Multifunctional Electrically Conductive Copper Electroplated Fabrics Sensitizes by In-Situ Deposition of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Pretreatment
2.2.2. Copper Particles Deposition
2.2.3. Silver Particles Deposition
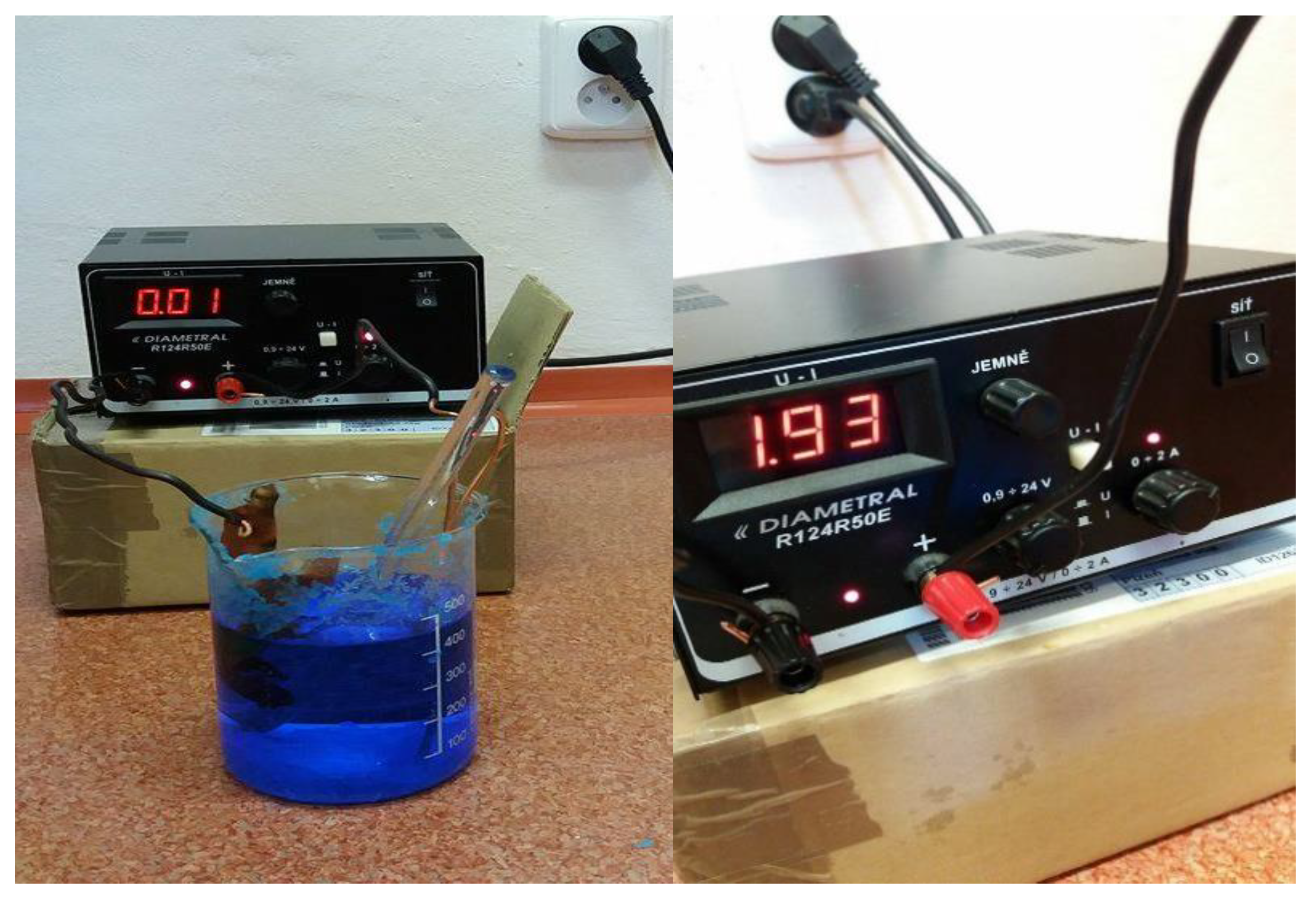
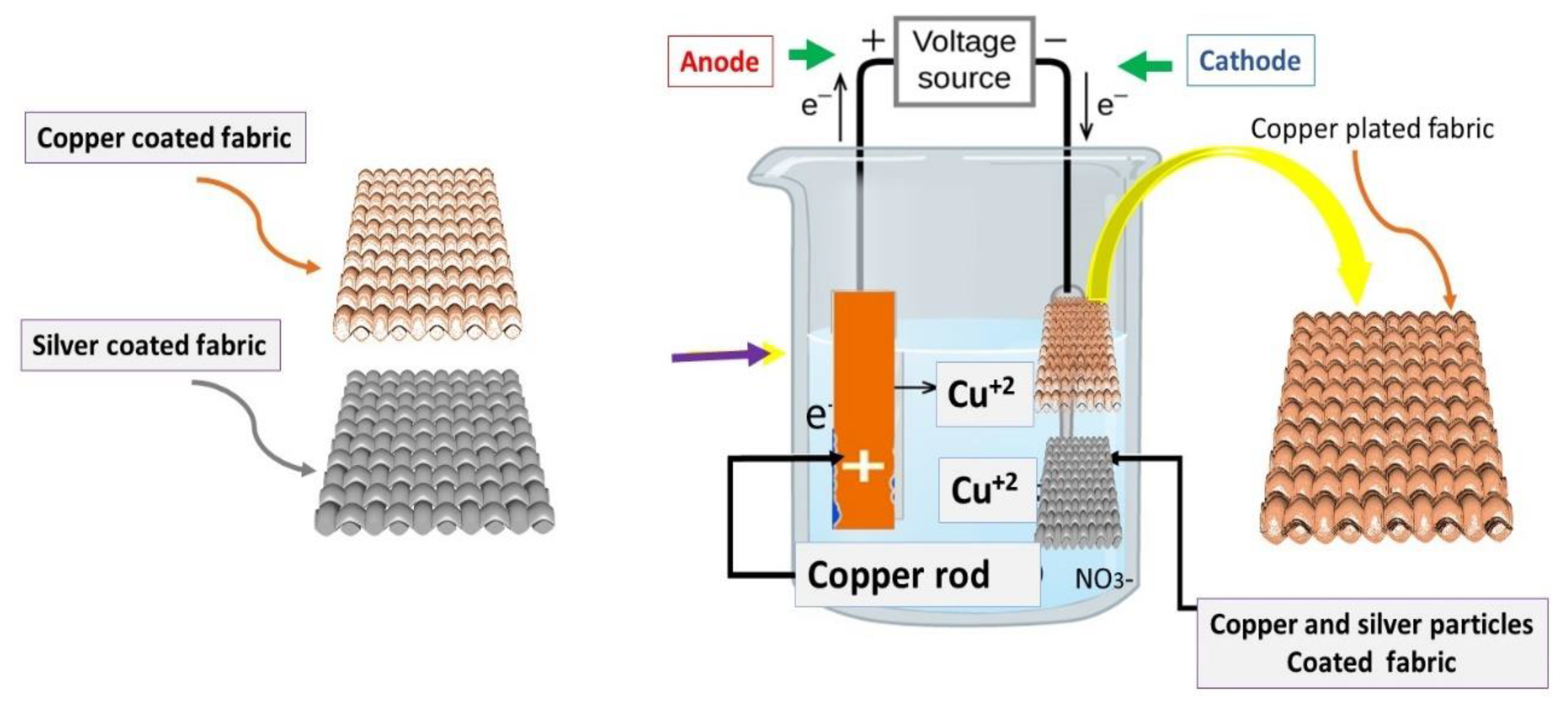
2.2.4. Electrolytic Copper Plating
2.3. Testing
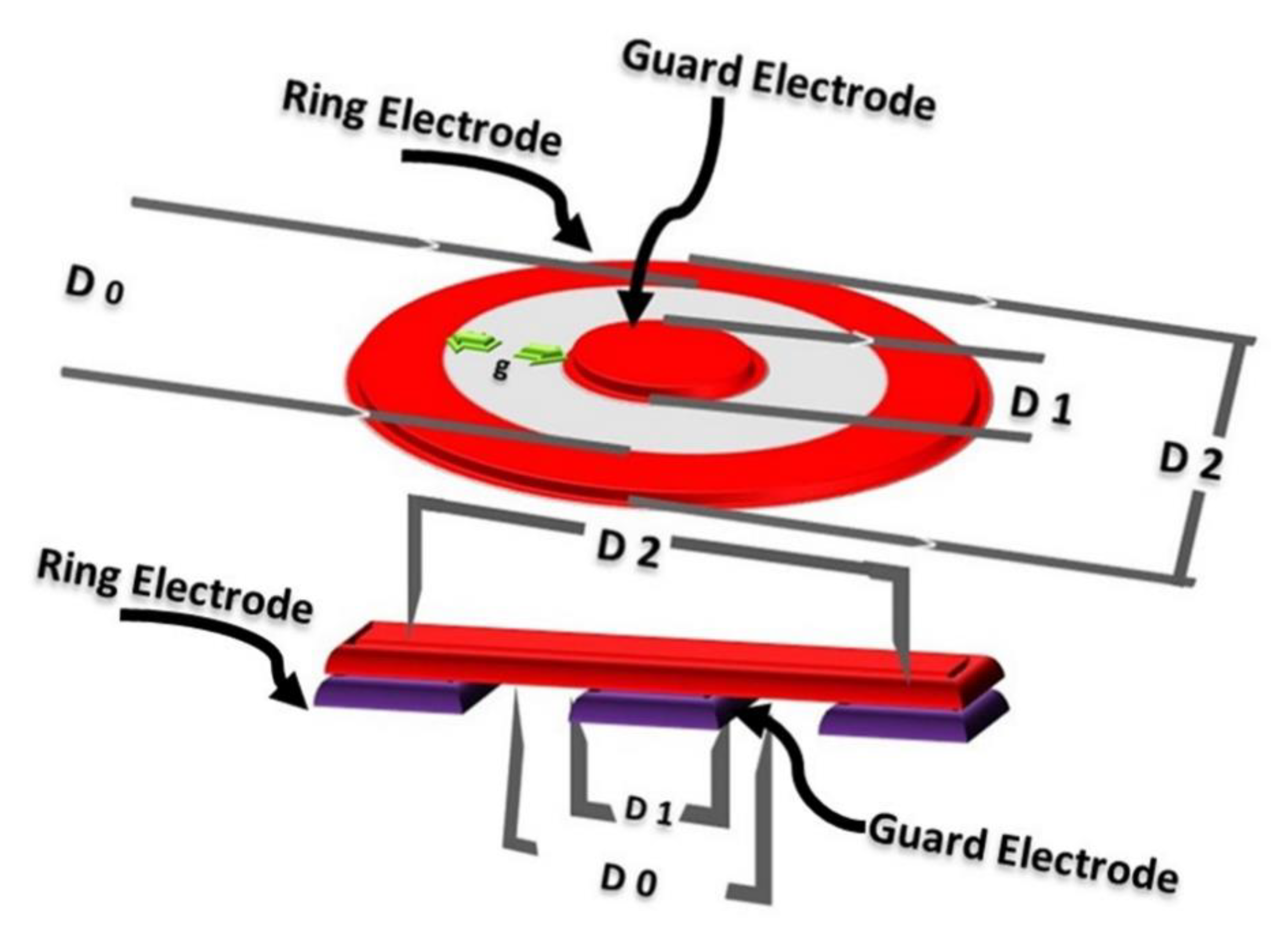
2.3.1. Surface Properties Evaluation
2.3.2. Electrical Properties Evaluation
2.3.3. Weight Gain Percentage
2.3.4. Measurement of EMI Shielding
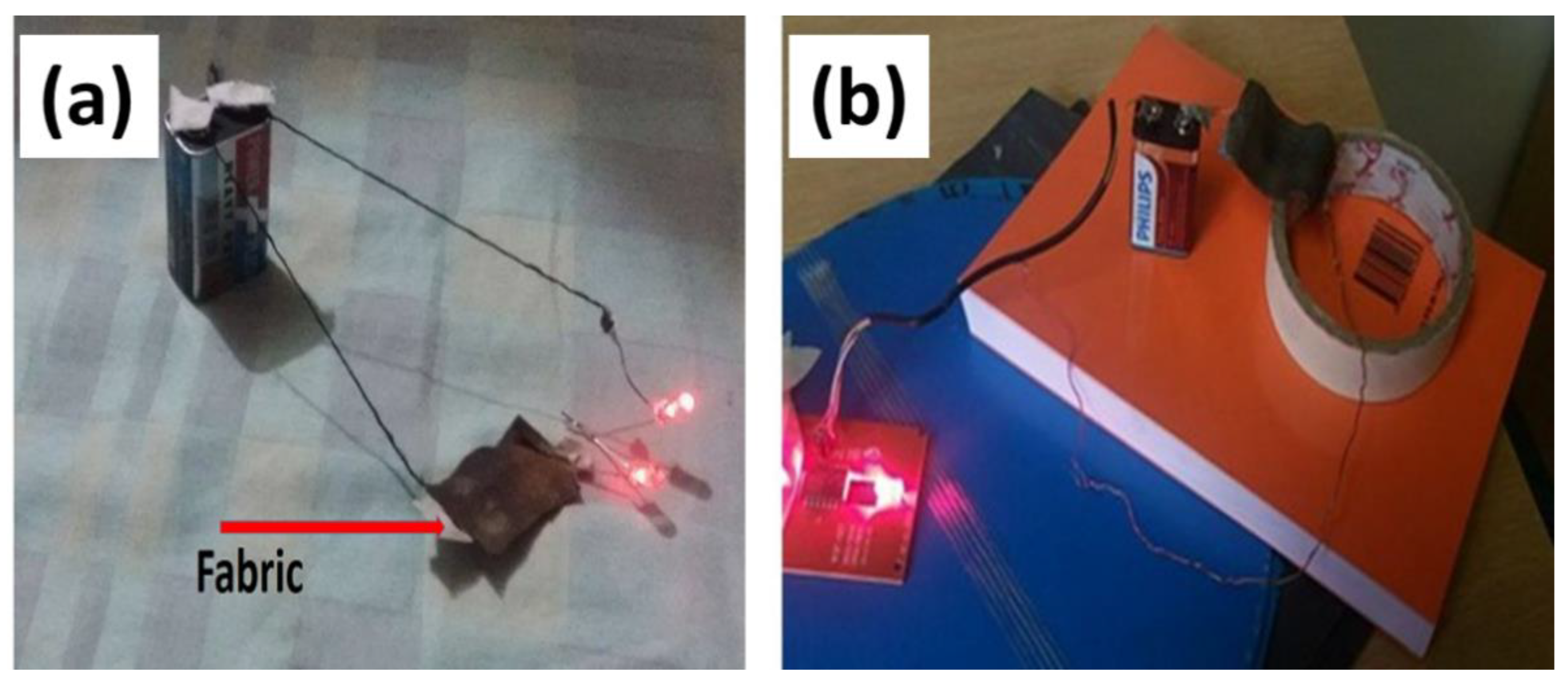
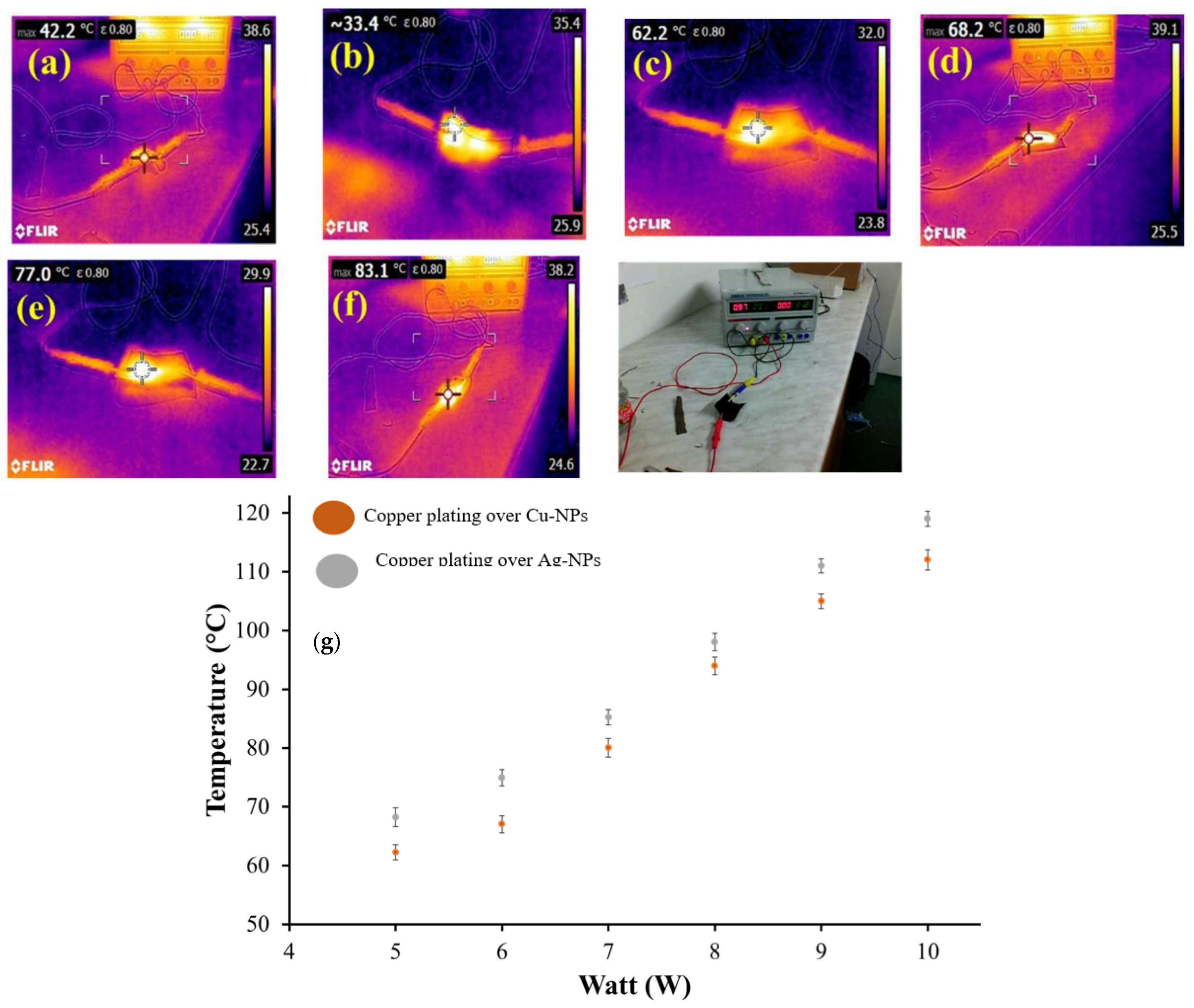
2.3.5. Heat Generating Performance of Conductive Textiles
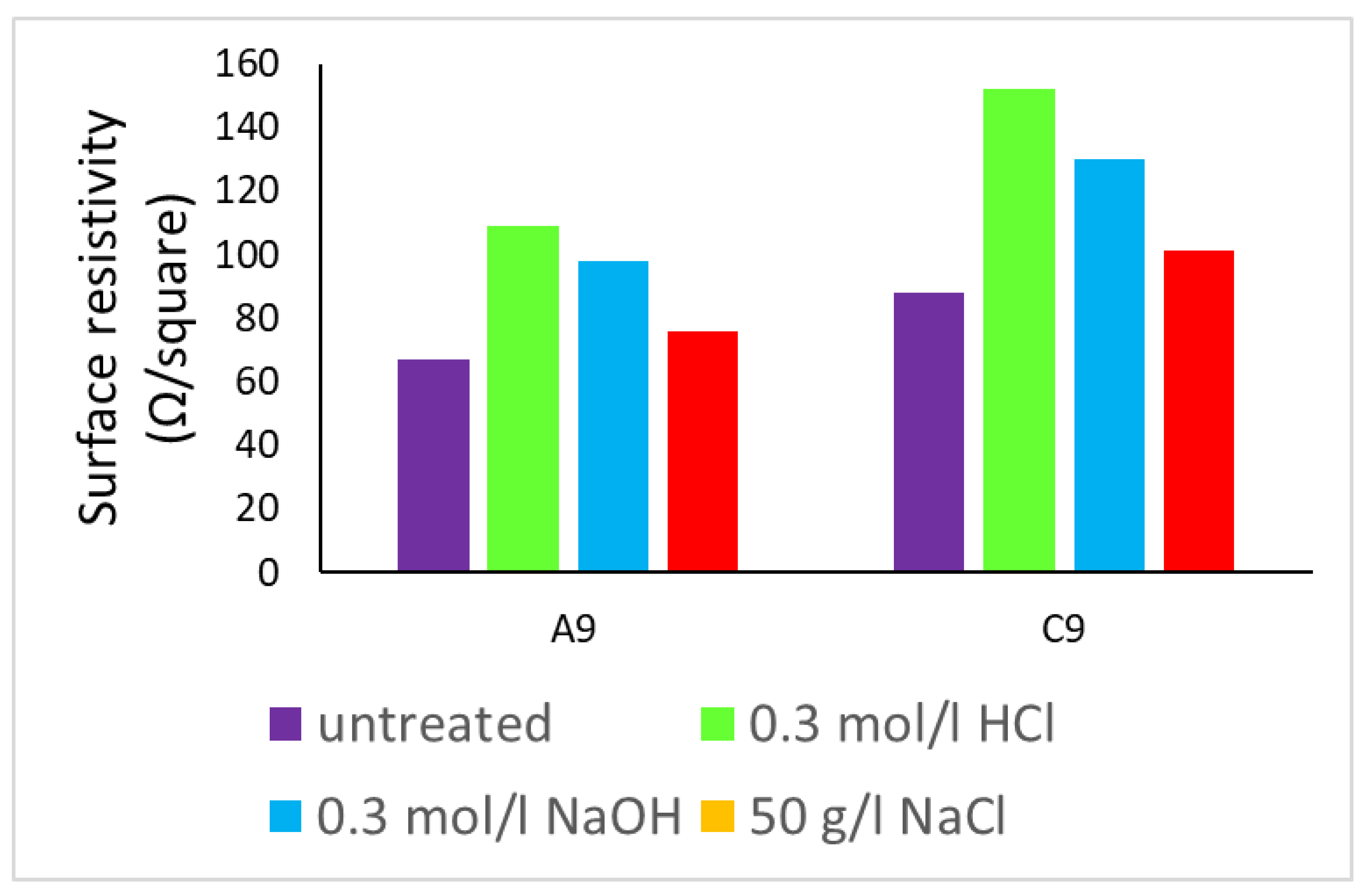
2.3.6. Durability of Conductive Fabrics
3. Results and Discussion
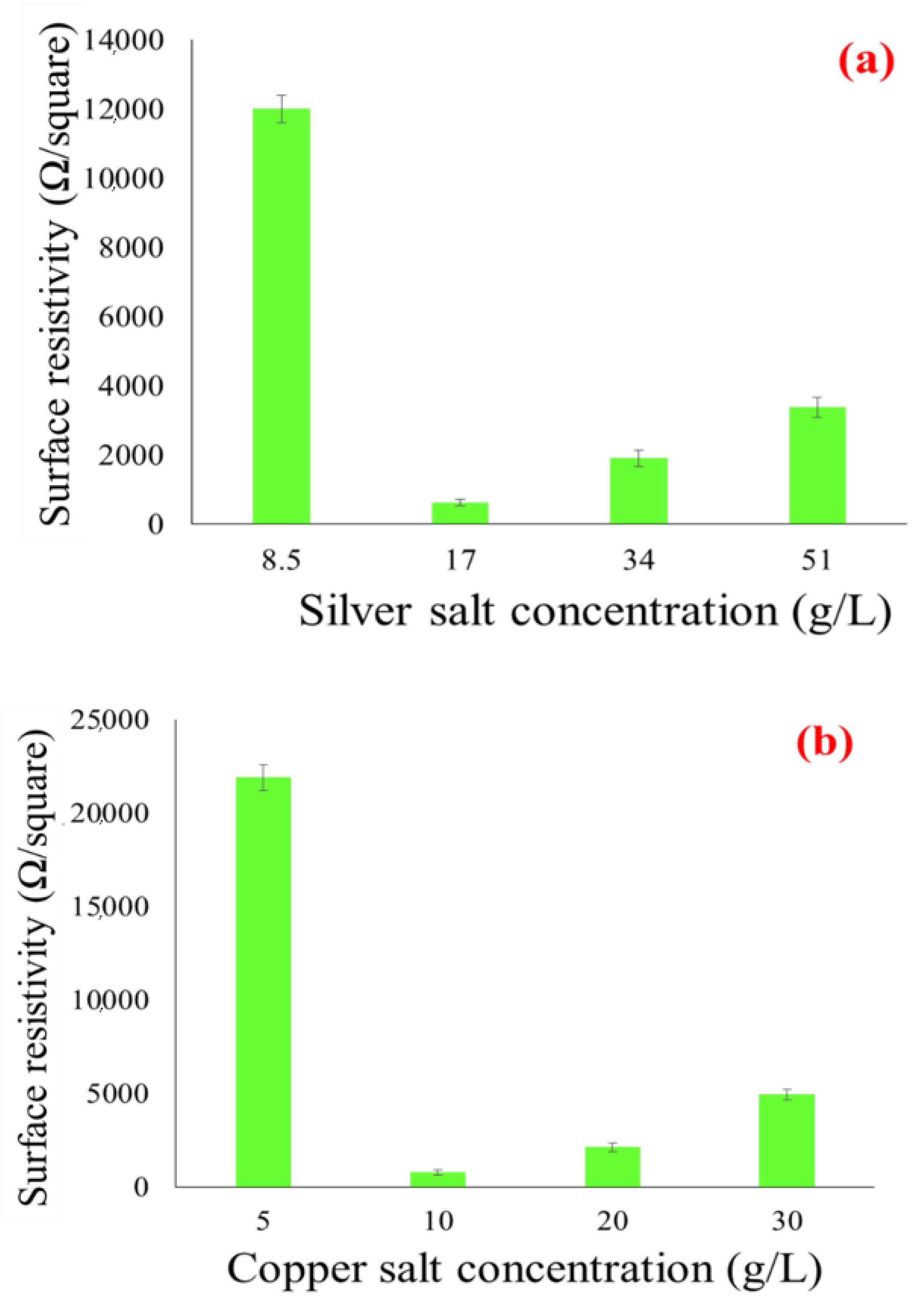
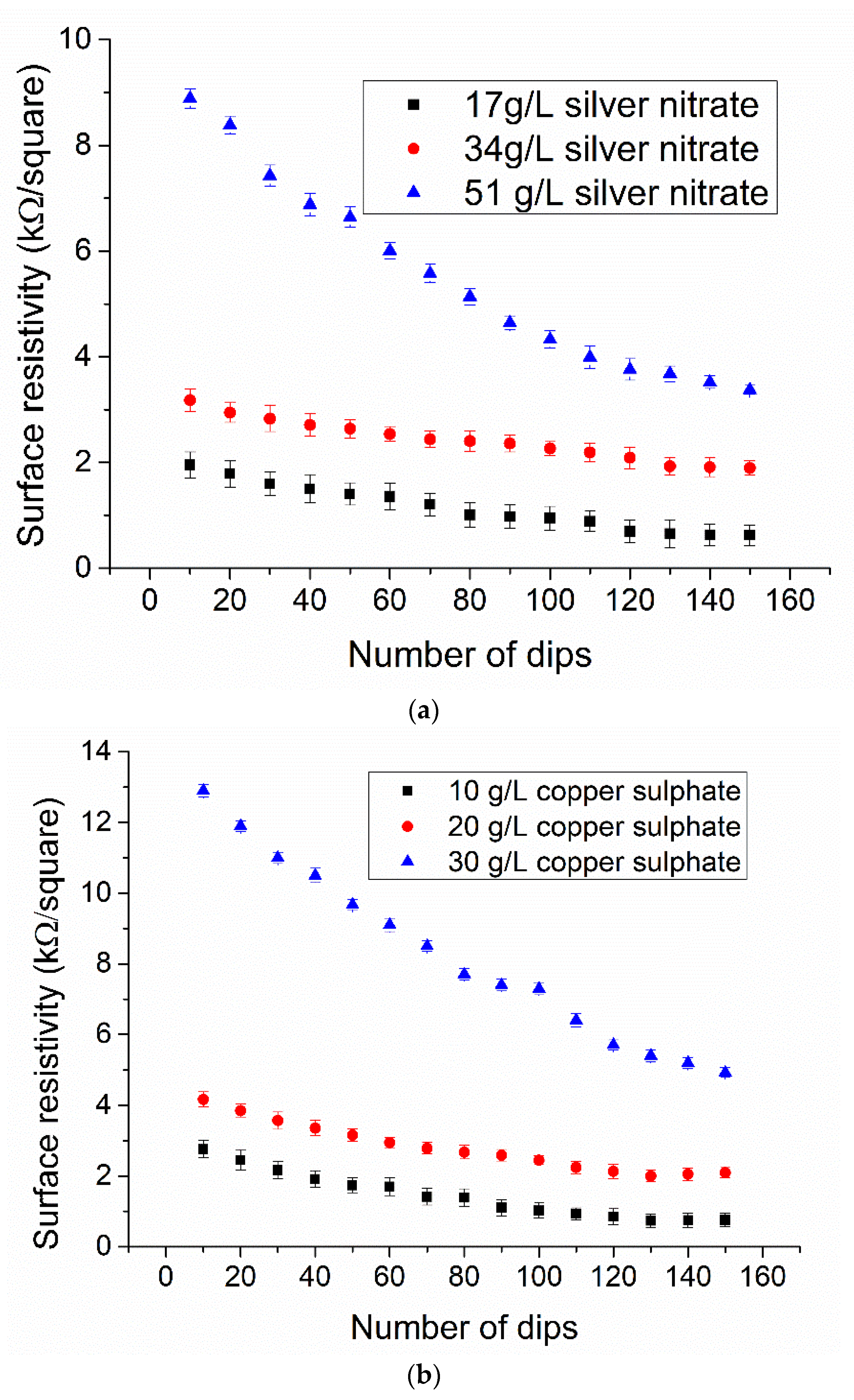
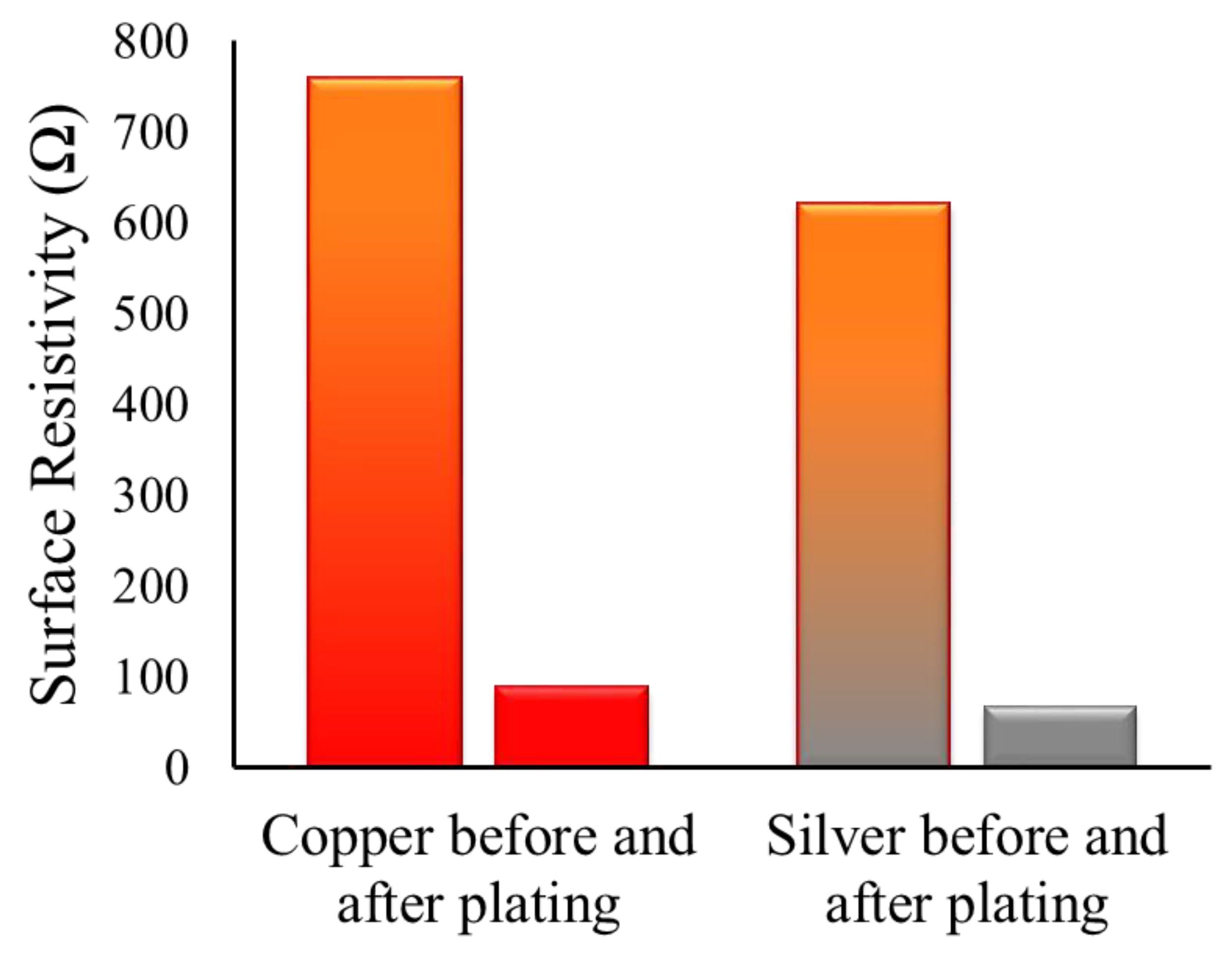
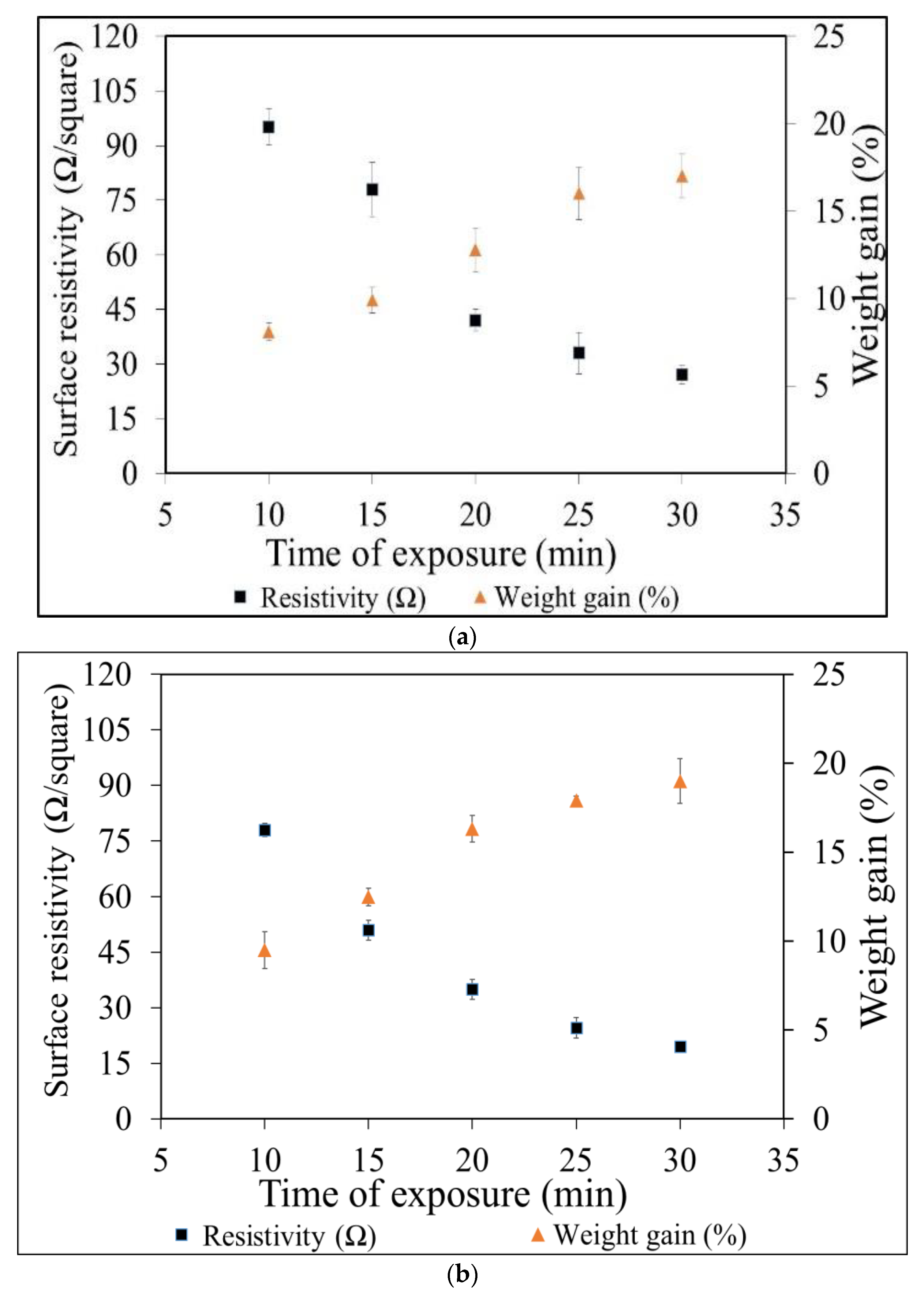
3.1. Electrical Conductivity of Copper-and Silver Particles Coated Fabrics
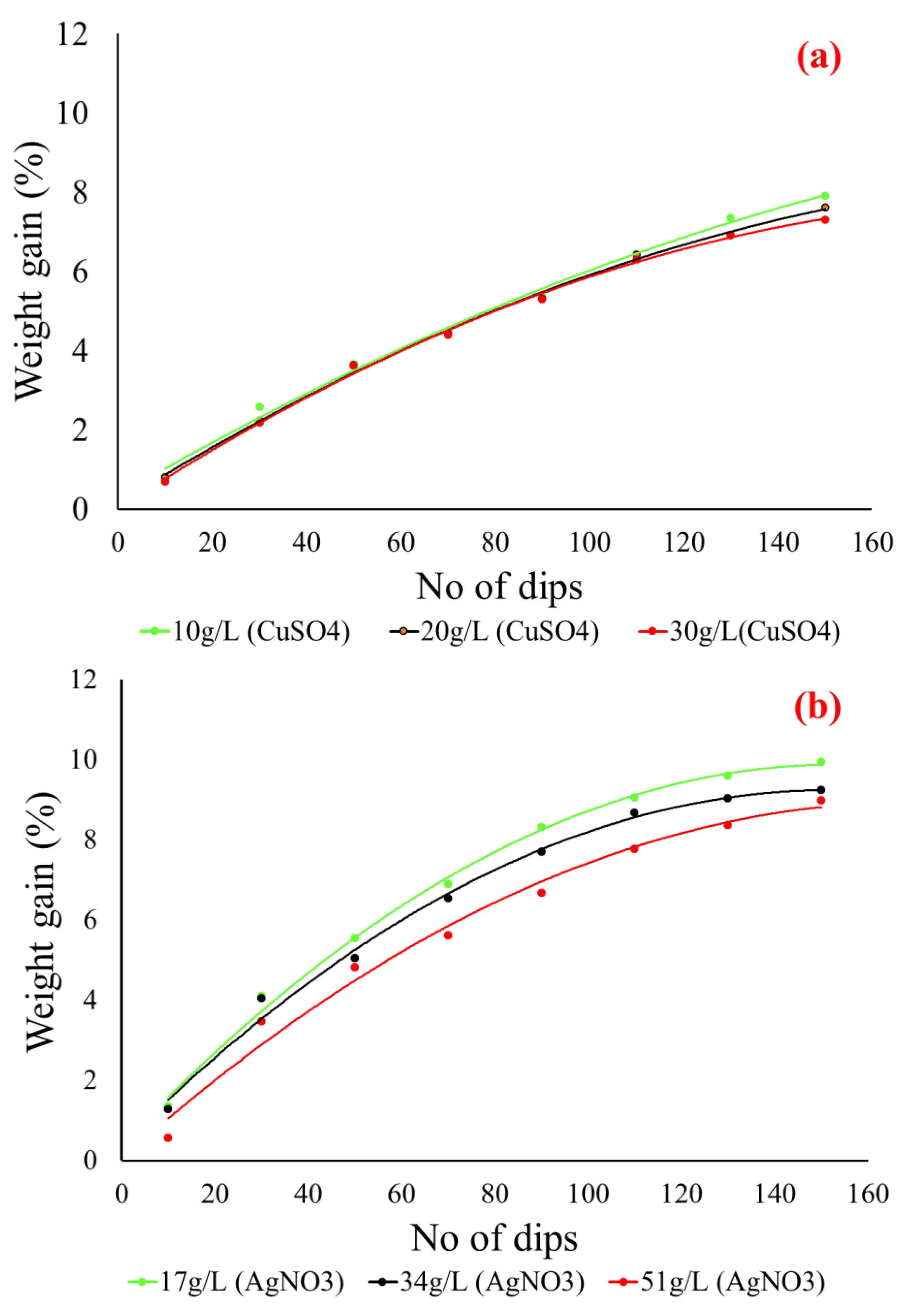
3.2. Weight Gain Percentage
3.3. Surface Morphology
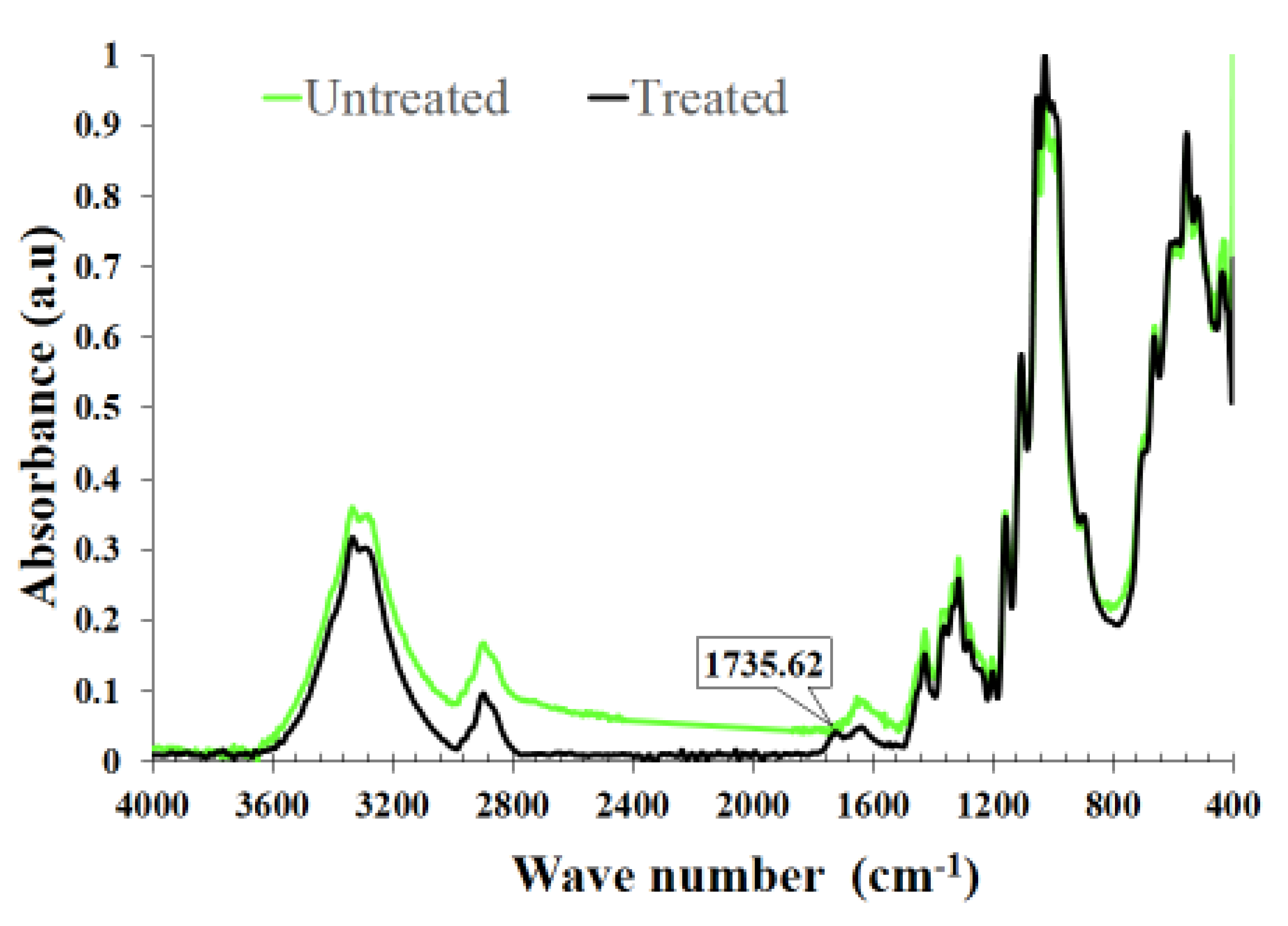
3.3.1. FTIR Measurements of Cotton Fabrics
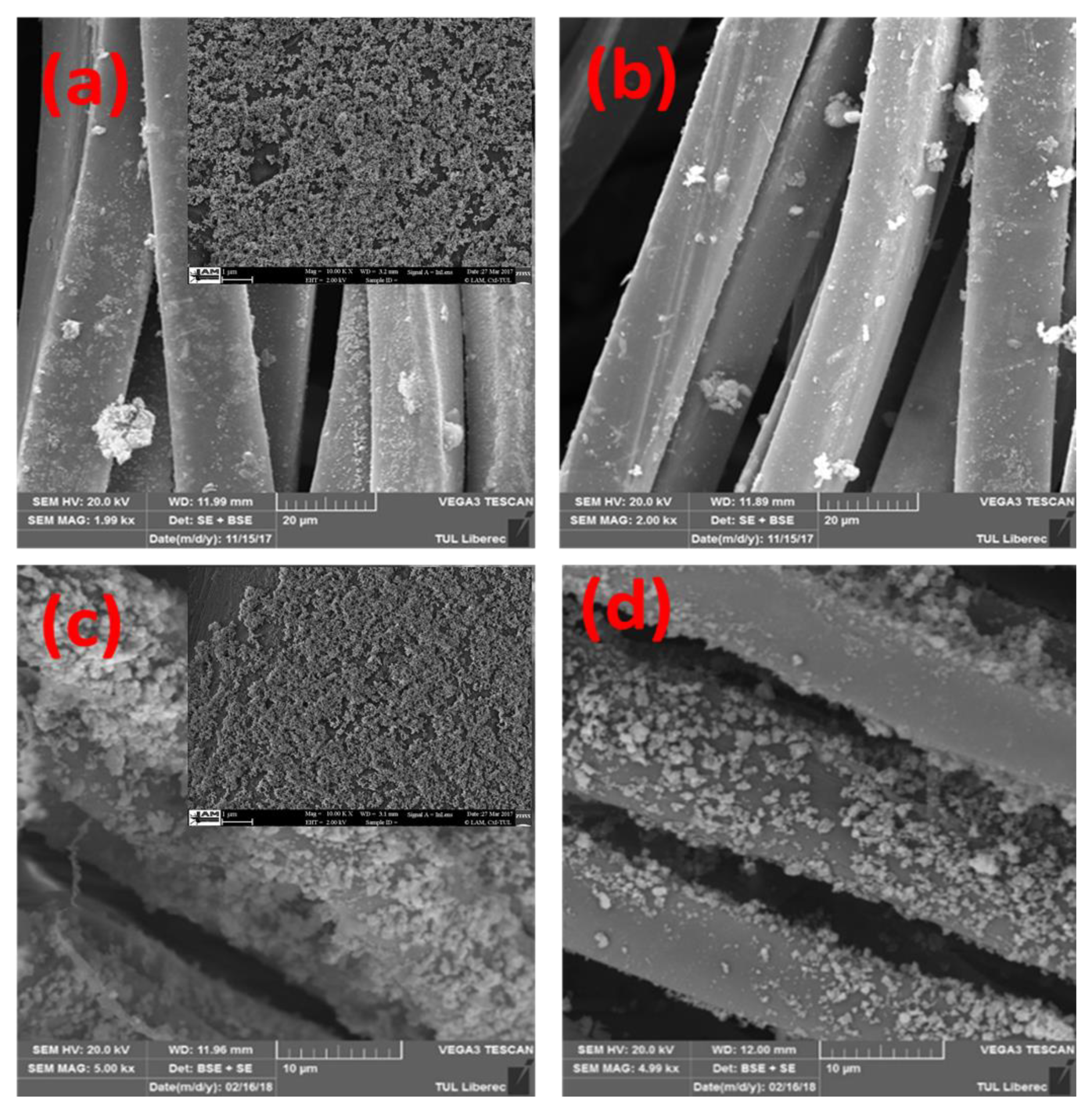
