Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4 Originating from the Synergistic Effect of ZnO and C Co-Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental procedure
2.1. Sample Synthesis
2.2. Structural–Morphological Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
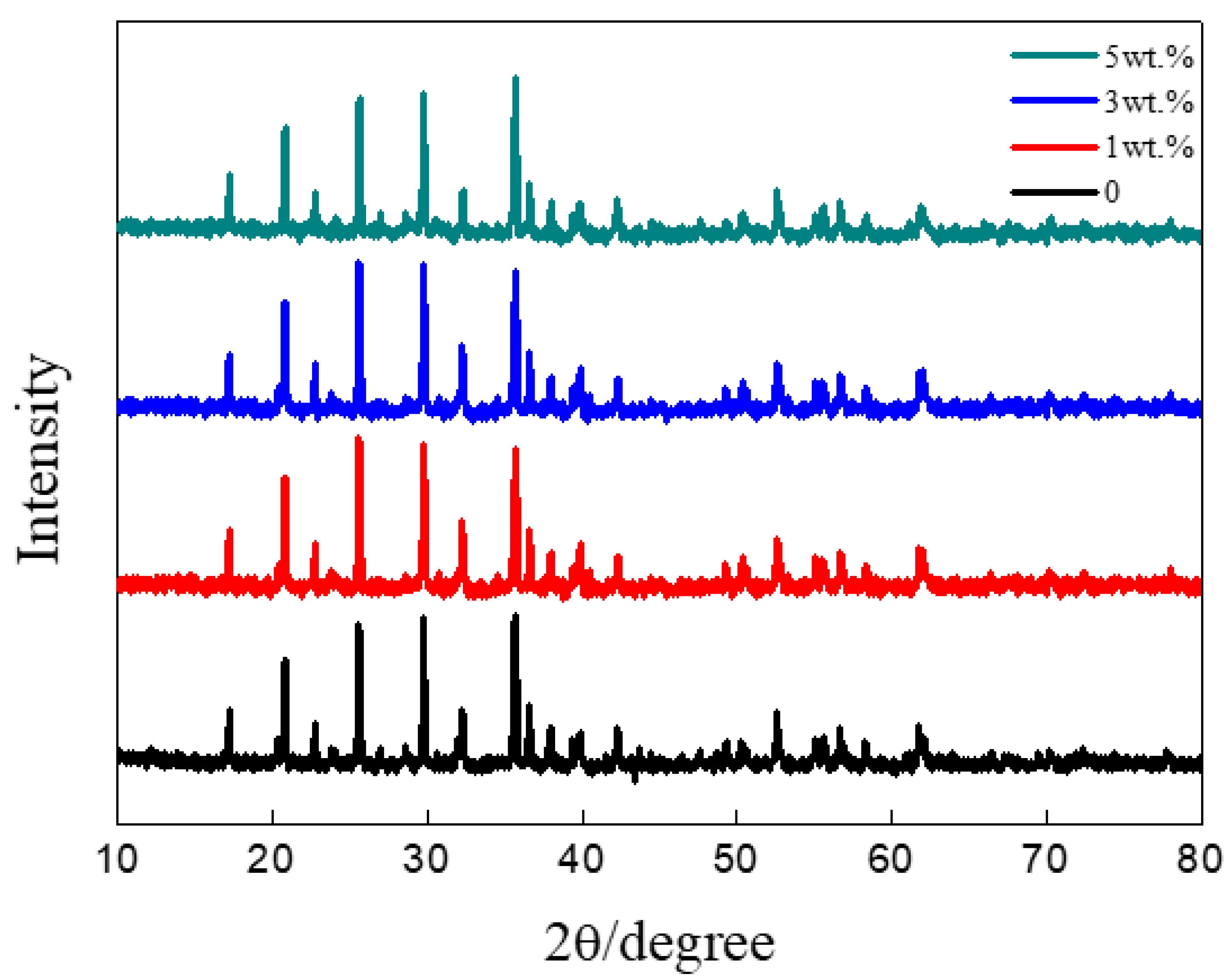
3.1. Structural Analysis
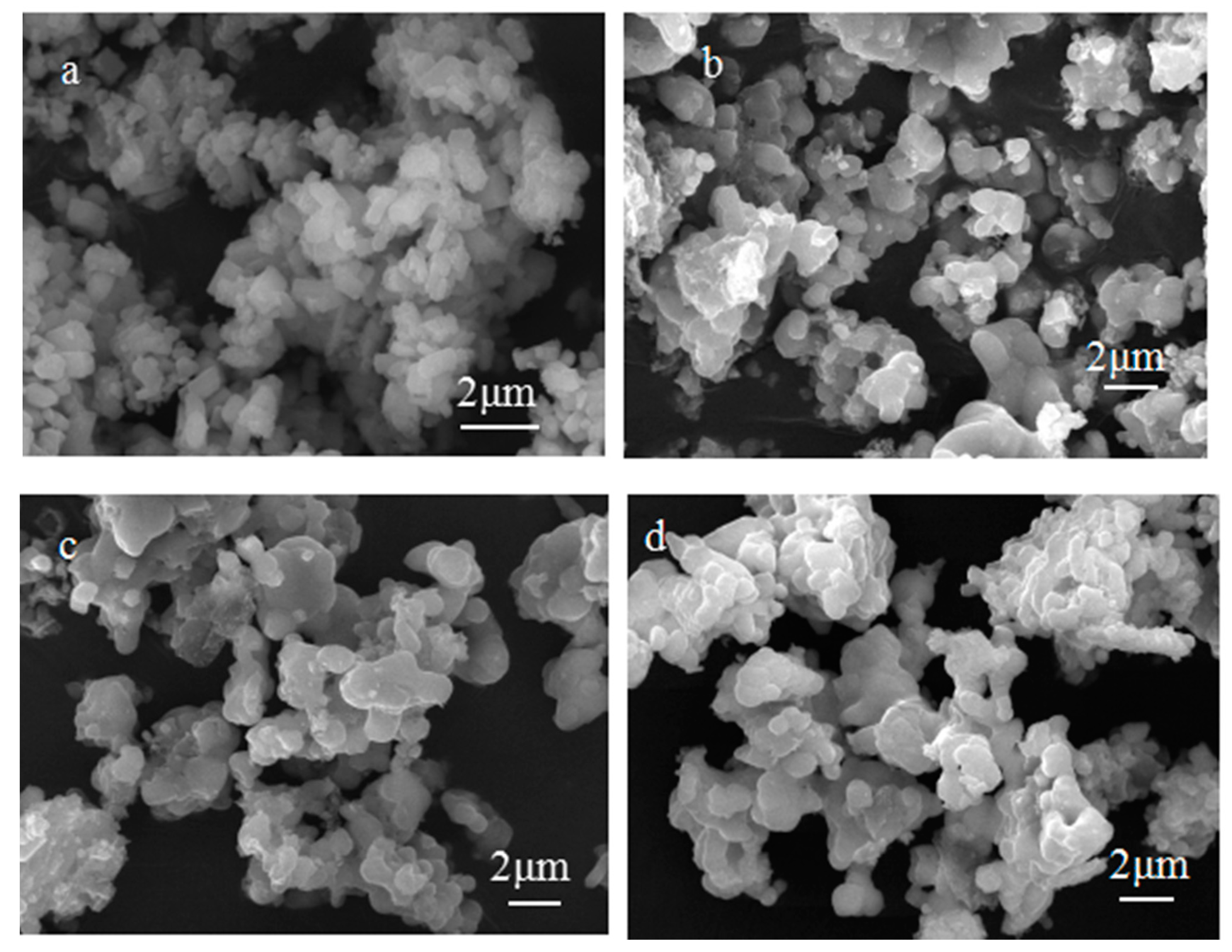
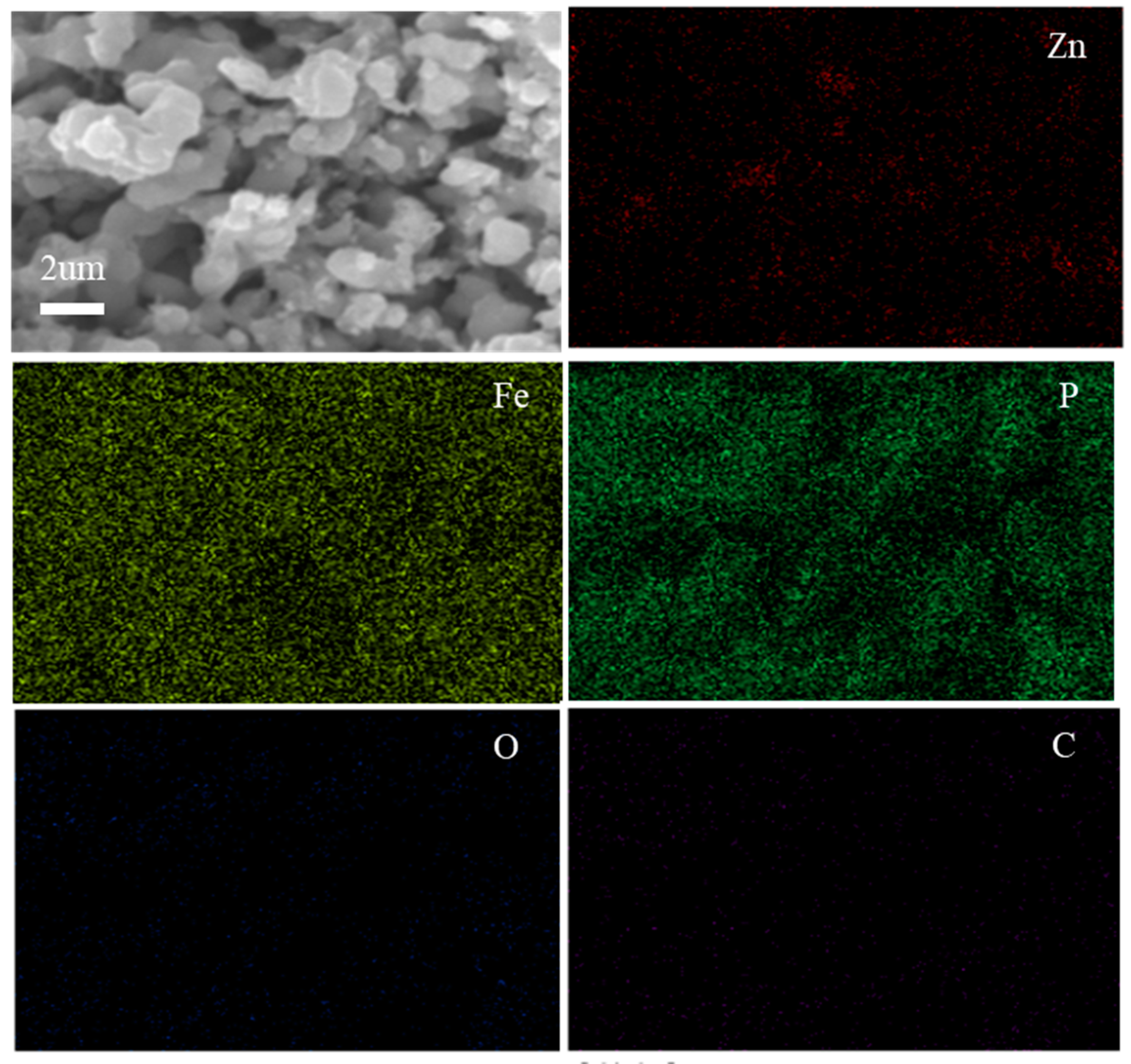
3.2. Morphological Analysis
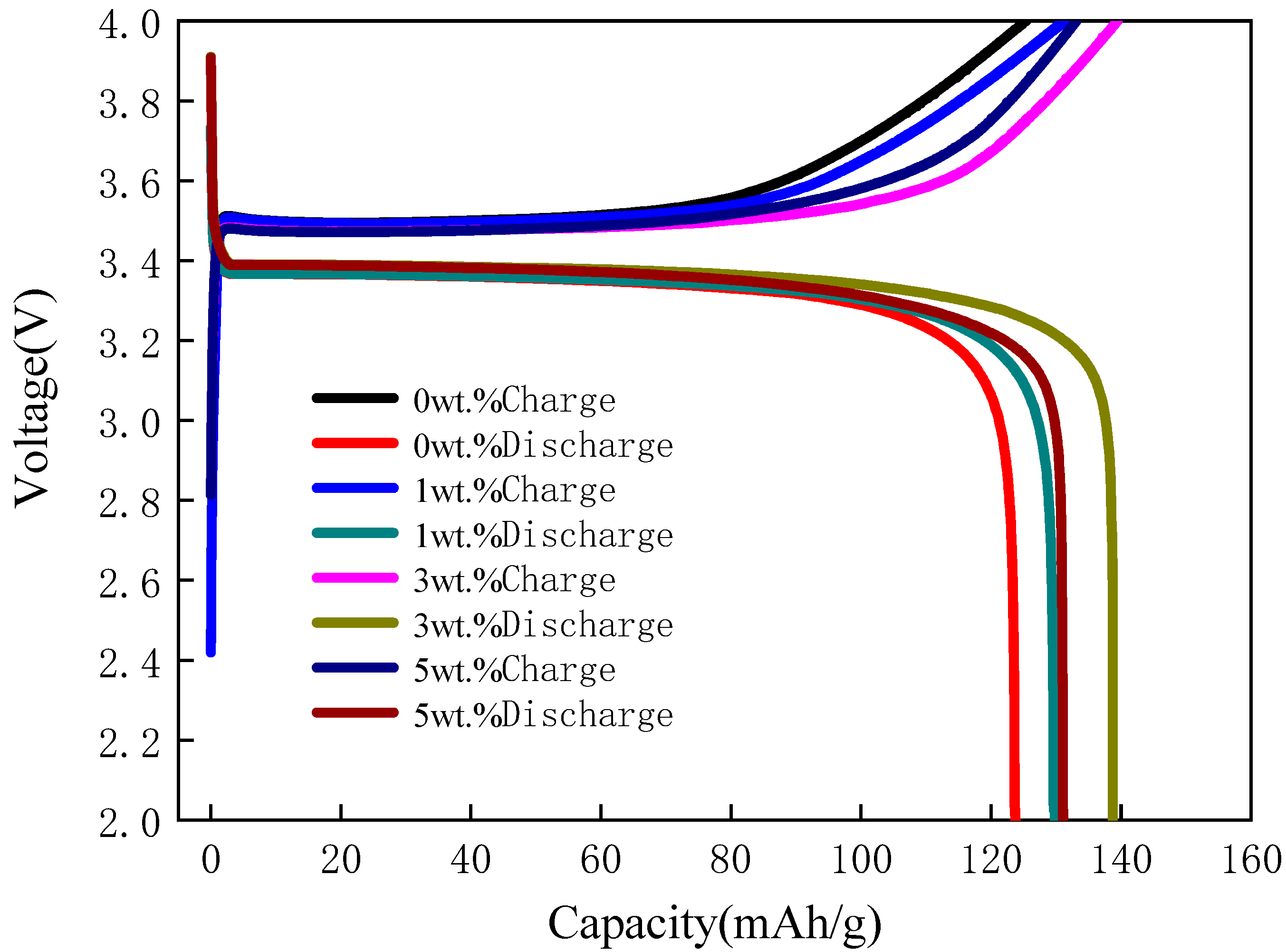
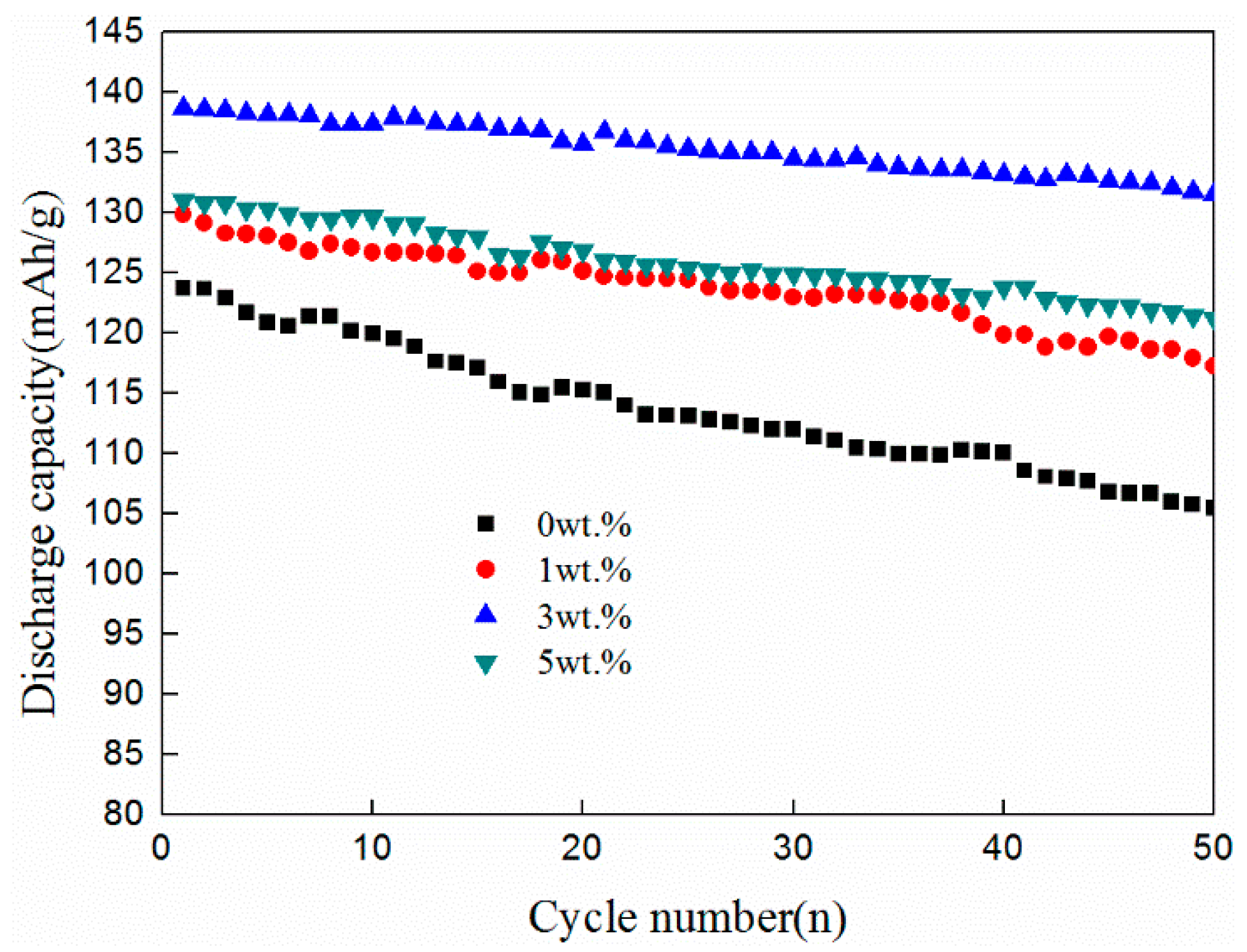
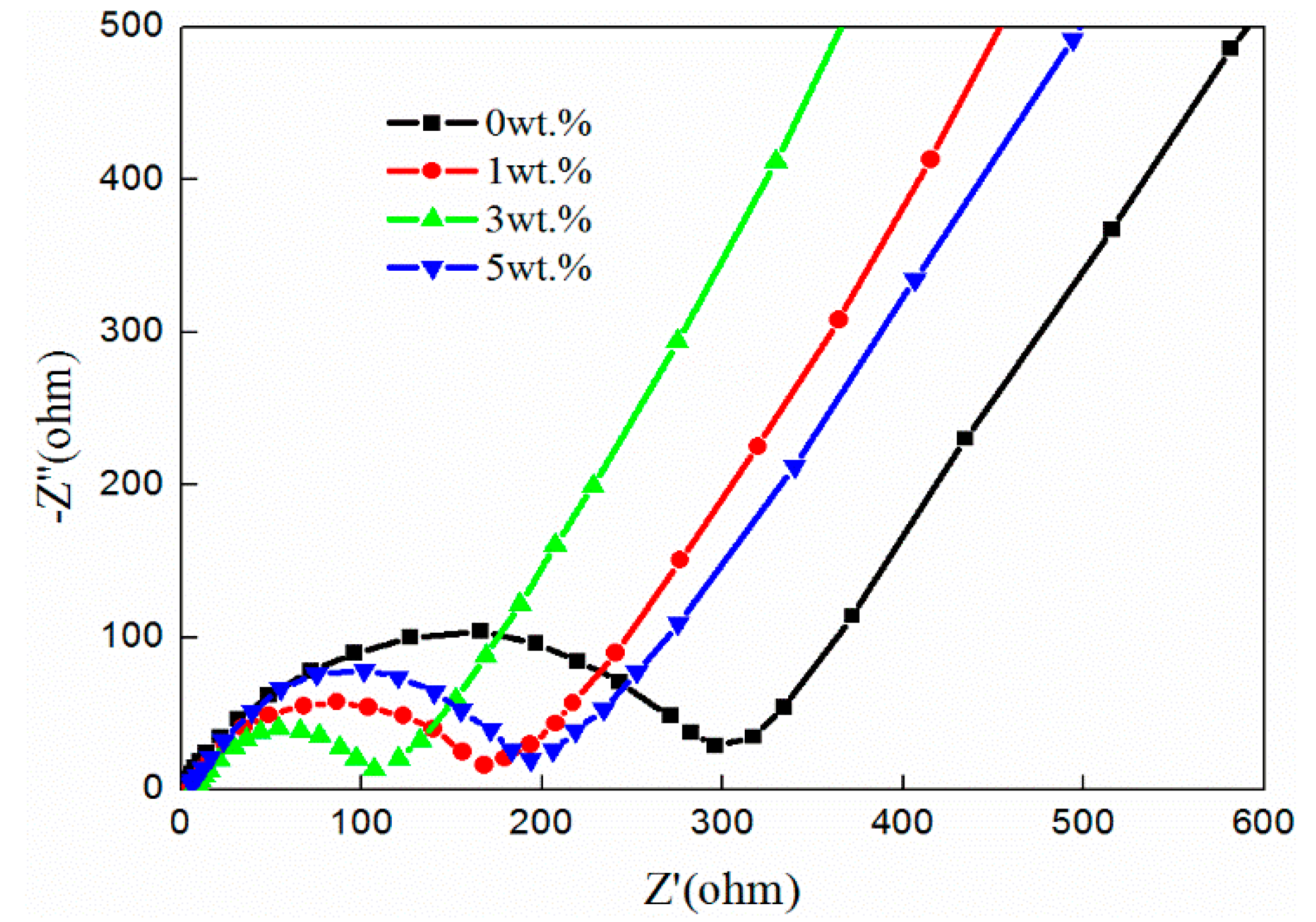
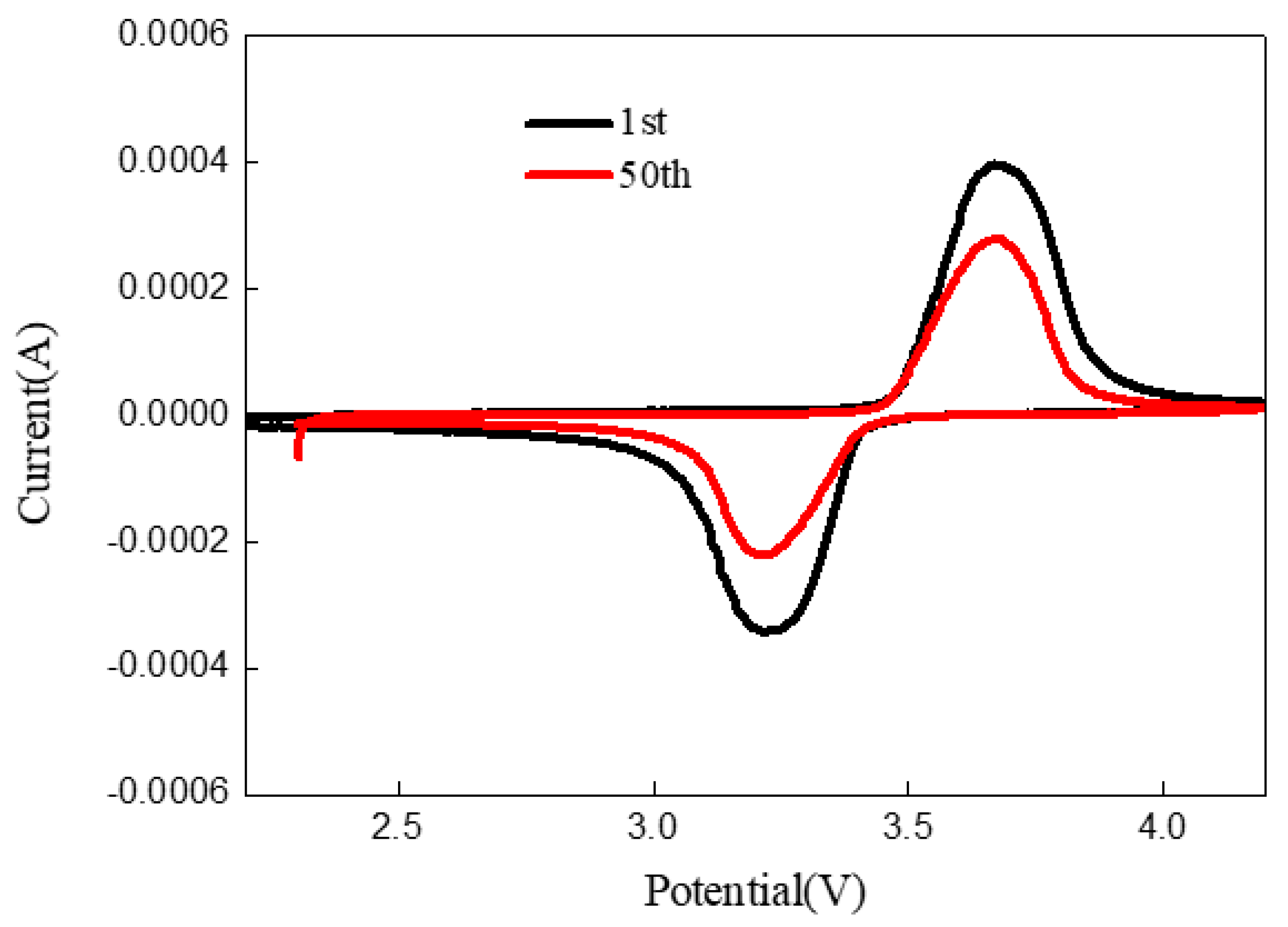
3.3. Electrochemical Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padhi, A.K.; Nanjundaswamy, K.S.; Goodenough, J.B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Nanosci, J. Research on High Rate Capabilities B-Substituted LiFePO4. Nanotechnology 2013, 13, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Lee, J.T.; Li, P.; Kang, B.