Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Iron(II) Doped Copper Ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4) as Novel Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of NPs
2.3. Characterization of NPs
2.4. Assessment of Photocatalytic Activity
2.5. Assessment of Reusability
3. Results
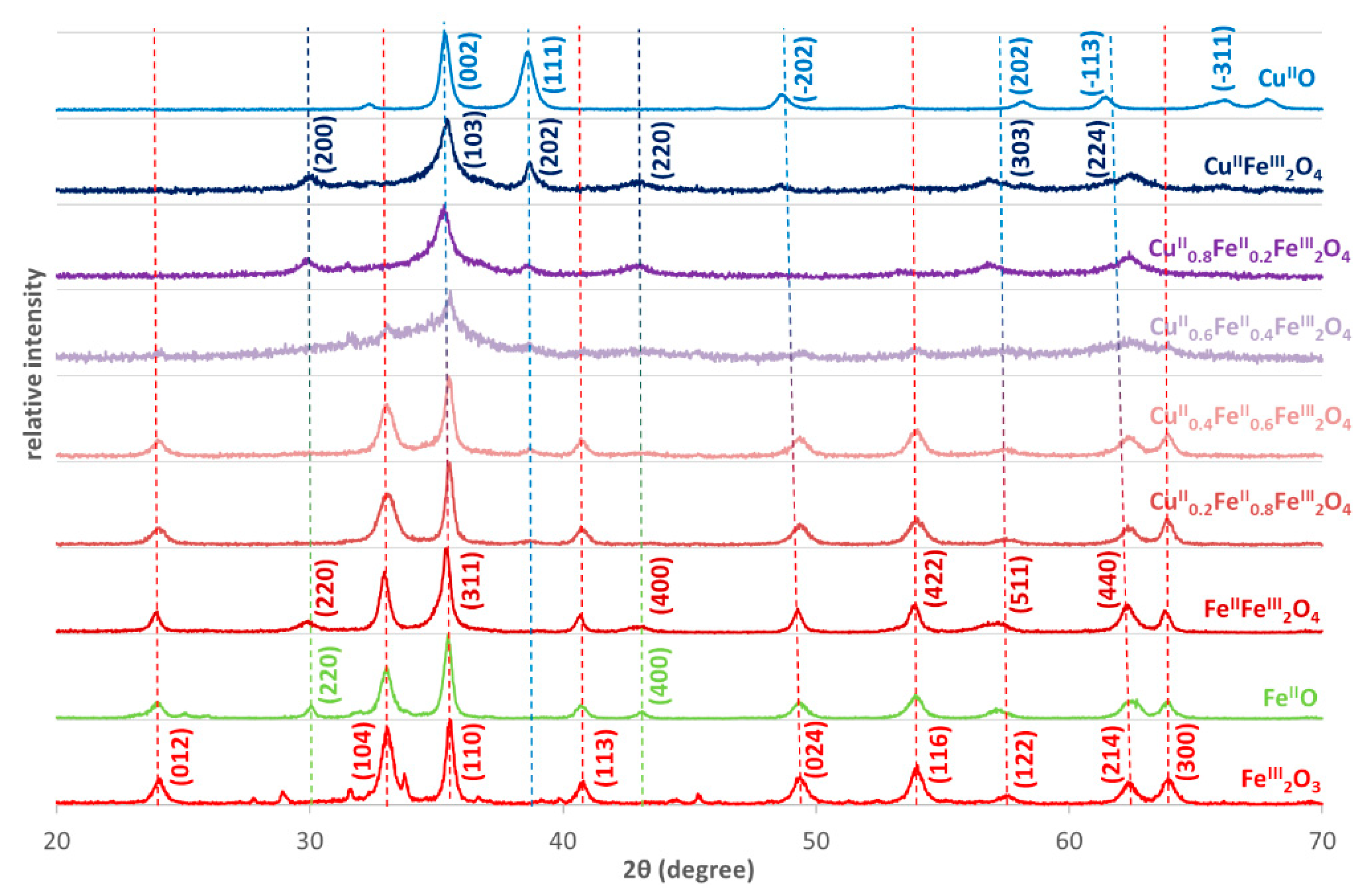
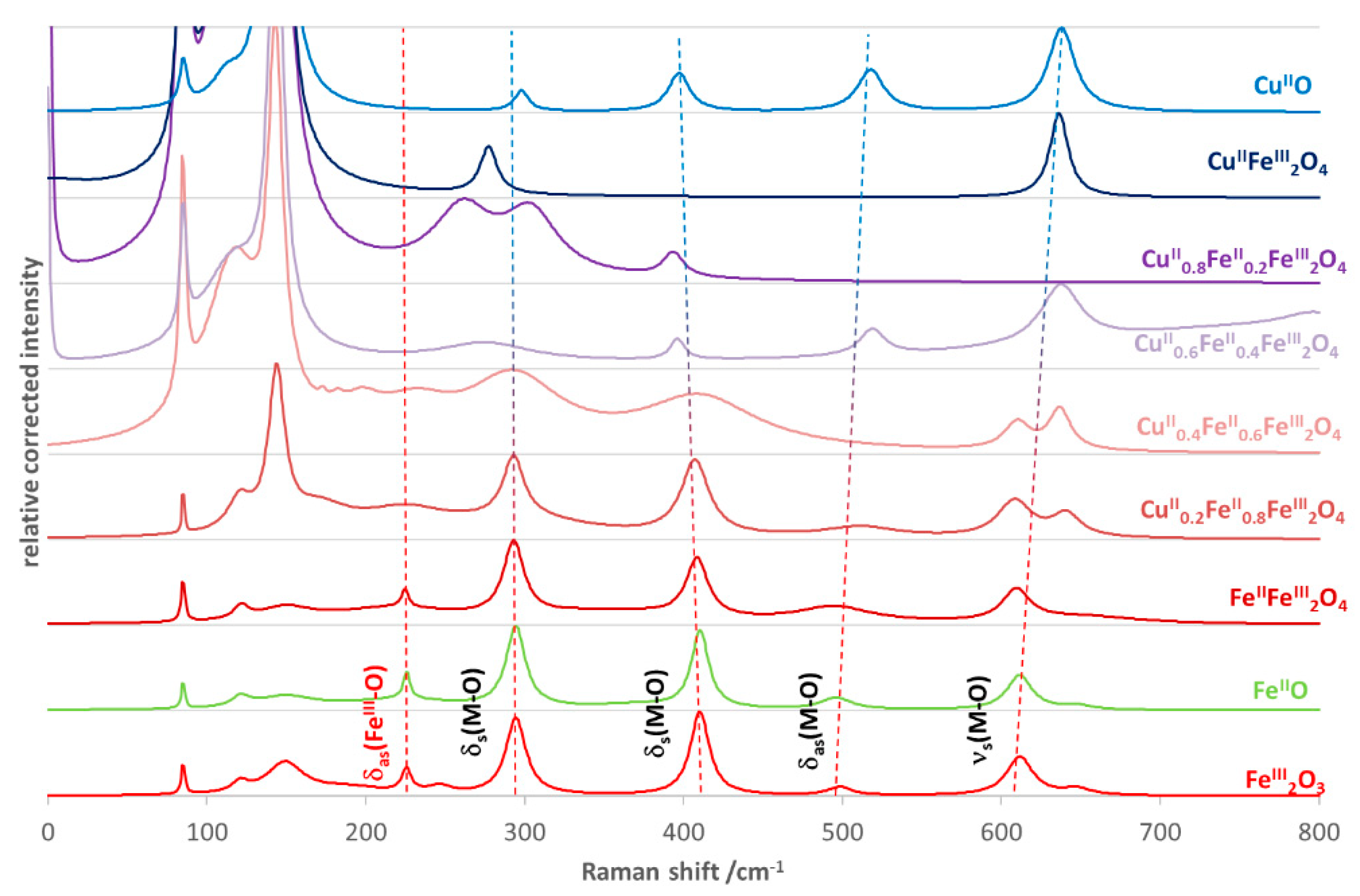
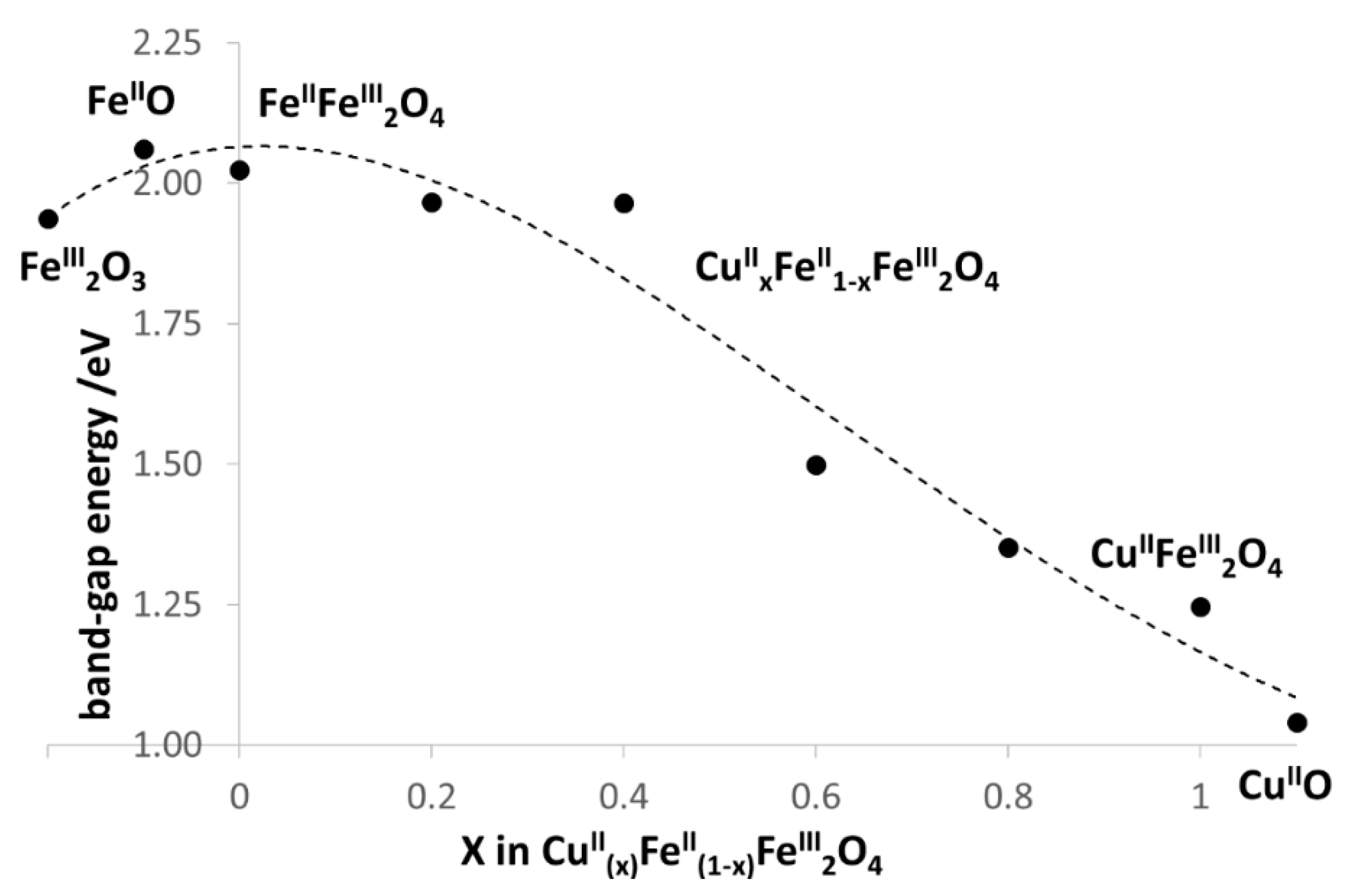
3.1. Characterization of CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4 NPs
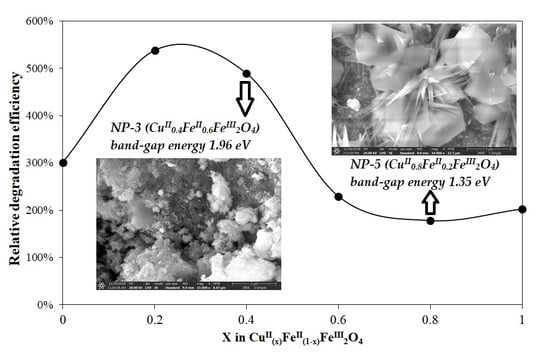
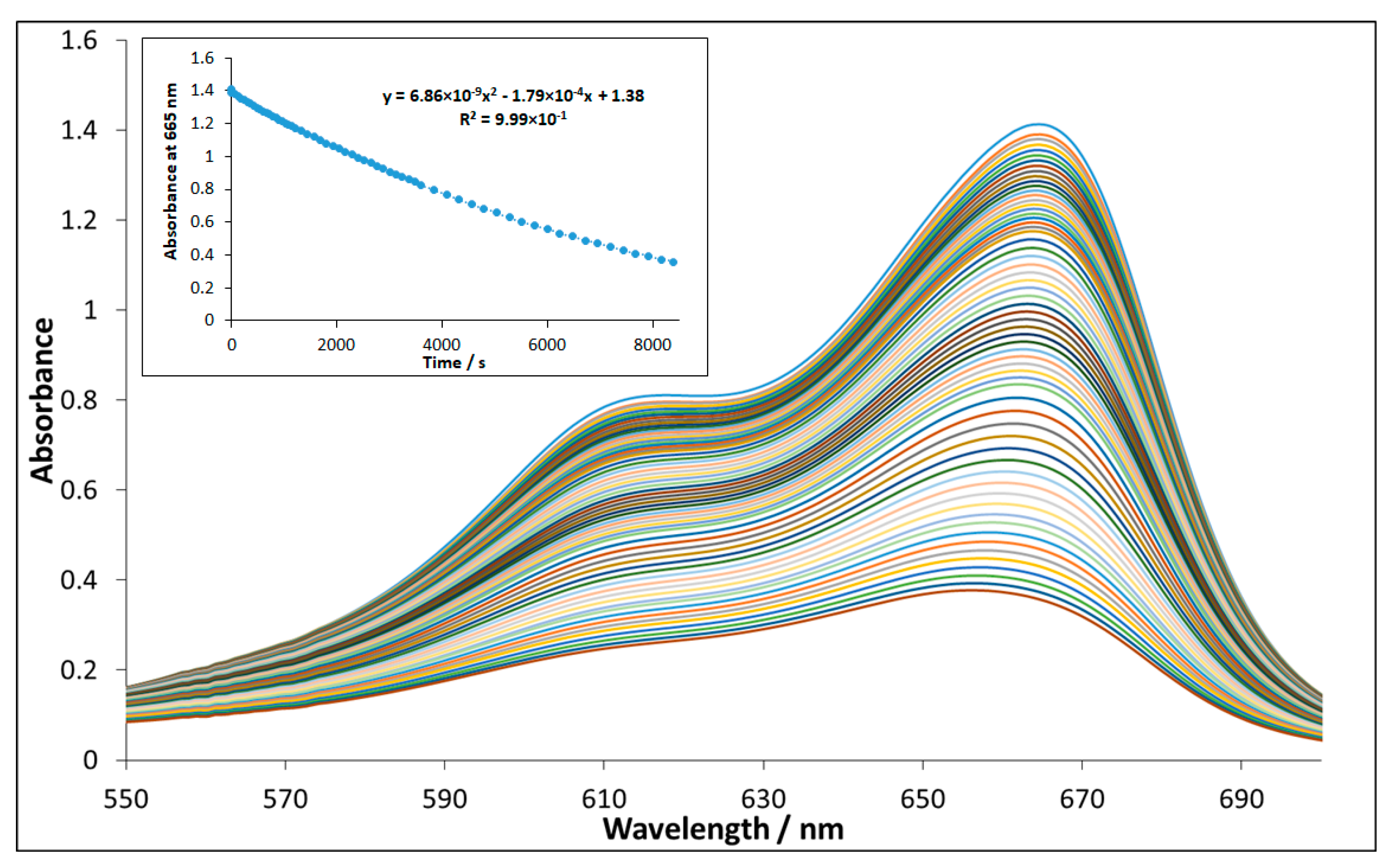
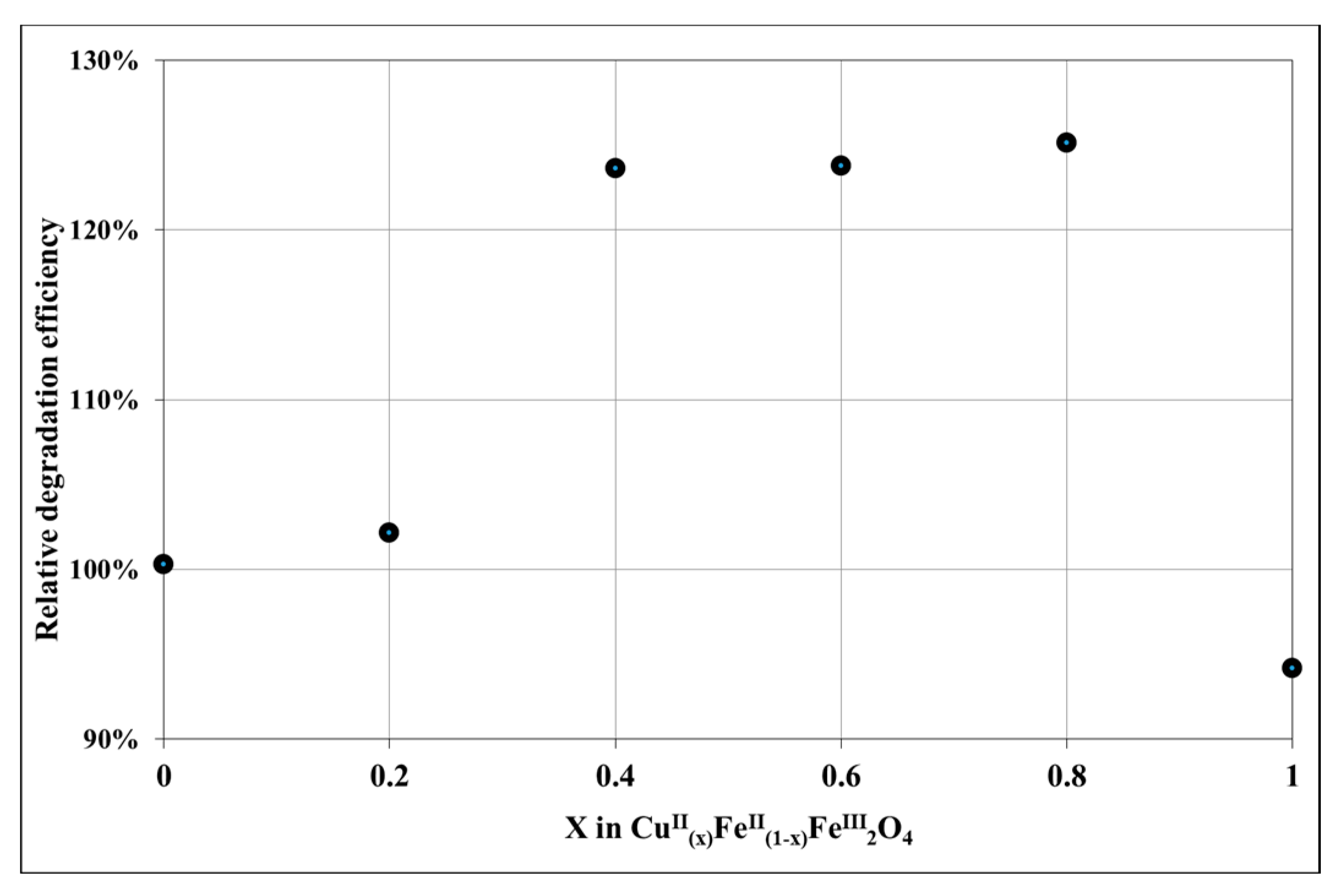
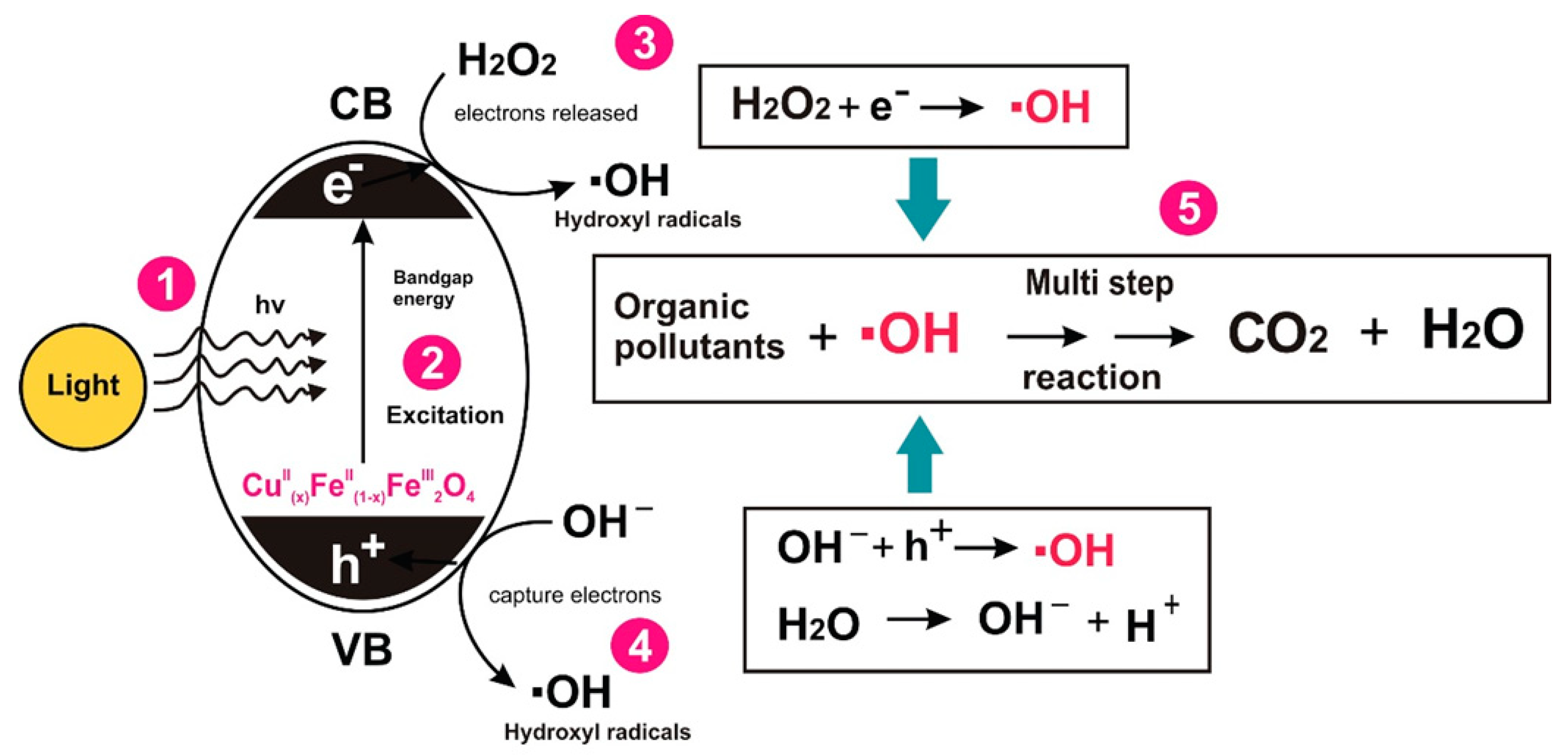
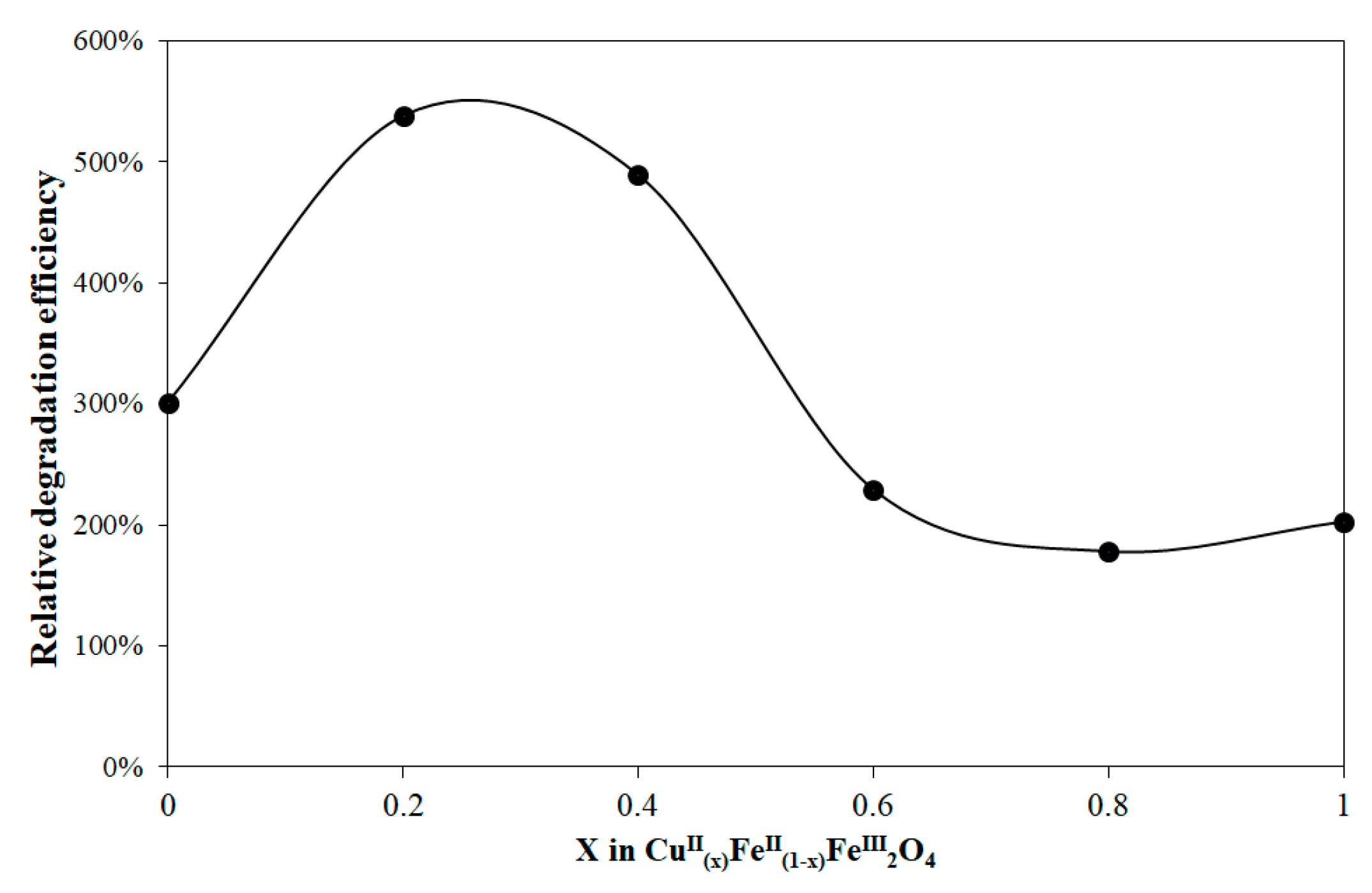
3.2. Evaluation of Photocatalytic Activity of CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4 NPs
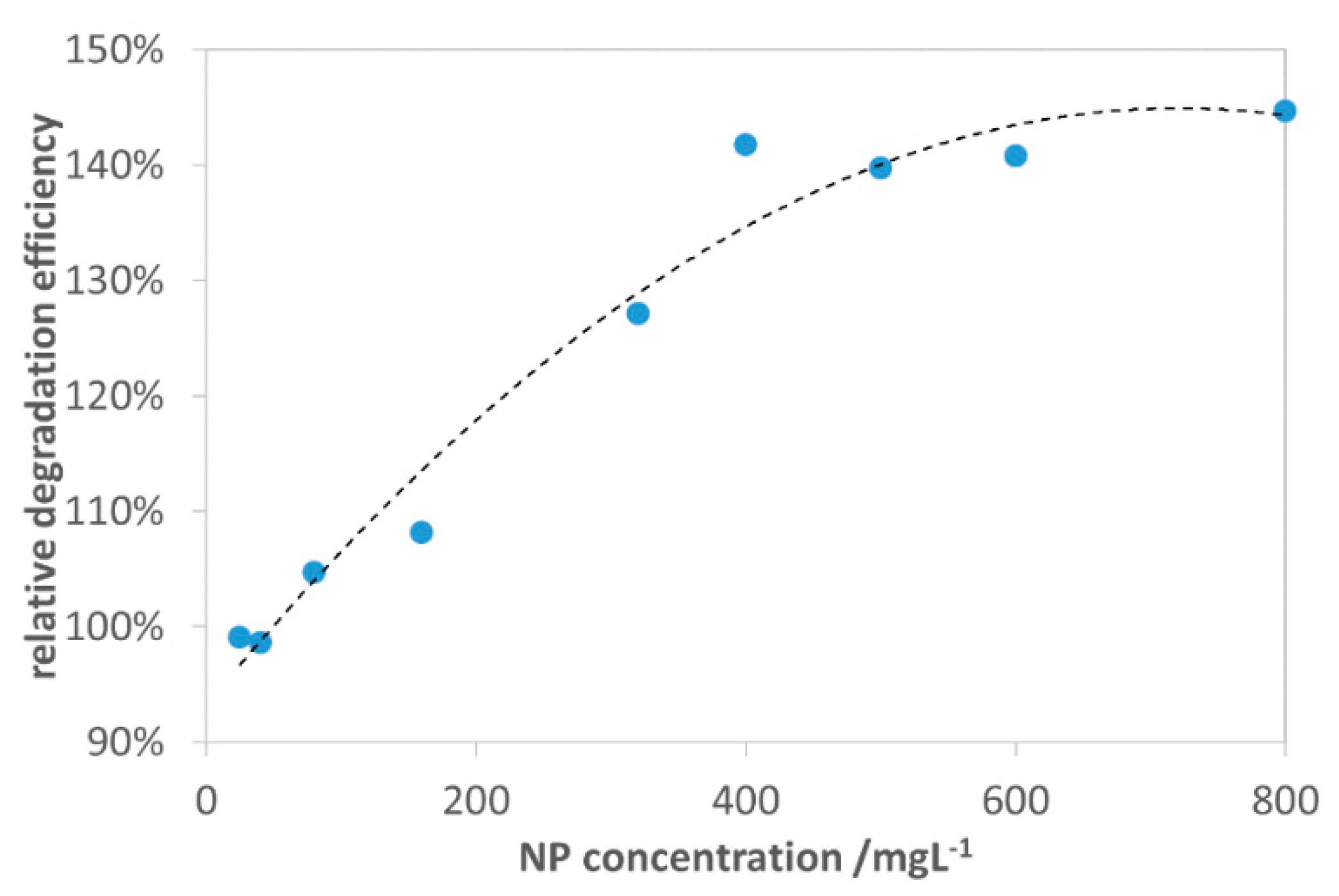
3.2.1. Effect of CuII0.4FeII0.6FeIII2O4 Dosage
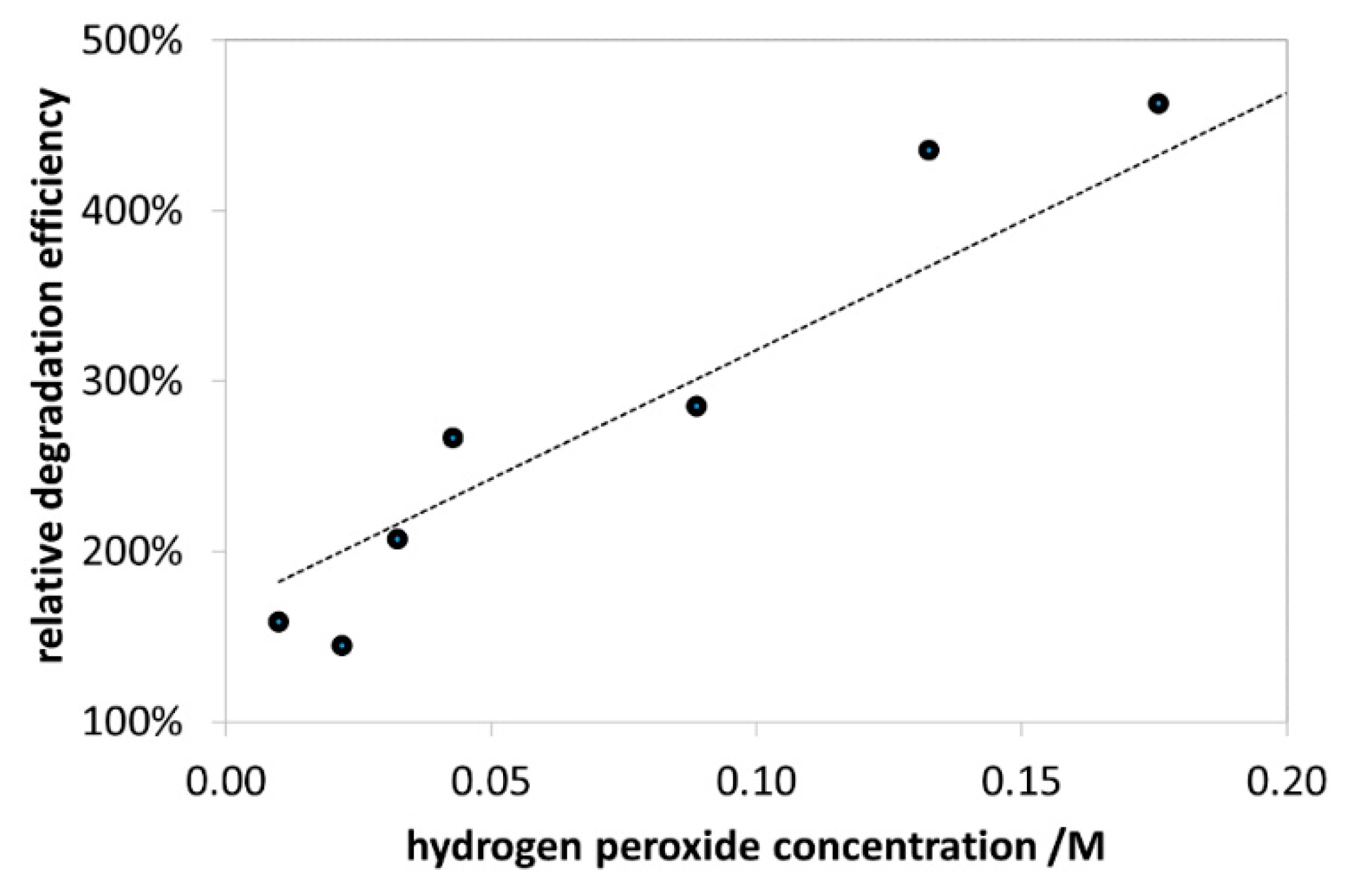
3.2.2. Effect of H2O2 Concentration
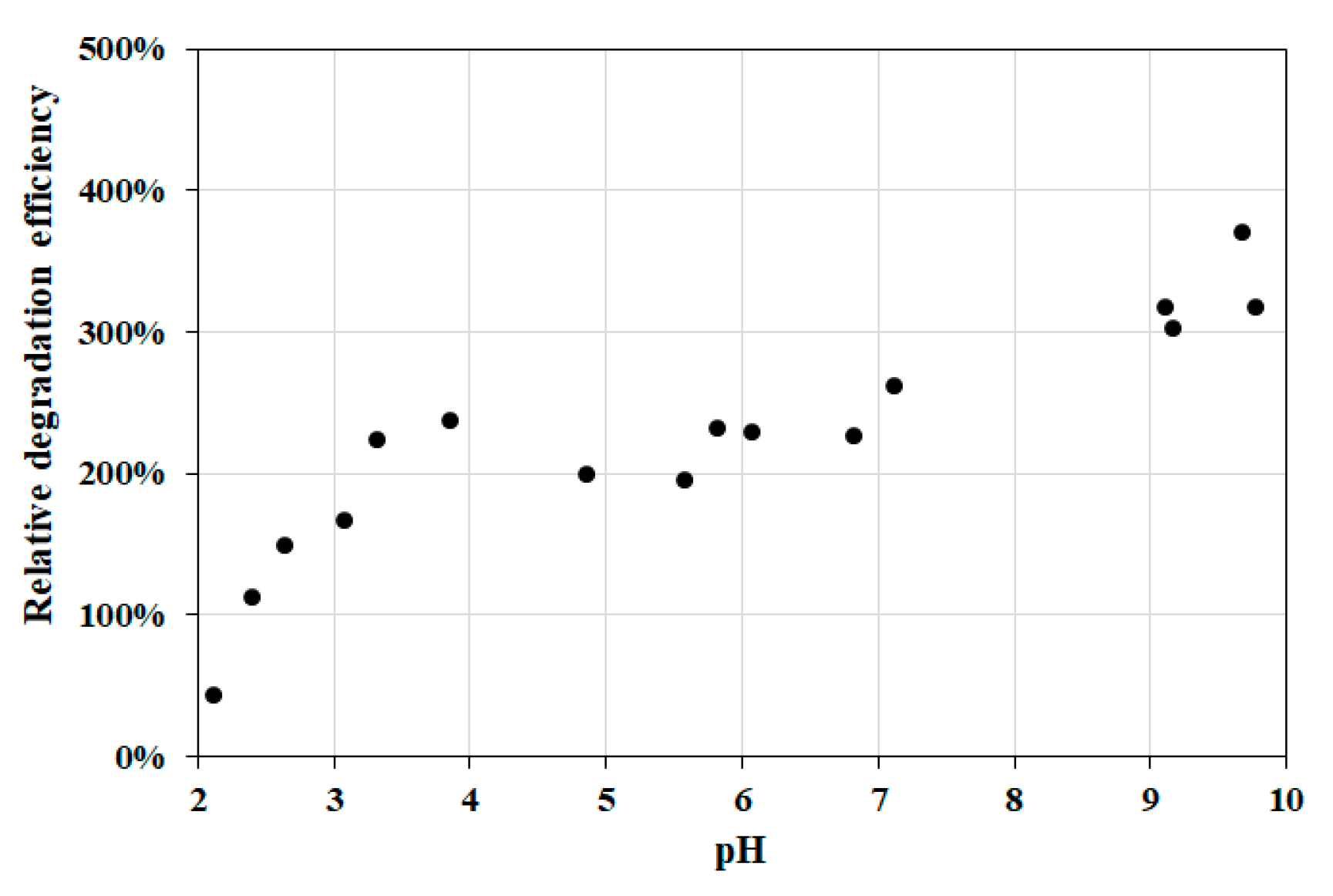
3.2.3. Effect of pH
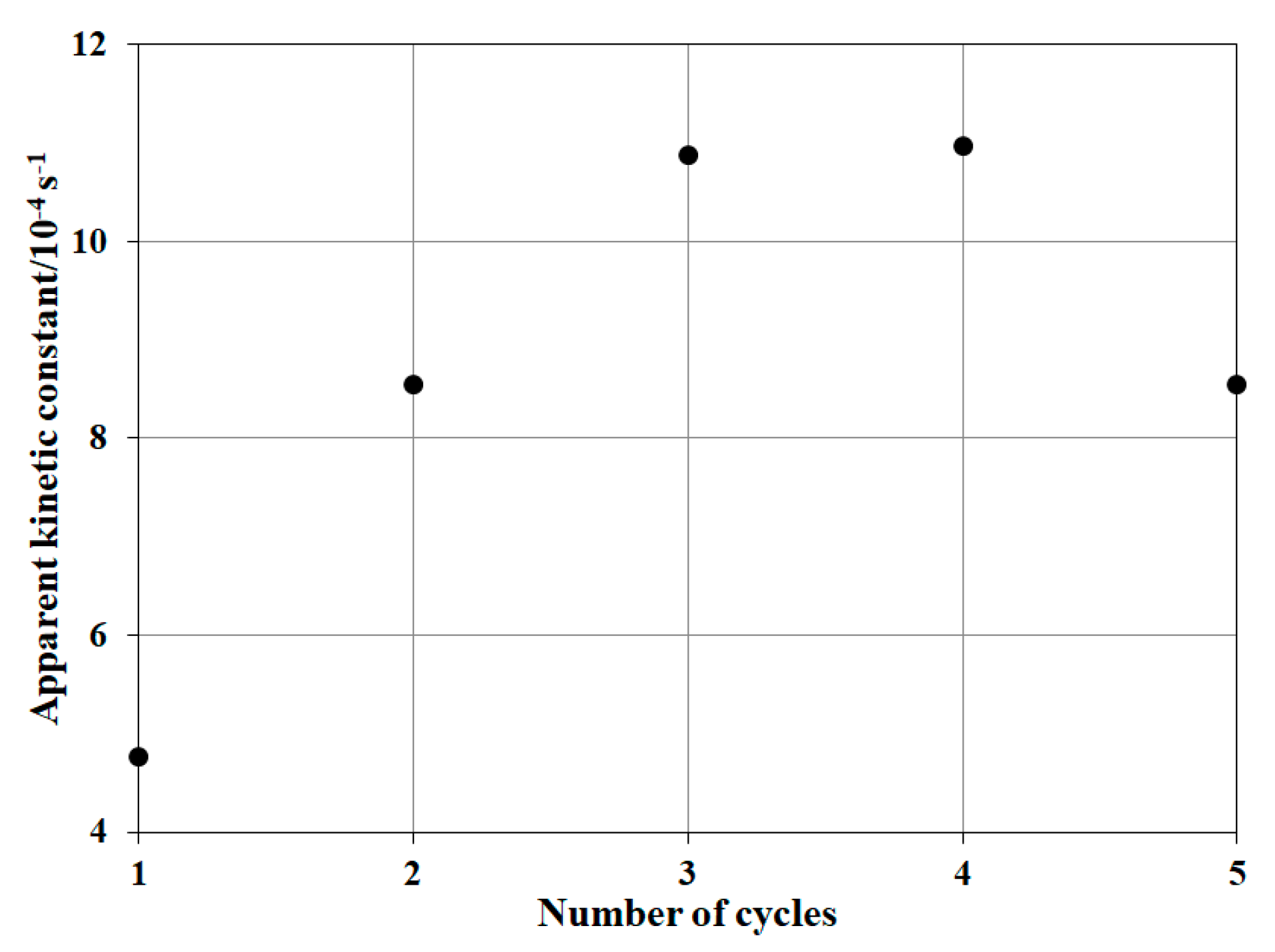
3.2.4. Reusability of NP-3 (CuII0.4FeII0.6FeIII2O4)
3.2.5. Summarizing the Optimized Photocatalytic Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, X.T.; Dastan, D.; Wu, F.Y.; Li, J. Facile synthesis of SnO2/LaFeO3− XNX composite: Photocatalytic activity and gas sensing performance. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rupa, E.J.; Kaliraj, L.; Abid, S.; Yang, D.C.; Jung, S.K. Synthesis of a Zinc Oxide Nanoflower Photocatalyst from Sea Buckthorn Fruit for Degradation of Industrial Dyes in Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valero Luna, C.; Palomares Sanchéz, S.; Ruíz, F. Catalytic activity of the barium hexaferrite with H2O2/visible light irradiation for degradation of Methylene Blue. Catal. Today 2016, 266, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. Advanced oxidation of phenol: A comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallel, M.; Belaid, C.; Mechichi, T.; Ksibi, M.; Elleuch, B. Removal of organic load and phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Yang, H.; Xian, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. Photocatalytic and photo-Fenton catalytic degradation activities of Z-scheme Ag2S/BiFeO3 heterojunction composites under visible-light irradiation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amat, A.M.; Arques, A.; Beneyto, H.; Garcıa, A.; Miranda, M.A.; Seguı́, S. Ozonisation coupled with biological degradation for treatment of phenolic pollutants: A mechanistically based study. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.; Sohn, K.; Lee, K. Hydrogen peroxide interference in chemical oxygen demand during ozone based advanced oxidation of anaerobically digested livestock wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Removal of COD from olive mill wastewater by Fenton‘s reagent: Kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjouji, H.; Barje, F.; Pinelli, E.; Bailly, J.R.; Richard, C.; Winterton, P.; Revel, J.C.; Hafidi, M. Photochemical UV/TiO2 treatment of olive mill wastewater (OMW). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7264–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karunakaran, C.; Anilkumar, P. Semiconductor-catalyzed solar photooxidation of iodide ion. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2007, 265, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.P.; Zeng, X.; Li, C.; Lemley, A.T. Enhanced heterogeneous and homogeneous Fenton-like degradation of carbamazepine by nano-Fe3O4/H2O2 with nitrilotriacetic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Li, M.