Characterization of Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Synthetic Glycopolymers Using an Analytical Approach Based on spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
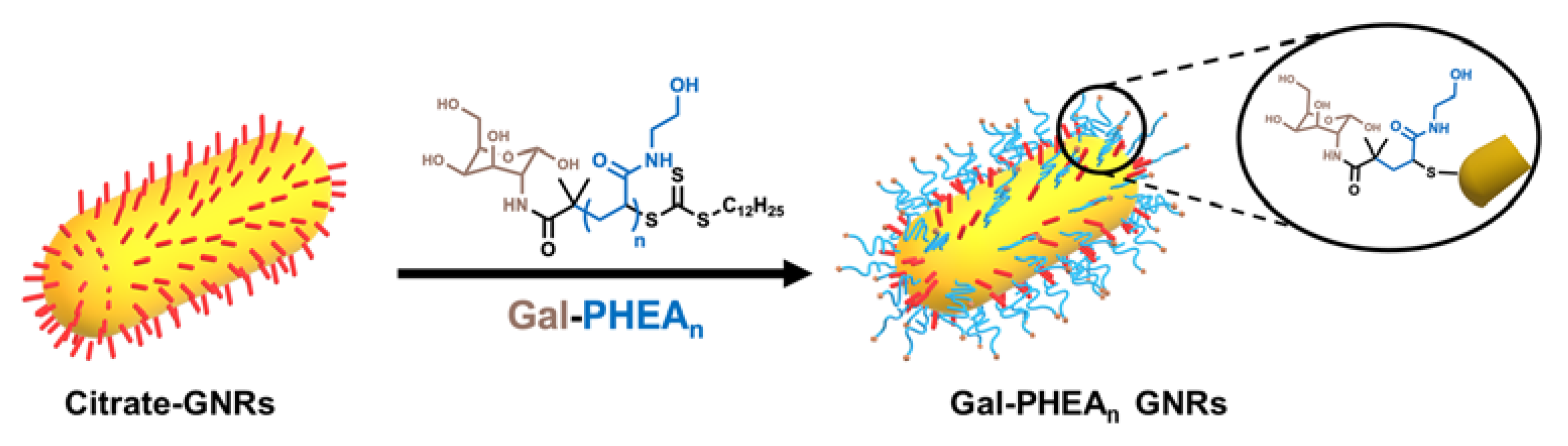
2.2. Preparation of Glycoconjugated GNRs
2.3. Instrumental Analysis
2.3.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.3.4. Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation (DCS)
2.3.5. spICP-SFMS
2.3.6. EAF4-MALS
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GNRs and Glycoconjugated GNRs by spICP-SFMS
3.2. Characterization of GNRs and Glycoconjugated GNRs Using EAF4-MALS
3.2.1. Optimization of EAF4-MALS Method
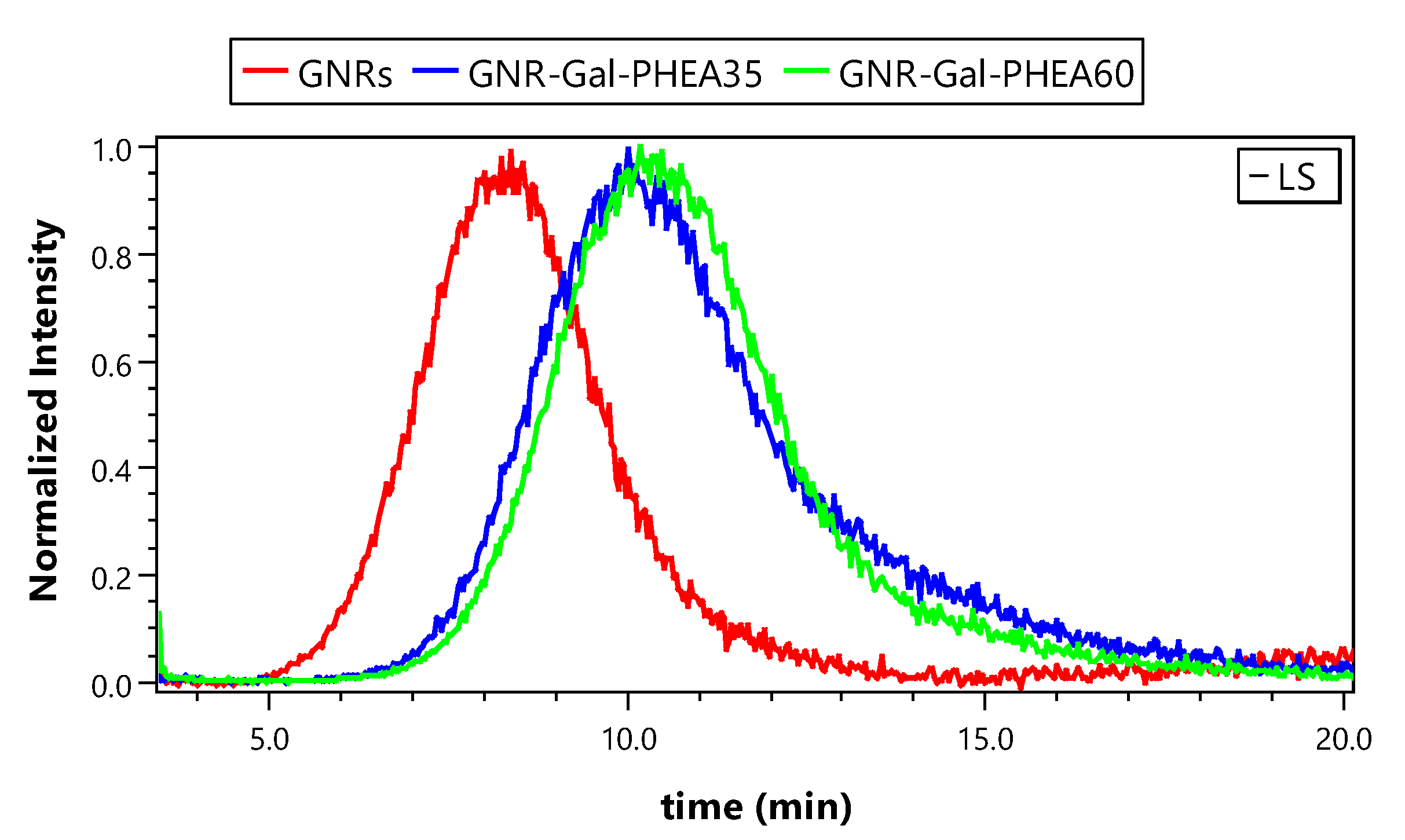
3.2.2. Performance of EAF4-MALS Method
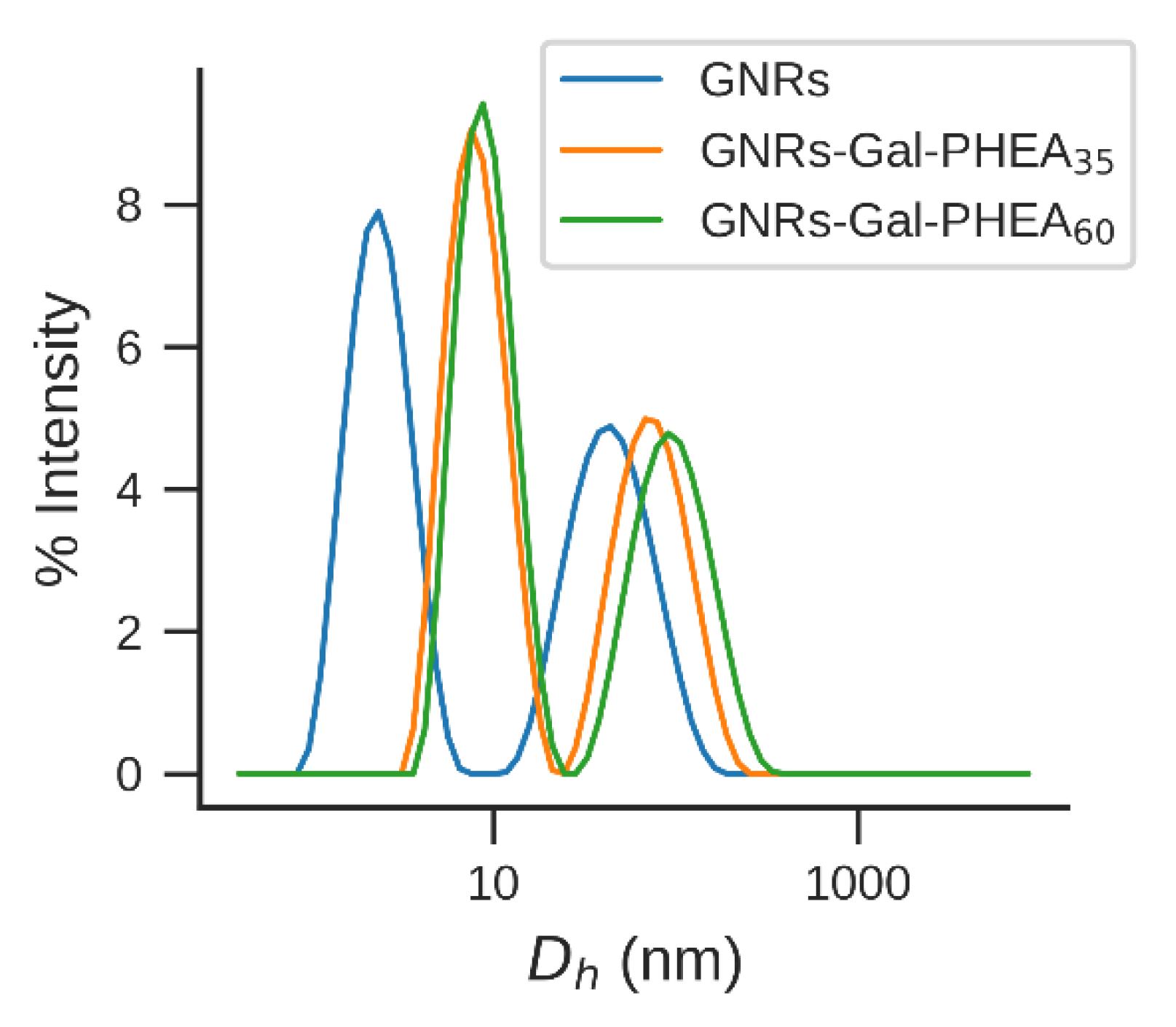
3.3. spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS as a Complementary Techniques to DLS, DCS and NTA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Mancini, M.C.; Nie, S.M. Bioimaging second window for in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, K.; Yong, T.; Roy, I.; Hu, R.; Ding, H.; Zhao, L.L.; Swihart, M.T.; He, G.S.; Cui, Y.P.; Prasad, P.N. Additive controlled synthesis of gold nanorods (GNRs) for two-photon luminescence imaging of cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 285106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, A.T.; Niidome, T. Gold Nanorods as Nanodevices for Bioimaging, Photothermal Therapeutics, and Drug Delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.L.; Gu, M. Surface plasmonic gold nanorods for enhanced two-photon microscopic imaging and apoptosis induction of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9492–9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Dreaden, E.C.; Huang, X.H.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Chu, H.H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, T.; Kato, S.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Okajima, J.; Maruyama, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Mori, S.; Kodama, T. Photothermal therapy of tumors in lymph nodes using gold nanorods and near-infrared laser light. