3O4 | ZnO | ZrO2 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | 20 | 25 | 20–30 | 10–20 | 20–30 | 50 |
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 40 | 19 ± 5 | 15–35 | 60–100 | 120–140 | 80 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 5.1 * | 5.6 | 4.8–6.0 | 0.6~1.8 | 3–3.98 * | |
| Dielectric Constant | 80 * | 8.5 | 10–23 | 3.9 | 9–10.1 * | |
| Purity (%) | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99 | 99.8 | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| NFs | Zeta Potential (mV) | Elec. Conductivity (mS/cm) × 10−3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0.1 g/L) | SE/Fe3O4 (20 nm) | −22.4 | 2.16 |
| SE/ZnO (25 nm) | +22.9 | 0.94 | |
| SE/ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | −24.4 | 2.09 | |
| SE/SiO2 (10–20 nm) | −36.2 | 1.73 | |
| SE/Al2O3 (20–30 nm) | +15.9 | 1.24 | |
| SE/Al2O3 (50 nm) | +24.9 | 1.37 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | SE/Fe3O4 (20 nm) | −23.6 | 2.31 |
| SE/ZnO (25 nm) | +19.7 | 1.26 | |
| SE/ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | −21.8 | 1.89 | |
| SE/SiO2 (10–20 nm) | −33.7 | 1.57 | |
| SE/Al2O3 (20–30nm) | +20.4 | 0.85 | |
| SE/Al2O3 (50 nm) | +29.0 | 1.06 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | SE/Fe3O4 (20 nm) | −17.9 | 2.78 |
| SE/ZnO (25 nm) | +17.0 | 1.41 | |
| SE/ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | - | - | |
| SE/SiO2 (10–20 nm) | −31.9 | 1.02 | |
| SE/Al2O3 (20–30 nm) | - | - | |
| SE/Al2O3 (50 nm) | +21.0 | 0.67 |
| EV | Normal | Weibull | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | p-Value | Decision | p-Value | Decision | p-Value | Decision |
| Pure SE | 0.2621 | Accepted | 0.1175 | Accepted | 0.2020 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with Fe3O4 (20 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.3170 | Accepted | 0.2484 | Accepted | 0.4167 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.2473 | Accepted | 0.2256 | Accepted | 0.2436 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.2993 | Accepted | 0.9808 | Accepted | 0.4374 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.0262 | Not-Accepted | 0.2699 | Accepted | 0.0387 | Not-Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.0986 | Accepted | 0.5949 | Accepted | 0.1481 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with ZnO (25 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.0250 | Not-Accepted | 0.5068 | Accepted | 0.0564 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.3274 | Accepted | 0.1113 | Accepted | 0.3743 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.5768 | Accepted | 0.6064 | Accepted | 0.7095 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.5845 | Accepted | 0.5523 | Accepted | 0.6087 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.0410 | Not-Accepted | 0.0050 | Not-Accepted | 0.0247 | Not-Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.0394 | Not-Accepted | 0.3584 | Accepted | 0.0889 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.7796 | Accepted | 0.9230 | Accepted | 0.8879 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.2449 | Accepted | 0.1495 | Accepted | 0.2099 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.1931 | Accepted | 0.5805 | Accepted | 0.2398 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.0198 | Not-Accepted | 0.3314 | Accepted | 0.0408 | Not-Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with SiO2 (25 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.9152 | Accepted | 0.7484 | Accepted | 0.9302 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.3551 | Accepted | 0.8744 | Accepted | 0.5429 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.2302 | Accepted | 0.8775 | Accepted | 0.3447 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.0170 | Not-Accepted | 0.5653 | Accepted | 0.0381 | Not-Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.1700 | Accepted | 0.7144 | Accepted | 0.2678 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with Al2O3 (20–30 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.8544 | Accepted | 0.6733 | Accepted | 0.8801 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.1537 | Accepted | 0.8117 | Accepted | 0.2183 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.0068 | Not-Accepted | 0.0111 | Not-Accepted | 0.0066 | Not-Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.3330 | Accepted | 0.0459 | Not-Accepted | 0.3060 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.8477 | Accepted | 0.6342 | Accepted | 0.8440 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with Al2O3 (50 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.0363 | Accepted | 0.6200 | Accepted | 0.0644 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.0009 | Not-Accepted | 0.0056 | Not-Accepted | 0.0012 | Not-Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.7286 | Accepted | 0.3314 | Accepted | 0.6836 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.5240 | Accepted | 0.2928 | Accepted | 0.5125 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.4755 | Accepted | 0.0203 | Not-Accepted | 0.3848 | Accepted |
| 1% | 10% | 50% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Concentration | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) |
| Pure SE | Normal | 49.30 | - | 55.90 | - | 64.00 | - |
| EV | 43.60 | - | 55.60 | - | 65.10 | - | |
| SE-based NFs with Fe3O4 (20 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 69.50 | 40.97 | 75.10 | 34.34 | 81.90 | 27.96 |
| EV | 62.10 | 42.43 | 73.50 | 32.19 | 82.60 | 26.88 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 69.70 | 41.37 | 74.90 | 33.98 | 81.40 | 21.18 |
| EV | 64.00 | 46.79 | 74.10 | 33.27 | 82.30 | 26.42 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 76.10 | 54.36 | 80.60 | 44.18 | 86.00 | 34.37 |
| EV | 69.30 | 58.94 | 78.90 | 41.91 | 86.60 | 33.03 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 83.70 | 69.77 | 86.90 | 55.45 | 90.80 | 41.87 |
| EV | 77.20 | 77.06 | 84.90 | 52.70 | 91.10 | 39.94 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 79.30 | 60.85 | 83.80 | 49.91 | 89.40 | 39.78 |
| EV | 72.20 | 65.60 | 82.10 | 47.66 | 90.00 | 38.25 | |
| SE-based NFs with ZnO (25 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 66.10 | 34.07 | 71.50 | 27.90 | 78.00 | 21.87 |
| EV | 55.60 | 27.52 | 68.40 | 23.02 | 78.70 | 20.89 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 62.00 | 25.76 | 66.30 | 18.60 | 71.60 | 11.87 |
| EV | 58.20 | 33.49 | 66.00 | 18.71 | 72.20 | 10.91 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 60.20 | 22.10 | 66.50 | 18.96 | 74.20 | 15.93 |
| EV | 52.60 | 20.64 | 65.10 | 17.09 | 75.10 | 15.36 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 68.20 | 38.33 | 72.80 | 30.23 | 78.40 | 22.5 |
| EV | 63.90 | 46.56 | 72.40 | 30.22 | 79.20 | 21.66 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 58.10 | 17.84 | 63.10 | 12.88 | 69.30 | 8.28 |
| EV | 56.20 | 28.90 | 64.00 | 15.11 | 70.20 | 7.83 | |
| SE-based NFs with ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 57.60 | 16.83 | 64.20 | 14.84 | 72.90 | 13.90 |
| EV | 44.00 | 0.92 | 60.50 | 8.81 | 73.80 | 13.36 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 58.80 | 19.26 | 63.90 | 14.31 | 70.20 | 9.68 |
| EV | 52.10 | 19.50 | 62.50 | 12.41 | 70.90 | 8.91 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 57.90 | 17.44 | 64.50 | 15.38 | 72.70 | 13.59 |
| EV | 52.90 | 21.33 | 64.50 | 16.01 | 73.80 | 13.36 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 73.40 | 48.88 | 76.80 | 37.38 | 80.80 | 26.25 |
| EV | 68.60 | 57.34 | 75.70 | 36.15 | 81.30 | 24.88 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 64.80 | 31.44 | 70.00 | 25.22 | 76.40 | 19.37 |
| EV | 54.70 | 25.46 | 67.10 | 20.68 | 77.00 | 18.28 | |
| SE-based NFs with SiO2 (25 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 66.40 | 34.68 | 70.60 | 26.29 | 75.80 | 18.43 |
| EV | 63.00 | 44.50 | 70.50 | 26.80 | 76.40 | 17.36 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 62.50 | 26.77 | 67.90 | 21.46 | 74.60 | 16.56 |
| EV | 54.10 | 24.08 | 65.90 | 18.53 | 75.30 | 15.67 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 68.70 | 39.35 | 73.60 | 31.66 | 79.60 | 24.35 |
| EV | 61.80 | 41.74 | 72.10 | 29.68 | 80.30 | 23.35 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 67.00 | 35.90 | 71.00 | 27.01 | 76.00 | 18.75 |
