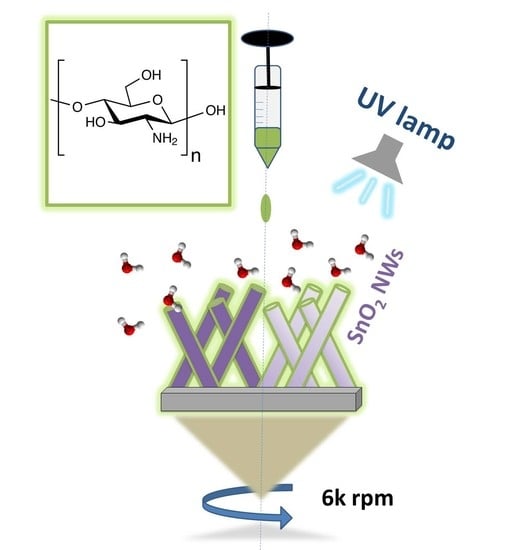
UV-Enhanced Humidity Sensing of Chitosan–SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of SnO2 Nanowires
2.2. Synthesis of Chitosan@SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires
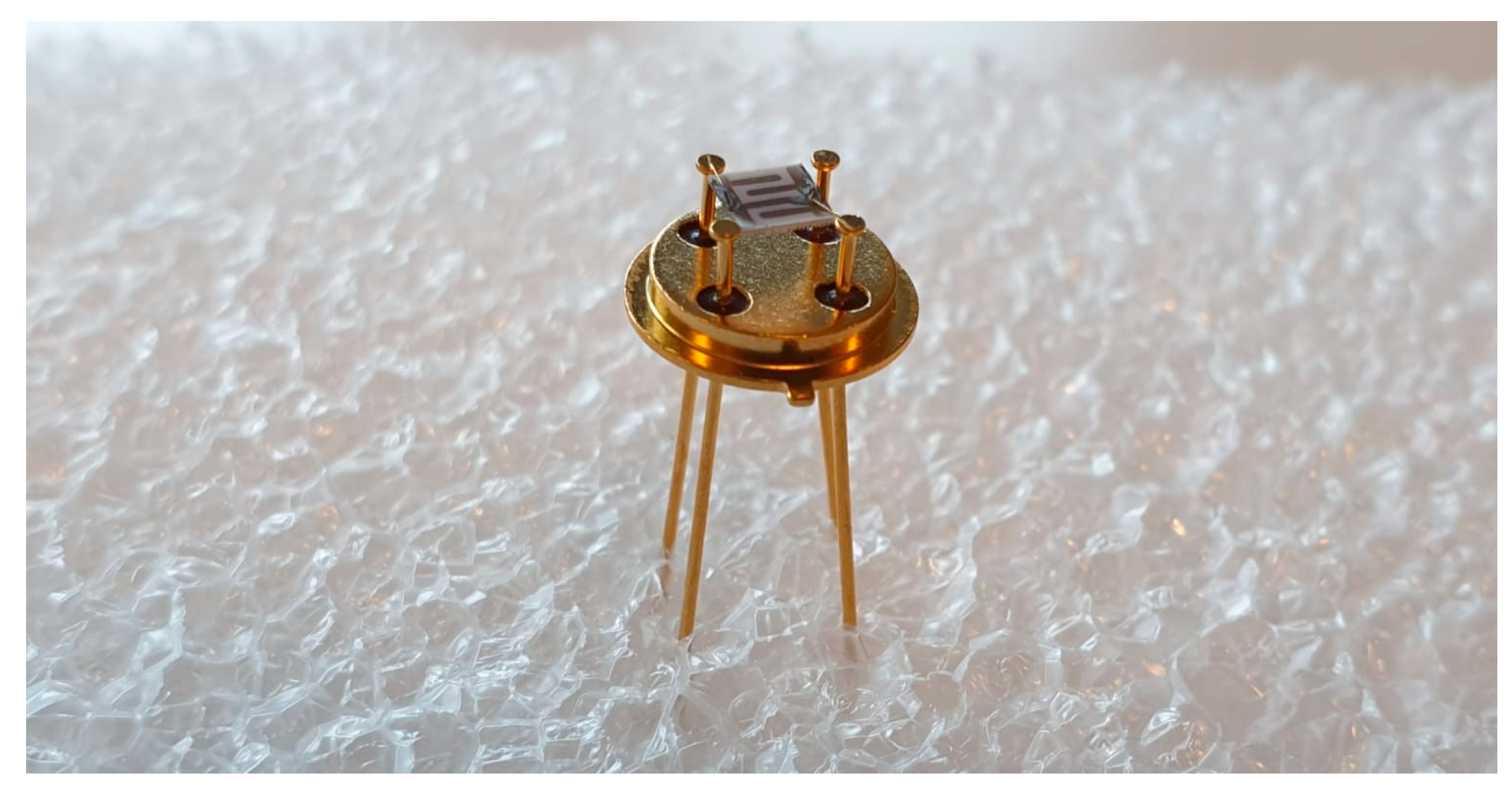
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.4. Conductometric Humidity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
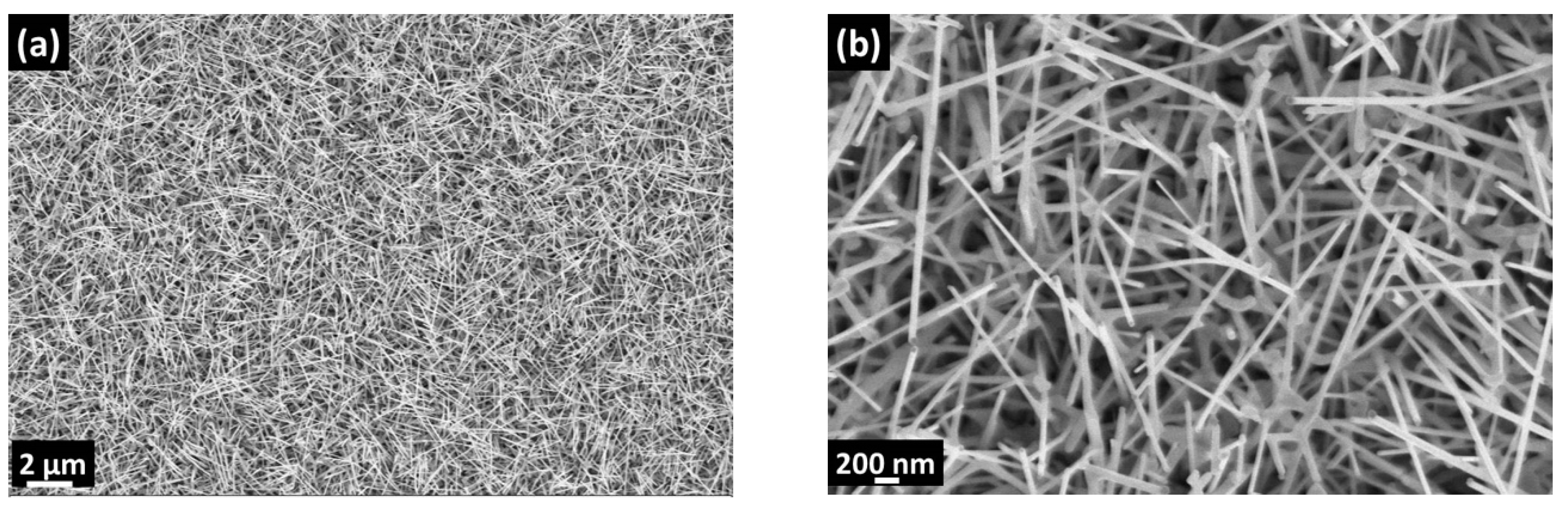
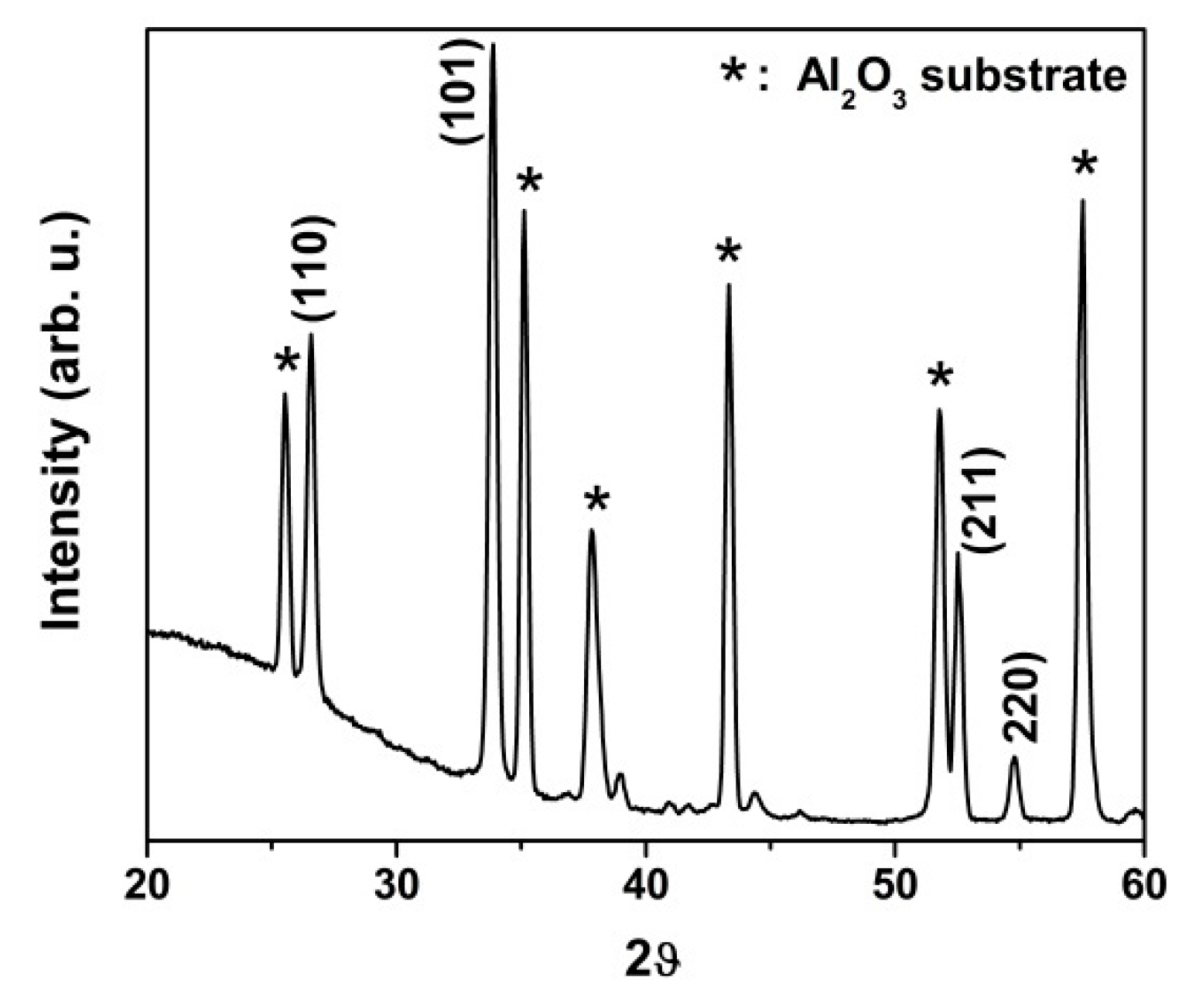
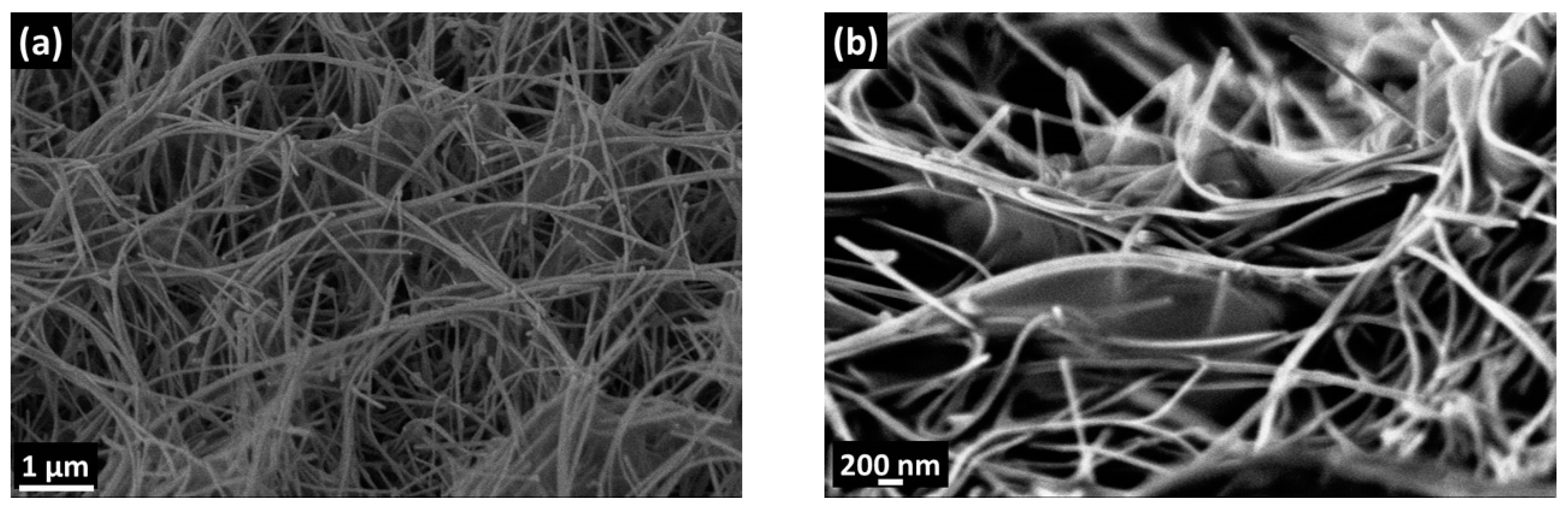
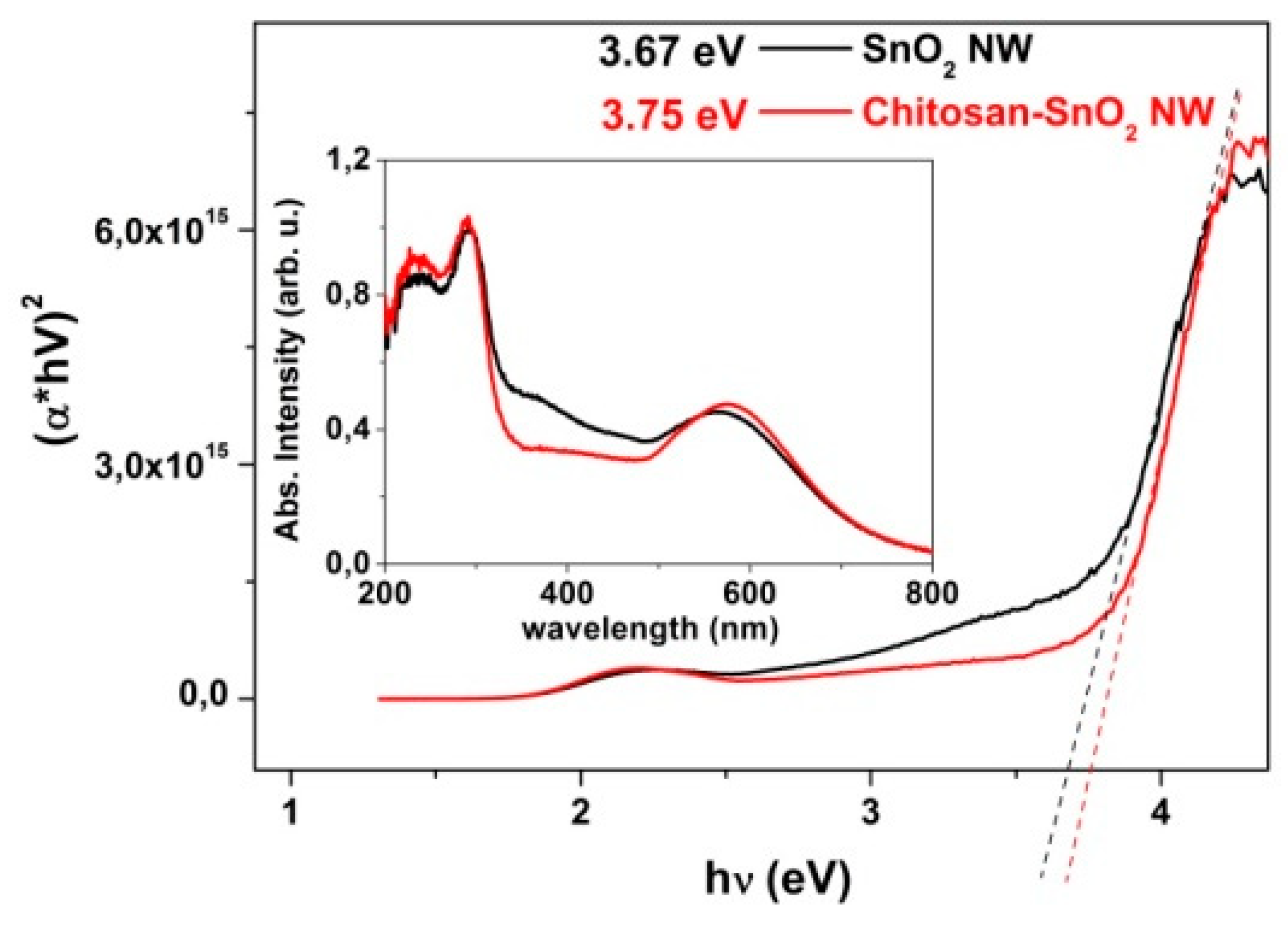
3.1. Material Characterizations
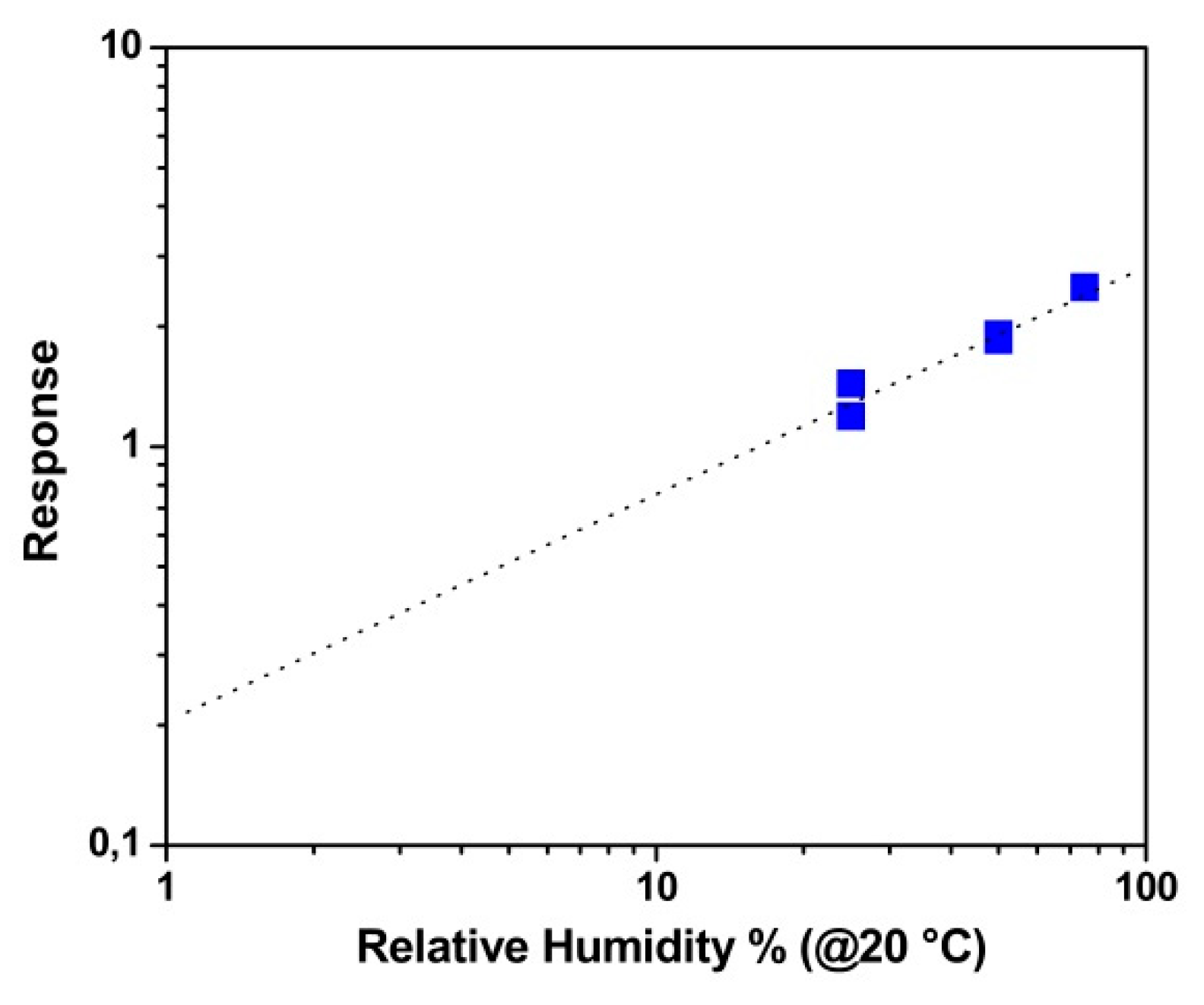
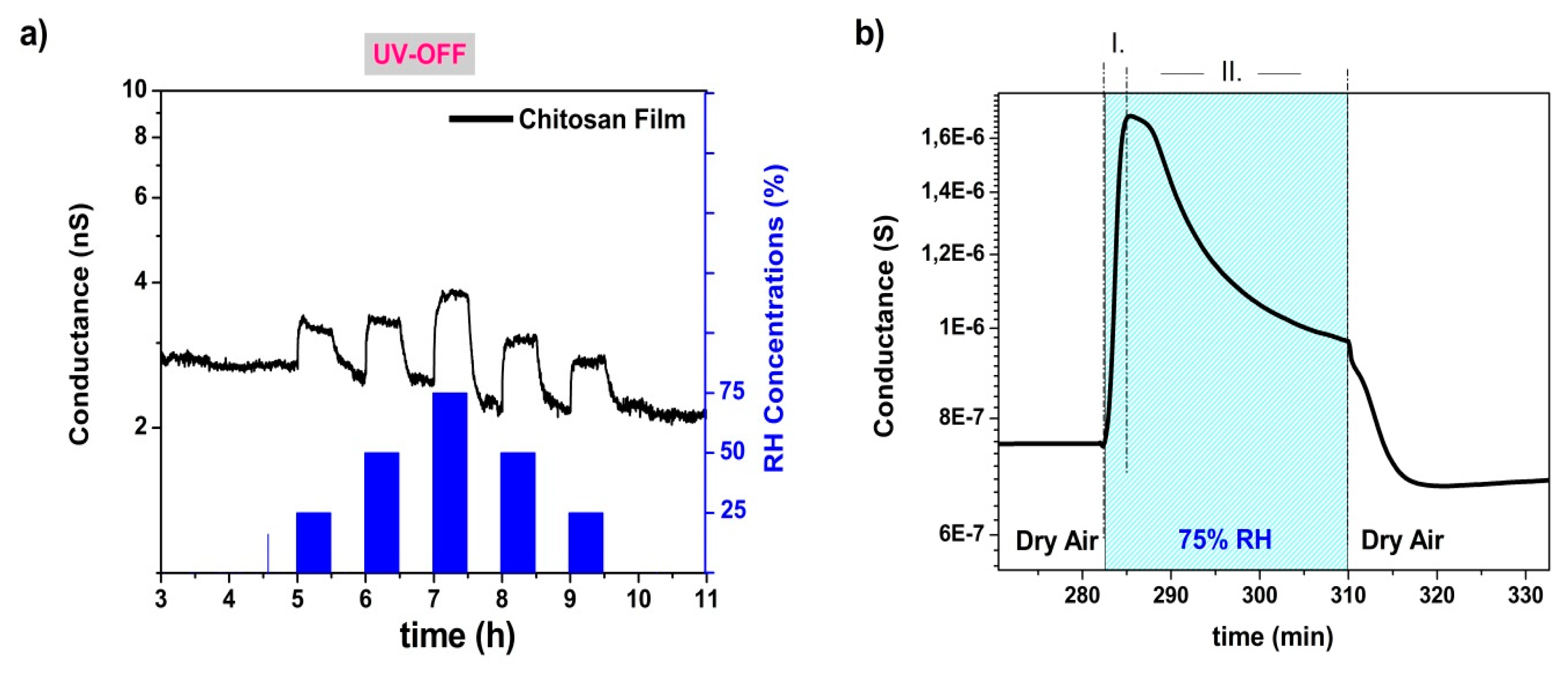
3.2. Humidity Sensing
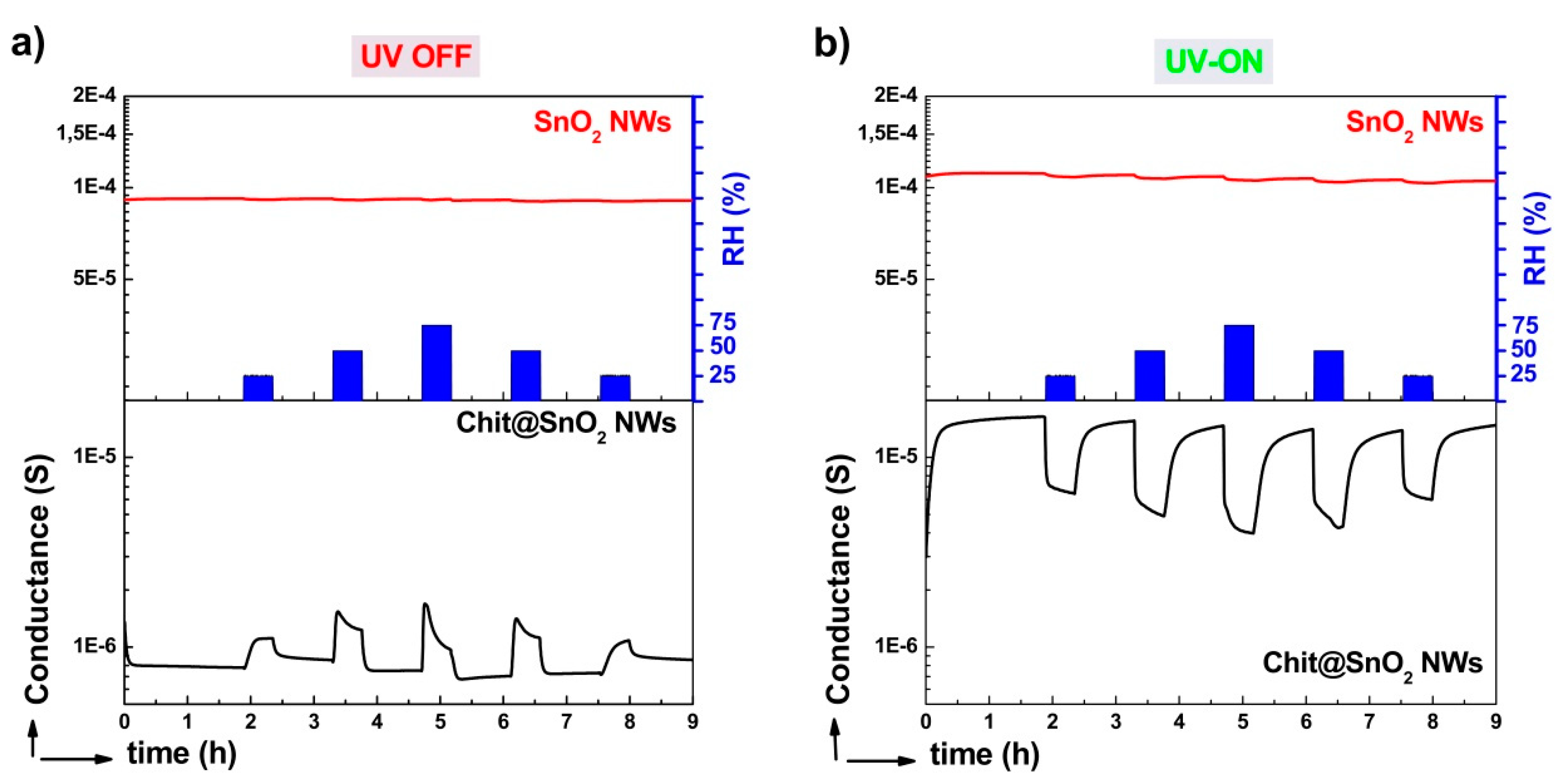
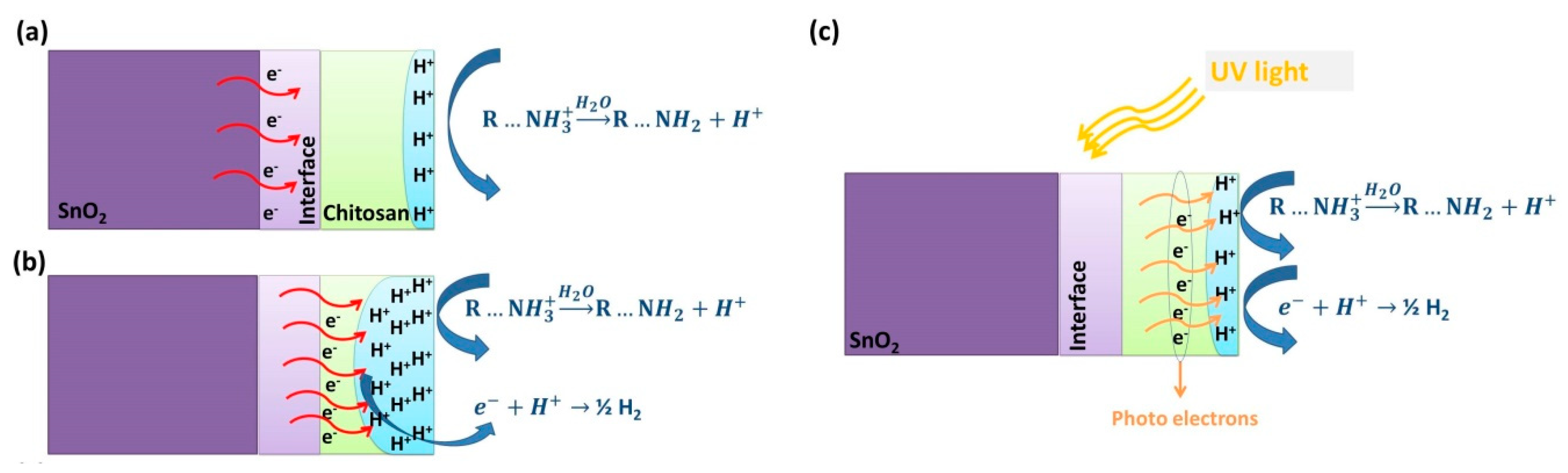
3.3. UV Effect on Sensing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Lai, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, W. Printable Transparent Conductive Films for Flexible Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, M.; Singh, A.; Samanta, S.; Aswal, D.K. Conductive polymers for thermoelectric power generation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 