Multifunctional Fe3O4-Au Nanoparticles for the MRI Diagnosis and Potential Treatment of Liver Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis
2.2. Characterization of NPs
2.3. Cytotoxicity, Relaxivity and Biological Assessment
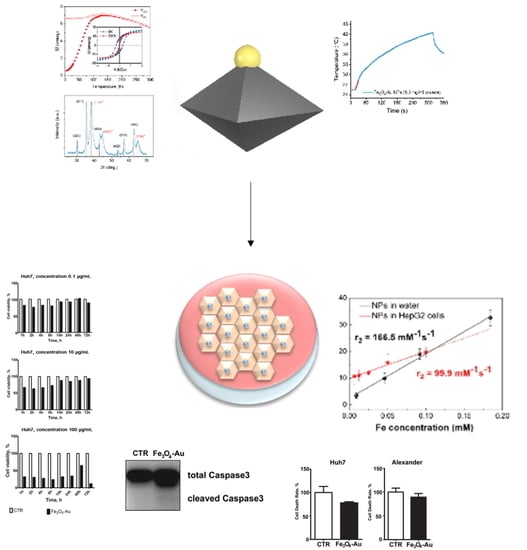
3. Results and Discussions
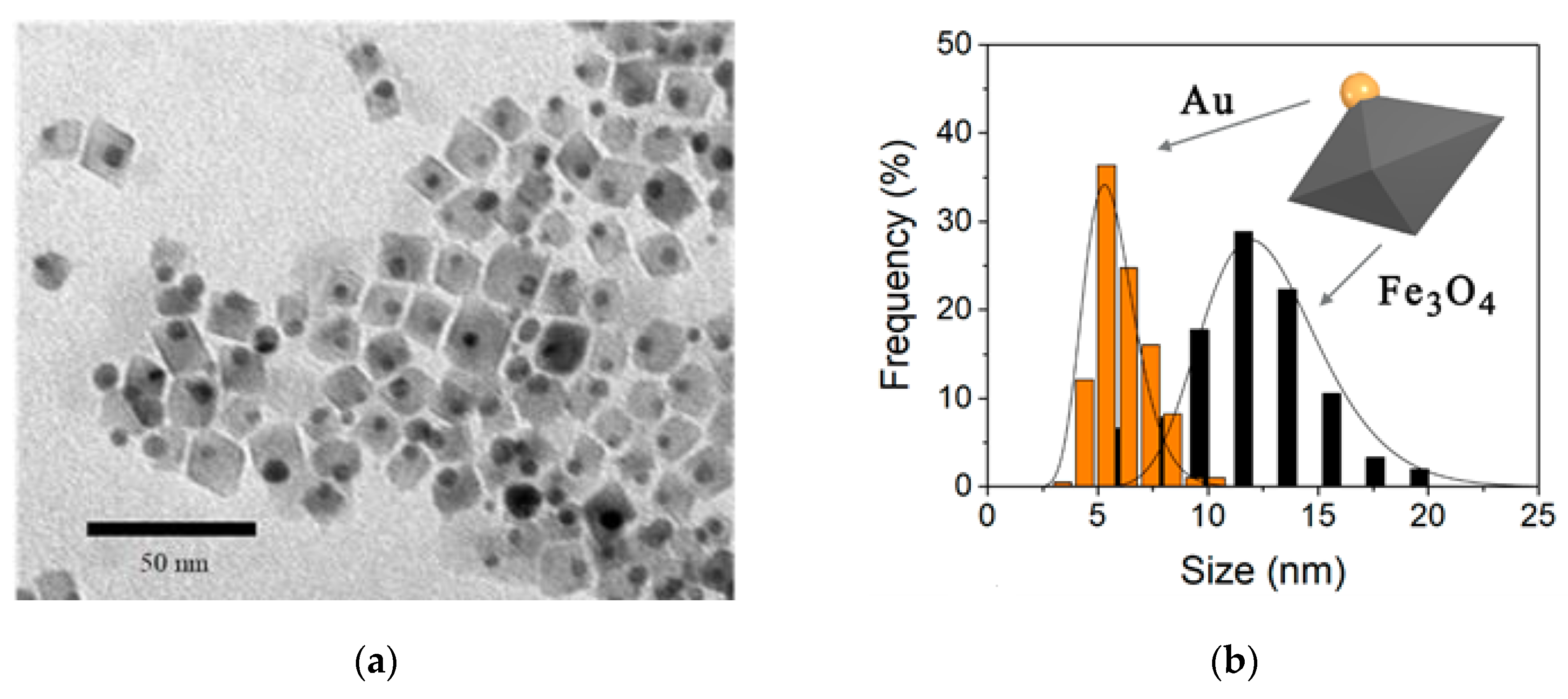
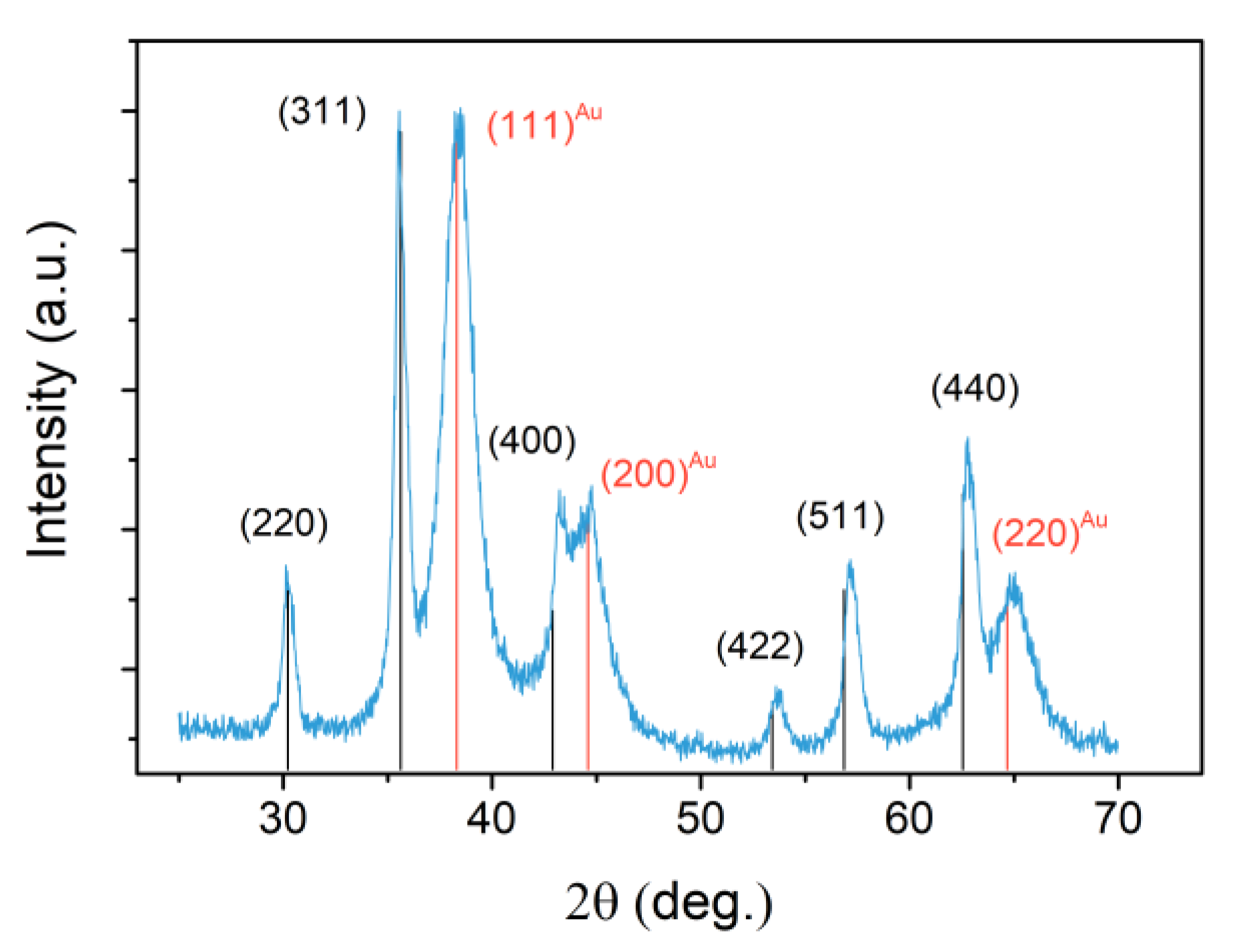
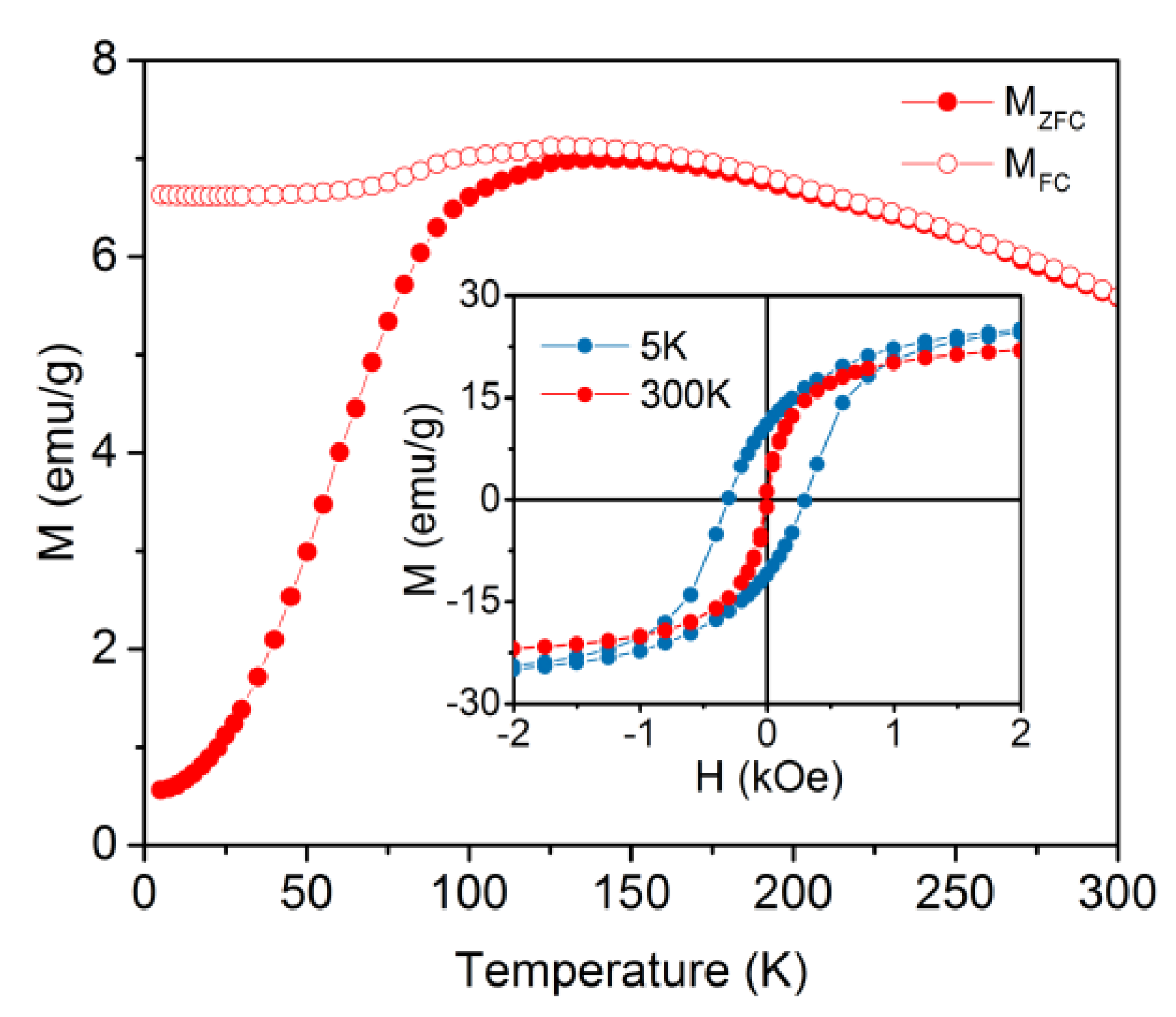
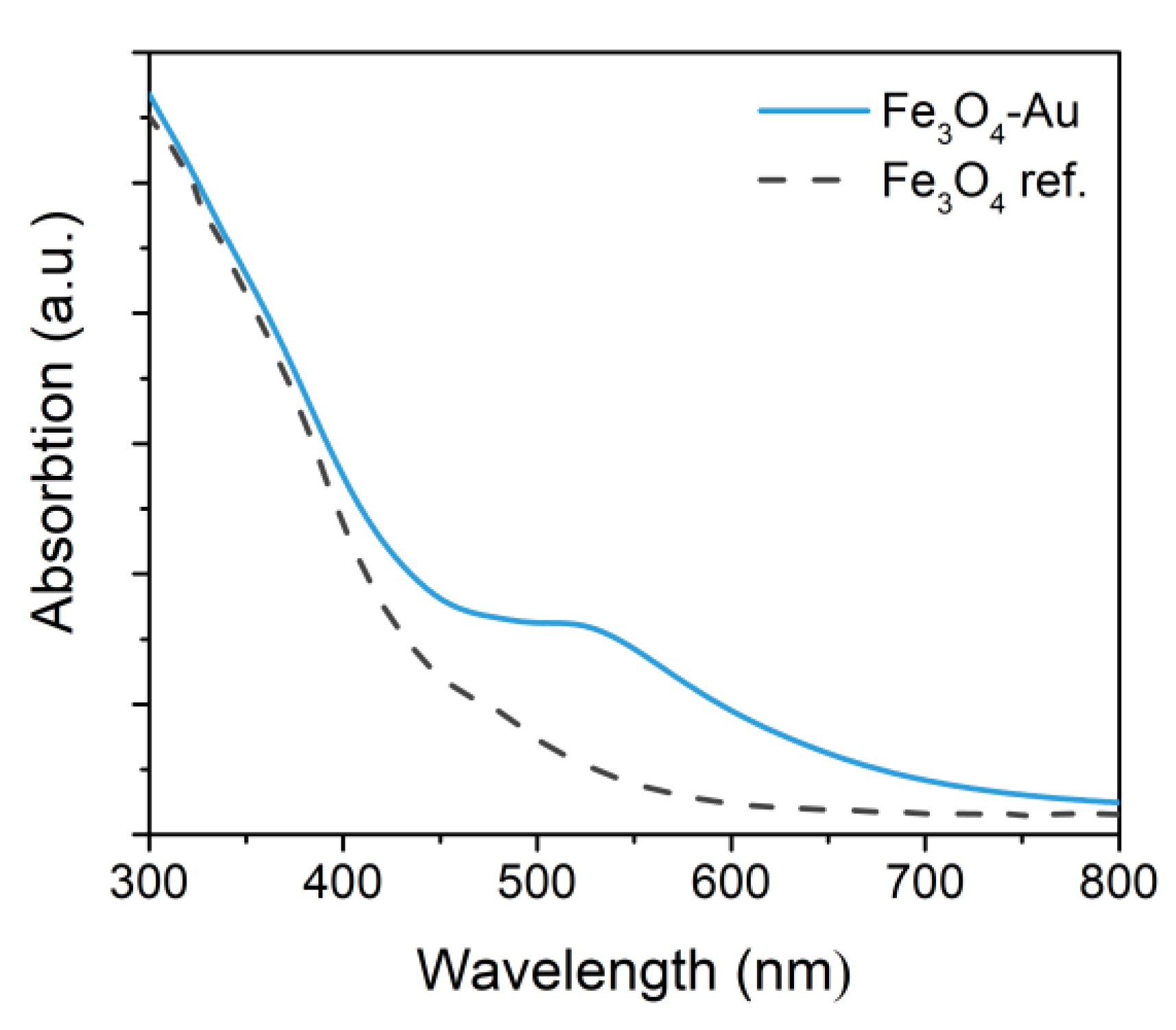
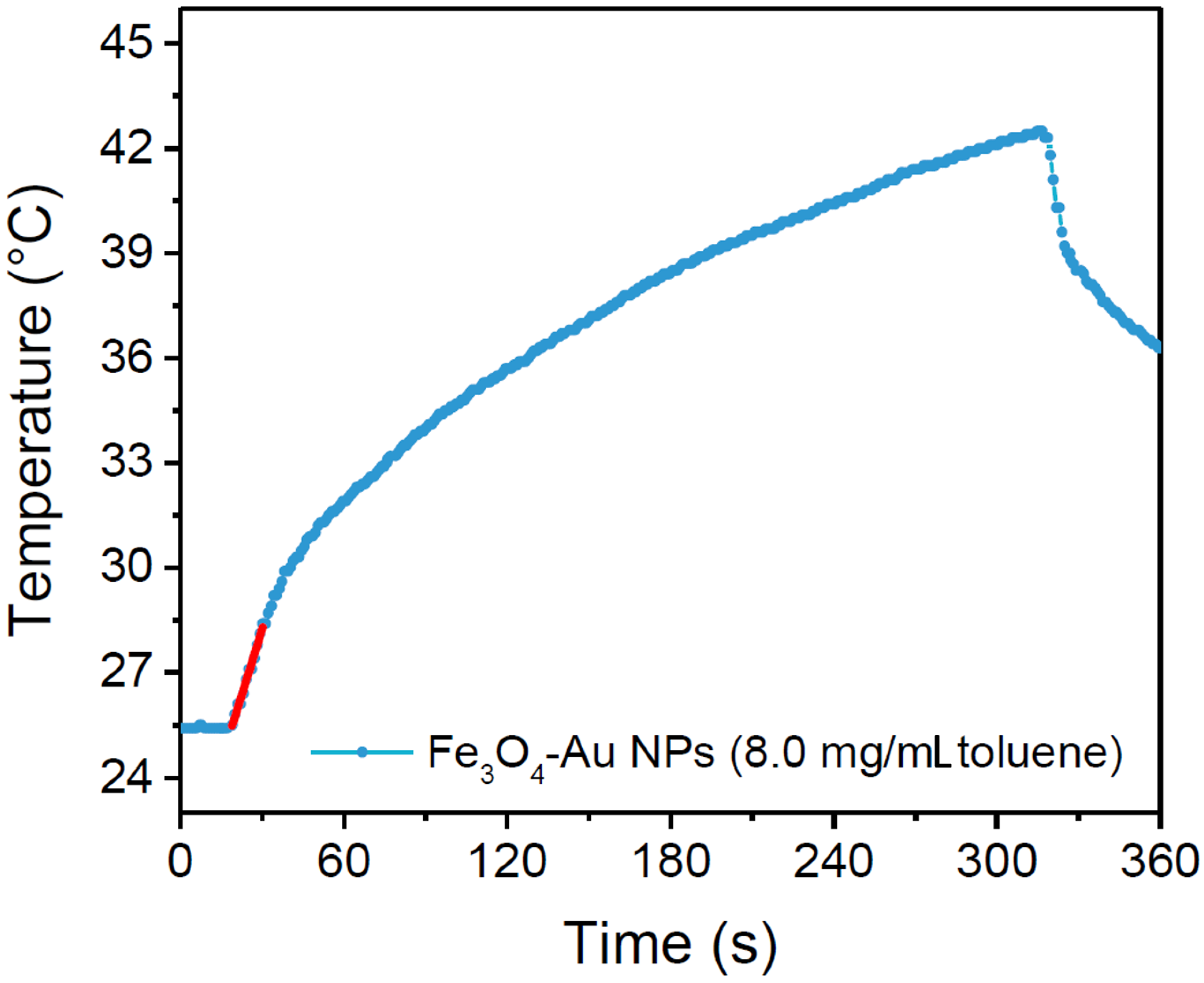
3.1. Physical Properties of the Nano-Heterostructures
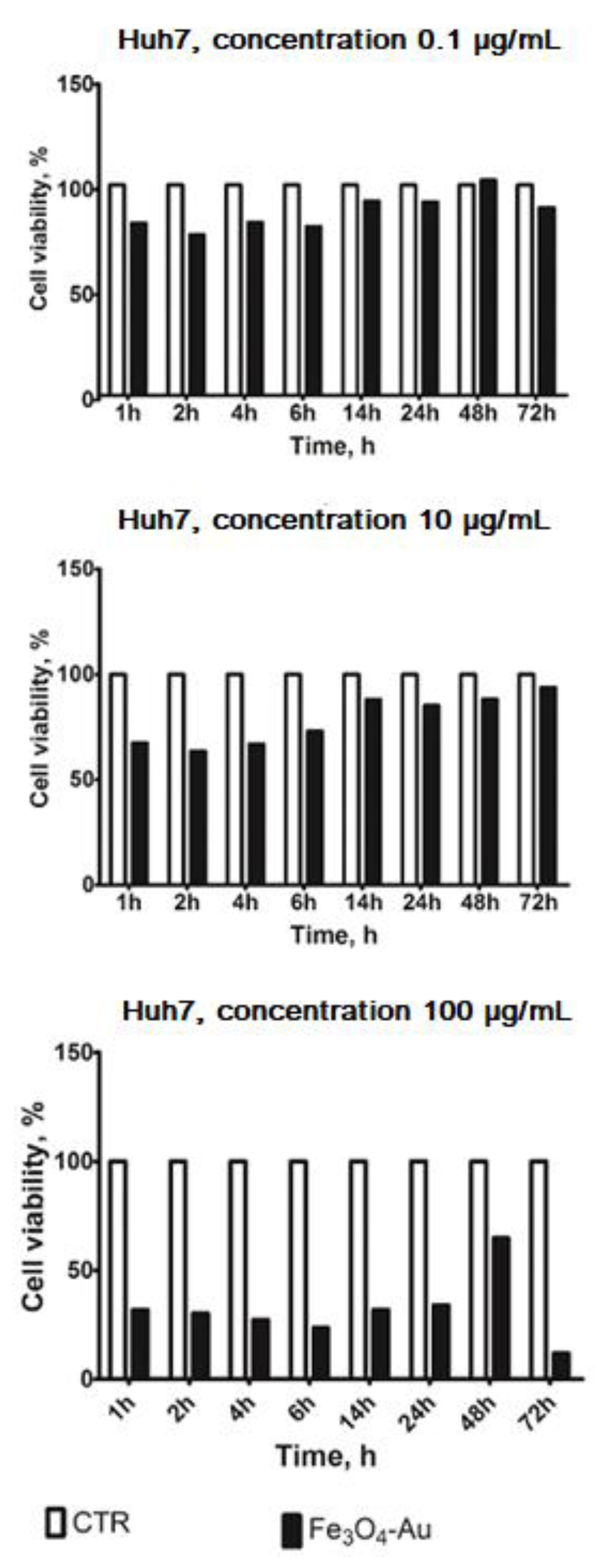
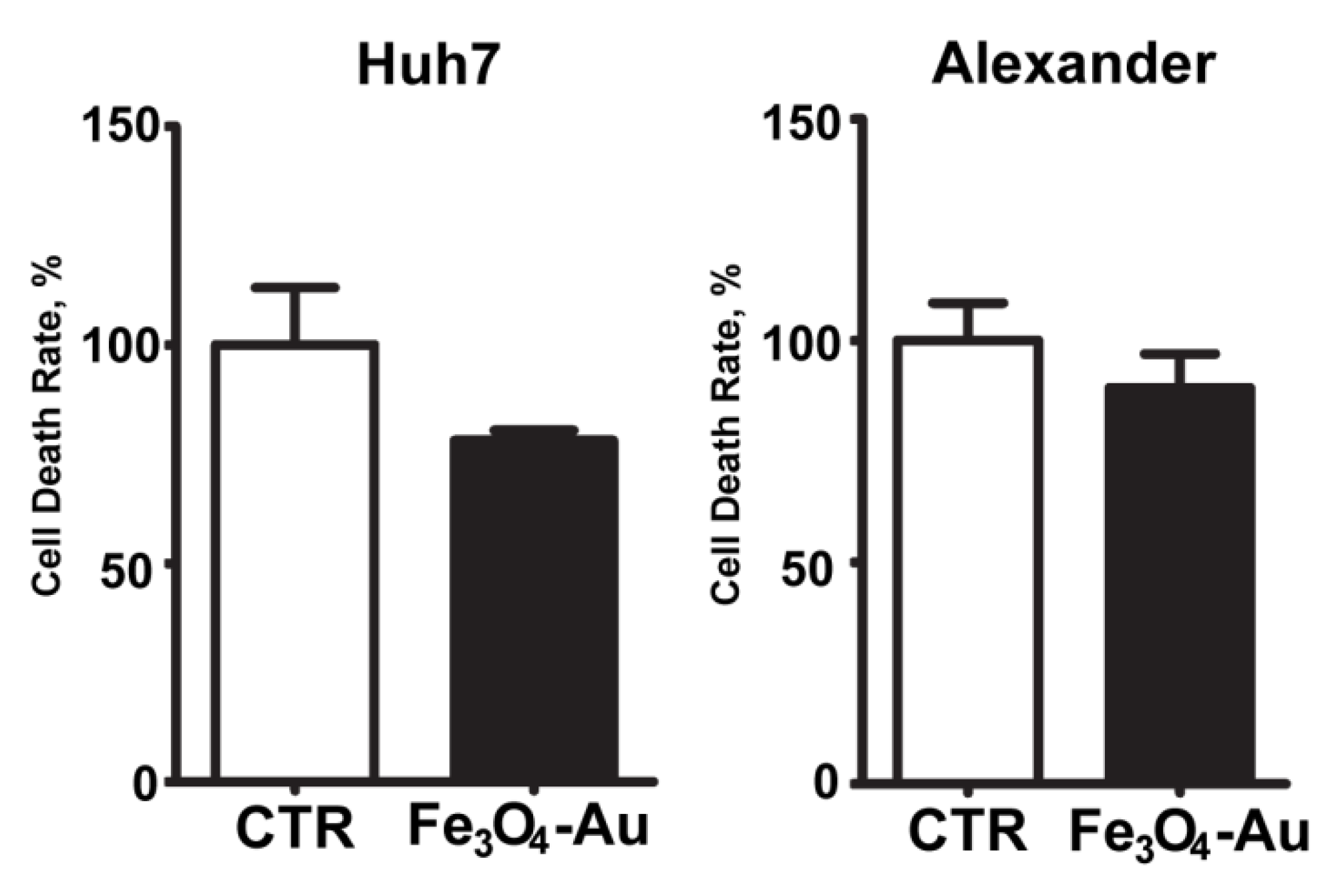
3.2. Cytotoxicity Tests
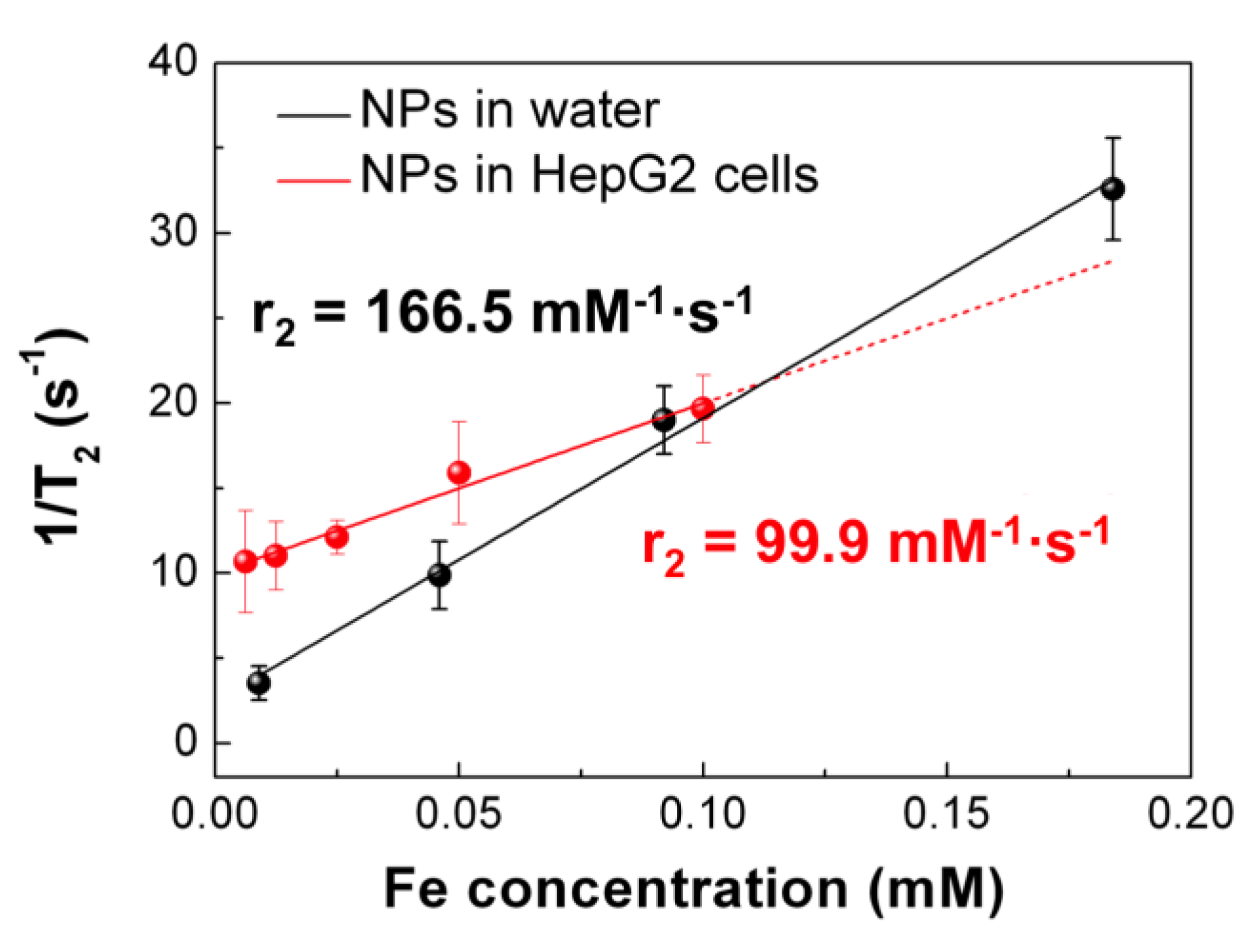
3.3. MRI Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Chen, M.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; White, R.L.; Sun, S. Dumbbell-like bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, N.A.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H.; Srinath, S.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Interparticle interactions in coupled Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 07B502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.C.F.; Xuan, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Chak, C.P.; Lee, S.F.; Ho, W.K.W.; Chung, B.C.T. Gold and iron oxide hybrid nanocomposite materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, S.; Sun, S.; You, X.Z. Dumbbell-like Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles: A new nanostructure for supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4890–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantechi, E.; Roca, A.G.; Sepúlveda, B.; Torruella, P.; Estradé, S.; Peiró, F.; Coy, E.; Jurga, S.; Bastús, N.G.; Nogués, J.; et al. Seeded Growth Synthesis of Au-Fe3O4 Heterostructured Nanocrystals: Rational Design and Mechanistic Insights. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4022–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, Y.; An, Y.; Kim, B.Y.S. Remodeling Tumor Vasculature to Enhance Delivery of Intermediate-Sized Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8689–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Starsich, F.; Dasargyri, A.; Wurnig, M.C.; Krumeich, F.; Boss, A.; Leroux, J.C.; Pratsinis, S.E. Photothermal killing of cancer cells by the controlled plasmonic coupling of silica-coated Au/Fe2O3 nanoaggregates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Bugnet, M.; Radtke, G.; Neveu, S.; Botton, G.A.; Wilhelm, C.; Abou-Hassan, A. Can magneto-plasmonic nanohybrids efficiently combine photothermia with magnetic hyperthermia? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18872–18877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y. Bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles for protein separation. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, S. Dumbbell-like Au-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Target-Specific Platin Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4216–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, S. Synthesis and Application of Au-Fe3O4 Dumbbell-Like Nanoparticles; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128141359. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Huh, Y.M.; Jun, Y.W.; Seo, J.W.; Jang, J.T.; Song, H.T.; Kim, S.; Cho, E.J.; Yoon, H.G.; Suh, J.S.; et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, B.H.; Singh, G.; Hak, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Augestad, I.L.; Peddis, D.; Sandvig, I.; Sandvig, A.; Glomm, W.R. L -DOPA-Coated Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles as Dual MRI Contrast Agents and Drug-Delivery Vehicles. Small 2016, 12, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haun, J.B.; Yoon, T.J.; Lee, H.; Weissleder, R. Magnetic nanoparticle biosensors. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariti, A.; Desai, P.; Maddirala, S.K.Y.; Ercal, N.; Katti, K.V.; Liang, X.; Nath, M. Superparamagnetic Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles: One-pot synthesis, biofunctionalization and toxicity evaluation. Mater. Res. Express 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Gu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Lactoferrin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a specific MRI contrast agent for detection of brain glioma in vivo. