Portable Instrument for Hemoglobin Determination Using Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Synthesis of the CDs
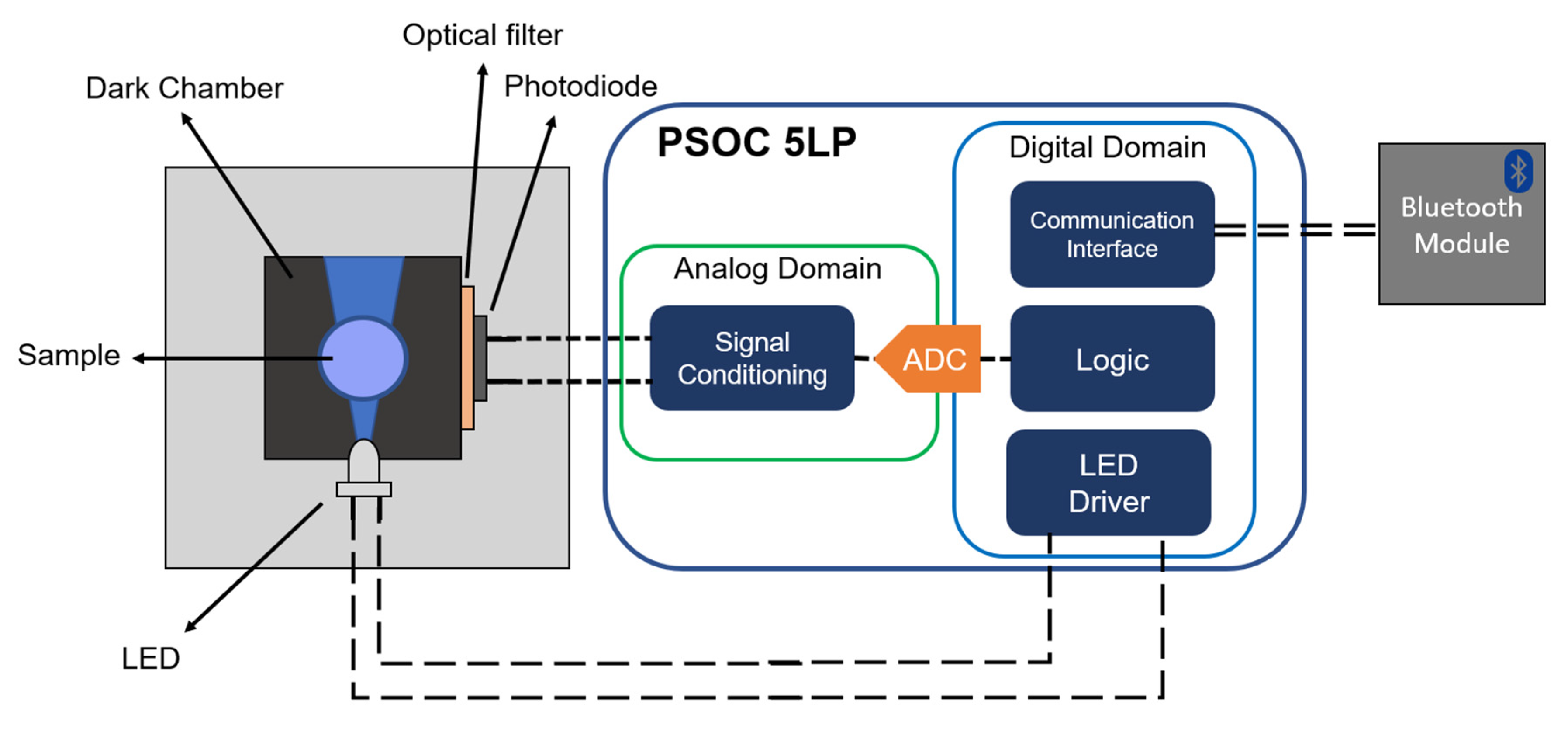
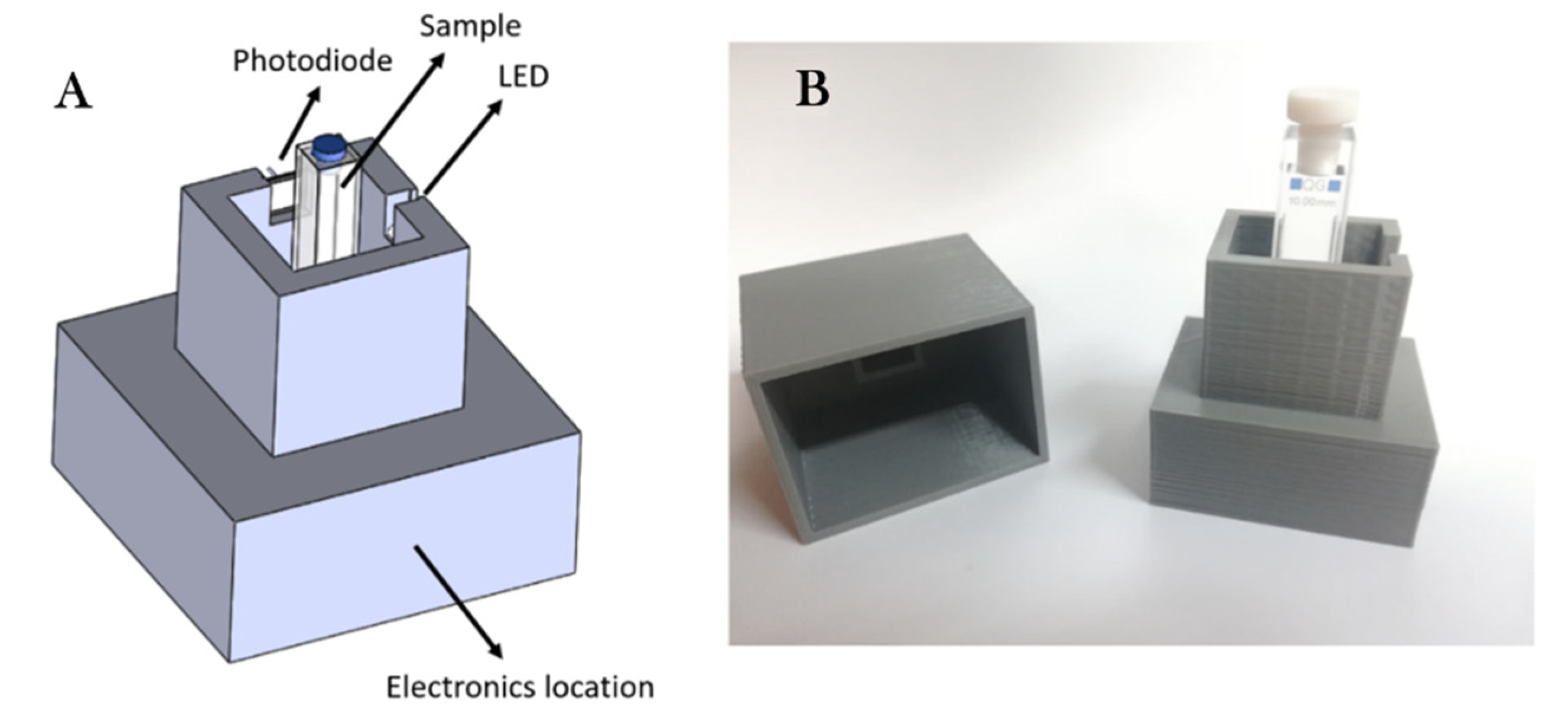
2.4. Measuring Setup for the Portable Device
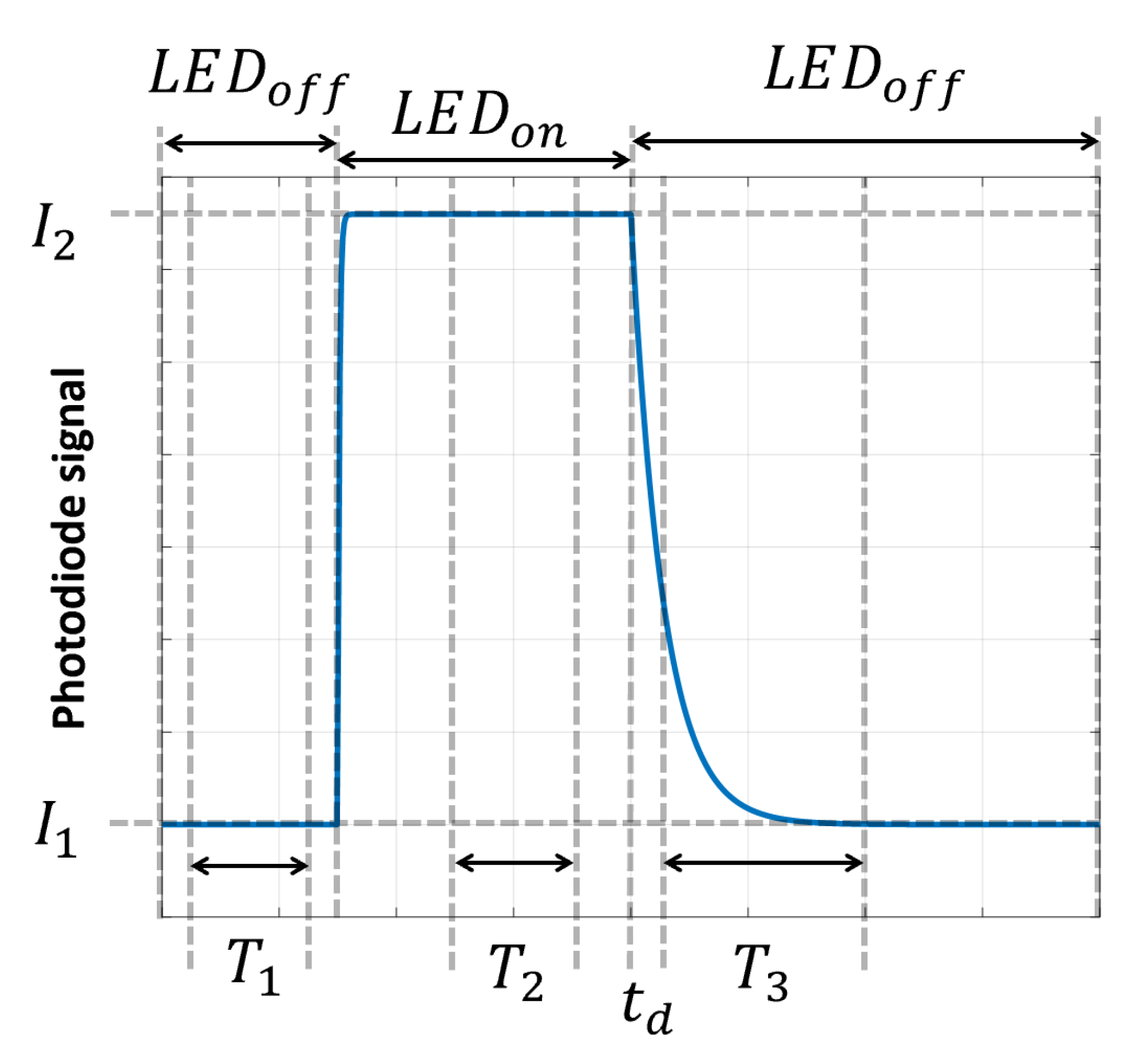
2.5. Measurement Algorithm
2.6. Room-Temperature Phosphorescence Hb Determination
2.7. Real Sample Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
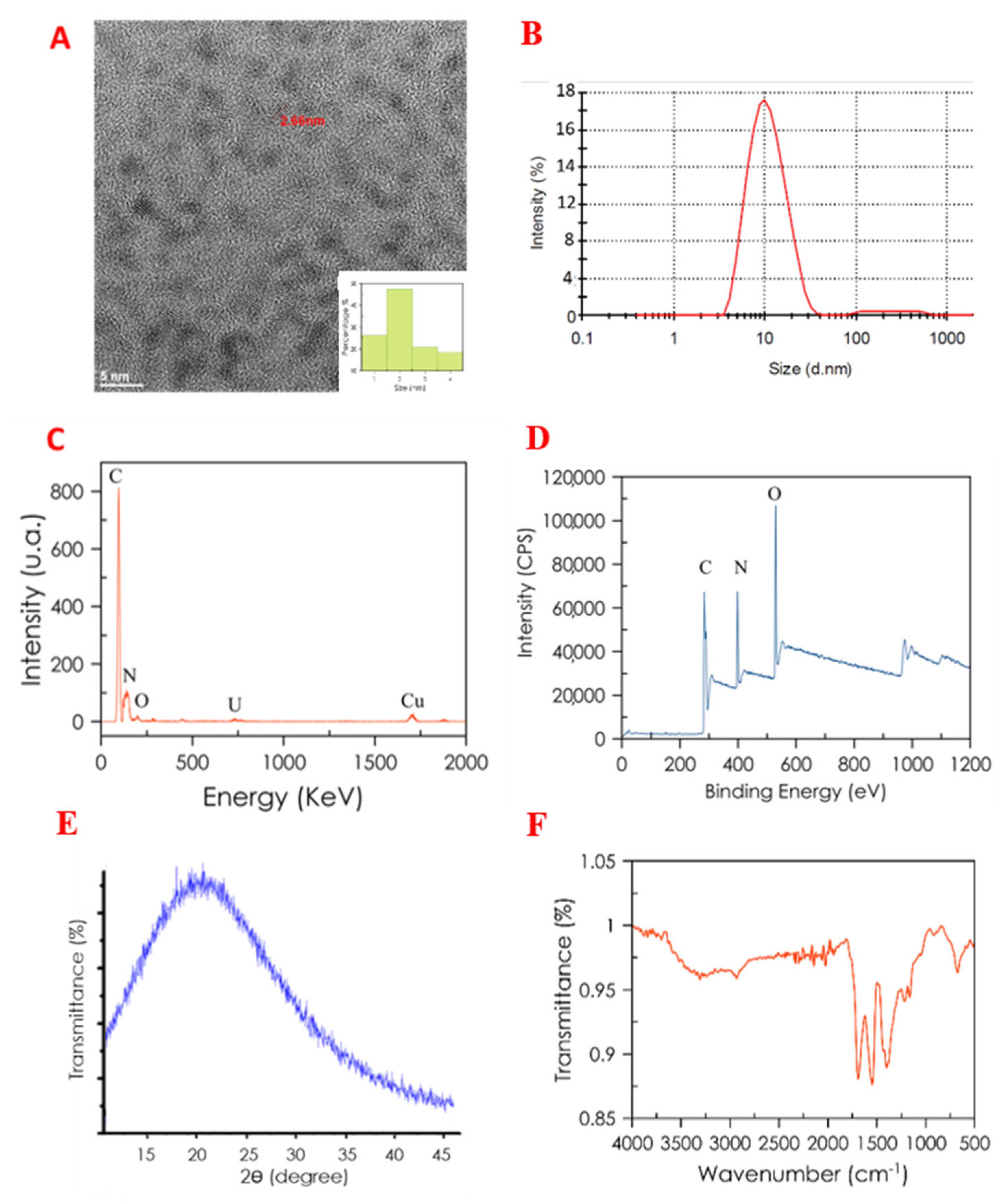
3.1. Carbon Dot Characterization
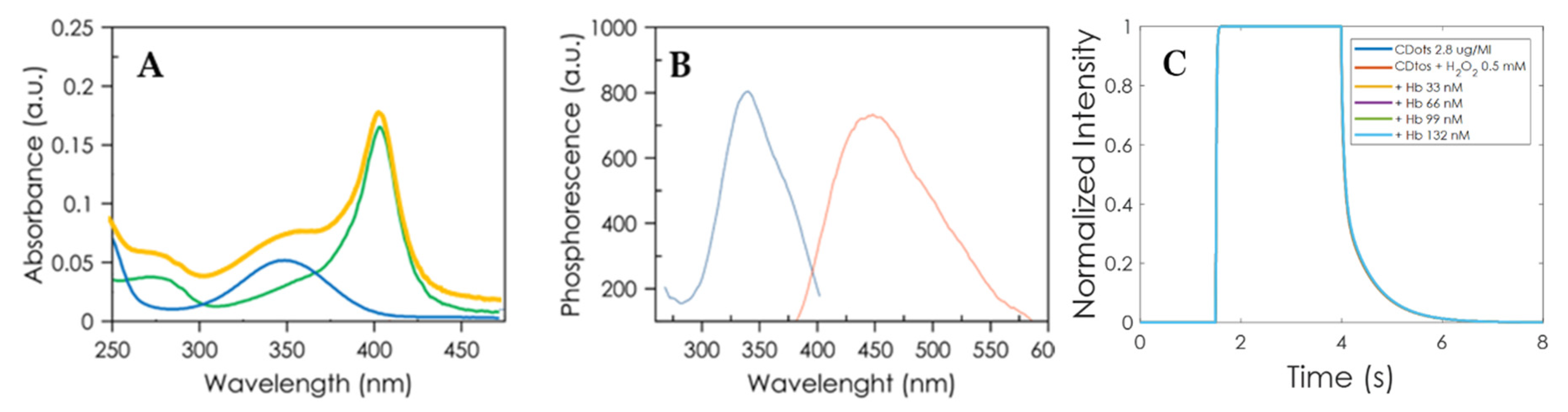
3.2. Optical Properties of the Synthesized CDs
3.3. The Mechanism of Quenching Carbon Dots Luminescence by Hb
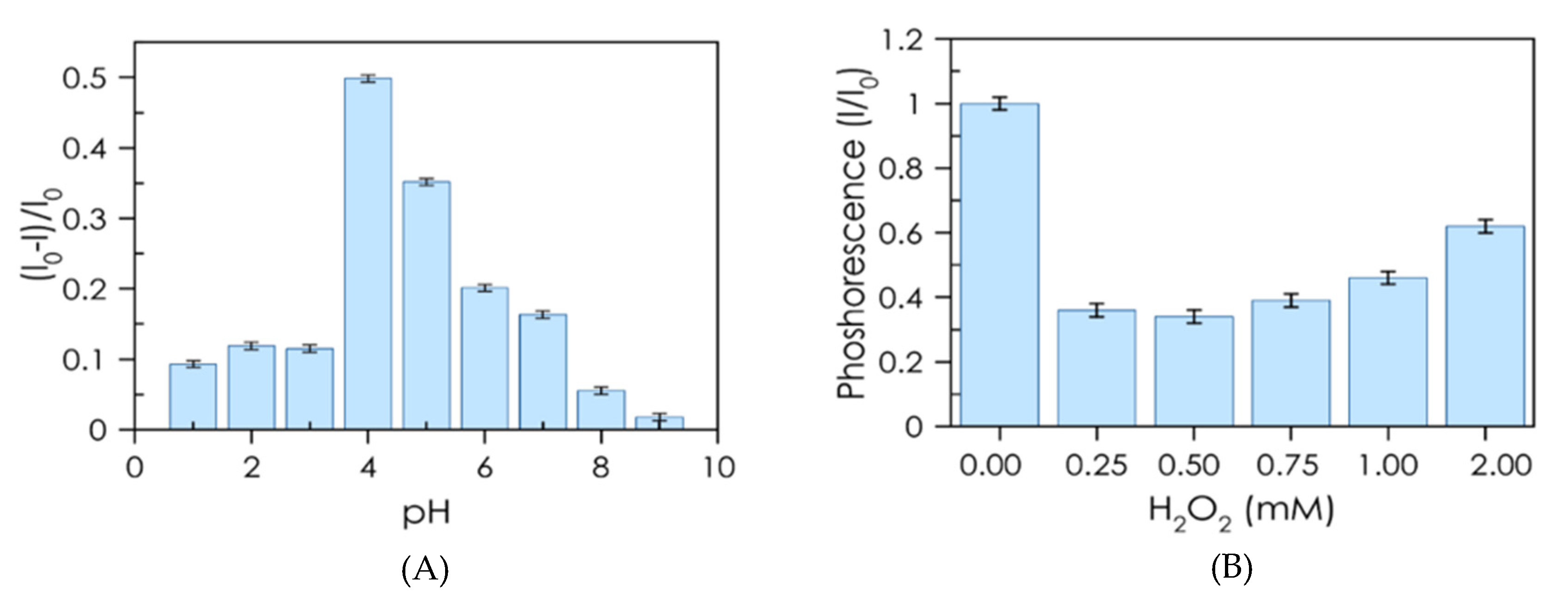
3.4. Assay Optimization
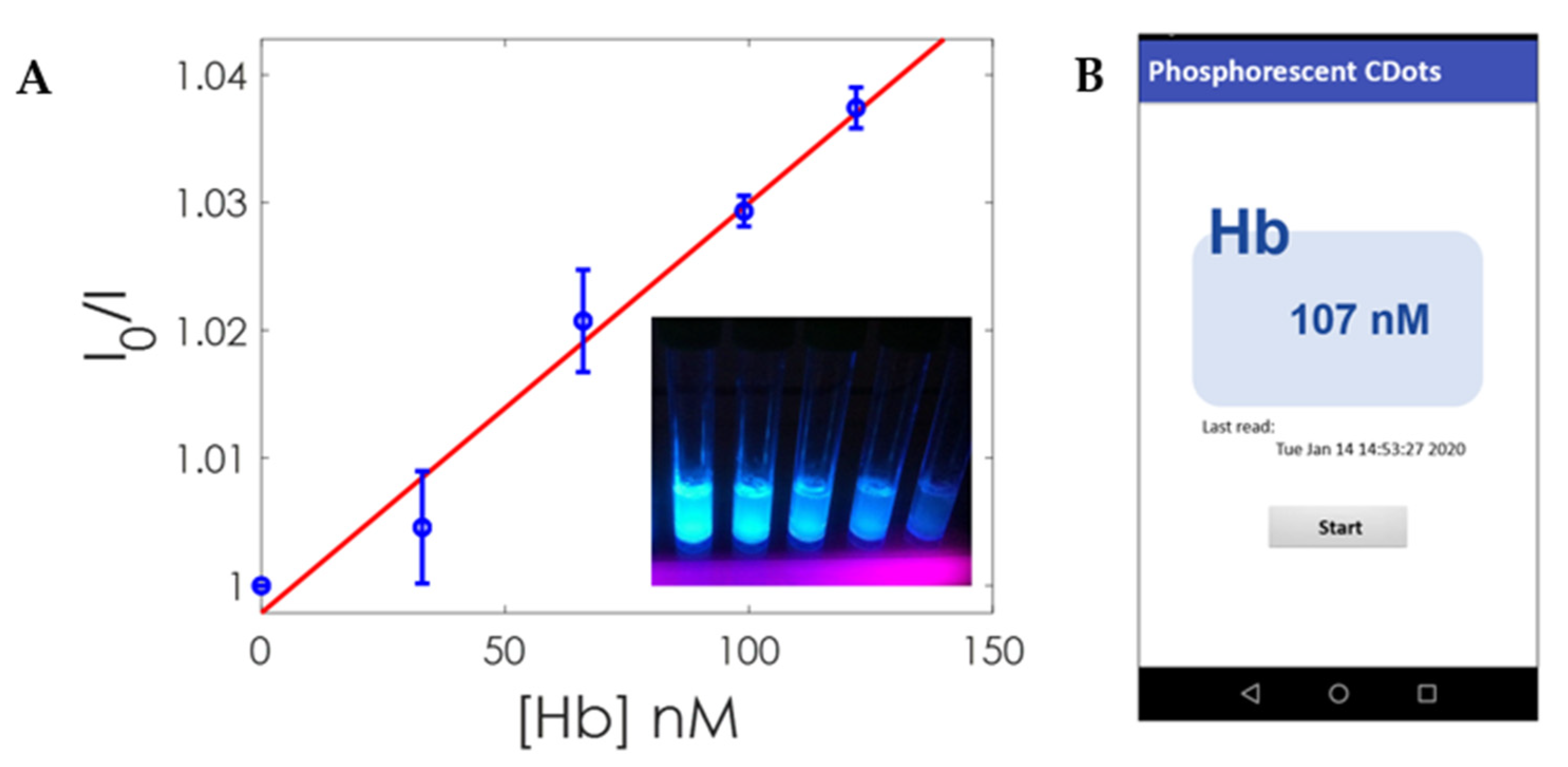
3.5. Prototype Implementation and App Application
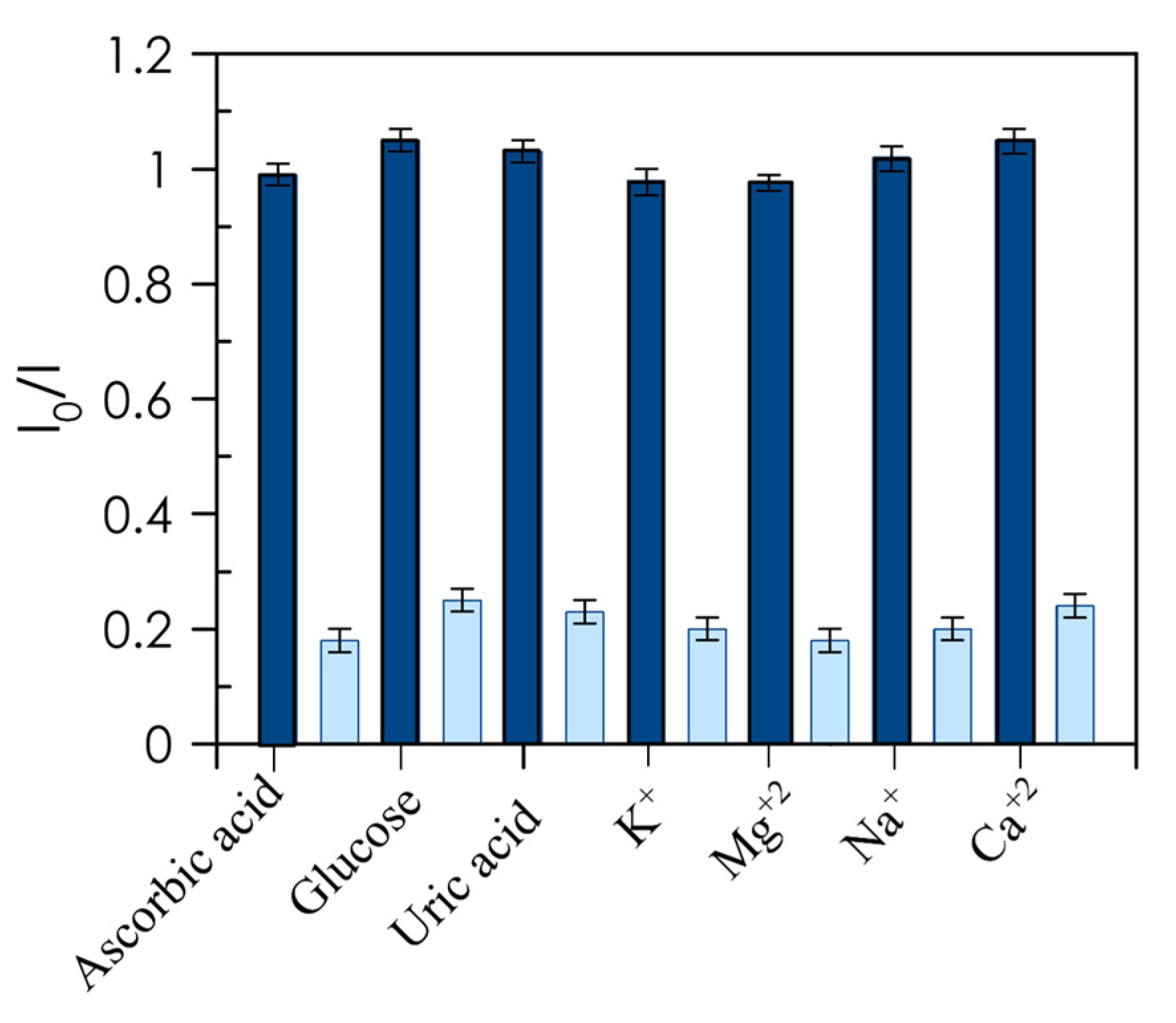
3.6. Interference Study
3.7. Analytical Characterization of the Portable Luminescent Instrumentation
3.8. Application to Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: A review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werle, P.; Slemr, F.; Maurer, K.; Kormann, R.; Mücke, R.; Jänker, B. Near- and mid-infrared laser-optical sensors for gas analysis. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2002, 37, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Castillo, A.; Morales, D.P.; Lapresta-Fernández, A.; Ariza-Avidad, M.; Castillo, E.; Martínez-Olmos, A.; Palma, A.J.