Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Modified with Polythiophene: Applications to Mercuric Ions Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Adsorbents Preparation
2.2.1. Synthesis of CuFe2O4
2.2.2. Synthesis of CuFe2O4@Polythiophene Composite
2.3. Adsorption Techniques
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5. Impact of Hg(II) Solution pH
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
2.7. Regeneration of CuFe2O4@Polythiophene Composite
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of CuFe2O4 and CuFe2O4@Polythiophene Composite
3.1.1. X-Ray diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.1.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis (FESEM) before and after Adsorption
3.1.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
3.1.4. Surface Area and Pore Structure
3.2. Adsorption Studies
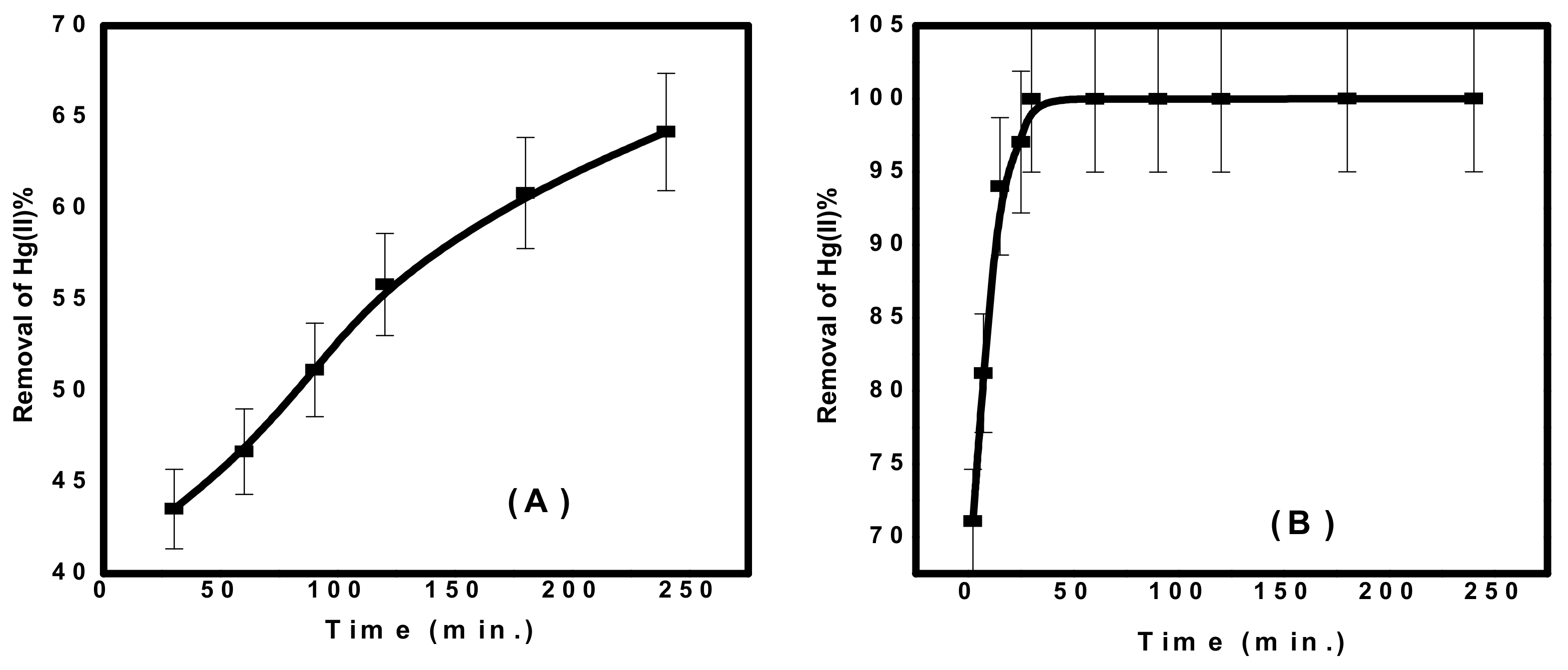
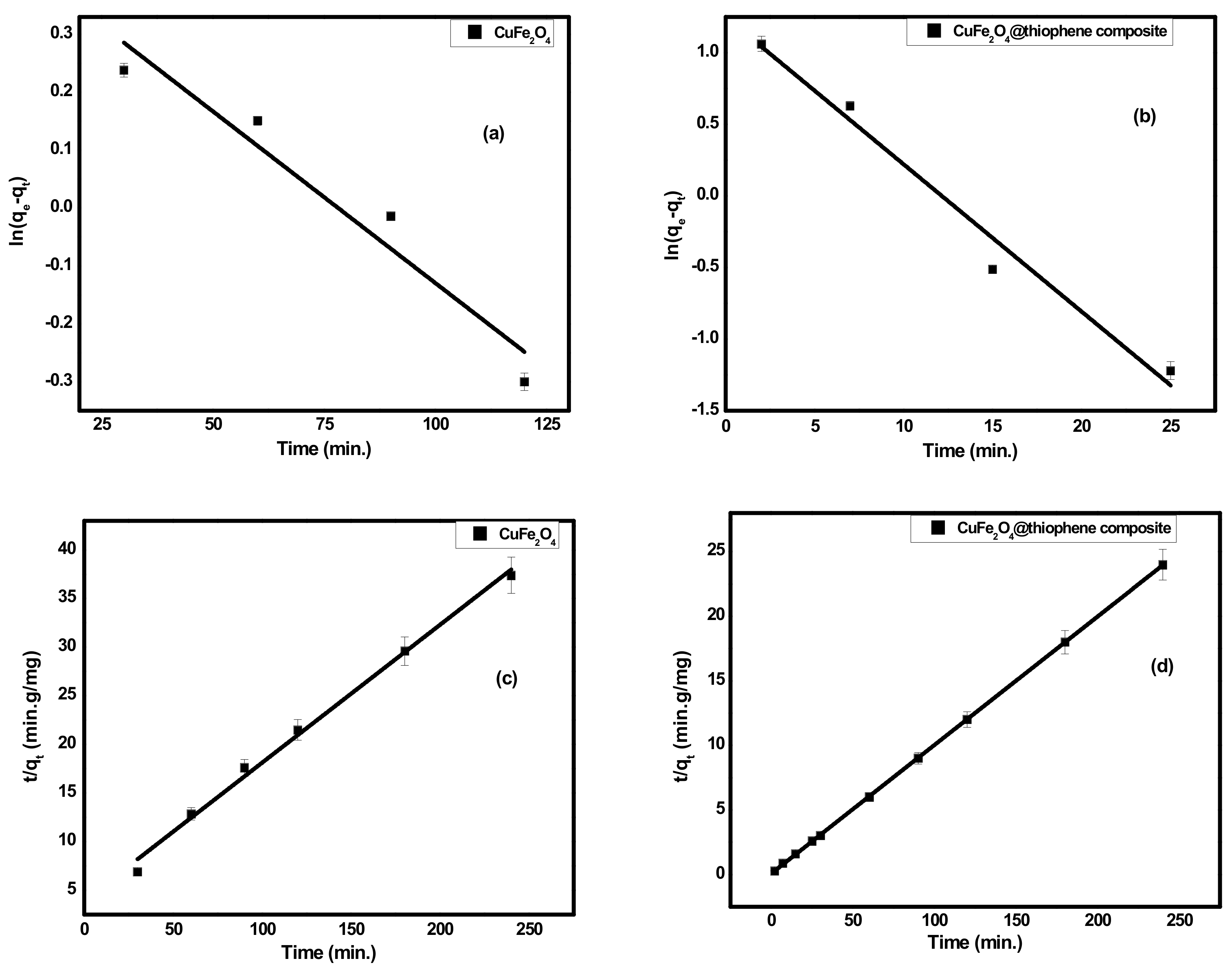
3.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics
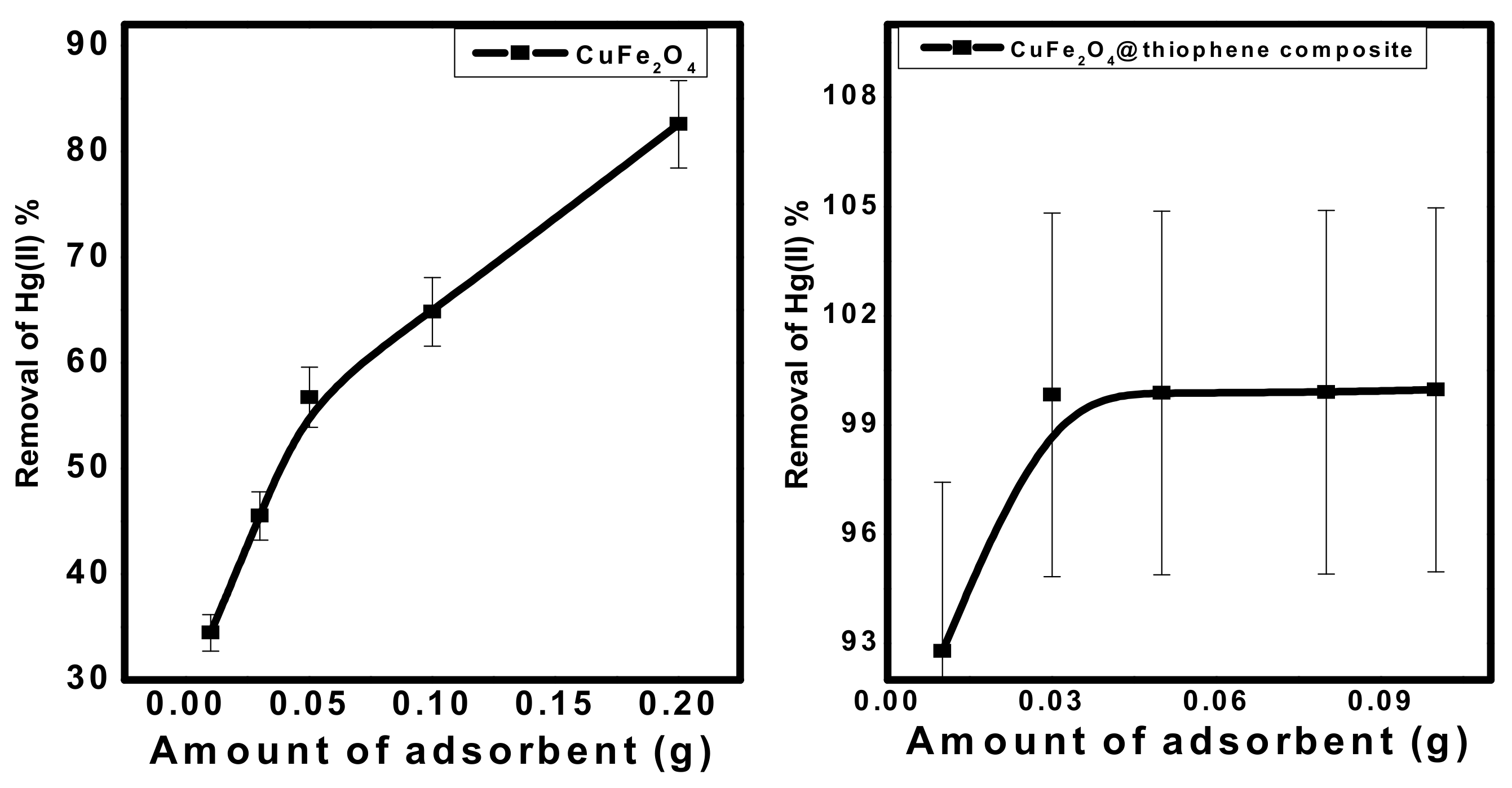
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
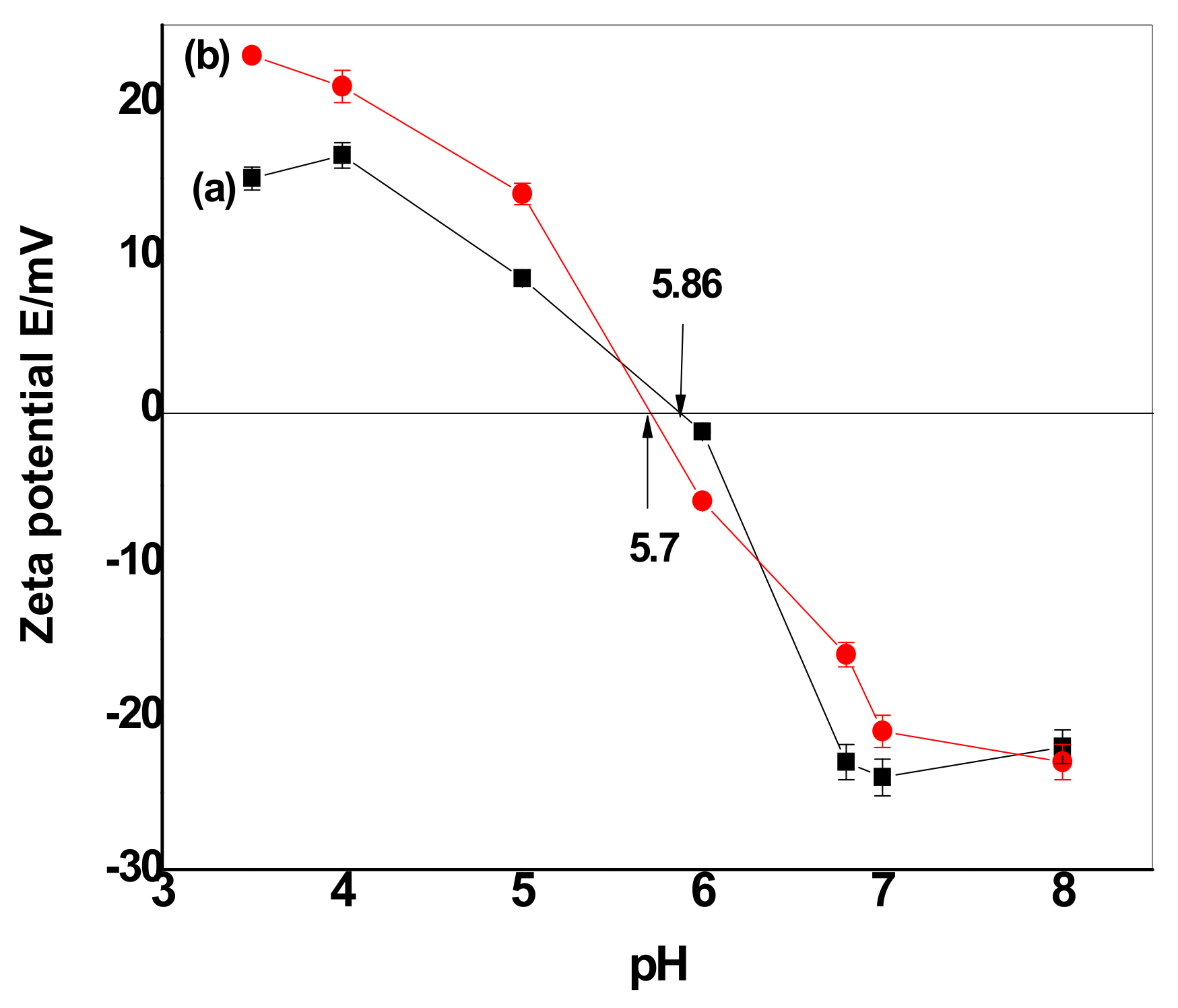
