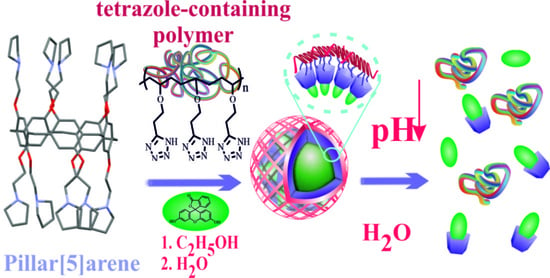
Towards Universal Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: Pillar[5]arenes Synthesis and Self-Assembly into Nanocontainers with Tetrazole Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization
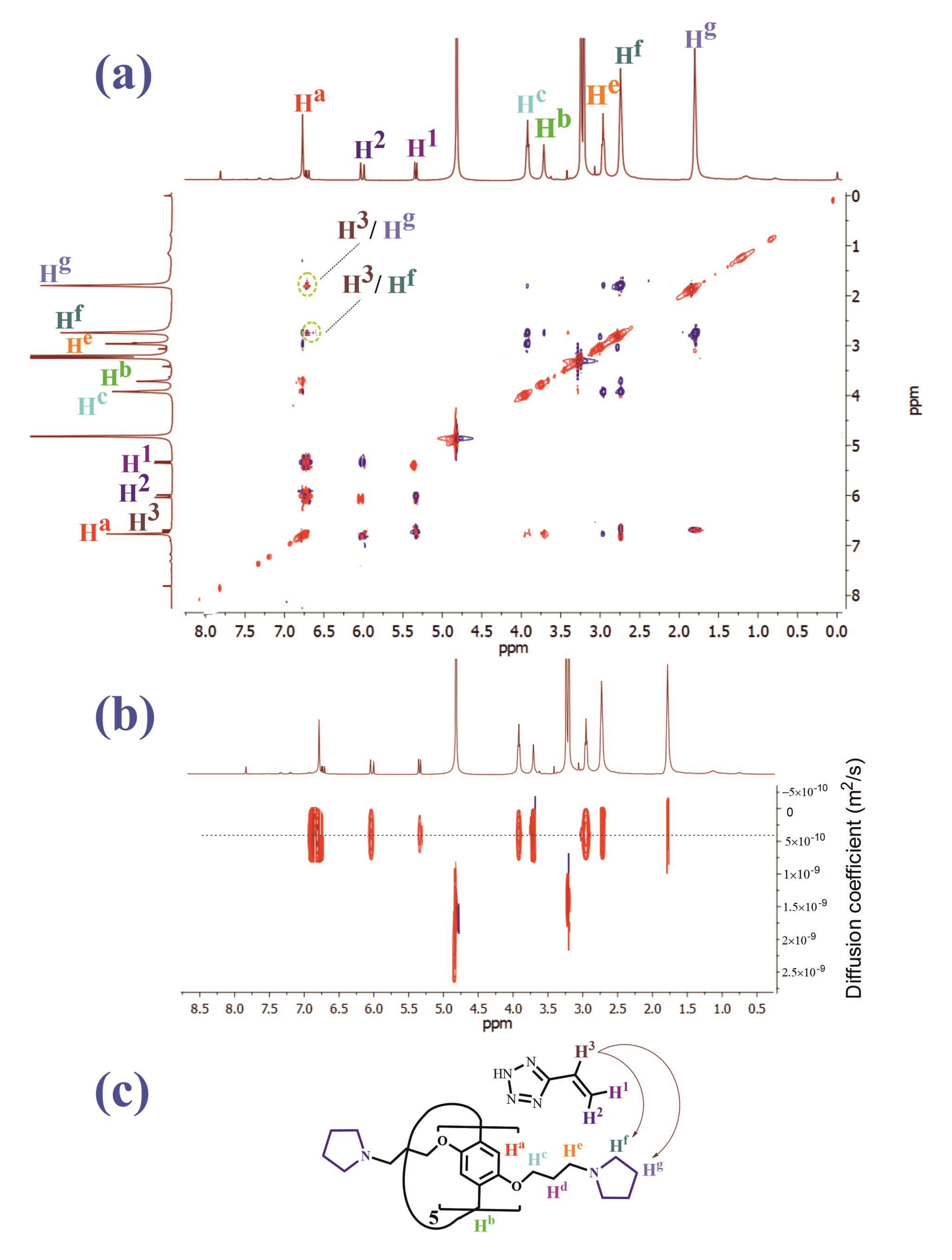
2.2. Diffusion Ordered Spectroscopy (DOSY)
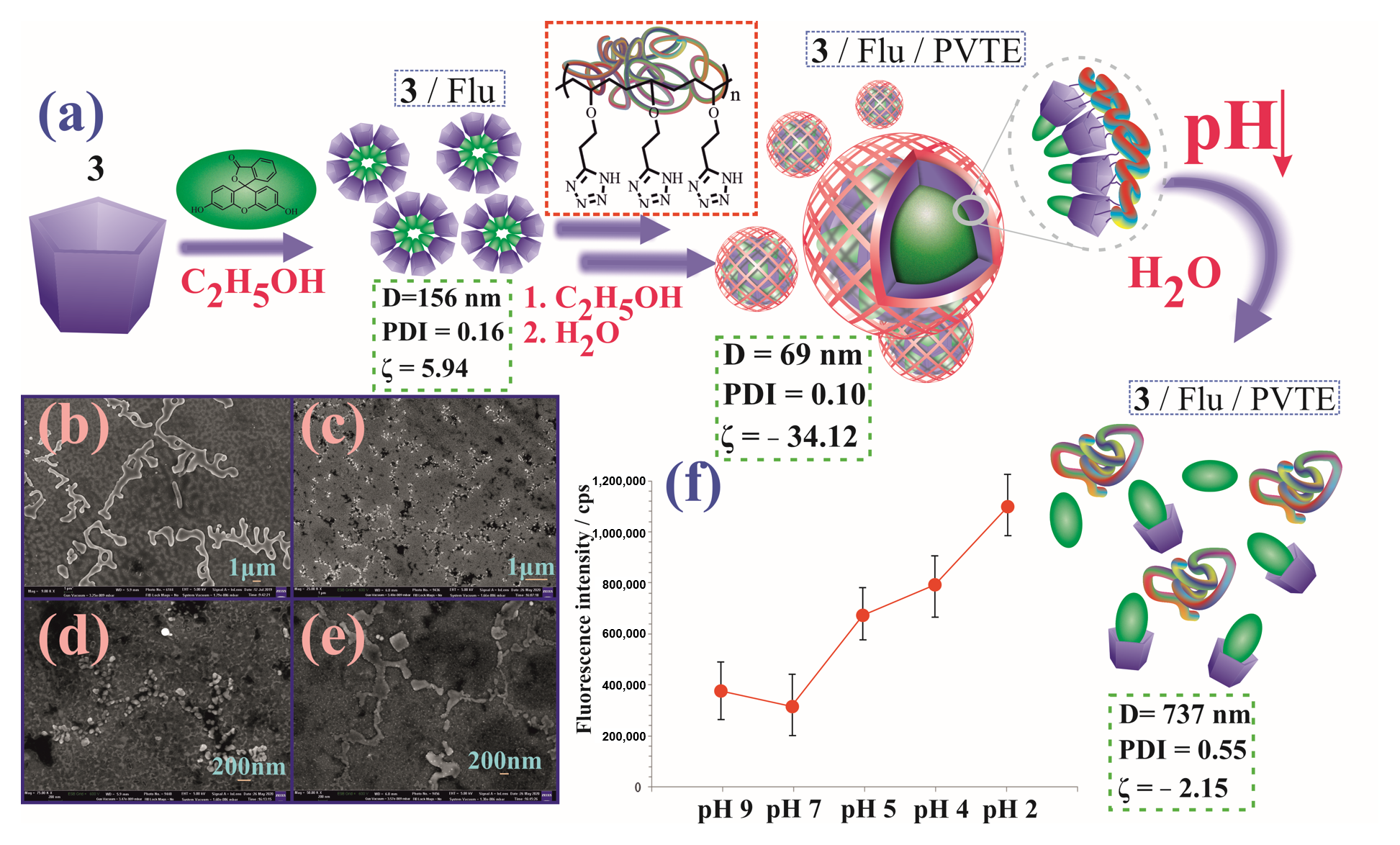
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.6.1. Particle Size
2.6.2. Zeta Potentials
2.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
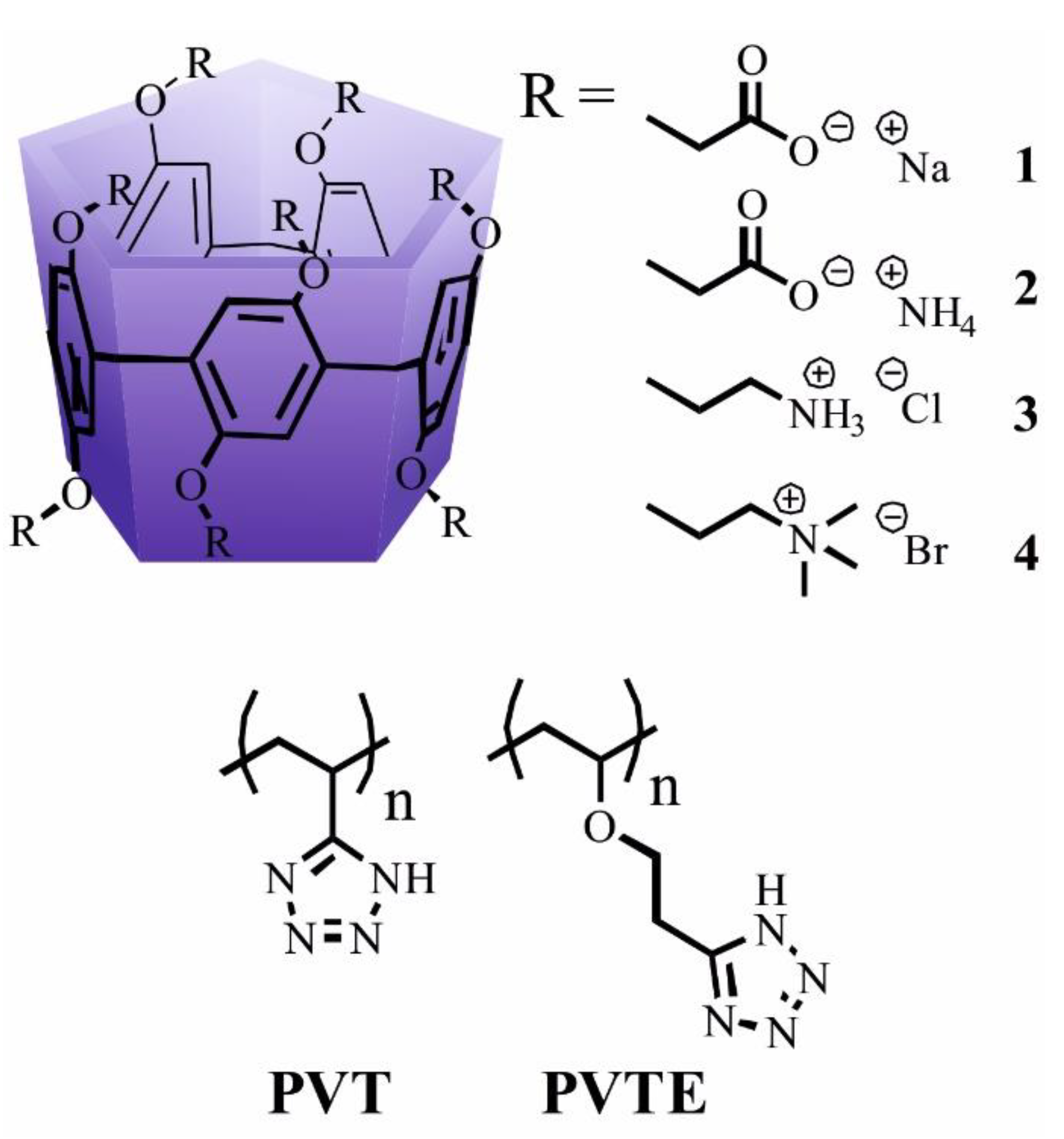
2.8. Synthesis of O-Substituted Hydroquinones and PVT and PVTE Polymers
2.9. Synthesis
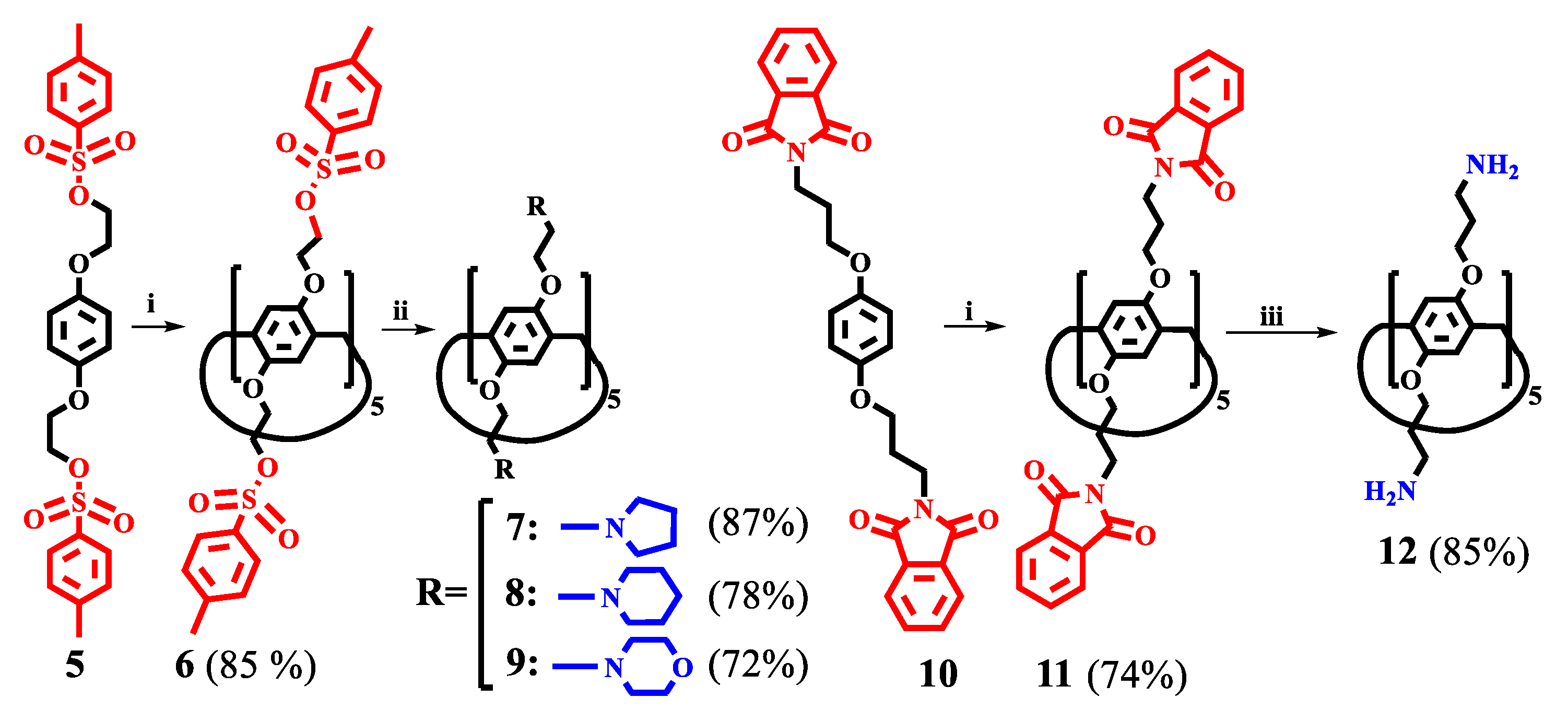
2.9.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 6 and 11
2.9.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 7–9 and 12
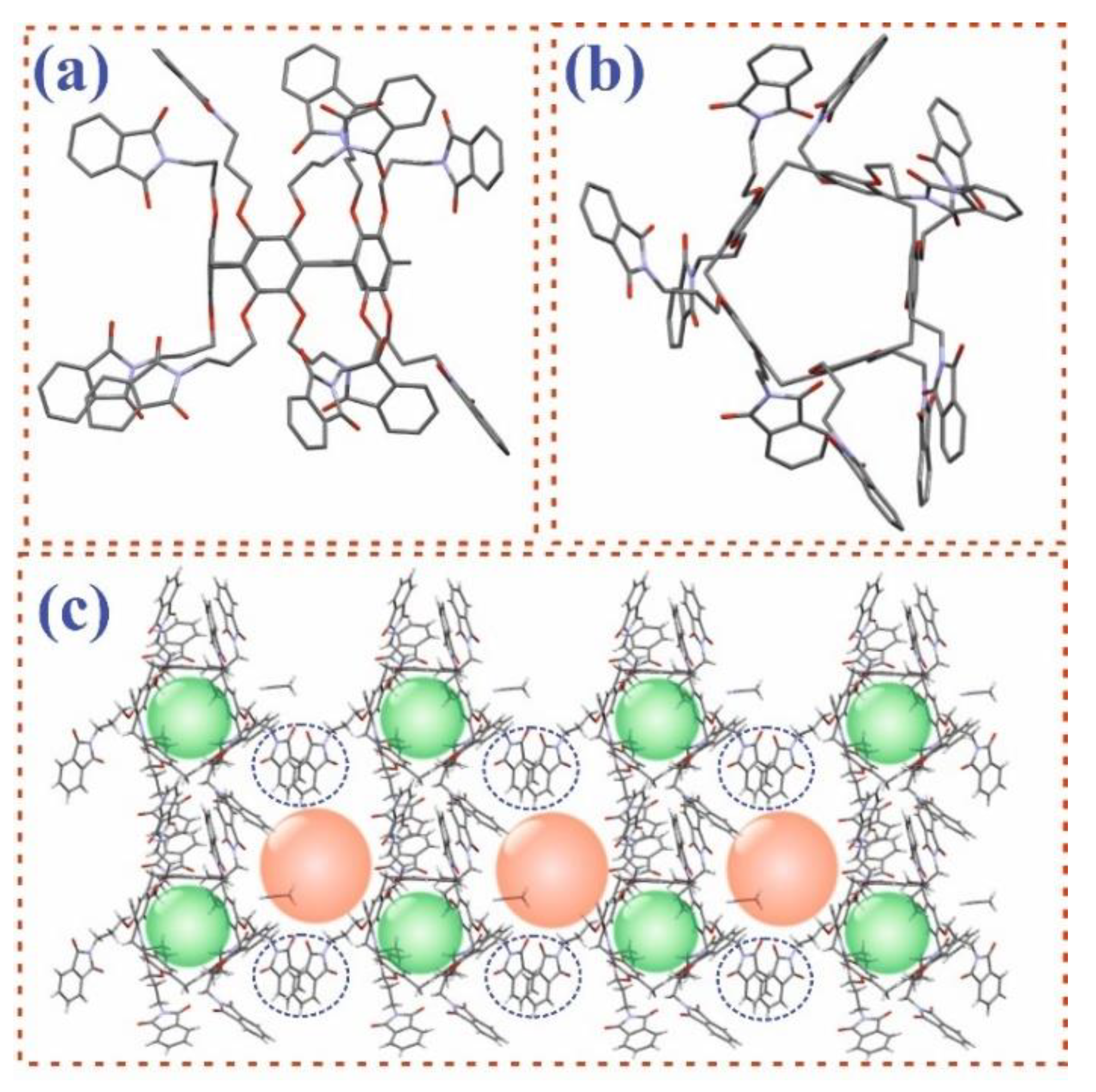
3. Results
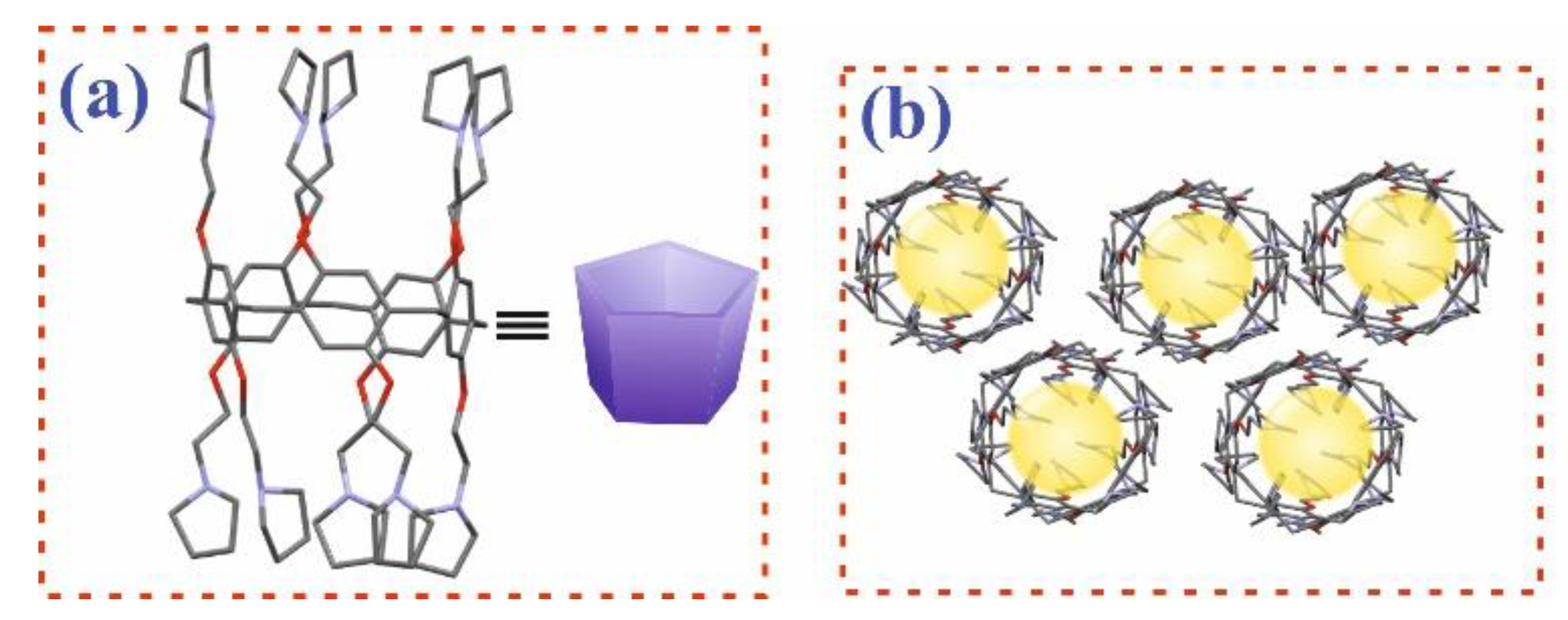
3.1. Synthesis of Pillar[5]arene Derivatives
3.2. Study of the Interaction of Pillar[5]arenes with PVT and PVTE Polymers
3.3. Study of the Interaction of Pillar[5]arenes with Fluorescein
3.4. Study of Self-Assembly of a Three-Component System 7/Flu/PVTE
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marasini, N.; Haque, S.; Kaminskas, L.M. Polymer-drug conjugates as inhalable drug delivery systems: A review. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 31, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossen, P.; Witzigmann, D.; Sieber, S.; Huwyler, J. PEG-PCL-based nanomedicines: A biodegradable drug delivery system and its application. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Ahmed, M.; Long, L.; Khashab, N.M.; Huang, F.; Sessler, J.L. Adhesive supramolecular polymeric materials constructed from macrocycle-based host–guest interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2682–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F. Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery system for cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, X.; Tang, G. Mechanisms of drug release in pH-sensitive micelles for tumour targeted drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S. Natural biodegradable polymers based nano-formulations for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, A.; Traverso, G.