Testing of Silicon Rubber/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Mechanical and Tribological Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Details
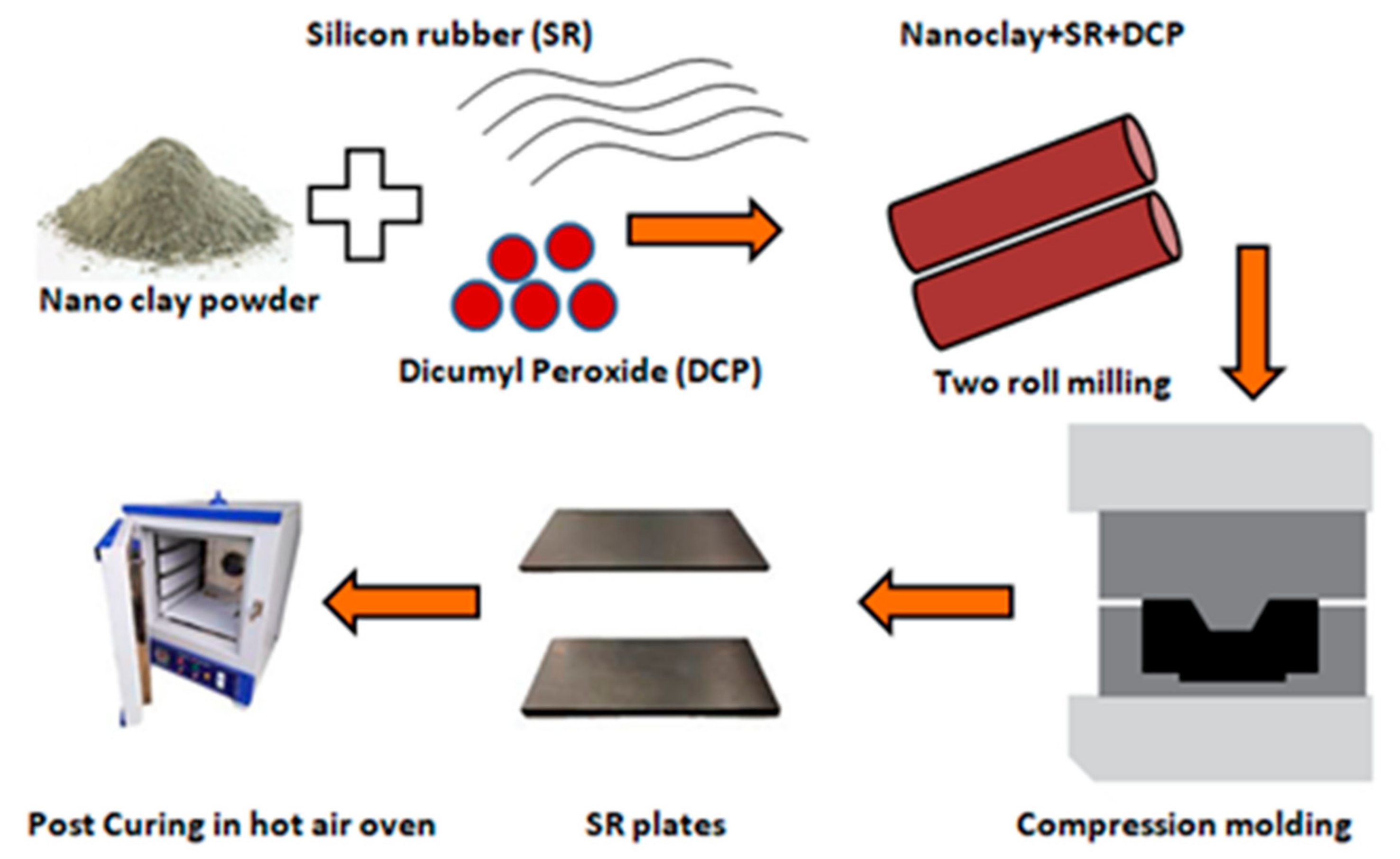
2.2. Preparation of Silicon Rubber–Nanoclay Composites
2.3. Characterizations
2.3.1. Morphology Testing
2.3.2. Mechanical Testing
2.3.3. Experimental Design of Tribological Study