270–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.S.; Ren, G.; Jenekhe, S.A. One-dimensional nanostructures of π-conjugated molecular systems: Assembly, properties, and applications from photovoltaics, sensors, and nanophotonics to nanoelectronics. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 682–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.A.; Persaud, K.C. Sensing Volatile Chemicals Using Conducting Polymer Arrays. In Polymer Sensors and Actuators; Osada, Y., De Rossi, D.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 149–181. ISBN 978-3-662-04068-3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Virji, S.; Weiller, B.H.; Kaner, R.B. Nanostructured Polyaniline Sensors. Chem. A Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Santhanam, S.; Schultz, L.; Jeffries-EL, M.; Iovu, M.C.; Sauvé, G.; Cooper, J.; Zhang, R.; Revelli, J.C.; Kusne, A.G.; et al. Inkjet printed chemical sensor array based on polythiophene conductive polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, Q.; Adeloju, S.B. Polypyrrole-based electronic noses for environmental and industrial analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 106, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Ferreira, P. Tailoring Functional Chitosan-Based Composites for Food Applications. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironenko, A.Y.; Sergeev, A.A.; Nazirov, A.E.; Modin, E.B.; Voznesenskiy, S.S.; Bratskaya, S.Y. H2S optical waveguide gas sensors based on chitosan/Au and chitosan/Ag nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hani, A.F.S.; Greish, Y.E.; Mahmoud, S.T.; Awwad, F.; Ayesh, A.I. Low-temperature and fast response H2S gas sensor using semiconducting chitosan film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Feller, J.F.; Castro, M.; Lu, J. Conductive bio-Polymer nano-Composites (CPC): Chitosan-carbon nanotube transducers assembled via spray layer-by-layer for volatile organic compound sensing. Talanta 2010, 81, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jang, D.M.; An, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, H. Polyaniline-chitosan nanocomposite: High performance hydrogen sensor from new principle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.M.; Salahuddin, N.A.; Minisy, I.M.; Amer, W.A. Chitosan/polyaniline nanofibers coating on the quartz crystal microbalance