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Weissleder, R.; Langer, R. Evolution of macromolecular complexity in drug delivery systems. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Rakesh, K.; Manukumar, H.; Mohammed, Y.H.E.; Karthik, C.; Sumathi, S.; Mallu, P.; Qin, H.-L. Innovative nano-carriers in anticancer drug delivery-a comprehensive review. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 85, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Sime, F.B.; Cabot, P.J.; Maqbool, F.; Roberts, J.A.; Falconer, J.R. Solid nanoparticles for oral antimicrobial drug delivery: A review. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; Gopi, S. Biopolymer based nanomaterials in drug delivery systems: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, S.; Hossain, M.K.; Basher, M.; Mia, M.; Rahman, M.; Uddin, M.J. Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Lu, D.; Shi, Y.; Yao, Y. Water-soluble supramolecular polymers constructed by macrocycle-based host-guest interactions. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fa, S.; Kakuta, T.; Yamagishi, T.A.; Ogoshi, T. One-, Two-, and Three-Dimensional Supramolecular Assemblies Based on Tubular and Regular Polygonal Structures of Pillar[n]arenes. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, Y.W. Gated Materials: Installing Macrocyclic Arenes-Based Supramolecular Nanovalves on Porous Nanomaterials for Controlled Cargo Release. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, 1800354–1800363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Shangguan, L.; Shi, B.; Yu, G.; Huang, F. Recent progress in macrocyclic amphiphiles and macrocyclic host-based supra-amphiphiles. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 2152–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, P.J. Pillar[n ]arenes at the Chemistry-Biology Interface. Isr. J. Chem. 2018, 58, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolko, V.; Shurpik, D.; Porfireva, A.; Evtugyn, G.; Stoikov, I.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Poly(Neutral Red) and Carboxylated Pillar[5]arene for Sensitive Determination of Aflatoxin M1. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurpik, D.N.; Padnya, P.L.; Basimova, L.T.; Evtugin, V.G.; Plemenkov, V.V.; Stoikov, I.I. Synthesis of new decasubstituted pillar[5]arenes containing glycine fragments and their interactions with Bismarck brown Y. Mendeleev Commun. 