PMMA-TiO2 Fibers for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants
Abstract
1. Introduction
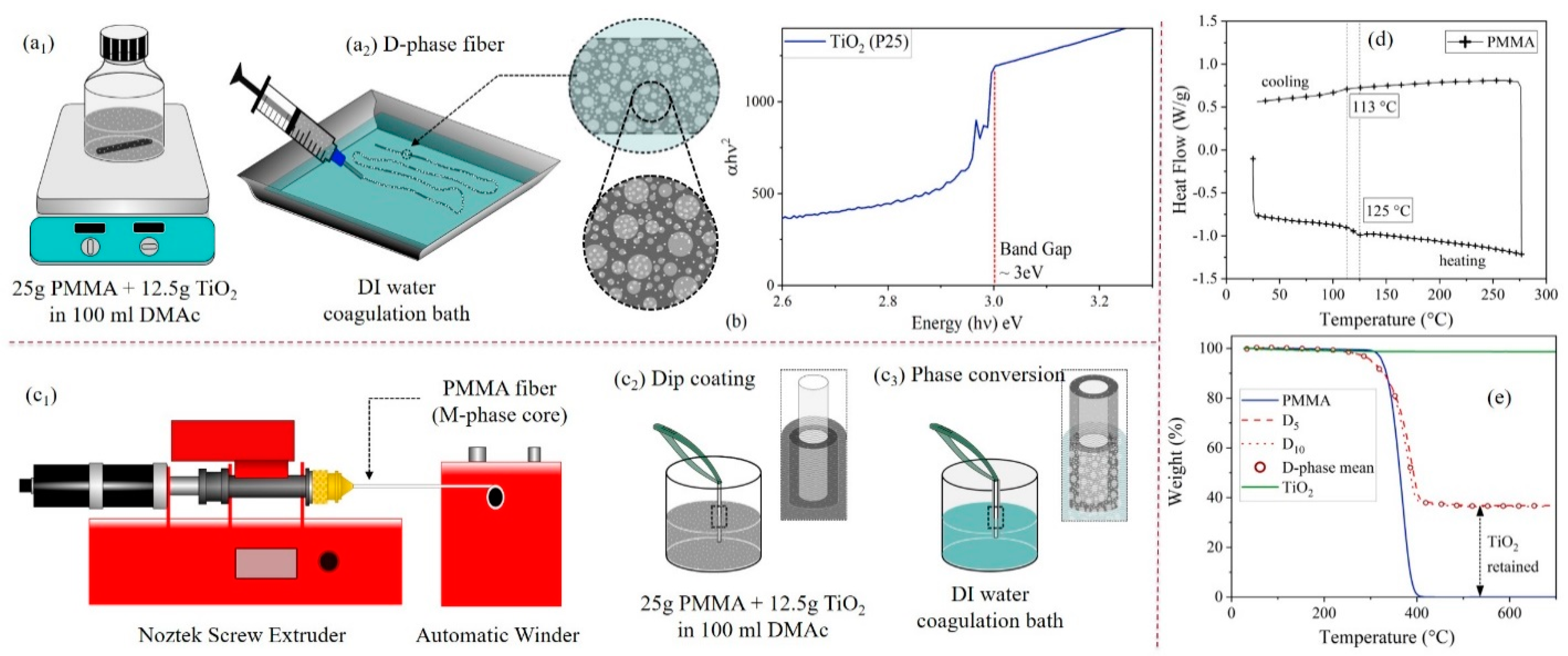
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
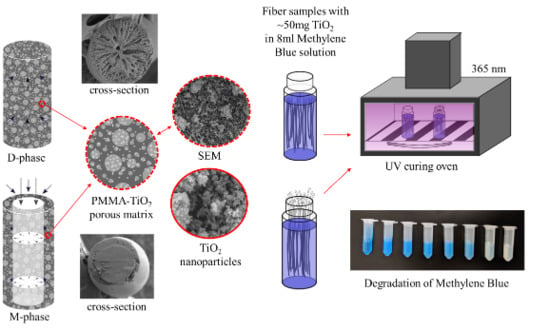
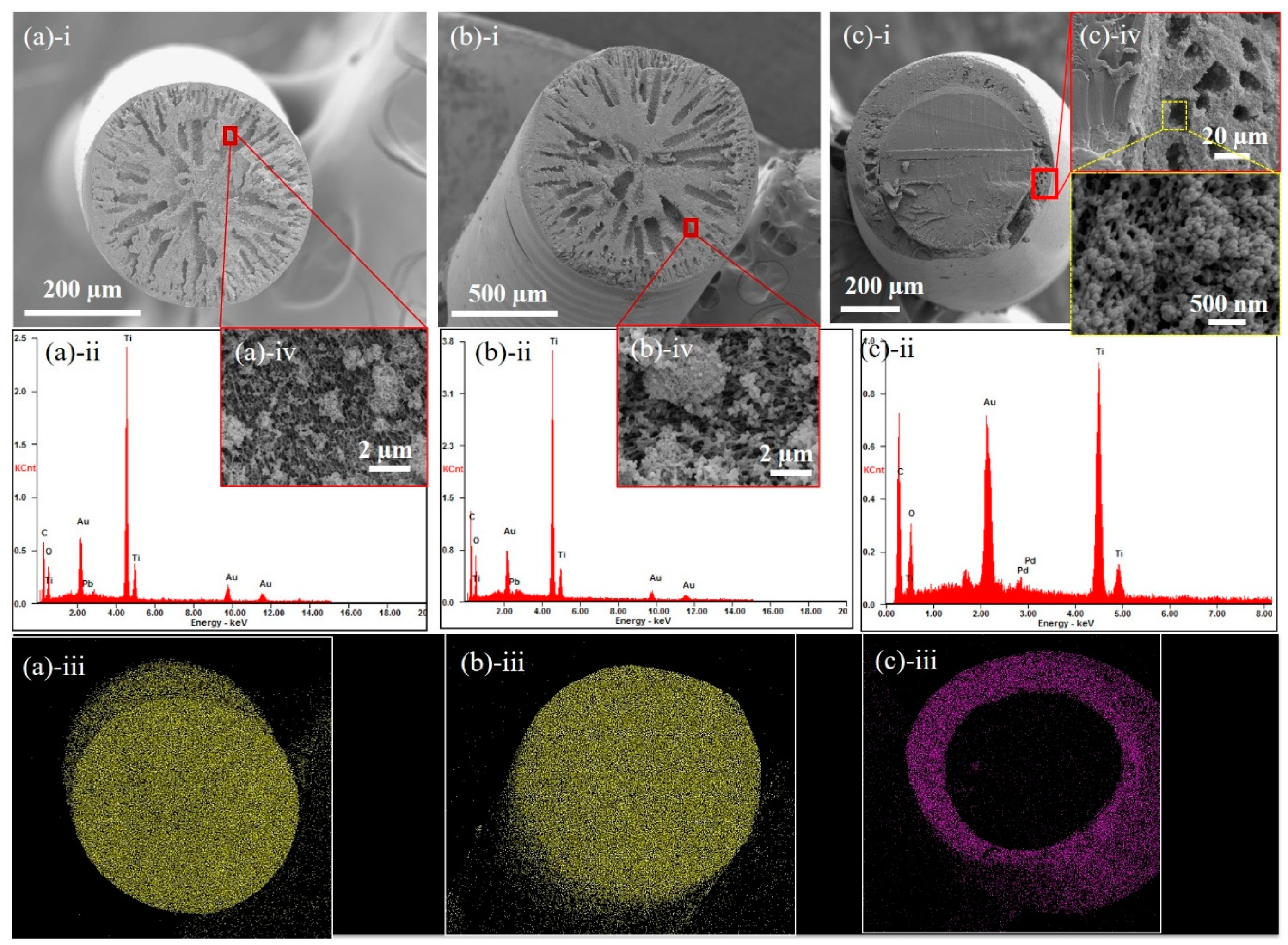
3.1. Fiber Morphology
3.2. Overall Photocatalytic Performance
3.3. Effectiveness of the M-Phase Core
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J.; Lim, L.Y.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Gong, D.; Tang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Z. Titanate and titania nanostructured materials for environmental and energy applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79479–79510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, M.M.; Nair, A.S.; Babu, V.J.; Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8075–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonami, T.; Hase, H.; Funakoshi, K. Apatite-coated titanium dioxide photocatalyst for air purification. Catal. Today 2004, 96, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Tan, Y.N.; Mohamed, A.R. A review on the formation of titania nanotube photocatalysts by hydrothermal treatment. J. Environ. Manage. 2011, 92, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marĩas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z. Robust hollow spheres consisting of alternating titania nanosheets and graphene nanosheets with high photocatalytic activity for CO2 conversion into renewable fuels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: Principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, O.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Review of material design and reactor engineering on TiO2 photocatalysis for CO2 reduction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2015, 24, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mahalingam, H.; Singh, P.K. Polymer-supported titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental remediation: A review. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 462, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, A.Y.