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchapakesan, B.; Wickstrom, E. Nanotechnology for Sensing, Imaging, and Treating Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 16, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socoliuc, V.; Peddis, D.; Petrenko, V.I.; Avdeev, M.V.; Susan-resiga, D.; Szabó, T.; Turcu, R.; Tombácz, E.; Vékás, L. Magnetic Nanoparticle Systems for Nanomedicine—A Materials Science Perspective. Magetochemistry 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, S.I.; Huo, F.; Lee, J.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Three-layer composite magnetic nanoparticle probes for DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15362–15363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Dutz, S.; Häfeli, U.O.; Mahmoudi, M. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: Focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Beyond traditional hyperthermia: In vivo cancer treatment with magnetic-responsive mesoporous silica nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.M. The application of magnetic nanoparticles in the treatment and monitoring of cancer and infectious diseases. Biosci. Horiz. Int. J. Stud. Res. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Andujar, C.; Teran, F.J.; Ortega, D. Current Outlook and Perspectives on Nanoparticle-Mediated Magnetic Hyperthermia. In Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 197–245. ISBN 9780081019252. [Google Scholar]
- Martinkova, P.; Brtnicky, M.; Kynicky, J.; Pohanka, M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Innovative Tool in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchapakesan, B.; Book-Newell, B.; Sethu, P.; Rao, M.; Irudayaraj, J. Gold nanoprobes for theranostics. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1787–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Soni, R.K.; Ghai, D.P. Pulsed photoacoustic and photothermal response of gold nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 35704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, D.; Dong, S.; Meng, X.; Lu, Q.; Meng, L.; Ye, J. Gold nanoparticles as computerized tomography (CT) contrast agents. Rsc. Adv. 2012, 2, 12515–12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, M.M.; Doiron, A.L. Gold