3.2.3. Effect of pH
3.2.4. Effect of Initial Concentration of Hg(II) Solutions
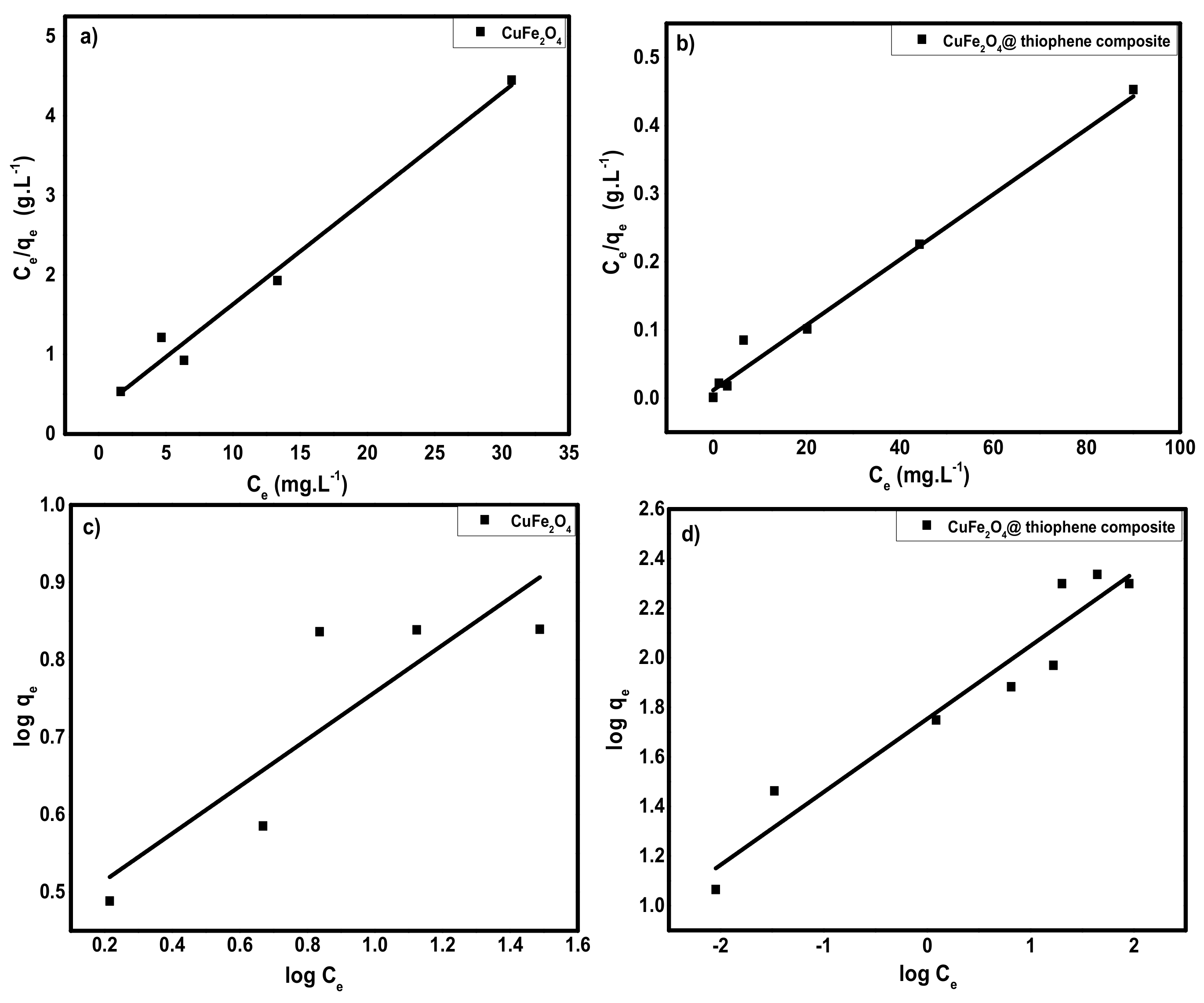
3.2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
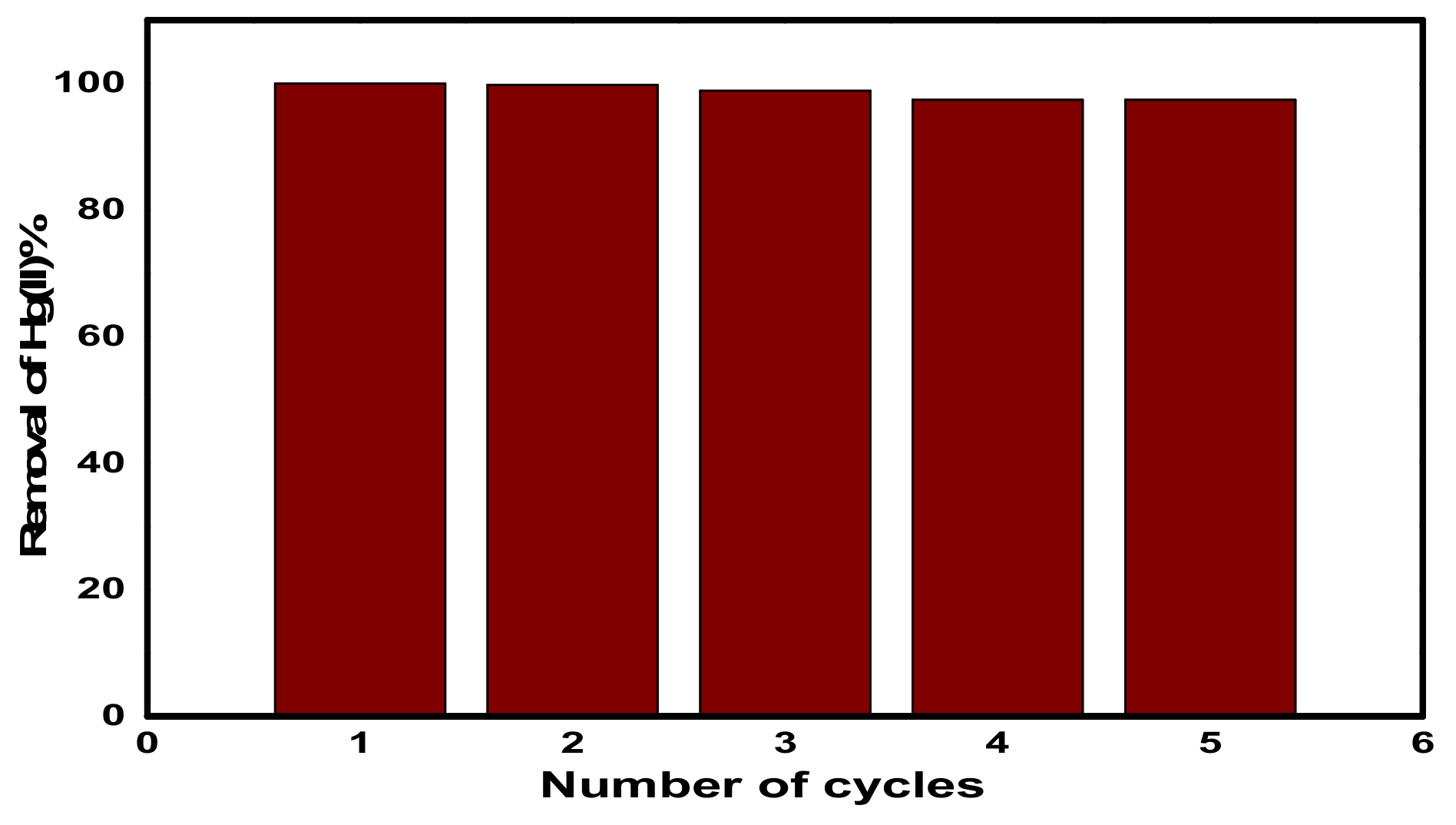
3.2.6. Reusability of CuFe2O4@Polythiophene Composite
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Huq, A.K.O.; Yahya, R.B. The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14778–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.T.; Chung, P.Y.; Tsang, H.C.; Tang, J.O.; Cheng, G.Y.M.; Gambari, R.; Chui, C.H.; Lam, K.H. Preparation and characterization of bio-safe activated charcoal derived from coffee waste residue and its application for removal of lead and copper ions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38839–38847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Luo, X. Facile preparation of a novel Hg(II)-ion-imprinted polymer based on magnetic hybrids for rapid and highly selective removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14916–14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Contamination of heavy metals in aquatic media: Transport, toxicity and technologies for