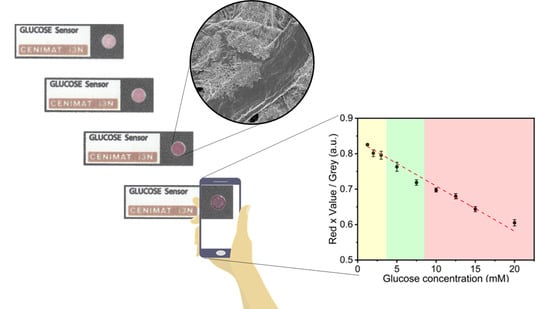
Paper-Based In-Situ Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis for Colorimetric, Non-Enzymatic Glucose Level Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of AuNPs in Solution
2.2. AuNPs Characterization
2.3. Paper-Based Platform Fabrication
2.4. Synthesis of AuNPs at Paper Substrate
2.5. Data Acquisition and Colorimetric Analysis
2.6. Testing Against Interfering Agents
2.7. AuNPs Characterization at Paper Substrate
2.8. Colorimetric Sensing in Complex Samples
3. Results
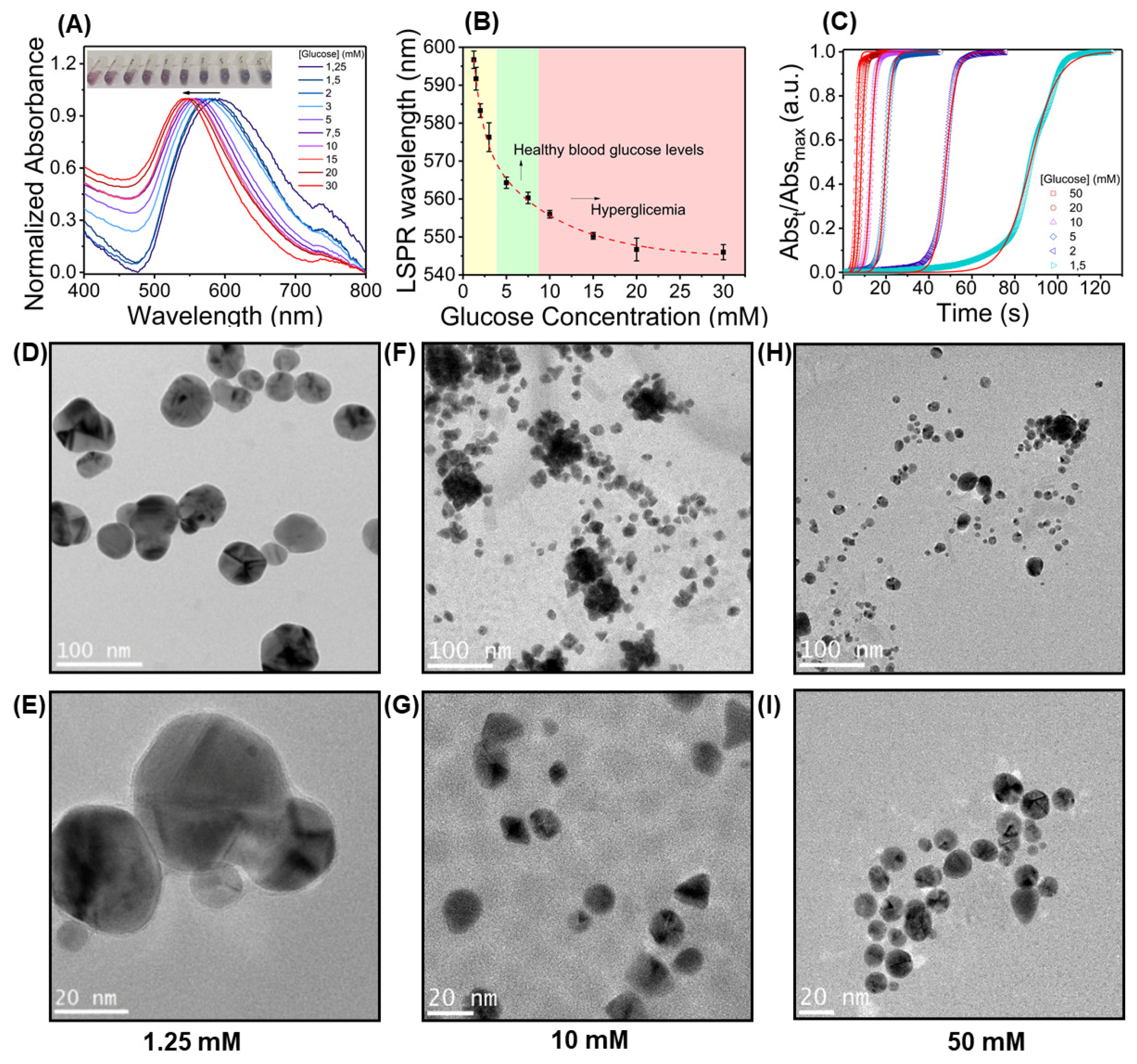
3.1. AuNPs Synthesis Mechanisms through Reduction and Capping by Glucose
3.1.1. Effect of Reaction Parameters towards Optical and Kinetic Properties
