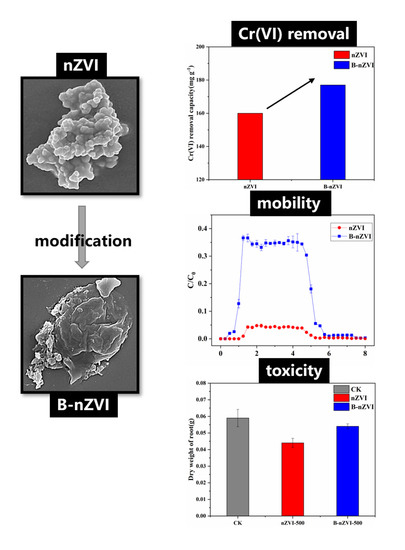
Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Modified by Bentonite with Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency, Improved Mobility, and Reduced Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of nZVI and Bentonite-Supported nZVI
2.3. Characterization of nZVI and B-nZVI
2.4. Batch Experiments
2.5. Column Transport Experiments
2.6. Luminous Bacteria Toxicity Test
2.7. Ryegrass Hydroponic Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
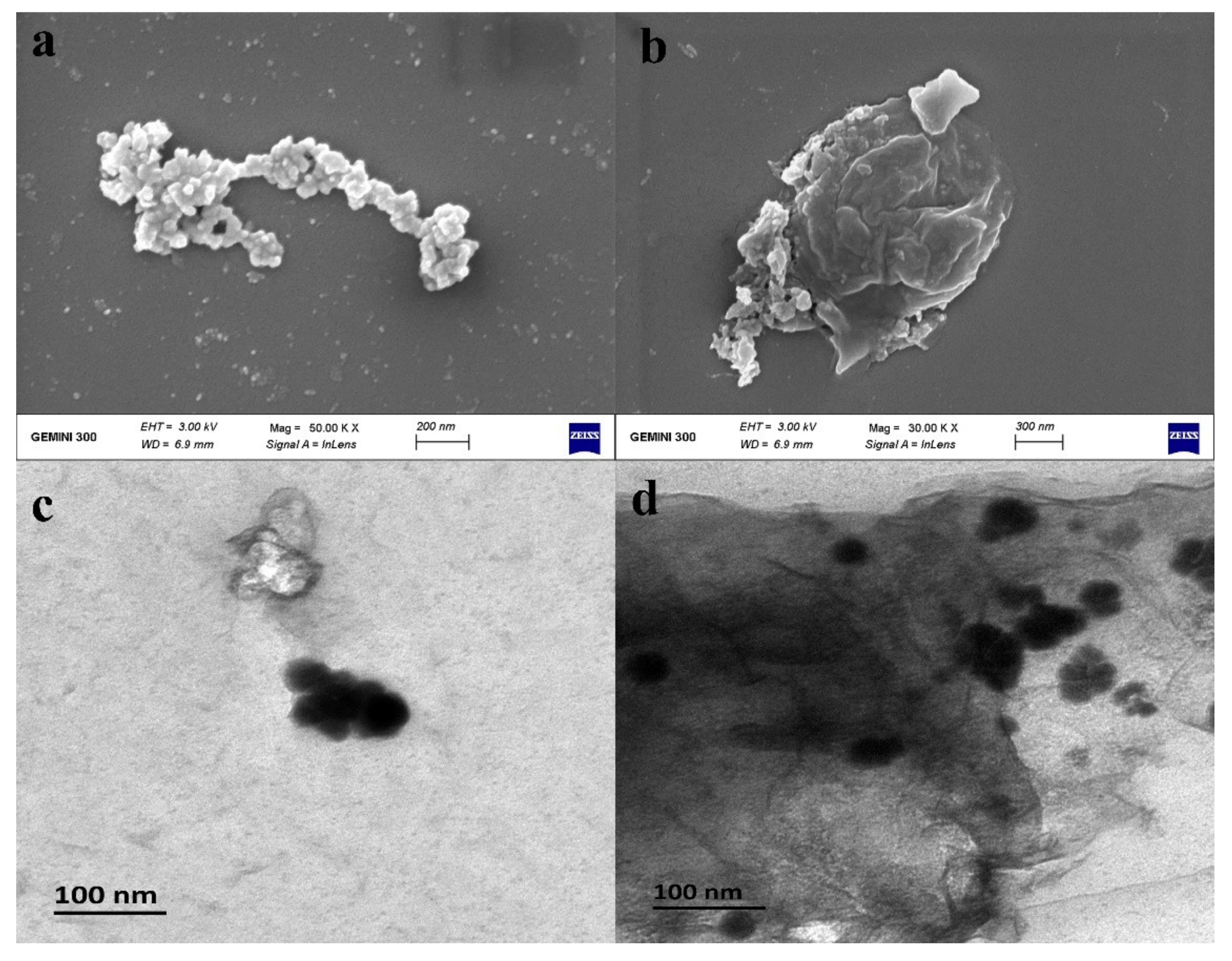
3.1. Characterization of nZVI and B-nZVI
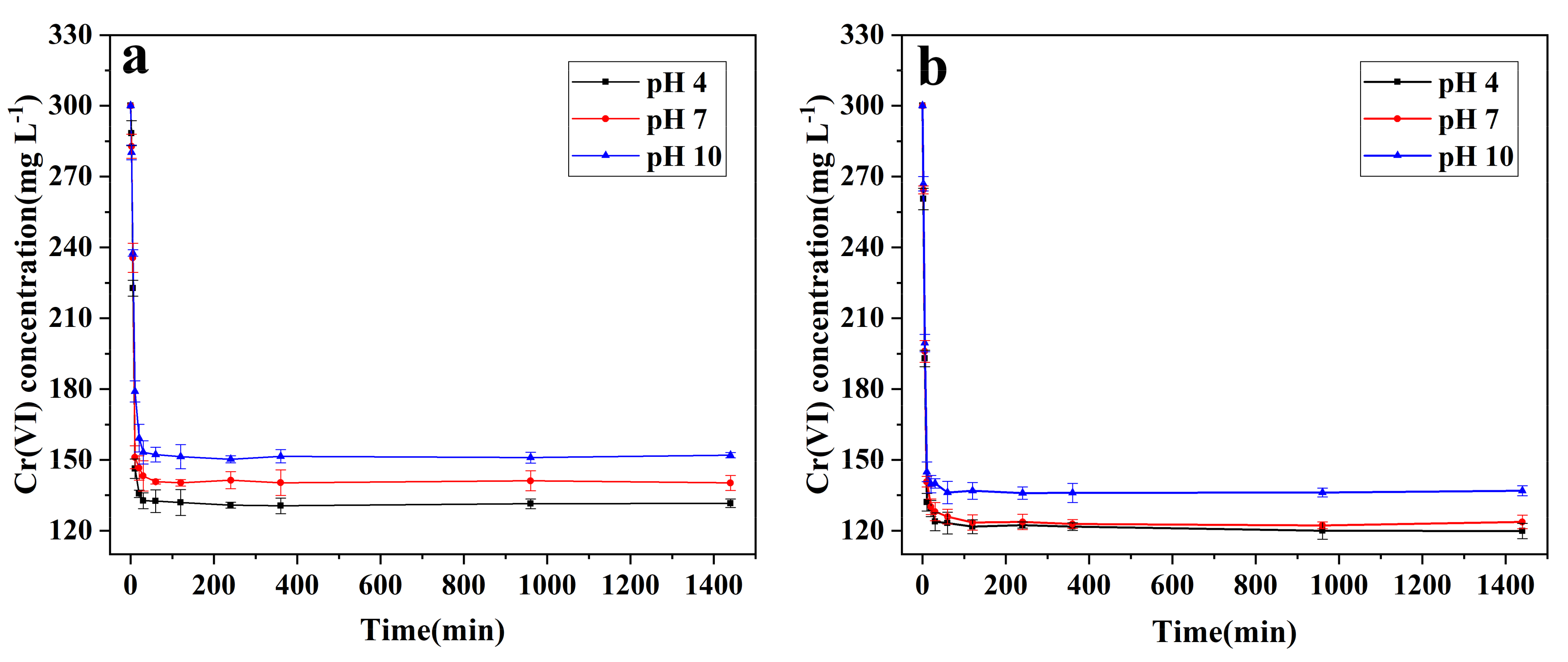
3.2. Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI and B-nZVI
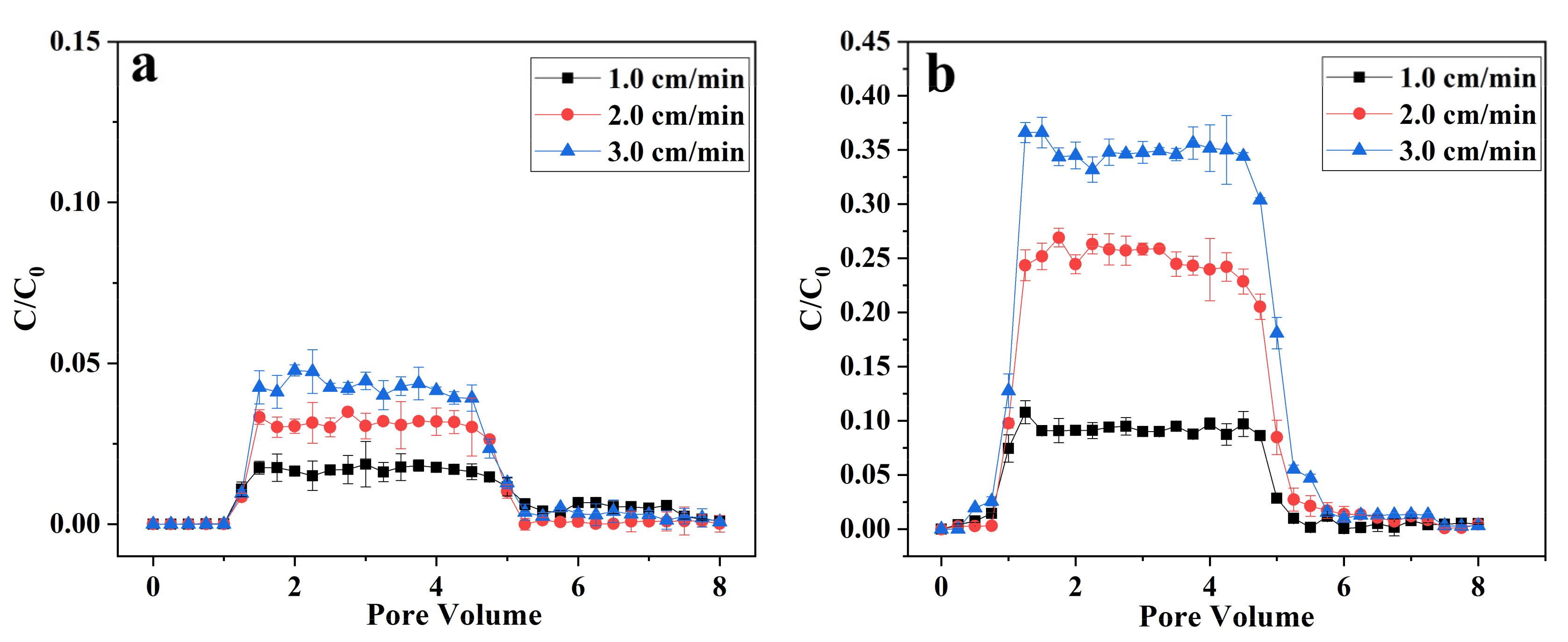
3.3. Transport of nZVI and B-nZVI in Quartz Sand Columns
3.4. Transport of nZVI and B-nZVI in Soil Columns
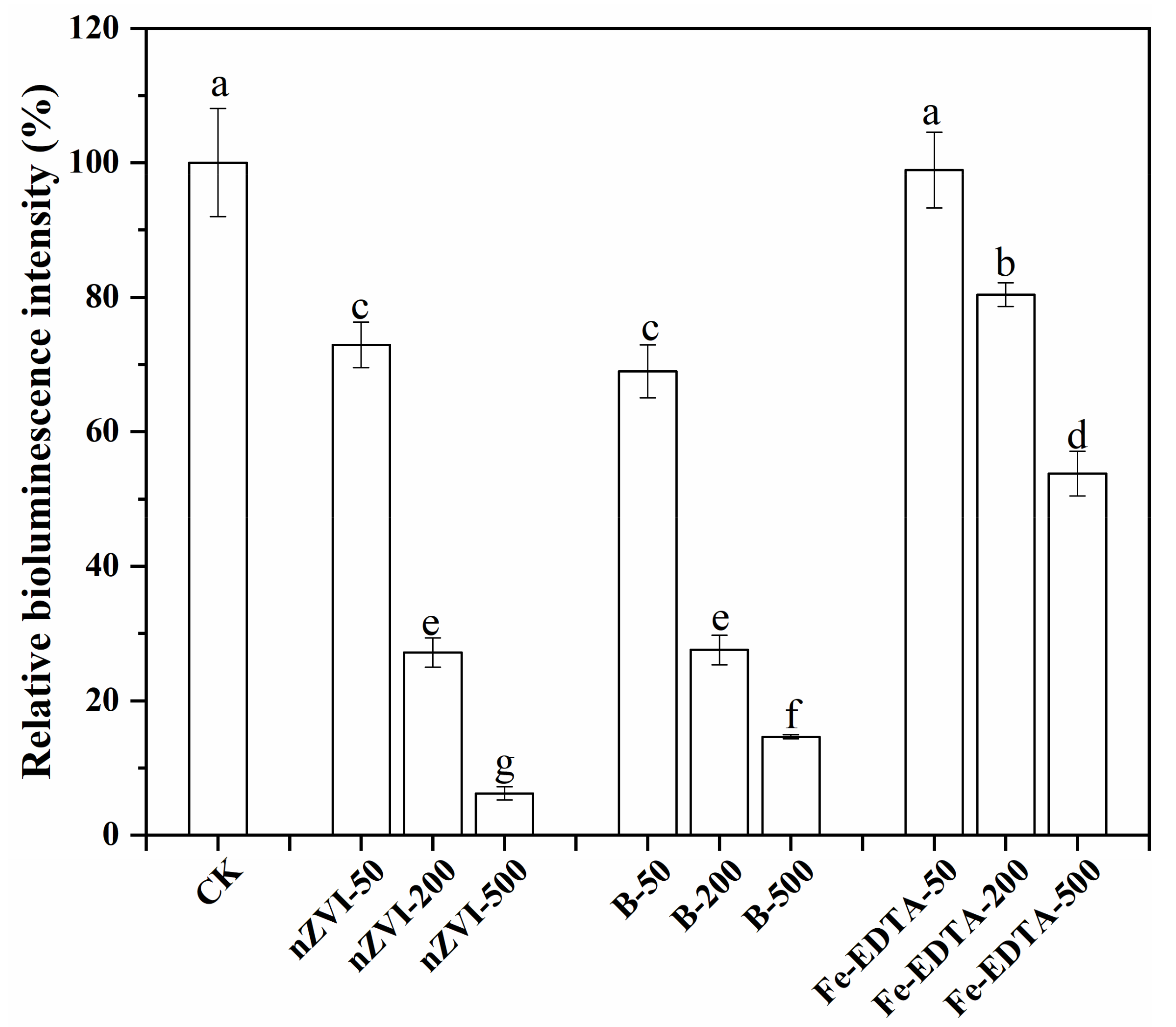
3.5. Luminous Bacteria Toxicity Test
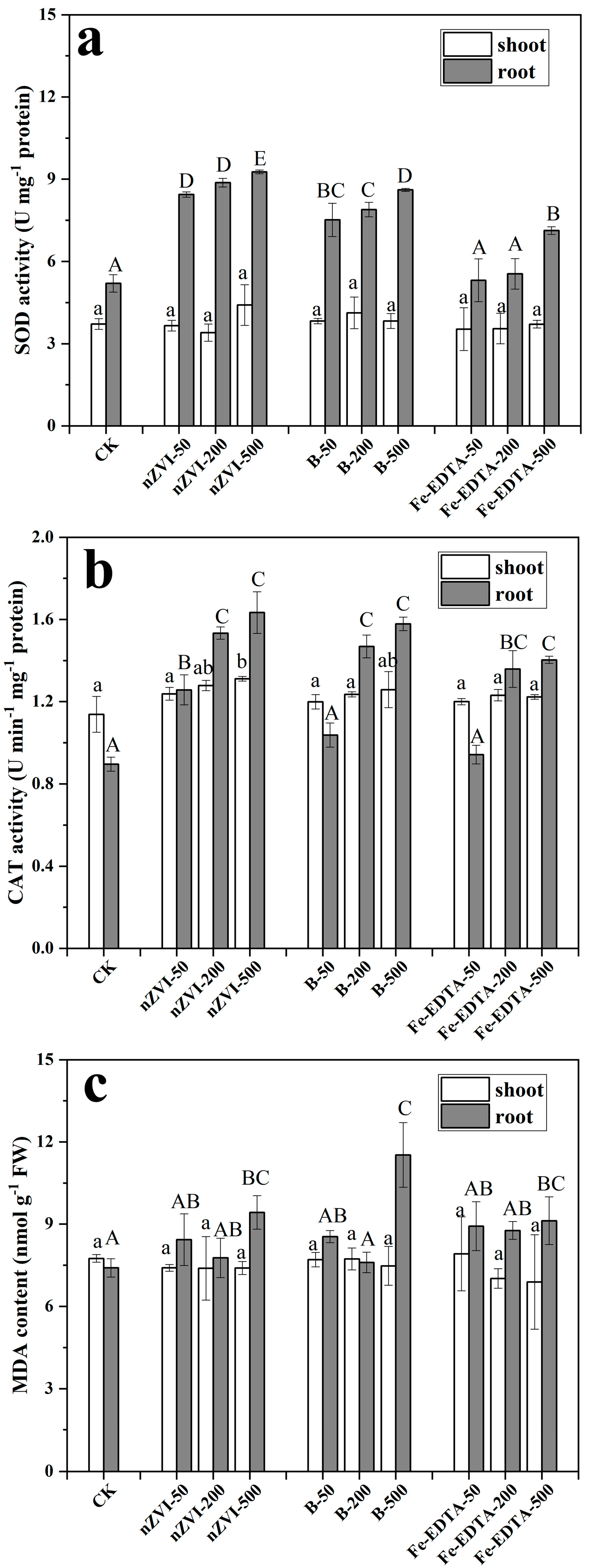
3.6. Ryegrass Hydroponic Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, D.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Huang, C.; Wan, J. Remediation of contaminated soils by enhanced nanoscale zero valent iron. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, E.; Bossa, N.; Wiesner, M.R.; Gunsch, C.K. A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI): Behavior, transport and impacts on microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Wei, E.; Gong, T.; Xian, Q. Facile synthesis of graphene nano zero-valent iron composites and their efficient removal of trichloronitromethane from drinking water. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Yang, W.; Bai, S. Application of nanoscale zero-valent iron in hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.-P.; Zhu, L. Remediation of soil contaminated with organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosco, T.; Papini, M.P.; Viggi, C.C.; Sethi, R. Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 77, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, C.; Ma, W.; Sun, Y. Modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in persulfate activation for organic pollution remediation: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34229–34247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, R.T.; Su, C.; Ford, R.G.; Paul, C.J. Chromium-Removal Processes during Groundwater Remediation by a Zerovalent Iron Permeable Reactive Barrier. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, B.; Kuiken, T.; Otto, M. Nanotechnology and in Situ Remediation: A Review of the Benefits and Potential Risks. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.-N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.-L. Removal of Chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2011, 45, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhan, W.; Du, D.; Zhang, T.C. Nanoscale zero-valent iron coupling with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for enhanced reduction/removal of aque-ous Cr(VI). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Jin, Z.; Li, T.; Qi, X. Preparation of chitosan-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4994–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, B.; Jin, Z.; Li, T.; Qi, X. Kinetics of hexavalent chromium removal from water by chitosan-Fe0 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Awad, M.; Al-Farraj, A.S.; Al-Turki, A.M. Stability and Dynamic Aggregation of Bare and Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles under Variable Solution Chemistry. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lo, I.M. Influence of calcium ions on the colloidal stability of surface-modified nano zero-valent iron in the absence or presence of humic acid. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, C.; Tan, X.; Lin, A.; Yang, W. Preparation of Activated Carbon Supported Bead String Structure Nano Zero Valent Iron in a Polyethylene Glycol-Aqueous Solution and Its Efficient Treatment of Cr(VI) Wastewater. Molecules 2019, 25, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Fang, Z.; Tsang, P.E.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Zhao, D. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by biochar-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavian, S.; An, H.; Chun, D.; Moon, J. Activated carbon impregnated by zero-valent iron nanoparticles (AC/nZVI) optimized for simultaneous adsorption and reduction of aqueous hexavalent chromium: Material characterizations and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bedia, J.; Li, H.; Ren, L.Y.; Naluswata, F.; Belver, C. Nanoscale zero-valent iron@mesoporous hydrated silica core-shell particles with enhanced dispersibility, transportability and degradation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Tang, X.; Xu, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Meng, J.; Liu, X. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for immobilization of cadmium, lead, and arsenic in farmland soils: Encapsulation mechanisms and indigenous microbial responses. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Han, L.; Shang, X.; Li, J.; Gu, M.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by attapulgite produced at different acid modification: Synthesis mechanism and the role of silicon on Cr(VI) removal. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, S.; Ayoko, G.; Frost, R.L.; Xi, Y. Degradation of simazine from aqueous solutions by diatomite-supported nanosized zero-valent iron composite materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, P.; Khataee, A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vahid, B. Synthesis of N-Doped Magnetic WO3–x@Mesoporous Carbon Using a Diatom Template and Plasma Modification: Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Activities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 13072–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, P.; Khataee, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Environmentally superior cleaning of diatom frustules using sono-Fenton process: Facile fabrication of nanoporous silica with homogeneous morphology and controlled size. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, W.; Meng, F.; Yang, Q.; Guo, N. Efficient Sequestration of Hexavalent Chromium by Graphene-Based Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Composite Coupled with Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckham, P.F.; Rossi, S. The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 82, 43–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yi, K.; Zhang, X.; Han, P.; Liu, W.; Tong, M. Modification of zero valent iron nanoparticles by sodium alginate and bentonite: Enhanced transport, effective hexavalent chromium removal and reduced bacterial toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, M.R.; Lowry, G.V.; Alvarez, P.; Dionysiou, D.; Biswas, P. Assessing the Risks of Manufactured Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4336–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.S.