2015, 25, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoikova, E.E.; Sorvin, M.I.; Shurpik, D.N.; Budnikov, H.C.; Stoikov, I.I.; Evtugyn, G.A. Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor Based on Polyaniline and Unsubstituted Pillar[5]Arene. Electroanalysis. 2014, 27, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimova, L.S.; Shurpik, D.N.; Makhmutova, A.R.; Stoikov, I.I. Pillar[5]arenes Bearing Amide and Carboxylic Groups as Synthetic Receptors for Alkali Metal Ions. Macroheterocycles 2017, 10, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurpik, D.N.; Sevastyanov, D.A.; Zelenikhin, P.V.; Subakaeva, E.V.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Osin, Y.N.; Cragg, P.J.; Stoikov, I.I. Hydrazides of glycine-containing decasubstituted pillar[5]arenes: Synthesis and encapsulation of Floxuridine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 4410–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurpik, D.N.; Mostovaya, O.A.; Sevastyanov, D.A.; Lenina, O.A.; Sapunova, A.S.; Voloshina, A.D.; Petrov, K.A.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Cragg, P.J.; Stoikov, I.I. Supramolecular neuromuscular blocker inhibition by a pillar[5]arene through aqueous inclusion of rocuronium bromide. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 9951–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Chen, S.; Gou, X.; Yang, J.; An, J.; Jin, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, H. Biodegradable Supramolecular Materials Based on Cationic Polyaspartamides and Pillar[5]arene for Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria and Mitigating Antimicrobial Resistance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904683–1904694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Tang, Q.; Ju, Y.; Lin, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhou, J.; Luo, H.; Lei, Z.; Tong, Z. Redox and pH responsive polymeric vesicles constructed from a water-soluble pillar[5]arene and a paraquat-containing block copolymer for rate-tunable controlled release. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, L.; De Plano, L.M.; Franco, D.; Gattuso, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P.; Lando, G.; Notti, A.; Parisi, M.F.; Pisagatti, I. Antiadhesive and antibacterial properties of pillar[5]arene-based multilayers. