Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4@CA MNPs
2.3. Characterization of Fe3O4@CA MNP’s
2.4. FO Filtrations
3. Results and Discussion
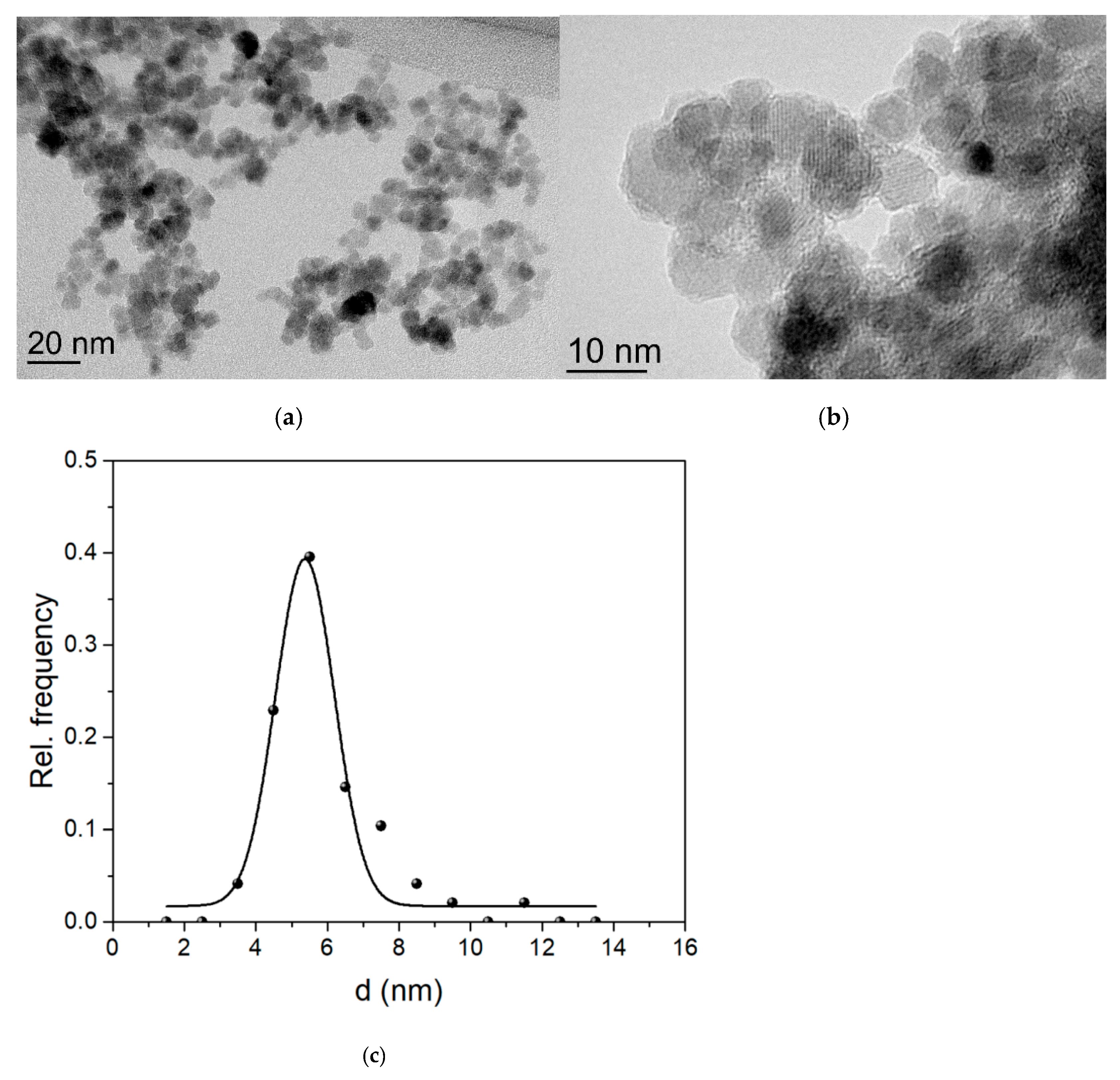
3.1. Magnetic Particle Preparation
3.2. Characterization of Fe3O4@CA MNPs
3.3. Properties of Fe3O4@CA
3.4. Forward Osmosis Process Evaluation
3.4.1. Determination of Jw and Js
3.4.2. Development of the FS and DS Osmotic Pressures
3.5. Characterization after FO Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farmany, A.; Mortazavi, S.S.; Mahdavi, H. Ultrasond-assisted synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell with enhanced adsorption capacity for diazinon removal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Deng, S.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorooctane sulfonate on nanosized inorganic oxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 474, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roto, R.; Yusran, Y.; Kuncaka, A. Magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiol group for chloroauric ion adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, R.; Socoliuc, V.; Craciunescu, I.; Petran, A.; Paulus, A.; Franzreb, M.; Vasile, E.; Vekas, L. Magnetic microgels, a promising candidate for enhanced magnetic adsorbent particles in bioseparation: Synthesis, physicochemical characterization, and separation performance. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L. Nanotechnologies for environmental cleanup. Nano Today 2006, 1, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hobaib, A.; Al-Sheetan, K.; El Mir, L. Effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on the performance of polyamide membrane for ground water purification. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 42, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Daraei, P.; Rajabi, H.; Zinadini, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Heydari, R.; Beygzadeh, M.; Ghouzivand, S. Polyethersulfone membrane enhanced with iron oxide nanoparticles for copper removal from water: Application of new functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbatini, P.; Yrazu, F.; Rossi, F.; Thern, G.; Marajofsky, A.; de Cortalezzi, M.F. Fabrication and characterization of iron oxide ceramic membranes for arsenic removal. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5702–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.F.; Tang, J.; Nie, Z.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, L. Tailoring size and structural distortion of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the purification of contaminated water. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yantasee, W.; Warner, C.L.; Sangvanich, T.; Addleman, R.S.; Carter, T.G.; Wiacek, R.J.; Fryxell, G.E.; Timchalk, C.; Warner, M.G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Systems with Thiol Functionalized Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5114–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhang, S.; Cui, Y.; Ong, R.C.; Chung, N.T.-S.; Helmer, B.J.; de Wit, J.S. Highly permeable forward osmosis (FO) membranes for high osmotic pressure but viscous draw solutes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; Rastgar, M.; Shakeri, A. Anti-fouling and high water permeable forward osmosis membrane fabricated via layer by layer assembly of chitosan/graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Salehi, H.; Rastgar, M. Chitosan-based thin active layer membrane for forward osmosis desalination. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Tanaka, M. Softness of some metal ions. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1975, 37, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.D.; Bondaruk, M.M.; Burney, Z. Nonideal Solution Behavior in Forward Osmosis Processes Using Magnetic Nanoparticles. In Osmotically Driven Membrane Processes—Approach, Development and Current Status; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Removal of organic micro-pollutants (phenol, aniline and nitrobenzene) via forward osmosis (FO) process: Evaluation of FO as an alternative method to reverse osmosis (RO). Water Res. 2016, 91, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, W.; Yamamoto, K.; Tobino, T. Membrane fouling and long-term performance of seawater-driven forward osmosis for enrichment of nutrients in treated municipal wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liang, C.-Z.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Combination of forward osmosis (FO) process with coagulation/flocculation (CF) for potential treatment of textile wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 91, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, M.; Darwish, N.A.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Water desalination by forward (direct) osmosis phenomenon: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2015, 374, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.M.; Chung, T.-S. Desalination process using super hydrophilic nanoparticles via forward osmosis integrated with ultrafiltration regeneration. Desalination 2011, 278, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, S.; Guo, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, X. Multi-functional forward osmosis draw solutes for seawater desalination. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.; Moody, C. Drinking water from sea water by forward osmosis. Desalination 1976, 18, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. A novel ammonia—carbon dioxide forward (direct) osmosis desalination process. Desalination 2005, 174, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Energy requirements of ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 207, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Su, J.; Amy, G.L.; Chung, N.T.-S. Exploration of polyelectrolytes as draw solutes in forward osmosis processes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.M.; Wang, K.Y.; Chung, N.T.-S. Highly Water-Soluble Magnetic Nanoparticles as Novel Draw Solutes in Forward Osmosis for Water Reuse. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 5869–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.X.; Huang, S.; Lu, X. A solventless thermolysis route to large-scale production of ultra-small hydrophilic and biocompatible magnetic ferrite nanocrystals and their application for efficient protein enrichment. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, I.; Markuš, S.; Gyergyek, S.; Drofenik, M.; Korenak, J.; Helix-Nielsen, C.; Petrinić, I. Synthesis of Poly-Sodium-Acrylate (PSA)-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Use in Forward Osmosis Draw Solutions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.-S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufia-Rivas, J.; Morales, P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Effect of the Sodium Polyacrylate on the Magnetite Nanoparticles Produced by Green Chemistry Routes: Applicability in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Dai, C.; Hu, Y. Aqueous aggregation behavior of citric acid coated magnetite nanoparticles: Effects of pH, cations, anions, and humic acid. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, N.T.-S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.Y.; Su, J.; Ling, M.M. Forward osmosis processes: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. Desalination 2012, 287, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Feng, B.