Electrochemical Performance of Thick-Film Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Cathode with Hierarchic Structures and Laser Ablation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cathode Materials
2.2. Laser Structuring
2.3. Coin Cell Assembly
2.4. Electrochemical Analysis
2.4.1. Rate Capability Tests
2.4.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.4.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Electrodes
3.2. Electrochemical Analysis
3.2.1. Rate Capability Tests
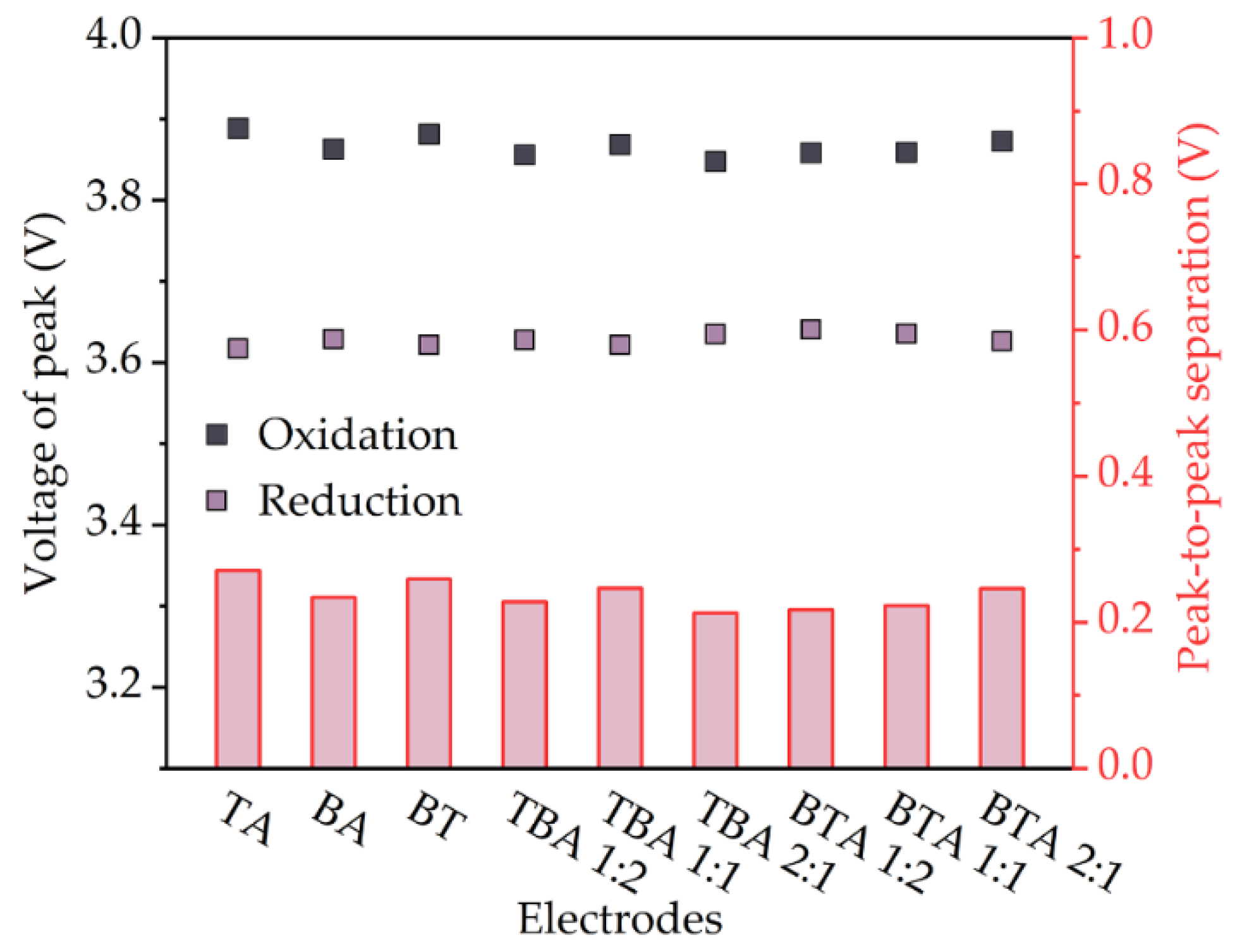
3.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
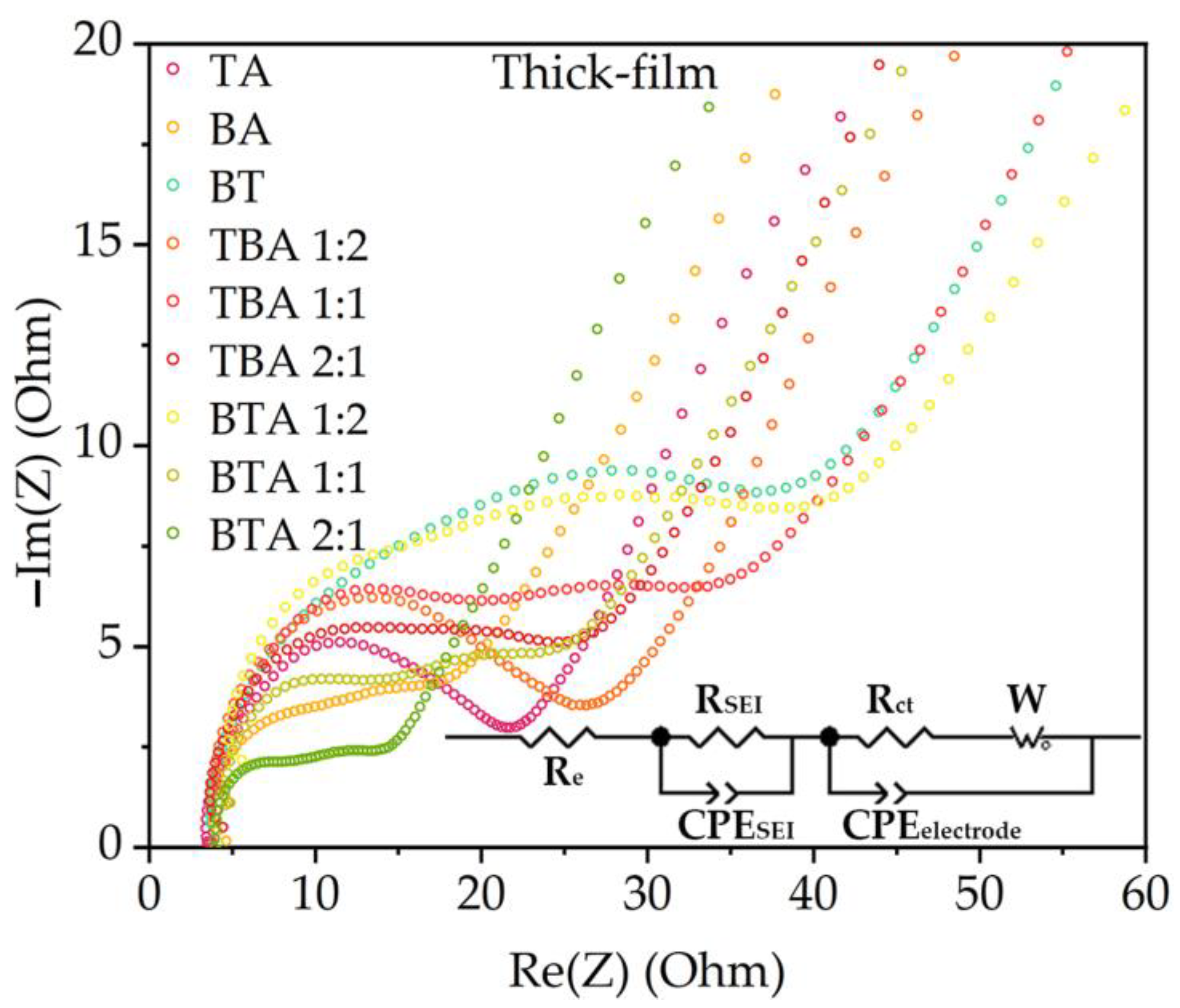
3.2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
4.1. Electrode Manufacturing and Laser Structuring
4.2. Electrochemical Analysis
4.2.1. Rate Capability Tests
4.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
4.2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfleging, W. A review of laser electrode processing for development and manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries. Nanophotonics 2017, 7, 549–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Tong, J.; Pfleging, W.; Sun, J. A review: Learning from the flight of beetles. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-S. A Review of Recent Advancements in Electrospun Anode Materials to Improve Rechargeable Lithium Battery Performance. Polymers 2020, 12, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H. Lithium migration between blended cathodes of a lithium-ion battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8653–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Du, R.; Tang, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Effect of Ni2+ on Lithium-Ion Diffusion in Layered LiNi1−x−yMnxCoyO2 Materials. Crystals 2021, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, N.V.; Devyatkina, E.T.; Kaichev, V.V. Optimization of Ni2+/Ni3+ ratio in layered Li(Ni,Mn,Co)O2 cathodes for better electrochemistry. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K.G.; Trask, S.E.; Bauer, C.; Woehrle, T.; Lux, S.F.; Tschech, M.; Lamp, P.; Polzin, B.J.; Ha, S.; Long, B.; et al. Optimizing Areal Capacities through Understanding the Limitations of Lithium-Ion Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A138–A149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Liu, G.; Battaglia, V.S. A comprehensive understanding of electrode thickness effects on the electrochemical performances of Li-ion battery cathodes. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 71, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hyeon, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.-J. Performance enhancement of Li-ion battery by laser structuring of thick electrode with low porosity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleging, W. Recent progress in laser texturing of battery materials: A review of tuning electrochemical performances, related material development, and prospects for large-scale manufacturing. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 3, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Seifert, H.J.; Pfleging, W. The ultrafast laser ablation of Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 electrodes with high mass loading. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfleging, W.; Gotcu, P. Femtosecond Laser Processing of Thick Film Cathodes and Its Impact on Lithium-Ion Diffusion Kinetics. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraft, L.; Habedank, J.B.; Frank, A.; Rheinfeld, A.; Jossen, A. Modeling and Simulation of Pore Morphology Modifications using Laser-Structured Graphite Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 013506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleging, W.; Pröll, J. A new approach for rapid electrolyte wetting in tape cast electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14918–14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangang, M.; Seifert, H.J.; Pfleging, W. Influence of laser pulse duration on the electrochemical performance of laser structured LiFePO4 composite electrodes. J. Power Sources 2016, 304, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Lee, D. Effect of fluence and multi-pass on groove morphology and process efficiency of laser structuring for 3D electrodes of lithium-ion batteries. Materials 2021, 14, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Han, J.; Pfleging, W. Characterization and Laser Structuring of Aqueous Processed Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Thick-Film Cathodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kaiser, J.; Hahn, H. A systematic study of thick electrodes for high energy lithium ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 782, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, N.; Itou, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Takeuchi, Y. Impedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Porous Electrodes under Different Electrode Thickness Using a Symmetric Cell for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 4612–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaju, K.; Subba Rao, G.; Chowdari, B.V. Performance of layered Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2 as cathode for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 48, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, W.; Nötzel, D. Rheological properties and stability of NMP based cathode slurries for lithium ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 4591–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jeon, C.; Kim, W.; Bong, S.J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.J. Challenges, laser