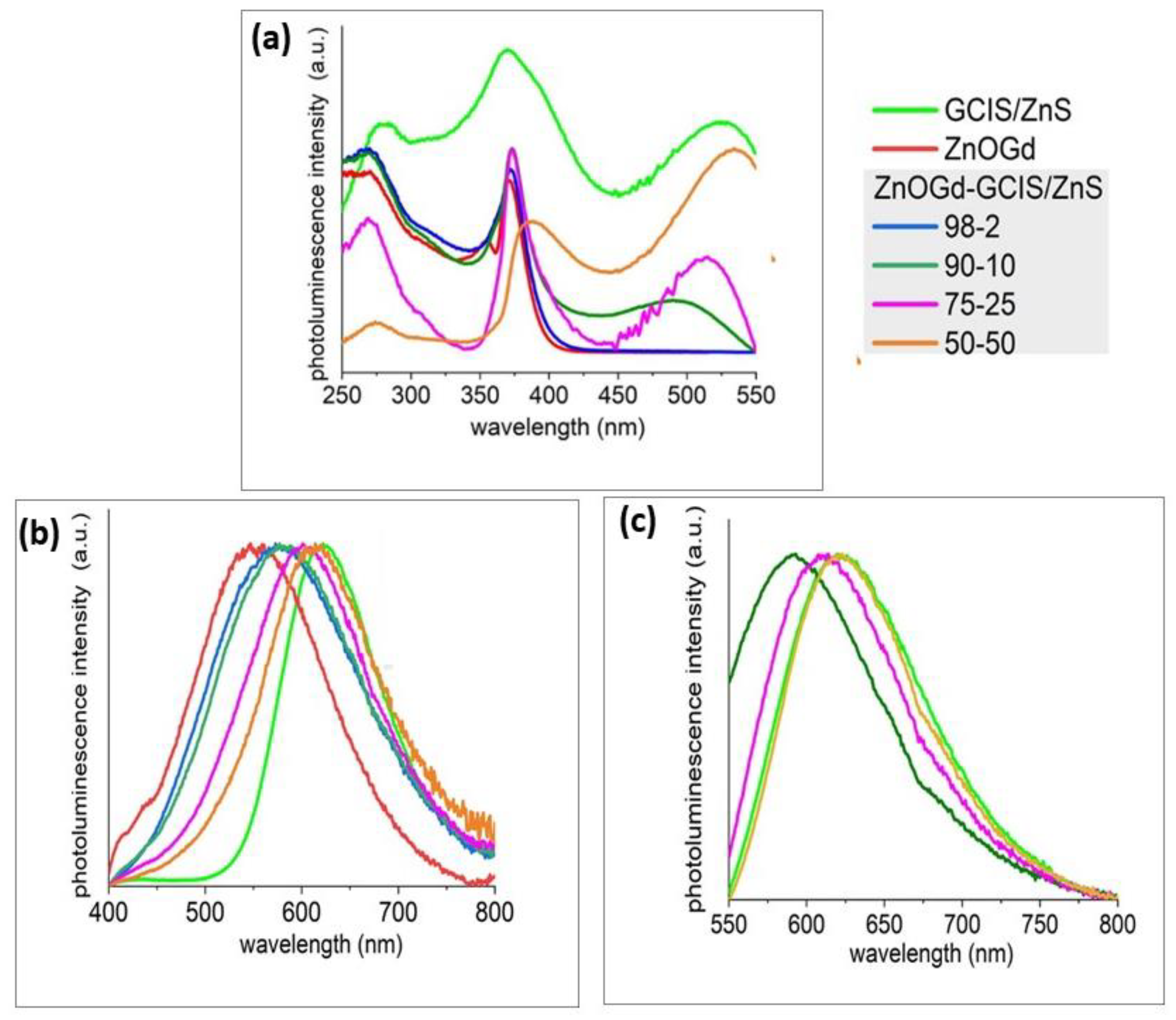
Magnetic and Highly Luminescent Heterostructures of Gd3+/ZnO Conjugated to GCIS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Multimodal Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Gd3+/ZnO Quantum Dot (Qdot) Synthesis
2.2.2. Gadolinium, Copper, Indium, and Sulphur/Zinc Sulphide (GCIS/ZnS) Qdots
2.2.3. Heat Treatment to Promote Qdot Junctions
2.2.4. Qdot Surface Modification
2.2.5. Qdot Association with Lipid Nanocapsules
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Evaluation of Qdot Luminescent Properties
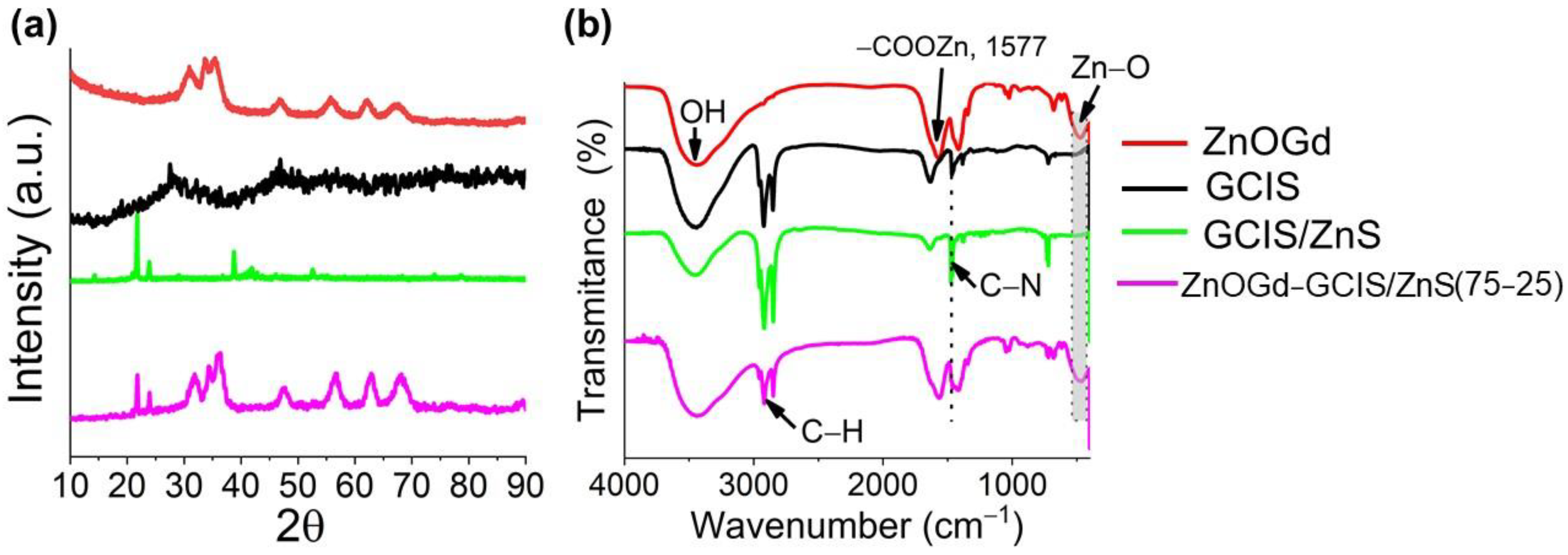
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
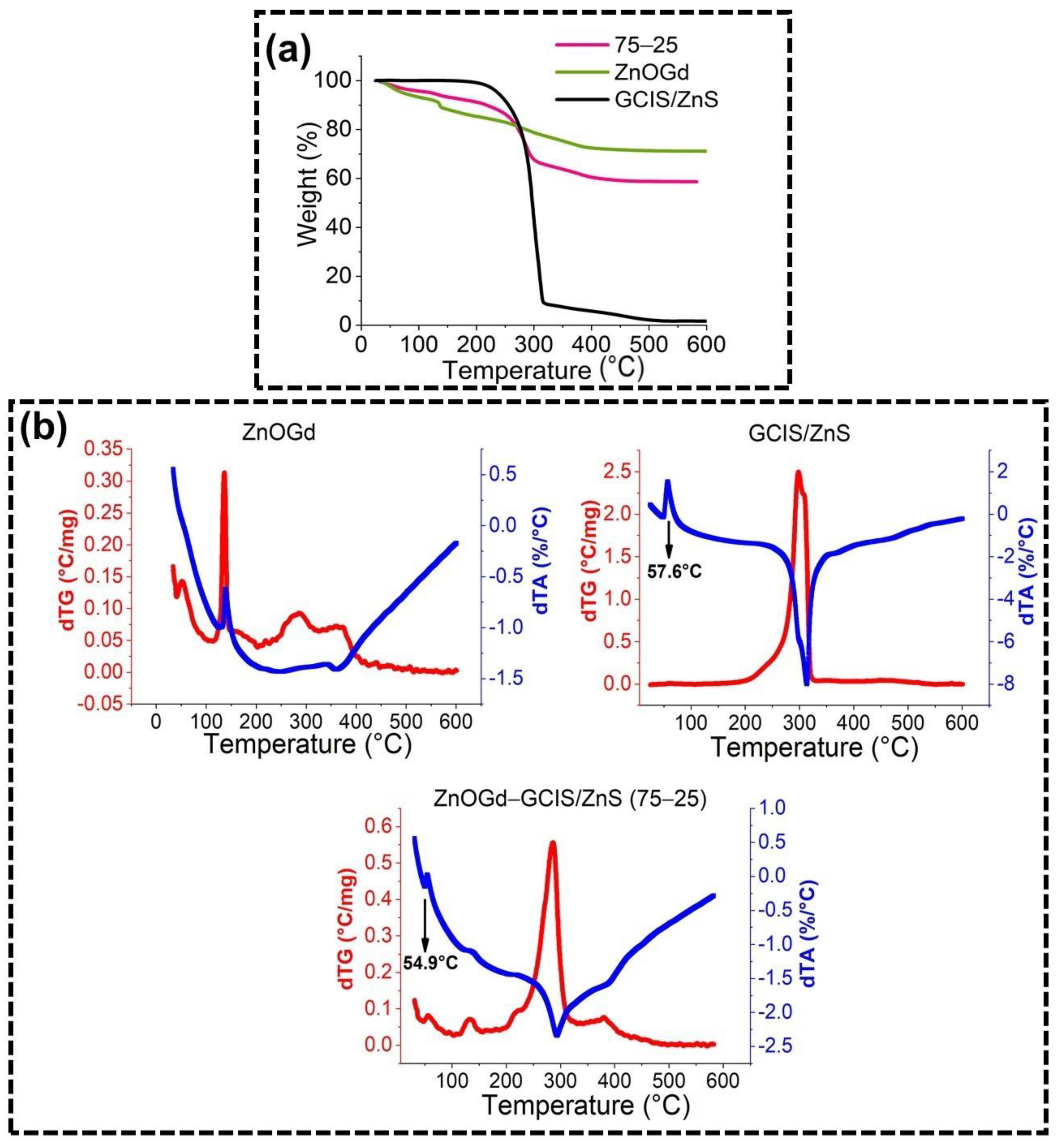
2.3.5. Thermogravimetric (TG) Analysis
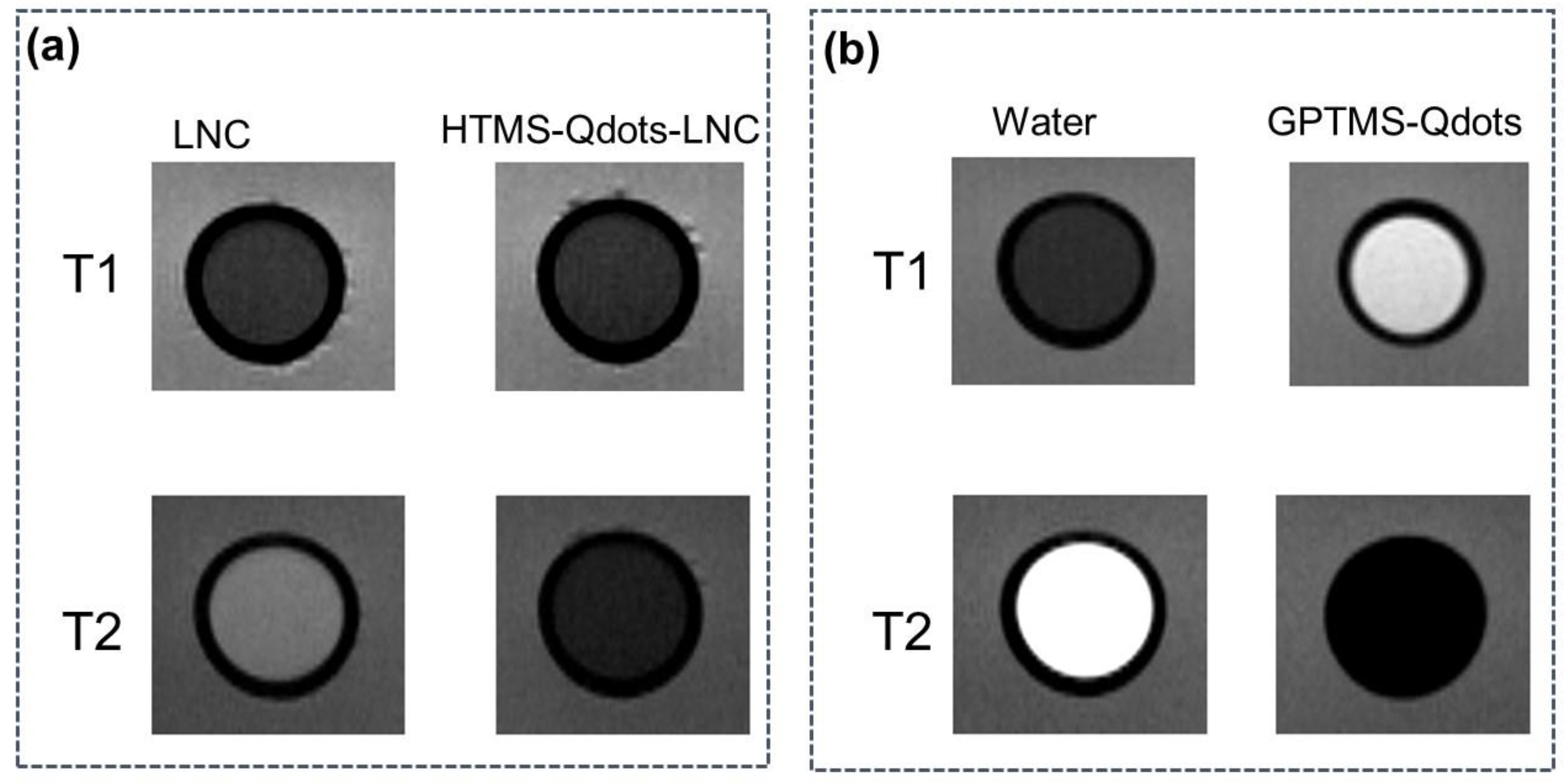
2.3.6. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of GPTMS-Qdots Dispersed in Water, and Hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HTMS)-Qdots within an Lipid Nanocapsule (LNC) Preparation
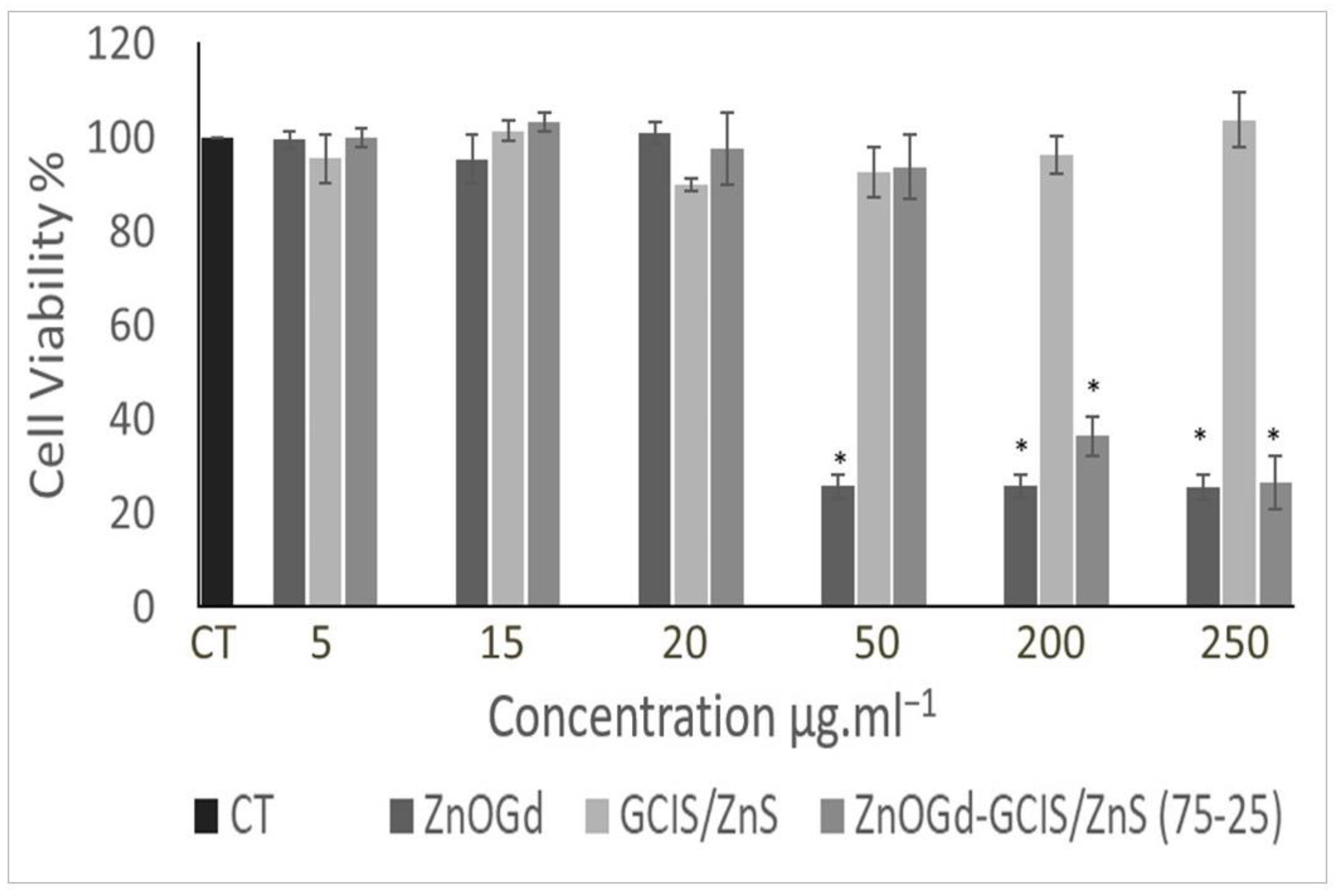
2.3.7. Cytotoxicity Assay Using Resazurin Test
2.3.8. Cell Uptake Assay
3. Results and Discussions
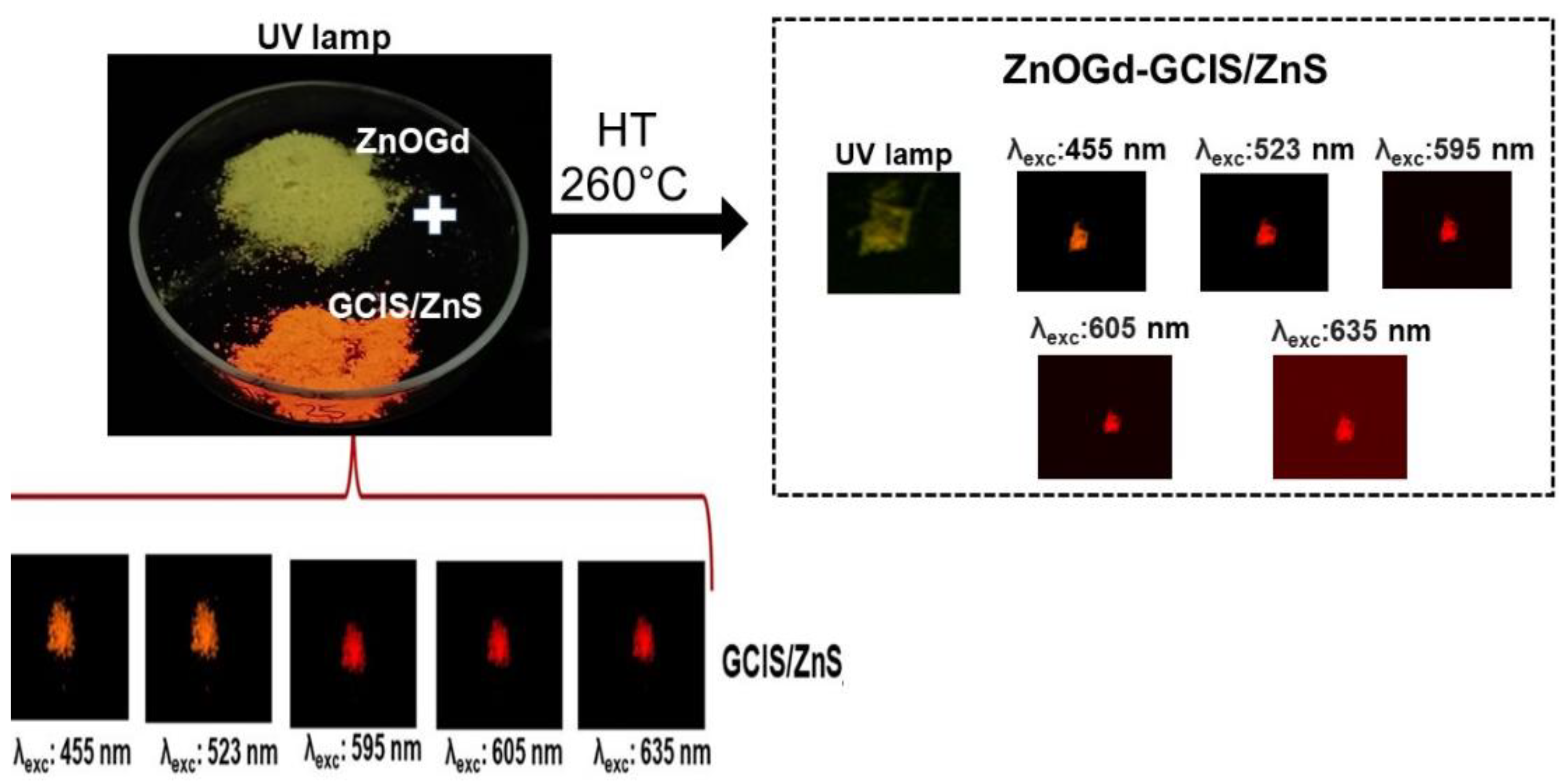
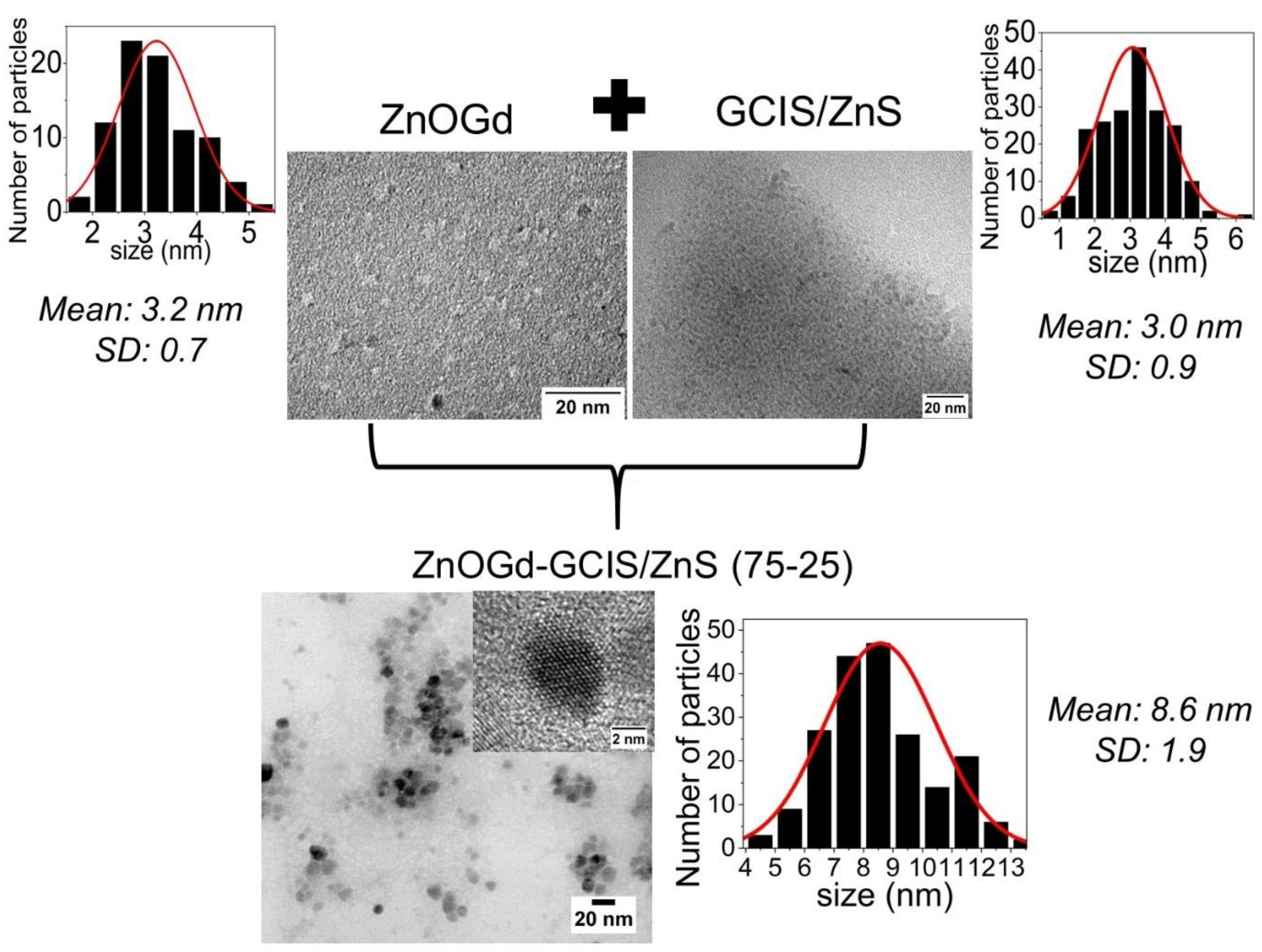
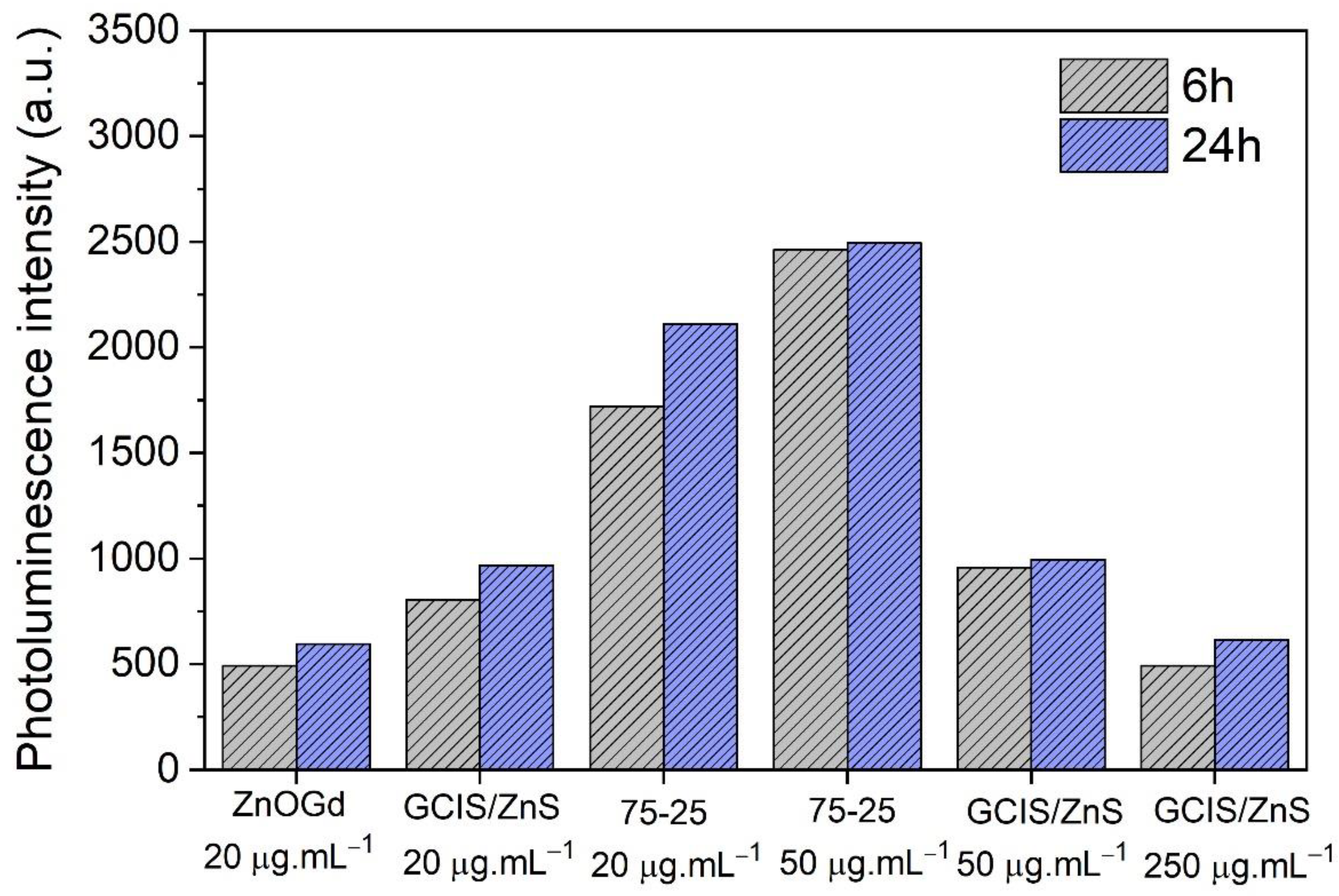
3.1. Qdot Characterization
3.2. Magnetic Resonance Images of GPTMS-Qdots Dispersed in Water and HTMS-Qdots within LNC Preparation
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.4. Cell Uptake Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dazzazi, A.; Coppel, Y.; In, M.; Chassenieux, C.; Mascalchi, P.; Salomé, L.; Bouhaouss, A.; Kahn, M.L.; Gauffre, F. Oligomeric and polymeric surfactants for the transfer of luminescent ZnO nanocrystals to water. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.J. A review on nanostructured carbon quantum dots and their applications in biotechnology, sensors, and chemiluminescence. Talanta 2019, 196, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, W.; Gong, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, N.; Yang, W.; Tu, Y.; Fang, X.; Chang, J. Facile synthesis of Gd–Cu–In–S/ZnS bimodal quantum dots with optimized properties for tumor targeted fluorescence/MR in vivo imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18759–18768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Xu, C.; Gu, B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Ba, L.; Xiao, Z. Effects of mg incorporation on microstructure and optical properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Sol-gel Method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, S.; Kakkar, R. ZnO quantum dots for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2013, 4, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, B.L.; Caetano, B.L.; Chiari-Andréo, B.G.; Pietro, R.C.L.R.; Chiavacci, L.A. Increased antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles: Influence of size and surface modification. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Engle, J.W.; Nickles, R.J.; Wang, X.; Cai, W. Cancer-targeted optical imaging with fluorescent zinc oxide nanowires. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3744–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissi, N.C.; Hammer, P.; Chiavacci, L.A. Surface modification of ZnO quantum dots by organosilanes and oleic acid with enhanced luminescence for potential biological application. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 015027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Krishnakumar, B.; Sobral, A.J.; Koh, J. Bio-based (chitosan/PVA/ZnO) nanocomposites film: Thermally stable and photoluminescence material for removal of organic dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Norello, R.; Abraham, A.N.; Tetienne, J.-P.; Karle, T.J.; Lui, E.W.C.; Xia, K.; Tran, P.A.; O’Connor, A.J.; Mann, B.G.; et al. Biocompatible and biodegradable magnesium oxide nanoparticles with in vitro photostable near-infrared emission: Short-term fluorescent markers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monici, M. Cell and tissue autofluorescence research and diagnostic applications. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sun, Z.; Li, R.; Dong, M.; Zhang, L.; Qi, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. ZnO nanocomposites modified by hydrophobic and hydrophilic silanes with dramatically enhanced tunable fluorescence and aqueous ultrastability toward biological imaging applications. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čepin, M.; Jovanovski, V.; Podlogar, M.; Orel, Z.C. Amino-and ionic liquid-functionalised nanocrystalline ZnO via silane anchoring–an antimicrobial synergy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussodia, R.-O.; Balan, L.; Merlin, C.; Mustin, C.; Schneider, R. Biocompatible and stable ZnO quantum dots generated by functionalization with siloxane-core PAMAM dendrons. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaia, E.B.; Kaminski, R.C.K.; Caetano, B.L.; Briois, V.; Chiavacci, L.A.; Bourgaux, C. Surface modified Mg-doped ZnO QDs for biological imaging. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2015, 7, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowik, J.; Miodyńska, M.; Bajorowicz, B.; Mikołajczyk, A.; Lisowski, W.; Klimczuk, T.; Kaczor, D.; Medynska, A.Z.; Malankowska, A. Optical and photocatalytic properties of rare earth metal-modified ZnO quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Bian, H.; Gao, L.; Cai, P.; Luo, X. Strongly emitting and long-lived silver indium sulfide quantum dots for bioimaging: Insight into co-ligand effect on enhanced photoluminescence. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, F.; Corbel, S.; Alem, H.; Pontvianne, S.; Balan, L.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. ZnO nanoparticles sensitized by CuInZnxS2+x quantum dots as highly efficient solar light driven photocatalysts. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, L.; Anderson, M.A. Semiconductor clusters in the sol-gel process: Quantized aggregation, gelation, and crystal growth in concentrated zinc oxide colloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 2826–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenkamp, E.A. Synthesis and Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5566–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xin, W.; Yao, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, W.; Yang, B.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Cu–In–S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots in 1-Dodecanethiol for efficient light-emitting diodes with an external quantum efficiency of 7.8%. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8939–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.; Benoit, J. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Kim, J.; Na, H.B.; Kim, D.; Baek, J.S.; Ko, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Hyeon, T. Wrap–bake–peel process for nanostructural transformation from β-FeOOH nanorods to biocompatible iron oxide nanocapsules. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoufi, D.; Raoufi, T. The effect of heat treatment on the physical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, B.L.; Briois, V.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Meneau, F.; Santilli, C.V. Revisiting the ZnO Q-dot formation toward an integrated growth model: From coupled time resolved UV–Vis/SAXS/XAS data to multivariate analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 121, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Purcell-Milton, F.; Gun’Ko, Y.K. Optical properties, synthesis, and potential applications of Cu-based ternary or quaternary anisotropic quantum dots, Polytypic Nanocrystals, and Core/Shell Heterostructures. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjetovic, Z.; Jarrett, S.G.; Lee, E.F.; Duprey, C.; Reiter, R.J.; Slominski, A.T. Melatonin and its metabolites protect human melanocytes against UVB-induced damage: Involvement of NRF2-mediated pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, H.; Park, M.H.; Owens, E.A.; Wada, H.; Henary, M.; Handgraaf, H.J.M.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Frangioni, J.V.; Choi, H.S. Structure-inherent targeting of near-infrared fluorophores for parathyroid and thyroid gland imaging. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromova, M.; Lefrançois, A.; Vaure, L.; Agnese, F.; Aldakov, D.; Maurice, A.; Djurado, D.; Lebrun, C.; De Geyer, A.; Schülli, T.U.; et al. Growth Mechanism and Surface State of CuInS2 Nanocrystals Synthesized with Dodecanethiol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15748–15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Dong, C.; Li, L.; Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Ren, J. Non-blinking (Zn)CuInS/ZnS Quantum Dots Prepared by In Situ Interfacial Alloying Approach. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabharathi, J.; Sundari, G.A.; Thanikachalam, V.; Jeeva, P.; Panimozhi, S. A dodecanethiol-functionalized Ag nanoparticle-modified ITO anode for efficient performance of organic light-emitting devices. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38923–38934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdas, T.; Distaso, M.; Kuhri, S.; Winter, B.; Birajdar, B.; Spiecker, E.; Guldi, D.M.; Peukert, W. The effects of post-processing on the surface and the optical properties of copper indium sulfide quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, H.; Mahjoub, A.; Khavar, A.C. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/CuInS2 nanocomposite and investigation of their photocatalytic properties under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 318, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Outokesh, M.; Tayebi, M.; Shafikhani, A.; Şengör, S.S. ZnO quantum dots-graphene composites: Formation mechanism and enhanced photocatalytic activity for degradation of methyl orange dye. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.P.; Chin, W.S. Dodecanethiol-protected copper/silver bimetallic nanoclusters and their surface properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22228–22236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinazzo, E. Propriedades Luminescentes de Membranas de Polidimetilsiloxano Contendo Nanopartículas de Fluoreto de Lantânio Dopado com íons Lantanídeos; State University of Campinas: Campinas, SP, Brazil, 2013; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, C.; Iso, Y.; Isobe, T.; Sasaki, H. Preparation and photoluminescence properties of yellow-emitting CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots embedded in TMAS-derived silica. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7936–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulaich, A.; Tilmaciu, C.-M.; Merlin, C.; Mercier, C.; Guilloteau, H.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Physicochemical properties and cellular toxicity of (poly)aminoalkoxysilanes-functionalized ZnO quantum dots. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 335101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Earhart, C.; Ying, J. Synthesis of water-soluble and functionalized nanoparticles by silica coating. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5074–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Abo-Zeid, Y.; Bear, J.C.; Davies, G.-L.; Lei, X.; Williams, G.R. SiO2-coated layered gadolinium hydroxides for simultaneous drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 286, 121291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ZnOGd (%) | GCIS/ZnS (%) |
|---|---|
| 98 | 2 |
| 90 | 10 |
| 75 | 25 |
| 50 | 50 |
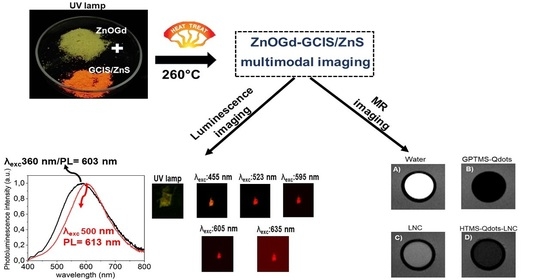