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. Evaluation of a reconfigurable portable instrument for copper determination based on luminescent carbon dots. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebsch, G.; Klimant, I.; Frank, B.; Holst, G.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Luminescence Lifetime Imaging of Oxygen, pH, and Carbon Dioxide Distribution Using Optical Sensors. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; Makarona, E.; Botsialas, A.; Salapatas, A.; Oikonomou, P.; Psarouli, A.; Petrou, P.S.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Tukkiniemi, K.; et al. All-silicon monolithic Mach-Zehnder interferometer as a refractive index and bio-chemical sensor. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 26803–26813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulep, T.-H.; Yoon, J.-Y. Challenges in paper-based fluorogenic optical sensing with smartphones. Nano Converg. 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Smartphone-based analytical biosensors. Analyst 2018, 143, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvi, S.; Credi, A. Luminescent sensors based on quantum dot–molecule conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4275–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, C.; Burke, C.S.; MacCraith, B.D. Optical Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 400–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, R.; Holst, G. Frequency-domain fluorescence lifetime imaging system (pco.flim) based on a in-pixel dual tap control CMOS image sensor. SPIE 2015, 9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Holst, G.; Gratton, E. Modulated CMOS camera for fluorescence lifetime microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Sonkusale, S.R. A CMOS Luminescence Intensity and Lifetime Dual Sensor Based on Multicycle Charge Modulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 2018, 12, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.E.; Charbon, E.; Shepard, K.L. A Single-Photon Avalanche Diode Array for Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2008, 43, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassal, P.; Steinberg, M.D.; Steinberg, I.M. Wireless chemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ruiz, N.; Hernández-Bélanger, D.; Carvajal, M.A.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Palma, A.J.; Martínez-Olmos, A. Fast lifetime and amplitude determination in luminescence exponential decays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Golmohammadi, H. Hemoglobin detection using curcumin nanoparticles as a colorimetric chemosensor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Meng, H.; Tu, Y.; Yan, J. A nanocluster-based fluorescent sensor for sensitive hemoglobin detection. Talanta 2017, 170, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Xiao, B.-L.