Abstract
Spin-to-charge conversion is a central process in the emerging field of spintronics. One of its main applications is the electrical detection of spin currents, and for this, the inverse spin Hall effect (ISHE) has become one of the preferred methods. We studied the thickness dependence of the ISHE in iridium oxide (IrO) thin films, producing spin currents by means of the spin Seebeck effect in FeO/IrO bilayers prepared by pulsed laser deposition (PLD). The observed ISHE charge current density, which features a maximum as a consequence of the spin diffusion length scale, follows the typical behaviour of spin-Hall-related phenomena. By fitting to the theory developed by Castel et al., we find that the spin Hall angle scales proportionally to the thin film resistivity, , and obtains a value for the spin diffusion length of nm. In addition, we observe a negative for every studied thickness and temperature, unlike previously reported works, which brings the possibility of tuning the desired functionality of high-resistance spin-Hall-based devices. We attribute this behaviour to the textured growth of the sample in the context of a highly anisotropic value of the spin Hall conductivity in this material.
1. Introduction
The spin Hall effect (SHE) refers to the creation of a spin current transverse to a charge current in a nanometric metallic material [1,2,3,4,5]. It emerges in materials with high spin-orbit coupling (SOC), which endows electrons with a spin-dependent component of velocity perpendicular to the charge current. The specification for nanodimensions is due to the magnitude of the decay lengths of spin currents [6]. The reciprocal of SHE is known as the inverse spin Hall effect (ISHE). It appears as a conventional charge current induced by a transverse spin current in metallic nanostructured materials with high SOC [5,7,8]. This charge current leads to charge accumulation at the edges of the device that can be easily detected as an electrical voltage. The spin-to-charge conversion by the ISHE is thus one of the preferred methods for spin current detection. An important parameter in this regard is the spin Hall angle , which determines the efficiency of the spin-to-charge conversion:
where and denote the spin and charge current densities, respectively, and is the spin polarization. The spin Hall conductivity in a metal is here defined as , where is the component of the conductivity tensor for up-spin polarized and down-spin polarized carriers. This transverse conductivity is related to its resistivity counterpart by
where is the longitudinal resistivity and we have taken the limit [9,10]. Renaming the longitudinal electrical conductivity and resistivity as and , the spin Hall angle can be expressed as
where is the spin Hall resistivity.
The SHE and ISHE arise from extrinsic and intrinsic microscopic mechanisms [10,11]. The extrinsic SHE/ISHE results from spin-asymmetric scattering at impurities, boundaries or defects (non-periodic or disorder potential) [1,2,3,12]. Skew scattering [13] and side jump [14] mechanisms are recognized as sources of spin-dependent displacement of electrons during scattering events: skew scattering is the dependence of the scattering angle sign on the electron spin, and side jump refers to a transverse shift of the electron trajectory that is dependent on the spin. The intrinsic contribution to the SHE/ISHE occurs between scattering events and arises from the band structure of the perfect crystal (periodic or lattice potential) [15,16].
Usually, heavy transition metals, such as Au or Pt, are employed for spin-to-current conversion by the SHE or ISHE. However, these noble metals show extremely low electrical resistivity , and whereas this fact represents an advantage when they are used for spin current injection (by the SHE), it degrades their performance in spin current detection (by the ISHE) since the generated voltage is proportional to [8]:
In the search for materials with good performance as spin current detectors via the ISHE, transition metal oxides (TMOs) have attracted the interest of the community because of their strong SOC [17] and moderate electrical conductivities [18,19]. In particular, the family of iridates shows intriguing phenomena such as metal-insulator transitions [20,21], exotic magnetic ground states [22,23] or novel topological phenomena [21,24,25]. The parental compound IrO, a metallic material showing no magnetic order, has been targeted as a highly valid spin current detector. Fujiwara and coworkers studied the performance of polycrystalline and amorphous samples of IrO in spin absorption experiments carried out with non-local spin-valve structures [19], finding a value for one order of magnitude larger than those of noble metals. In contrast, Qiu et al. studied the performance of IrO in a longitudinal spin Seebeck effect (LSSE) device and found it to be significantly lower than that of Pt [26]. In an LSSE experiment, a spin current was excited in a magnetically ordered material (FM) as a consequence of the application of a thermal gradient [27,28,29]. The current consensus is that this spin Seebeck-spin current is transported by the collective excitations of local moments (magnons) [28,30], and it is therefore better studied in insulators where there is no contribution of free carriers to the output. The thermal spin current is injected into an adjacent non-magnetic (NM) material (interface normal to the spin current, which in turn is parallel to the applied thermal gradient), where it is converted into a transverse charge current by means of the ISHE. Qiu et al. [26] attributed the small signal of the ISHE found in IrO in their experiment to a low spin mixing conductance, a parameter that quantifies the efficiency of the transmission of spin across the interface between two layers.