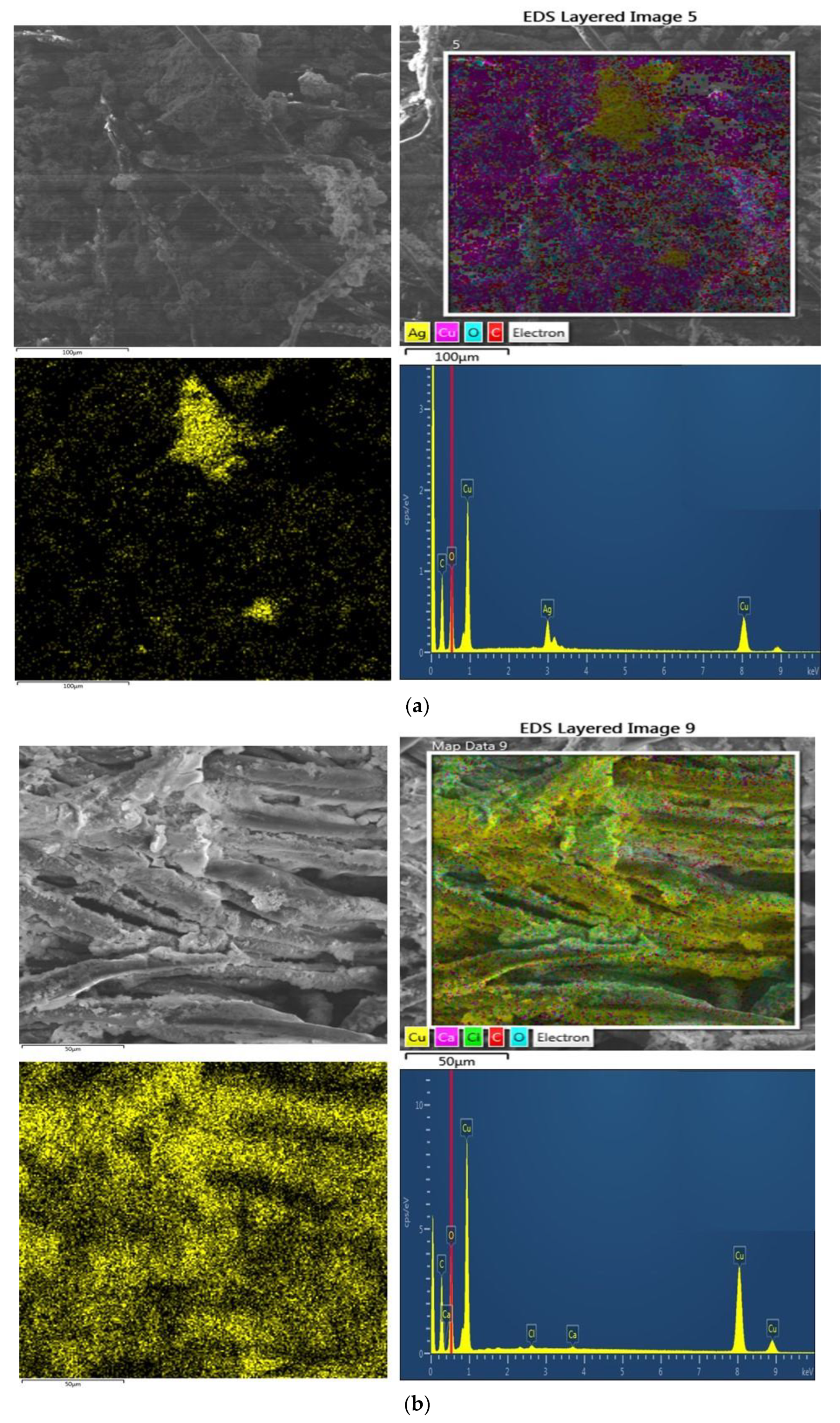
3.3.2. SEM Structures
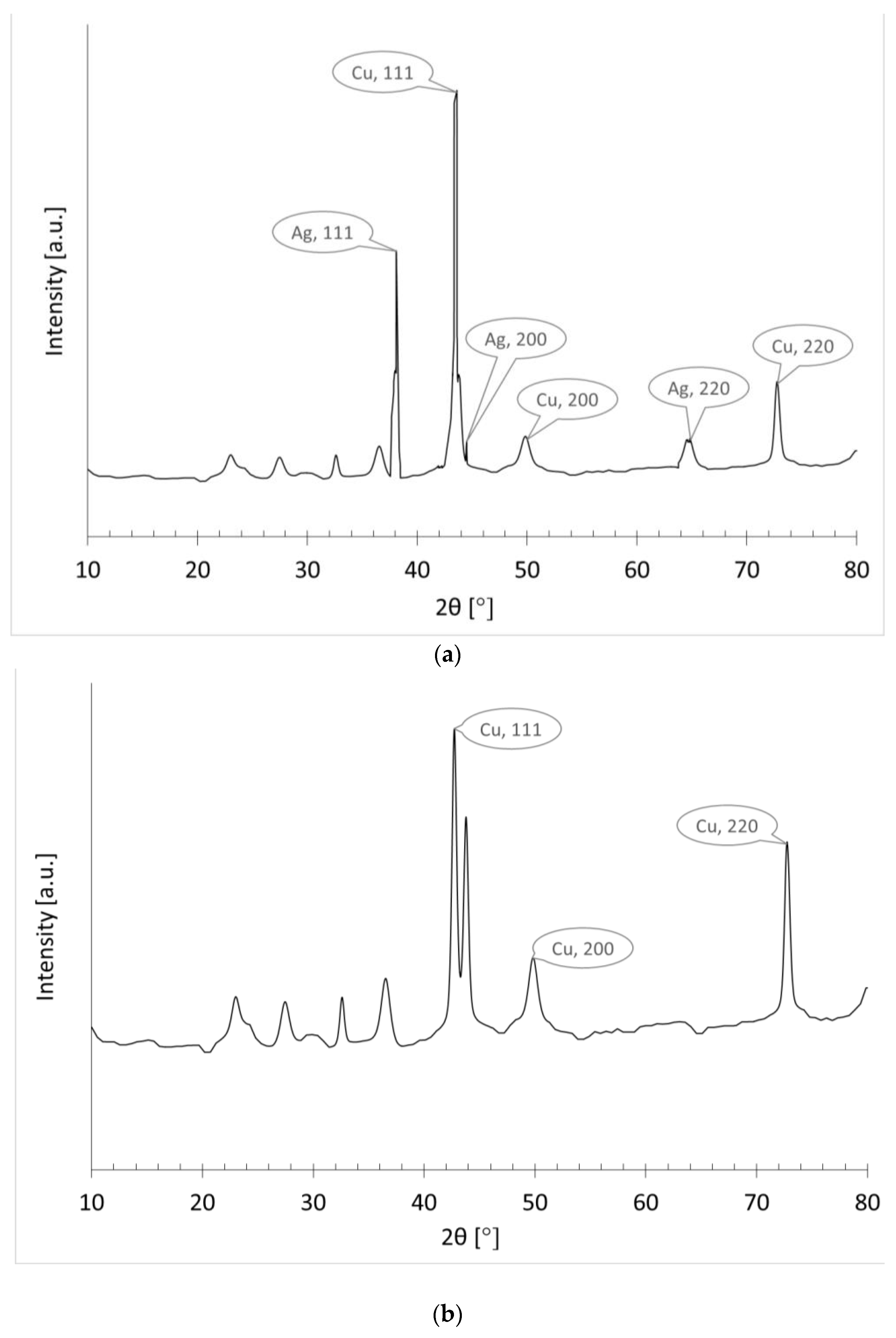
3.3.3. XRD Analysis
3.4. Mechanism and Reactions Involve for Metallization
3.4.1. Mechanism for the Attachment of Silver Particles
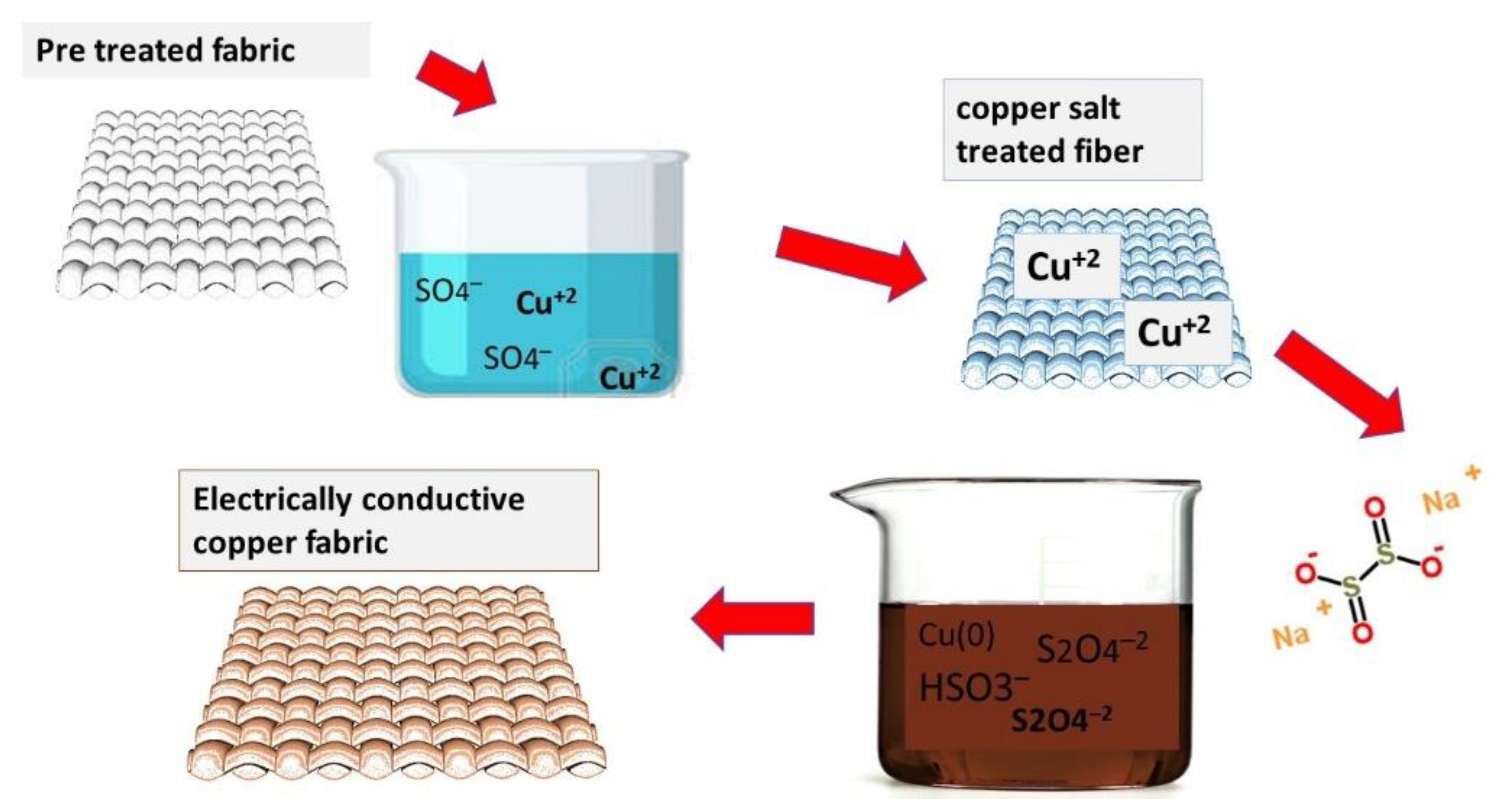
3.4.2. A Mechanism for the Attachment of Copper Particles
3.4.3. Copper Electroplating on Conductive Fabrics
3.5. Heating Performance
3.6. Electromagnetic Shielding of Conductive Fabrics
3.7. Ageing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, A.; Sattar, M.; Hussain, F.; Humble, M.; Tareen, K.; Militky, J. Single-Step Green Synthesis of Highly Concentrated and Stable Colloidal Dispersion of Core-Shell Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial and Ultra-High Catalytic Properties. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Baheti, V.; Militky, J.; Khan, Z.; Tunakova, V.; Naeem, S. Copper coated multifunctional cotton fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 48, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Baheti, V.; Militky, J.; Khan, Z. Utility of silver-coated fabrics as electrodes in electrotherapy applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.; Galib, C.M.A.