Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
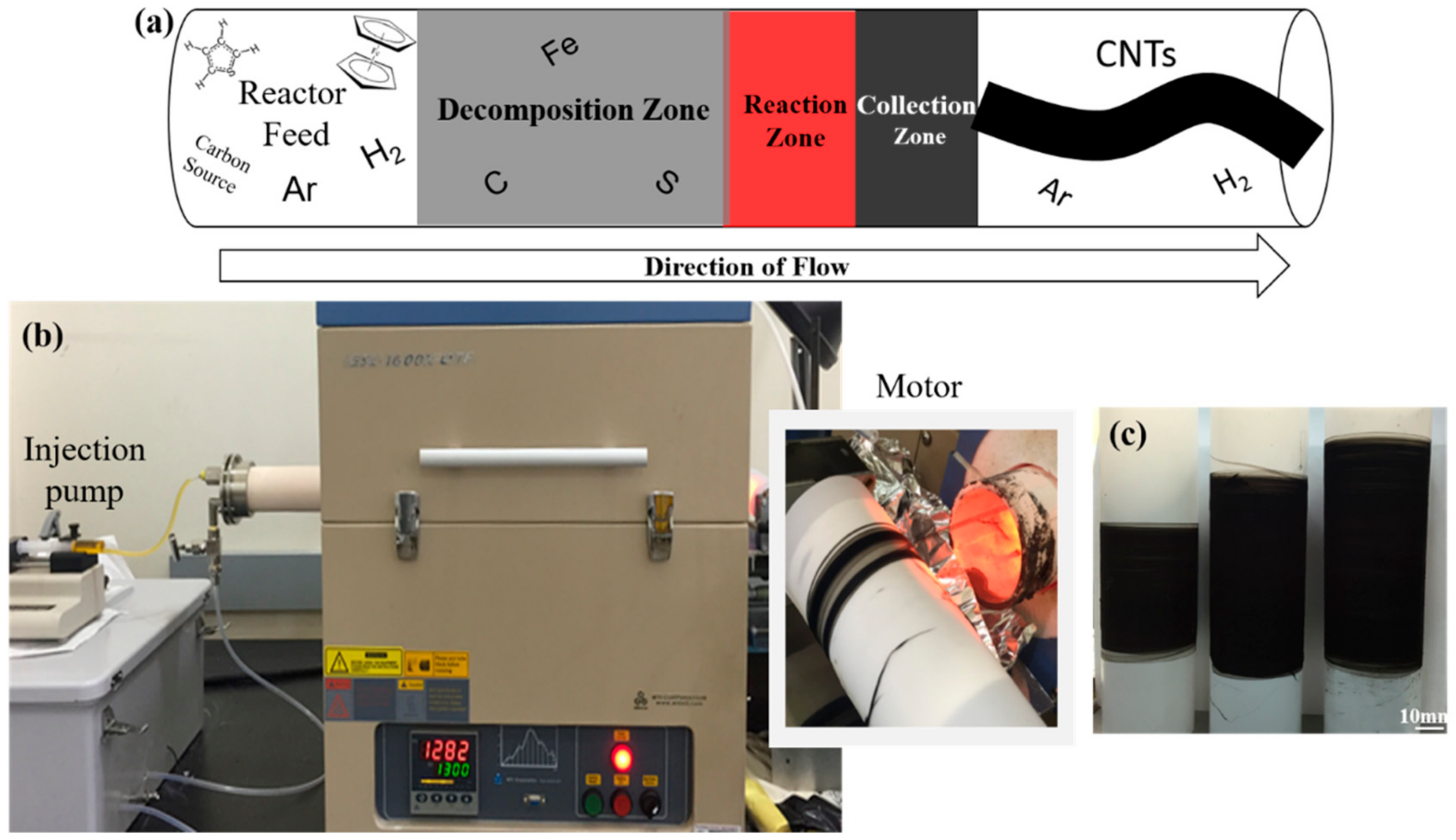
2. Materials and Methods
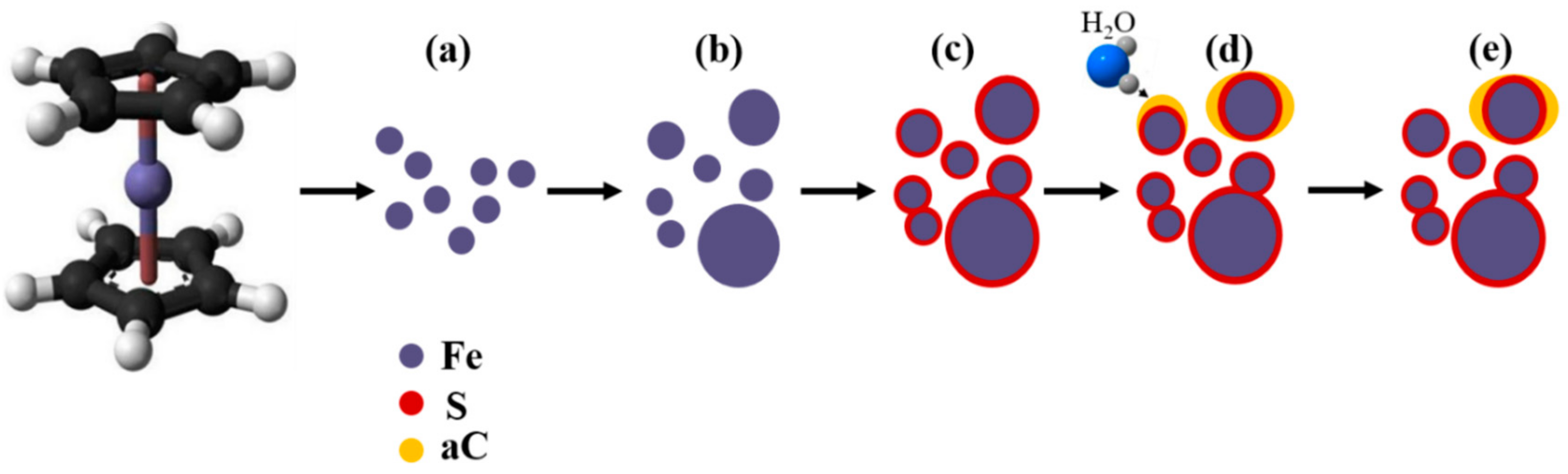
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Oxidation Resistance
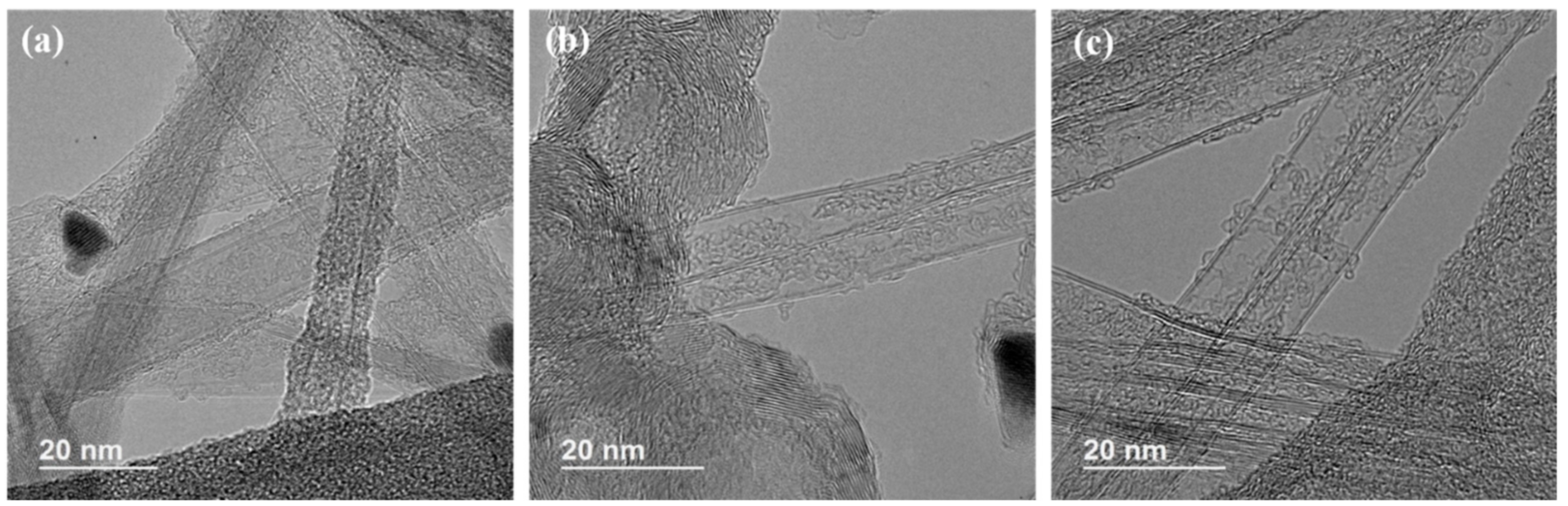
3.2. Morphology Analysis
3.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Electrical Conductivities
3.6. Mechanical Properties from Nano-Indentation Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, M.; Li, Y.-L.; Kinloch, I.; Windle, A. Mechanical Properties of Continuously Spun Fibers of Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Fan, Z.; Liu, P.; Myint, S.M.; Duong, H.M. Super-strong and highly conductive carbon nanotube ribbons from post-treatment methods. Carbon 2016, 99, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journet, C.; Maser, W.K.; Bernier, P.; Loiseau, A.; De La Chapelle, M.L.; Lefrant, S.; Deniard, P.; Lee, R.; Fischer, J.E. Large-scale production of single-walled carbon nanotubes by the electric-arc technique. Nature 1997, 388, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Nikolaev, P.; Rinzler, A.G.; Tománek, D.; Colbert, D.T.; Smalley, R.E. Self-Assembly of Tubular Fullerenes. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 10694–10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Igarashi, S.; Kobori, K.; Shiraishi, M.; Kroto, H.W. The production and structure of pyrolytic carbon nanotubes (PCNTs). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1993, 54, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayan, P.M.; Ebbesen, T.W.; Ichihashi, T.; Iijima, S.; Tanigaki, K.; Hiura, H. Opening carbon nanotubes with oxygen and implications for filling. Nature 1993, 362, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, A.R.; Pradhan, B.K.; Chang, J.; Chen, G.; Eklund, P.C. Purification of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes by Selective Microwave Heating of Catalyst Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 8671–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-Y.; Kaufmann, A.; Mukasyan, A.; Varma, A. Single-and multi-wall carbon nanotubes produced using the floating catalyst method: Synthesis, purification and hydrogen up-take. Carbon 2006, 44, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Bekyarova, E.; E Itkis, M.; Fakhrutdinov, D.; Webster, R.; Haddon, R. Application of Centrifugation to the Large-Scale Purification of Electric Arc-Produced Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9902–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandow, S.; Rao, A.M.; Williams, K.A.; Thess, A.; Smalley, R.E.; Eklund, P.C. Purification of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes by Microfiltration. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 8839–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, K.; Linden, S.; Enkrich, C.; Wegener, M.; Zhou, J.; Koschny, T.; Soukoulis, E.O.C.M. Water-Assisted Highly Efficient Synthesis of Impurity-Free Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Science 2004, 306, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K.; Namai, T.; Yamada, T.; Mizuno, K.; Hayamizu, Y.; Yumura, M.; Iijima, S. 84% Catalyst Activity of Water-Assisted Growth of Single Walled Carbon Nanotube Forest Characterization by a Statistical and Macroscopic Approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8035–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K.; Yamada, T.; Mizuno, K.; Yumura, M.; Iijima, S. Kinetics of Water-Assisted Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Synthesis Revealed by a Time-Evolution Analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 056104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Kinloch, I.A.; Windle, A.H. Direct Spinning of Carbon Nanotube Fibers from Chemical Vapor Deposition Synthesis. Science 2004, 304, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.-R. Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanotube fibers by controlling the effects of sulfur on the catalyst agglomeration during the direct spinning process. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 41894–41900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukner, C.; Koziol, K.K. Ultra-pure single wall carbon nanotube fibres continuously spun without promoter. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Su, R.; Wang, A.; Ng, V.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sundaram, M.; Shanov, V.; Mast, D.; et al. The effect of a convection vortex on sock formation in the floating catalyst method for carbon nanotube synthesis. Carbon 2016, 102, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-H.; Li, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.-K.; Qiao, X.-H.; Feng, Y.; Liang, J.; Jin, J.; Zhu, L.; Hou, F.; Li, J.-Y. Continuous Multilayered Carbon Nanotube Yarns. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chauhan, D.; Xu, C.; Ng, V.; Hou, G.; Shanov, V.; Mast, D.; Fialkova, S.; Schulz, M.J. Floating Catalyst Reactor Design and Safety Features for Carbon Nanotube Synthesis; William Andrew Publishing: Norwick, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 851–866. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Haldane, D.; Liang, R.; Smithyman, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Nanoscale infiltration behaviour and through-thickness permeability of carbon nanotube buckypapers. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 015704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.; Pharr, G. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.; Oliver, W. Measurement of Thin Film Mechanical Properties Using Nanoindentation. MRS Bull. 1992, 17, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, A. (Ed.) Understanding the Direct Spinning of CNT Fibers in Terms of the Thermodynamic and Kinetic Landscape: A Personal View. In Nanotube Superfiber Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 149–184. [Google Scholar]
- Smail, F.R.; Boies, A.; Windle, A. Direct spinning of CNT fibres: Past, present and future scale up. Carbon 2019, 152, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniyoor, A.; Bulmer, J.; Gspann, T.S.; Mizen, J.; Ryley, J.B.; Kiley, P.J.; Terrones, J.; Miranda-Reyes, C.; Divitini, G.; Sparkes, M.R.; et al. High throughput production of single-wall carbon nanotube fibres independent of sulfur-source. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18483–18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Maigne, A.; Yudasaka, M.; Mizuno, K.; Futaba, D.N.; Yumura, M.; Iijima, S.; Hata, K. Revealing the Secret of Water-Assisted Carbon Nanotube Synthesis by Microscopic Observation of the Interaction of Water on the Catalysts. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4288–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnott, S.B.; Andrews, R.; Qian, D.; Rao, A.; Mao, Z.; Dickey, E.; Derbyshire, F. Model of carbon nanotube growth through chemical vapor deposition. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 315, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, A.W.; Silva, W.; Martens, W.; Waclawik, E.; Frost, R.L. Thermal decomposition and electron microscopy studies of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 88, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.S.K.; Saxby, J.D.; Chatfield, S.P. Thermogravimetric analysis of carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 6941–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, D.; Andrews, R.; Jacques, D.; Anthony, J.E.; Chen, B.; Meier, M.S.; Selegue, J.P. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the Oxidation of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: Evidence for the Role of Defect Sites in Carbon Nanotube Chemistry. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, L.; Pasquini, L.; Savini, L.; Carboni, R.; Boscherini, F.; Bonetti, E.; Giglia, A.; Pedio, M.; Mahne, N.; Nannarone, S. Size-dependent oxidation in iron/iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, R.D.; Hao, A.; Park, J.G.; Su, Y.