Nanoparticles as X-Ray, CT, and Multimodal Imaging Contrast Agents: Formulation, Targeting, and Methodology. J. Nanomater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, M.E.; Del Carlo, M.; Hussein, H.A.; Salah, T.A.; El-Deeb, A.H.; Emara, M.M.; Pezzoni, G.; Compagnone, D. Development of gold nanoparticles biosensor for ultrasensitive diagnosis of foot and mouth disease virus. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Gold nanoparticle based biosensors. New Dev. Gold Nanomater. Res. 2016, 43, 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.T. Using gold nanoparticles for catalysis. Nano Today 2007, 2, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisel, R.; Weststrate, K.J.; Gluhoi, A.; Nieuwenhuys, B.E. Catalysis by gold nanoparticles. Gold Bull. 2002, 35, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Mammeri, F.; Ammar, S. Iron oxide and gold based magneto-plasmonic nanostructures for medical applications: A review. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.T.; Kim, J.; Tufa, L.T.; Oh, S.; Kwon, J.; Lee, J. Magnetoplasmonic Nanomaterials for Biosensing/Imaging and in Vitro/in Vivo Biousability. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.F. Using nanoparticles in medicine for liver cancer imaging. Oman Med. J. 2017, 32, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Alimardani, V.; Roudbali, P.L.; Ghasemi, Y.; Kaviani, E. Gold nanoparticles application in liver cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 25, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, M.V.; Naumenko, V.A.; Spasova, M.; Garanina, A.S.; Abakumov, M.A.; Blokhina, A.D.; Melnikov, P.A.; Prelovskaya, A.O.; Heidelmann, M.; Li, Z.A.; et al. Magnetite-Gold nanohybrids as ideal all-in-one platforms for theranostics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, M.V.; Nalench, Y.A.; Myrovali, E.; Garanina, A.S.; Grebennikov, I.S.; Gifer, P.K.; Abakumov, M.A.; Spasova, M.; Angelakeris, M.; Savchenko, A.G.; et al. Size-selected Fe3O4-Au hybrid nanoparticles for improved magnetism-based theranostics. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2684–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levada, K.; Pshenichnikov, S.; Omelyanchik, A.; Rodionova, V.; Nikitin, A.; Savchenko, A.; Schetinin, I.; Zhukov, D.; Abakumov, M.; Majouga, A.; et al. Progressive lysosomal membrane permeabilization induced by iron oxide nanoparticles drives hepatic cell autophagy and apoptosis. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.M.; Thorat, N.D.; Shete, P.B.; Bedge, P.A.; Gavde, S.; Joshi, M.G.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Bohara, R.A. Comprehensive cytotoxicity studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 13, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Dutz, S. Magnetic particle hyperthermia-biophysical limitations of a visionary tumour therapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Jovanović, S.; Vukomanović, M.; Spreitzer, M.; Peddis, D. Zn-doped cobalt ferrite: Tuning the interactions by chemical composition. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 796, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro-Cruces, J.; Roca, A.G.; López-Ortega, A.; Fantechi, E.; Del-Pozo-Bueno, D.; Estradé, S.; Peiró, F.; Sepúlveda, B.; Pineider, F.; Sangregorio, C.; et al. Precise Size Control of the Growth of Fe3O4 Nanocubes over a Wide Size Range Using a Rationally Designed One-Pot Synthesis. ACS Nano 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, A.; Lottini, E.; Fernández, C.D.J.; Sangregorio, C. Exploring the Magnetic Properties of Cobalt-Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Development of a Rare-Earth-Free Permanent Magnet. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4048–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Chiang, R.-K.; Wang, J.-S.; Wang, S.-L. Synthesis and magnetic properties of octahedral magnetite nanoparticles in 20–110 nm range. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.W.; Choksi, T.; Milligan, C.; Majumdar, P.; Manto, M.; Cui, Y.; Sang, X.; Unocic, R.R.; Zemlyanov, D.; Wang, C.; et al. A Discovery of Strong Metal-Support Bonding in Nanoengineered Au-Fe3O4 Dumbbell-like Nanoparticles by in Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 