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, C. A new approach to fabricate graphene electro-conductive networkson natural fibers by ultraviolet curing method. Synth. Met. 2014, 193, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, R.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Xie, J. Graphene-based heterojunction photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.H.; Jiang, S.X.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Ng, M.C.F.; Lan, J.W. Metallized textile design through electroless plating and tie-dyeing technique. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongsung, P.; Ji-Kwan, K.; Swati, J.P.; Jun-Kyu, P.; Su, P.; Dong, W.L. A Wireless Pressure Sensor Integrated with a Biodegradable Polymer Stent for Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Swati, J.P.; Deepak, P.D.; Dong, W.L. Gold nanoparticles decorated rGO-ZnCo2O4 nanocomposite: A promising positive electrode for high performance hybrid supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122–211. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, F.; Gogotsi1, Y.; Ali1, A.; Naguib, N.; Ye, H.; Yang, G.L. Electrospinning of Continuous Carbon Nanotube-Filled Nanofiber Yarns. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chang, H.; Li, Y.; Huck, W.T.S.; Zheng, Z. Polyelectrolyte-Bridged Metal/Cotton Hierarchical Structures for Highly Durable Conductive Yarns. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, J.; Jiang, S.; Wong, C. Characterization of metallic textiles deposited by magnetron sputtering and traditional metallic treatments. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, M.; Horch, K. Metallized polymer fibers as leadwires and intrafascicular microelectrodes. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 70, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Vijay, B.; Muhammad, U.; Militky, J. Enhancement in ageing and functional properties of copper-coated fabrics by subsequent electroplating. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 651. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Baheti, V.; Vik, M.; Militky, J. Copper electroless plating of cotton fabrics after surface activation with deposition of silver and copper nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 137, 109–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri-Khalilabad, M.; Mey, J. Fabricating multifunctional silver nanoparticles-coated cotton fabric. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balamurugan, M.; Saravanan, S.; Soga, T. Coating of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles on cotton fabric. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppusamy, S.; Demudu, B.G.; Venkatesh, V.K.; Marken, F.; Kulandainathan, M.A. Highly conductive nano-silver textile for sensing hydrogen peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 799, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Chen, J.; Yin, W.; Jia, S.T.; Ma, J.Z. Superhydrophobic conductive textiles with antibacterial property by coating fibers with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 2468–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Shen, B.; Hu, W. Electroless plating of Cu-Ni-P alloy on PET fabrics and effect of plating parameters on the properties of conductive fabrics. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 455, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Fu, X.; Song, B.; Zhu, H. Electrochemical deposition and characterization of copper crystals on polyaniline/poly(ethylene terephthalate) conductive textiles. Synth. Met. 2013, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, A.; Doyle, J.M. Uptake of Copper(II) by Wool. Text. Res. J. 2002, 75, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseri, S.; Zadhoush, A.; Morshed, M.; Amirnasr, M.; Azarnasab, M. Synthesis and Optimization of Copper Sulfide-Coated Electrically Conducting Poly(acrylonitrile) Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Baheti, V.; Militky, J.; Khan, M.Z. Comparative Performance of Copper and Silver Coated Stretchable Fabrics. Fiber Polym. 2018, 19, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalagedara, L.R.; Siriwardane, I.W.; Tissera, N.D.; Wijesena, R.N.; Silva, K.M.N. Carbon black functionalized stretchable conductive fabrics for wearable heating applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19174–19180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvert, P.; Duggal, D.; Patra, P.; Agrawal, A.S. Conducting polymer and conducting composite strain sensors on textiles. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 1, 291–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinski, N.; Colvin, V.; Drezek, R. reviews Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sr. # | Sample ID | Concentration of Copper Sulphate g/L | Time of Exposure (Minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C1 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | C2 | 20 | |
| 3 | C3 | 30 | |
| 4 | C4 | 20 | 10 |
| 5 | C5 | 20 | |
| 6 | C6 | 30 | |
| 7 | C7 | 30 | 10 |
| 8 | C8 | 20 | |