| EV | 58.10 | 33.26 | 68.30 | 22.84 | 76.40 | 17.36 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 64.10 | 30.02 | 69.10 | 23.61 | 75.30 | 17.65 |
| EV | 55.50 | 27.29 | 66.80 | 20.14 | 75.90 | 16.59 | |
| SE-based NFs with Al2O3 (20–30 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 68.30 | 38.53 | 74.40 | 33.09 | 81.90 | 27.96 |
| EV | 62.60 | 43.58 | 73.80 | 32.73 | 82.80 | 27.19 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 68.30 | 38.53 | 82.00 | 46.69 | 86.70 | 35.46 |
| EV | 72.40 | 66.06 | 80.60 | 44.96 | 87.20 | 33.95 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 82.70 | 67.74 | 87.40 | 56.35 | 93.20 | 45.62 |
| EV | 79.80 | 83.03 | 87.70 | 57.73 | 94.00 | 44.39 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 84.50 | 71.39 | 87.70 | 56.88 | 91.60 | 43.125 |
| EV | 82.40 | 88.99 | 87.80 | 57.91 | 92.10 | 41.47 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 72.00 | 46.04 | 78.70 | 40.78 | 87.00 | 35.93 |
| EV | 65.10 | 49.31 | 77.80 | 39.93 | 88.10 | 35.33 | |
| SE-based NFs with Al2O3 (50 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 70.30 | 42.59 | 74.20 | 32.73 | 78.80 | 23.12 |
| EV | 62.70 | 43.81 | 71.90 | 29.32 | 79.20 | 21.66 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 76.00 | 54.15 | 79.50 | 42.21 | 83.90 | 31.09 |
| EV | 70.90 | 62.61 | 78.40 | 41.01 | 84.40 | 29.65 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 76.90 | 55.98 | 83.20 | 48.83 | 91.00 | 42.18 |
| EV | 72.30 | 65.83 | 83.30 | 49.82 | 92.00 | 41.32 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 83.00 | 68.35 | 87.40 | 56.35 | 92.70 | 44.84 |
| EV | 79.10 | 81.42 | 87.10 | 56.65 | 93.40 | 43.47 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 81.80 | 65.92 | 86.70 | 55.09 | 92.60 | 44.68 |
| EV | 80.10 | 83.72 | 87.50 | 57.37 | 93.40 | 43.47 | |
| EV | Normal | Weibull | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | p-Value | Decision | p-Value | Decision | p-Value | Decision |
| Pure SE | 0.5275 | Accepted | 0.5750 | Accepted | 0.5733 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with ZnO (25 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.7823 | Accepted | 0.9705 | Accepted | 0.8702 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.3589 | Accepted | 0.2998 | Accepted | 0.3613 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.9900 | Accepted | 0.4293 | Accepted | 0.9907 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.6970 | Accepted | 0.6941 | Accepted | 0.7461 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.4051 | Accepted | 0.8049 | Accepted | 0.4919 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.0565 | Accepted | 0.0438 | Not-Accepted | 0.0507 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.5412 | Accepted | 0.3017 | Accepted | 0.5162 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.1277 | Accepted | 0.5189 | Accepted | 0.1612 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.3543 | Accepted | 0.6686 | Accepted | 0.4006 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.5753 | Accepted | 0.8512 | Accepted | 0.6822 | Accepted |
| SE-based NFs with SiO2 (10–20 nm) | ||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | 0.4659 | Accepted | 0.6010 | Accepted | 0.5045 | Accepted |
| (0.2 g/L) | 0.7526 | Accepted | 0.3288 | Accepted | 0.7011 | Accepted |
| (0.3 g/L) | 0.8697 | Accepted | 0.7511 | Accepted | 0.8937 | Accepted |
| (0.4 g/L) | 0.1784 | Accepted | 0.5097 | Accepted | 0.2118 | Accepted |
| (0.5 g/L) | 0.4773 | Accepted | 0.7549 | Accepted | 0.5634 | Accepted |
| 1% | 10% | 50% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Distribution | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) | BDV (kV) | Increment (%) |
| Pure SE | Normal | 69.70 | - | 75.40 | - | 82.40 | - |
| EV | 63.70 | - | 74.60 | - | 83.30 | - | |
| SE-based NFs with ZnO (25 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 77.40 | 11.04 | 81.90 | 8.62 | 87.30 | 5.94 |
| EV | 72.10 | 13.18 | 80.90 | 8.440 | 88.00 | 5.642 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 79.90 | 14.63 | 84.20 | 11.67 | 89.60 | 8.73 |
