Laser Fragmentation Synthesis of Colloidal Bismuth Ferrite Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
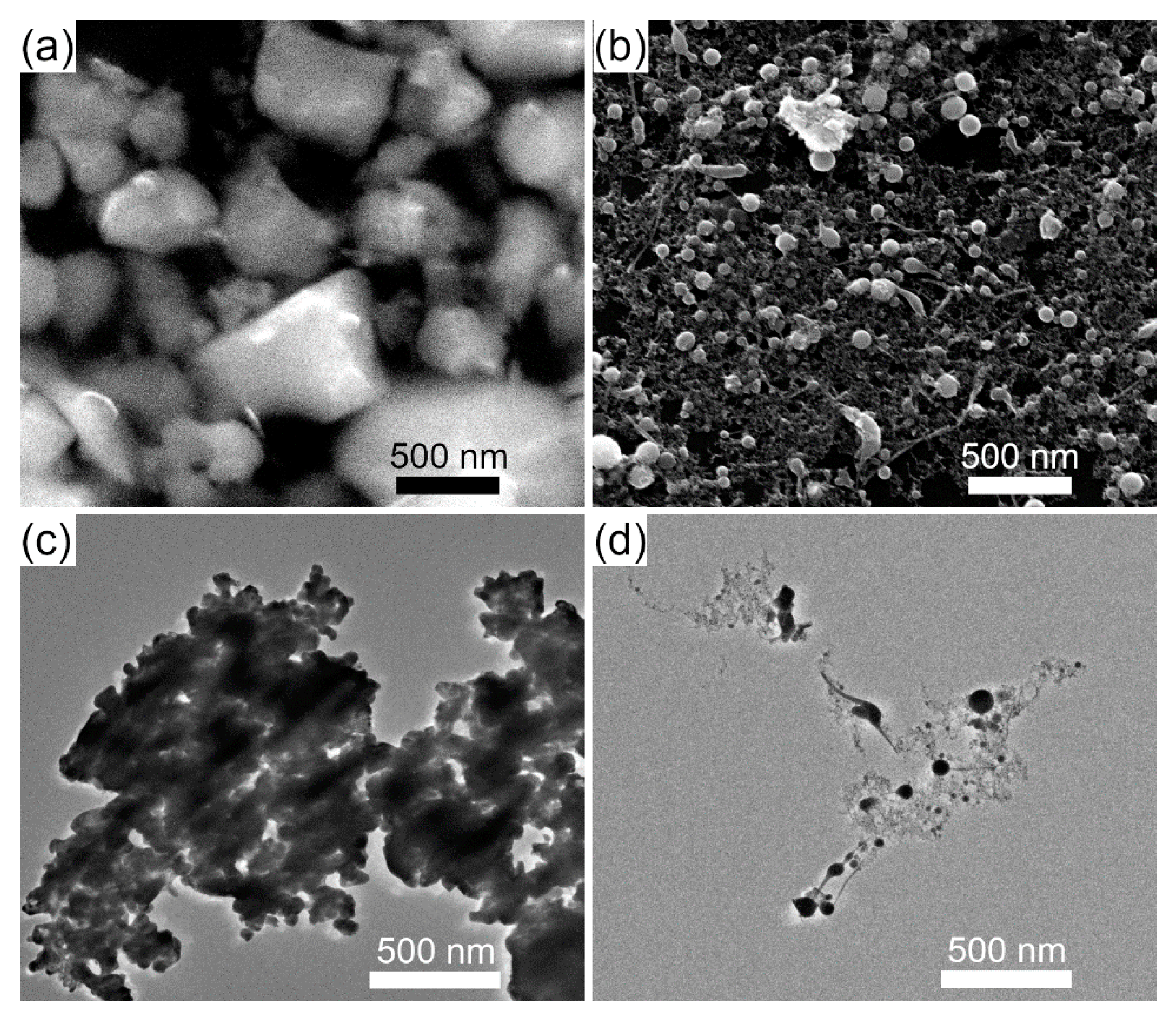
2.1. Synthesis of Educt Powder
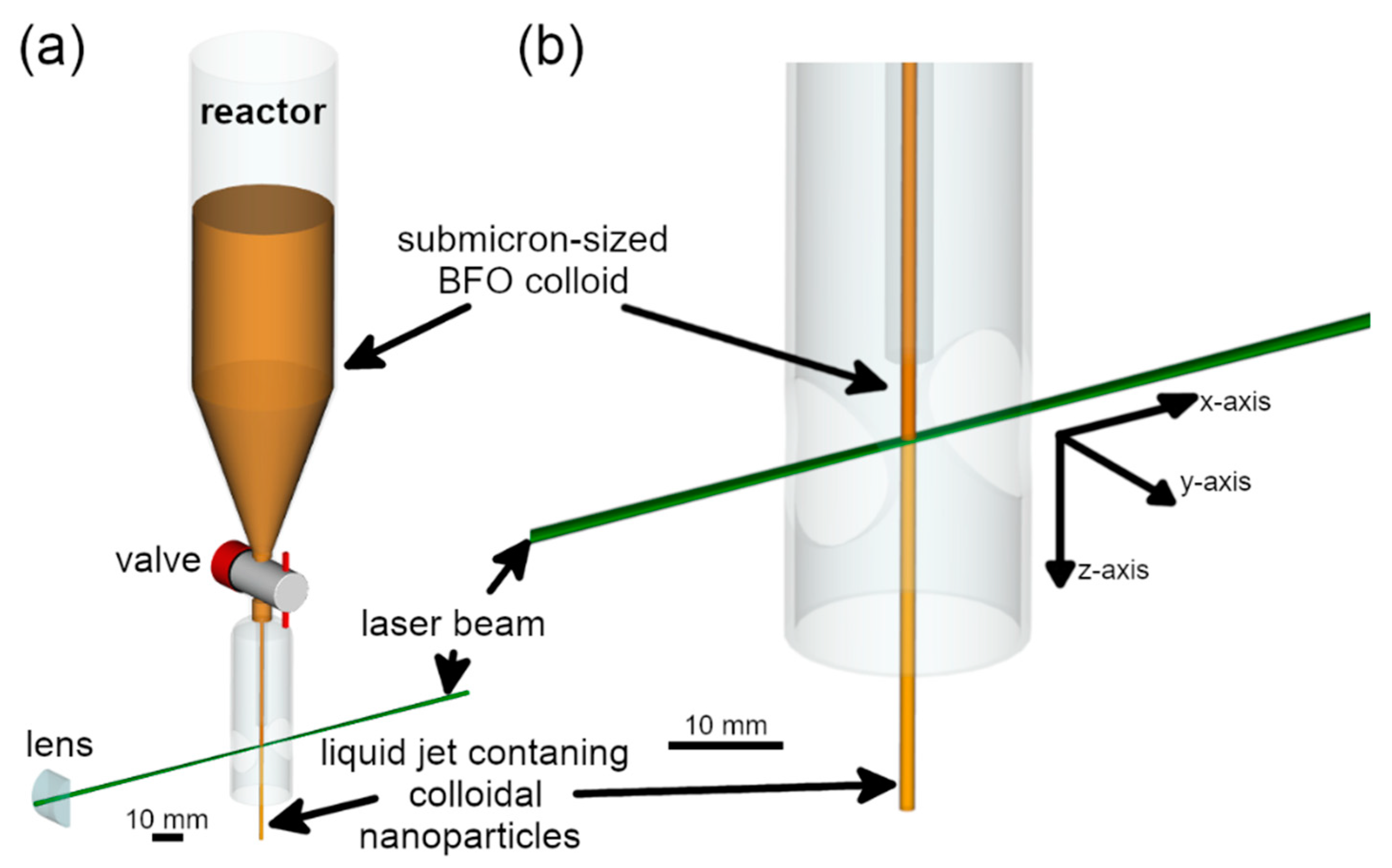
2.2. Laser Fragmentation Setup
2.3. Analytical Instruments
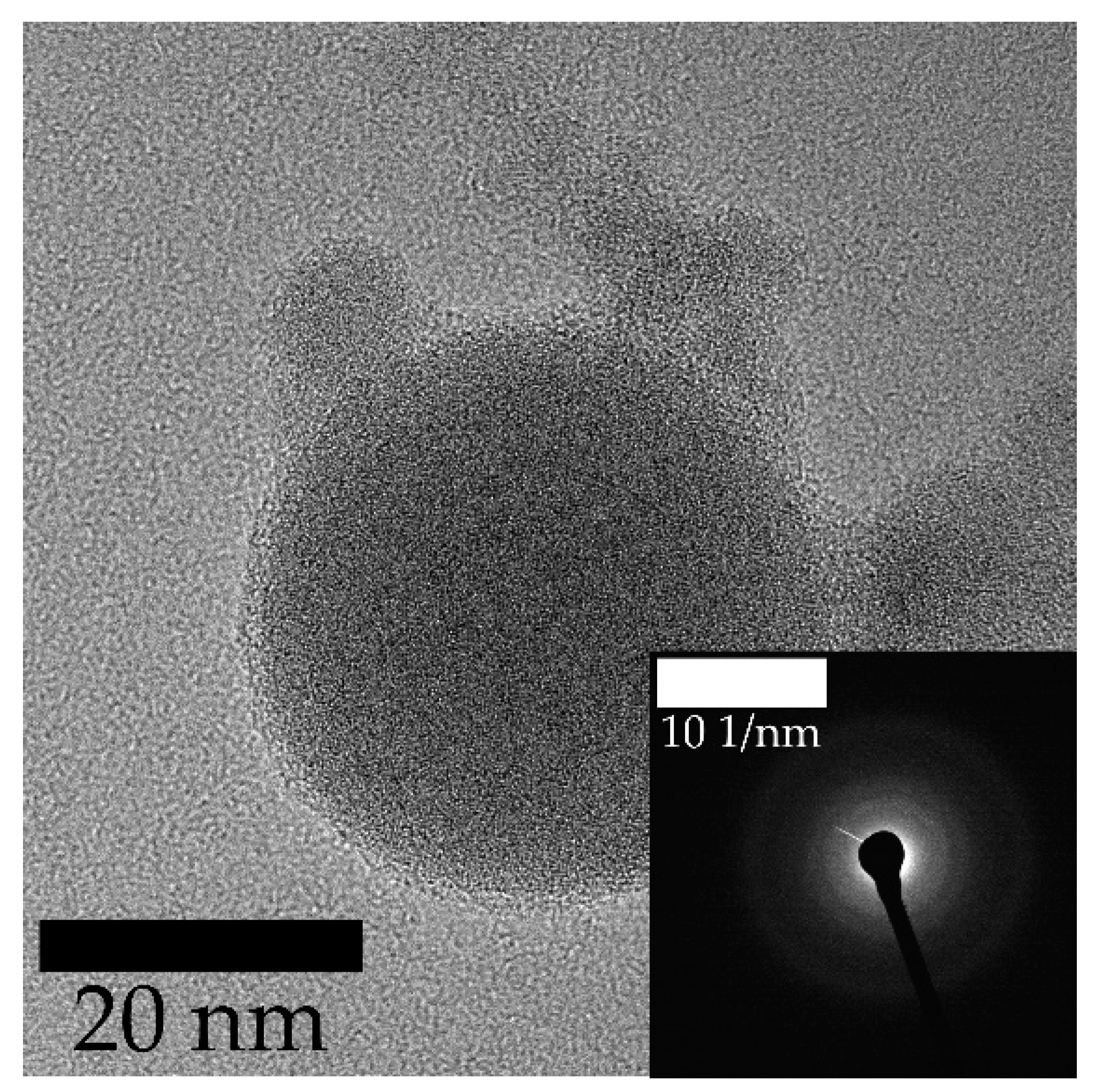
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Laser Fragmentation Using a Circular Colloid Jet
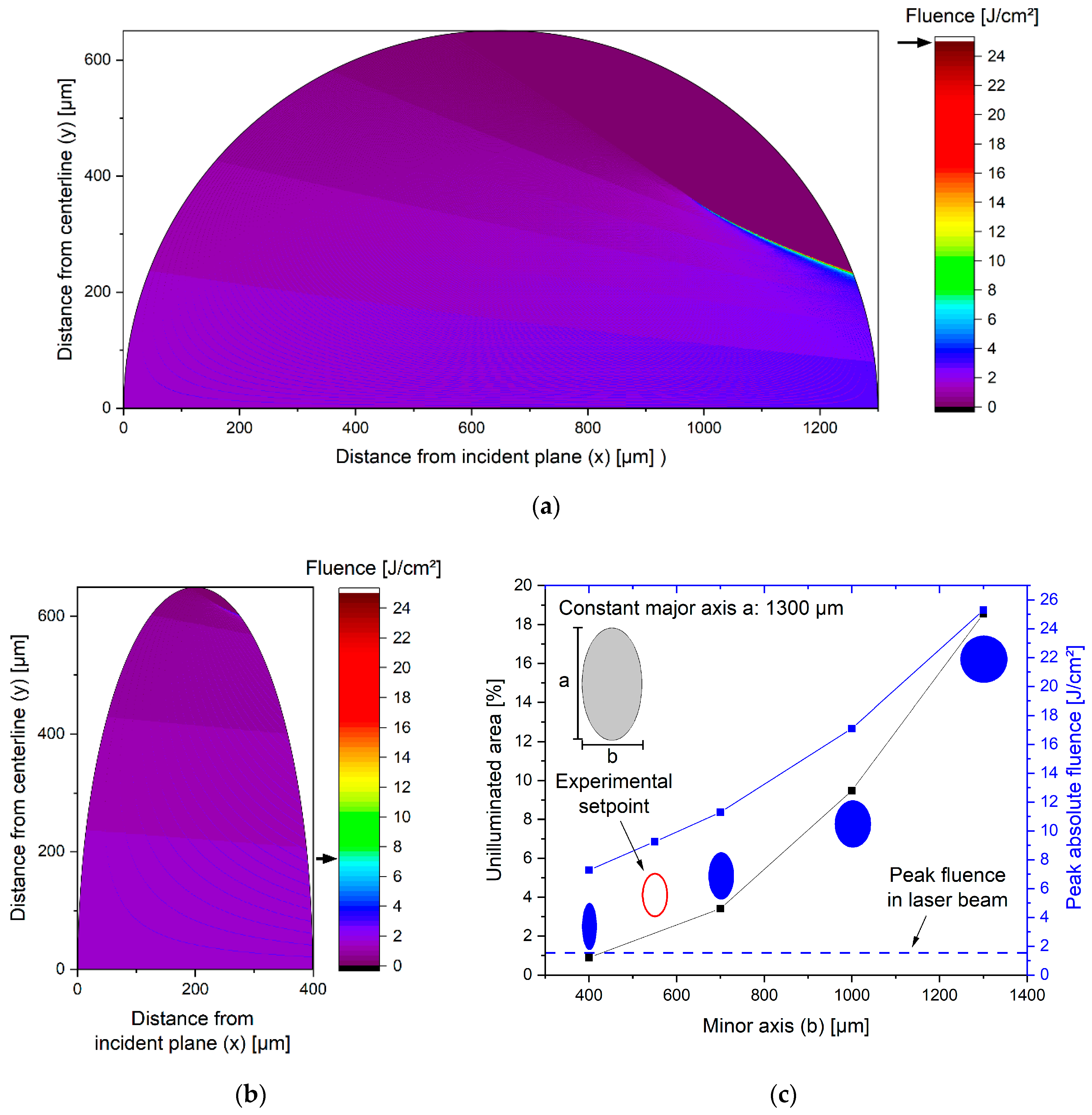
3.2. Fluence Simulation in Laser-Irradiated Colloid Jets of Different Geometries
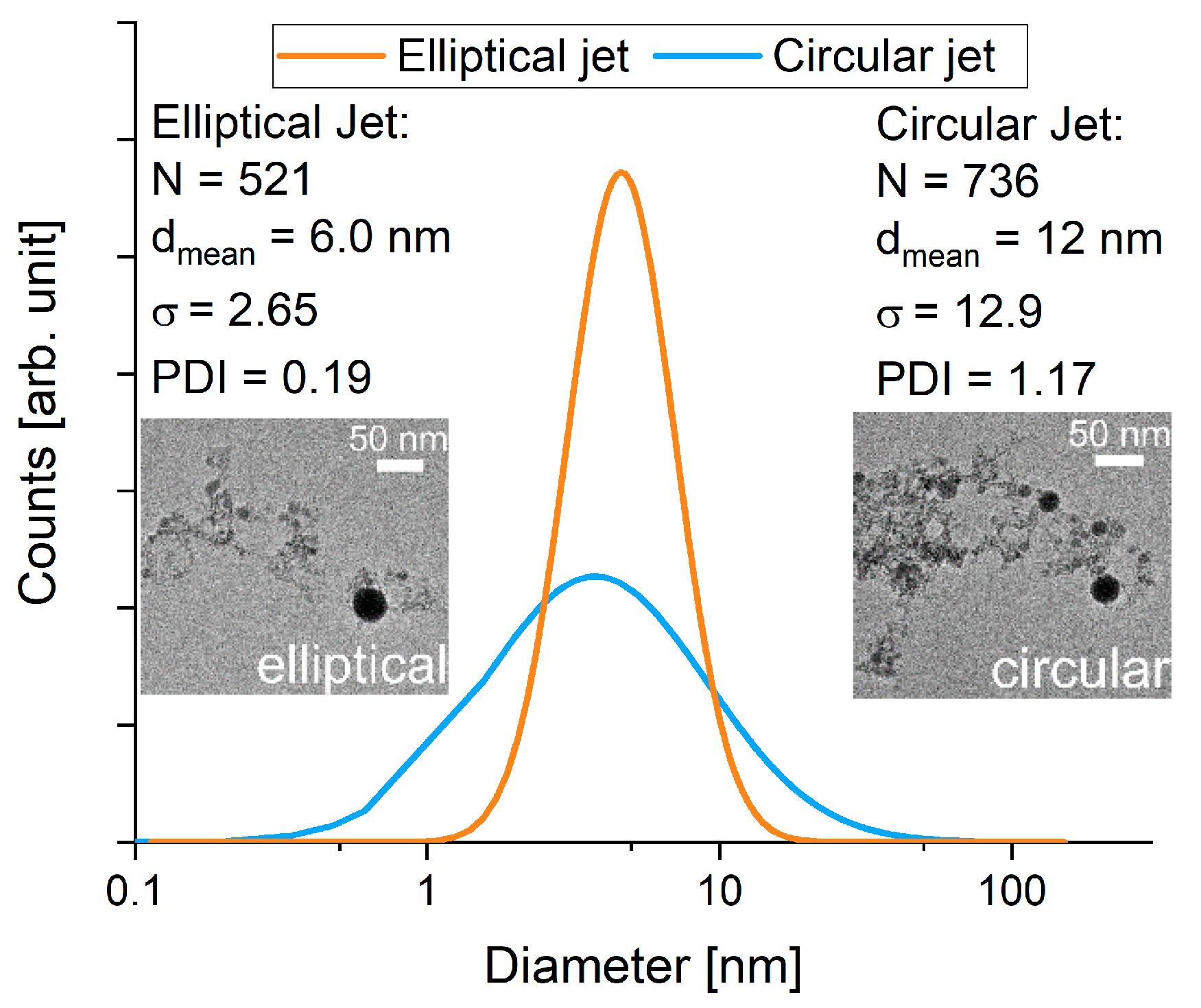
3.3. Comparison of Laser Fragmentation Using Circular and Elliptical Colloid Jets
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catalan, G.; Scott, J.F. Physics and Applications of Bismuth Ferrite. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2463–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J. Multiferroic Bismuth Ferrite-Based Materials for Multifunctional Applications: Ceramic Bulks, Thin Films and Nanostructures. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 335–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.T.; Choi, T.; Choi, S.G.; Oh, Y.S.; Cheong, S.-W. Mechanism of the Switchable Photovoltaic Effect in Ferroelectric BiFeO3. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3403–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Yao, K.; Liang, Y.C. Bulk Photovoltaic Effect at Visible Wavelength in Epitaxial Ferroelectric BiFeO 3 Thin