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.S.; Chang, C.N.; Chang, Y.T.; Yang, M.H.; Chien, Y.H.; Chen, S.J.; Yeh, C.S. Gold nanorods in photodynamic therapy, as hyperthermia agents, and in near-infrared optical imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2711–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.N.; Peng, Q.A. Plasmonic gold nanorods can carry sulfonated aluminum phthalocyanine to improve photodynamic detection and therapy of cancers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 17194–17200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.W.; Tzeng, H.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.P.; Chen, L.C.; Wu, Y.C. DNA-gold nanorod conjugates for remote control of localized gene expression by near infrared irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3709–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Barua, S.; Kay, D.B.; Rege, K. Simultaneous enhancement of photothermal stability and gene delivery efficacy of gold nanorods using polyelectrolytes. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusz, G.J.; Curry, A.C.; Marinakos, S.M.; Wax, A.; Chilkoti, A. Rational selection of gold nanorod geometry for label-free plasmonic biosensors. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Sun, G.M.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.J.; Luo, J.J.; Yang, P.H. Multifunctional optical probe based on gold nanorods for detection and identification of cancer cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, P.L.; Cao, C.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Sim, S.J. A new method for non-labeling attomolar detection of diseases based on an individual gold nanorod immunosensor. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2591–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, P.G.; Baker, A.N.; Richards, S.J.; Laezza, A.; Walker, M.; Gibson, M. Tuning aggregative versus non-Aggregative lectin binding with glycosylated nanoparticles by the nature of the polymer ligand. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamnev, A.A.; Dyatlova, Y.A.; Kenzhegulov, O.A.; Vladimirova, A.A.; Mamchenkova, P.V.; Tugarova, A.V. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Analyses of Microbiological Samples and Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles of Microbial Origin: Sample Preparation Effects. Molecules 2021, 26, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnev, A.A. Infrared Spectroscopy in Studying Biofunctionalised Gold Nanoparticles. In Nanomaterials Imaging Techniques, Surface Studies, and Applications. Springer Proceedings in Physics; Fesenko, O., Yatsenko, L., Brodin, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 146. [Google Scholar]