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10203–10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qu, Z.R.; Ye, H.Y.; Xiong, R.G. ChemInform Abstract: In situ Hydrothermal Synthesis of Tetrazole Coordination Polymers with Interesting Physical Properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 39, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaponik, P.N.; Ivashkevich, O.A.; Karavai, V.P.; Lesnikovich, A.I.; Chernavina, N.I.; Sukhanov, G.T.; Gareev, G.A. Polymers and copolymers based on vinyl tetrazoles, 1. Synthesis of poly(5-vinyl tetrazole) by polymer-analogous conversion of polyacrylonitrile. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1994, 219, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakerzadeh, E.; Salehi, R.; Mahkam, M. Smart tetrazole-based antibacterial nanoparticles as multifunctional drug carriers for cancer combination therapy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1963–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piradashvili, K.; Simon, J.; Paßlick, D.; Höhner, J.R.; Mailänder, V.; Wurm, F.R.; Landfester, K. Fully degradable protein nanocarriers by orthogonal photoclick tetrazole-ene chemistry for the encapsulation and release. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhnyaev, V.N.; Vereshchagin, L.I. Vinyltetrazoles: Synthesis and properties. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2003, 72, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Luo, H.; Wan, D. Synthesis and properties of amphoteric copolymer of 5-vinyltetrazole and vinylbenzyl phos-phonic acid. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanase, L.I.; Riess, G. Micellization of pH-stimulable poly (2-vinylpyridine)-b-poly (ethylene oxide) copolymers and their complexation with anionic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 395, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurciuc-Tincu, C.E.; Cretan, M.S.; Purcar, V.; Popa, M.; Daraba, O.M.; Atanase, L.I.; Ochiuz, L. Drug delivery system based on pH-sensitive biocompatible poly (2-vinyl pyridine)-b-poly (ethylene oxide) nanomicelles loaded with curcumin and 5-fluorouracil. Polymers 2020, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanase, L.I.; Lerch, J.P.; Caprarescu, S.; Tincu, C.E.I.; Riess, G. Micellization