| EV | 75.10 | 17.89 | 83.50 | 11.93 | 90.30 | 8.403 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 82.70 | 18.65 | 86.10 | 14.19 | 90.30 | 9.58 |
| EV | 80.70 | 26.68 | 86.40 | 15.81 | 90.90 | 9.123 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 85.00 | 21.95 | 88.20 | 16.67 | 92.00 | 11.65 |
| EV | 81.30 | 27.62 | 87.50 | 17.29 | 92.50 | 11.04 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 79.00 | 13.34 | 83.30 | 10.47 | 88.60 | 7.52 |
| EV | 73.40 | 15.22 | 82.20 | 10.18 | 89.30 | 7.202 | |
| SE-based NFs with ZrO2 (20–30 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 71.80 | 3.01 | 77.80 | 3.18 | 85.30 | 3.51 |
| EV | 66.90 | 5.02 | 77.70 | 4.150 | 86.30 | 3.601 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 76.80 | 10.18 | 81.80 | 8.48 | 87.90 | 6.67 |
| EV | 73.50 | 15.38 | 82.00 | 9.910 | 88.80 | 6.602 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 81.70 | 17.21 | 85.50 | 13.39 | 90.10 | 9.34 |
| EV | 76.40 | 19.93 | 84.30 | 13.00 | 90.70 | 8.883 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 83.00 | 19.08 | 87.00 | 15.38 | 91.80 | 11.40 |
| EV | 78.70 | 23.54 | 86.30 | 15.68 | 92.40 | 10.92 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 78.50 | 12.62 | 83.30 | 10.47 | 89.20 | 8.25 |
| EV | 73.10 | 14.75 | 81.60 | 9.400 | 89.90 | 7.923 | |
| SE-based NFs with SiO2 (25 nm) | |||||||
| (0.1 g/L) | Normal | 76.80 | 10.18 | 81.90 | 8.62 | 88.10 | 6.91 |
| EV | 71.60 | 12.40 | 81.20 | 8.84 | 88.90 | 6.722 | |
| (0.2 g/L) | Normal | 78.10 | 12.05 | 83.40 | 10.61 | 89.80 | 8.98 |
| EV | 75.10 | 17.89 | 83.70 | 12.19 | 90.70 | 8.883 | |
| (0.3 g/L) | Normal | 86.10 | 23.52 | 89.30 | 18.43 | 93.30 | 13.22 |
| EV | 82.60 | 29.67 | 88.80 | 19.03 | 93.70 | 12.48 | |
| (0.4 g/L) | Normal | 82.00 | 17.64 | 84.90 | 12.59 | 88.50 | 7.40 |
| EV | 77.50 | 21.66 | 83.90 | 12.46 | 88.90 | 6.722 | |
| (0.5 g/L) | Normal | 75.00 | 7.60 | 79.10 | 4.90 | 84.20 | 2.18 |
| EV | 70.10 | 10.04 | 78.30 | 4.95 | 84.90 | 1.920 | |
| Pure SE MIDEL 7131 | Fe3O4 (20 nm) NF at 0.4 g/L | Al2O3 (20–30 nm) NF at 0.3 g/L | Al2O3 (50 nm) NF at 0.4 g/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDIV (kV) | 10.286 | 12.647 | 12.815 | 12.77 |
| St. Dev (kV) | 0.763 | 1.0435 | 0.511 | 0.325 |
| Increment (%) | - | 22.95 | 24.58 | 24.14 |
| PDEV (kV) | 8.9226 | 11.840 | 10.243 | 11.48 |
| St. Dev (kV) | 2.1567 | 0.9922 | 1.352 | 1.054 |
| Increment (%) | - | 32.69 | 14.79 | 28.66 |
| Qavr (pC) | 123.8 | 3.30 | 3.933 | 4.15 |
| St. Dev (pC) | 20.06 | 1.574 | 0.377 | 5.864 |
| Increment (%) | - | −97.33 | −96.82 | −96.64 |
| Qpeak (pC) | 740.44 | 122.68 | 48.95 | 510.6 |
| St. Dev (pC) | 49.250 | 97.07 | 29.23 | 104.20 |
| Increment (%) | - | −83.43 | −93.38 | −31.04 |
| NPDs/s (PDs/s) | 9.20 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 1.16 |
| St. Dev (PDs/s) | 27.686 | 0.00 | 0.408 | 0.408 |
| Increment (%) | - | −93.92 | −90.14 | −86.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khelifa, H.; Beroual, A.; Vagnon, E. Effect of Conducting, Semi-Conducting and Insulating Nanoparticles on AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity of Synthetic Ester: A Statistical Analysis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122105
Khelifa H, Beroual A, Vagnon E. Effect of Conducting, Semi-Conducting and Insulating Nanoparticles on AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity of Synthetic Ester: A Statistical Analysis. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122105
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhelifa, Hocine, Abderrahmane Beroual, and Eric Vagnon. 2022. "Effect of Conducting, Semi-Conducting and Insulating Nanoparticles on AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity of Synthetic Ester: A Statistical Analysis" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122105
APA StyleKhelifa, H., Beroual, A., & Vagnon, E. (2022). Effect of Conducting, Semi-Conducting and Insulating Nanoparticles on AC Breakdown Voltage and Partial Discharge Activity of Synthetic Ester: A Statistical Analysis. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122105







