The Effect of Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing on the Roughness of the Enamel, Three Different Nanocomposites, and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
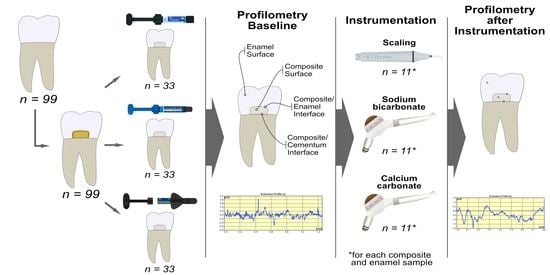
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Composite Surface
3.2. Enamel
3.3. Composite/Enamel Interface
3.4. Composite/Cementum Interface
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, M.S.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.H.; Spencer, A.J.; Ju, X.; Do, L.G. Periodontal diseases in the Australian adult population. Aust. Dent. J. 2020, 65, S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Al-Ansari, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.; Alhareky, M.; Gaffar, B.; Almas, K. Global Prevalence of Periodontal Disease and Lack of Its Surveillance. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 2146160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiroglu, M.B.; Kahramanoglu, E.; Ay, M.; Kuru, L.; Agrali, O.B. Comparison of Root Surface Wear and Roughness Resulted from Different Ultrasonic Scalers and Polishing Devices Applied on Human Teeth: An In-Vitro Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valm, A.M. The Structure of Dental Plaque Microbial Communities in the Transition from Health to Dental Caries and Periodontal Disease. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubovics, N.S.; Goodman, S.D.; Mashburn-Warren, L.; Stafford, G.P.; Cieplik, F. The dental plaque biofilm matrix. Periodontology 2000 2021, 86, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Buhlin, K.; Dufrêne, Y.; Gomelsky, M.; Moroni, A.; Ramstedt, M.; Rumbaugh, K.P.; Schulte, T.; Sun, L.; Åkerlund, B.; et al. Biofilm formation—What we can learn from recent developments. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, D.S.W.; Sims, J.K.R.; Fraser, D. Nanoparticles for Oral Biofilm Treatments. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4869–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritato, M.; Orazi, L.; Laurito, D.; Formisano, G.; Serra, E.; Lollobrigida, M.; Molinari, A.; De Biase, A. Root surface alterations following manual and mechanical scaling: A comparative study. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2018, 16, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Kameyama, A.; Enokuchi, T.; Haruyama, A.; Chiba, A.; Hosaka, M.; Takahashi, T. Effect of professional dental prophylaxis on the surface gloss and roughness of CAD/CAM restorative materials. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e772–e778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Drozdzik, A.; Tandecka, K.; Grocholewicz, K. Effect of air-polishing on surface roughness of composite dental restorative material—Comparison of three different air-polishing powders. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, T.T.; Oztekin, F.; Keklik, E.; Tozum, M.D. Surface roughness of enamel and root surface after scaling, root planning and polishing procedures: An in-vitro study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2021, 11, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavarez, R.R.D.J.; Gomes, I.A.; Mendes, H.G.; Filho, E.M.M.; Rizzi, C.D.C.; Nina, M.G.; Turssi, C.P.; Vasconcelos, A.J. Effect of Dental Prophylaxis Techniques on the Surface Roughness of Resin Composites. J. Contemp. Dent. Pr. 2018, 19, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.S.; Lee, S.Y. Effects of Sonic and Ultrasonic Scaling on the Surface Roughness of Tooth-colored Restorative Materials for Cervical Lesions. Oper. Dent. 2007, 32, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, A.E.; Rafi, A.T.; Ahmed, A.S.; Sumanth, P.C. Surface topography of composite restorative materials following ultrasonic scaling and its Impact on bacterial plaque accumulation. An in-vitro SEM study. J. Int. Oral Health 2013, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mourouzis, P.; Koulaouzidou, E.A.; Vassiliadis, L.; Helvatjoglu-Antoniades, M. Effects of sonic scaling on the surface roughness of restorative materials. J. Oral Sci. 2009, 51, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefimanesh, H.; Robati, M.; Kadkhodazadeh, M.; Molla, R. A comparison of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic scaling devices: An in vitro study. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2012, 42, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdilek, D.; Sismanoglu, S.; Gumustas, B.; Efes, B. Effects of ultrasonic and sonic scaling on surfaces of tooth-colored restorative materials: An in vitro study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 18, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, A.U.; Duran, İ.; Yücel, A.