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Truskewycz, A.; Chopade, B.A.; Ball, A.S. Nanoparticles for environmental clean-up: A review of potential risks and emerging solutions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, M.; Puschenreiter, M.; Komárek, M. Effect of nano zero-valent iron application on As, Cd, Pb, and Zn availability in the rhizosphere of metal(loid) contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Yan, X.; Tsang, P.E.; Zhao, D. Higher concentrations of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil induced rice chlorosis due to inhibited active iron transportation. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccà, M.L.; Fajardo, C.; Martinez-Gomariz, M.; Costa, G.; Nande, M.; Martin, M. Molecular Stress Responses to Nano-Sized Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Particles in the Soil Bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccà, M.L.; Fajardo, C.; Costa, G.; Lobo, C.; Nande, M.; Martin, M. Integrating classical and molecular approaches to evaluate the impact of nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on soil organisms. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yang, Y.; Deng, R.; Gong, X.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Wang, G. Remediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil by Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: Role of Plant Root Exudates and Inner Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, R.; Scott, T. Nanoscale zero-valent iron: Future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, E.L.; Guerinot, M. Iron stress in plants. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, reviews1024.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Yang, S.; Xia, S. Potential effects of loading nano zero valent iron discharged on membrane fouling in an anoxic/oxic membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2017, 111, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-B.; Zhang, W.-X. Synthesizing Nanoscale Iron Particles for Rapid and Complete Dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Peng, D.; Hou, S.; Tang, B.; Wang, C.; Xu, H. Dynamic study of Cr (VI) removal performance and mechanism from water using multilayer material coated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, L.; Ho, K.