Abstract
Impressive room-temperature gas-sensing capabilities have been reported for nanomaterials of many metal oxides, including SnO2, ZnO, TiO2, WO3, and Fe2O3, while little attention has been paid to the intrinsic difference among them. Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics have been prepared through convenient pressing and sintering. The former shows strong and stable responses to hydrogen in 20% O2-N2 (synthetic air) at room temperature, while the responses to hydrogen in N2 cannot be stabilized in limited times; the latter shows strong and stable responses to hydrogen in N2, while the responses to hydrogen in synthetic air are greatly depressed. Further analyses reveal that for Pt-ZnO, the responses result from the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen chemisorbed on ZnO; while for Pt-SnO2, the responses result from two reactions of hydrogen, one is that with oxygen chemisorbed on SnO2 and the other is hydrogen chemisorption on SnO2. These results reveal two different room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanisms among MOXs, which results in highly contrasting room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capabilities attractive for sensing hydrogen in oxygen-contained and oxygen-free environments, separately.
1. Introduction
Because of their high sensitivity, simple preparation, good stability, low production cost, and controllable morphology, gas sensors based on SnO2 thick films have been successfully commercialized for several decades. However, they all have to work at elevated temperatures (~500 °C) [1], which leads to increased energy consumption, shortened service life, and increased safety risks [2]. In order to develop room-temperature metal oxide (MOX) gas sensors, nano-materials of various MOXs have been synthesized and impressive room-temperature gas-sensing capabilities have been observed for many of them, including SnO2 [3], TiO2 [4,5], WO3 [6], Fe2O3 [7,8], ZnO [9,10,11,12,13,14]. It is generally believed that the large specific surface of nano-structured MOXs is the key for them to be room-temperature gas sensitive. However, highly impressive room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capabilities have been observed in Pt-WO3 and Pt-Nb2O5 composite ceramics with 1.5–2.5 µm WO3 grains and 1–2.5 µm Nb2O5 grains [15,16], respectively, and the catalytic role of Pt has been proven responsible for both kinds of composite ceramics to respond strongly to hydrogen at room temperature. As for the advantages of nano-structured MOXs, their large number of point defects, especially oxygen vacancies, have been found to play a vital role in enhancing their room-temperature gas sensitivities [17,18].
For sensing reducing gases in air by n-type MOXs, a well-known mechanism is established as follows [19,20]: oxygen is chemisorbed on MOXs, which captures electrons from MOXs and an electron-deficient layer, or depletion layer is formed beneath the surface of MOXs. When a reducing gas reacts with chemisorbed oxygen, the electrons are returned to MOXs and the resistance is decreased. This mechanism was first established to account for gas sensing by MOXs at elevated temperatures, and in recent years, it has been widely adopted to account for room-temperature gas-sensing capabilities revealed in various nanostructured MOXs, and much attention has been paid to decrease the grains of MOXs to sizes comparable to the thickness of depletion layer to achieve high sensitivities [21,22,23]. It should be pointed out, however, that the reaction between reducing gases and MOXs may strongly depend on the temperature and room-temperature gas-sensing mechanism may be different from that at elevated temperatures for MOXs. Up to date, the reaction between reducing gases and MOXs at room temperature has been actually quite neglected, and the difference between different MOXs has rarely been investigated, either. As a matter of fact, highly contrasting room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capabilities have already been observed for Pt-TiO2 and Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics prepared in the same way [24], which suggests that the room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanism should be studied for various MOXs individually.
As two typical MOXs for gas sensing, SnO2 and ZnO have been chosen for their room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanism to be studied in-depth in this study. Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics were first prepared through convenient pressing and sintering, and their room-temperature hydrogen-sensing characteristics were then investigated. As bulk materials prepared through pressing and sintering, they have such advantages of low fabrication cost, high mechanical robustness, and high thermal stability over those one and two-dimensional nanostructured MOXs. Roughly speaking, Pt-SnO2 was found attractive for sensing hydrogen in oxygen-contained atmospheres while Pt-ZnO was capable for sensing hydrogen in oxygen-free atmospheres. Two different room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanisms were further revealed for them: for Pt-ZnO, hydrogen only reacts with chemisorbed oxygen on ZnO at room temperature; while for Pt-SnO2, hydrogen not only reacts with chemisorbed oxygen on SnO2 but also is chemisorbed on SnO2 at room temperature by itself. Obviously, these different mechanisms are responsible for the highly contrasting room-temperature hydrogen-sensing characteristics observed for them.