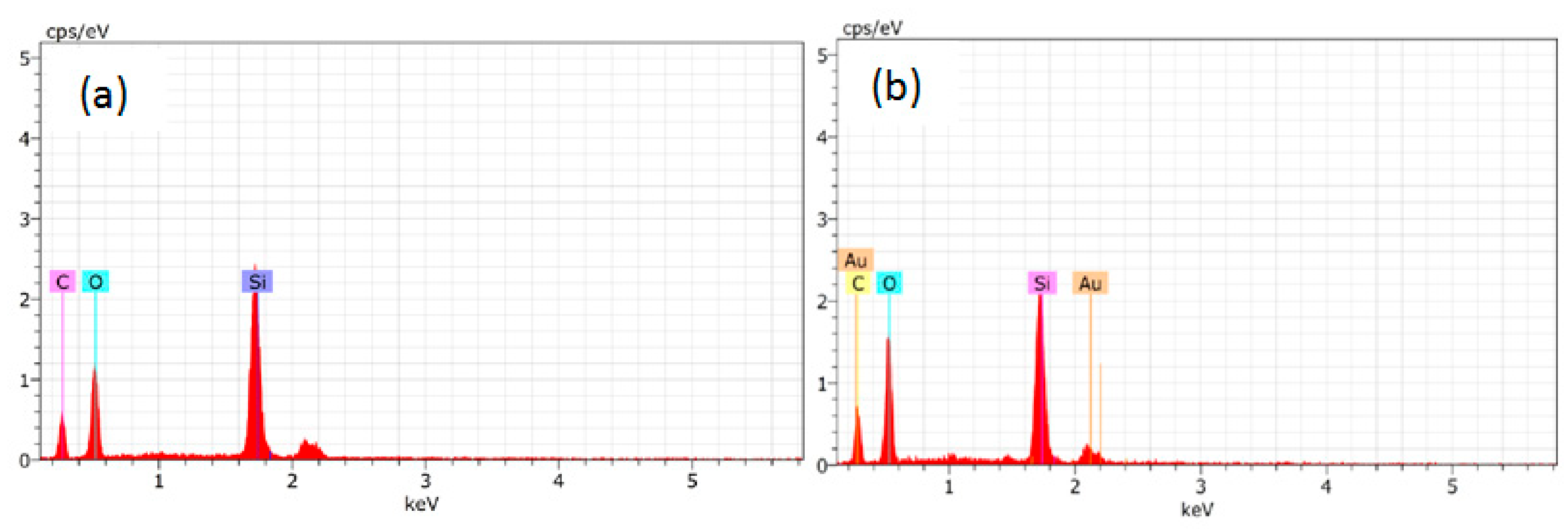
2.3.4. SEM and EDS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Studies
3.2. Mechanical Properties
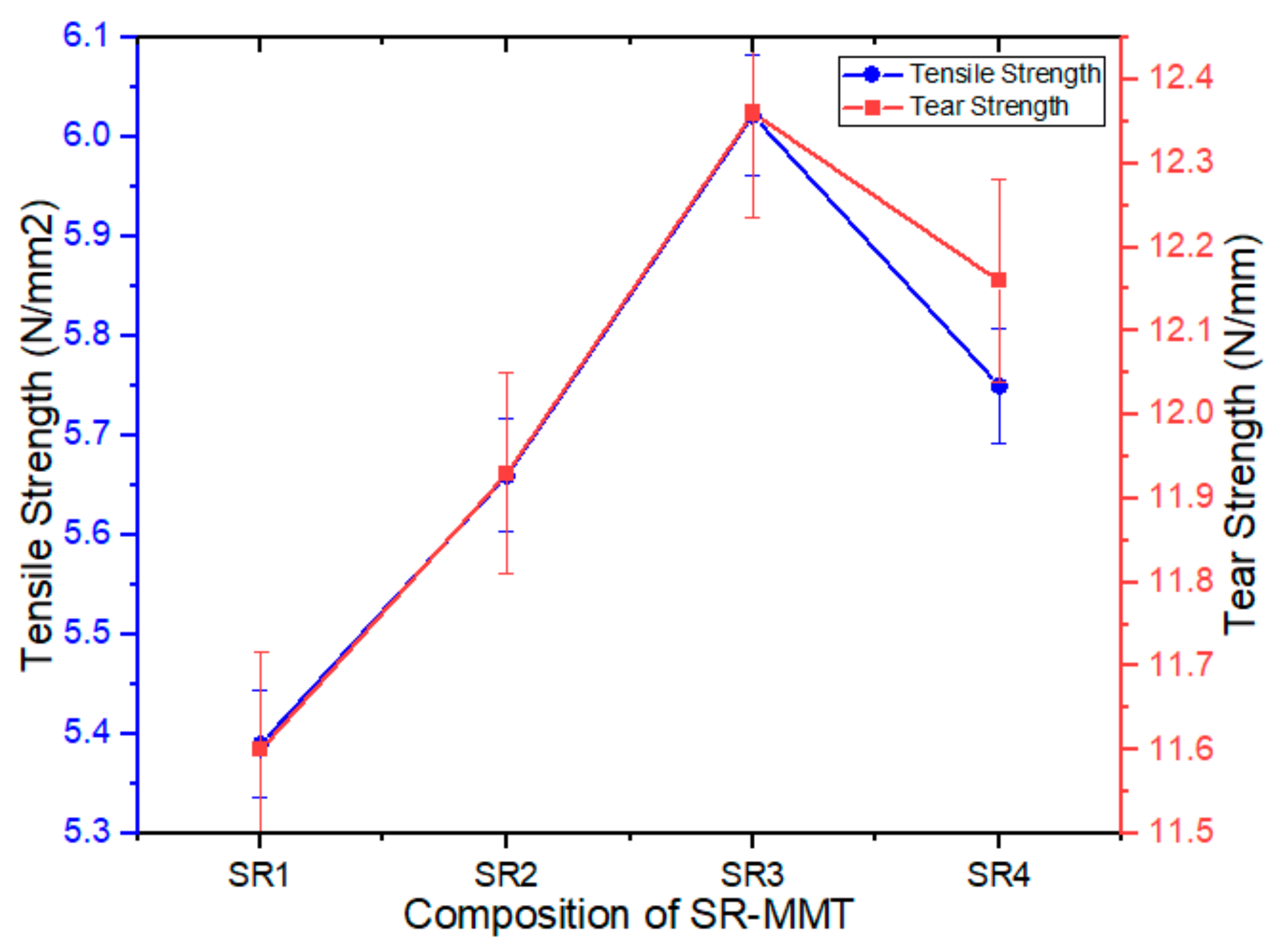
3.2.1. Tensile Strength
3.2.2. Tear Strength
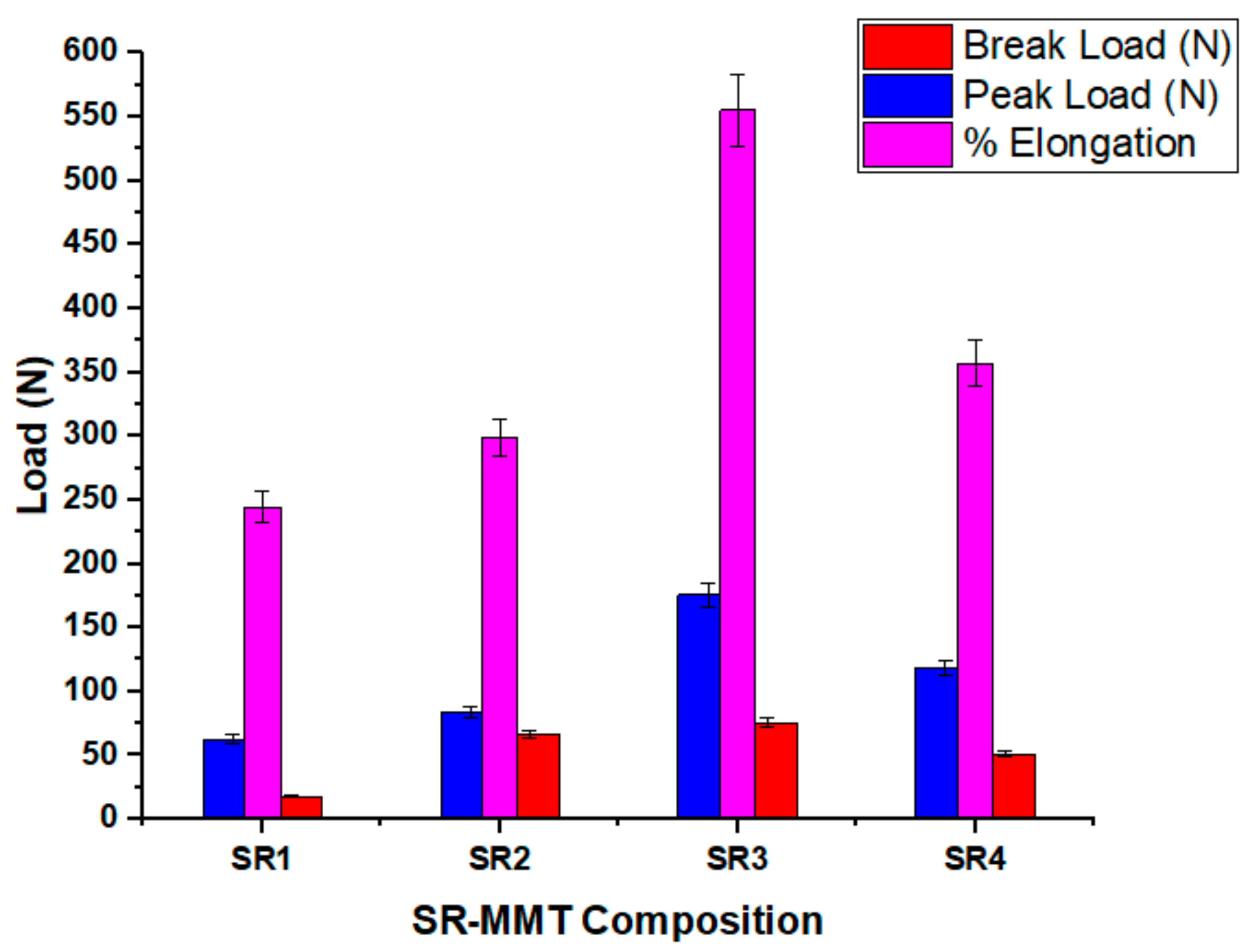
3.2.3. Peak Load, Braking Load, Elongation at Break
3.2.4. Percentage Elongation at Break