processing and electrochemical characteristics on application of ultra-thick electrode for high-energy lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2021, 482, 228948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genieser, R.; Ferrari, S.; Loveridge, M.; Beattie, S.D.; Beanland, R.; Amari, H.; West, G.; Bhagat, R. Lithium ion batteries (NMC/graphite) cycling at 80 °C: Different electrolytes and related degradation mechanism. J. Power Sources 2018, 373, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongy, C.; Gaillot, A.C.; Jouanneau, S.; Guyomard, D.; Lestriez, B. Ionic vs Electronic Power Limitations and Analysis of the Fraction of Wired Grains in LiFePO4 Composite Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Recent insights into the electrochemical behavior of blended lithium insertion cathodes: A review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclar, H.; Kovacheva, D.; Zhecheva, E.; Stoyanova, R.; Lavi, R.; Kimmel, G.; Grinblat, J.; Girshevitz, O.; Amalraj, F.; Haik, O.; et al. On the Performance of LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 Nanoparticles as a Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkannanavar, S.B.; Bernardi, D.M.; Liu, L. A review of blended cathode materials for use in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, W.A.; Park, J.; Van Khue, L.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Ryou, M.H.; Lee, Y.M. Comparative study on experiments and simulation of blended cathode active materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Chen, C.F.; Mullings, M.; Jaime, D.; Zaleski, A.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Rhodes, C.P. Probing the Effect of High Energy Ball Milling on the Structure and Properties of LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 Cathodes for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2016, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, W.S.; Park, K.