2. Materials and Methods
SnO2 nanoparticles (70 nm), ZnO nanoparticles (50 nm), and Pt particles (~1 μm), all from Aladdin, Shanghai, China, were used as the starting materials. First of all, SnO2 nanoparticles and Pt particles were dispersed into deionized water at a weight ratio of 99:1. Then the mixtures were stirred for 4 h on a magnetic stirrer, next dried in an oven at 120 °C for 12 h. After that a pressure of about 4 MPa was applied by a hydraulic press to press the dry powders into pellets with a diameter of about 10 mm and a thickness of about 1 mm. Pellets of Pt-ZnO were prepared in the same way starting from ZnO nanoparticles and Pt particles. A series of sintering temperatures were investigated for both kinds of nanoceramics, and the pellets of Pt-SnO2 sintered at 825 °C in air for 2 h showed the best performance among the Pt-SnO2 nanoceramics, and the Pt-ZnO pellets sintered at 700 °C showed the best performance among the Pt-ZnO nanoceramics, which were systematically investigated in this study. A pair of rectangular Au electrodes was coated on the main surface of the pellets by DC magnetron sputtering to facilitate gas-sensitive measurement.
A commercial gas sensor measurement system (GRMS-215, Partulab Com., Wuhan, China) [4] was used to measure the hydrogen-sensing characteristics of the sintered samples. During the measurement, the room temperature was maintained at 25 °C, and the relative humidity (RH) in air was maintained at about 50%.
An X-ray diffractometer (BRUKER AXS D8 ADVANCE) was used to perform phase identifications using Cu Kα radiation. A scanning electron microscopy (SIRION TMP) was used to conduct microstructural observations. Composition analyses were obtained through energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) using OXFORD Aztec 250 instrument.
3. Results and Discussions
Figure 1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns taken for the surface of Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO nanoceramics with 1 wt% Pt sintered at 825 and 700 °C, respectively. As marked in Figure 1a, it is obvious that there are two peaks from metallic Pt, all other peaks belong to SnO2, which exists in a rutile phase according to JCPDS file No. 41-1445. Two peaks from metallic Pt can also be observed in Figure 1b, and all other peaks are from ZnO, which exists in hexagonal phase according to JCPDS file No. 36-1451. Hence what we prepared in this study are composites of SnO2 and Pt, and ZnO and Pt, separately. It is reasonable that Pt exists in metallic state in those nanoceramics due to the high stability of Pt [4,15,24].
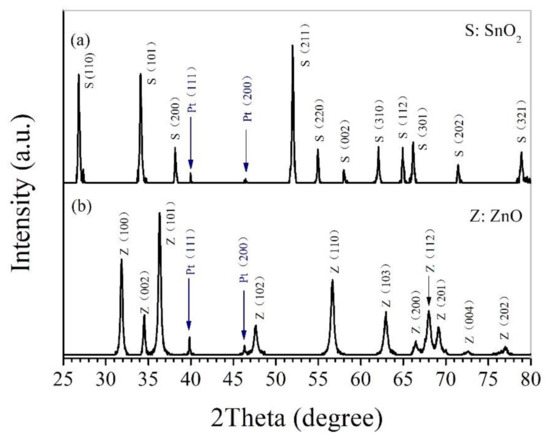
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction patterns taken for the surface of (a) Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics with 1 wt% Pt sintered at 825 °C and (b) Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics with 1 wt% Pt sintered at 700 °C.
Figure 2 shows SEM micrographs of Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics, separately. For Figure 2a, it can be seen that most grains are around 70 nm in size, which are the same as that of the as-received SnO2 nanoparticles, indicating no obvious grain growth in the sintering. As shown in Figure 2b, ZnO grains are quite non-uniform, some are around 50 nm while many other grains are much larger, indicating that some grain growth has occurred in local areas during the sintering. For both kinds of composite nanoceramics, there is no noticeable shrinkage in diameter after sintering. As a matter of fact, densification should be avoided for the sintering of ceramics intended for gas-sensing applications [5].