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Rashid, S.A. Immobilisation of titanium dioxide onto supporting materials in heterogeneous photocatalysis: A review. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 389, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Leo, C.P.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2013, 308, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Javed, H.; Zhang, D.; Kim, J.H.; Westerhoff, P.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Porous electrospun fibers embedding TiO2 for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peill, N.J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Development and optimization of a TiO2-coated fiber-optic cable reactor: Photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Lim, S.K.; Park, Y. Titania-coated plastic optical fiber fabrics for remote photocatalytic degradation of aqueous pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, H.O.; Garcia-segura, S.; Hristovski, K.; Westerhoff, P. Compact light-emitting diode optical fiber immobilized TiO2 reactor for photocatalytic water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jambhulkar, S.; Verma, R.; Franklin, R.; Ravichandran, D.; Song, K. In situ alignment of graphene nanoplatelets in poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite fibers with controlled stepwise interfacial exfoliation. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, V.; Sarma, A.K.; Rao, V.V.R.N. Optical properties of pure and doped PMMA-CO-P4VPNO polymer films. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 4678–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, R.M.; Portela, R.; Gutierrez-Martin, M.; Sánchez, B. Evaluation of several commercial polymers as support for TiO2 in photocatalytic applications. Glob. NEST J. 2014, 16, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstadler, K.; Bauer, R.; Novallc, S.; Heisler, G. New reactor design for photocatalytic wastewater treatment with TiO2 immobilized on fused-silica glass fibers: Photomineralization of 4-chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.; Razmjou, A.; Wang, K.; Hapgood, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. TiO2 based photocatalytic membranes: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 472, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gong, A.S.; Zhu, M.; Chen, G.; Lacey, S.D.