-W. Nanostructure cathode materials prepared by high-energy ball milling method. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3313–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Banerjee, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Brandon, N. Simulation of bi-layer cathode materials with experimentally validated parameters to improve ion diffusion and discharge capacity. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, W. New insight into the discharge process of sulfur cathode by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.J.; McCarthy, B.D.; Rountree, E.S.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. A Practical Beginner’s Guide to Cyclic Voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Shin, H.-C.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, W.S. Modeling and Applications of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) for Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
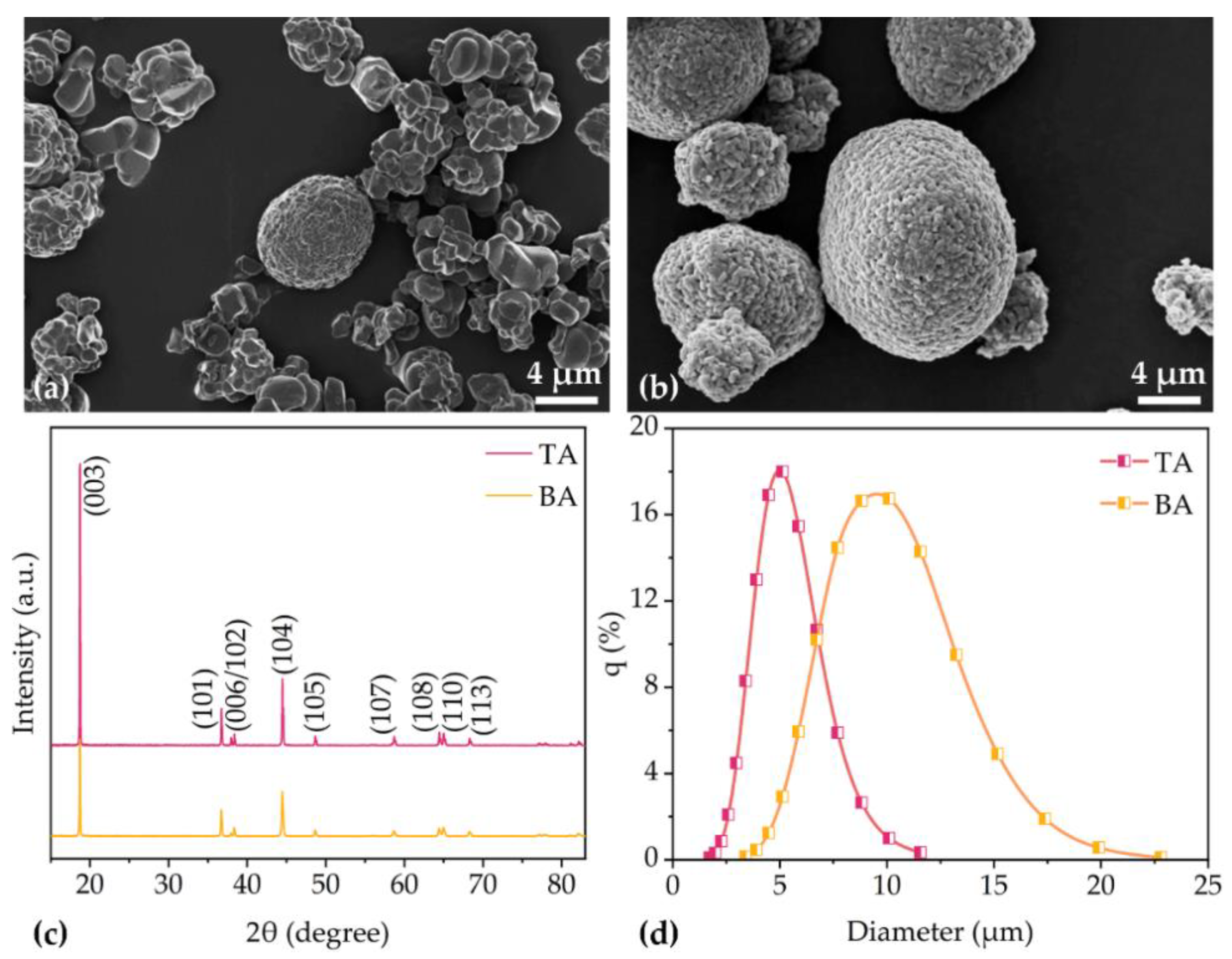

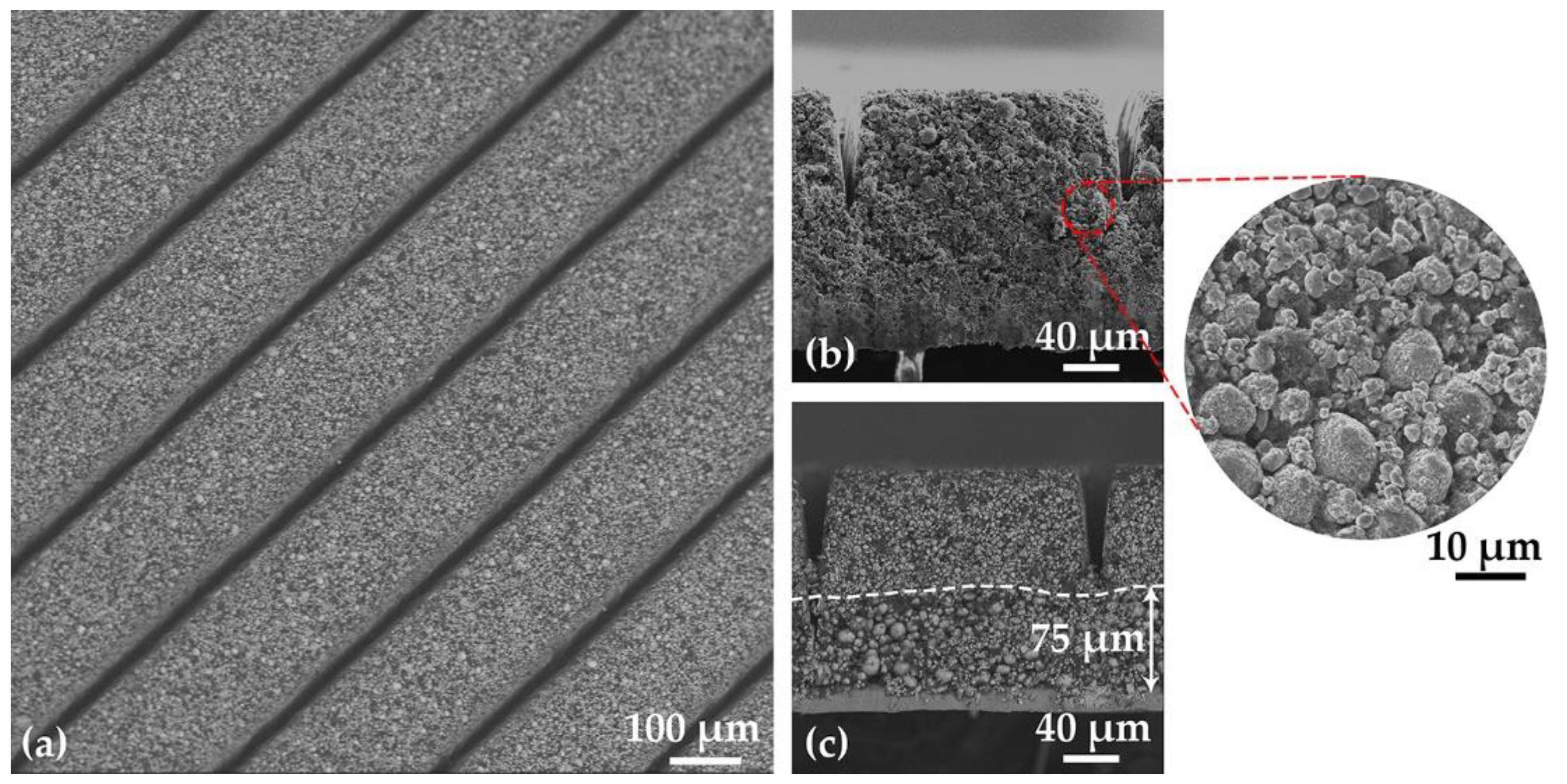



| Cathode | Thickness without Al Foil (µm) | Porosity (%) | Active Mass Loading (mg/cm2) | Areal Capacity (mAh/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA thin | 73 ± 1 | 35.1 | 18.2 ± 0.1 | 3.13 ± 0.02 |
| BA thin | 74 ± 1 | 35.3 | 18.4 ± 0.1 | 3.16 ± 0.02 |
| BT thin | 73 ± 1 | 35.2 | 18.1 ± 0.1 | 3.13 ± 0.02 |
| TA thick | 157 ± 1 | 35.3 | 38.9 ± 0.1 | 6.71 ± 0.01 |
| BA thick | 152 ± 1 | 35.4 | 37.6 ± 0.1 | 6.49 ± 0.02 |
| BT thick | 155 ± 2 | 35.3 | 38.5 ± 0.3 | 6.63 ± 0.05 |
| TBA 1:2 | 152 ± 1 | 35.3 | 37.7 ± 0.2 | 6.50 ± 0.03 |
| TBA 1:1 | 155 ± 1 | 35.2 | 38.5 ± 0.2 | 6.64 ± 0.03 |
| TBA 2:1 | 153 ± 1 | 35.2 | 37.9 ± 0.1 | 6.53 ± 0.01 |
| BTA 1:2 | 153 ± 1 | 35.2 | 38.0 ± 0.1 | 6.55 ± 0.02 |
| BTA 1:1 | 151 ± 1 | 35.1 | 37.6 ± 0.1 | 6.47 ± 0.01 |
| BTA 2:1 | 154 ± 1 | 35.1 | 38.3 ± 0.2 | 6.61 ± 0.03 |