The electronic band structure of IrO has been theoretically [31,32,33,34,35,36,36] and experimentally [17,33,36,37,38,39,40,41] addressed as early as 1977 [42]; nevertheless, it was the experimental evidence of very efficient spin-to-charge conversion [19] that renewed interest in this fascinating material and triggered many works dedicated to explaining the large SHE/ISHE. However, the precise role of the different SHE and ISHE mechanisms in IrO has not yet been clearly elucidated.
In this paper, we performed a systematic study of the ISHE detection of the SSE in –FeO/IrO bilayer structures for different thicknesses of the IrO layer, ranging from 2 to 22 nm. We obtained the value of the spin diffusion length of IrO and found that the spin Hall angle is proportional to the longitudinal charge resistivity, ; equivalently, the value of is constant and independent of the longitudinal charge conductivity , and scales as (see Equations (2) and (3)).
2. Materials and Methods
FeO/IrO bilayers were grown using the pulsed laser deposition technique on AlO(0001) substrates. Both layers were consecutively in situ deposited in the same vacuum chamber without exposure to room atmosphere in between. Each sample was prepared according to the following procedure: first, PLD was used to deposit a layer from a 99.99% pure FeO (magnetite) target under vacuum conditions. The repetition rate of the KrF excimer 248 nm wavelength laser was set to 10 Hz with a 3.7 J/cm fluence. The base pressure in the deposition chamber was ∼10 Torr. Second, the FeO layer was in situ annealed in an oxygen atmosphere ( mTorr) at 325 ℃ to transform it into the FeO phase (maghemite), a ferrimagnetic insulator [43]. Finally, the IrO detection layer was PLD grown at the same temperature and oxygen pressure by striking a 99.9% pure IrO target with a fluence of 1.6 J/cm at a 3 Hz repetition rate. The thickness of maghemite was kept at 50 nm throughout every sample, whereas the thickness of IrO, , was varied from 2 to 22 nm.
X-ray characterization of the samples was performed in a high-resolution Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer Prior to LSSE experiments, the longitudinal resistivities of the different IrO layers were determined using an in-line four probe geometry to ensure the metallic behaviour of IrO thin films, measuring the characteristic curves between A.
3. Results and Discussion
The scans around the (0006) substrate Bragg peak are shown in Figure 1a. The (200) IrO peak is visible and increases in intensity as the layer thickness is increased. In Figure 1b, a wide-range scan for one of the samples is also provided: only the {100} reflections of IrO are present, indicating that this sample is strongly textured in this direction. Scherrer’s empirical formula [44] was applied to the diffraction peak of the two thickest samples (= 22 and 16 nm) in order to determine the crystalline domain size of IrO in the [100] direction, yielding ≈13 nm and ≈11 nm. The domain size is smaller than the respective thicknesses of the IrO layer, and therefore, the single-crystalline orientation must be discarded. However, the obtained crystal coherence lengths are close to the thicknesses, indicating a texture preference for the [100] direction. Regarding FeO, it grows on top of AlO in the [111] orientation; the inset in Figure 1 displays, for one of the samples, a more extended range including the (222) Bragg peak of maghemite as an illustrative example. This was also confirmed by the longer-range pattern presented in Figure 1b, where only the {111} reflections of FeO are visible.