| Sample | PL (nm) λexc: 360 nm | PL (nm) λexc: 500 nm |
|---|---|---|
| ZnOGd | 550 | N.D |
| GCIS/ZnS | 620 | 620 |
| 98-2 | 576 | N.D |
| 90-10 | 580 | 593 |
| 75-25 | 603 | 613 |
| 50-50 | 618 | 620 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lallo da Silva, B.; Lemaire, L.; Benoit, J.-P.; Borges, F.H.; Gonçalves, R.R.; Amantino, C.F.; Primo, F.L.; Chiavacci, L.A. Magnetic and Highly Luminescent Heterostructures of Gd3+/ZnO Conjugated to GCIS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Multimodal Imaging. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071817
Lallo da Silva B, Lemaire L, Benoit J-P, Borges FH, Gonçalves RR, Amantino CF, Primo FL, Chiavacci LA. Magnetic and Highly Luminescent Heterostructures of Gd3+/ZnO Conjugated to GCIS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Multimodal Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071817
Chicago/Turabian StyleLallo da Silva, Bruna, Laurent Lemaire, Jean-Pierre Benoit, Fernanda Hediger Borges, Rogéria Rocha Gonçalves, Camila Fernanda Amantino, Fernando Lucas Primo, and Leila Aparecida Chiavacci. 2021. "Magnetic and Highly Luminescent Heterostructures of Gd3+/ZnO Conjugated to GCIS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Multimodal Imaging" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071817
APA StyleLallo da Silva, B., Lemaire, L., Benoit, J.-P., Borges, F. H., Gonçalves, R. R., Amantino, C. F., Primo, F. L., & Chiavacci, L. A. (2021). Magnetic and Highly Luminescent Heterostructures of Gd3+/ZnO Conjugated to GCIS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Multimodal Imaging. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071817