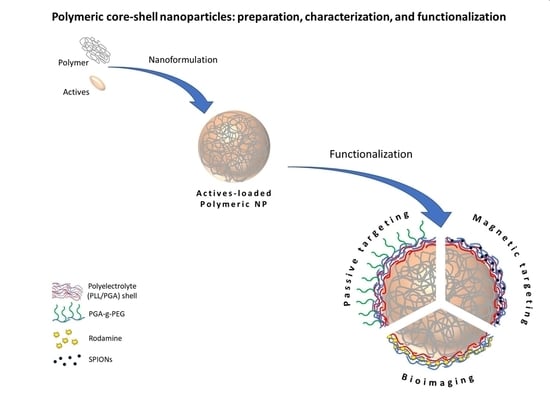
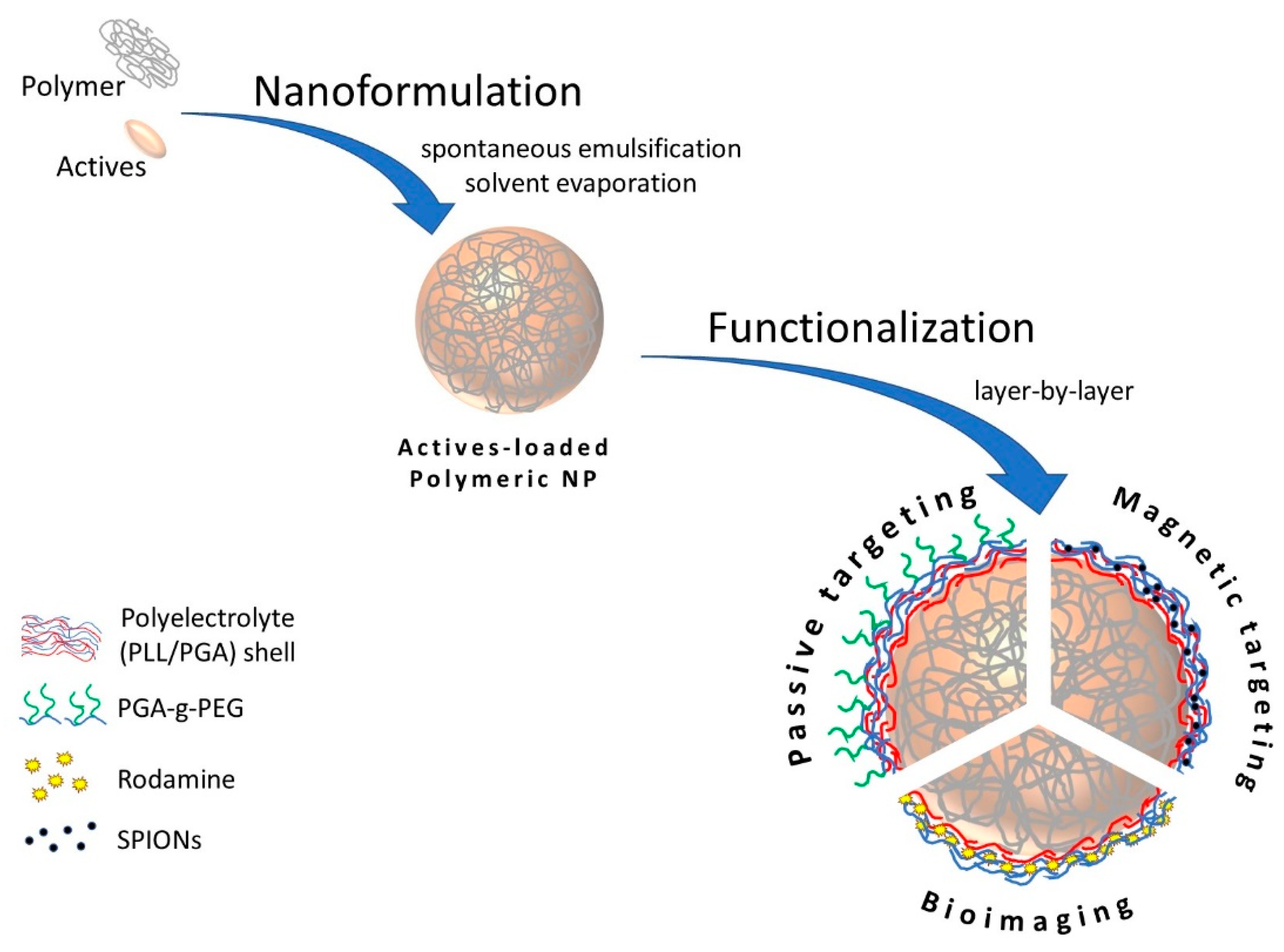
Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles’ Preparation
2.3. Drug Encapsulation and Efficiency of Encapsulation (EE)
2.4. Modification and Functionalization—Formation of Polymeric Core-Multilayer Polyelectrolyte Shell Nanoparticles
2.5. Nanoparticles’ Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
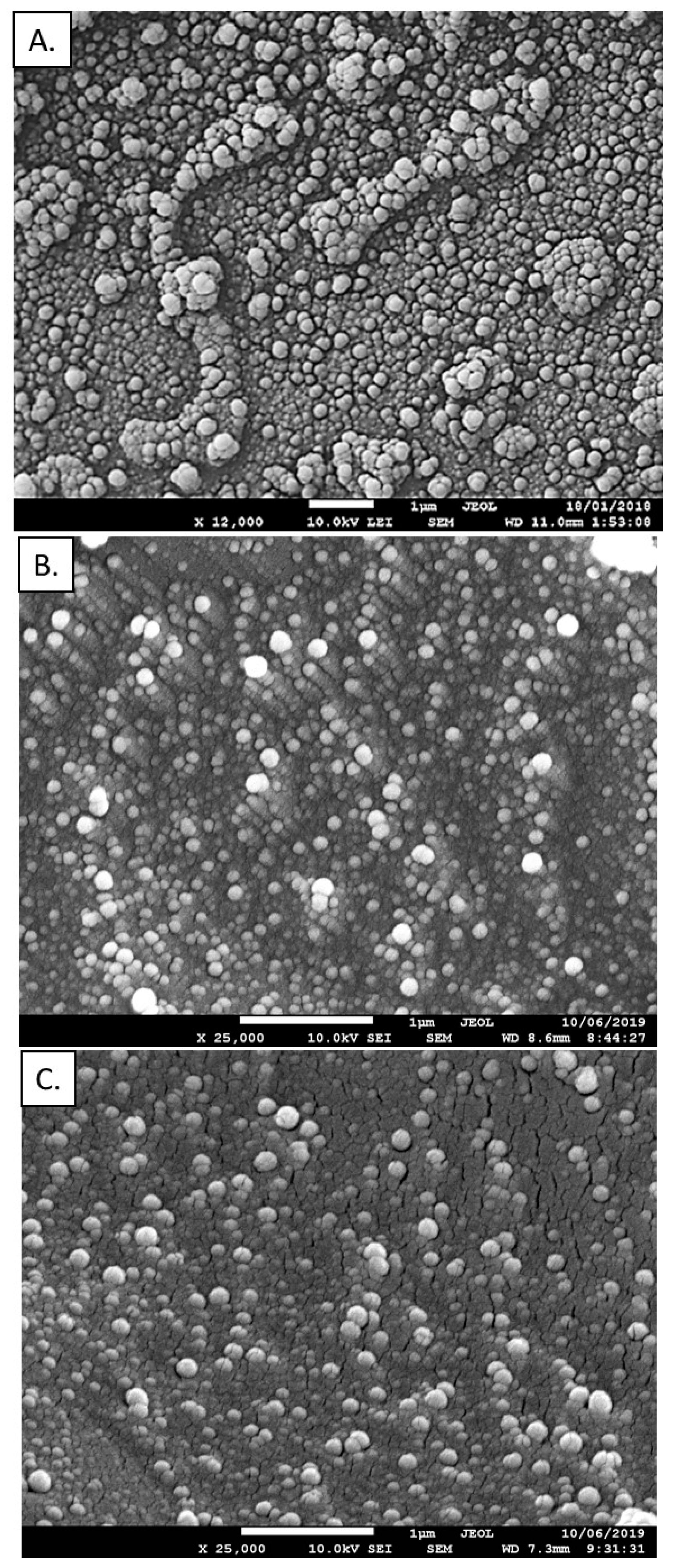
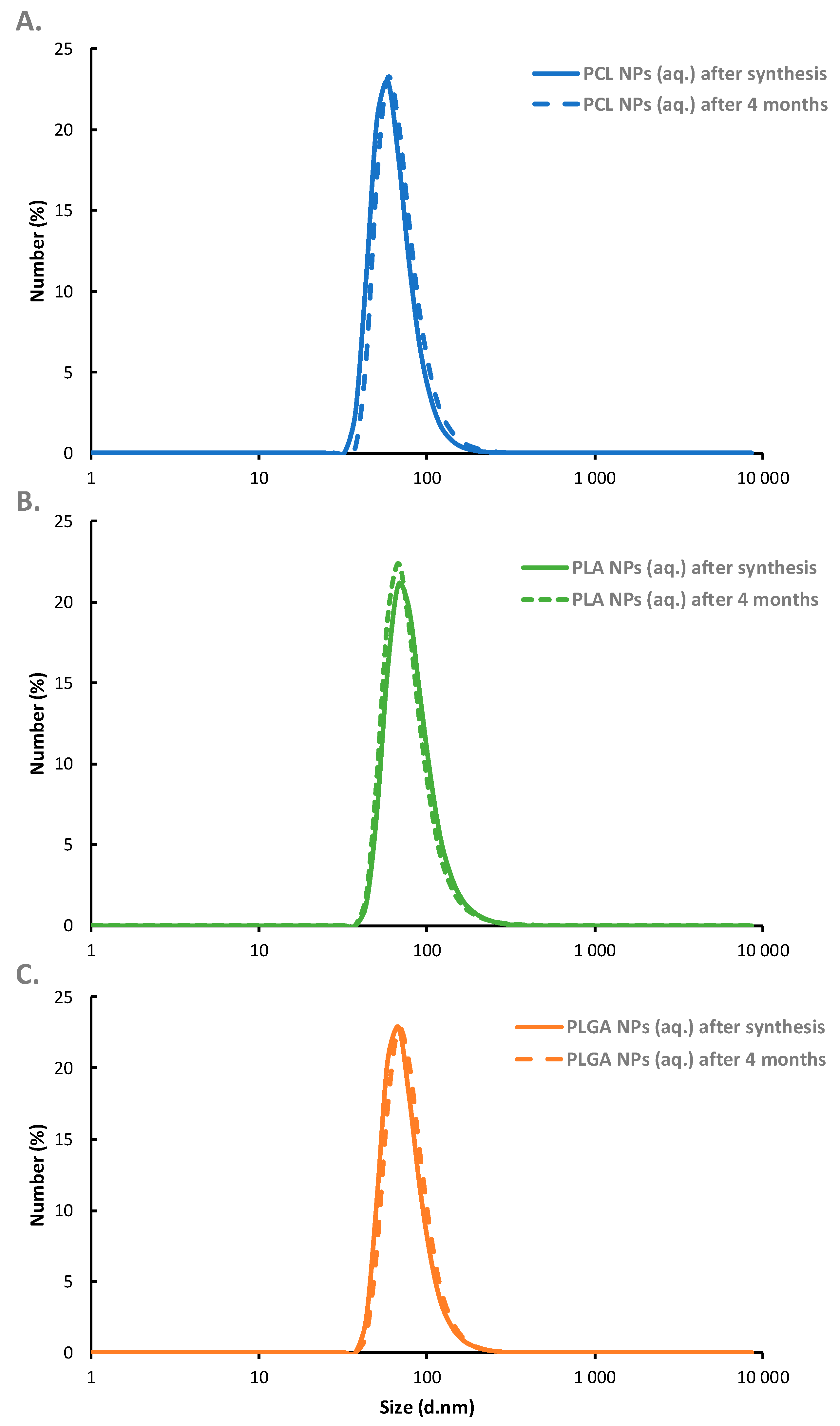
3.1. Polymeric Nanoparticles—Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Active’s Encapsulation
3.3. Functionalization of Polymeric Nanoparticles—Multilayer Shell Preparation
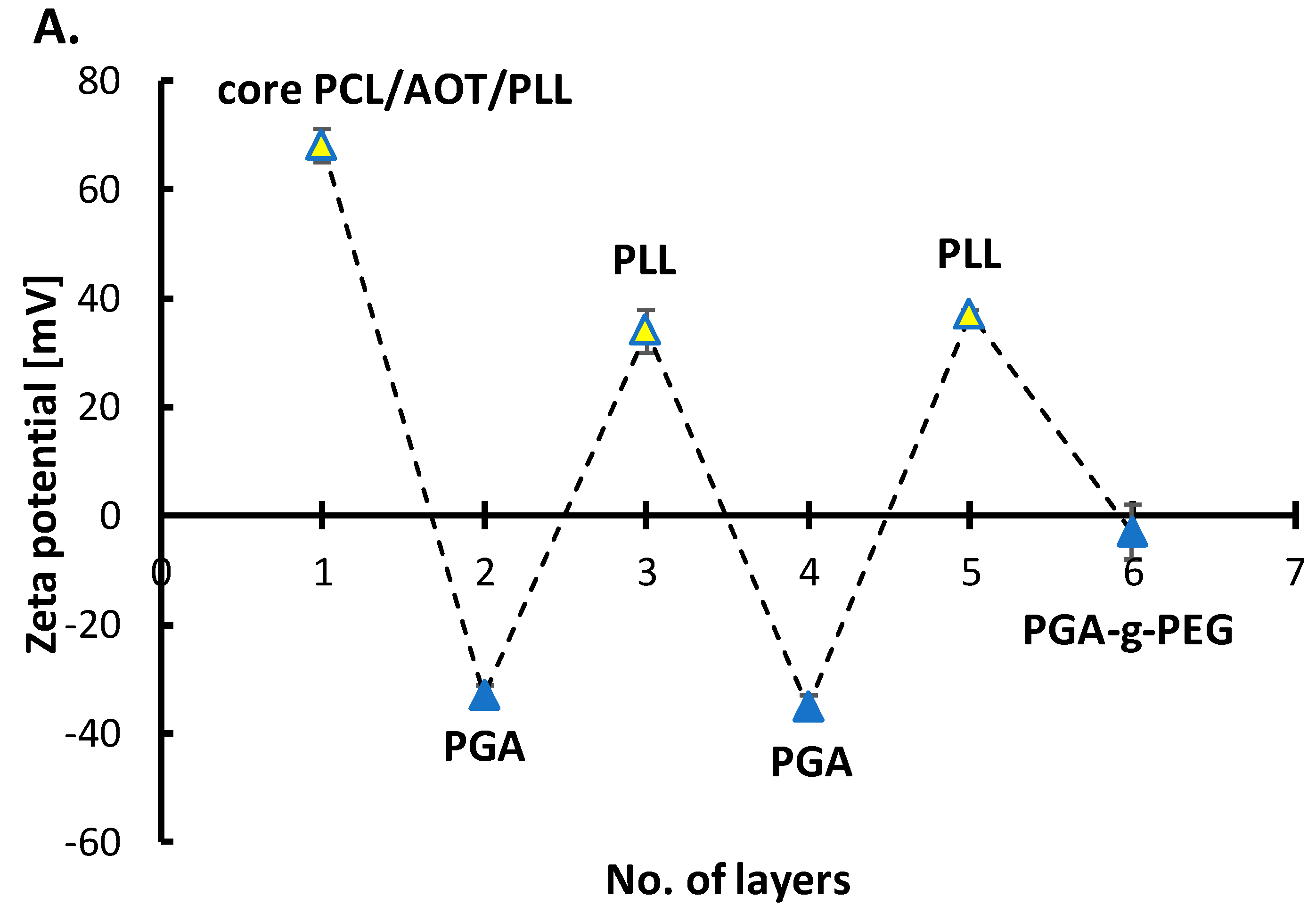
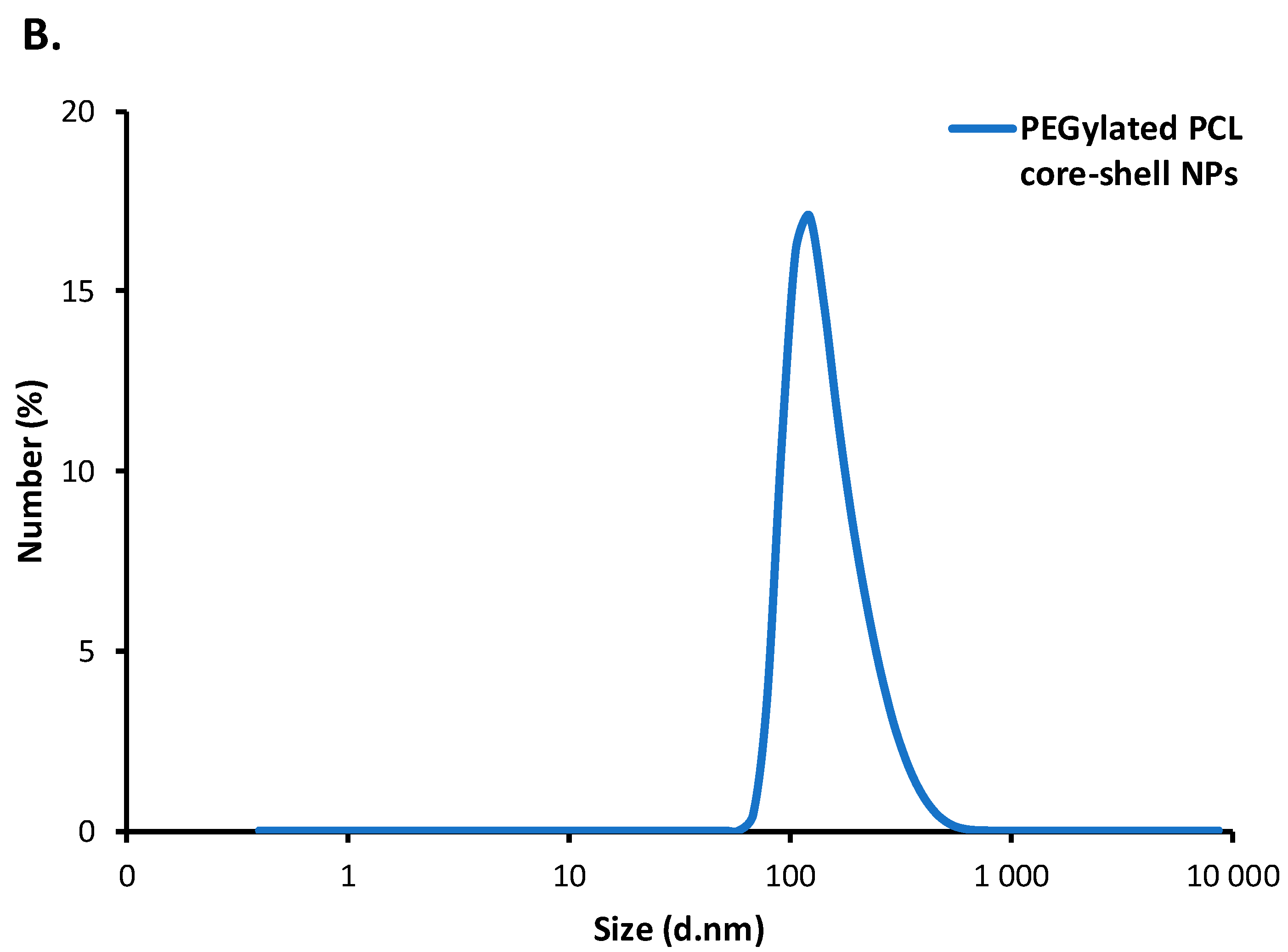
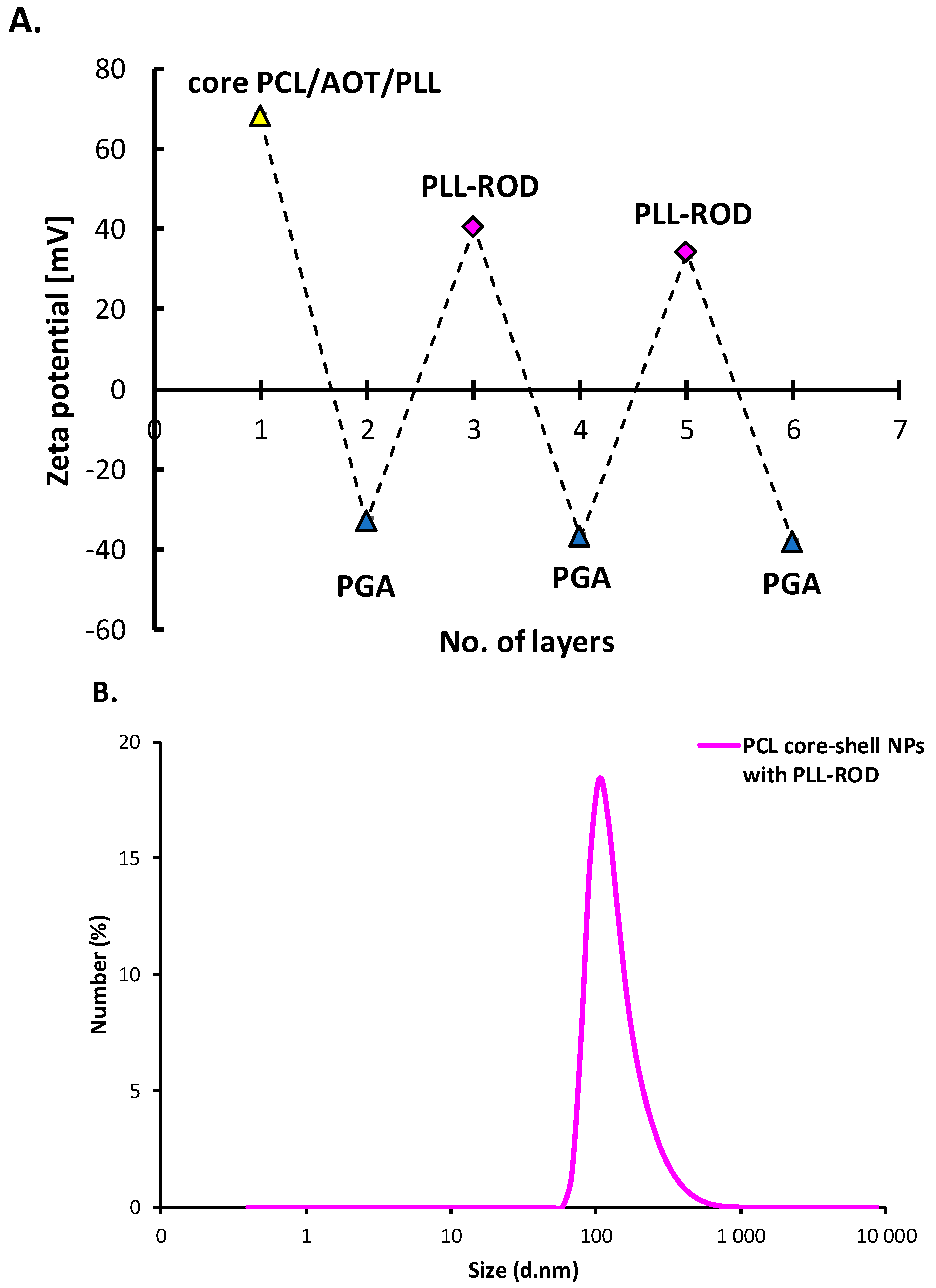
3.3.1. Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Passive Targeting
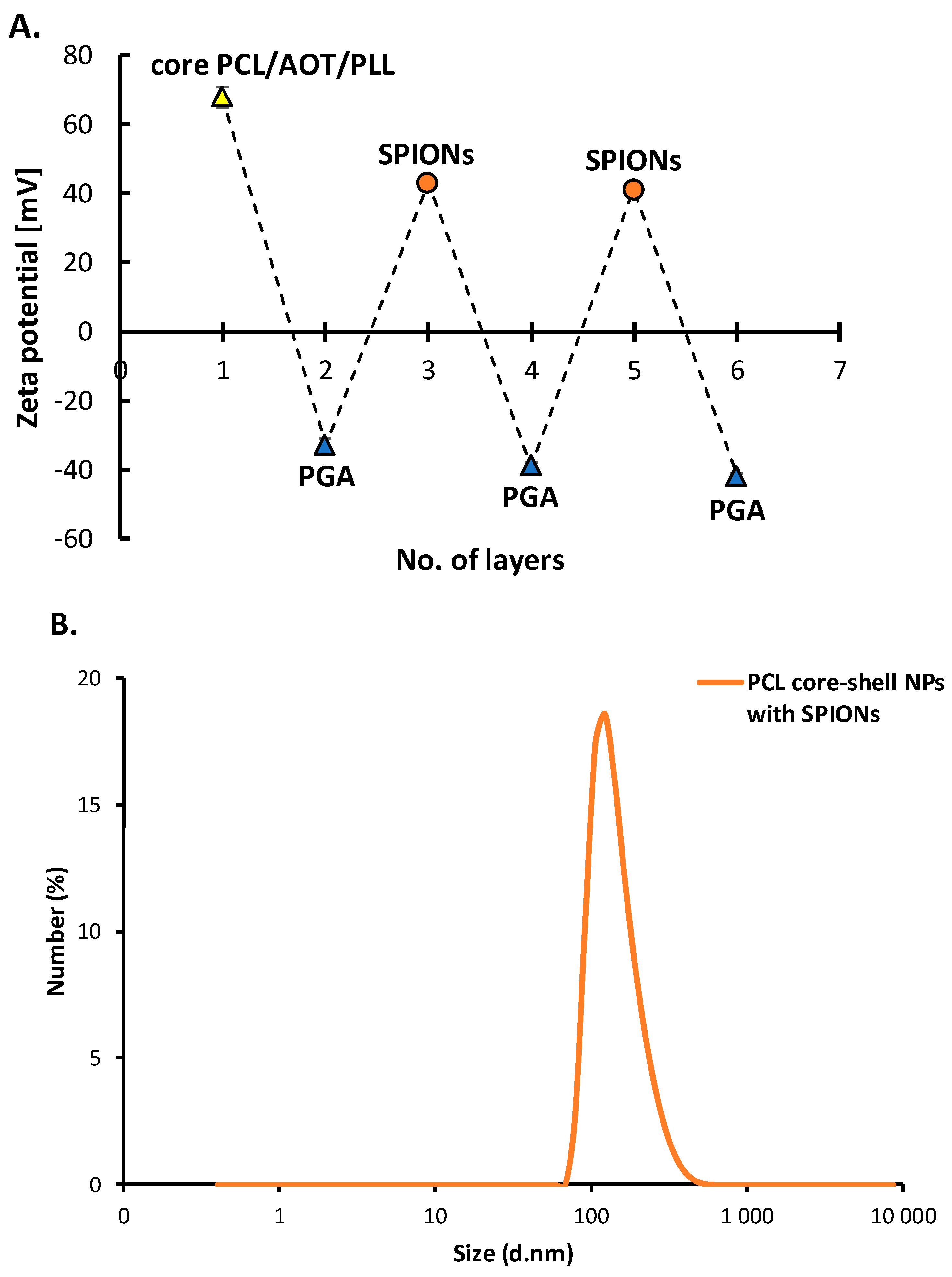
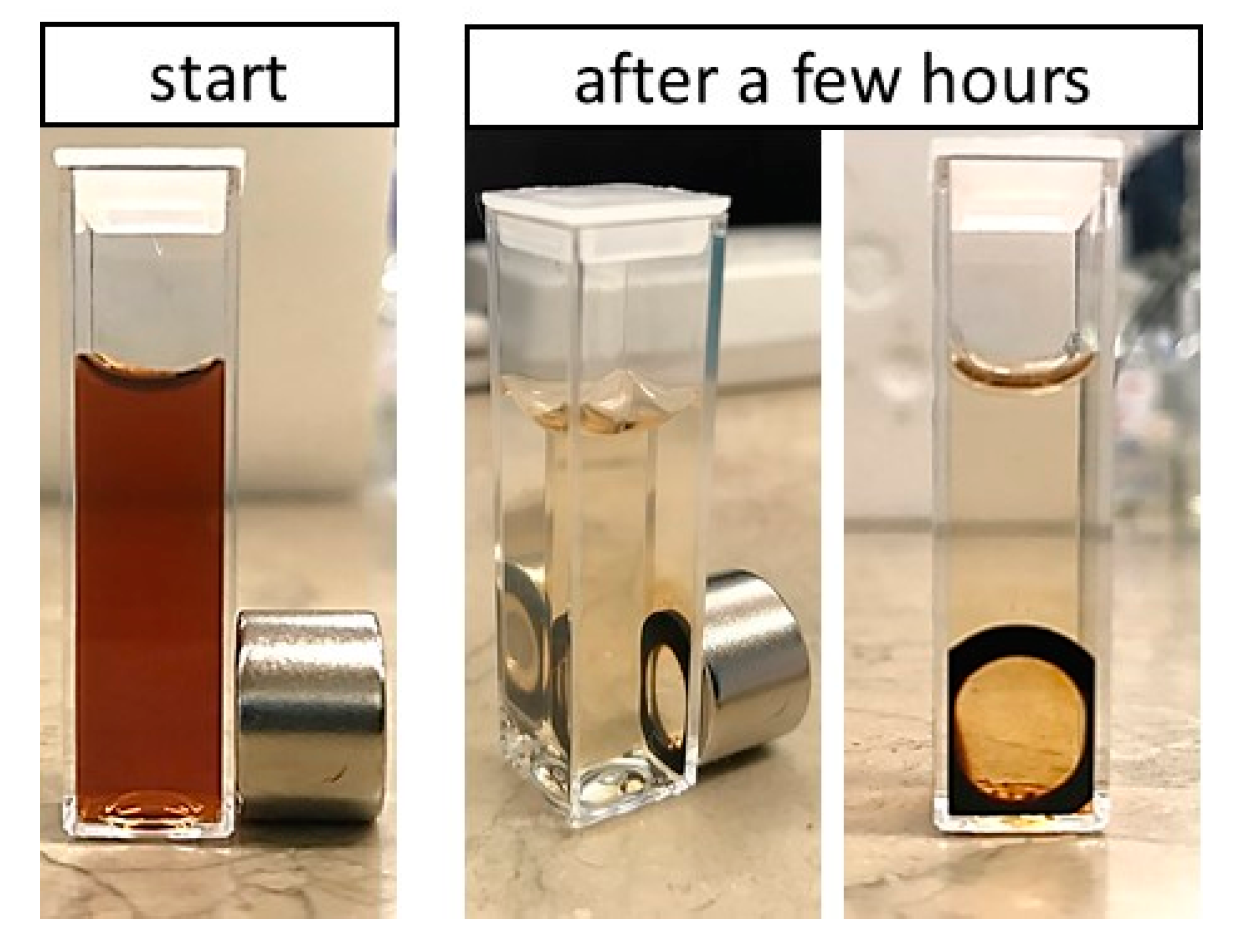
3.3.2. Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Magnetic Targeting
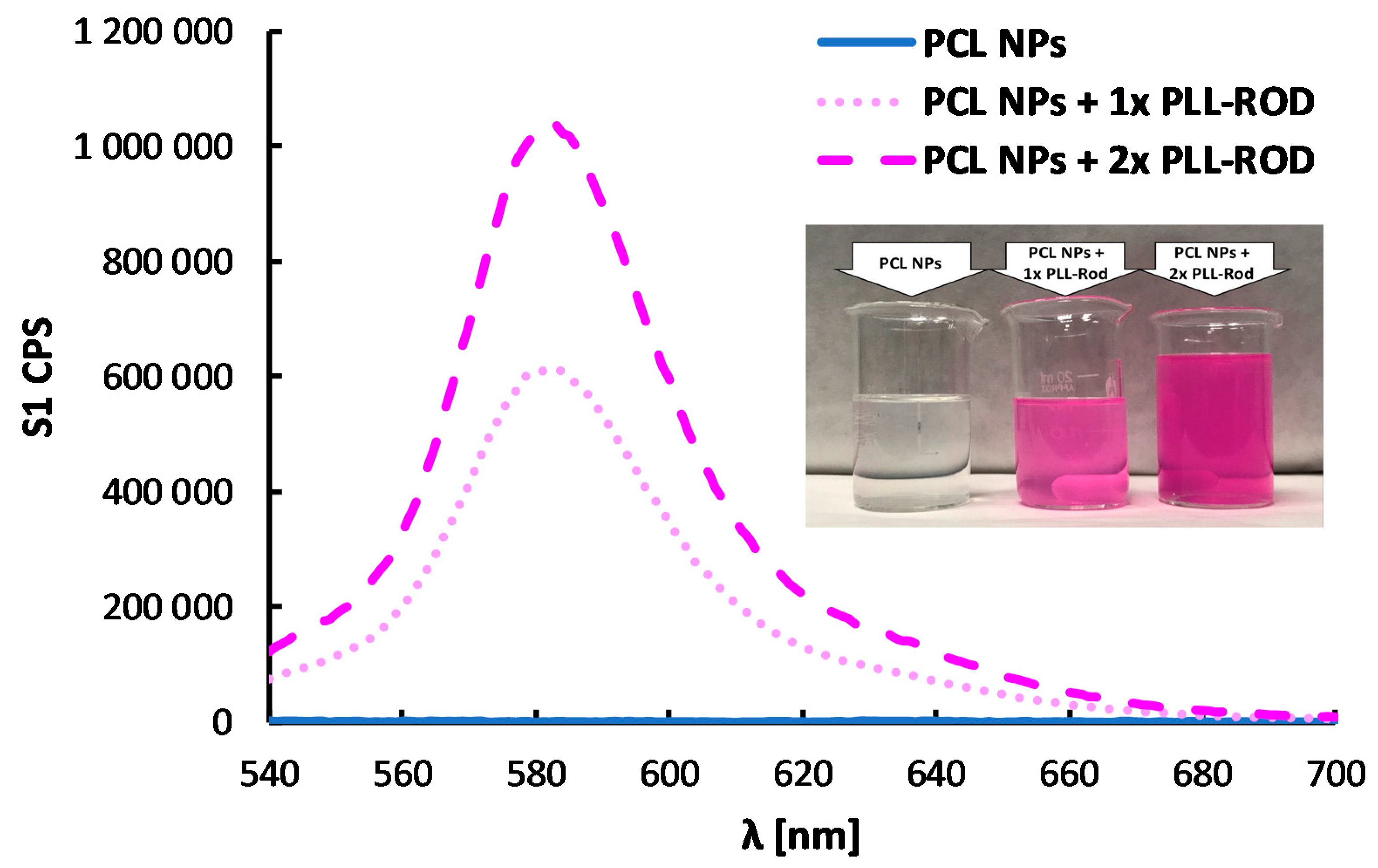
3.3.3. Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Bioimaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebler, D.C.; Guengerich, F.P. Elucidating mechanisms of drug-induced toxicity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchilin, V. Nanopreparations for delivery of non-deliverable pharmaceuticals. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2013, 16, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; El-Sawy, H.S. Polymeric nanoparticles: Promising platform for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 675–691. [Google Scholar]
- Hans, M.L.; Lowman, A.M. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery and targeting. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.J.; Fang, R.H.; Luk, B.T.; Zhang, L. Polymeric nanotherapeutics: Clinical development and advances in stealth functionalization strategies. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabasz, A.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Cierniak, A.; Bereta, J.; Bzowska, M. In vitro toxicity studies of biodegradable, polyelectrolyte nanocapsules. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang Thi, T.T.; Pilkington, E.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.D.; Truong, N.P. The Importance of Poly(ethylene glycol) Alternatives for Overcoming PEG Immunogenicity in Drug Delivery and Bioconjugation. Polymers 2020, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhorukov, G.B.; Donath, E.; Lichtenfeld, H.; Knippel, E.; Knippel, M.; Budde, A.; Möhwald, H. Layer-by-layer self assembly of polyelectrolytes on colloidal particles. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 137, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picart, C.; Caruso, F.; Voegel, J. Layer-by-Layer Films for Biomedical Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.J.; Bjornmalm, M.; Caruso, F. Multilayer assembly. Technology-driven layer-by-layer assembly of nanofilms. Science 2015, 348, aaa2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelatos, A.S.; Katagiri, K.; Caruso, F. Bioinspired colloidal systems via layer-by-layer assembly. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; McShane, M.J. Macromolecule Encapsulation in Diazoresin-Based Hollow Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules. Langmuir 2005, 21, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Caruso, F. Monodisperse Polyelectrolyte-Supported Asymmetric Lipid-Bilayer Vesicles. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchukin, D.; Sukhorukov, G. Nanoparticle Synthesis in Engineered Organic Nanoscale Reactors. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H. Key targeting approaches for pharmaceutical drug delivery. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2013, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Dellian, M.; Fukumura, D.; Leunig, M.; Berk, D.A.; Torchilin, V.P.; Jain, R.K. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: Molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3752–3756. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Greish, K.; Fang, J. The EPR Effect and Polymeric Drugs: AÂ Paradigm Shift for Cancer Chemotherapy in the 21st Century; Satchi-Fainaro, R., Duncan, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Widder, K.J.; Senyei, A.E.; Scarpelli, D.G. Magnetic microspheres: A model system for site specific drug delivery in vivo. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1978, 158, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, F.; Susha, A.S.; Giersig, M.; Möhwald, H. Magnetic Core? Shell Particles: Preparation of Magnetite Multilayers on Polymer Latex Microspheres. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, D.A.; Portnov, S.A.; Inozemtseva, O.A.; Luklinska, Z.; Yashchenok, A.M.; Pavlov, A.M.; Skirtach, A.G.; Mohwald, H.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Magnetic/gold nanoparticle functionalized biocompatible microcapsules with sensitivity to laser irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6899–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, B.; Liu, P.; Du, P.; Dong, Y.; Lu, C. Magnetic-targeted pH-responsive drug delivery system via layer-by-layer self-assembly of polyelectrolytes onto drug-containing emulsion droplets and its controlled release. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odrobinńska, J.; Gumieniczek-Chłopek, E.; Szuwarzynński, M.; Radziszewska, A.; Fiejdasz, S.; Strączek, T.; Zapotoczny, S. Magnetically Navigated Core–Shell Polymer Capsules as Nanoreactors Loadable at the Oil/Water Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10905–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, J.K.; Van Bruggen, N.; Dinkelborg, L.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Molecular imaging in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.E.; Koo, H.; Sun, I.C.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Multifunctional nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and theragnosis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H. Layer-by-layer capsules for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, S.; Truong, N.P.; Esser, L.; Senyschyn, D.; Sanyal, A.; Sanyal, R.; Whittaker, M.R. Influence of size and shape on the biodistribution of nanoparticles prepared by polymerization-induced self-assembly. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3963–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.Y.; Vu, M.N.; Pilkington, E.H.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Whittaker, M.R.; Quinn, J.F.; Truong, N.P.; Davis, T.P. Elucidating the influences of size, surface chemistry, and dynamic flow on cellular association of nanoparticles made by polymerization-Induced self-assembly. Small 2018, 14, 1801702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Błasiak, E.; Dziedzicka-Wasylewska, M. Biocompatible Polymeric Nanoparticles as Promising Candidates for Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6415–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Rockford, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Podgórna, K.; Szczepanowicz, K. Synthesis of polyelectrolyte nanocapsules with iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for magnetic targeting. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 505, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanowicz, K.; Dronka-Góra, D.; Para, G.; Warszyński, P. Encapsulation of liquid cores by layer-by-layer adsorption of polyelectrolytes. J. Microencapsul. 2010, 27, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.S.; Goel, M.; Aqil, F.; Vadhanam, M.V.; Gupta, R.C. Advanced drug delivery systems of curcumin for cancer chemoprevention. Cancer. Prev. Res. (Phila) 2011, 4, 1158–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanowicz, K.; Bazylińska, U.; Pietkiewicz, J.; Szyk-Warszyńska, L.; Wilk, K.A.; Warszyński, P. Biocompatible long-sustained release oil-core polyelectrolyte nanocarriers: From controlling physical state and stability to biological impact. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanowicz, K.; Hoel, H.J.; Szyk-Warszynska, L.; Bielanska, E.; Bouzga, A.M.; Gaudernack, G.; Simon, C.; Warszynski, P. Formation of Biocompatible Nanocapsules with Emulsion Core and Pegylated Shell by Polyelectrolyte Multi layer Adsorption. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12592–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Brown, S.; Walter, G.; Santra, S.; Moudgil, B. Nanoparticles for bioimaging. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, S.A.; Parish, C.R. New fluorescent dyes for lymphocyte migration studies: Analysis by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. J. Immunol. Methods 1990, 133, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