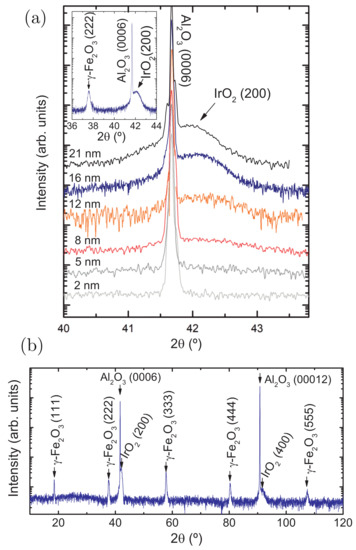
Figure 1.
(a) Symmetric diffraction patterns around the (0006) AlO Bragg peak. Inset: longer-range measurement for the sample with a 16 nm-thick IrO layer, including the (222) diffraction peak of FeO; (b) Wide-range symmetric XRD scan for the sample with a 16 nm-thick IrO layer.
The measured characteristic curves displayed ohmic behaviour for all samples (see the inset of Figure 2a), which proves the metallic nature of IrO. As shown in Figure 2a, the resistivity increases with decreasing thickness, a fact that may suggest a variable density of defects as the growth progresses. However, this behaviour is also consistent with recent theoretical works that predict changes in the metallic properties of IrO through thickness variation [45] and epitaxial strain along the c axis [33].
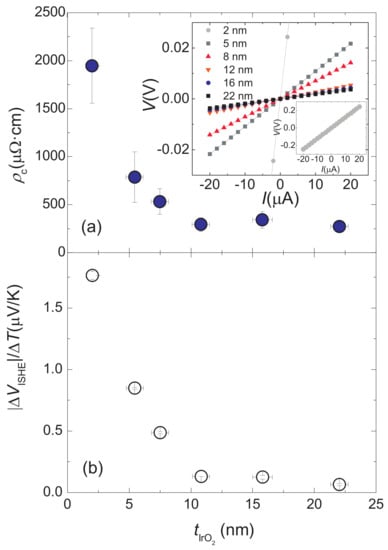
Figure 2.
(a) Longitudinal resistivities of samples. The characteristic curves measured to determine the electrical resistances of the IrO thin films are displayed in the inset. The characteristic curve of the thinner sample is zoomed out; (b) Voltage detected via the ISHE from LSSE experiments.
For every FeO/IrO bilayer, we measured the output voltages for different thermal drops applied to thermally excite spin currents by means of the LSSE. Following a widespread practice, these quantities have been normalized by the total thermal difference using the slopes of the linear fits of as a function of different . The data of the output voltages measured per applied Kelvin for every thickness of IrO are depicted in Figure 2b. The common behaviour of and indicates that strongly dominates the dependence on . However, the contribution to this dependence that interests us is that of the spin-to-charge conversion process, as expressed in Equation (1). Therefore, we calculate as , where represents the distance between the electrical contacts used to measure . In this way, we eliminate the influence of on the thickness dependence of Equation (4) and focus on that of . The obtained values are plotted in Figure 3. We note that indeed features a peak at low values of followed by a monotonic decrease for higher values. This behaviour constitutes the fingerprint of a typical diffusion mechanism with a characteristic length, , comparable to the layer thickness [6]. This curve is similar to that reported for other ISHE media, such as prototypical Pt [46,47].
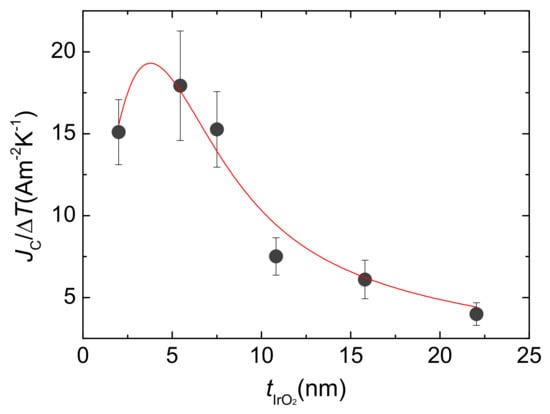
Figure 3.