-P.; Wong, K.-Y. Rapid Determination of Nanotoxicity Using Luminous Bacteria. Anal. Sci. 2010, 26, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.-Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Na, P. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions using Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: Characterization, kinetics and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50699–50707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirong, L.; Uddin, A.; Zhanxue, S. FT-IR and XRD analysis of natural Na-bentonite and Cu(II)-loaded Na-bentonite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-F. Reduction of hexachlorobenzene by nanoscale zero-valent iron: Kinetics, pH effect, and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Lou, Z.; Lou, L.; Xu, X. Mechanism and influence factors of chromium(VI) removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Tai, Y.-T. Reaction of decabrominated diphenyl ether by zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X. Enhancing Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetic core-shell structured NZVI@MOF derivative hybrids. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. A novel cellulose hydrogel coating with nanoscale Fe0 for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Oku, M.; Waseda, Y. Changes in the chemical state and composition of the clean surface of K2CrO4 and K2Cr2O7 due to air exposure and argon ion bombardment. Surf. Interface Anal. 1997, 25, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; You, T.; Guo, Y.; Yao, S.; Zang, S.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y. High dispersions of nano zero valent iron supported on biochar by one-step carbothermal synthesis and its application in chromate removal. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12428–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.-X. Stoichiometry of Cr(VI) Immobilization Using Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron (nZVI): A Study with High-Resolution X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (HR-XPS). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Xiao, G.; Qian, L.; Song, Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium from groundwater using sodium alginate dispersed nano zero-valent iron. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Klumpp, E.; Azzam, R.; Neukum, C. Transport and deposition of stabilized engineered silver nanoparticles in water saturated loamy sand and silty loam. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 535, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Moshe, T.; Dror, I.; Berkowitz, B. Transport of metal oxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginatto, C.; Cecchin, I.; Heineck, K.S.; Thomé, A.; Reddy, K.R. Use of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron for Remediation of Clayey Soil Contaminated with Hexavalent Chromium: Batch and Column Tests. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Awad, M.; Al-Farraj, A.S.; Al-Turki, A.M. Effect of Flow Rate and Particle Concentration on the Transport and Deposition of Bare and Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles in Sandy Soil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lo, I.M.C. Transport of Surface-Modified Nano Zero-Valent Iron (SM-NZVI) in Saturated Porous Media: Effects of Surface Stabilizer Type, Subsurface Geochemistry, and Contaminant Loading. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakub, E.; Agarry, S.E.; Omoruwou, F.; Owabor, C.N. Comparative study of the batch adsorption kinetics and mass transfer in phenol-sand and phenol-clay adsorption systems. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.M.; Martínez-Gaitero, R.; Gismera-Diez, S.; Puertas, F. PCE and BNS admixture adsorption in sands with different composition and particle size distribution. Mater. Constr. 2017, 67, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, C.; Ortiz, L.; Rodríguez-Membibre, M.; Nande, M.; Lobo, M.; Martin, M. Assessing the impact of zero-valent iron (ZVI) nanotechnology on soil microbial structure and functionality: A molecular approach. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Achouak, W.; Rose, J.; Roncato, M.-A.; Chanéac, C.; Waite, D.T.; Masion, A.; Woicik, J.C.; Wiesner, M.R.; Bottero, J.-Y. Relation between the Redox State of Iron-Based Nanoparticles and Their Cytotoxicity toward Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6730–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiu, Z.; Lowry, G.V.; Alvarez, P.J. Effect of natural organic matter on toxicity and reactivity of nano-scale zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Greden, K.