- Wojnarowska-Nowak, R.; Polit, J.; Sheregii, E.M. Interaction of gold nanoparticles with cholesterol oxidase enzyme in bionanocomplex—determination of the protein structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancaro, A.; Szymonik, M.; Georgiou, P.G.; Baker, A.N.; Walker, M.; Adriaensens, P.; Hendrix, J.; Gibson, M.I. The polymeric glyco-linker controls the signal outputs for plasmonic gold nanorod biosensors due to biocorona formation. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 10837–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Jiménez-Lamana, J. Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: A Powerful Tool for Nanoanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño, M.D.; Olesik, J.W.; Barber, A.G.; Challis, K.; Ranville, J.F. Single particle ICP-MS: Advances toward routine analysis of nanomaterials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5053–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Donard, A. Nano-particle analysis using dwell times between 10 μs and 70 μs with an upper counting limit of greater than 3 × 107 cps and a gold nanoparticle detection limit of less than 10 nm diameter. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kálomista, I.; Kéri, A.; Ungor, D.; Csapó, E.; Dékány, I.; Prohaska, T.; Galbács, G. Dimensional characterization of gold nanorods by combining millisecond and microsecond temporal resolution single particle ICP-MS measurements. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marassi, V.; Casolari, S.; Roda, B.; Zattoni, A.; Reschiglian, P.; Panzavolta, S.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Ortelli, S.; Delpivo, C.; Blosi, M.; et al. Hollow-fiber flow field-flow fractionation and multi-angle light scattering investigation of the size, shape and metal-release of silver nanoparticles in aqueous medium for nano-risk assessment. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 106, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexel, R.; Siupa, A.; Carnell-Morris, P.; Carboni, M.; Sullivan, J.; Meier, F. Fast and Purification-Free Characterization of Bio-Nanoparticles in Biological Media by Electrical Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation Hyphenated with Multi-Angle Light Scattering and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis Detection. Molecules 2020, 25, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, C.; Elsenberg, S.; Schuch, H.; Rösch, U. Instrument and method to determine the electrophoretic mobility of nanoparticles and proteins by combining electrical and flow field-flow fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4292–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Report of Investigation, Reference Material 8012, Gold Nanoparticles, Nominal 30 nm Diameter. Available online: https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/certificates/8012.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Report of Investigation, Reference Material 8013, Gold Nanoparticles, Nominal 60 nm Diameter. Available online: https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/certificates/8013.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining transport efficiency for the purpose of counting and sizing nanoparticles via single particle inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johann, C. WP2606: Exosome Characterization with FFF-MALS-DLS; Wyatt: Dernbach, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.O.; Barros-Timmons, A.; Trindade, T. Polymer@gold Nanoparticles Prepared via RAFT Polymerization for Opto-Biodetection. Polymers 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beija, M.; Marty, J.-D.; Destarac, M. RAFT/MADIX Polymers for the Preparation of Polymer/Inorganic Nanohybrids. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 845–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.; Bulmus, V.; Davis, T.P.; Ladmiral, V.; Liu, J.; Perrier, S. Bioapplications of RAFT Polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5402–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.-J.; Gibson, M.I. Optimization of the Polymer Coating for Glycosylated Gold Nanoparticle Biosensors to Ensure Stability and Rapid Optical Readouts. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Richards, S.