-F.; Liang, R.; Jensen, B.D.; Siochi, E.J.; Wise, K.E. Geometrically constrained self-assembly and crystal packing of flattened and aligned carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2015, 93, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, Q. Bio-Inspired Aggregation Control of Carbon Nanotubes for Ultra-Strong Composites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, C.V.; Krishnan, K.S. A New Type of Secondary Radiation. Nature 1928, 121, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Borowiak-Palen, E.; Kruszynska, M.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Kalenczuk, R.J. Characterization of carbon nanotubes by Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2008, 26, 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Keszler, A.M.; Nemes, L.; Ahmad, S.R.; Fang, X. Characterization of Carbon Nanotube Materials by Raman Spectroscopy and Microscopy—A Case Study of Multiwalled and Singlewalled Samples. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2004, 6, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R.; Jorio, A. Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 2005, 409, 47–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Sauvajol, J.-L.; Cambedouzou, J.; Benoit, C. Raman-active modes in finite and infinite double-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Bao, J.; Park, J.G.; Liang, R.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. High Mechanical Performance Composite Conductor: Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Sheet/Bismaleimide Nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetat, J.-P.; Bonard, J.-M.; Thomson, N.H.; Kulik, A.J.; Forr´o, L.; Benoit, W.; Zuppiroli, L. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEuen, P.L.; Fuhrer, M.S.; Park, H. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Electronics. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2002, 1, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Yi, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; De Heer, W. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes are ballistic conductors at room temperature. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 74, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Luo, X.G.; Wu, T.; Chen, Y. High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekawa-Raus, A.; Patmore, J.; Kurzepa, L.; Bulmer, J.; Koziol, K.K. Electrical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Based Fibers and Their Future Use in Electrical