Tunable Thermal Camouflage Based on GST Plasmonic Metamaterial
Abstract
1. Introduction
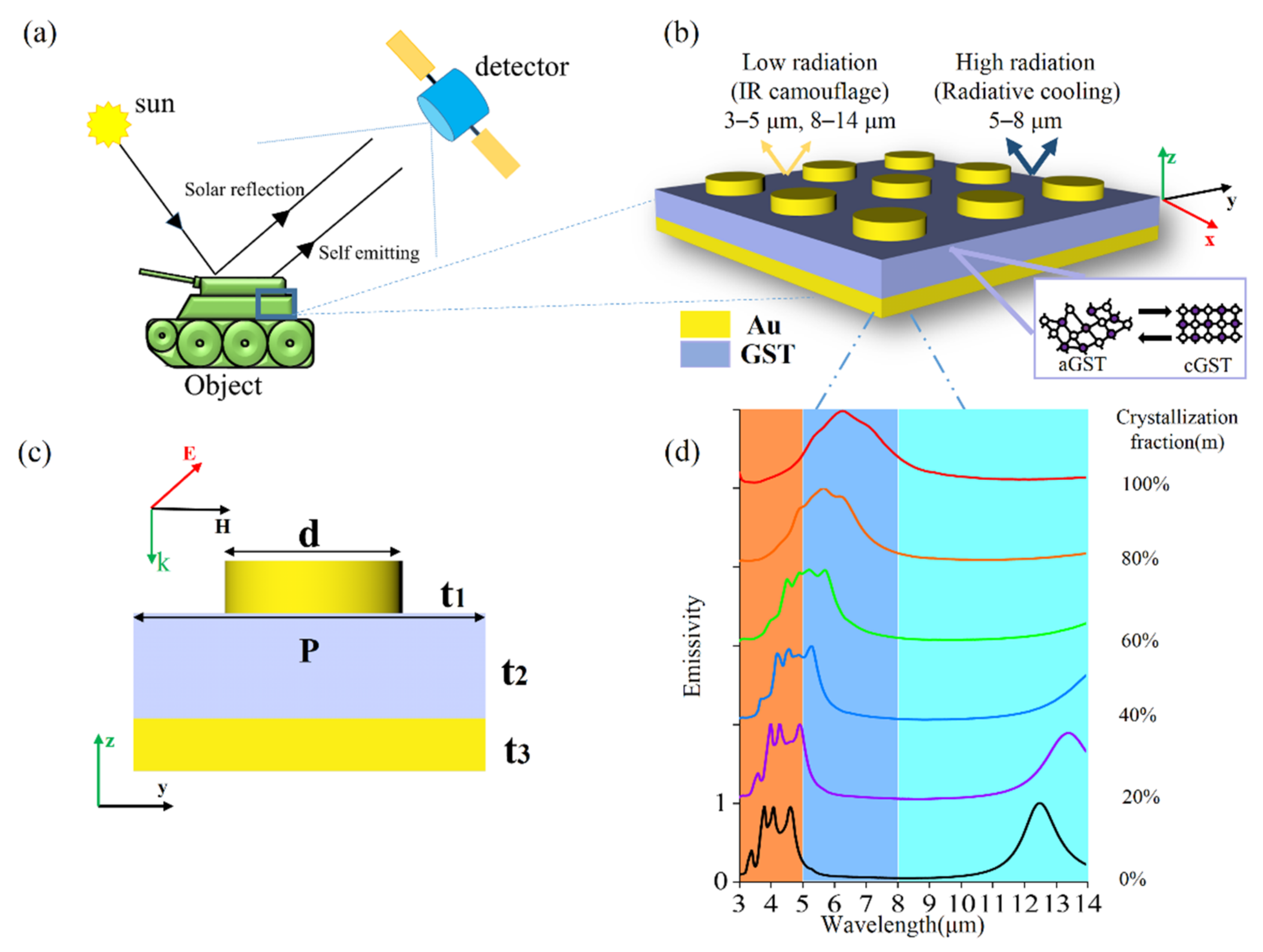
2. Structure Design
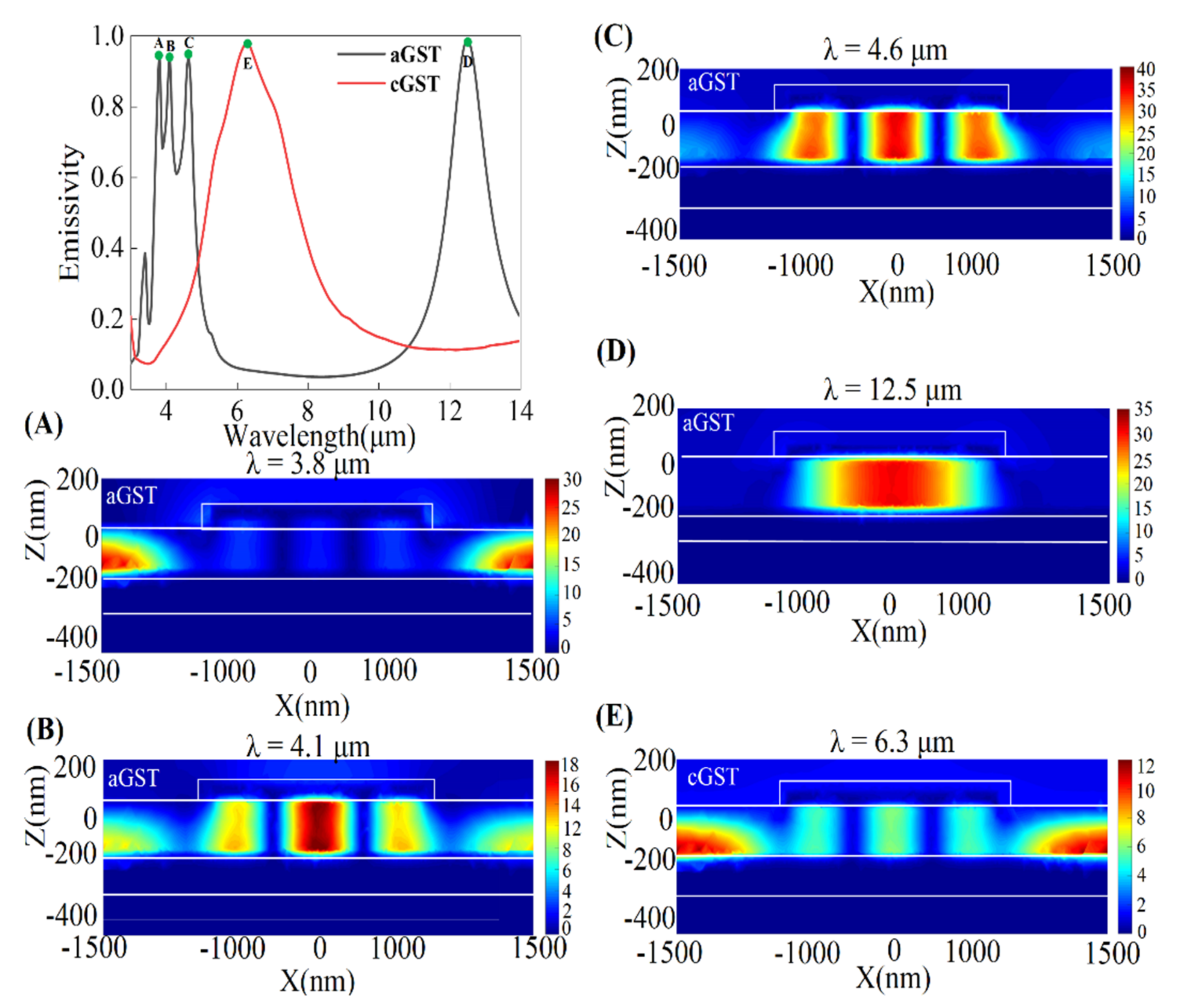
3. Physical Mechanism
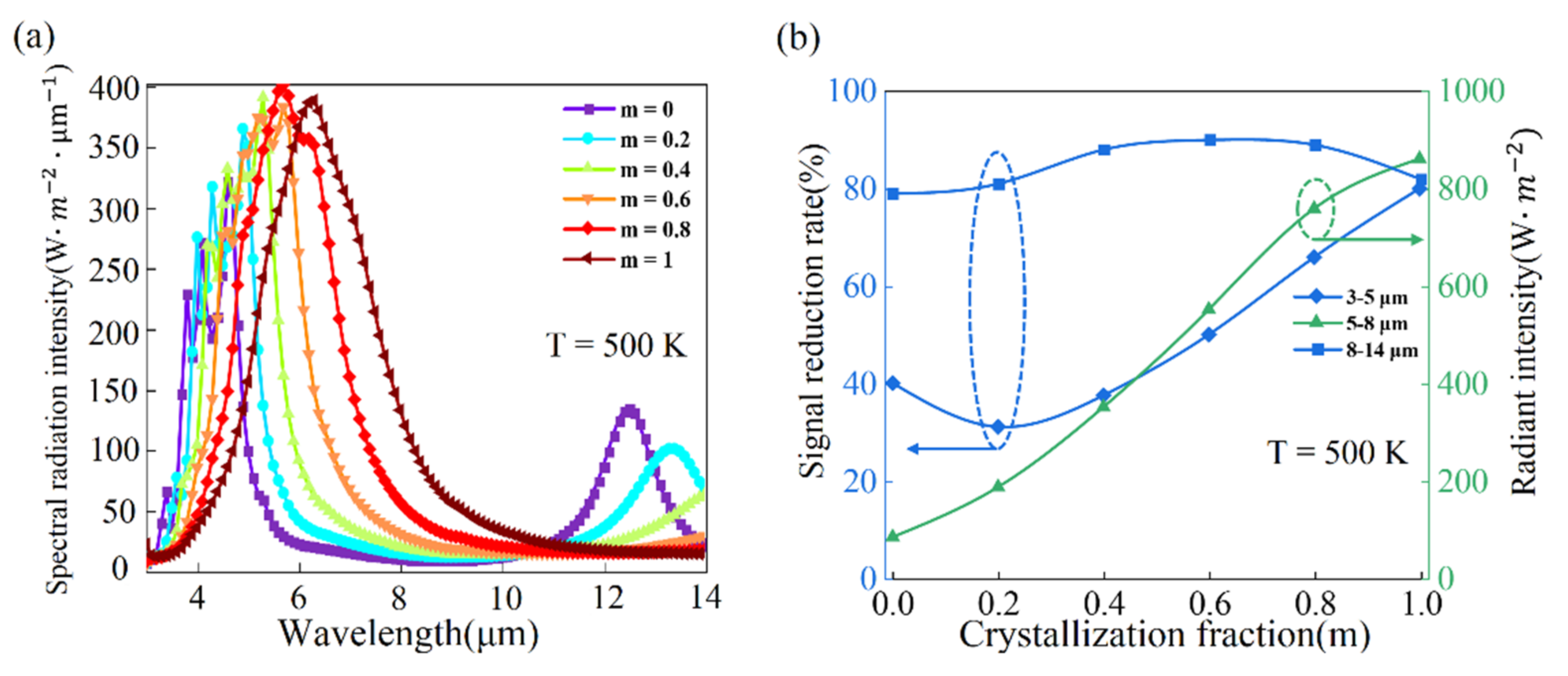
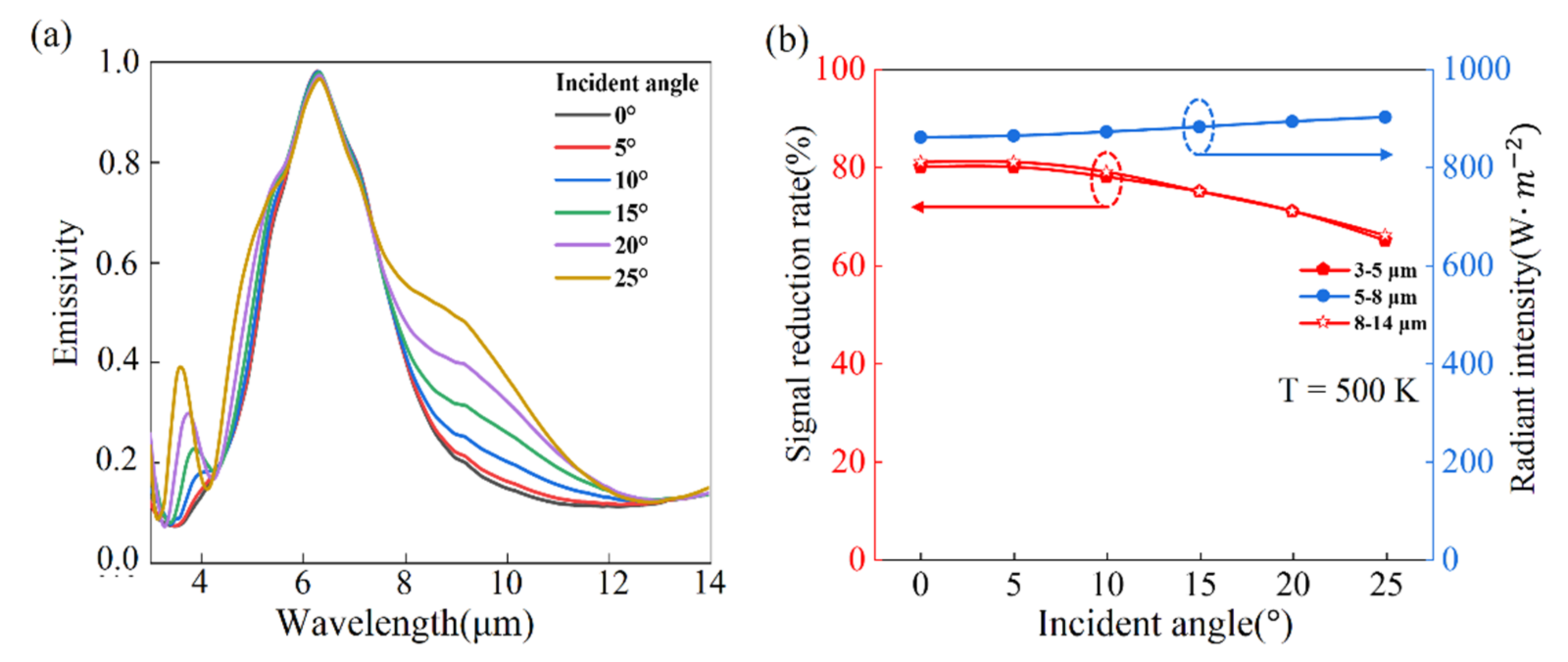
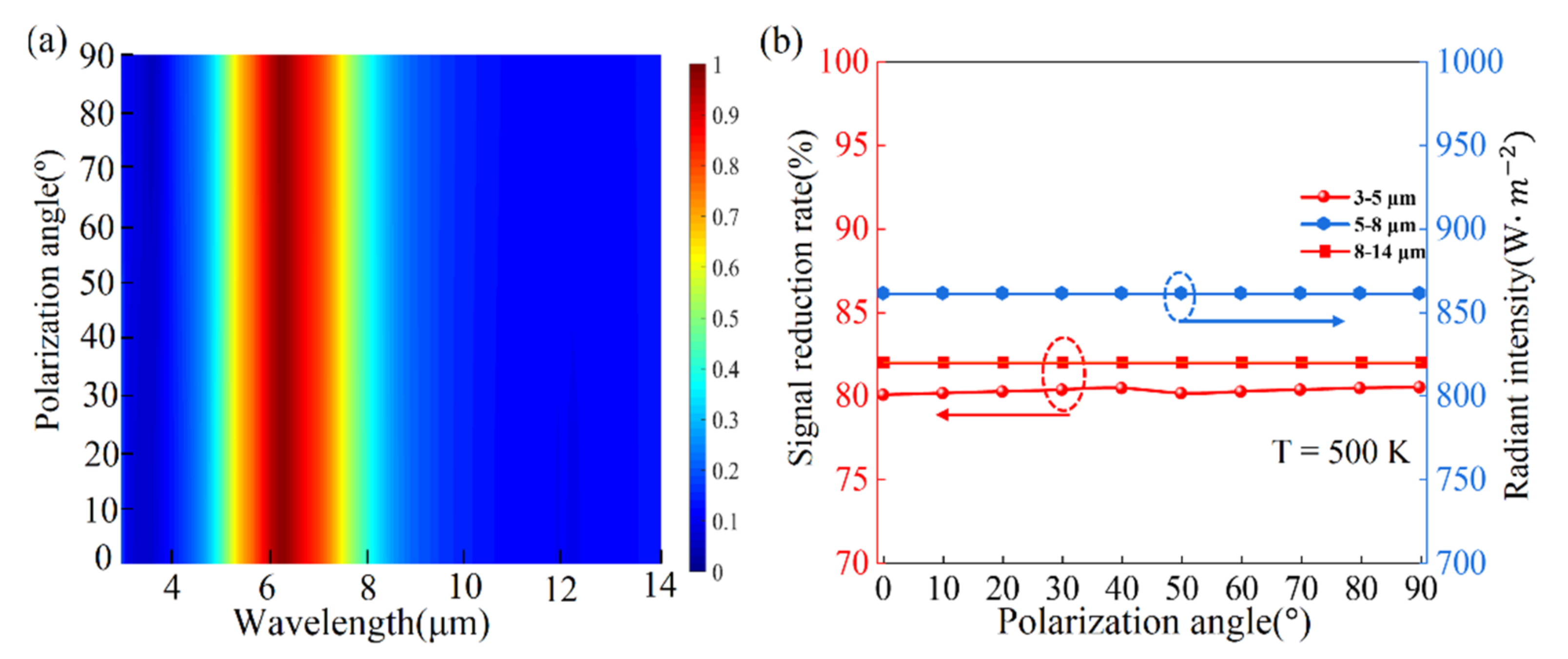
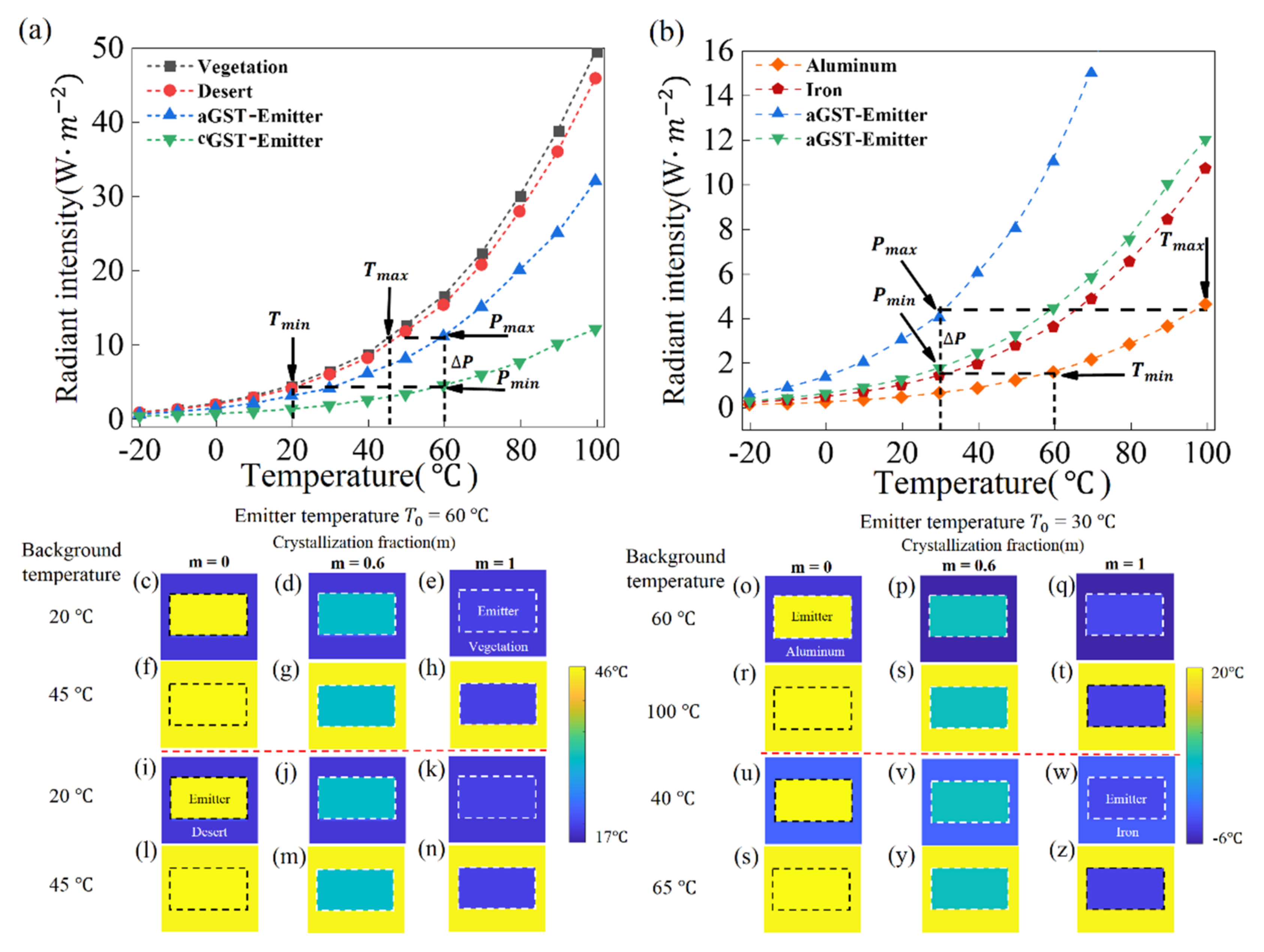
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raman, A.P.; Anoma, M.A.; Zhu, L.; Rephaeli, E.; Fan, S. Passive radiative cooling below ambient air temperature under direct sunlight. Nature 2014, 515, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Fan, S. Self-adaptive radiative cooling based on phase change materials. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A777–A787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.R.; Lai, K.L.; Wang, C.M. Passive temperature control based on a phase change metasurface. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, D.; Lefebvre, A.; Coutrot, A.L.; Moldovan-Doyen, I.; Hugonin, J.P.; Boutami, S.; Marquier, F.; Benisty, H.; Greffet, J.J. Plasmonic metasurface for directional and frequency-selective thermal emission. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 4, 014023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raponi, A.; Ciarniello, M.; Capaccioni, F.; Mennella, V.; Filacchione, G.; Vinogradoff, V.; Moroz, L.V.; Rinaldi, G.; Istiqomah, I.; Leyrat, C. Infrared detection of aliphatic organics on a cometary nucleus. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, A.; Bierman, D.M.; Nam, Y.; Chan, W.R.; Celanović, I.; Soljačić, M.; Wang, E.N. A nanophotonic solar thermophotovoltaic device. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyf, H.R.; Henry, A. Thermophotovoltaics: A potential pathway to high efficiency concentrated solar power. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2654–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Santhanam, P.; Fan, S. Suppressing sub-bandgap phonon-polariton heat transfer in near-field thermophotovoltaic devices for waste heat recovery. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 091106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Franklin, D.; Cozart, J.; Safaei, A.; Chanda, D. Adaptive multispectral infrared camouflage. ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhu, H.; Kaur, S.; Qiu, M. Multi-band middle-infrared-compatible camouflage with thermal management via simple photonic structures. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Fan, S.; et al. Fast adaptive thermal camouflage based on flexible VO2/graphene/CNT thin films. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8365–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ye, H. Optimization and preparation of a visible-infrared compatible stealth film based on D/M/D structure. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fan, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Meng, Z. A visible-light-transparent camouflage-compatible flexible metasurface for infrared-radar stealth applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 54, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Kou, W.; Yang, L.; Du, Y.C. Two-dimensional thermal illusion device with arbitrary shape based on complementary media. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Gong, R. Multi-layer composite structure covered polytetrafluoroethylene for visible-infrared-radar spectral Compatibility. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 505108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Morsy, A.M.; Povinelli, M.L. Design of VO2-coated silicon microspheres for thermally-regulating paint. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 21787–21793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Zheng, C.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, W.; Kaur, S.; Ghosh, P.; Qiu, M. High-temperature infrared camouflage with efficient thermal management. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, C.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Guo, Z. High-efficiency and broadband near-infrared bi-functional metasurface based on rotary different-size silicon nanobricks. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, C.; Guo, K.; Guo, Z. Spin-selected Dual-wavelength plasmonic metalenses. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Kang, Q.L.; Wang, J.; Guo, K.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, Z. Dielectric metasurface-based high-efficiency mid-infrared optical filter. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Nie, X.; Shen, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, J.; Guo, K. Actively tunable terahertz switches based on subwavelength graphene waveguide. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, H.; Guo, K.; Shen, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, Z. High-efficiency visible transmitting polarizations devices based on the GaN metasurface. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, K.; Shen, F.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, H. Review of the functions of Archimedes’ spiral metallic nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 405. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ma, W.Z.; Chen, W.; Yu, G.X.; Chen, Y.S.; Deng, X.C.; Yang, C.F. Numerical analysis of an ultra-wideband metamaterial absorber with high absorptivity from visible light to near-infrared. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 23748–23760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Shen, F.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, J.; Guo, K. Active-tuning and polarization-independent absorber and sensor in the infrared region based on the phase change material of Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fang, Y.; Luo, L.; Guo, K.; Guo, Z. A dynamically tunable and wide-angle terahertz absorber based on graphene-dielectric grating. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2050292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, Q.; Du, K.; Cai, L.; Lu, J.; Qiu, M. Dynamic Thermal Emission Control Based on Ultrathin Plasmonic Metamaterials Including Phase-Changing Material GST. Laser Photonics Rev. 2017, 11, 1700091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tyler, T.; Starr, T.; Starr, A.F.; Jokerst, N.M.; Padilla, W.J. Taming the blackbody with infrared metamaterials as selective thermal emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 045901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; He, Z.; Dong, S. All-metal frequency-selective absorber/emitter for laser stealth and infrared stealth. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, V.W.; Sherrott, M.C.; Jang, M.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, L.; Choi, M.; Sweatlock, L.A.; Atwater, H.A. Electronic modulation of infrared radiation in graphene plasmonic resonators. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerislioglu, B.; Bakan, G.; Ahuja, R.; Adam, J.; Mishra, Y.K.; Ahmadivand, A. The role of Ge2Sb2Te5 in enhancing the performance of functional plasmonic devices. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 12, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakan, G.; Gerislioglu, B.; Dirisaglik, F.; Jurado, Z.; Sullivan, L.; Dana, A.; Silva, H. Extracting the temperature distribution on a phase-change memory cell during crystallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 164504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, K.; Shen, F.; Zhou, H.; Guo, Z. Theoretical analysis and simulation of a tunable mid-infrared filter based on Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST) metasurface. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 132, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Kang, Q.; Guo, K.; Guo, Z. Tunable GST metasurfaces for chromatic aberration compensation in the mid-infrared. Opt. Mater. 