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Ghourchian, H.; Sheibani, N. Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on a functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles nanocomplex-modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors 2013, 13, 8595–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, M.R.; de Jong, A.P.J.M.; Tjaden, U.R.; Irth, H.; van der Greef, J. High-performance liquid chromatography coupled to enzyme-amplified biochemical detection for the analysis of hemoglobin after pre-column biotinylation. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 886, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakata, M.; Hiroshi, O.; Umeko, S. A modification of Van Kampen-Zijlstra’s reagent for the hemiglobincyanide method. Clin. Chim. Acta 1979, 93, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Ternary Emission of a Blue-, Green-, and Red-Based Molecular Imprinting Fluorescence Sensor for the Multiplexed and Visual Detection of Bovine Hemoglobin. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6561–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Yang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Nakanishi, T.; Lu, C.; He, Y. Highly fluorescent polyethyleneimine protected Au8 nanoclusters: One-pot synthesis and application in hemoglobin detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Lu, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Redfern, S.A.T.; Song, Y.; Feng, T.; Xu, W.; Yang, B. Design of Metal-Free Polymer Carbon Dots: A New Class of Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, F.; Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X. The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Aminophenol-based carbon dots with dual wavelength fluorescence emission for determination of heparin. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J. Carbon Dots-in-Matrix Boosting Intriguing Luminescence Properties and Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1805504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, M.A.; Ballesta-Claver, J.; Morales, D.P.; Palma, A.J.; Valencia-Mirón, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Portable reconfigurable instrument for analytical determinations using disposable electrochemiluminescent screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, F.J.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Toral, V.; Castillo, E.; García-Ruiz, F.; Morales, D.P.; Rodriguez, N. Design guidelines of laser reduced graphene oxide conformal thermistor for IoT applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 274, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Reyes-Berbel, E.; Ortiz-Gomez, I.; Ortega-Muñoz, M.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Carbon dots-inspired fluorescent cyclodextrins: Competitive supramolecular “off–on” (bio)sensors. Nanoscale 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakard, S.; Herlem, G.; Lakard, B.; Fahys, B. Theoretical