-J.; Walker, M.; Gibson, M.I. Externally Controllable Glycan Presentation on Nanoparticle Surfaces to Modulate Lectin Recognition. Nanoscale Horiz. 2017, 2, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, J.; Emrick, T. Pentafluorophenyl Ester-Functionalized Nanoparticles as a Versatile Platform for Selective and Covalent Inter-nanoparticle Coupling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Walczyk, D.; Campbell, A.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Dawson, K.A. Physical−Chemical Aspects of Protein Corona: Relevance to in Vitro and in Vivo Biological Impacts of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, J.A.; Krueger, K.M.; Yavuz, C.T.; Mayo, J.T.; LeCrone, D.; Redden, J.J.; Colvin, V.L. Size-dependent sedimentation properties of nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszewska, J.; Kulpińska, D.; Grabowska-Jadach, I.; Matczuk, M. Joint forces of direct, single particle, CE– and HPLC–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry techniques for the examination of gold nanoparticle accumulation, distribution and changes inside human cells. Metallomics 2020, 12, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, T.J.; Hackley, V.A. Fractionation and characterization of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with MALS, DLS, and UV–Vis detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D.K. Dynamic Light Scattering with Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics (Berne, Bruce, J.; Pecora, Robert). J. Chem. Educ. 1977, 54, A430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehner, D.; Lindner, H.; Glatter, O. Determination of the Translational and Rotational Diffusion Coefficients of Rodlike Particles Using Depolarized Dynamic Light Scattering. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zande, B.M.I.; Dhont, J.K.G.; Böhmer, M.R.; Philipse, A.P. Colloidal Dispersions of Gold Rods Characterized by Dynamic Light Scattering and Electrophoresis. Langmuir 2000, 16, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pierre-Pierre, N.; Huo, Q. Dynamic light scattering for gold nanorod size characterization and study of nanorod–protein interactions. Gold Bull. 2012, 45, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, J.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Lang, P.L. Dynamic Light Scattering of Short Au Rods with Low Aspect Ratios. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 5020–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Khlebtsov, N.G. On the measurement of gold nanoparticle sizes by the dynamic light scattering method. Colloid J. 2011, 73, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehtala, J.G.; Wei, A. Nanometric Resolution in the Hydrodynamic Size Analysis of Ligand-Stabilized Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13737–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez-Garcia, S.; Chen, L.; Morris, M.A.; Dawson, K.A. A new methodology for studying nanoparticle interactions in biological systems: Dispersing titania in biocompatible media using chemical stabilisers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieckmann, Y.; Cölfen, H.; Hofmann, H.; Petri-Fink, A. Particle Size Distribution Measurements of Manganese-Doped ZnS Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krpetić, Ž.; Davidson, A.M.; Volk, M.; Lévy, R.; Brust, M.; Cooper, D.L. High-Resolution Sizing of Monolayer-Protected Gold Clusters by Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8881–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.C.; Minelli, C.; Shard, A. Quantitation of IgG protein adsorption to gold nanoparticles using particle size measurement. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4591–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

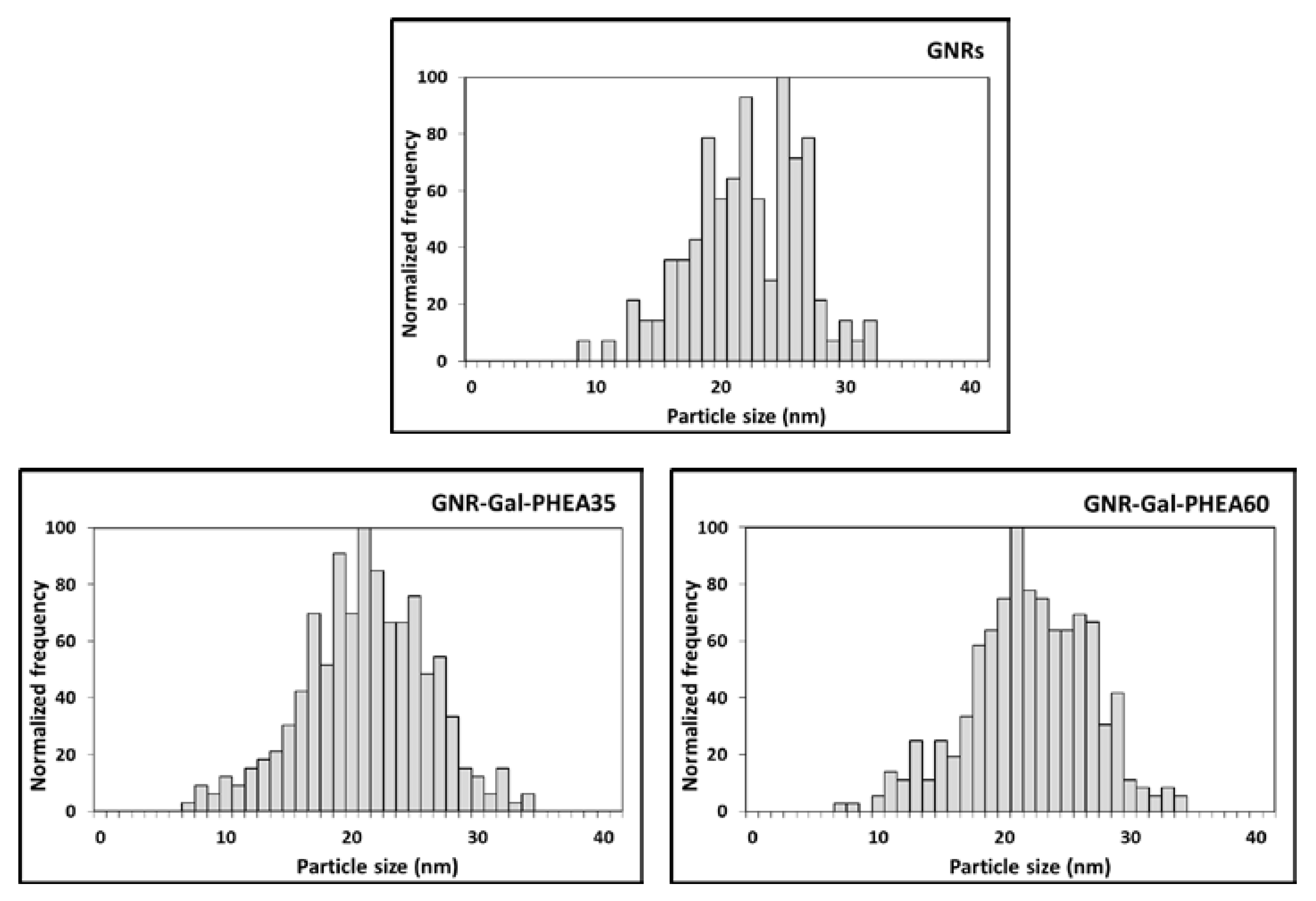
| Peak Size (nm) | Calculated Coating Thickness (nm) | |
|---|---|---|
| GNRs a | 22.0 ± 0.1 | n/a |
| GNR-Gal-PHEA35 b | 19.7 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| GNR-Gal-PHEA60 | 19.2 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Radio frequency power | 1300 W |
| Plasma gas flow rate | 13 L min−1 |
| Carrier gas flow rate | 0.93 L min−1 |
| Measurement mode | TRA |
| Nuclide monitored | 197Au |
| Dwell time | 40 µs |
| Acquisition time | 60 s |
| Nebulizer | MicroMist |
| Spray chamber | Cyclonic |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Tip to tip channel length | 26.5 cm |
| Spacer | 350 μm |
| Focus flow rate | 1 mL min−1 |
| Injection flow rate | 0.2 mL min−1 |
| Injection time | 3 min |
| Focus time | 2 min |
| Elution time | 30 min |
| Detector flow rate | 1 mL min−1 |
| Cross-flow rate | 0.5 mL min−1 |