4576–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalench, Y.A.; Shchetinin, I.V.; Skorikov, A.S.; Mogilnikov, P.S.; Farle, M.; Savchenko, A.G.; Majouga, A.G.; Abakumov, M.A.; Wiedwald, U. Unravelling the nucleation, growth, and faceting of magnetite-gold nanohybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3886–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.M. Experimental Magnetochemistry: Nonmetallic Magnetic Materials; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1967; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Salvador, M.; D’Orazio, F.; Mameli, V.; Cannas, C.; Fiorani, D.; Musinu, A.; Rivas, M.; Rodionova, V.; Varvaro, G.; et al. Magnetocrystalline and Surface Anisotropy in CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Peddis, D.; Cobianchi, M.; Lascialfari, A.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Omelyanchik, A.; Rodionova, V.; Fiorani, D.; Mameli, V. Magnetic Interactions Versus Magnetic Anisotropy in Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2019, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, F. The Verwey transition—A topical review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddis, D.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Orrù, F.; Fiorani, D.; Laureti, S.; Rinaldi, D.; Muscas, G.; Concas, G.; et al. Beyond the Effect of Particle Size: Influence of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticle Arrangements on Magnetic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Efremova, M.; Myslitskaya, N.; Zybin, A.; Carey, B.J.; Sickel, J.; Kohl, H.; Bratschitsch, R.; Abakumov, M.; Majouga, A.; et al. Magnetic and Optical Properties of Gold-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 4987–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantechi, E.; Innocenti, C.; Bertoni, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Pineider, F. Modulation of the magnetic properties of gold-spinel ferrite heterostructured nanocrystals. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, L.; Innocenti, C.; Kalaivani, T.; Awwad, A.; Duque, M.D.M.S.; Guari, Y.; Larionova, J.; Gueírin, C.; Montero, J.L.G.; Barragan-Montero, V.; et al. Water-dispersible sugar-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. An evaluation of their relaxometric and magnetic hyperthermia properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10459–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, P.; Di Corato, R.; Lartigue, L.; Wilhelm, C.; Espinosa, A.