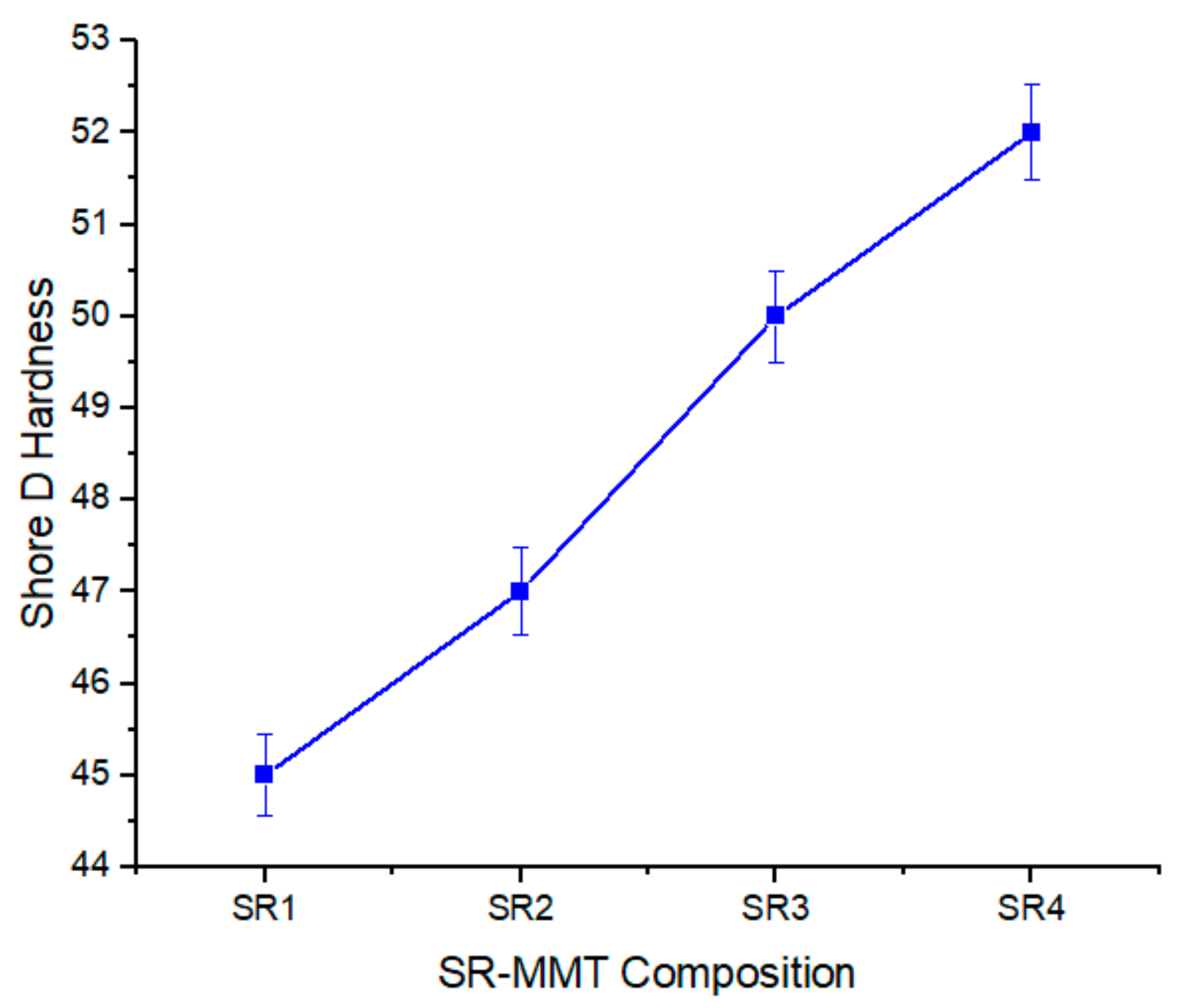
3.2.5. Shore D Hardness
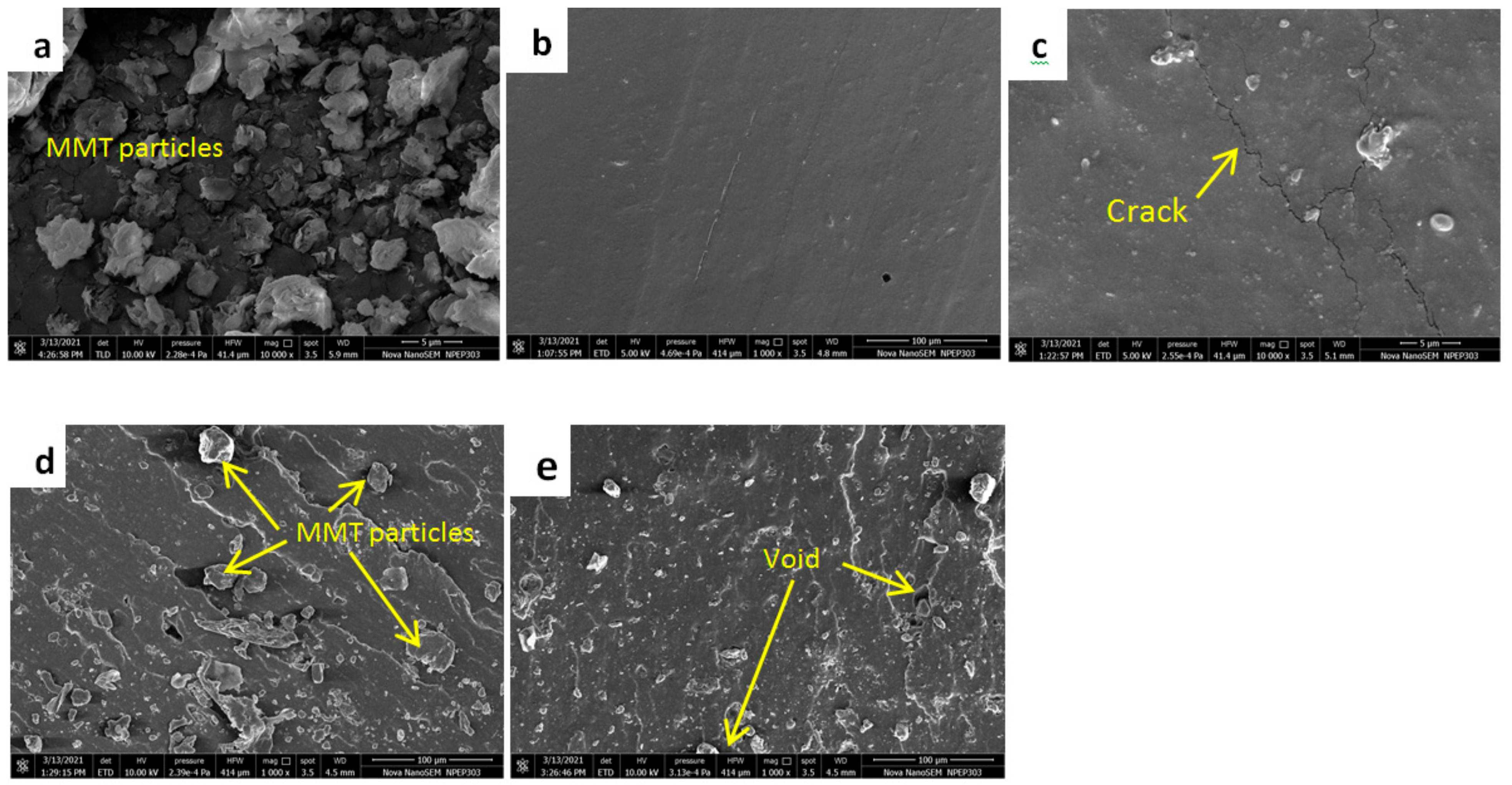
3.2.6. Tensile Fracture Surface Morphology
3.3. Tribological Analysis
3.3.1. ANOVA Analysis of Friction Coefficient
3.3.2. ANOVA Analysis of Weight Loss
3.3.3. ANOVA Analysis of Specific Wear Rate
3.3.4. Influence of Normal Load and Sliding Velocity
3.3.5. Worn Surface Morphology under Dry Sliding
3.3.6. EDS Spectrum of the Worn Surface
4. Conclusions
- The SR–MMT nanocomposite with 2% exhibited the highest tensile and tear strength. Compared to SR1, the SR3 composition showed almost 10% and 6% improvement in tensile and tear strength.
- Hardness showed continuous improvement with an increase in the MMT percentage.
- The tribological experiments and its ANOVA revealed that the load has more influence on the friction coefficient while the sliding velocity influences the wear rate.
- A reducing trend of the specific wear rate and the COF was found up to the SR3 composition, and after that, it increased for the SR4 composition. Also, with an increase in the loading, the COF increased but the wear rate decreased. The increasing trend is observed for both the COF and the wear rate, increasing the sliding velocity.
- The surface morphology of different configurations obtained by FE-SEM justifies the results obtained from the mechanical and tribological experiments. The smoother and uniform distribution of the MMT can be observed for the SR3 composition.