| Cathode (Laser Structured) | Active Mass Loading (mg/cm2) | Areal Capacity (mAh/cm2) | Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 34.3 ± 0.2 | 5.91 ± 0.04 | 11.2 |
| BA | 35.3 ± 0.1 | 6.09 ± 0.01 | 6.1 |
| BT | 35.8 ± 0.1 | 6.17 ± 0.02 | 6.6 |
| TBA 1:2 | 35.6 ± 0.1 | 6.15 ± 0.02 | 5.4 |
| TBA 1:1 | 36.1 ± 0.2 | 6.22 ± 0.03 | 6.2 |
| TBA 2:1 | 35.8 ± 0.2 | 6.17 ± 0.03 | 5.5 |
| BTA 1:2 | 34.1 ± 0.4 | 5.87 ± 0.02 | 10.3 |
| BTA 1:1 | 34.5 ± 0.1 | 5.95 ± 0.01 | 8.1 |
| BTA 2:1 | 36.3 ± 0.2 | 6.27 ± 0.01 | 5.1 |
| R | TA | BA | BT | TBA 1:2 | TBA 1:1 | TBA 2:1 | BTA 1:2 | BTA 1:1 | BTA 2:1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSEI (Ω) | 11.5 | 4.5 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 9.2 | 8.6 | 3.3 | 7.3 | 3.1 |
| Rct (Ω) | 6.7 | 9.1 | 42.4 | 15.3 | 36.7 | 23.8 | 39.2 | 16.2 | 8.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Zhu, P.; Pfleging, W.; Sun, J. Electrochemical Performance of Thick-Film Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Cathode with Hierarchic Structures and Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112962
Song Z, Zhu P, Pfleging W, Sun J. Electrochemical Performance of Thick-Film Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Cathode with Hierarchic Structures and Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112962
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zelai, Penghui Zhu, Wilhelm Pfleging, and Jiyu Sun. 2021. "Electrochemical Performance of Thick-Film Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Cathode with Hierarchic Structures and Laser Ablation" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112962
APA StyleSong, Z., Zhu, P., Pfleging, W., & Sun, J. (2021). Electrochemical Performance of Thick-Film Li(Ni0.6Mn0.2Co0.2)O2 Cathode with Hierarchic Structures and Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112962