Films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.F. Multiferroic Memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, J.; Eng, L.M. Shedding Light on Nanoscale Ferroelectrics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, F.; Huang, X.; Qin, L.; Huang, Y. A Review: Preparation of Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles and Its Applications in Visible-Light Induced Photocatalyses. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Epitaxial BiFeO3 Multiferroic Thin Film Heterostructures. Science 2003, 299, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Sen, A.; Sekhar Maiti, H. Low-Temperature Synthesis of Nanosized Bismuth Ferrite by Soft Chemical Route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, J.; Salamon, S.; Escobar Castillo, M.; Lupascu, D.C.; Wende, H. Mössbauer Study of Temperature-Dependent Cycloidal Ordering in BiFeO 3 Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6061–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Palkar, V.; Pinto, R. Size Effect Study in Magnetoelectric BiFeO3 System. Pramana 2002, 58, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Sen, A.; Maiti, H.S. Low Temperature Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles by a Ferrioxalate Precursor Method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, H.; Sasaki, T.; Koshizaki, N. Optical Transmittance of Indium Tin Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser-Induced Fragmentation in Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 12890–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, C.-K.; Han, L.; Yang, J.; Du, X.-W. Top-Down Preparation of Active Cobalt Oxide Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6699–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.; Wiedwald, U.; Dubs, C.; Gökce, B. Ultrasmall Yttrium Iron Garnet Nanoparticles with High Coercivity at Low Temperature Synthesized by Laser Ablation and Fragmentation of Pressed Powders. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser Synthesis and Processing of Colloids: Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.X.; Hong, M.H.; Ong, T.S.; Lam, H.M.; Chen, W.Z.; Elim, H.I.; Ji, W.; Chong, T.C. Carbon Nanoparticles Based Nonlinear Optical Liquid. Carbon N. Y. 2004, 42, 2735–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Hong, M.H.; Lan, B.; Wang, Z.B.; Lu, Y.F.; Chong, T.C. A Convenient Way to Prepare Magnetic Colloids by Direct Nd:YAG Laser Ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 228, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waag, F.; Gökce, B.; Kalapu, C.; Bendt, G.; Salamon, S.; Landers, J.; Hagemann, U.; Heidelmann, M.; Schulz, S.; Wende, H.; et al. Adjusting the Catalytic Properties of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Fragmentation in Water with Defined Energy Dose. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Koshizaki, N. Guided Slow Continuous Suspension Film Flow for Mass Production of Submicrometer Spherical Particles by Pulsed Laser Melting in Liquid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuné, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. Formation of Gold Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Solution of Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5114–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.; Furube, A.; Okamoto, T.; Hashimoto, S. Femtosecond Laser-Induced Size Reduction of Aqueous Gold Nanoparticles: In Situ and Pump−Probe Spectroscopy Investigations Revealing Coulomb Explosion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8503–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.; Barcikowski, S. Quantification of Mass-Specific Laser Energy Input Converted into Particle Properties during Picosecond Pulsed Laser Fragmentation of Zinc Oxide and Boron Carbide in Liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 348, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, D.N.; Launikonis, A.; Sasse, W.H.F.; Sanders, J.V. Colloidal Platinum Sols. Preparation, Characterization and Stability towards Salt. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1984, 80, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbock, C.; Merk, V.; Gamrad, L.; Streubel, R.; Barcikowski, S. Size Control of Laser-Fabricated Surfactant-Free Gold Nanoparticles with Highly Diluted Electrolytes and Their Subsequent Bioconjugation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, D.; Filice, S.; Miritello, M.; Bongiorno, C.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Compagnini, G.; Scalese, S. β-Bi 2 O 3 Reduction by Laser Irradiation in a Liquid Environment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 10292–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, J.P.; Poulin, S.; Kabashin, A.V.; Sacher, E.; Meunier, M.; Luong, J.H.T. Surface Chemistry of Gold Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Media. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16864–16869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.-Y.; Streubel, R.; Heberle, J.; Letzel, A.; Shugaev, M.V.; Wu, C.; Schmidt, M.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Two Mechanisms of Nanoparticle Generation in Picosecond Laser Ablation in Liquids: The Origin of the Bimodal Size Distribution. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6900–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigilei, L.V.; Garrison, B.J. Computer Simulation Study of Damage and Ablation of Submicron Particles from Short-Pulse Laser Irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 127–129, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Spectral Properties and Relaxation Dynamics of Surface Plasmon Electronic Oscillations in Gold and Silver Nanodots and Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8410–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sugioka, K. Hierarchical Microstructures with High Spatial Frequency Laser Induced Periodic Surface Structures Possessing Different Orientations Created by Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Silicon in Liquids. Opto-Electronic Adv. 2019, 2, 19000201–19000218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; You, L.; Du, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z.; Ma, G.; Leng, Y. Ultrafast Electron-Phonon Coupling and Photo-Induced Strain in the Morphotropic Phase Boundary of BixDy1−xFeO3 Films. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Das, S.; Majumdar, A.; Katiyal, S.; Poojitha, B.; Saha, S.; Shripathi, T. Phase Pure Epitaxial Growth of BiFeO3 Films: An Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure. Solid State Commun. 2017, 264, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béa, H.; Bibes, M.; Barthélémy, A.; Bouzehouane, K.; Jacquet, E.; Khodan, A.; Contour, J.-P.; Fusil, S.; Wyczisk, F.; Forget, A.; et al. Influence of Parasitic Phases on the Properties of BiFeO3 Epitaxial Thin Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 072508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, N.; Wolfman, J.; Daumont, C.; Négulescu, B.; Ruyter, A.; Sauvage, T.; Courtois, B.; Bouyanfif, H.; Longuet, J.L.; Autret-Lambert, C.; et al. Laser Fluence and Spot Size Effect on Compositional and Structural Properties of BiFeO 3 Thin Films Grown by Pulsed Laser Deposition. Thin Solid Films 2017, 634, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (m) | 532 |
| Beam quality factor (M2) | 1.2 |
| Pulse length (ps) | 10 |
| Beam diameter (mm) | 3 |
| Parameter | Elliptical Jet | CIRCULAR Jet |
|---|---|---|
