Carbon-Nanotube-Coated Surface Electrodes for Cortical Recordings In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Requirement of Small Electrode Contact Diameters
1.2. Applications of CNTs to Improve Effective Electrode Contact Surface Areas
1.3. The CNT-Coated Surface Electrode
2. Materials and Methods
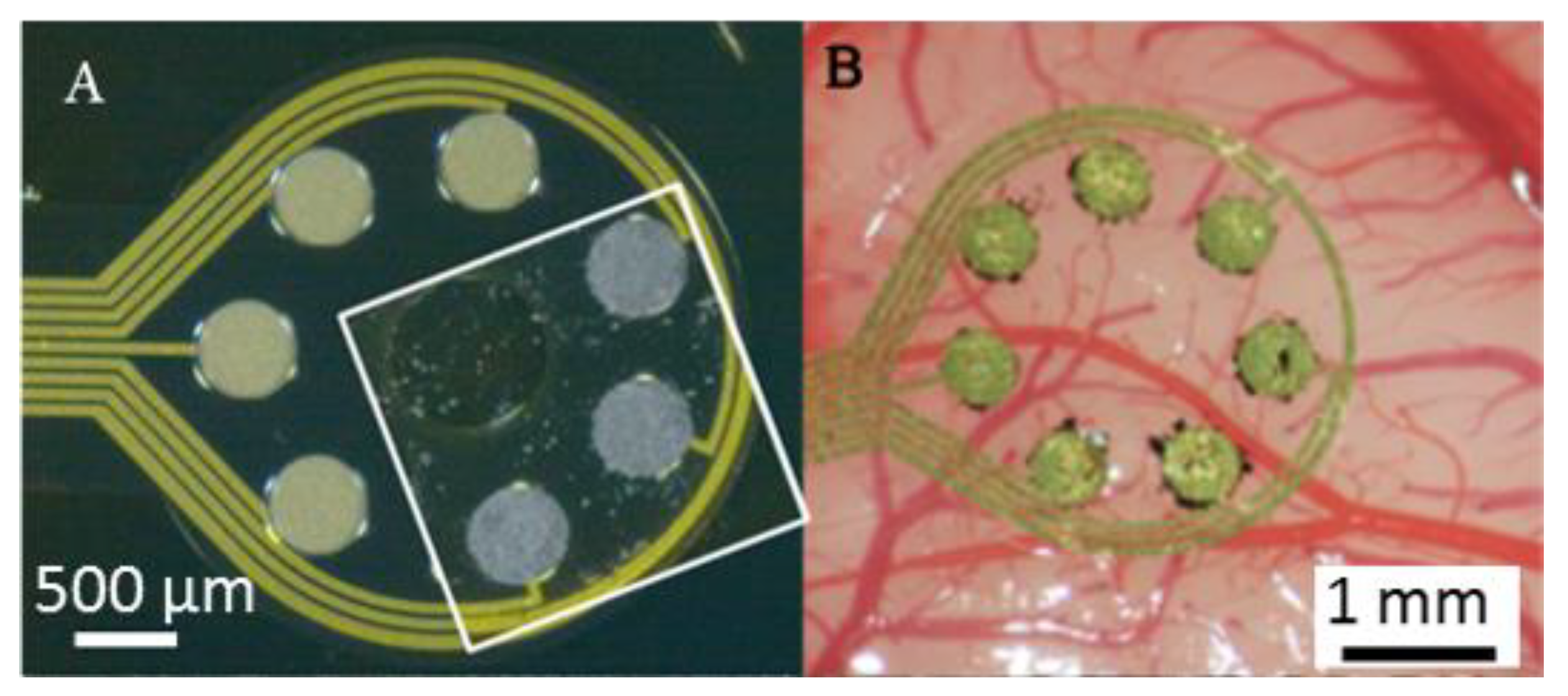
2.1. CNT-Coated ECoC Electrodes
2.2. In Vivo Recordings
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
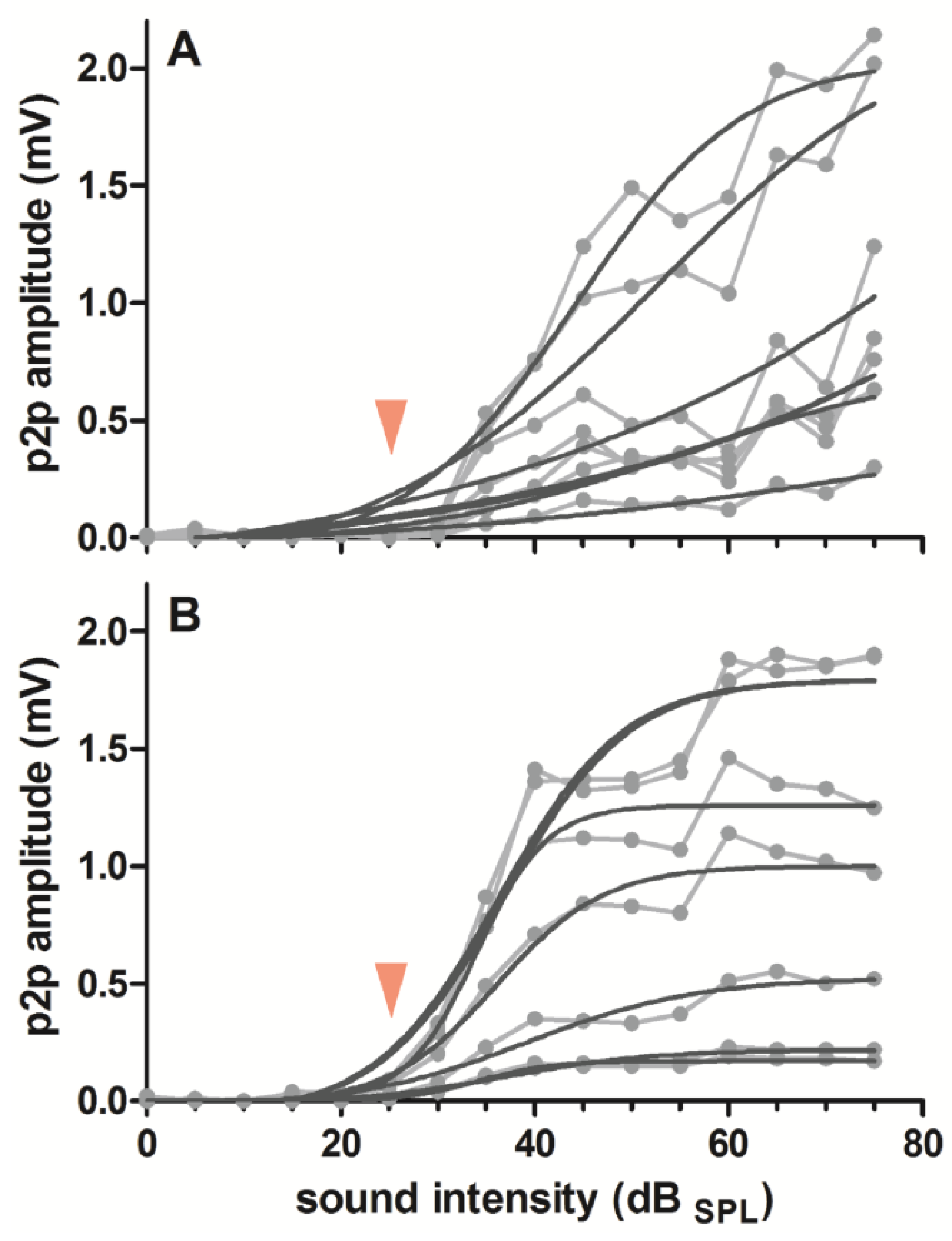
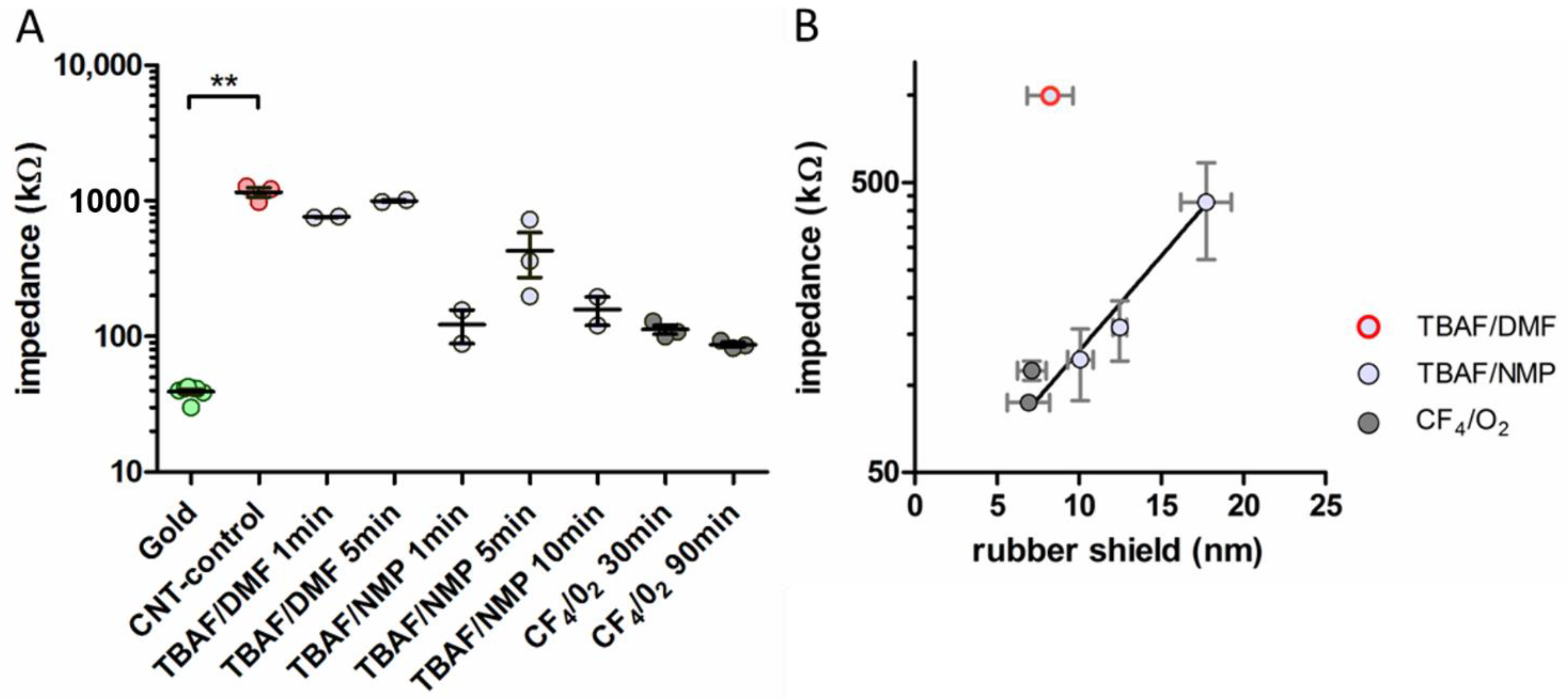
3.1. Impedances
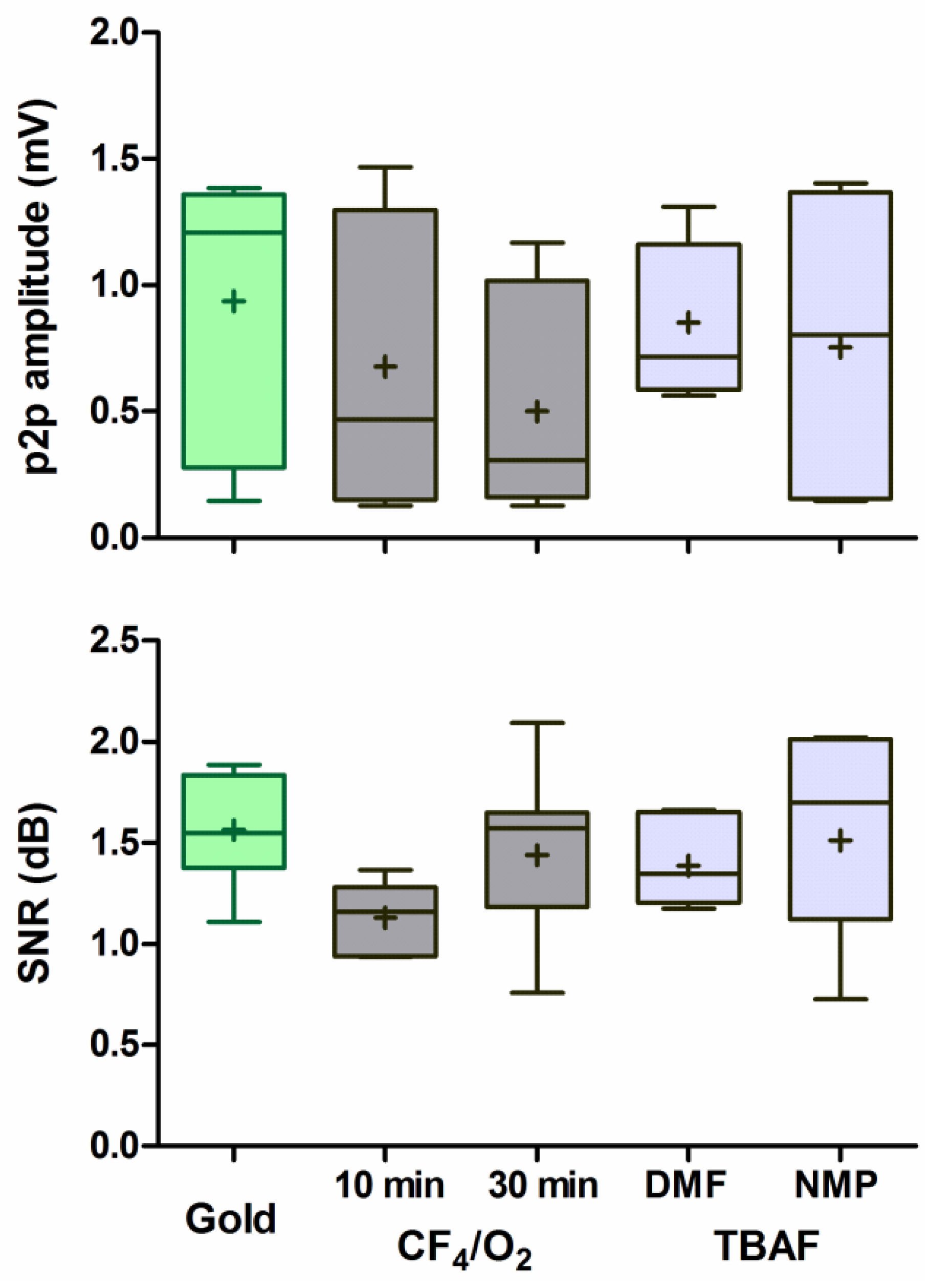
3.2. Response Amplitude and Signal-to-Noise Ratio
4. Discussion
4.1. Impedance
4.2. Response Amplitude and Signal-to-Noise Ratio
4.3. Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kral, A.; Yusuf, P.A.; Land, R. Higher-order auditory areas in congenital deafness: Top-down interactions and corticocortical decoupling. Hear. Res. 2017, 343, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, E.; Fabó, D.; Entz, L.; Ulbert, I.; Erőss, L. Intracranial neuronal ensemble recordings and analysis in epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 260, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konerding, W.S.; Janssen, H.; Hubka, P.; Tornøe, J.; Mistrik, P.; Wahlberg, L.; Lenarz, T.; Kral, A.; Scheper, V. Encapsulated cell device approach for combined electrical stimulation and neurotrophic treatment of the deaf cochlea. Hear. Res. 2017, 350, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareket-Keren, L.; Hanein, Y. Carbon nanotube-based multi electrode arrays for neuronal interfacing: Progress and prospects. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, E.W.; Botterman, B.R.; Romero, M.I.; Rossi, A.F.; Gross, G.W. Carbon nanotube coating improves neuronal recordings. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelov, S.D.; Koenen, S.; Jakobi, J.; Heissler, H.E.; Alam, M.; Schwabe, K.; Barcikowski, S.; Krauss, J.K. Electrophoretic deposition of ligand-free platinum nanoparticles on neural electrodes affects their impedance in vitro and in vivo with no negative effect on reactive gliosis. J. Nanobiotechnology 2016, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagiwa, S.; Fujishiro, A.; Sawahata, H.; Numano, R.; Ishida, M.; Kawano, T. Layer-by-layer assembled nanorough iridium-oxide/platinum-black for low-voltage microscale electrode neurostimulation. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Uram, J.D.; Yang, J.; Martin, D.C.; Kipke, D.R. Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) Film. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Fishman, H.A.; Dai, H.; Harris, J.S. Neural stimulation with a carbon nanotube microelectrode array. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2043–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, T.; Ben-David, M.; Kalifa, I.; Sorkin, R.; Ze’ev, R.A.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Hanein, Y.; Abrams, Z.R.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Hanein, Y. Electro-chemical and biological properties of carbon nanotube based multi-electrode arrays. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 35201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Giugliano, M.; Campidelli, S.; Gambazzi, L.; Businaro, L.; Markram, H.; Prato, M.; Ballerini, L. Interfacing neurons with carbon nanotubes: Electrical signal transfer and synaptic stimulation in cultured brain circuits. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6931–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-C.; Chuang, M.-C.; Chu, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Lai, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-T.; Chu, W.-L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y. Implantable graphene-based neural electrode interfaces for electrophysiology and neurochemistry in in vivo hyperacute stroke model. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, M.; Skousen, J.L.; Weder, C.; Capadona, J.R. Progress towards biocompatible intracortical microelectrodes for neural interfacing applications. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Akasaka, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Totsuka, Y.; Watari, F. Improvement in cell proliferation on silicone rubber by carbon nanotube coating. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2009, 19, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Akasaka, T.; Totsuka, Y.; Watari, F. Strong adhesion of saos-2 cells to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 173, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mattson, M.P.; Haddon, R.C.; Rao, A.M. Molecular functionalization of carbon nanotubes and use as substrates for neuronal growth. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2000, 14, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, G.B.; Lee, E.J.; An, T.; Shin, K.; Lee, S.E.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.; Latchoumane, C.; Shin, H.-S.; et al. Carbon-nanotube-modified electrodes for highly efficient acute neural recording. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, E.; Ansaldo, A.; Fadiga, L.; Ricci, D. Chemical vapour deposited carbon nanotube coated microelectrodes for intracortical neural recording. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 247, 2703–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.M.; Lee, Y.-T.T.; Yeh, S.-R.R.; Fang, W. Flexible carbon nanotubes electrode for neural recording. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Moon, J.H.; Baek, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.Y.; Hong, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, H.; Moon, J.; Baek, D.-H.; et al. CNT/PDMS Composite Flexible Dry Electrodesfor Long-Term ECG Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David-Pur, M.; Bareket-Keren, L.; Beit-Yaakov, G.; Raz-Prag, D.; Hanein, Y. All-carbon-nanotube flexible multi-electrode array for neuronal recording and stimulation. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burblies, N.; Schulze, J.; Schwarz, H.-C.C.; Kranz, K.; Motz, D.; Vogt, C.; Lenarz, T.; Warnecke, A.; Behrens, P. Coatings of different carbon nanotubes on platinum electrodes for neuronal devices: Preparation, cytocompatibility and interaction with spiral ganglion cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittinghausen, S.; Hackbarth, A.; Creutzenberg, O.; Ernst, H.; Heinrich, U.; Leonhardt, A.; Schaudien, D. The carcinogenic effect of various multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) after intraperitoneal injection in rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegtmeier, K.; Aliuos, P.; Lenarz, T.; Doll, T. Residual rubber shielded multi walled carbon nanotube electrodes for neural interfacing in active medical implants. Phys. Med. 2016, 1, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, A.; Foremny, K.; Doll, T. Carbon nanotube-silicone rubber on active thin-film implants. Phys. Status Solidi 2018, 215, 1700873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegtmeier, K.; Borrmann, F.; Doll, T. Wet-etch induced changes in impedance of carbon nanotube-silicone rubber electrode materials for active implants. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konerding, W.S.; Froriep, U.P.; Kral, A.; Baumhoff, P. New thin-film surface electrode array enables brain mapping with high spatial acuity in rodents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodger, D.C.; Fong, A.J.; Li, W.; Ameri, H.; Ahuja, A.K.; Gutierrez, C.; Lavrov, I.; Zhong, H.; Menon, P.R.; Meng, E.; et al. Flexible parylene-based multielectrode array technology for high-density neural stimulation and recording. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Baumhoff, P.; Kral, A. Cochlear implant stimulation of a hearing ear generates separate electrophonic and electroneural responses. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thostenson, E.T.; Chou, T.