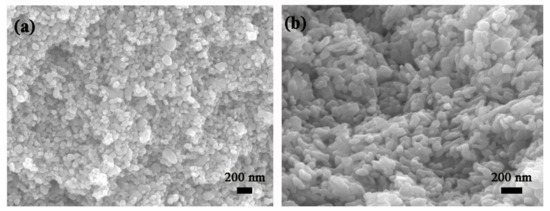
Figure 2.
(a) SEM micrography of Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramic sintered in the air at 825 °C for 2 h. (b) SEM micrography of Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramic sintered in the air at 700 °C for 2 h.
Highly attractive room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capabilities have been reported for Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics [24]. As shown in Figure 3, such an attractive room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capability has also been obtained for the Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics prepared in this study. For H2 over the range from 1% to 0.125% in 20% O2-N2 (synthetic air), the resistance of the sample decreases quickly upon being exposed to hydrogen and becomes stable in limited time. When the concentration of H2 decreases from 1% to 0.125%, the resistance decrease, or the response decreases monotonously. As the content of O2 in air is around 20%, these results suggest that Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics are able to sense hydrogen of a range of concentrations in air at room temperature. On the other hand, for 0.125% H2 in N2, the resistance decreases sharply with increasing time until goes beyond the measuring limit, as shown in Figure 3. Obviously, this response forms a sharp contrast with that for 0.125% H2 in synthetic air and Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics therefore should not be able to sense hydrogen in oxygen-free environments at room temperature.
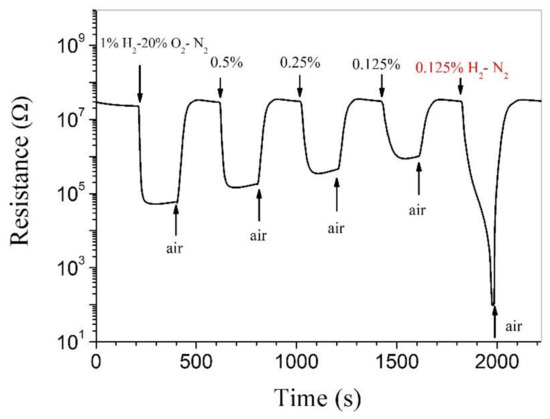
Figure 3.
Room-temperature responses to 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, 0.125% H2 in synthetic air (20% O2-N2) and to 0.125% H2 in N2, separately, for Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramic sintered at 825 °C.
The room-temperature responses of Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics to hydrogen in N2 and hydrogen in synthetic air are shown in Figure 4. As shown in Figure 4a, the resistance of the Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramic sample decreases rapidly with time upon being exposed to hydrogen in N2 and becomes stable in a limited time. The sensitivity of a gas sensitive material is usually defined as Ra/Rg, where Ra and Rg are the electrical resistances of the material in clean air and in the measuring gas, respectively [4]. It can be calculated that the sensitivity of the sample is 733, 623, 483, and 208 to 5%, 1%, 0.5%, and 0.125% H2 in N2, respectively. It is clear that Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics are able to sense hydrogen in oxygen-free atmospheres at room temperature, where hydrogen sensors based on Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics cannot be applied. As shown in Figure 4b, the sensitivity of the sample is 60, 35, and 5 to 1%, 0.5%, and 0.125% H2 in synthetic air, respectively. Compared with Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics, Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics show a much smaller sensitivity to the same concentration of hydrogen in synthetic air. In short, Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics are attractive for sensing hydrogen in oxygen-free atmospheres, while Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics are attractive for sensing hydrogen in air.
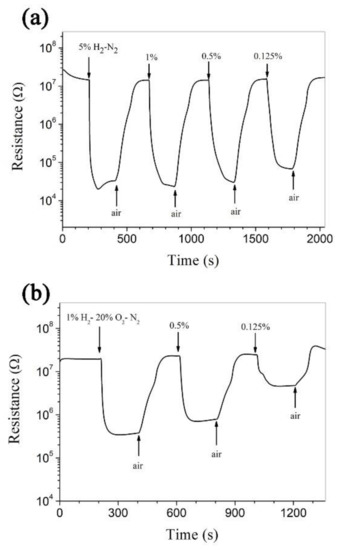
Figure 4.