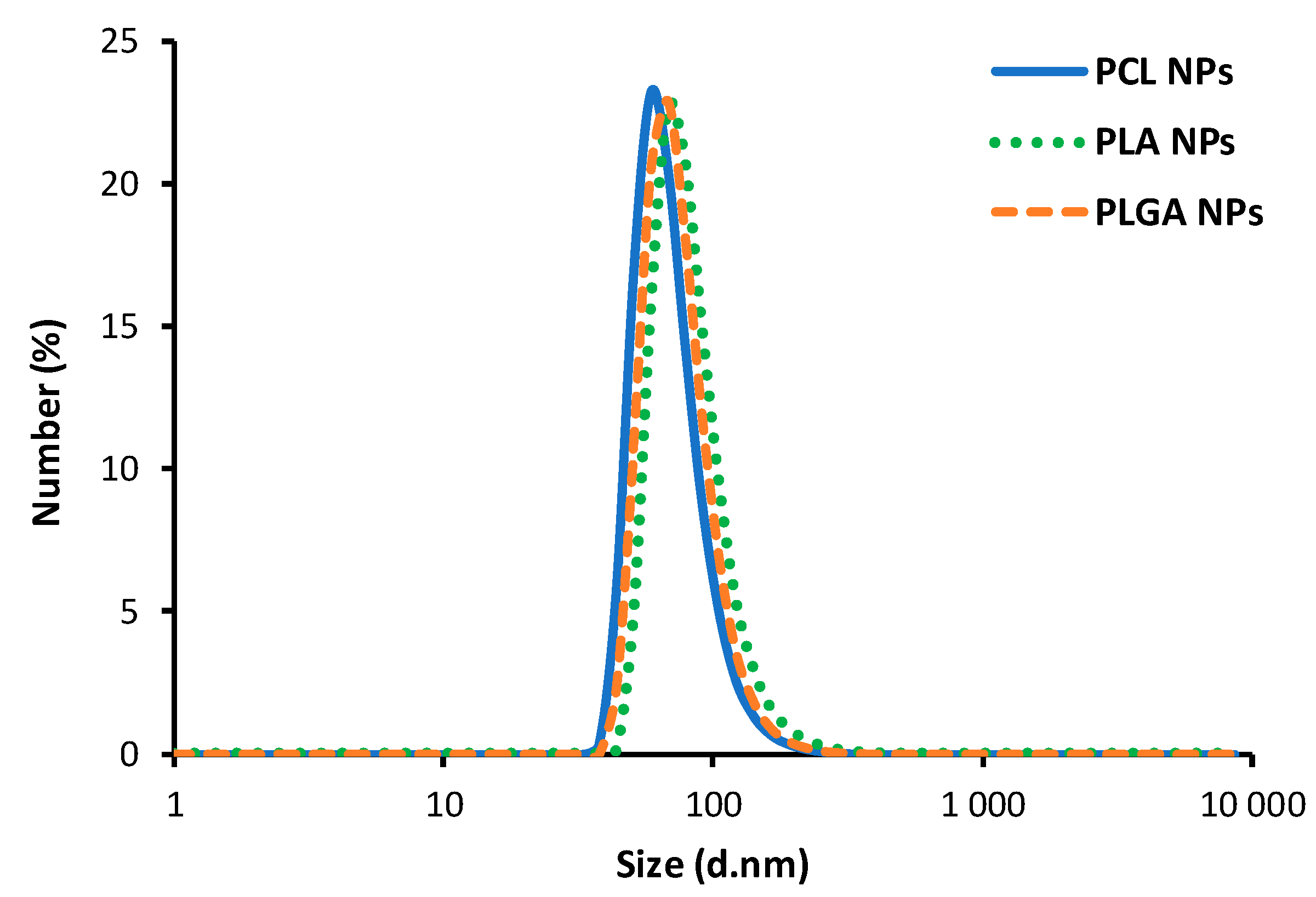
| Polymer (Optimized Concentration) | Average Size | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(caprolactone), PCL (10 mg/mL) | 76 (±5) nm | 0.134 (±0.027) | 68 (±3) mV | ~1 × 1011 nanoparticle/mL |
| Poly(lactic acid), PLA (2.5 mg/mL) | 80 (±7) nm | 0.166 (±0.021) | 71 (±4) mV | ~1 × 1011 nanoparticle/mL |
| Poly(lactide-co-glycolide), PLGA (5 mg/mL) | 77 (±2) nm | 0.179 (±0.048) | 78 (±2) mV | ~1 × 1011 nanoparticle/mL |
| Optimized Coumarin-6 Concentration in the Oil Phase | Final Coumrine-6 Concentration in Nanoparticles’ Suspension | Encapsulation Efficiency | Polymer/drug Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 0.3 mg/mL | 0.150 mg/L | 98.9% | 33 |
| PLA | 0.25 mg/mL | 0.125 mg/L | 98.7% | 10 |
| PLGA | 0.25 mg/mL | 0.125 mg/L | 98.8% | 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczęch, M.; Szczepanowicz, K. Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030496
Szczęch M, Szczepanowicz K. Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczęch, Marta, and Krzysztof Szczepanowicz. 2020. "Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030496
APA StyleSzczęch, M., & Szczepanowicz, K. (2020). Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030496