2020, 109, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihoglu, O.; Uzlu, H.B.; Yakar, O.; Aas, S.; Balci, O.; Kakenov, N.; Balci, S.; Olcum, S.; Siizer, S.; Kocabas, C. Graphene-based adaptive thermal camouflage. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4541–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Stiubianu, G.T.; Gorodetsky, A.A. Adaptive infrared-reflecting systems inspired by cephalopods. Science 2018, 359, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, L.; Pan, M.; Ghosh, P.; Du, K.; Qiu, M. Thermal camouflage based on the phase-changing material GST. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Dong, W.; Behera, J.K.; Chew, L.; Simpson, R.E. Inter-diffusion of plasmonic metals and phase change materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palik, E.D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Du, K.K.; Li, Q.; Lyu, Y.B.; Ding, J.C.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Qiu, M. Control over emissivity of zero-static-power thermal emitters based on phase-changing material GST. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e16194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voshchinnikov, N.V.; Videen, G.; Henning, T. Effective medium theories for irregular fluffy structures: Aggregation of small particles. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Tseng, M.L.; Chen, J.; Wu, P.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Hsieh, W.T.; Wu, H.J.; Sun, G.; et al. Active dielectric metasurface based on phase-change medium. Laser Photonics Rev. 2016, 10, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Kao, T.S.; Ng, B.; Li, X.; Luo, X.G.; Luk’Yanchuk, B.; Maier, S.A.; Hong, M.H. Hybrid phase-change plasmonic crystals for active tuning of lattice resonances. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 13691–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspnes, D.E. Local-field effects and effective-medium theory: A microscopic perspective. Am. J. Phys. 1982, 50, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y.A.; Ghajar, A.J. Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & Applications; Prentice-Hall: Englewood-Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Lim, J.S.; Chang, I.; Cho, H.H. Metamaterial-selective emitter for maximizing infrared camouflage performance with energy dissipation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21250–21257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Q.; Li, D.; Guo, K.; Gao, J.; Guo, Z. Tunable Thermal Camouflage Based on GST Plasmonic Metamaterial. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020260
Kang Q, Li D, Guo K, Gao J, Guo Z. Tunable Thermal Camouflage Based on GST Plasmonic Metamaterial. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020260
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Qianlong, Dekui Li, Kai Guo, Jun Gao, and Zhongyi Guo. 2021. "Tunable Thermal Camouflage Based on GST Plasmonic Metamaterial" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020260
APA StyleKang, Q., Li, D., Guo, K., Gao, J., & Guo, Z. (2021). Tunable Thermal Camouflage Based on GST Plasmonic Metamaterial. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020260