-W. Dominant role of tunneling resistance in the electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube–based composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 223114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigbeder, A.; Linares, M.; Devalckenaere, M.; Degée, P.; Claes, M.; Beljonne, D.; Lazzaroni, R.; Dubois, P. CH-π interactions as the driving force for silicone-based nanocomposites with exceptional properties. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.J.; Pouget, P. Do Electrode properties create a problem in interpreting local field potential recordings? J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 2315–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-L.; Teng, I.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, W.-L.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yen, S.-J.; Su, H.-C.; Yeh, S.-R.; Chen, H.; Yew, T.-R. Flexible UV-ozone-modified carbon nanotube electrodes for neuronal recording. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2177–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foremny, K.; Konerding, W.S.; Behrens, A.; Baumhoff, P.; Froriep, U.P.; Kral, A.; Doll, T. Carbon-Nanotube-Coated Surface Electrodes for Cortical Recordings In Vivo. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041029
Foremny K, Konerding WS, Behrens A, Baumhoff P, Froriep UP, Kral A, Doll T. Carbon-Nanotube-Coated Surface Electrodes for Cortical Recordings In Vivo. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041029
Chicago/Turabian StyleForemny, Katharina, Wiebke S. Konerding, Ailke Behrens, Peter Baumhoff, Ulrich P. Froriep, Andrej Kral, and Theodor Doll. 2021. "Carbon-Nanotube-Coated Surface Electrodes for Cortical Recordings In Vivo" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041029
APA StyleForemny, K., Konerding, W. S., Behrens, A., Baumhoff, P., Froriep, U. P., Kral, A., & Doll, T. (2021). Carbon-Nanotube-Coated Surface Electrodes for Cortical Recordings In Vivo. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041029