study of the vibrational spectra of polyethylenimine and polypropylenimine. J. Mol. Struct.: THEOCHEM 2004, 685, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, A.; Shamsipur, M.; Abdollahi, H. Hemoglobin detection using carbon dots as a fluorescence probe. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Chen, J.-L.; Su, M.-X.; Yan, F.; Li, B.; Di, B. Phosphate-containing metabolites switch on phosphorescence of ferric ion engineered carbon dots in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 22318–22323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.R.; Winfield, S.A.; Miller, J.N. Relative fluorescence quantum yields using a computer-controlled luminescence spectrometer. Analyst 1983, 108, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Dong, S. Design of Fluorescent Assays for Cyanide and Hydrogen Peroxide Based on the Inner Filter Effect of Metal Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhen, M.; Chen, D.; Ge, J.; Mao, L.; Wang, C.; Shu, C. G-quadruplex DNAzymes-induced highly selective and sensitive colorimetric sensing of free heme in rat brain. Analyst 2014, 139, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegorova, A.V.; Leonenko, I.I.; Aleksandrova, D.I.; Scrypynets, Y.V.; Antonovich, V.P.; Ukrainets, I.V. Novel Luminescent Probe Based on a Terbium(III) Complex for Hemoglobin Determination. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2014, 81, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhan, G.; Li, C. Facile synthesis of N-acetyl-l-cysteine capped CdHgSe quantum dots and selective determination of hemoglobin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Xie, J.; Su, W.; Sheng, J.; Xiao, Q. A carbon dots based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of hemoglobin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, K.; Yu, Y.; Ruan, X.; Wei, Y. One-pot synthesis of highly fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for sensitive and selective detection of hemoglobin. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Materials | Linear Range (nM) | LOD (nM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetry | Curcumin nanoparticles | 15.5–620 | 1.55 | [16] |
| Colorimetry | G-quadrupolex DNAzymes | 1–120 | 0.64 | [36] |
| Fluorimetry | Molecular Imprinting Polymers | 25–3000 | 7.8 | [21] |
| Fluorimetry | Terbium complexes | 9–540 | 3 | [37] |
| Fluorimetry | CdHgSe QDs | 4–440 | 2 | [38] |
| Fluorimetry | CDs | 1–4000 | 0.12 | [39] |
| Fluorimetry | BSA-AuNCs | 1–250 | 0.36 | [17] |
| Fluorimetry | AuNCs | 10–2000 | 5 | [22] |
| Fluorimetry | Silicon nanoparticles | 50–4000 | 40.0 | [40] |
| RTP | CDs | 19–125 | 6.2 | This work |
| Samples | Concentration of Hb | Recovery % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected (µM) | Blood (mM) | Added (µM) | Recovered (µM) | ||
| Volunteer 1 | 0.050 | 10.500 | 0.040 | 0.052 | 93.6 |