remediation. In Heavy Metals in Water: Presence, Removal and Safety; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.; Murthy, Z.V.P.; Jha, B. Sorption of Hg(II) onto Carica papaya: Experimental studies and design of batch sorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Sommar, J.; Wang, S. A review of studies on atmospheric mercury in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Xing, Y.; Shang, L. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caner, N.; Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Adsorption characteristics of mercury(II) ions from aqueous solution onto chitosan-coated diatomite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on Hg(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by silica-multiwall carbon nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16721–16731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A.; Shamsuddeen, A.A. Response surface methodology optimization of adsorptive desulfurization on nickel/activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A. Effects of bimetallic Ce/Fe nanoparticles on the desulfurization of thiophenes using activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Du, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Removal of mercury(II) from wastewater by polyvinylamine-enhanced ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Techn. 2015, 154, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Mercury sorption by silica/carbon nanotubes and silica/activated carbon: A comparison study. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2015, 64, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Nanocomposite of carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles and their use for adsorption of Pb(II): From surface properties to sorption mechanism. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10730–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Naeemullah; Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Polyethylenimine modified activated carbon as novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of uranium from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 117, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.A.; Naeemullah; Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Chitosan-modified vermiculite for As(III) adsorption from aqueous solution: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. A strategy for integrating basic concepts of nanotechnology to enhance undergraduate nano-education: Statistical evaluation of an application study. J. Nano Educ. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Younesi, H.; Ghoreyshi, A.A.; Bahramifar, N.; Heidari, A. Thiol-incorporated activated carbon derived from fir wood sawdust as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of mercury ion: Batch and fixed-bedcolumn studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 100, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Elserw, M.I.A. Development of microwave-assisted functionalized nanosilicas for instantaneous removal of heavy metals. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Elserw, M.I.A. Fast microwave-assisted sorption of heavy metals on the surface of nanosilica-functionalized-glycine and reduced glutathione. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Elserw, M.I.A. Efficient and fast microwave sorption of heavy metals on nanosilica sorbents-microwave immobilized-vitamin C and vitamin L1. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Hassan, A.A.; Amr, A.E.; Abd El-Naby, H.; Elsayed, E.A. A SnO2/CeO2nano-composite catalyst for alizarin dye removal from aqueous solutions. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaeigohar, S. The Nanosized Dye Adsorbents for Water Treatment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Botcha, N.K.; Zarie, E.S.; Elbahri, M. Ups and downs of water photodecolorization by nanocomposite polymer nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. An amphiphilic, graphitic buckypaper capturing enzyme biomolecules from water. Water 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and soft acids and bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H. Preparation and characterization of innovative selective imprinted polymers for the removal of hazardousmercury compounds from aqueous solution. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons-a comparative study. Dyes Pigments 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, B.; Ghorbani, M.; Salehi, M.A. Application of polyrhodanine modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes for high efficiency removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


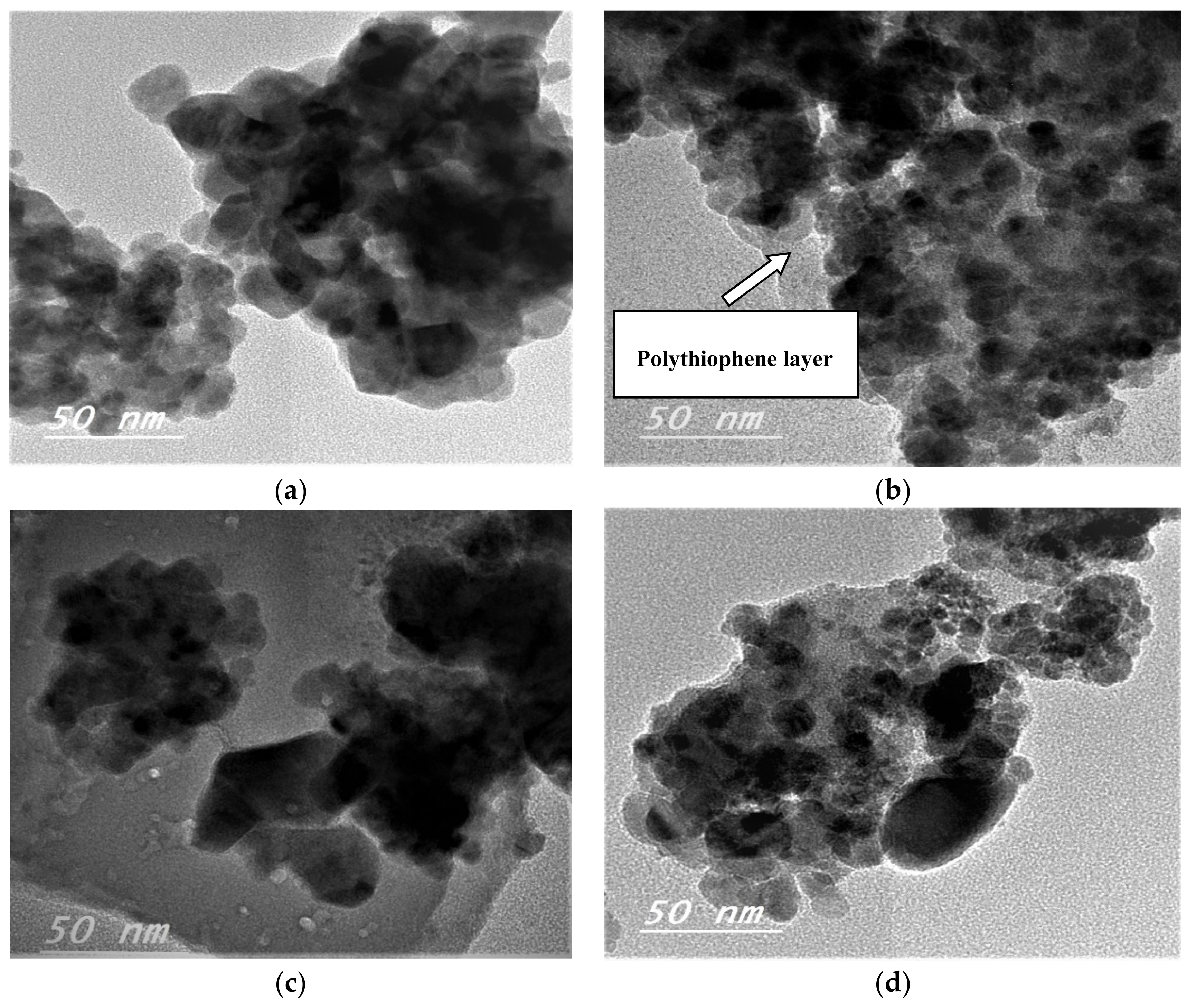

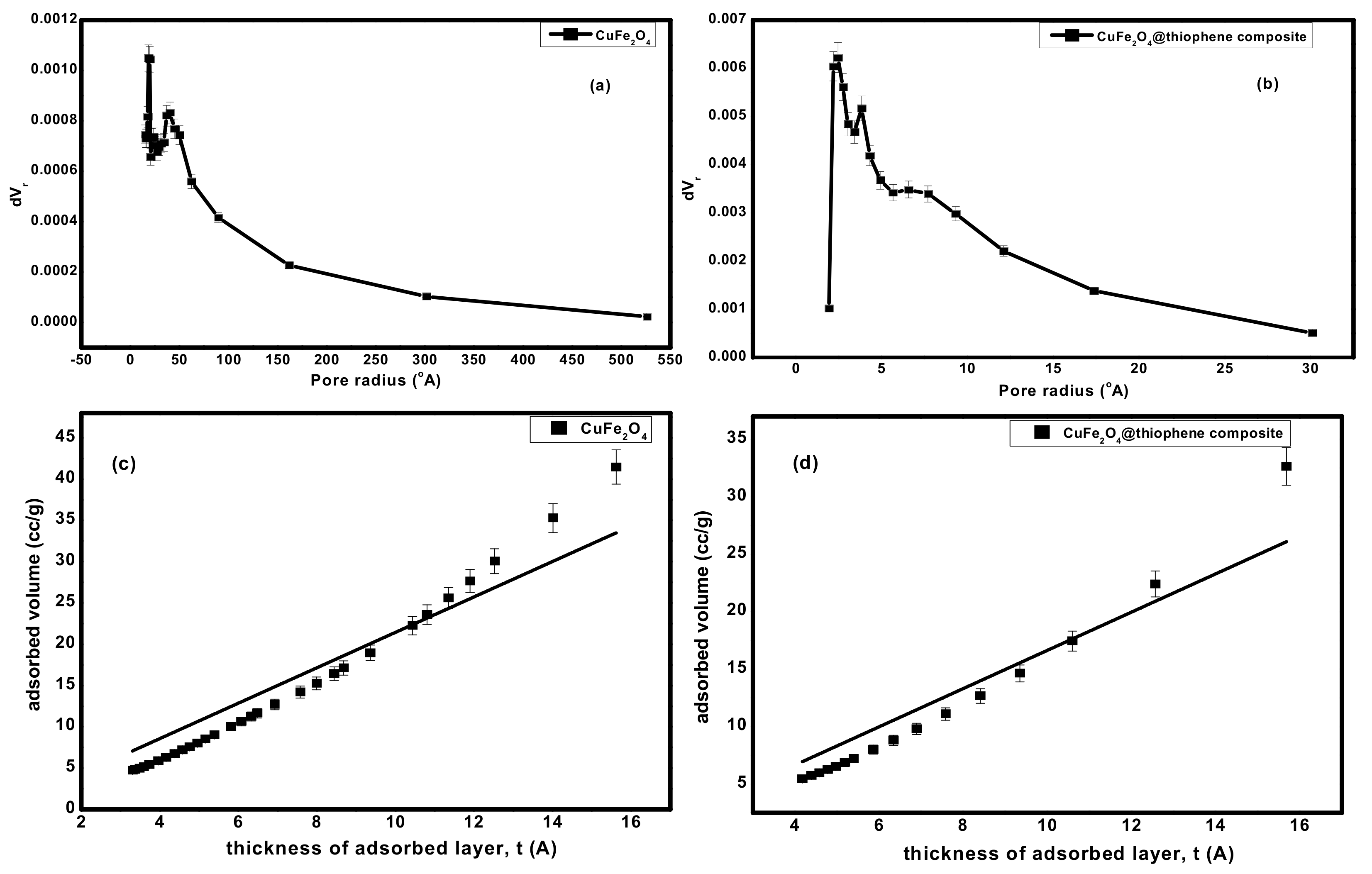



| Sample | * Surface Area (m2·g−1) | * Average Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | * Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuFe2O4 | 34.1 ± 2.3 | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 2.46 ± 0.3 |
| CuFe2O4@Polythiophene composite | 30.9 ± 1.5 | 0.06 ± 0.003 | 1.85 ± 0.2 |
| Adsorbent | Pseudo-First Order | Second Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe1 (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/(mg·min)) | qe2 (mg/g) | qeexp | R2 | |
| CuFe2O4 | 0.00593 | 1.5896 | 0.91 | 5.12 × 10−3 | 6.0837 | 7.0452 | 0.993 |
| CuFe2O4@Polythiophene composite | 0.10287 | 3.4878 | 0.968 | 0.1273 | 9.9978 | 10.046 | 1 |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | b (1/mg) | R2 (n = 5) | KF (mg(n−1)/nL1/ng−1) | n | R2 (n = 5) | |
| CuFe2O4 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | 0.438 | 0.979 | 2.845 | 3.29 | 0.661 |
| CuFe2O4@Polythiophene composite | 208.7 ± 2.5 | 0.417 | 0.982 | 56.724 | 3.39 | 0.919 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
H. Kamel, A.; Hassan, A.A.; Amr, A.E.-G.E.; El-Shalakany, H.H.; A. Al-Omar, M. Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Modified with Polythiophene: Applications to Mercuric Ions Removal. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030586
H. Kamel A, Hassan AA, Amr AE-GE, El-Shalakany HH, A. Al-Omar M. Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Modified with Polythiophene: Applications to Mercuric Ions Removal. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030586
Chicago/Turabian StyleH. Kamel, Ayman, Amr A. Hassan, Abd El-Galil E. Amr, Hadeel H. El-Shalakany, and Mohamed A. Al-Omar. 2020. "Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Modified with Polythiophene: Applications to Mercuric Ions Removal" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030586
APA StyleH. Kamel, A., Hassan, A. A., Amr, A. E.-G. E., El-Shalakany, H. H., & A. Al-Omar, M. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Modified with Polythiophene: Applications to Mercuric Ions Removal. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030586