Room-temperature responses (a) to 5%, 1%, 0.5%, and 0.125% H2 in N2, and (b) to 1%, 0.5%, and 0.125% H2 in synthetic air (20% O2-N2), separately, for Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramic sintered at 700 °C.
To study the hydrogen-sensing mechanisms for Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics, we have measured their responses to some special atmospheres in certain well-designed sequences. For Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics, it has been concluded that hydrogen can be chemisorbed on SnO2 at room temperature in the presence of Pt [24]. Figure 5 shows the measuring result obtained for a Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramic sample. The resistance of the sample decreases sharply with increasing time in flowing 0.01% H2-N2. When the atmosphere is changed to N2, a turning point appears and the resistance increases gradually with time in flowing N2. Both the decrease and the increase in resistance can be well explained in terms of hydrogen chemisorption on SnO2: in flowing 0.01% H2-N2, more and more hydrogen atoms are chemisorbed on SnO2 and so the resistance of SnO2 decreases continuously; when the atmosphere is changed to N2, hydrogen atoms chemisorbed on SnO2 desorb as hydrogen molecules and the electrons they have donated to SnO2 leave with them, so the resistance increases with time in flowing N2.
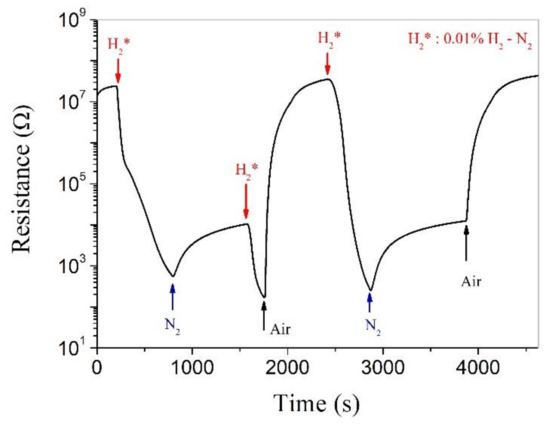
Figure 5.
Real-time electrical resistance response of a Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramic pellet, sintered at 825 °C and coated with a pair of Au electrodes, to different kinds of atmospheres at room temperature.
As shown in the second cycle, when the sample is kept in flowing N2 for a relatively long time and the resistance of the sample is almost stabilized, indicating that the hydrogen desorption has gradually finished. However, the resistance at this state is still much smaller than the initial resistance in air, and when the atmosphere is then changed from N2 to air, the resistance is increased quickly until its initial value in air. These results suggest that in flowing 0.01% H2-N2, hydrogen must have two kinds of reactions with SnO2: one is the reaction with SnO2, or hydrogen chemisorption on SnO2, and the other is the reaction with oxygen chemisorbed on SnO2. When the atmosphere is changed from 0.01% H2-N2 to N2, oxygen chemisorption destroyed by hydrogen cannot be restored and so the resistance cannot be fully recovered; while for the recovery in air, oxygen not only reacts quickly with hydrogen chemisorbed on SnO2 but also is chemisorbed on SnO2 by itself, so the resistance is fully recovered to its initial state in air.
The room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capability of SnO2 is thus related to both oxygen adsorption and hydrogen adsorption. Under anaerobic conditions, more and more hydrogen atoms are chemisorbed on SnO2, and the resistance of SnO2 becomes smaller and smaller, which cannot be stabilized in a limited time. In the case of hydrogen in air, the surface of SnO2 has both hydrogen adsorption and oxygen adsorption. The former contributes electrons to the conduction band of SnO2, and the latter captures electrons from SnO2, which finally reach equilibrium and the resistance of SnO2 can be stabilized in a limited time. Therefore, the Pt-SnO2 system can effectively detect hydrogen in an aerobic environment, but it is unable to detect hydrogen in an oxygen-free environment.
