Morphology Adjustment and Optimization of CuS as Enzyme Mimics for the High Efficient Colorimetric Determination of Cr(VI) in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of CuS
2.3. Activity Analysis
2.4. Investigation of Catalytic Mechanism
2.5. Determination of Cr(VI)
3. Results and Discussion
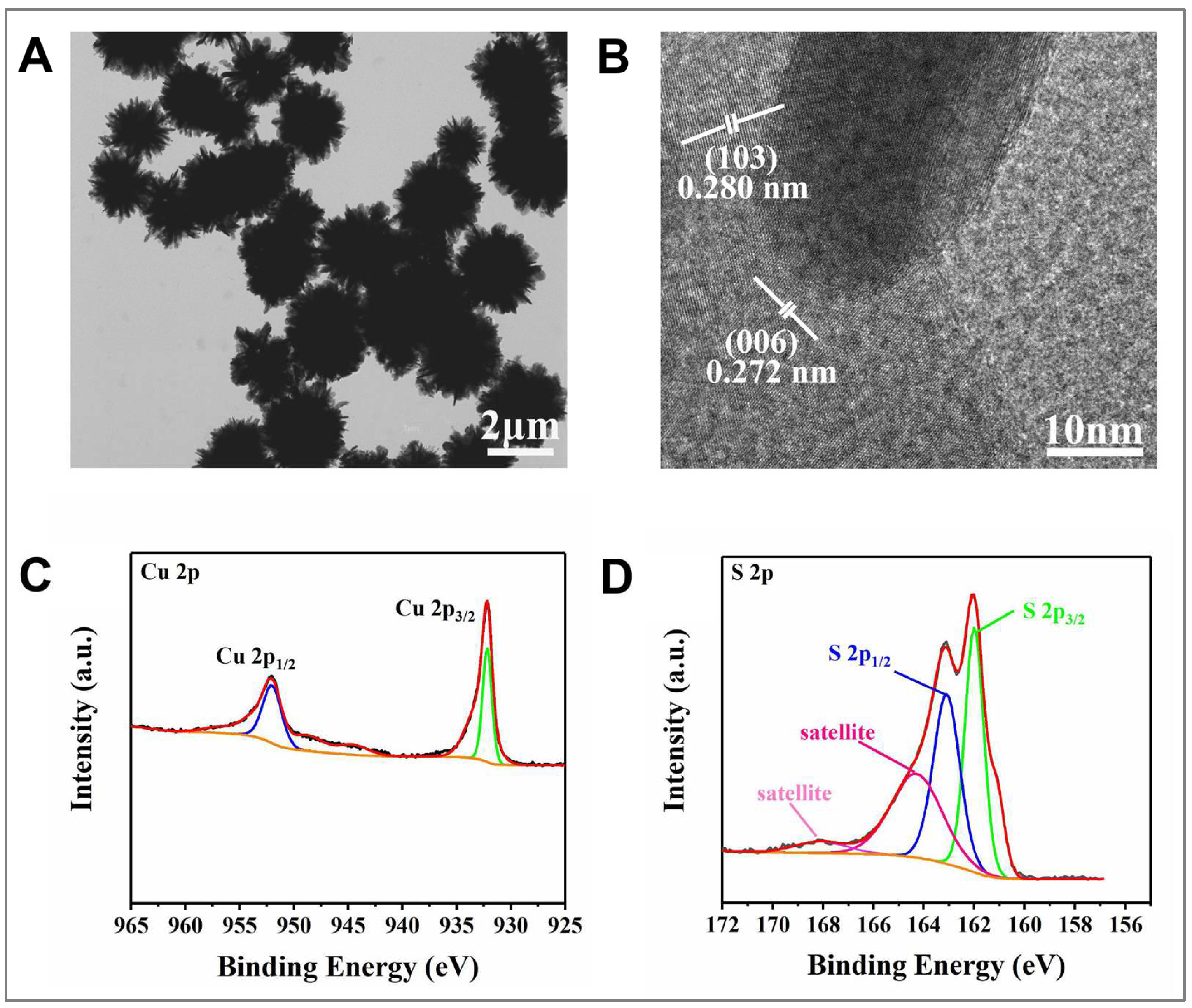
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. Morphology Adjustment and Optimization
3.3. Activity Analysis
3.4. Condition Optimization
3.5. Determination Property Assessment
- 1.1.