| 0.080 | 0.085 | 105.9 | |||
| Volunteer 2 | 0.045 | 9.450 | 0.040 | 0.038 | 95.0 |
| 0.080 | 0.087 | 108.4 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murru, F.; Romero, F.J.; Sánchez-Mudarra, R.; García Ruiz, F.J.; Morales, D.P.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Salinas-Castillo, A. Portable Instrument for Hemoglobin Determination Using Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050825
Murru F, Romero FJ, Sánchez-Mudarra R, García Ruiz FJ, Morales DP, Capitán-Vallvey LF, Salinas-Castillo A. Portable Instrument for Hemoglobin Determination Using Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(5):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050825
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurru, Fabio, Francisco J. Romero, Roberto Sánchez-Mudarra, Francisco J. García Ruiz, Diego P. Morales, Luis Fermín Capitán-Vallvey, and Alfonso Salinas-Castillo. 2020. "Portable Instrument for Hemoglobin Determination Using Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots" Nanomaterials 10, no. 5: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050825
APA StyleMurru, F., Romero, F. J., Sánchez-Mudarra, R., García Ruiz, F. J., Morales, D. P., Capitán-Vallvey, L. F., & Salinas-Castillo, A. (2020). Portable Instrument for Hemoglobin Determination Using Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials, 10(5), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050825