Figure 6 shows the responses to some special atmospheres in a certain sequence for a Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramic sample, which forms a sharp contrast with Figure 5 mainly in two respects. First, the resistance of the sample can be stabilized in flowing 5% H2-N2 in a limited time, while in Figure 5, the resistance of the sample cannot be stabilized in a very low concentration of hydrogen (0.01% H2-N2). Second, the sample shows no responses in its resistance to subsequent changes in the surrounding atmosphere, from 5% H2-N2 to N2, and then from N2 to 5% H2-N2. From these results, we can infer that the hydrogen-sensing mechanism of ZnO is as follows: in flowing 5% H2-N2, hydrogen reacts with adsorbed oxygen on the surface of ZnO, which release the electrons captured by oxygen to ZnO and the resistance of ZnO is decreased. After the reaction is finished for this concentration of hydrogen, the resistance is stabilized. There must be no hydrogen chemisorption on ZnO, and the resistance of the sample thus remains unchanged when its surrounding atmosphere is changed from 5% H2-N2 to N2, and then from N2 to 5% H2-N2. Finally, when air is introduced, oxygen is chemisorbed on ZnO and the resistance is fully recovered. In this way, Pt-ZnO system is able to detect hydrogen in an oxygen-free environment.
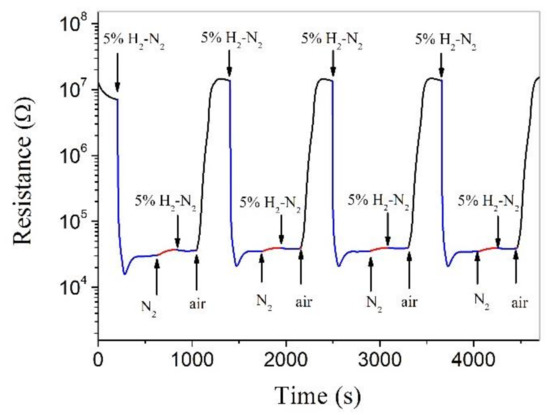
Figure 6.
Real-time electrical resistance response of a Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramic pellet, sintered at 700 °C and coated with a pair of Au electrodes, to different kinds of atmospheres at room temperature.
It is interesting to compare the room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanisms between Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics. As shown in Figure 7a, for Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics, hydrogen molecules are split into atoms by Pt, which are highly reactive and some of them react with oxygen chemisorbed on SnO2, and the others are chemisorbed on SnO2. Both kinds of reactions release electrons to SnO2 and for hydrogen in N2, due to hydrogen chemisorption, the resistance of SnO2 cannot be stabilized even when all chemisorbed oxygen has been reacted by hydrogen. For Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics, on the contrary, there is no hydrogen chemisorption on ZnO, as shown in Figure 7b. The resistance of ZnO will be stabilized when the reaction between chemisorbed oxygen and hydrogen atoms is finished, in this way they show stable responses to hydrogen in N2. Obviously, some intrinsic differences between SnO2 and ZnO are responsible for their different reactions with hydrogen atoms, which result in highly contrasting room-temperature hydrogen-sensing characteristics between Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics.
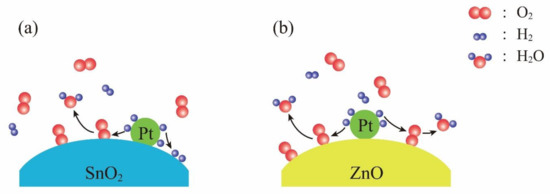
Figure 7.
Schematic illustrations for room-temperature hydrogen-sensing mechanisms of (a) Pt-SnO2 composite nanoceramics, and (b) Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics.