Symbols: ISHE current density normalized by the thermal drop through the sample for every IrO thickness. Line: fit to Equation (6).
To extract quantitative information about , we make use of the model developed by Castel et al., which relates the thickness of an NM layer to the detected transverse ISHE voltage caused by a spin current [46]. According to this model, the NM thickness (t) dependence of can be expressed as
where represents the spin-Hall angle, is the spin mixing conductance of the FM/NM interface, denotes the spin diffusion length of the NM layer and is its electrical resistivity. Equivalently:
In their work [46], based on spin-pumping experiments with YIG/Pt bilayers, Castel and coworkers supposed that the ISHE originated from extrinsic mechanisms due to skew scattering and therefore , yielding a constant [9,10,11]. However, such an assumption does not explain the observed experimental results. Equation (5) will only adequately describe the experimental data when taking (i.e., is independent of and ). Admitting this scenario, a fit of Equation (6) to the current density data converges, providing a value for the spin diffusion length of IrO of nm. This result rules out a dominant role of skew scattering in the ISHE process, as this mechanism is characterized by a constant [9,10,11].
The behaviour of the absolute ISHE charge current above the spin diffusion length also provides information about the mechanism responsible for the ISHE. If skew scattering is the main term, assuming that the injected spin current is the same for all samples (since is maintained constant), then would be independent of and thus, of , which would make saturate to a constant value for . In contrast, in the case that the spin Hall angle scales as , needs to be normalized by to observe a saturation level, as the efficiency of the spin-to-charge conversion (represented by ) increases with increasing . As shown in Figure 4, the experimental data follow this latter trend, supporting the scaling and thus excluding skew scattering as the main ISHE mechanism in the experiment.
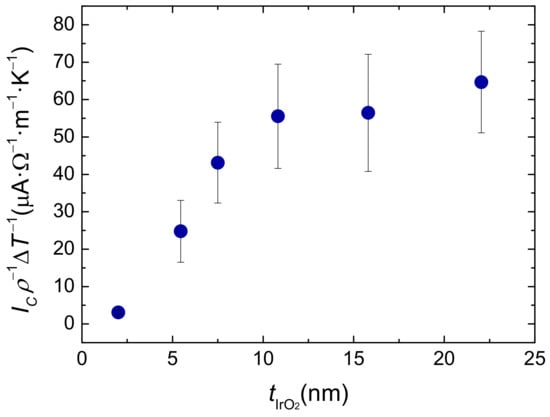
Figure 4.
Evolution of with the thickness of IrO.
Therefore, these results entail that either the intrinsic mechanism or the extrinsic side jump must govern the ISHE in IrO thin films with [100] preferential texture because both of them share the same dependence on resistivity [9,10,11,14].
However, the separation of intrinsic and side jump contributions has been a long-standing problem, also controversial from a theoretical point of view. Some authors [48] predicted that a side jump is always negligible compared to skew scattering (by a factor of ); in contrast, others concluded that both contributions can be comparable [49,50]. In either case, the intrinsic contribution is the most likely candidate to play the dominant role in our experiment, as we discuss in the following.
First, if we accept the result in reference [48]—side jump is generally negligible relative to skew scattering—considering that we have ruled out a predominant role of skew scattering, we can conclude that the intrinsic SOC governs the ISHE. Alternatively, we examine the situation that aligns with the results in [49,50,51]—that the side jump is not always negligible. In this regard, we recall that the side jump contribution to is proportional to the impurity concentration [11,49]; this is why, although it may dominate the overall effect at sufficiently high impurity concentrations, its contribution to the spin Hall conductivity is usually smaller than those of skew scattering or the intrinsic mechanism [11]. As a consequence, the side jump is usually manifested either in doped systems or alloys (not our case) or at low temperatures, where it gains importance and may become comparable to skew scattering even at low impurity concentrations [51,52,53]. Nevertheless, our experiments were performed at room temperature. Additionally, Fert and Levy showed that for impurities at the beginning and end of the series (Lu, Hf, Ir, Pt), the side jump contribution at impurity concentrations of ≈2% is much smaller than the skew scattering contribution [49]. In view of all of the above, it seems reasonable to accept that the ISHE in thin films of IrO is most likely driven by the intrinsic SOC.