| Membrane | PES, 5 kDa |
| Carrier | 0.5 mM sodium nitrate |
| Spherical Equivalent Diameter (nm) | Particle Number Concentration (Particles per mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| GNRs | 21.0 ± 0.5 | 1.83 × 107 ± 1.30 × 106 |
| GNR-Gal-PHEA35 | 21.0 ± 0.4 | 4.78 × 107 ± 1.10 × 106 |
| GNR-Gal-PHEA60 | 22.0 ± 0.0 | 5.27 × 107 ± 4.29 × 106 |
| GNRs | GNR-Gal-PHEA35 | GNR-Gal-PHEA60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injected Mass (µg) | 0.84 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| LS peak area Flow Through (cm−1 min−1) | 2.617 × 10−5 | 1.053 × 10−5 | 1.443 × 10−5 |
| LS peak area Separation run (cm−1 min−1) | 4.431 × 10−6 | 8.786 × 10−6 | 1.242 × 10−6 |
| Recovery (%) | 16.9 | 83.4 | 86.1 |
| GNRs | GNR-Gal-PHEA35 | GNR-Gal-PHEA60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dh (nm) | 17.0 | 21.3 | 22.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velimirovic, M.; Pancaro, A.; Mildner, R.; Georgiou, P.G.; Tirez, K.; Nelissen, I.; Johann, C.; Gibson, M.I.; Vanhaecke, F. Characterization of Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Synthetic Glycopolymers Using an Analytical Approach Based on spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102720
Velimirovic M, Pancaro A, Mildner R, Georgiou PG, Tirez K, Nelissen I, Johann C, Gibson MI, Vanhaecke F. Characterization of Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Synthetic Glycopolymers Using an Analytical Approach Based on spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102720
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelimirovic, Milica, Alessia Pancaro, Robert Mildner, Panagiotis G. Georgiou, Kristof Tirez, Inge Nelissen, Christoph Johann, Matthew I. Gibson, and Frank Vanhaecke. 2021. "Characterization of Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Synthetic Glycopolymers Using an Analytical Approach Based on spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102720
APA StyleVelimirovic, M., Pancaro, A., Mildner, R., Georgiou, P. G., Tirez, K., Nelissen, I., Johann, C., Gibson, M. I., & Vanhaecke, F. (2021). Characterization of Gold Nanorods Conjugated with Synthetic Glycopolymers Using an Analytical Approach Based on spICP-SFMS and EAF4-MALS. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102720