- The adhesive wear mechanism is the leading mechanism of wear observed for the developed nanocomposite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Ke, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Yao, X. Effect of stress relaxation on sealing performance of the fabric rubber seal. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 151, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Luo, G.; Xia, H.; He, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; Tan, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Novel bilayer wound dressing composed of silicone rubber with particular micropores enhanced wound re-epithelialization and contraction. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Lee, G.; Singh, K.; Choi, J.; Lee, D.-J. Structure-property relationship in silicone rubber nanocomposites reinforced with carbon nanomaterials for sensors and actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Quan, X.; Shao, Y.; Niu, K. Tribological properties of phenyl-silicone rubber composites with nano-CeO2 and graphene under thermal-oxidative aging. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gedde, U.W.; Hillborg, H. Structure and electrical properties of silicone rubber filled with thermally reduced graphene oxide. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tao, S.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z.; Zheng, J. The improved thermal oxidative stability of silicone rubber by using iron oxide and carbon nanotubes as thermal resistant additives. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 76, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyszka, R.; Strzelecki, D. Tribology in Industry Tribological Properties of Silicone Rubber-Based Ceramizable Composites Destined for Wire Covers. Part I. Studies of Block-On-Ring Friction Contact. Tribiology Ind. 2015, 37, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Kong, L. A study on mechanical and tribological properties of silicone rubber reinforced with white carbon black. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, A.; Pal, P.; Das, C.K. Effect of expanded graphite and modified graphite flakes on the physical and thermo-mechanical properties of styrene butadiene rubber/polybutadiene rubber (SBR/BR) blends. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Yao, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, X. Kinetic friction characterizations of the tubular rubber seals. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Das, T.; Rajasekar, R.; Pal, S.K.; Das, C.K. Wear Characteristics of Styrene Butadiene Rubber/Natural Rubber Blends with Varying Carbon Blacks by DIN Abrader and Mining Rock Surfaces. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarath, P.; Samson, S.V.; Reghunath, R.; Pandey, M.K.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; George, S.C. Fabrication of exfoliated graphite reinforced silicone rubber composites—Mechanical, tribological and dielectric properties. Polym. Test. 2020, 89, 106601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hidalgo, R.; Blanco, C.; Menendez, R.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Multifunctional Silicone Rubber Nanocomposites by Controlling the Structure and Morphology of Graphene Material. Polymers 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Yao, X. Wear-Resistant Graphene–Silicone Rubber Composites. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 63, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghian, G. Synthesis and properties of polyacrylamide by nanoparticles, effect nanoclay on stability polyacrylamide solution. Micro Nano Lett. 2017, 12, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-R.; Rhee, K.-Y.; Shin, H. Effect of MMT concentration on tribological behavior of MMT/Epoxy nanocomposite. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 4869–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S. Thermal, mechanical, and tribological properties of sodium-montmorillonite-nanoparticle-reinforced polyethersulfone and polytetrafluoroethylene ternary composites. Friction 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xian, Y.; Wan, H.; Ye, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Highly Dispersed Ag2S Nanoparticles: In Situ Synthesis, Size Control, and Modification to Mechanical and Tribological Properties towards Nanocomposite Coatings. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazemi-Khasragh, E.; Bahari-Sambran, F.; Platzer, C.; Eslami-Farsani, R. The synergistic effect of graphene nanoplatelets–montmorillonite hybrid system on tribological behavior of epoxy-based nanocomposites. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Peretyagin, P.; Pinargote, N.W.S.; Gershman, I.; Bartolomé, J.F. Wear Behavior of Graphene-Reinforced Alumina–Silicon Carbide Whisker Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, S.J.; Egodage, S.M.; Walpalage, S. Enhancement of mechanical properties of natural rubber–clay nanocomposites through incorporation of silanated organoclay into natural rubber latex. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L. Polyoxymethylene/graphene oxide-perfluoropolyether nano-composite with ultra-low friction coefficient fabricated by formation of superior interfacial tribofilm. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 132, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, S.; Sunkara, C. Effect of transfer film structure, composition and bonding on the tribological behavior of polyphenylene sulfide filled with nano particles of TiO2, ZnO, CuO and SiC. Wear 2005, 258, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.J.; Bahadur, S. Studies on the tribological behavior and transfer film—Counterface bond strength for polyphenylene sulfide filled with nanoscale alumina particles. Wear 2000, 237, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. Hysteresis Losses in the Friction of Lubricated Rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1960, 33, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tabor, D. The Friction of Hard Sliders on Lubricated Rubber: The Importance of Deformation Losses. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1958, 71, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, B.; Kumar, B.R.; Venkataramareddy, M.; Jayaraju, T. Role of micro/nano fillers on mechanical and tribological properties of polyamide66/polypropylene composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type/Grade | Silicon Rubber (SH5060 U) | MMT |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity (g/cc) | 1.15 | 1.98 |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate (MPa) | 5 | 101 |
| Elongation (%) | 500 | 8 |
| Hardness, Shore | 50 (A) | 83 (D) |
| Particle size (nm) | - | 100 |
| Type/Grade | SR1 | SR2 | SR3 | SR4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMT | 0 | 0.5 | 2 | 5 |
| DCP | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Parameter | Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | SR1 | SR2 | SR3 | SR4 |
| Load (N) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Sliding Speed (m/s) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Sliding Distance (mm) | 1000 | 1800 | 2600 | 3200 |
| Exp. No. | Composition | Load | Sliding Speed | Sliding Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SR1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | SR1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | SR1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | SR1 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | SR2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 6 | SR2 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| 7 | SR2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 8 | SR2 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| 9 | SR3 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 10 | SR3 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| 11 | SR3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 12 | SR3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 13 | SR4 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| 14 | SR4 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 15 | SR4 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| 16 | SR4 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares (SS) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value | Effect Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (%) | 1 | 0.08102 | 0.08102 | 2 | 0.185 | 6.59 |
| Load (N) | 1 | 0.67881 | 0.37881 | 9.36 | 0.011 | 55.24 |
| Sliding Speed (m/s) | 1 | 0.06949 | 0.06949 | 1.72 | 0.217 | 5.65 |
| Sliding Distance (mm) | 1 | 0.25437 | 0.25437 | 6.28 | 0.029 | 20.70 |
| Error | 11 | 0.14525 | 0.04048 | 11.82 | ||
| Total | 15 | 1.22894 | 100.00 | |||
| Significance | R-sq = 80.95% | R-sq (adj) = 76.60% | ||||
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares (SS) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value | Effect Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (%) | 1 | 0.000434 | 0.000434 | 1.64 | 0.226 | 8.11 |
| Load (N) | 1 | 0.002953 | 0.000343 | 1.3 | 0.278 | 55.19 |
| Sliding Speed (m/s) | 1 | 0.000199 | 0.000199 | 0.75 | 0.404 | 3.72 |
| Sliding Distance (mm) | 1 | 0.001474 | 0.001474 | 5.58 | 0.038 | 27.55 |
| Error | 11 | 0.000291 | 0.000264 | 5.43 | ||
| Total | 15 | 0.005351 | 100.00 | |||
| Significance | R-sq = 92.22 % | R-sq (adj) = 84.12 % | ||||
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares (SS) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value | Effect Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (%) | 1 | 7 × 10−6 | 0.000007 | 1.54 | 0.241 | 7.53 |
| Load (N) | 1 | 3.25 × 10−5 | 0.00001 | 2.09 | 0.176 | 34.95 |
| Sliding Speed (m/s) | 1 | 1 × 10−6 | 0.000001 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 1.08 |
| Sliding Distance (mm) | 1 | 4.75 × 10−5 | 0.000025 | 5.37 | 0.041 | 51.08 |
| Error | 11 | 5 × 10−6 | 0.000005 | 5.38 | ||
| Total | 15 | 93 × 10−6 | 100.00 | |||
| Significance | R-sq = 83.04% | R-sq (adj) = 71.43% | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinde, A.; Siva, I.; Munde, Y.; Deore, V.; Hameed Sultan, M.T.; Md Shah, A.U.; Mustapha, F. Testing of Silicon Rubber/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Mechanical and Tribological Performance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113050
Shinde A, Siva I, Munde Y, Deore V, Hameed Sultan MT, Md Shah AU, Mustapha F. Testing of Silicon Rubber/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Mechanical and Tribological Performance. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113050
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinde, Avinash, I. Siva, Yashwant Munde, Vishal Deore, Mohamed Thariq Hameed Sultan, Ain Umaira Md Shah, and Faizal Mustapha. 2021. "Testing of Silicon Rubber/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Mechanical and Tribological Performance" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113050
APA StyleShinde, A., Siva, I., Munde, Y., Deore, V., Hameed Sultan, M. T., Md Shah, A. U., & Mustapha, F. (2021). Testing of Silicon Rubber/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Mechanical and Tribological Performance. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113050