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Gregory, K.B.; Lowry, G.V. Adsorbed Polymer and NOM Limits Adhesion and Toxicity of Nano Scale Zerovalent Iron to E. coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3462–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Fang, Z.; Yan, X.; Cheng, W.; Lin, K. Chemical stability and toxicity of nanoscale zero-valent iron in the remediation of chromium-contaminated watershed. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Peng, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Distinctive effects of TiO2 and CuO nanoparticles on soil microbes and their community structures in flooded paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 86, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Nelson, K.L.; Yoon, J.; Sedlak, D.L. Bactericidal Effect of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4927–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillissen, A.; Schärling, B.; Jaworska, M.; Bartling, A.; Rasche, K.; Schultze-Werninghaus, G. Oxidant scavenger function of ambroxol in vitro: A comparison with N-acetylcysteine. Res. Exp. Med. 1997, 196, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Yoon, H.; Singh, J.P.; Chae, K.H.; Rho, S.-C.; Hwang, D.S.; Chang, Y.-S. Uptake, Distribution, and Transformation of Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles in the Edible Plant Cucumis sativus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10057–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Xing, B. Root Uptake and Phytotoxicity of ZnO Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5580–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, I.; Mukherjee, A.; Mukherjee, A. In planta genotoxicity of nZVI: Influence of colloidal stability on uptake, DNA damage, oxidative stress and cell death. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, R.; Wan, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Qin, X.; Xue, W. Stabilized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron Mediated Cadmium Accumulation and Oxidative Damage of Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich Cultivated in Cadmium Contaminated Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11308–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, T.; Gopal, G.; Chatterjee, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Kundu, R. Differential