electrode for gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous chitosan membranes modified with polyethyleneimine for formaldehyde detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Shi, X.; Hou, I.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z. Development of molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors based on Fe3O4@MWNT-COOH/CS nanocomposite layers for detecting traces of acephate and trichlorfon. Analyst 2014, 139, 6406–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, E.; Wang, L.; Jing, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, G. One-step fabrication of integrated disposable biosensor based on ADH/NAD+/meldola’s blue/graphitized mesoporous carbons/chitosan nanobiocomposite for ethanol detection. Talanta 2013, 111, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla-Abbasi, P.; Ghaffarian, S.R. Decoration of carbon nanotubes by chitosan in a nanohybrid conductive polymer composite for detection of polar vapours. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30906–30913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Feng, N.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Chemiresistive humidity sensor based on chitosan/zinc oxide/single-walled carbon nanotube composite film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bertke, M.; Li, X.; Mu, H.; Zhou, H.; Yu, F.; Hamdana, G.; Schmidt, A.; Bremers, H.; Peiner, E. Fabrication of ZnO nanorods and Chitosan@ZnO nanorods on MEMS piezoresistive self-actuating silicon microcantilever for humidity sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, M.; Gong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, W.; Ding, W. Influence of Charge Carriers Concentration and Mobility on the Gas Sensing Behavior of Tin Dioxide Thin Films. Coatings 2019, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, P.; Hao, J.; Koev, S.T.; Payne, G.F.; Yu, L.; Ghodssi, R. An optical MEMS sensor utilizing a chitosan film for catechol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.; Ahmad, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Karuppiah, N.; Sidek, H. An optical biosensor based on immobilization of lacease and MBTH in stacked films for the detection of catechol. Sensors 2007, 7, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, M.A.; Koev, S.T.; Schleunitz, A.; Yi, H.; Hodzic, V.; Bentley, W.E.; Payne, G.F.; Rubloff, G.W.; Ghodssi, R. A fabrication platform for electrically mediated optically active biofunctionalized sites in BioMEMS. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koev, S.T.; Dykstra, P.H.; Luo, X.; Rubloff, G.W.; Bentley, W.E.; Payne, G.F.; Ghodssi, R. Chitosan: An integrative biomaterial for lab-on-a-chip devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3026–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Carmona, E.; Bertuna, A.; Abbatangelo, M.; Sberveglieri, V.; Comini, E.; Sberveglieri, G. BC-MOS: The novel bacterial cellulose based MOS gas sensors. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvree, A.; Feller, J.F.; Castro, M.; Grohens, Y.; Rinaudo, M. Conductive Polymer nano-bioComposites (CPC): Chitosan-carbon nanoparticle a good candidate to design polar vapour sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q. Giant Humidity Response Using a Chitosan-Based Protonic Conductive Sensor. IEEE Sensors J. 2016, 16, 8884–8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, V.K.; Akhtar, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mishra, S.; Singh, R.P.; Ha, C.S. Chitosan and Chitosan-co-Poly(-caprolactone) Grafted Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Transducers for Vapor Sensing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Wu, L.Q.; Bentley, W.E.; Ghodssi, R.; Rubloff, G.W.; Culver, J.N.; Payne, G.F. Biofabrication with chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; An, S.; Mun, Y.; Lee, C. UV-enhanced NO2 gas sensing properties of SnO2-Core/ZnO-shell nanowires at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4285–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, D.; Yang, Y.; Du, H.; Li, X. UV Light Activated SnO2/ZnO Nanofibers for Gas Sensing at Room Temperature. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prades, J.D.; Jimenez-Diaz, R.; Manzanares, M.; Hernandez-Ramirez, F.; Cirera, A.; Romano-Rodriguez, A.; Mathur, S.; Morante, J.R. A model for the response towards oxidizing gases of photoactivated sensors based on individual SnO2 nanowires. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 10881–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Material | Transducer | RH Conc. | Response | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2% CNT-Chitosan | Chemoresistor | 1% Vapor Conc. | 1 | [12] |