| Laser power (W) | 83.7 | 48.4 |
| Pulse frequency (kHz) | 92.95 | 54.52 |
| Pulse energy (µJ) | 900 | 888 |
| Peak fluence of incident Gaussian beam (J/cm2) | 1.54 | 1.52 |
| Focus length (mm) | 100 | 100 |
| Distance from lens back (from housing) (mm) | 103.4 (100.96) | 103.4 (100.96) |
| Colloid volume (mL) | 196 | 195 |
| Orifice dimension (major axes) (µm) | 550 × 1200 | 1300 × 1300 |
| Flow time (s) | 119 | 91 |
| Pulse per particle | 1.16 | 1.13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siebeneicher, S.; Waag, F.; Escobar Castillo, M.; Shvartsman, V.V.; Lupascu, D.C.; Gökce, B. Laser Fragmentation Synthesis of Colloidal Bismuth Ferrite Particles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020359
Siebeneicher S, Waag F, Escobar Castillo M, Shvartsman VV, Lupascu DC, Gökce B. Laser Fragmentation Synthesis of Colloidal Bismuth Ferrite Particles. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020359
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiebeneicher, Simon, Friedrich Waag, Marianela Escobar Castillo, Vladimir V. Shvartsman, Doru C. Lupascu, and Bilal Gökce. 2020. "Laser Fragmentation Synthesis of Colloidal Bismuth Ferrite Particles" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020359
APA StyleSiebeneicher, S., Waag, F., Escobar Castillo, M., Shvartsman, V. V., Lupascu, D. C., & Gökce, B. (2020). Laser Fragmentation Synthesis of Colloidal Bismuth Ferrite Particles. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020359