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D. Synthesis, characterization and MRI application of dextran-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 42, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manal-Mounir, R.; Eglal, H.; Gadallah, A.; Ali Azab, H.M. Comparative study for the preparation of superparamagnetic-citric coated magnetic nanoparticle and fodesalination application. ARPN J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2018, 13, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.; Yang, L.; Cai, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Liu, M. Hydroacid magnetic nanoparticles in forward osmosis for seawater desalination and efficient regeneration via integrated magnetic and membrane separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Awasthi, R.; Gajbhiye, N.S.; Agarwal, V.; Singh, A.; Yadav, A.; Gupta, R.K. Innovative synthesis of citrate-coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its preliminary applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaie, F.; Sheshmani, S.; Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Shahvelayati, A.S. Desalination of Saline Water via Forward Osmosis Using Magnetic Nanoparticles Covalently Functionalized with Citrate Ions as Osmotic Agent. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizani, M.; Saito, M.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. Engineering of size-controlled magnetic nanoparticles for use as a draw solution in a forward osmosis process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 154, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, R.M.; Al-Abodi, E.E.; Al-Alawy, A.F. Citrate-coated magnetite nanoparticles as osmotic agent in a forward osmosis process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 115, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Yang, S.; Lee, S. Evaluation of citrate-coated magnetic nanoparticles as draw solute for forward osmosis. Desalination 2014, 347, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszuba, M.; Corbett, J.; Watson, F.M.; Jones, A. High-concentration zeta potential measurements using light-scattering techniques. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 4439–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.Y.; Ahn, H.-W.; Chung, J.W.; Kwak, S.-Y. Magnetic core-hydrophilic shell nanosphere as stability-enhanced draw solute for forward osmosis (FO) application. Desalination 2016, 397, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrinic, I.; Bukšek, H.; Galambos, I.; Gerencsér-Berta, R.; Sheldon, M.S.; Helix-Nielsen, C. Removal of naproxen and diclofenac using an aquaporin hollow fibre forward osmosis module. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 192, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-H.; Im, S.-J.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A. Nanoparticle charge affects water and reverse salt fluxes in forward osmosis process. Desalination 2018, 438, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Desalination by ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis: Influence of draw and feed solution concentrations on process performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by using an improved polyol method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaihre, B.; Khil, M.S.; Lee, D.R.; Kim, H.Y. Gelatin-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as carrier system: Drug loading and in vitro drug release study. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Gautam, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, B.K.; Shankar, V.; Krishna, V. Citric acid coated magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and application in removal of Cd (II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Water Process. Eng. 2014, 4, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Răcuciu, M. Synthesis protocol influence on aqueous magnetic fluid properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wen, Y.; Xu, X.; Gu, H. Tunable synthesis of carboxyl-functionalized magnetite nanocrystal clusters with uniform size. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8782–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelj, S.; Makovec, D.; Drofenik, M. Preparation and properties of water-based magnetic fluids. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Riaz, S.; Sanaullah, I.; Khan, U.; Sabri, A.N.; Naseem, S. Microwave assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Fe3O4-doped ZrO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10106–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U.U. The Iron Oxides: Structure Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Completely Revised and Extended Edition; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, R. Magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagerma, M.A.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Azimi, G.; Scowen, I.J. Raman spectroscopic determination of the acidity constants of salicylaldoxime in aqueous solution. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Izake, E.L. Magnetic nanoparticles boosting the osmotic efficiency of a polymeric FO draw agent: Effect of polymer conformation. Desalination 2015, 373, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajraktari, N.; Madsen, H.T.; Gruber, M.F.; Truelsen, S.F.; Jensen, E.L.; Jensen, H.; Hélix-Nielsen, C. Separation of Peptides with Forward Osmosis Biomimetic Membranes. Membranes 2016, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Su, J.; Chung, T.-S.; Amy, G. Hydrophilic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance in Forward Osmosis Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 50, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| DS | FS | VDS (mL) | VFS (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MNP (3.7% w/w) | DI water | 100 | 250 |
| 2 | 0.45 M NaCl | DI water | 100 | 250 |
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | pH | Osmotic Pressure (bar) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| After synthesis | 69.4 | 12.5 | 33.2 |
| Drained water | 70.8 | 12.9 | 32.2 |
| 1. Cleaning with DI water | 28.8 | 12.4 | 10.3 |
| Drained water | 27.7 | 12.5 | 10.2 |
| 2. Cleaning with DI water | 16.1 | 12.1 | 5.4 |
| Drained water | 15.5 | 12.2 | 5.4 |
| 3. Cleaning with DI water | 7.6 | 11.9 | 2.5 |
| Drained water | 7.3 | 11.9 | 2.6 |
| 4. Cleaning with DI water | 3.3 | 11.6 | 0.9 |
| Drained water | 2.7 | 11.4 | 0.9 |
| 5. Cleaning with ethanol | 0.38 | 11.9 | 89.6 |
| Drained ethanol | / | / | / |
| 6. Cleaning with DI water | 0.62 | 11.3 | / |
| Drained water | 0.5 | 11.3 | / |
| Prepared DS | 0.77 | 10.3 | 13.2 |
| Sample Name | Concentration [%] | pH | Osmotic Pressure [bar] | dx [nm] | nS [molecules/nm2] | IEP | Ms [emu/g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@CA | 3.7 | 7 | 18.7 | 3–7 | 0.904 | 4.93 | 44 |
| S | I | |
|---|---|---|
| MNP@CA | 434 | 3.92 |
| CA | 142 | −0.17 |
| DS | FS | VDS (mL) Initial | VFS (mL) Initial | VDS (mL) | VFS (mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at 1 h | at 2 h | at 1 h | at 2 h | |||||
| 1 | MNP | DI water | 100 | 250 | 185.1 | 206.2 | 163.6 | 142.5 |
| 2 | 0.45 M NaCl | DI water | 100 | 250 | 273.7 | / | 75.2 | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrinic, I.; Stergar, J.; Bukšek, H.; Drofenik, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Ban, I. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112965
Petrinic I, Stergar J, Bukšek H, Drofenik M, Gyergyek S, Hélix-Nielsen C, Ban I. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112965
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrinic, Irena, Janja Stergar, Hermina Bukšek, Miha Drofenik, Sašo Gyergyek, Claus Hélix-Nielsen, and Irena Ban. 2021. "Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112965
APA StylePetrinic, I., Stergar, J., Bukšek, H., Drofenik, M., Gyergyek, S., Hélix-Nielsen, C., & Ban, I. (2021). Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Draw Solution Agents in Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112965