Ç.; Özkan, P. Effects of air polishing powders on the surface roughness of composite resins. J. Dent. Sci. 2010, 5, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kimyai, S.; Pournaghi-Azar, F.; Daneshpooy, M.; Kahnamoii, M.A.; Davoodi, F. Effect of two prophylaxis methods on marginal gap of Cl Vresin-modified glass-ionomer restorations. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2016, 10, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, D.; Luz, M.A.A.D.C. Effect of prophylactic treatments on the superficial roughness of dental tissues and of two esthetic restorative materials. Pesqui. Odontol. Bras. 2003, 17, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalefa, M.; Finke, C.; Jost-Brinkmann, P.-G. Effects of air-polishing devices with different abrasives on bovine primary and second teeth and deciduous human teeth. J. Orofac. Orthop. Fortschr. Kieferorthopädie 2013, 74, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilselvi, S.; Nagate, R.R.; Al-Ahmari, M.M.M.; Kokila, G.; Tikare, S.; Chaturvedi, S. Comparison of the effect of sodium bicarbonate and glycine air polishing systems on tooth surface roughness: An atomic force microscopic analysis. Technol. Health Care 2021, 29, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, J.; Amato, M.; Weiger, R.; Walter, C. A systematic review on the effects of air polishing devices on oral tissues. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2015, 14, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, F.; De Melo, T.P.; Delgado, A.; Monteiro, P.; Rua, J.; Proença, L.; Caldeira, J.; Azul, A.M.; Mendes, J. Varying the Polishing Protocol Influences the Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Bulk-Fill Resin-Based Composites. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandt, K.D.; Watts, D.C. Nanotechnology in dentistry: Present and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliu, S.; Racovita, S.; Gugoasa, I.; Lungan, M.-A.; Popa, M.; Desbrieres, J. The Benefits of Smart Nanoparticles in Dental Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzraikat, H.; Burrow, M.F.; Maghaireh, G.A.; Taha, N.A. Nanofilled Resin Composite Properties and Clinical Performance: A Review. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, E173–E190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, C.M.; Bhat, K.M.; Bansal, R. Evaluation of surface roughness of different restorative composites after polishing using atomic force microscopy. J. Conserv. Dent. 2016, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.; Gupta, S.; Nikhil, V.; Jaiswal, S.; Jain, A.; Aggarwal, N. Effect of Different Finishing and Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Resin Composite and Enamel: An In vitro Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopy Study. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2019, 9, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, K.; Polyakova, M.; Sokhova, I.; Doroshina, V.; Arakelyan, M.; Novozhilova, N. The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Sequences on The Surface Roughness of Three Different Nanocomposites and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimyai, S.; Mohammadi, N.; Oskoee, P.A.; Pournaghi-Azar, F.; Chaharom, M.E.E.; Amini, M. Effect of Different Prophylaxis Methods on Microleakage of Microfilled Composite Restorations. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2012, 6, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbo, L.R.; Lacefield, W.R.; Barnes, C.M.; Russell, C.M. Enamel roughness after air-powder polishing. Am. J. Dent. 1993, 6, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sygkounas, E.; Louropoulou, A.; Schoenmaker, T.; De Vries, T.J.; Van Der Weijden, F.A. Influence of various air-abrasive powders on the viability and density of periodontal cells: An in vitro study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkstein, S.; Reiff, R.L.; McKinney, J.F.; Killoy, W.J. Supragingival Root Surface Removal during Maintenance Procedures Utilizing an Air-Powder Abrasive System or Hand Scaling. J. Periodontol. 1987, 58, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, A.R.; Aznar, F.D.D.C.; Da Silva, A.L.; Sales-Peres, A.; Sales-Peres, S.H.D.C. Assessment of the effects of decontamination and storage methods on the structural integrity of human enamel. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2016, 45, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humel, M.M.C.; Oliveira, M.T.; Cavalli, V.; Giannini, M. Effect of storage and disinfection methods of extracted bovine teeth on bond strength to dentin. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 6, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, B.; Pamir, T.; Baltaci, A.; Orman, M.N.; Turk, T. Effect of storage solutions on microhardness of crown enamel and dentin. Eur. J. Dent. 2015, 9, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deljoo, Z.; Sadeghi, M.; Azar, M.; Bagheri, R. The Effect of Different Polishing Methods and Storage Media on Discoloration of Resin Composites. J. Dent. Biomater. 2016, 3, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen, S.; Caton, J.G.; Albandar, J.M.; Bissada, N.F.; Bouchard, P.; Cortellini, P.; Demirel, K.; de Sanctis, M.; Ercoli, C.; Fan, J.; et al. Periodontal manifestations of systemic diseases and developmental and acquired conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 3 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S237–S248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollenl, C.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsar, A.; Yuzbasioglu, E.; Sarac, D. The Effect of Finishing and Polishing Techniques on the Surface Roughness and the Color of Nanocomposite Resin Restorative Materials. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, F.; Liang, X.; Li, D. Effects of surface properties of polymer-based restorative materials on early adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in vitro. J. Dent. 2016, 54, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkovics, M.; Baumann, T.; Carvalho, T.S.; Assunção, C.M.; Lussi, A. In vitro evaluation of modified surface microhardness measurement, focus variation 3D microscopy and contact stylus profilometry to assess enamel surface loss after erosive–abrasive challenges. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, H.; Kocaagaoglu, H.; Aslan, T.; Gürbulak, A.; Albayrak, H.; Taşdemir, Z. Efficacy of polishing kits on the surface roughness and color stability of different composite resins. Niger. J. Clin. Pr. 2017, 20, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo-Cartagena, R.; López-Galeano, E.J.; Latorre-Correa, F.; Agudelo-Suárez, A.A. Effect of Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness of Nano-Hybrid and Nano-Filling Composite Resins: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, M.; Pirvu, C.; Demetrescu, I. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in understanding the influence of ultrasonic dental scaling on the dental structure-dental filling interface. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2014, 122, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, J.; Schmidli, F.; Weiger, R.; Walter, C. Analysis of the effects of air polishing powders containing sodium bicarbonate and glycine on human teeth. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 19, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, A.U.J.; Wu, S.S.; Chelvan, S.; Tan, E.S.F. Effect of hygiene maintenance procedures on surface roughness of composite restoratives. Oper. Dent. 2005, 30, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, S.; Jost-Brinkmann, P.-G.; Spors, C.K.; Mohammadian, S.; Müller-Hartwich, R. Abrasive Effect of Air-powder Polishing on Smooth-surface Sealants Abrasive Wirkung von Pulver-Wasser-Strahlgeräten auf Glattflächenversiegler. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2009, 70, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Nichani, A.S.; Venugopal, R.; Rajani, V. The effect of various ultrasonic and hand instruments on the root surfaces of human single rooted teeth: A Planimetric and Profilometric study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2014, 18, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folwaczny, M.; Merkel, U.; Mehl, A.; Hickel, R. Influence of Parameters on Root Surface Roughness Following Treatment With a Magnetostrictive Ultrasonic Scaler: An In Vitro Study. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglianone, L.; Martins, J.D.; Rossi, T.R.A.; Saraiva, L.O.; Cavalcanti, A.N.; Mathias, P. Changes on the color parameters of air-abraded resin composite exposed to different colored beverages. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2011, 2, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.C.; Tran, C.; Meredith, N.; Walsh, L.J. Effectiveness of implant surface debridement using particle beams at differing air pressures. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2017, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelka, M.A.; Altmaier, K.; Petschelt, A.; Lohbauer, U. The effect of air-polishing abrasives on wear of direct restoration materials and sealants. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2010, 141, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravina, R.D.; Roeder, L.; Lu, H.; Vogel, K.; Powers, J.M. Effect of finishing and polishing procedures on surface roughness, gloss and color of resin-based composites. Am. J. Dent. 2004, 17, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.B.F.; Magalhães, D.; Neto, A.J.F.; Castro, C.G.; Filho, P.C.F.S.; Soares, C.J. Effect of periodontal therapies on indirect restoration: A scanning electron microscopic analysis. Braz. Dent. J. 2010, 21, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Takamizawa, T.; Shimamura, Y.; Akiba, S.; Yabuki, C.; Imai, A.; Tsujimoto, A.; Kurokawa, H.; Miyazaki, M. Influence of air-powder polishing on bond strength and surface-free energy of universal adhesive systems. Dent. Mater. J. 2017, 36, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratolin, M.M.; Bianco, V.C.; Santos, M.J.M.C.; Rizkalla, A.S.; Santos, G.C. The effect of prophylactic powders on the surface roughness of enamel. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2014, 35, e31–e35. [Google Scholar]
| Resin Composite | Manufacturer | Filler Type | Filler Loading, % by Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premise | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); fumed silica nanofiller (20 nm); prepolymerized filler (≈20–30 μm) | 84 |
| Herculite Ultra | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); fumed silica nanofiller (50 nm); prepolymerized filler (≈1 μm) | 78 |
| Harmonize | Kerr, Scafati, Italy | Barium-aluminum-borosilicate glass (mean particle size 0.4 μm); aggregated zirconia/silica cluster filler (2–3 μm) comprised of 20 nm spherical fumed silica and 5 nm zirconia particles | 81.5 |
| Substrate | USS | APPCC | APPSB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Composite | Baseline | Post treatment | Baseline | Post treatment | Baseline | Post treatment |
| CR | Premise | 0.23 (0.12) a | 0.31 (0.06) abc | 0.24 (0.14) a | 0.40 (0.06) c | 0.24 (0.13) a | 0.41 (0.06) c |
| H. Ultra | 0.13 (0.04) a | 0.26 (0.04) b | 0.15 (0.07) a | 0.40 (0.07) c | 0.14 (0.06) a | 0.43 (0.16) c | |
| Harmonize | 0.18 (0.15) a | 0.40 (0.11) c | 0.23 (0.19) a | 0.81 (0.08) d | 0.21 (0.03) a | 0.82 (0.06) d | |
| Total | 0.18 (0.12) | 0.32 (0.09) * | 0.20 (0.14) | 0.54 (0.21) * | 0.19 (0.09) | 0.55 (0.22) * | |
| CR–E | Premise | 1.2 (0.21) e | 1.22 (0.14) ef | 1.29 (0.15) e | 1.48 (0.22) f | 1.22 (0.10) e | 1.50 (0.22) f |
| H. Ultra | 1.05 (0.29) e | 1.46 (0.40) f | 0.92 (0.22) e | 1.61 (0.38) fg | 0.94 (0.23) e | 1.69 (0.42) fg | |
| Harmonize | 0.92 (0.14) e | 1.32 (0.19) f | 0.96 (0.11) e | 1.96 (0.58) g | 0.98 (0.10) e | 2.00 (0.62) g | |
| Total | 1.06 (0.24) | 1.33 (0.28) * | 1.06 (0.23) | 1.68 (0.46) * | 1.05 (0.20) | 1.73 (0.48) * | |
| CR–C | Premise | 1.3 (0.19) e | 1.22 (0.27) e | 1.18 (0.22) e | 1.35 (0.08) f | 1.11 (0.13) e | 1.38 (0.06) f |
| H. Ultra | 1.18 (0.16) e | 1.26 (0.31) ef | 1.04 (0.16) e | 1.40 (0.21) f | 1.01 (0.12) e | 1.42 (0.21) f | |
| Harmonize | 1.11 (0.24) e | 1.27 (0.28) ef | 1.10 (0.23) e | 1.29 (0.15) f | 1.07 (0.18) e | 1.29 (0.08) f | |
| Total | 1.20 (0.21) | 1.25 (0.29) | 1.11 (0.21) | 1.35 (0.16) * | 1.06 (0.15) | 1.36 (0.14) * | |
| Substrate | USS | p Value | APPCC | p Value | APPSB | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post treatment | Baseline | Post treatment | Baseline | Post treatment | ||||
| Enamel | 1.01 (0.22) | 1.18 (0.18) | 0.058 | 1.11 (0.28) | 1.32 (0.25) | 0.083 | 1.13 (0.29) | 1.40 (0.31) | 0.047 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babina, K.; Polyakova, M.; Sokhova, I.; Doroshina, V.; Arakelyan, M.; Zaytsev, A.; Novozhilova, N. The Effect of Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing on the Roughness of the Enamel, Three Different Nanocomposites, and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113072
Babina K, Polyakova M, Sokhova I, Doroshina V, Arakelyan M, Zaytsev A, Novozhilova N. The Effect of Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing on the Roughness of the Enamel, Three Different Nanocomposites, and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113072
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabina, Ksenia, Maria Polyakova, Inna Sokhova, Vladlena Doroshina, Marianna Arakelyan, Alexandr Zaytsev, and Nina Novozhilova. 2021. "The Effect of Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing on the Roughness of the Enamel, Three Different Nanocomposites, and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113072
APA StyleBabina, K., Polyakova, M., Sokhova, I., Doroshina, V., Arakelyan, M., Zaytsev, A., & Novozhilova, N. (2021). The Effect of Ultrasonic Scaling and Air-Powder Polishing on the Roughness of the Enamel, Three Different Nanocomposites, and Composite/Enamel and Composite/Cementum Interfaces. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113072