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, G.R.; Park, J.H. Conformal Coating Strategy Comprising N-doped Carbon and Conventional Graphene for Achieving Ultrahigh Power and Cyclability of LiFePO4. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6756–6763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J. Structure and performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials: A review. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Song, G.Z. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous LiFePO4/C microsphere by spray drying assisted template method. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 794–797. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhu, M.Y.; An, Y.X.; Xia, L.L.; Wang, X.G.; Dai, B. Overwhelming microwave irradiation assisted synthesis of olivine-structured LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn, Co and Ni) for Li-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2014, 3, 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Xu, L.; Lai, Q.Y.; Ji, X.Y. A PEG assisted sol–gel synthesis of LiFePO4 as cathodic material for lithium ion cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 2007, 42, 883–891. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.X.; Yin, H.B.; Wang, H.B.; Nanosci, H.W.J. Synthesis and Characterization of LiFePO4/C Cathode Materials by Sol–Gel Method. Nanotechnology 2014, 14, 7060–7065. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Li, X.E.; Wang, F.F.; Han, Y. Spindle LiFePO4 particles as cathode of lithium-ion batteries synthesized by solvothermal method with glucose as auxiliary reductant. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.X.; Fiore, J.; Li, D.S.; Kinsinger, N.M.; Wang, Q.Q.; Masi, E.D.; Guo, J.C. Solvothermal Synthesis, Development, and Performance of LiFePO4. Nanostructures. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4659–4666. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Q.G. Enhanced electrochemical performance of Li–Co-BTC ternary metal–organic frameworks as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.Q.; Wan, W.; Tan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Chen, J.T.; Zhang, X.X. High power performance of nano-LiFePo4/c cathode material synthesized via lauric acid-assisted solid-state reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.R.; Deng, Z.H.; Suo, J.H. Synthesis and characterization of LiFePO4 and LiFePO4/C cathode material from lithium carboxylic acid and Fe3+. J. Power Sources 2012, 201, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Yi, G.R.; Lee, S.C. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of hybrid lithium iron phosphate nanoparticles for enhancing electrochemical performance. J. Solid State Chem. 2013, 197, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Krumeich, F.; Waser, O.; Pratsinis, S.E. Thermal annealing dynamics of carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanoparticles studied by in-situ analysis. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 242, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.P.; Shao, G.J.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.P. Effects of Nb-doped on the structure and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C composites. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 210, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H.P.; Fu, L.J. Cathode materials modified by surface coating for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3872–3883. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.X.; Wexler, D. Electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode material coated with ZrO2 nanolayer. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 185, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.S.; Benayad, A.; Park, M.S. Tailoring the electrochemical properties of composite electrodes by introducing surface redox-active oxide film: VO x-impregnated LiFePO4 electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 46, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.H.; Chang, C.C.; Su, C.Y. Effects of TiO2 coating on high-temperature cycle performance of LiFePO4-based lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, C.; Lu, J.; Chen, C. Solvothermal synthesis of lithium iron phosphate nanoplates. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9994–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Li, X.K.; Jiang, H.X.; Liu, J.L.; Feng, J. Electrochemical property of LiFePO4/C composite cathode with different carbon sources. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Sim, D.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Tan, H.; Wong, K.; Lim, T.M.; Yan, Q. One-pot synthesis of carbon-coated VO 2 (B) nanobelts for high-rate lithium storage. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gu, Y.J.; Kong, W.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Chen, Y.B. Effect of carbon coating on the crystal orientation and electrochemical performance of nanocrystalline LiFePO4. Solid State Ion. 2018, 327, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Bae, G.H.; Lee, S.M.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, J.K. Properties of lithium iron phosphate prepared by biomass-derived carbon coating for flexible lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 300, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ramar, V.; Balaya, P. Enhancing the electrochemical kinetics of high voltage olivine LiMnPO4 by isovalent co-doping. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 17240–17249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, G.; Vazquez-Arenas, J.; Ramos-Sánchez, G.; Bautista-Ramírez, M.; González, I. Improved performance of LiFePO4 cathode for Li-ion batteries through percolation studies. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 247, 451–459. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4 Originating from the Synergistic Effect of ZnO and C Co-Modification. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010012
Chen X, Li Y, Wang J. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4 Originating from the Synergistic Effect of ZnO and C Co-Modification. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaohua, Yong Li, and Juan Wang. 2021. "Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4 Originating from the Synergistic Effect of ZnO and C Co-Modification" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010012
APA StyleChen, X., Li, Y., & Wang, J. (2021). Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4 Originating from the Synergistic Effect of ZnO and C Co-Modification. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010012