growth and metabolic responses induced by nano-scale zero valent iron in germinating seeds and seedlings of Oryza sativa L. cv. Swarna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Tsang, P.E.; Zhao, D. Ageing decreases the phytotoxicity of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in soil cultivated with Oryza sativa. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, M.; Yao, M. Use of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in inactivating microbes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5243–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kou, X.; Pei, Z.; Xiao, J.Q.; Shan, X.; Xing, B. Physiological effects of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and pumpkin (Cucurbita mixta) plants. Nanotoxicology 2010, 5, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Adeel, M.; Guo, Z.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Ma, C.; Bai, T.; Hao, Y.; Rui, Y. Physiological impacts of zero valent iron, Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 nanoparticles in rice plants and their potential as Fe fertilizers. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Luo, Y.; Sun, J.; Shi, J. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Modified by Bentonite with Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency, Improved Mobility, and Reduced Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102580
Ye J, Luo Y, Sun J, Shi J. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Modified by Bentonite with Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency, Improved Mobility, and Reduced Toxicity. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102580
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jien, Yating Luo, Jiacong Sun, and Jiyan Shi. 2021. "Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Modified by Bentonite with Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency, Improved Mobility, and Reduced Toxicity" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102580
APA StyleYe, J., Luo, Y., Sun, J., & Shi, J. (2021). Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Modified by Bentonite with Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency, Improved Mobility, and Reduced Toxicity. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102580