Application of a Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis 3D Printed Lab-on-a-Chip for Micro-Nanoparticles Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
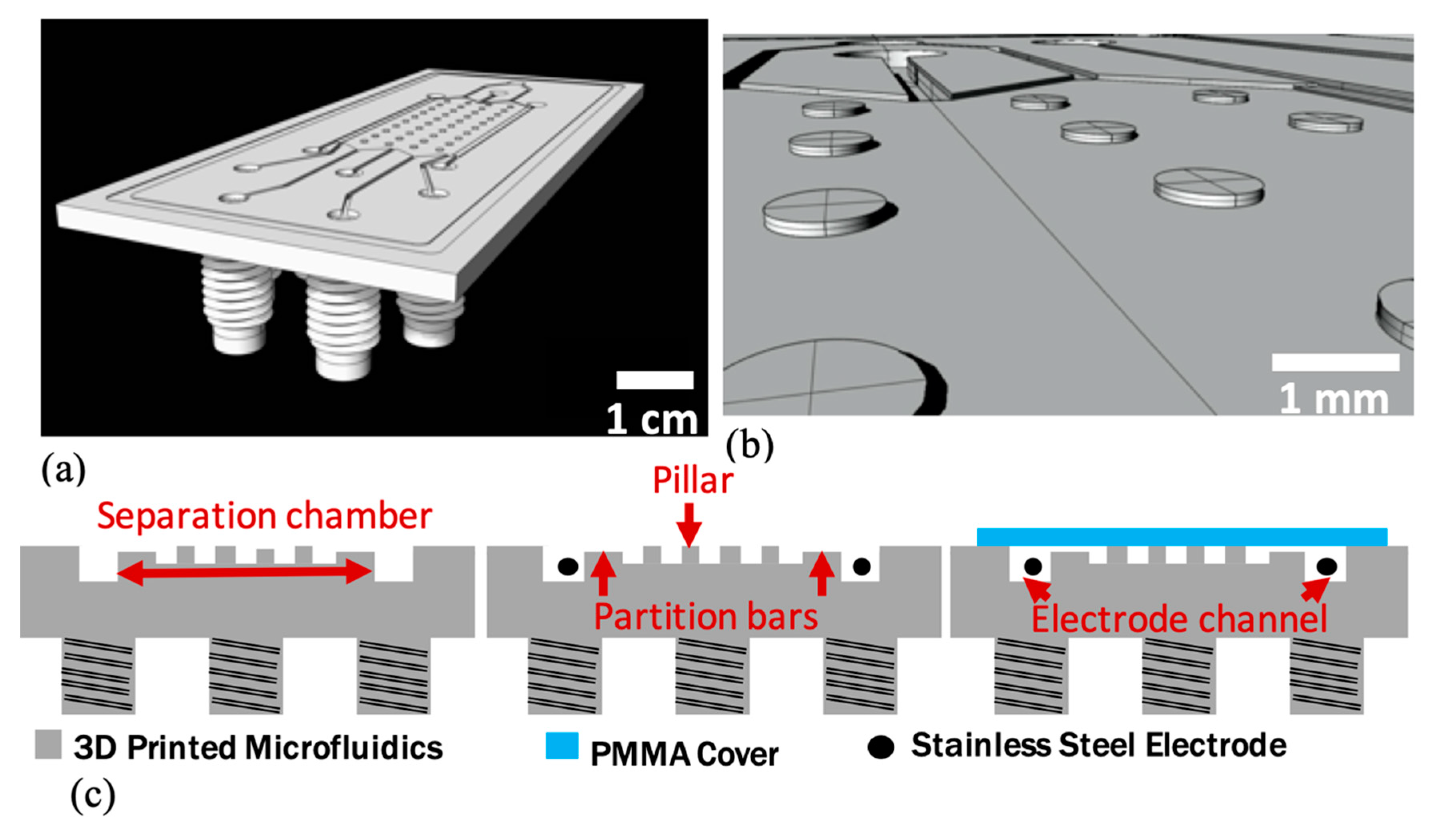
2.1. Design
2.2. Fabrication
2.3. Device Characterization and Experiment Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Device Processes
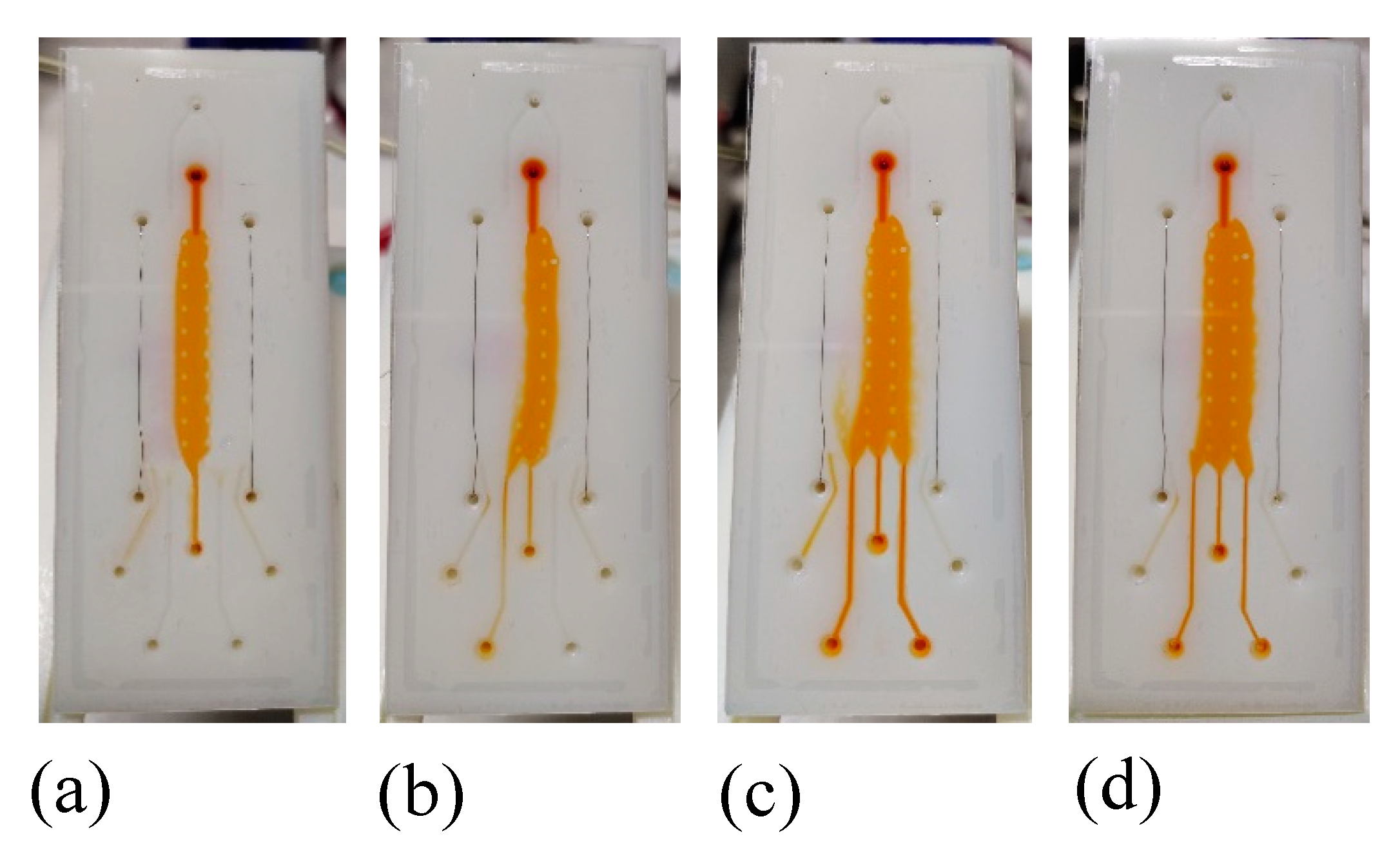
3.2. Flow Confinement Test
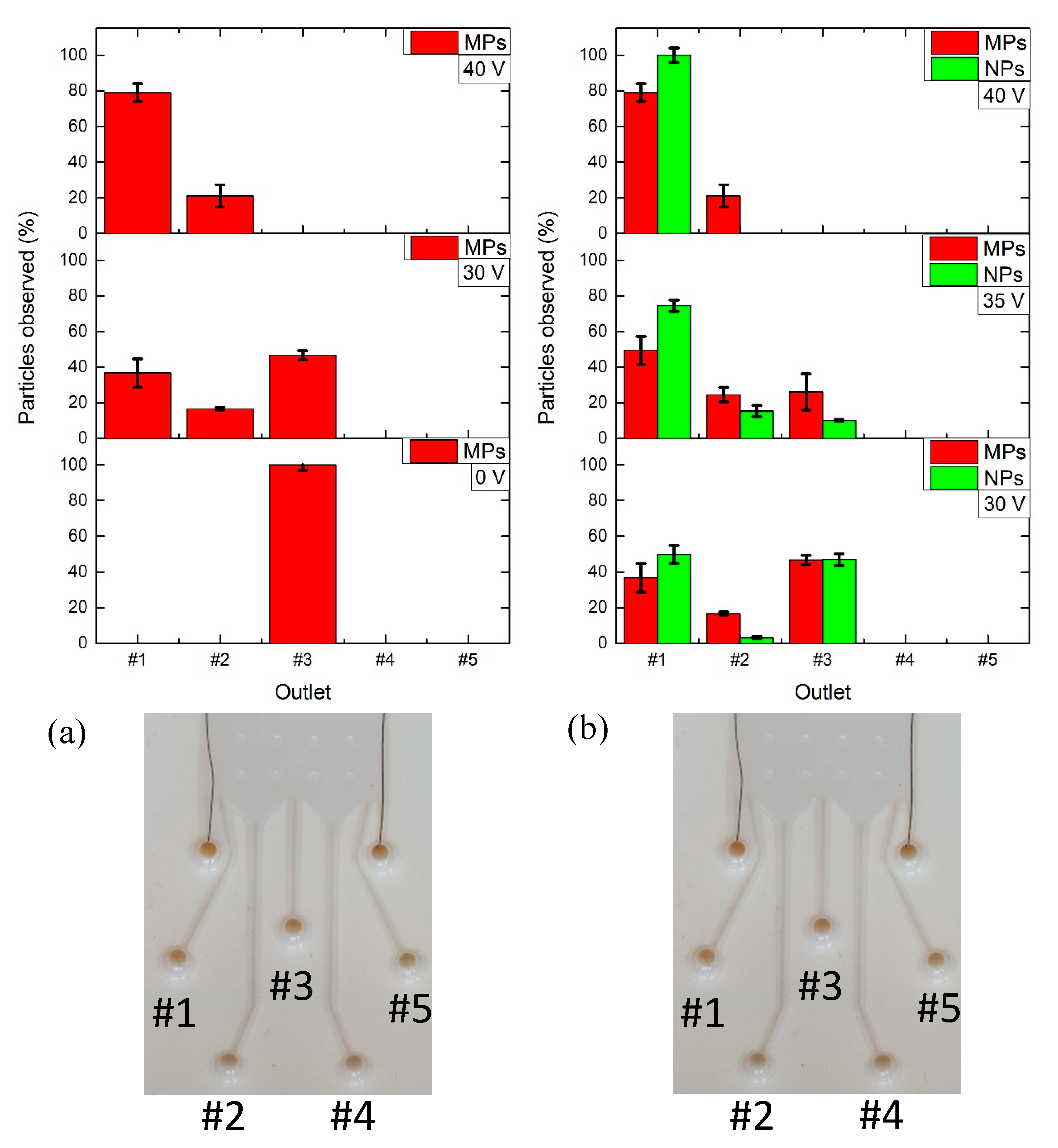
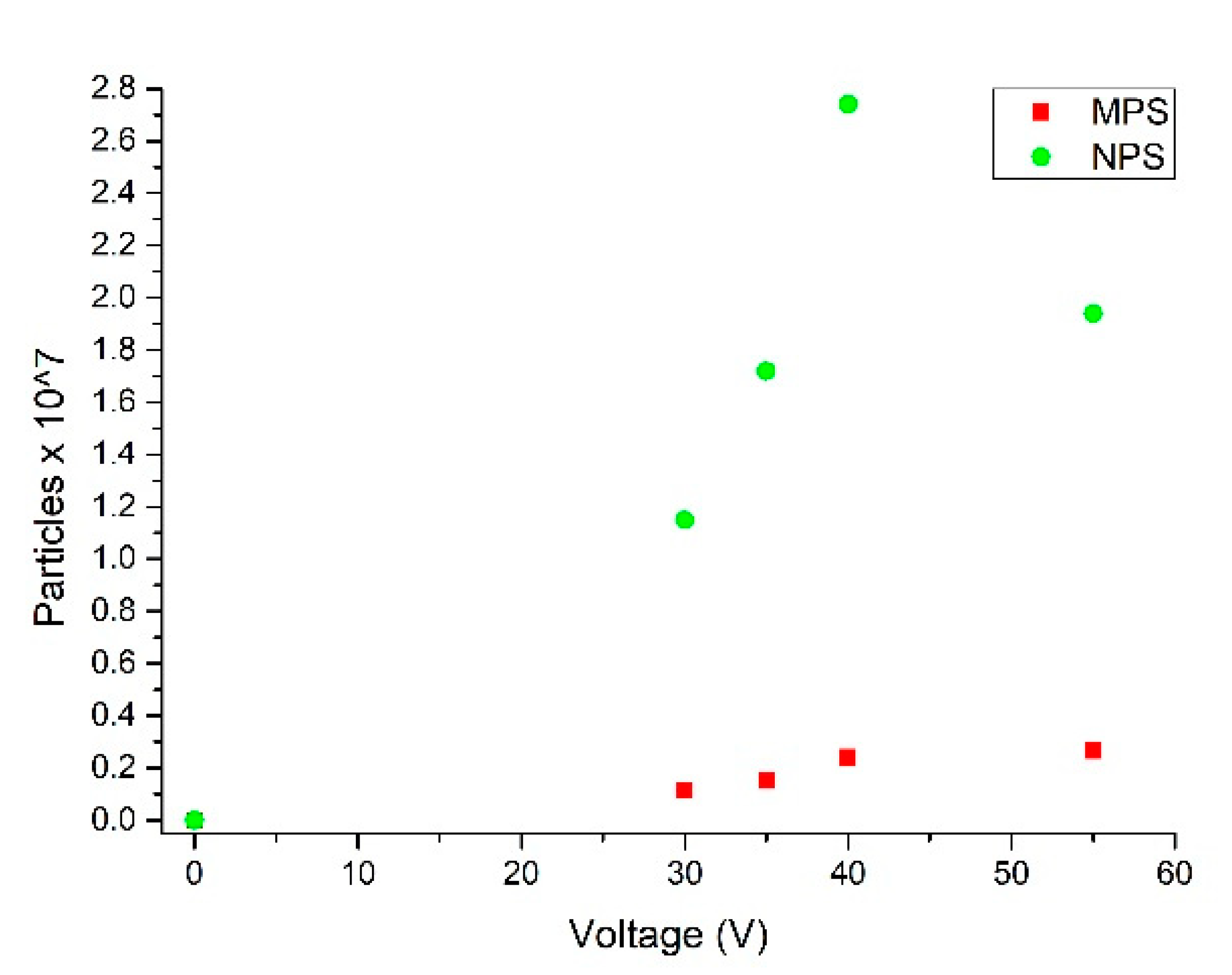
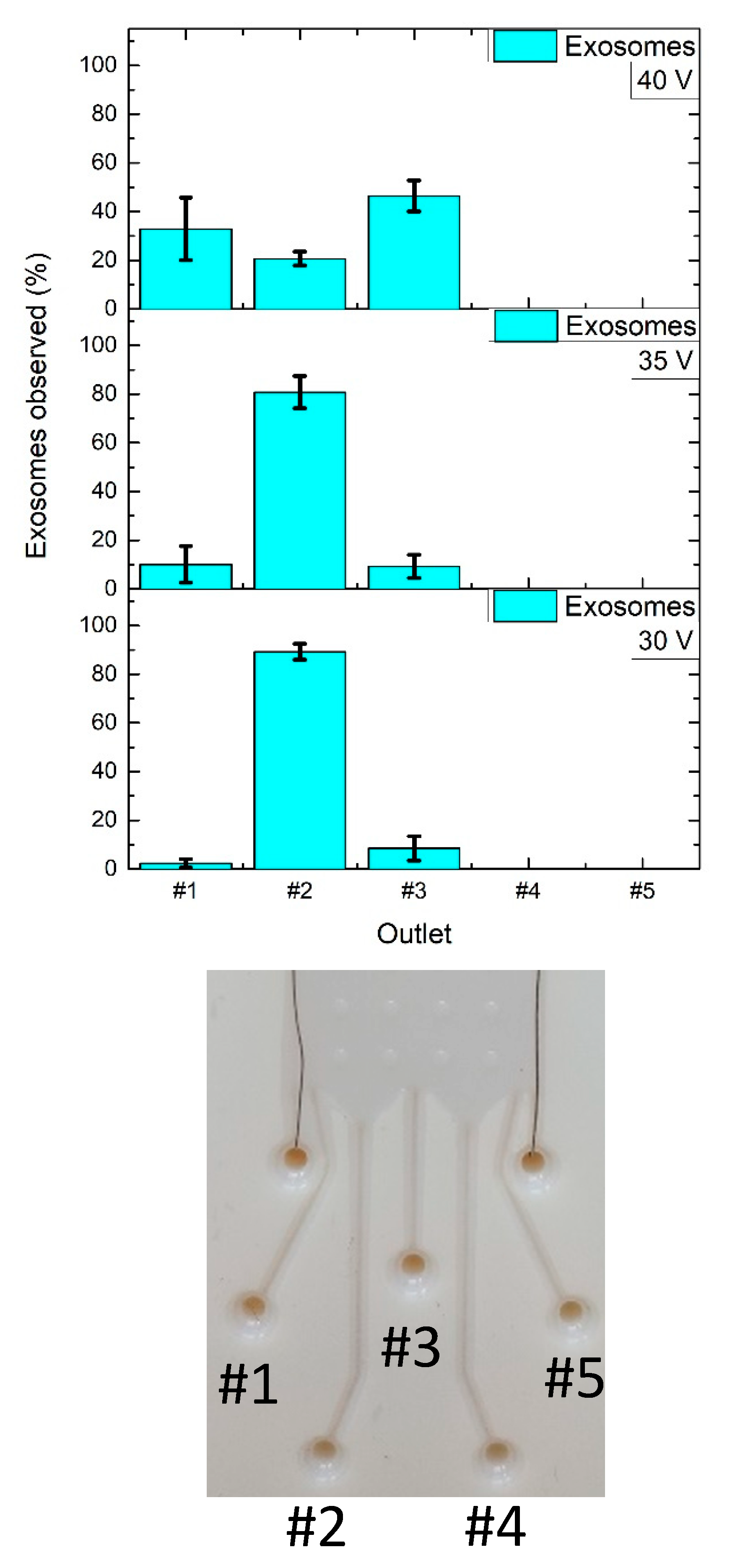
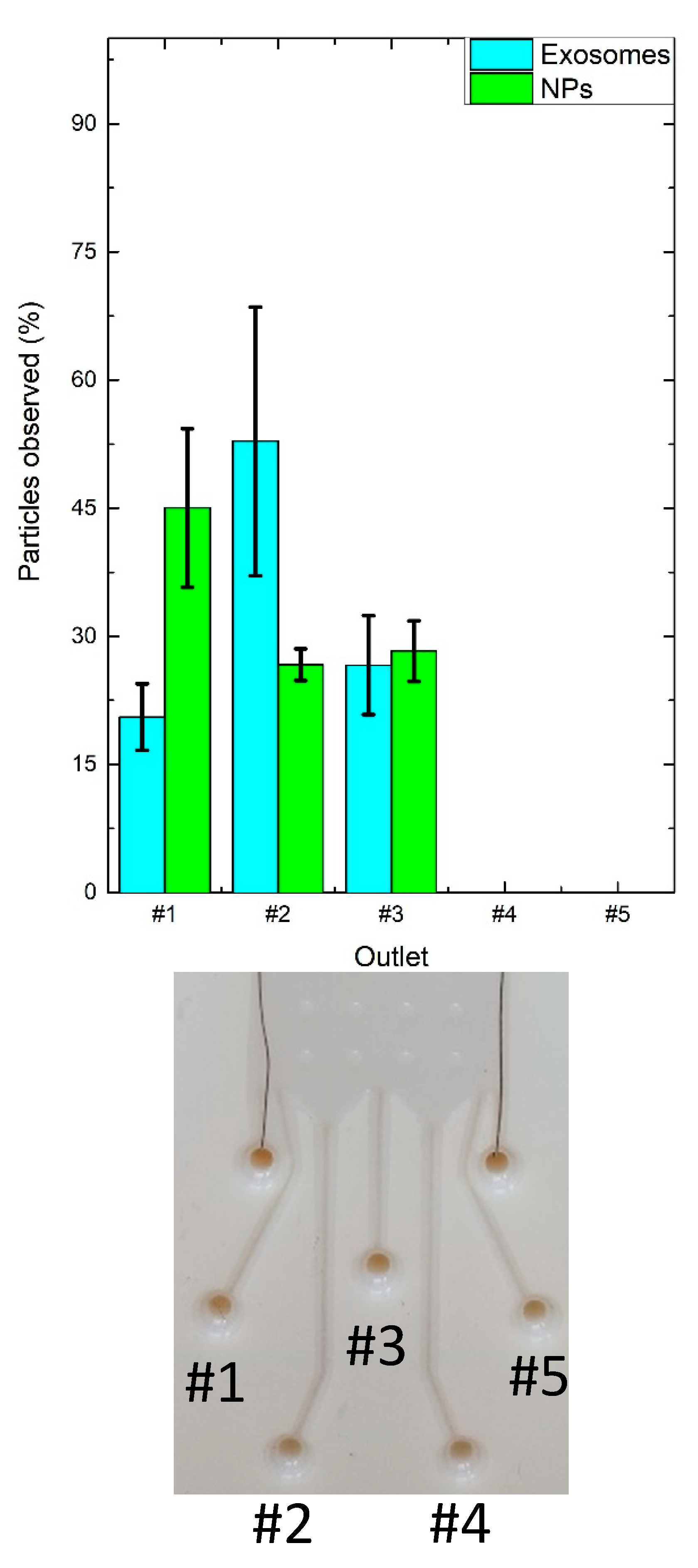
3.3. M/NPs Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.; Park, K. PLA micro- and nano-particles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, J. Nanoparticles and microparticles for drug and vaccine delivery. J. Anat. 1996, 189, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naahidi, S.; Jafari, M.; Edalat, F.; Raymond, K.; Khademhosseini, A.; Chen, P. Biocompatibility of engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafisi, S.; Maibach, H.I. Nanotechnology in cosmetics. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro(nano)plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.J.; Huang, B.; Irvine, D.J. Engineering Nano- and microparticles to tune immunity. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3724–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Dielectrophoresis for manipulation of micro/nano particles in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Quik, J.T.K.; Sun, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Fate of nano- and microplastic in freshwater systems: A modeling study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Nano-plastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Nizzetto, L. Fate and occurrence of micro(nano)plastics in soils: Knowledge gaps and possible risks. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 2018, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberle, S.; Zengerle, R. Microfluidic platforms for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1094–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasso, S.L.; Giuri, E.; Canavese, G.; Castagna, R.; Quaglio, M.; Ferrante, I.; Perrone, D.; Cocuzza, M. A multilevel Lab on chip platform for DNA analysis. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potrich, C.; Lunelli, L.; Cocuzza, M.; Marasso, S.L.; Pirri, C.F.; Pederzolli, C. Simple PDMS microdevice for biomedical applications. Talanta 2019, 193, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasso, S.L.; Puliafito, A.; Mombello, D.; Benetto, S.; Primo, L.; Bussolino, F.; Pirri, C.F.; Cocuzza, M. Optimized design and fabrication of a microfluidic platform to study single cells and multicellular aggregates in 3D. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2017, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, G.C.C.; Potrich, C.; Lunelli, L.; Vanzetti, L.; Marasso, S.L.L.; Cocuzza, M.; Pirri, F.C.C.; Pederzolli, C. miRNA purification with an optimized PDMS microdevice: Toward the direct purification of low abundant circulating biomarkers. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 229, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasso, S.L.; Mombello, D.; Cocuzza, M.; Casalena, D.; Ferrante, I.; Nesca, A.; Poiklik, P.; Rekker, K.; Aaspollu, A.; Ferrero, S.; et al. A polymer lab-on-a-chip for genetic analysis using the arrayed primer extension on microarray chips. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.W. 3D printed microfluidic devices. In Microfluidics for Biologists: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sochol, R.D.; Sweet, E.; Glick, C.