Wiring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3661–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lekawa-Raus, A.; Trevarthen, J.; Gizewski, T.; Lukawski, D.; Hazra, K.; Rahatekar, S.S.; Koziol, K.K. Carbon nanotube films spun from a gas phase reactor for manufacturing carbon nanotube film/carbon fibre epoxy hybrid composites for electrical applications. Carbon 2019, 158, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Xue, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, E.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Hou, H. Preparation of carbon nanotube film with high alignment and elevated density. Carbon 2017, 122, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Tan, Y.F.; Hu, D.C.; Jewell, D.; Duong, H.M. Multi-property enhancement of aligned carbon nanotube thin films from floating catalyst method. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadler, L.S.; Giannaris, S.C.; Ajayan, P.M. Load transfer in carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3842–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Electrical Conductivity (S/cm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial | Trans | T///T⊥ | Axial | Trans | E///E⊥ | Axial | Trans | σ///σ⊥ | |
| CNT-0 | 225 ± 43 | 44 ± 15 | 5.11 | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 3.53 | 885 ± 77 | 876 ± 22 | 1.01 |
| CNT-0/BMI | 515 ± 15 | 205 ± 21 | 2.51 | 23.4 ± 1.3 | 9.8 ± 0.9 | 2.39 | 1484 ± 121 | 575 ± 24 | 2.58 |
| CNT-1 | 284 ± 75 | 83 ± 22 | 3.42 | 7.8 ± 2.3 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 2.89 | 1473 ± 61 | 1455 ± 99 | 1.01 |
| CNT-1/BMI | 534 ± 39 | 252 ± 26 | 2.12 | 27.9 ± 1.8 | 9.8 ± 1.3 | 2.85 | 1720 ± 186 | 634 ± 54 | 2.71 |
| CNT-2 | 473 ± 46 | 64 ± 13 | 7.39 | 15.0 ± 3.9 | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 5.56 | 1820 ± 67 | 1727 ± 71 | 1.05 |
| CNT-2/BMI | 497 ± 78 | 235 ± 18 | 2.11 | 21.2 ± 2.8 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 2.23 | 1697 ± 125 | 652 ± 71 | 2.60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Park, J.G.; Leonhardt, B.E.; Zhang, S.; Liang, R. Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020365
Dong L, Park JG, Leonhardt BE, Zhang S, Liang R. Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020365
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Liyu, Jin Gyu Park, Branden E. Leonhardt, Songlin Zhang, and Richard Liang. 2020. "Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020365
APA StyleDong, L., Park, J. G., Leonhardt, B. E., Zhang, S., & Liang, R. (2020). Continuous Synthesis of Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Water-Assisted Floating Catalyst Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020365