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhai, B.G. Eu2+ and Eu3+ doubly doped ZnWO4 nanoplates with superior photocatalytic performance for dye degradation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesquita, I.; Matos, L.C.; Duarte, F.; Maldonado Hódar, F.; Mendes, A.; Madeira, L.M. Treatment of azo dye-containing wastewater by a Fenton-like process in a continuous packed-bed reactor filled with activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.; Maldonado Hódar, F.; Madeira, L.M. Influence of the characteristics of carbon materials on their behaviour as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the elimination of the azo dye Orange II from aqueous solutions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 103, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan Alaton, I. Degradation of a commercial textile biocide with advanced oxidation processes and ozone. J. Environ. Manage. 2007, 82, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, H.; Bilkay, O.; Ataberk, S.S.; Balta, T.H.; Ceribasi, I.H.; Sanin, F.D.; Dilek, F.B.; Yetis, U. Use of Fenton oxidation to improve the biodegradability of a pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, B.; De Michelis, I.; Vegliò, F. Fenton treatment of complex industrial wastewater: Optimization of process conditions by surface response method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Ghaly, M.Y.; Gad Allah, T.A. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of organophosphorus pesticides from wastewater. Desalination 2006, 194, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalkaya, E.C.; Kargi, F. Color, TOC and AOX removals from pulp mill effluent by advanced oxidation processes: A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.; Mascolo, G.; Detomaso, A.; Lovecchio, G.; Villani, G. Temperature activated degradation (mineralization) of 4-chloro-3-methyl phenol by Fenton’s reagent. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Gou, N.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Gu, A.Z. Efficient degradation of contaminants of emerging concerns by a new electro-Fenton process with Ti/MMO cathode. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2796–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irmak, S.; Yavuz, H.I.; Erbatur, O. Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol in aqueous solution by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton processes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 63, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirés, I.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Brillas, E. Degradation of clofibric acid in acidic aqueous medium by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Banos, M.A.; Skoumal, M.; Cabot, P.L.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M. Degradation of the herbicide 2, 4-DP by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton using platinum and boron-doped diamond anodes. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masomboon, N.; Ratanatamskul, C.; Lu, M.C. Mineralization of 2, 6-dimethylaniline by photoelectro-Fenton process. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 384, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Segura, S.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Arias, C.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of flumequine in acidic medium by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton processes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Banos, M.A.; Garrido, J.A. Mineralization of herbicide 3, 6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton. Electrochim. Acta. 2003, 48, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Bandara, J.; Kiwi, J.; Lopez, A.; Albers, P. Efficient photo-assisted Fenton catalysis mediated by Fe ions on Nafion membranes active in the abatement of non-biodegradable azo-dye. Chem. Commun. 1998, 14, 1493–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, M.B.; Aleboyeh, H.; Aleboyeh, A. Mineralization of CI Acid Red 14 azo dye by UV/Fe-ZSM5/H2O2 process. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Du, C.; Xiong, Y. FeVO4 as a highly active heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst towards the degradation of Orange II. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.L.T.; Lee, C.; Doyle, F.M.; Sedlak, D.L. A silica-supported iron oxide catalyst capable of activating hydrogen peroxide at neutral pH values. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8930–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, L.; Gonçalves, M.; Guerreiro, M.; Ramalho, T.; Fabris, J.; Pereira, M.; Sapag, K. A new catalyst material based on niobia/iron oxide composite on the oxidation of organic contaminants in water via heterogeneous Fenton mechanisms. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 316, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Goyal, A.; Singhal, S. Nickel-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Efficient catalysts for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and photo-oxidative degradation of toxic dyes. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7959–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Zhou, X.; Wan, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhan, S. Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoplates by succinic acid-assisted hydrothermal route and their photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, A.I.; Samoila, P.; Hulea, V.; Iordan, A.R.; Palamaru, M.N. Effect of Al3+ substituted zinc ferrite on photocatalytic degradation of Orange I azo dye. J. Photochem. Photobio.l A Chem. 2014, 279, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Zinc ferrite nanoparticle as a magnetic catalyst: Synthesis and dye degradation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 4255–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Naik, H.B.; Nagaraju, G.; Viswanath, R.; Rashmi, S. Sugarcane juice mediated eco-friendly synthesis of visible light active zinc ferrite nanoparticles: Application to degradation of mixed dyes and antibacterial activities. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abroshan, E.; Farhadi, S.; Zabardasti, A. Novel magnetically separable Ag3PO4/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite and its high photocatalytic degradation performance for organic dyes under solar-light irradiation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2018, 178, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högfeldt, E. Stability Constants of Metal-Ion Complexes: Part A: Inorganic Ligands; Pergamon Pr.: Oxford, UK, 1982; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Bououdina, M.; Macyk, W.; Shyichuk, O.; Paliychuk, N.; Yaremiy, I.; Al Najar, B.; Pacia, M. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Zn-doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Tian, A.; You, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Fe2SiS4 nanoparticle—A new heterogeneous Fenton reagent. Mater. Lett. 2016, 169, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tian, A.; You, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X. Degradation of organic dyes by a new heterogeneous Fenton reagent-Fe2GeS4 nanoparticle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 353, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Hou, Y. Facile preparation of sphere-like copper ferrite nanostructures and their enhanced visible-light-induced photocatalytic conversion of benzene. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 4216–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, P.; Srinivasan, M.; Velmurugan, S.; Narasimhan, S. Cation distribution and particle size effect on Raman spectrum of CoFe2O4. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, A.; Lassoued, M.S.; Dkhil, B.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Structural, optical and morphological characterization of Cu-doped α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized through co-precipitation technique. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1148, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I.; Blesa, M.A. Photodissolution of iron oxides. IV. A comparative study on the photodissolution of hematite, magnetite, and maghemite in EDTA media. Can. J. Chem. 1992, 70, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhineshbabu, N.; Rajendran, V.; Nithyavathy, N.; Vetumperumal, R. Study of structural and optical properties of cupric oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, Y.; Yaakob, Z.; Akhtar, P. Degradation and mineralization of methylene blue using a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible and solar light irradiation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, G.; Jimmy, C.Y. Enhanced photo-Fenton degradation of rhodamine B using graphene oxide–amorphous FePO4 as effective and stable heterogeneous catalyst. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 448, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
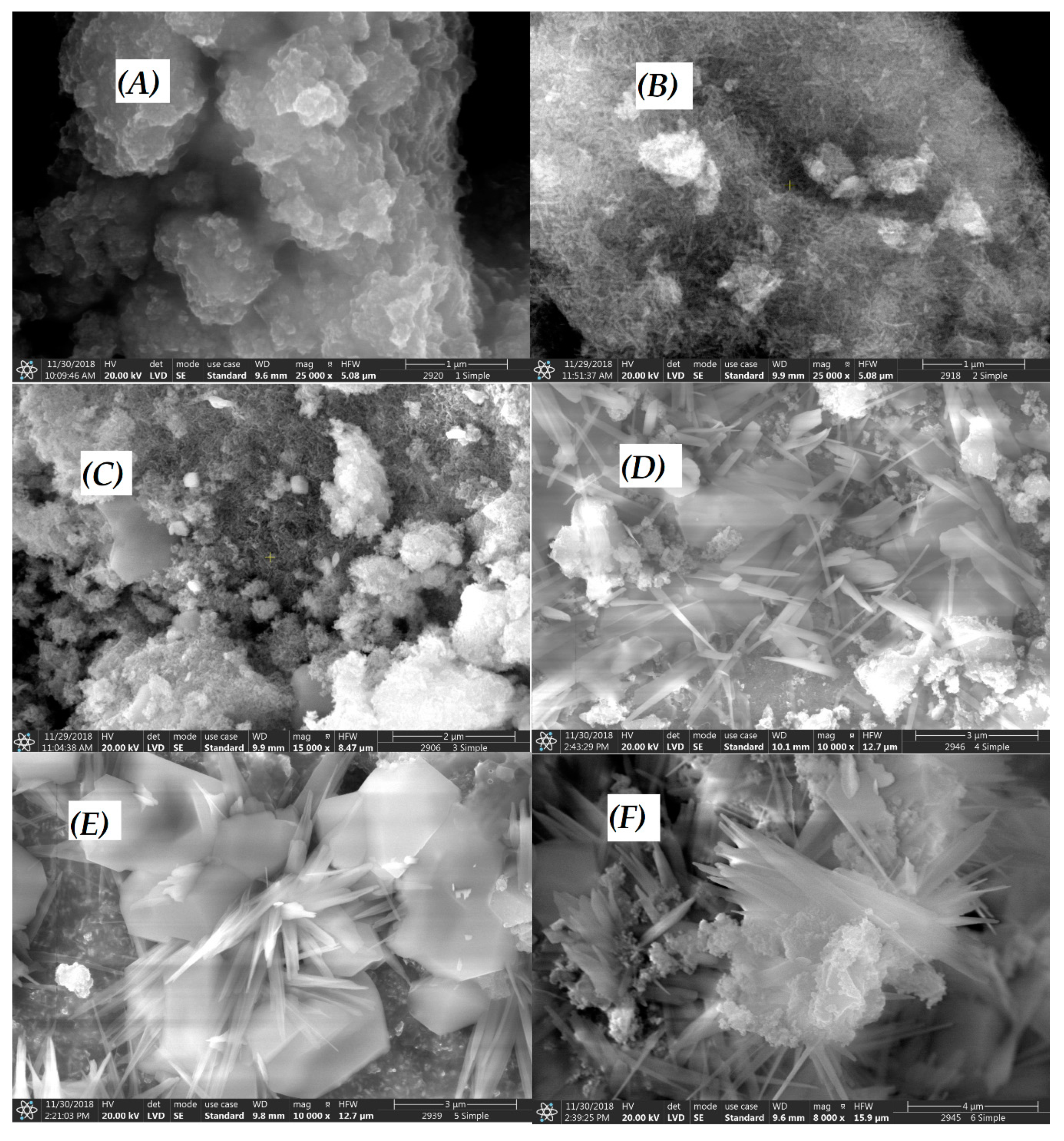
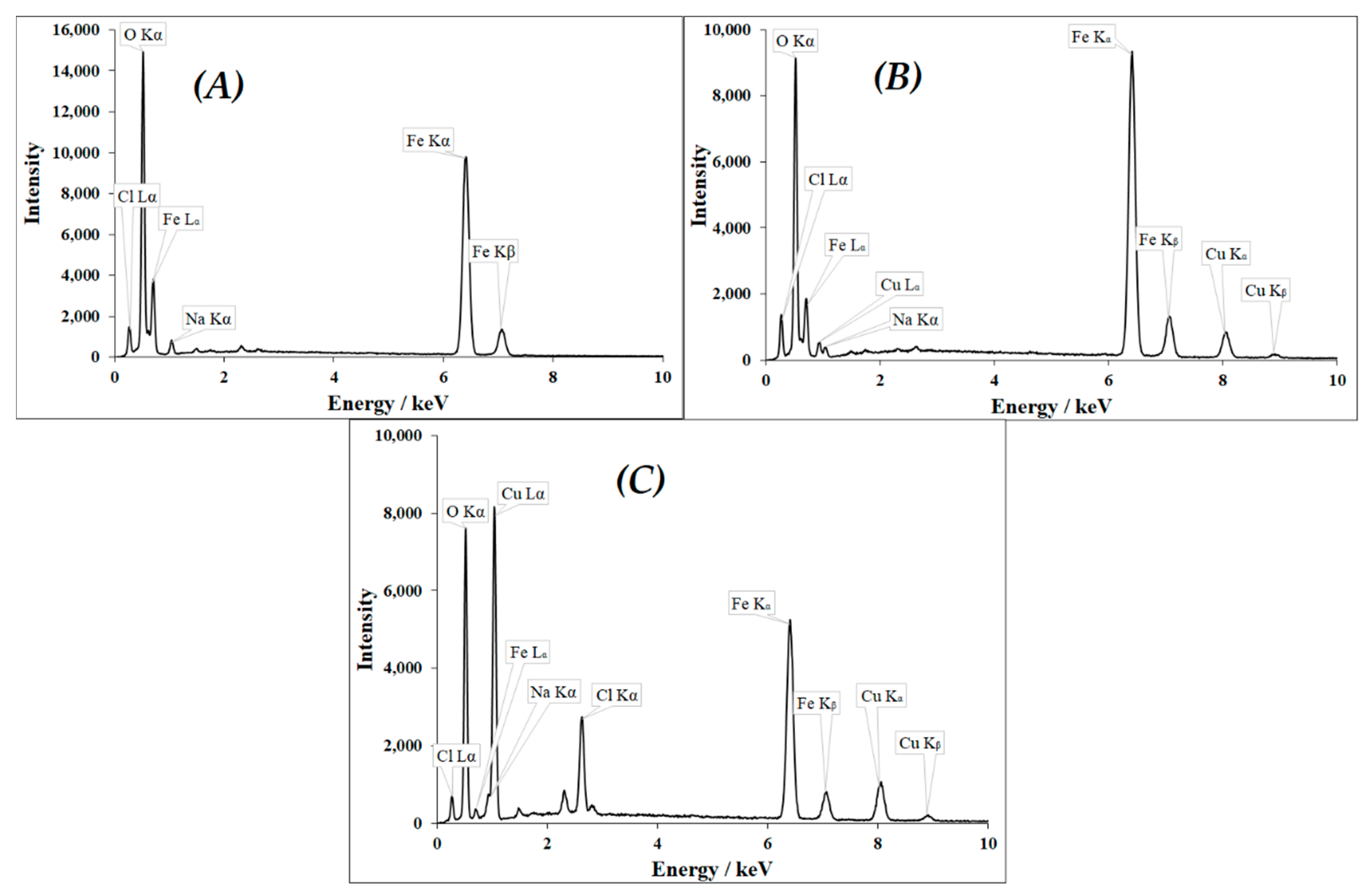
| CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4 | x = 0 | x = 0.2 | x = 0.4 | x = 0.6 | x = 0.8 | x = 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | NP-1 | NP-2 | NP-3 | NP-4 | NP-5 | NP-6 |
| Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2∙6H2O (g) | 1.961 | 1.569 | 1.176 | 0.784 | 0.392 | 0.000 |