of pH-sensitive poly(butadiene)-block -poly(2 vinylpyridine)-block -poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers: Complex formation with anionic surfactants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45313–45321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhnyaev, V.N.; Petrova, T.L.; Pokatilov, F.A.; Smirnov, V.I. Synthesis of crosslinked poly(5-vinyltetrazole) and properties of hydrogels formed on its basis. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2011, 53, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G.P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; Streek, J.V.D. Mercury: Visualization and analysis of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Curiel, D.; Cowley, A.R.; Beer, P.D. Dinuclear zinc(ii) dithiocarbamate macrocycles: Ditopic receptors for a variety of guest molecules. Dalton Trans. 2005, 2, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Sasahara, R.; Muranaka, A.; Miura, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kimura, M.; Miyagawa, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Uchiyama, M.; et al. Synthesis of a Chiral [2]Rotaxane: Induction of a Helical Structure through Double Threading. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4745–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J.C. Concise Polymeric Materials Encyclopedia; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Neochoritis, C.G.; Zhao, T.; Dömling, A. Tetrazoles via Multicomponent Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1970–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, J. Isosterism and molecular modification in drug design: Tetrazole analogue of GABA: Effects on enzymes of the γ-aminobutyrate system. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 1983, 15, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, A.E.; Dufresne, M.H.; Leroux, J.C. pH-sensitive vesicles, polymeric micelles, and nanospheres prepared with polycarboxylates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Olubummo, A.; Binder, W.H. Beyond the lipid-bilayer: Interaction of polymers and nanoparticles with membranes. Soft Matter. 2012, 8, 4849–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wan, M.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Fang, W. Polymyxin B Loosens Lipopolysaccharide Bilayer but Stiffens Phospholipid Bilayer. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurpik, D.N.; Nazarova, A.A.; Makhmutova, L.I.; Kizhnyaev, V.N.; Stoikov, I.I. Uncharged water-soluble amide de-rivatives of pillar[5]arene: Synthesis and supramolecular self-assembly with tetrazole-containing polymers. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Mukherjee, P.S. Carboxylatopillar[n]arenes: A versatile class of water soluble synthetic receptors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 15, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Pillararene-based self-assembled amphiphiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5491–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, T.; Kakuta, T.; Yamagishi, T.A. Separation and detection of meta-and ortho-substituted benzene isomers by water-soluble pillar[5]arene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Jin, M.; Yang, K.; Pei, Y.; Pei, Z. Supramolecular delivery systems based on pillararenes. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13626–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.B.; Chen, L.; Si, W.; Yu, Y.; Hou, J.L. Pillar[5]arene decaamine: Synthesis, encapsulation of very long linear diacids and formation of ion pair-stopped [2]rotaxanes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4694–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, X.; Xiang, F.; Chi, X.; Han, C.; He, J.; Abliz, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, F. A cationic water-soluble pillar[5]arene: Synthesis and host–guest complexation with sodium 1-octanesulfonate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12340–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jie, K.; Zhao, R.; Huang, F. Cis-Trans Selectivity of Haloalkene Isomers in Nonporous Adaptive Pillararene Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11847–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Li, E.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, W.; Huang, F. Separation of 2-Chloropyridine/3-Chloropyridine by Nonporous Adaptive Crystals of Pillararenes with Different Substituents and Cavity Sizes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6360–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jie, K.; Zhao, R.; Li, E.; Huang, F. Highly Selective Removal of Trace Isomers by