4. Conclusions
Pt-SnO2 and Pt-ZnO composite nanoceramics have been prepared through convenient pressing and sintering. These two typical MOXs exhibit different behaviors to hydrogen in different atmospheres. For Pt-SnO2, its response to hydrogen in synthetic air is strong and stable, but its response to hydrogen in N2 cannot be stabilized. For Pt-ZnO, it shows strong and stable responses to hydrogen in N2. Further study shows that the room-temperature hydrogen-sensing capability of Pt-SnO2 is determined by both oxygen chemisorption and hydrogen chemisorption while that of Pt-ZnO is determined by oxygen chemisorption alone. These results clearly show that the room-temperature gas-sensing mechanism of one MOX can be basically different that of another, which leads to contrasting room-temperature gas-sensing capabilities among MOXs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and W.C.; methodology, M.L., P.L., and Y.H. (Yong Huang); validation, Y.H. (Yongming Hu), Z.T., and W.C.; formal analysis, M.L., P.L., and W.C.; investigation, M.L., P.L., Y.H. (Yong Huang), and L.C.; data curation, M.L. and P.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, M.L., P.L., and W.C.; visualization, M.L.; supervision, W.C.; project administration, W.C.; funding acquisition, W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Program of Shenzhen under Grant No. JCYJ20190808152803567, the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant No. 2020YFB2008800, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. U2067207.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Boon-Brett, L.; Bousek, J.; Black, G.; Moretto, P.; Castello, P.; Huebert, T.; Banach, U. Identifying performance gaps in hydrogen safety sensor technology for automotive and stationary applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E.; Aglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z. Stable and highly sensitive gas sensors based on semiconducting oxide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Fei, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. Construction of ZnO/SnO2 heterostructure on reduced graphene oxide for enhanced nitrogen dioxide sensitive performances at room temperature. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, P.; Guo, S.; Chen, W.; Tang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Extraordinary room-temperature hydrogen sensing capabilities of porous bulk Pt-TiO2 nanocomposite ceramics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Chan, H.; Chen, W. Gas sensing capabilities of TiO2 porous nanoceramics prepared through premature sintering. J. Adv. Ceram. 2015, 4, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. Improved room-temperature hydrogen sensing performance of directly formed Pd/WO3 nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 193, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, G. Flexible and highly sensitive humidity sensor based on sandwich-like Ag/Fe3O4 nanowires composite for multiple dynamic monitoring. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, S. Core-shell α-Fe2O3@SnO2/Au hybrid structures and their enhanced gas sensing properties. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xi, R.; Huang, H.; Zhang, S.; Pan, G. Electrodeposition of ZnO nanorods onto GaN towards enhanced H2S sensing. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, R.; Qi, W.; Cai, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Xiang, L.; Xie, D. Reduced graphene oxide/mesoporous ZnO NSs hybrid fibers for flexible, stretchable, twisted, and wearable NO2 E-textile gas sensor. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2809–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Dong, T.; Jia, C.; Yang, P. Ultraselective acetone-gas sensor based ZnO flowers functionalized by Au nanoparticle loading on certain facet. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 288, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Kou, J.; Fan, H.; Tian, Z.; Kong, W.; Ju, S. Facile and versatile sol-gel strategy for the preparation of a High-Loaded ZnO/SiO2 adsorbent for room-temperature H2S removal. Langmuir 2019, 35, 7759–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejos, S.; Gracia, I.; Pizurova, N.; Figueras, E.; Cechal, J.; Hubalek, J.; Cane, C. Gas sensitive ZnO structures with reduced humidity-interference. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 301, 127054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, X. Fabrication of 3D ordered mesoporous ball-flower structures ZnO material with the excellent gas sensitive property. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 300, 127050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, G.; Sun, B.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, S.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W. Pt-WO3 porous composite ceramics outstanding for sensing low concentrations of hydrogen in air at room temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6420–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P. Singular room-temperature hydrogen sensing characteristics with ultrafast recovery of Pt-Nb2O5 porous composite ceramics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 30186–30192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Kilinc, N.; Torun, I.; Kosemen, A.; Sahin, Y.; Ozturk, Z. Hydrogen sensing properties of ZnO nanorods: Effects of annealing, temperature and electrode structure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5191–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Huang, R.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Lan, Z.; Chen, W.; Gu, H. Defect-original room-temperature hydrogen sensing of MoO3 nanoribbon: Experimental and theoretical studies. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 260, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Akbar, S.; Morris, P. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 211, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, M. Porous metal oxides as gas sensors. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, V.; Umarji, A. Analyzing the kinetic response of tin oxide-carbon and tin oxide-CNT composites gas sensors for alcohols detection. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 037138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, Y. A review of recent developments in tin dioxide composites for gas sensing application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Neri, G.; Pinna, N. Nanostructured materials for room-temperature gas sensors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 795–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, P.; Guo, S.; Chen, W.; Tang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Contrasting room-temperature hydrogen sensing capabilities of Pt-SnO2 and Pt-TiO2 composite nanoceramics. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3528–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).