Another relevant observation concerns the sign of : it is negative, entailing . To unambiguously define the sign of the ISHE in our setup, a –FeO/Pt bilayer was used. In Figure 5a, we compare two measurements performed in –FeO/Pt and in –FeO/IrO, to evidence that the corresponding transverse voltages display opposite signs. In sight of this, the negative sign of is necessarily originated by a negative value of , as evidenced by Equation (4).

Figure 5.
(a) Comparison between the measured as a function of the magnetic field for –FeO/Pt bilayer and a –FeO/IrO bilayer; (b) Evolution with temperature of the measured output excited by the LSSE in the sample with nm.
In the pioneering work with polycrystalline IrO of Fujiwara and coworkers [19], they observed a change in the sign of the ISHE signal with decreasing temperature (from positive at K to negative at K). They ascribed this to the coexistence of different SOC mechanisms with opposite signs. We also performed the LSSE experiment at different temperatures for the sample in which the largest room temperature value of was measured ( nm). The results are plotted in Figure 5b. As shown, we do not observe such a reversal in the signal with respect to the magnetic field, which defines the magnetization sign of FeO; rather, it is negative for every measured temperature. This suggests that the same ISHE mechanism dominates over the entire temperature range.
Regarding this, it was also recently shown that the intrinsic spin Hall conductivity in IrO is remarkably anisotropic, changing not only in magnitude, but also in sign depending on the directions of the spin current (i direction), spin polarization (k direction) and electric field (j direction) [35]. As a result, the sign of the induced ISHE electric field depends not only on the sign of the vector product , but also on the direction in which the spin-to-charge conversion process is occurring. Accordingly, the preferred direction (if any) of growth with respect to the measurement geometry might be determining for the observed sign if the intrinsic mechanism is dominant. This means that the sample preparation and crystallinity are probably crucial for the final balance in the competition between different mechanisms to dominate the ISHE in IrO. Thus, the explanation for the differences observed between samples with [100] preferential texture and previously reported results on polycrystalline IrO may be found here. Further measurements performed in IrO layers with other crystal orientations are needed to confirm this interpretation. The samples studied in reference [19], polycrystalline, were prepared by reactive sputtering from a pure Ir target and then patterned using e-beam lithography. Qiu and collaborators in reference [26] mentioned that they used RF sputtering. Competition between SOC mechanisms opposite in sign but similar in magnitude could be responsible for the low ISHE signal they observed in their experiment, together with a low spin mixing conductance. Very recently, Bose et al. experimentally determined by means of spin-torque ferromagnetic resonance that the ISHE regimen for epitaxial (001) IrO films was different to that of (110)-oriented films [54]. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reported results of ISHE experiments on textured thin films of IrO or on PLD-grown films.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we investigated the ISHE spin-to-charge conversion in PLD-grown thin films of IrO. We thermally excited spin currents by making use of the LSSE and measured the transverse ISHE voltage. First, we studied the IrO thickness dependence of the process. The analysis of the obtained data within the theoretical model allowed us to establish that the spin Hall angle scales with the longitudinal charge resistivity as , which excludes a predominant role of skew scattering in the ISHE. The fitting of the theoretical model in Ref. [46] to yields a spin diffusion length of nm, which is in accordance with the value previously reported by Fujiwara using a lateral spin valve methodology [19]. This spin diffusion length is very comparable to that of pure metals, such as those reported for prototypical Pt, which ranges between 1.2 and 8.0 nm (see, for example, Refs. [46,55,56,57,58,59]). Second, we observed a negative sign for the spin Hall angle throughout all our experiments, including temperature variation. This is in contrast to what was described in the other two works on the ISHE in polycrystalline or amorphous IrO, grown using other techniques. We attribute this to the pre-eminence of the intrinsic ISHE in the entire temperature range, with a negative intrinsic spin Hall conductivity, as proposed by [35]. This effect might be enhanced by the textured growth of IrO thin films, in view of the anisotropic nature predicted for IrO [35]. These results are relevant for the achievement of the better control of spin-to-charge conversion in this material, which shows great potential to be exploited in the spintronics field, once a deeper understanding of how the SOC in it works is attained.