- Cu(II) + H2O2 → Cu(III) + •OH + OH−
- 1.2.
- Cu(III) + H2O2 → Cu(II) + •OOH + H+
- 2.1.
- Cr(VI) + H2O2 + H+ → Cr(III) + H2O + O2
- 2.2.
- Cr(III) + H2O2 → Cr(VI) + •OH + OH−
- 3.
- OH + TMB (colorless) → oxTMB (blue color)
3.6. Practical Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Huang, K.; Xie, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.Z. An ecological new approach for treating Cr(VI)-containing industrial wastewater: Photochemical reduction. Water Res. 2016, 93, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Singh, K.A.; Kumar, V. A new approach for indexing groundwater heavy metal pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.N.; Duan, Q.N.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.M.; Gu, J.X.; Ai, W.J.; Dong, X.J. Biotreatment of pyrene and Cr(VI) combined water pollution by mixed bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Huang, R.F.; Ma, X.G.; Guo, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.M. Selective fluorescence sensor based on ion-imprinted polymer-modified quantum dots for trace detection of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7165–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, Z.; Davarani, H.S.S. Selective and sensitive speciation analysis of Cr(VI) and Cr(III), at sub-μgL-1 levels in water samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after electromembrane extraction. Talanta 2016, 161, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Binda, G.; Dossi, C.; Rampazzi, L.; Recchia, S. One-minute highly selective Cr(VI) determination at ultra-trace levels: An ICP-MS method based on the on-line trapping of Cr(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, C.D.; Riotte, J.; Sivry, Y.; Subramanian, S. Electroanalytical detection of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) ions using a novel microbial sensor. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati-Rad, M.; Fattahi, F. A simple equipment and colorimetric method for determination of chloroform in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1100, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.P. Rolling circle amplification based colorimetric determination of Staphylococcus aureus. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choleva, G.T.; Gatselou, A.V.; Tsogas, Z.G.; Giokas, L.D. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of rhodium nanoparticles, and their application to the colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.R.; Zhang, R.F.; Yan, X.Y.; Fan, K.L. Structure and activity of nanozymes: Inspirations for de novo design of nanozymes. Mater. Today 2020, 41, 81–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.W.; Ni, D.L.; Rosenkrans, T.Z.; Huang, P.; Yan, X.Y.; Cai, W.B. Nanozyme: New horizons for responsive biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3683–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, H.J.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.Z.; Pan, J.M.; Qiu, F.X.; Ni, L.; Niu, X.H. Realizing selective detection with nanozymes: Strategies and trends. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.S.; Cirone, J.; Chen, A.C. Fluorescent Fe3O4 quantum dots for H2O2 detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezgebe, M.M.; Ju, A.Q.; Wei, G.; Macharia, K.D.; Guang, S.Y.; Xu, H.Y. Structure based optical properties and catalytic activities of hydrothermally prepared CuS nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Chen, M.X.; Jiang, Y.L.; Chen, M.M.; Ding, Y.N.; Liu, Q.Y. A facile preparation of montmorillonite- supported copper sulfide nano-composites and their application in the detection of H2O2. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2017, 239, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Lin, B.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Guo, M.L.; Cao, Y.J. Nanozyme based on CoFe2O4 modified with MoS2 for colorimetric determination of cysteine and glutathione. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.K.; SivaKarthik, P. Ru-dye grafted CuS and reduced graphene oxide (CuS/rGO) composite: An efficient and photo tunable electrode for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, L.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Hollow CuS microflowers anchored porous carbon composites as lightweight and broadband microwave absorber with flame-retardant and thermal stealth functions. Carbon 2021, 184, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhong, W.; Bai, C.H.; Li, Y.W. Encapsulation of a metal-organic polyhedral in the pores of a metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Shen, Y.; Xu, L.H.; Wang, L.M.; Xing, Y.J. Preparation of flower-like CuS by solvothermal method and its photo-degradation and UV protection. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, C.; Rajendran, V. Synthesis and characterization of CuS nanostructures: Structural, optical, electrochemical and photocatalytic activity by the hydro/solvothermal process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26454–26463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hansen, L.A.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Davulcu, O.; Skalicky, J.J.; Chapman, S.M.; Brüschweiler, R. The michaelis complex of arginine kinase samples the transition state at a frequency that matches the catalytic rate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4846–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swaidan, A.; Borthakur, P.; Boruah, K.P.; Das, R.M.; Barras, A.; Hamieh, S.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, T.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. A facile preparation of CuS-BSA nanocomposite as enzyme mimics: Application for selective and sensitive sensing of Cr(VI) ions. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2019, 294, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, P.; Boruah, P.K.; Das, M.R.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Cu(0) nanoparticle-decorated functionalized reduced graphene oxide sheets as artificial peroxidase enzymes: Application for colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) ions. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Z.; Lin, X.; Liang, H.; Xiao, F.B.; Li, F.F.; Liu, C.; Fan, P.F.; Yang, S.Y.; Liu, Y. Colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) using silver nanoparticles functionalized with PVP. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5819–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.A.; Filik, H.; Demirata, B. Solid-phase extraction of Cr(VI) with magnetic melamine-formaldehyde resins, followed by its colorimetric sensing using gold nanoparticles modified with p-amino hippuric acid. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayyem, S.; Swaidan, A.; Barras, A.; Dolci, M.; Faridbod, F.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Colorimetric detection of chromium (VI) ion using poly (N-phenylglycine) nanoparticles acting as a peroxidase mimetic catalyst. Talanta 2021, 226, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotech. 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Majeed, S.; Xu, G. Copper nanoclusters as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 762, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Du, H.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Q.; Bian, B. Higher catalytic activity of porphyrin functionalized Co3O4 nanostructures for visual and colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Material | Line Range (nM) | Detection Limit (nM) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuS | 60–340 | 1.07 | This work |
| CuS-BSA | 0–100 and 1 × 103–2 × 104 | 50 and 6.8 × 103 | [25] |
| frGO-Cu | 0–200 | 67 | [26] |
| PVP-AgNPs | 1 × 102–2.4 × 103 | 34 | [27] |
| Fe3O4@MFR | 50–3000 | 38 | [28] |
| Sample | Spiked (nM) | This Method | Contrast Method (1,5-Diphenylcarbazide Spectrophotometry) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured (nM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Measured (nM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Qianhu Lake Water | 0 | ND | / | / | ND | / | / |
| 100 | 93.6 | 93.6 | 4.71 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 3.19 | |
| 200 | 208 | 104 | 3.08 | 195 | 97.5 | 2.26 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, X.; Ge, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, L. Morphology Adjustment and Optimization of CuS as Enzyme Mimics for the High Efficient Colorimetric Determination of Cr(VI) in Water. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122087
Tu X, Ge L, Deng L, Zhang L. Morphology Adjustment and Optimization of CuS as Enzyme Mimics for the High Efficient Colorimetric Determination of Cr(VI) in Water. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122087
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Xinman, Linhong Ge, Lamei Deng, and Li Zhang. 2022. "Morphology Adjustment and Optimization of CuS as Enzyme Mimics for the High Efficient Colorimetric Determination of Cr(VI) in Water" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122087
APA StyleTu, X., Ge, L., Deng, L., & Zhang, L. (2022). Morphology Adjustment and Optimization of CuS as Enzyme Mimics for the High Efficient Colorimetric Determination of Cr(VI) in Water. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122087