| 9 | C9 | 30 | |
| 10 | A1 | 10 | |
| 11 | A2 | 10 | 20 |
| 12 | A3 | 30 | |
| 13 | A4 | 10 | |
| 14 | A5 | 20 | 20 |
| 15 | A6 | 30 | |
| 16 | A7 | 10 | |
| 17 | A8 | 30 | 20 |
| 18 | A9 | 30 |
| Sr. # | Sample ID | Concentration of Copper Sulphate g/L | Time of Exposure (Minutes) | Ω/Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C1 | 10 | 10 | 856 ± 32 |
| 2 | C2 | 20 | 456 ± 41 | |
| 3 | C3 | 30 | 134 ± 12 | |
| 4 | C4 | 20 | 10 | 567 ± 29 |
| 5 | C5 | 20 | 272 ± 21 | |
| 6 | C6 | 30 | 109 ± 9 | |
| 7 | C7 | 30 | 10 | 372 ± 40 |
| 8 | C8 | 20 | 121 ±28 | |
| 9 | C9 | 30 | 88 ± 7 | |
| 10 | A1 | 10 | 705 ± 32 | |
| 11 | A2 | 10 | 20 | 312 ± 41 |
| 12 | A3 | 30 | 111 ± 12 | |
| 13 | A4 | 10 | 423 ± 29 | |
| 14 | A5 | 20 | 20 | 233 ± 23 |
| 15 | A6 | 30 | 109 ± 9 | |
| 16 | A7 | 10 | 282 ± 37 | |
| 17 | A8 | 30 | 20 | 99 ± 17 |
| 18 | A9 | 30 | 67 ± 8 |
| Fabric Samples | Electrical Resistivity (Ω/Square) | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Washing | After Washing | |
| Copper particles coated woven fabric | 912 ± 26 | 956 ± 38 |
| Silver particles coated woven fabric | 1145 ± 35 | 1198 ± 47 |
| Copper plating over copper particles coated woven fabric | 88 ± 7 | 97 ± 7 |