Nonporous Adaptive Pillararene Crystals for Chlorobutane Purification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6957–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.W. Molecular Tectonics: From Simple Tectons to Complex Molecular Networks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.W.; De Cian, A. Crystal engineering: Molecular networks based on inclusion phenomena. Chem. Commun. 1998, 7, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thordarson, P. Determining association constants from titration experiments in supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 40, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbert, D.B.; Thordarson, P. The death of the Job plot, transparency, open science and online tools, uncertainty estimation methods and other developments in supramolecular chemistry data analysis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12792–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindfit v0.5 (Open Data Fit, 2016). Available online: http://supramolecular.org/bindfit/ (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Panneerselvam, M.; Kumar, M.D.; Jaccob, M.; Solomon, R.V.; Panneesrselvam, M. Computational Unravelling of the Role of Alkyl Groups on the Host-Guest Complexation of Pillar[5]arenes with Neutral Dihalobutanes. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Singh, M.; Sundarajan, M.; Yuan, L.; Fang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Feng, W. Understanding the extraction and complexation of thorium using structurally modified CMPO functionalized pillar[5]arenes in ionic liquid: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 75, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cai, Y.; Feng, W.; Yuan, L. Pillararenes as macrocyclic hosts: A rising star in metal ion separation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7883–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.A.; Huddersman, K.D.; Taylor, M.J. Comparison of micro-and mesoporous inorganic materials in the uptake and release of the drug model fluorescein and its analogues. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 5873–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, H.S.; Chauhan, G.S. Designing Silica-Based Hybrid Polymers and Their Application in the Loading and Release of Fluorescein as a Model Drug and Diagnostic Agent. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2016, 37, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Mo, R.; Xue, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xue, L.; Ping, Q.; Zhang, C. Sequential Intra-Intercellular Nanoparticle Delivery System for Deep Tumor Penetration. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 6367–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: Polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 115, 4788–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöback, R.; Nygren, J.; Kubista, M. Absorption and fluorescence properties of fluorescein. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1995, 51, L7–L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Masters, B.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Kluwer-Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shurpik, D.N.; Makhmutova, L.I.; Usachev, K.S.; Islamov, D.R.; Mostovaya, O.A.; Nazarova, A.A.; Kizhnyaev, V.N.; Stoikov, I.I. Towards Universal Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: Pillar[5]arenes Synthesis and Self-Assembly into Nanocontainers with Tetrazole Polymers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040947
Shurpik DN, Makhmutova LI, Usachev KS, Islamov DR, Mostovaya OA, Nazarova AA, Kizhnyaev VN, Stoikov II. Towards Universal Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: Pillar[5]arenes Synthesis and Self-Assembly into Nanocontainers with Tetrazole Polymers. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040947
Chicago/Turabian StyleShurpik, Dmitriy N., Lyaysan I. Makhmutova, Konstantin S. Usachev, Daut R. Islamov, Olga A. Mostovaya, Anastasia A. Nazarova, Valeriy N. Kizhnyaev, and Ivan I. Stoikov. 2021. "Towards Universal Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: Pillar[5]arenes Synthesis and Self-Assembly into Nanocontainers with Tetrazole Polymers" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040947
APA StyleShurpik, D. N., Makhmutova, L. I., Usachev, K. S., Islamov, D. R., Mostovaya, O. A., Nazarova, A. A., Kizhnyaev, V. N., & Stoikov, I. I. (2021). Towards Universal Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: Pillar[5]arenes Synthesis and Self-Assembly into Nanocontainers with Tetrazole Polymers. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040947