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; et al. Mesoporous, three-dimensional wood membrane decorated with nanoparticles for highly efficient water treatment. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKelvey, S.; Koros, W.J. Phase separation, vitrification, and the manifestation of macrovoids in polymeric asymmetric membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2003, 112, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vild, A.; Teixeira, S.; Kühn, K.; Cuniberti, G.; Sencadas, V. Orthogonal experimental design of titanium dioxide—Poly(methyl methacrylate) electrospun nanocomposite membranes for photocatalytic applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fiber Morphologies | Sample | Dimensions (d, Core Diameter; t, Sheath Thickness; mm) | Mechanical Properties § | BET Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Langmuir–Hinshelwood Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Initial Concentration C0, mg/L | Degradation Rate kMB, min−1 | ||||
| D-phase | D5 | d = 0.5 | Fragile | 33.2 | 0.706 | 0.116 | |
| D10 | d = 1.0 | 17.4 | 2.466 | 0.053 | |||
| M-phase core-shell | MCS | d = 0.5, t = 0.1 | 7.52 ± 2.73 | 117.7 ± 43.2 | 15.7 | 2.545 | 0.059 |
| MC#1 | 1.364 | 0.0077 | |||||
| MC#2 | 0.581 | 0.0069 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanth, N.; Xu, W.; Prasad, U.; Ravichandran, D.; Kannan, A.M.; Song, K. PMMA-TiO2 Fibers for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071279
Kanth N, Xu W, Prasad U, Ravichandran D, Kannan AM, Song K. PMMA-TiO2 Fibers for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071279
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanth, Namrata, Weiheng Xu, Umesh Prasad, Dharneedar Ravichandran, Arunachala Mada Kannan, and Kenan Song. 2020. "PMMA-TiO2 Fibers for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071279
APA StyleKanth, N., Xu, W., Prasad, U., Ravichandran, D., Kannan, A. M., & Song, K. (2020). PMMA-TiO2 Fibers for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071279