| Copper plating over silver particles coated woven fabric | 67 ± 8 | 81 ± 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.; Hussain, F.; Kalsoom, A.; Riaz, T.; Zaman Khan, M.; Zubair, Z.; Shaker, K.; Militky, J.; Noman, M.T.; Ashraf, M. Multifunctional Electrically Conductive Copper Electroplated Fabrics Sensitizes by In-Situ Deposition of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113097
Ali A, Hussain F, Kalsoom A, Riaz T, Zaman Khan M, Zubair Z, Shaker K, Militky J, Noman MT, Ashraf M. Multifunctional Electrically Conductive Copper Electroplated Fabrics Sensitizes by In-Situ Deposition of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Azam, Fiaz Hussain, Ambreen Kalsoom, Tauqeer Riaz, Muhammad Zaman Khan, Zakariya Zubair, Khubab Shaker, Jiri Militky, Muhammad Tayyab Noman, and Munir Ashraf. 2021. "Multifunctional Electrically Conductive Copper Electroplated Fabrics Sensitizes by In-Situ Deposition of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113097
APA StyleAli, A., Hussain, F., Kalsoom, A., Riaz, T., Zaman Khan, M., Zubair, Z., Shaker, K., Militky, J., Noman, M. T., & Ashraf, M. (2021). Multifunctional Electrically Conductive Copper Electroplated Fabrics Sensitizes by In-Situ Deposition of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113097