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.L. and L.M.; methodology, P.J.-C. and I.L.; formal analysis, P.J.-C.; investigation, P.J.-C., I.L. and J.A.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, P.J.-C.; writing—review and editing, I.L., M.R.I., P.A.A. and L.M.; supervision, I.L. and L.M.; project administration, L.M.; funding acquisition, M.R.I., P.A.A. and L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science grant number MAT2017-82970-C2, including FEDER funding, and the Aragón Regional government grant number E26.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Pilar Jiménez-Cavero acknowledges Spanish MECD for support through the FPU program (reference FPU014/02546). The authors acknowledge the Advanced Microscopy Laboratory-INA University of Zaragoza for offering access to their instruments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dyakonov, M.I.; Perel, V.I. Possibility of orienting electron spins with current. JETP Lett. 1971, 13, 467–469. [Google Scholar]
- Dyakonov, M.I.; Perel, V.I. Current-induced spin orientation of electrons in semiconductors. Phys. Lett. A 1971, 35, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.E. Spin Hall Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1834–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.K.; Myers, R.C.; Gossard, A.C.; Awschalom, D.D. Observation of the spin hall effect in semiconductors. Science 2004, 306, 1910–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, S.; Valenzuela, S.; Saitoh, E.; Kimura, T. Spin Current; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Spin Hall effect in the presence of spin diffusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, S.O.; Tinkham, M. Direct electronic measurement of the spin Hall effect. Nature 2006, 442, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, E.; Ueda, M.; Miyajima, H.; Tatara, G. Conversion of spin current into charge current at room temperature: Inverse spin-Hall effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaosa, N.; Sinova, J.; Onoda, S.; MacDonald, A.H.; Ong, N.P. Anomalous Hall effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 1539–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinova, J.; Valenzuela, S.O.; Wunderlich, J.; Back, C.H.; Jungwirth, T. Spin Hall effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 1213–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A. Spin Hall Effects in Metals. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5172–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradhand, M.; Fedorov, D.V.; Zahn, P.; Mertig, I. Extrinsic spin hall effect from first principles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, J. The Spontaneous Hall Effect in Ferromagnets. Physica 1958, 24, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L. Side-jump mechanism for the hall effect of ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 2, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinova, J.; Culcer, D.; Niu, Q.; Sinitsyn, N.A.; Jungwirth, T.; MacDonald, A.H. Universal intrinsic spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 126603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Nagaosa, N.; Zhang, S.C. Dissipationless Quantum Spin Current at Room Temperature. Science 2003, 301, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.P.; Chen, N.; Kim, C.Y.; Chen, W.F.; Plumb, K.W.; Jeon, B.C.; Noh, T.W.; Kim, Y.J. Spin-orbit coupling in iridium-based 5d compounds probed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 195131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.R.; Gillson, J.L. Crystal growth, electrical resistivity and lattice parameters of RuO2 and IrO2. Mater. Res. Bull. 1971, 6, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Fukuma, Y.; Matsuno, J.; Idzuchi, H.; Niimi, Y.; Otani, Y.; Takagi, H. 5d iridium Oxide As a Material for Spin-Current Detection. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuhira, K.; Wakeshima, M.; Nakanishi, R.; Yamada, T.; Nakamura, A.; Kawano, W.; Takagi, S.; Hinatsu, Y. Metal-insulator transition in pyrochlore iridates Ln2Ir2O7 (Ln = Nd, Sm, and Eu). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 76, 043706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.J.; Kim, Y.B. Topological insulators and metal-insulator transition in the pyrochlore iridates. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2010, 82, 085111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, S.; MacHida, Y.; Maeno, Y.; Tayama, T.; Sakakibara, T.; Van Duijn, J.; Balicas, L.; Millican, J.N.; MacAluso, R.T.; Chan, J.Y. Metallic spin-liquid behavior of the geometrically frustrated kondo lattice Pr2Ir2O7. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 087204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disseler, S.M.; Giblin, S.R.; Dhital, C.; Lukas, K.C.; Wilson, S.D.; Graf, M.J. Magnetization and Hall effect studies on the pyrochlore iridate Nd2Ir2O7. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 060403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Ohsumi, H.; Komesu, T.; Sakai, S.; Morita, T.; Takagi, H.; Arima, T. Phase-Sensitive Observation of a Spin-Orbital Mott State in Sr2IrO4. Science 2009, 323, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.H.; Jeong, H.; Jin, H.; Yu, J. Strain-induced topological insulator phase and effective magnetic interactions in Li2IrO3. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 165117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Hou, D.; Kikkawa, T.; Uchida, K.I.; Saitoh, E. All-oxide spin Seebeck effects. Appl. Phys. Express 2015, 8, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uchida, K.; Ishida, M.; Kikkawa, T.; Kirihara, A.; Murakami, T.; Saitoh, E. Longitudinal spin seebeck effect: From fundamentals to applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 343202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, H.; Uchida, K.I.; Saitoh, E.; Maekawa, S. Theory of the spin Seebeck effect. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, A.; Basso, V.; Kuepferling, M.; Pasquale, M.; Ne Meier, D.C.; Reiss, G.; Kuschel, T.; Kikkawa, T.; Uchida, K.I.; Saitoh, E.; et al. Spincaloritronic Measurements: A Round Robin Comparison of the Longitudinal Spin Seebeck Effect. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.E.W.; Saitoh, E.; Wees, B.J.V.; St, P. Spin caloritronics. Nat. Publ. Group 2012, 11, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheiss, L.F. Electronic structure of RuO2, OsO2, and IrO2. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 2433–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, G.K.; Guggenheim, H.J. Conduction-electron screening in metallic oxides: IrO2. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 22, 4680–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahk, J.M.; Poll, C.G.; Oropeza, F.E.; Ablett, J.M.; Céolin, D.; Rueff, J.P.; Agrestini, S.; Utsumi, Y.; Tsuei, K.D.; Liao, Y.F.; et al. Understanding the Electronic Structure of IrO2 Using Hard-X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Density-Functional Theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 117601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Y.; Galli, G.; Goddard, W.A. Electronic Structure of IrO2: The Role of the Metal d Orbitals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 11570–11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.X.; Felser, C.; Yan, B. Dirac nodal lines and induced spin Hall effect in metallic rutile oxides. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 235104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Sławińska, J.; Vobornik, I.; Fujii, J.; Regoutz, A.; Kahk, J.M.; Scanlon, D.O.; Morgan, B.J.; McGuinness, C.; Plekhanov, E.; et al. Role of spin-orbit coupling in the electronic structure of IrO2. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2018, 2, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.R.; Margaritondo, G.; Georg, C.A.; Lévy, F. Electronic states of rutile dioxides: RuO2, IrO2, and RuxIr1-xO2. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.S.; Ahuja, R. Electronic and optical properties of RuO2 and IrO2. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 165102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Ohgushi, K.; Yamaura, J.i.; Ohsumi, H.; Takeshita, S.; Takata, M.; Arima, T.h. Complex orbital state stabilized by strong spin-orbit coupling in a metallic iridium oxide IrO2. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 161111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, J.K.; Uchida, M.; Paik, H.; Schlom, D.G.; Shen, K.M. Evolution of electronic correlations across the rutile, perovskite, and Ruddelsden-Popper iridates with octahedral connectivity. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 121104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Sohn, C.H.; Korneta, O.B.; Chae, S.C.; Noh, T.W. Spin-orbit coupling induced band structure change and orbital character of epitaxial IrO2 films. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 045104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riga, J.; Tenret-Noël, C.; Pireaux, J.J.; Caudano, R.; Verbist, J.J.; Gobillon, Y. Electronic structure of rutile oxides TiO2, RuO2 and IrO2 studied by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Phys. Scr. 1977, 16, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cavero, P.; Lucas, I.; Anadón, A.; Ramos, R.; Niizeki, T.; Aguirre, M.H.; Algarabel, P.A.; Uchida, K.; Ibarra, M.R.; Saitoh, E.; et al. Spin Seebeck effect in insulating epitaxial γ-Fe2O3 thin films. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 026103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I.; Wilson, A.J.C. Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Cryst. 1978, 11, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Yamauchi, K.; Oguchi, T.; Picozzi, S. Metal-Insulator Transition and Jeff = 1/2 Spin-Orbit Insulating State in Rutile-based IrO2/TiO2 Superlattices. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.04408. [Google Scholar]
- Castel, V.; Vlietstra, N.; Ben Youssef, J.; Van Wees, B.J. Platinum thickness dependence of the inverse spin-Hall voltage from spin pumping in a hybrid yttrium iron garnet/platinum system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 132414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiga, Y.; Mizunuma, K.; Kono, Y.; Ryu, J.C.; Ono, H.; Kohda, M.; Okuno, E. Platinum thickness dependence and annealing effect of the spin-Seebeck voltage in platinum/yttrium iron garnet structures. Appl. Phys. Express 2014, 7, 093001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushkov, O.P.; Milstein, A.I.; Mori, M.; Maekawa, S. Relativistic effects in scattering of polarized electrons. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2013, 103, 47003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fert, A.; Levy, P.M. Spin Hall Effect Induced by Resonant Scattering on Impurities in Metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 157208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadova, K.; Fedorov, D.V.; Herschbach, C.; Gradhand, M.; Mertig, I.; Ködderitzsch, D.; Ebert, H. Separation of the individual contributions to the spin Hall effect in dilute alloys within the first-principles Kubo-Středa approach. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 045120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, D.; Ye, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, J.; Su, G.; Jin, X. Evidence of the side jump mechanism in the anomalous Hall effect in paramagnets. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2015, 110, 27002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, L.; Jin, X. Proper Scaling of the Anomalous Hall Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 087206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Jin, X. Towards a Better Understanding of the Anomalous Hall Effect. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 86, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, A.; Nelson, J.N.; Zhang, X.S.; Jadaun, P.; Jain, R.; Schlom, D.G.; Ralph, D.C.; Muller, D.A.; Shen, K.M.; Buhrman, R.A. Effects of Anisotropic Strain on Spin-Orbit Torque Produced by the Dirac Nodal Line Semimetal IrO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55411–55416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.; Vilela-Leão, L.H.; Rodríguez-Suárez, R.L.; Lacerda Santos, A.F.; Rezende, S.M. Spin pumping and anisotropic magnetoresistance voltages in magnetic bilayers: Theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 144402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Vlaminck, V.; Pearson, J.E.; Divan, R.; Bader, S.D.; Hoffmann, A. Determination of the Pt spin diffusion length by spin-pumping and spin Hall effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 242414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Sánchez, J.C.; Reyren, N.; Laczkowski, P.; Savero, W.; Attané, J.P.; Deranlot, C.; Jamet, M.; George, J.M.; Vila, L.; Jaffrès, H. Spin Pumping and Inverse Spin Hall Effect in Platinum: The Essential Role of Spin-Memory Loss at Metallic Interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isasa, M.; Villamor, E.; Hueso, L.E.; Gradhand, M.; Casanova, F. Temperature dependence of spin diffusion length and spin Hall angle in Au and Pt. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 024402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Liu, Q.; Miao, B.; Yu, R.; Feng, Z.; Sun, L.; You, B.; Du, J.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; et al. Self-consistent determination of spin Hall angle and spin diffusion length in Pt and Pd: The role of the interface spin loss. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).