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Yang, C.; Restaino, M.; Lin, L. 3D printed microfluidics and microelectronics. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 189, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, A.K.; Huynh, W.; Horowitz, L.F.; Folch, A. 3D-Printed Microfluidics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3862–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrucci, F.; Bertana, V.; Marasso, S.L.; Scordo, G.; Ferrero, S.; Pirri, C.F.; Cocuzza, M.; El-Tamer, A.; Hinze, U.; Chichkov, B.N.; et al. Optimization of a suspended two photon polymerized microfluidic filtration system. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 195, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigarelli, L.; Bertana, V.; Marchisio, D.; Scaltrito, L.; Ferrero, S.; Cocuzza, M.; Marasso, S.L.; Canavese, G.; Pirri, C.F. A passive two-way microfluidic device for low volume blood-plasma separation. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 209, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, P.S.; Vanifatova, N.G.; Shkinev, V.M.; Spivakov, B.Y. Fractionation and characterization of nano- and microparticles in liquid media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1787–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islinger, M.; Eckerskorn, C.; Völkl, A. Free-flow electrophoresis in the proteomic era: A technique in flux. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.C.; Bowser, M.T. Micro free flow electrophoresis. Lab Chip 2017, 18, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, D.E.; Manz, A.; Widmer, H.M. Continuous Sample Pretreatment Using a Free-Flow Electrophoresis Device Integrated onto a Silicon Chip. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Kubota, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Ichiki, T. Development of a polymer-based easy-to-fabricate micro-free-flow electrophoresis device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 06FN05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saar, K.L.; Müller, T.; Charmet, J.; Challa, P.K.; Knowles, T.P.J. Enhancing the Resolution of Micro Free Flow Electrophoresis through Spatially Controlled Sample Injection. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8998–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.; Weilbeer, C.; Howitz, S.; Becker, H.; Beushausen, V.; Belder, D. PDMS free-flow electrophoresis chips with integrated partitioning bars for bubble segregation. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anciaux, S.K.; Geiger, M.; Bowser, M.T. 3D Printed Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis Device. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7675–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes—Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, A.; Di Vizio, D. Size matters in nanoscale communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Shehata Draz, M.; Zarghooni, M.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Ghavami, S.; Shafiee, H.; Akbari, M. Microfluidic approaches for isolation, detection, and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Current status and future directions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 588–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Sung, C.W.H.; Chen, C.; Cheng, C.M.; Lin, D.P.C.; Te Huang, C.; Hsu, M.Y. Advances in exosomes technology. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Hsu, J.L.; Lee, G. Bin Sample preconcentration in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 10, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, B.C.; Burgi, D.S.; Hart, S.J.; Terray, A. On-line sample pre-concentration in microfluidic devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 718, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, S.; Benz, C.; Becker, H.; Beckert, E.; Beushausen, V.; Belder, D. Micro free-flow electrophoresis with injection molded chips. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A.; Petersson, F.; Jönsson, H.; Laurell, T. Acoustic control of suspended particles in micro fluidic chips. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, D.W.; Xu, R.; Ji, H.; Tauro, B.J.; Simpson, R.J. A Protocol for Exosome Isolation and Characterization: Evaluation of Ultracentrifugation, Density-Gradient Separation, and Immunoaffinity Capture Methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 179–209. [Google Scholar]


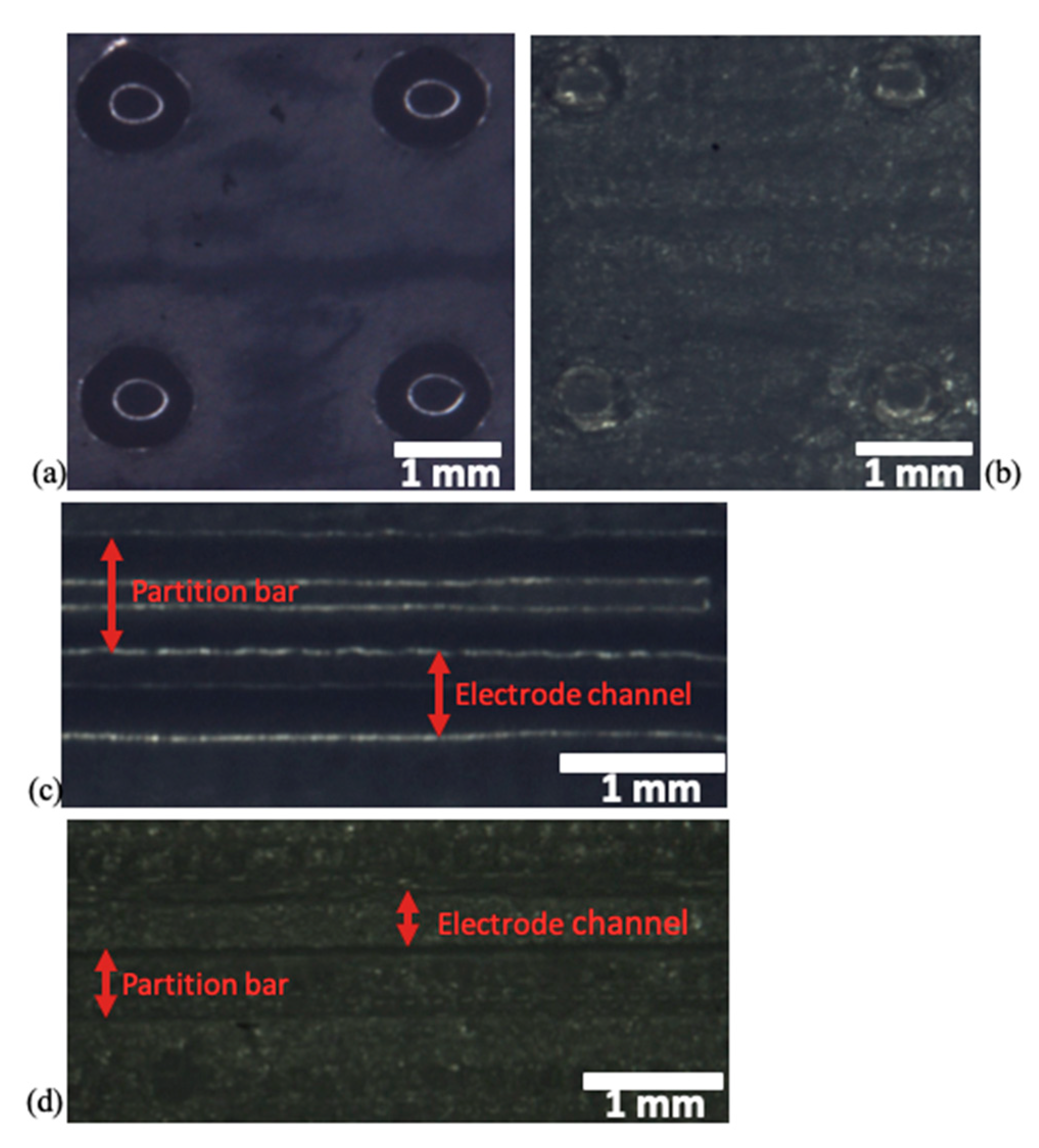
| Features | CAD (µm) | Glossy Surface (µm) | Matte Surface (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pillar length | 1000 | 1032 ± 13 | 725 ± 56 |
| Pillar width | 800 | 933 ± 23 | 603 ± 33 |
| Pillar height | 100 | 99 ± 2 | 103 ± 3 |
| Inlet/outlet diameter | 3200 | 3090 ± 195 | 2519 ± 81 |
| Electrode channel width | 500 | 612 ± 31 | 577 ± 33 |
| Partition bar width | 500 | 458 ± 15 | 524 ± 30 |
| Partition bar height | 50 | 55 ± 2 | 52 ± 8 |
| Sample | Size (μm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| MPs | 3.9 ± 0.2 | −10 ± 3 |
| NPs | 0.5 ± 0.05 | −21 ± 5 |
| EXs | 0.056 ± 0.02 | −9.61 ± 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbaresco, F.; Cocuzza, M.; Pirri, C.F.; Marasso, S.L. Application of a Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis 3D Printed Lab-on-a-Chip for Micro-Nanoparticles Analysis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071277
Barbaresco F, Cocuzza M, Pirri CF, Marasso SL. Application of a Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis 3D Printed Lab-on-a-Chip for Micro-Nanoparticles Analysis. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071277
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbaresco, Federica, Matteo Cocuzza, Candido Fabrizio Pirri, and Simone Luigi Marasso. 2020. "Application of a Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis 3D Printed Lab-on-a-Chip for Micro-Nanoparticles Analysis" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071277
APA StyleBarbaresco, F., Cocuzza, M., Pirri, C. F., & Marasso, S. L. (2020). Application of a Micro Free-Flow Electrophoresis 3D Printed Lab-on-a-Chip for Micro-Nanoparticles Analysis. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071277