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Gazeau, F.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. Water-soluble iron oxide nanocubes with high values of specific absorption rate for cancer cell hyperthermia treatment. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3080–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolková, B.; Lunova, M.; Lynnyk, A.; Uzhytchak, M.; Churpita, O.; Jirsa, M.; Kubinová, Š.; Lunov, O.; Dejneka, A. Non-thermal plasma, as a new physicochemical source, to induce redox imbalance and subsequent cell death in liver cancer cell lines. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basini, M.; Guerrini, A.; Cobianchi, M.; Orsini, F.; Bettega, D.; Avolio, M.; Innocenti, C.; Sangregorio, C.; Lascialfari, A.; Arosio, P. Tailoring the magnetic core of organic-coated iron oxides nanoparticles to influence their contrast efficiency for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xie, J.; Ho, D.; Wang, C.; Kohler, N.; Walsh, E.G.; Morgan, J.R.; Chin, Y.E.; Sun, S. Au-Fe3O4 dumbbell nanoparticles as dual-functional. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglio, D.; Benetti, F.; Minati, L.; Jovicich, J.; Valentini, A.; Speranza, G.; Migliaresi, C. Theranostic gold-magnetite hybrid nanoparticles for MRI-guided radiosensitization. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 315101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Sun, W.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. Facile one-pot synthesis of Fe3O4@Au composite nanoparticles for dual-mode MR/CT imaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10357–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Pan, C.C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Ding, Y.; Huo, D.; Hu, Y. Synthesis and application of strawberry-like Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles as CT-MR dual-modality contrast agents in accurate detection of the progressive liver disease. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hao, C.; Sun, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H. Spiky Fe3O4@Au Supraparticles for Multimodal In Vivo Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ji, G.; Lu, Q.; Dai, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Peng, G.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4@Au-C225 composite targeted nanoparticles for MRI of human glioma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolensky, E.D.; Park, H.-Y.E.; Zhou, Y.; Rolla, G.A.; Marjańska, M.; Botta, M.; Pierre, V.C. Scaling laws at the nanosize: The effect of particle size and shape on the magnetism and relaxivity of iron oxide nanoparticle contrast agents. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2818–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozenkova, E.; Levada, K.; Efremova, M.V.; Omelyanchik, A.; Nalench, Y.A.; Garanina, A.S.; Pshenichnikov, S.; Zhukov, D.G.; Lunov, O.; Lunova, M.; et al. Multifunctional Fe3O4-Au Nanoparticles for the MRI Diagnosis and Potential Treatment of Liver Cancer. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091646
Kozenkova E, Levada K, Efremova MV, Omelyanchik A, Nalench YA, Garanina AS, Pshenichnikov S, Zhukov DG, Lunov O, Lunova M, et al. Multifunctional Fe3O4-Au Nanoparticles for the MRI Diagnosis and Potential Treatment of Liver Cancer. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091646
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozenkova, Elena, Kateryna Levada, Maria V. Efremova, Alexander Omelyanchik, Yulia A. Nalench, Anastasiia S. Garanina, Stanislav Pshenichnikov, Dmitry G. Zhukov, Oleg Lunov, Mariia Lunova, and et al. 2020. "Multifunctional Fe3O4-Au Nanoparticles for the MRI Diagnosis and Potential Treatment of Liver Cancer" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091646
APA StyleKozenkova, E., Levada, K., Efremova, M. V., Omelyanchik, A., Nalench, Y. A., Garanina, A. S., Pshenichnikov, S., Zhukov, D. G., Lunov, O., Lunova, M., Kozenkov, I., Innocenti, C., Albino, M., Abakumov, M. A., Sangregorio, C., & Rodionova, V. (2020). Multifunctional Fe3O4-Au Nanoparticles for the MRI Diagnosis and Potential Treatment of Liver Cancer. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091646