| PVA/Chitosan/CNT | Chemoresistor | 10 ‰Vapor | 0.05 | [18] |
| Chitosan/ZnO/SWCNT | Chemoresistor | 75% | 0.75 | [19] |
| Chitosan | Chemoresistor | α% RH | 4.2 × α | [29] |
| Chitosan@SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires | Chemoresistor | 75% RH (dark) | 1.1 | This work |
| 75% RH (UV irradiation) | 2.5 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sisman, O.; Kaur, N.; Sberveglieri, G.; Núñez-Carmona, E.; Sberveglieri, V.; Comini, E. UV-Enhanced Humidity Sensing of Chitosan–SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020329
Sisman O, Kaur N, Sberveglieri G, Núñez-Carmona E, Sberveglieri V, Comini E. UV-Enhanced Humidity Sensing of Chitosan–SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleSisman, Orhan, Navpreet Kaur, Giorgio Sberveglieri, Estefania Núñez-Carmona, Veronica Sberveglieri, and Elisabetta Comini. 2020. "UV-Enhanced Humidity Sensing of Chitosan–SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020329
APA StyleSisman, O., Kaur, N., Sberveglieri, G., Núñez-Carmona, E., Sberveglieri, V., & Comini, E. (2020). UV-Enhanced Humidity Sensing of Chitosan–SnO2 Hybrid Nanowires. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020329