| FeCl3∙6H2O (g) | 2.703 | 2.703 | 2.703 | 2.703 | 2.703 | 2.703 |
| CuSO4 (g) | 0.000 | 0.160 | 0.319 | 0.479 | 0.638 | 0.798 |
| Experiment | Reaction Rate (M/s) | Relative Efficiency of Degradation |
|---|---|---|
| MB + NPs + Light | 1.24 × 10−10 | 41.8% |
| MB + Light | 1.13 × 10−10 | 38.3% |
| MB + H2O2 | 2.58 × 10−11 | 8.7% |
| MB + H2O2 + Light | 2.95 × 10−10 | 100.0% (the basis of comparison) |
| MB + NPs + H2O2 + Light | 3.96 × 10−10 | 133.9% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Valicsek, Z.; Horváth, O. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Iron(II) Doped Copper Ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4) as Novel Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalysts. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050921
Khan A, Valicsek Z, Horváth O. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Iron(II) Doped Copper Ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4) as Novel Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalysts. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(5):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050921
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Asfandyar, Zsolt Valicsek, and Ottó Horváth. 2020. "Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Iron(II) Doped Copper Ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4) as Novel Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalysts" Nanomaterials 10, no. 5: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050921
APA StyleKhan, A., Valicsek, Z., & Horváth, O. (2020). Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Iron(II) Doped Copper Ferrites (CuII(x)FeII(1-x)FeIII2O4) as Novel Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalysts. Nanomaterials, 10(5), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050921