3.1.2. Effect of Reducing Agent Concentration and Direct Colorimetric Glucose Sensing
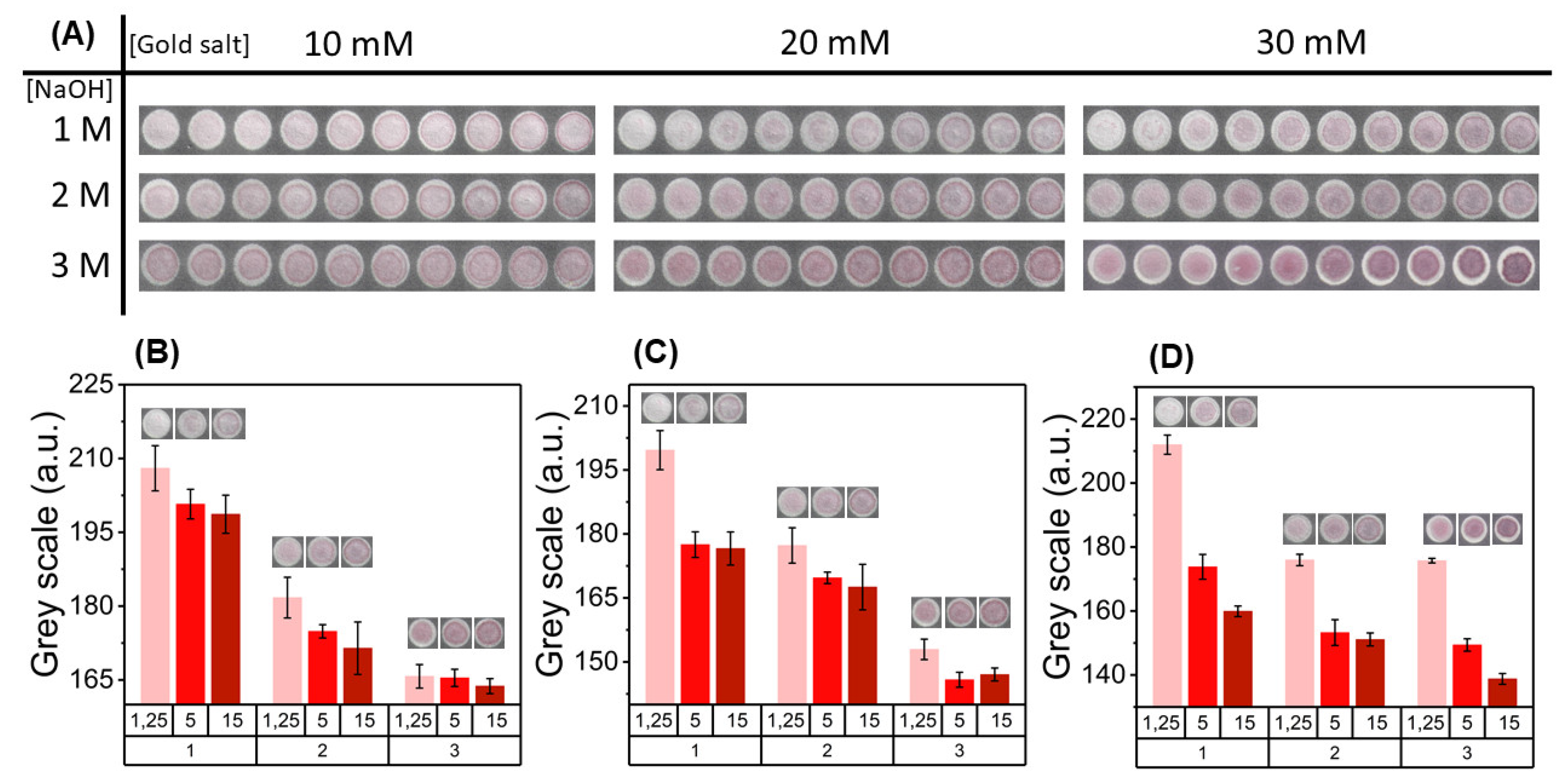
3.2. Colorimetric Assay in Paper Substrate
Parameter Optimization
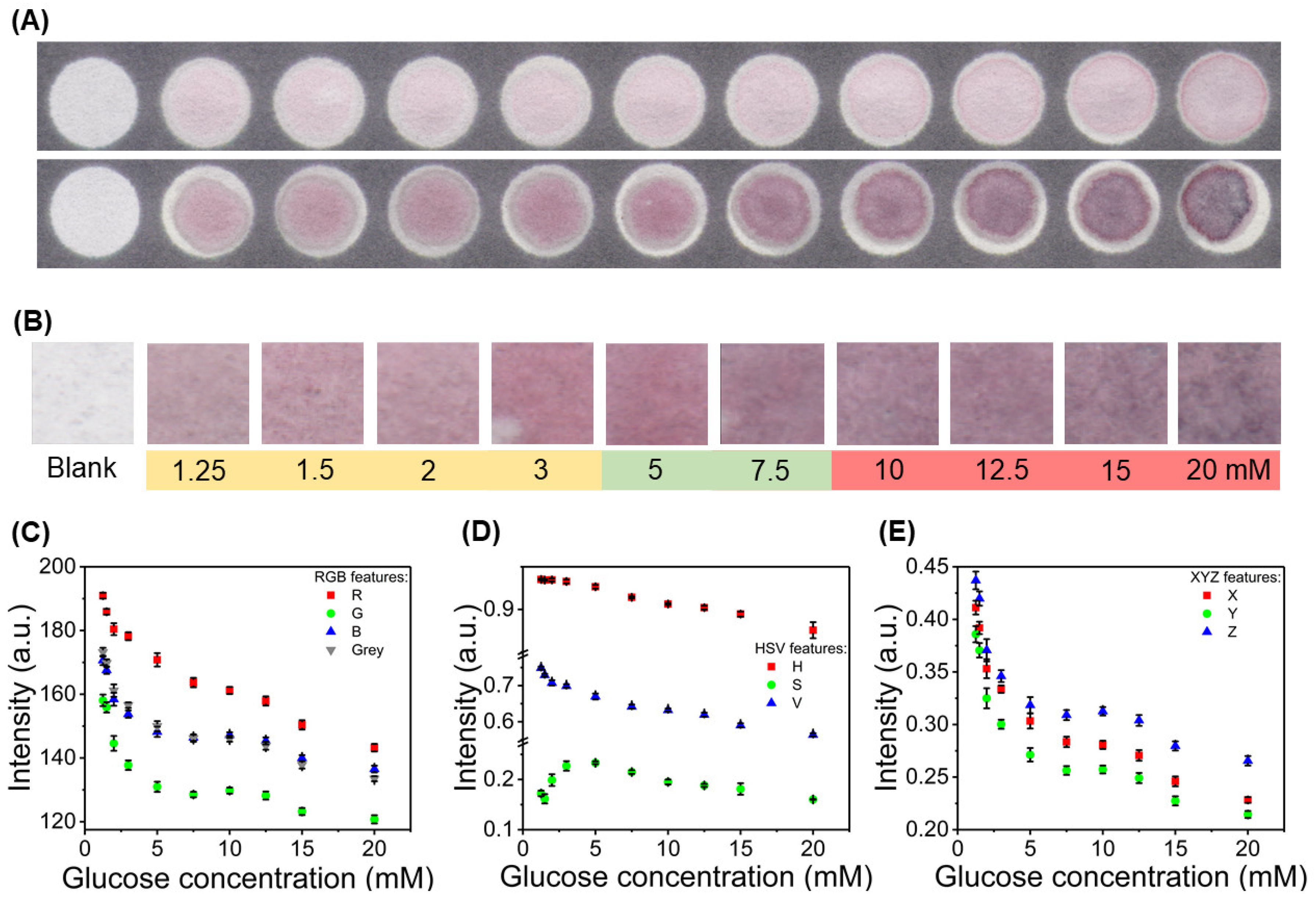
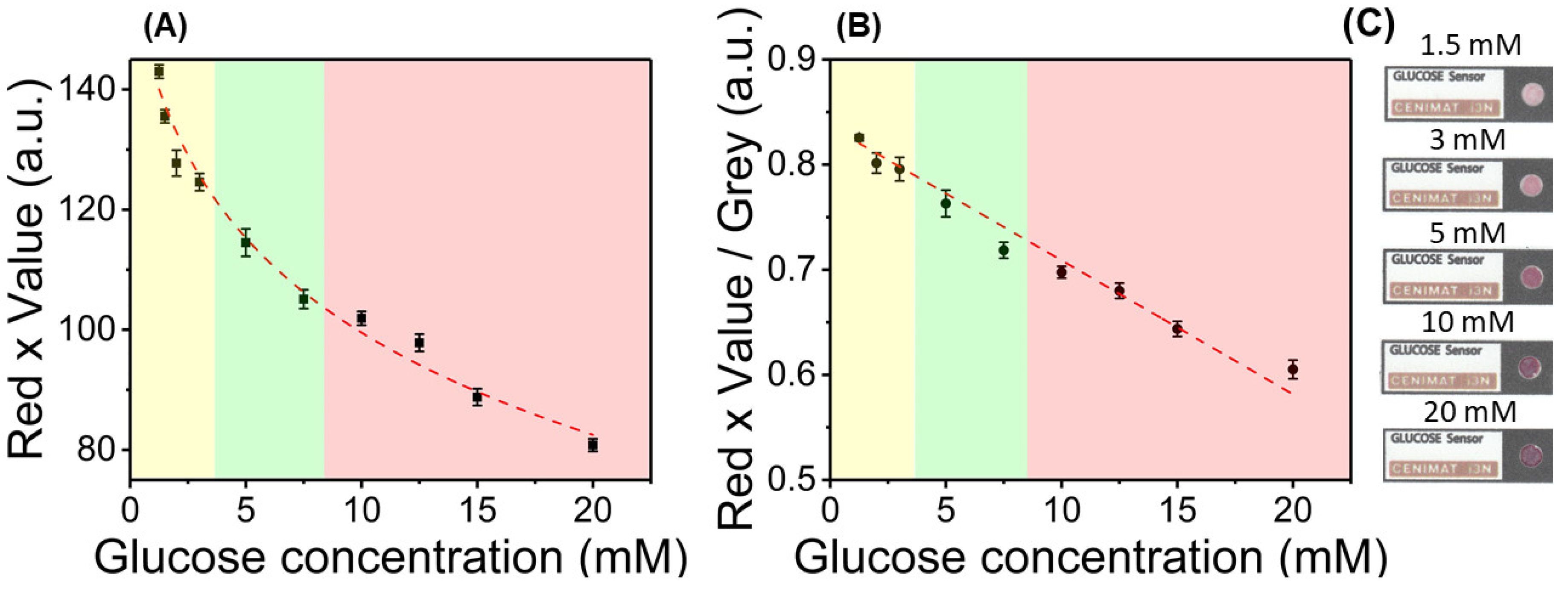
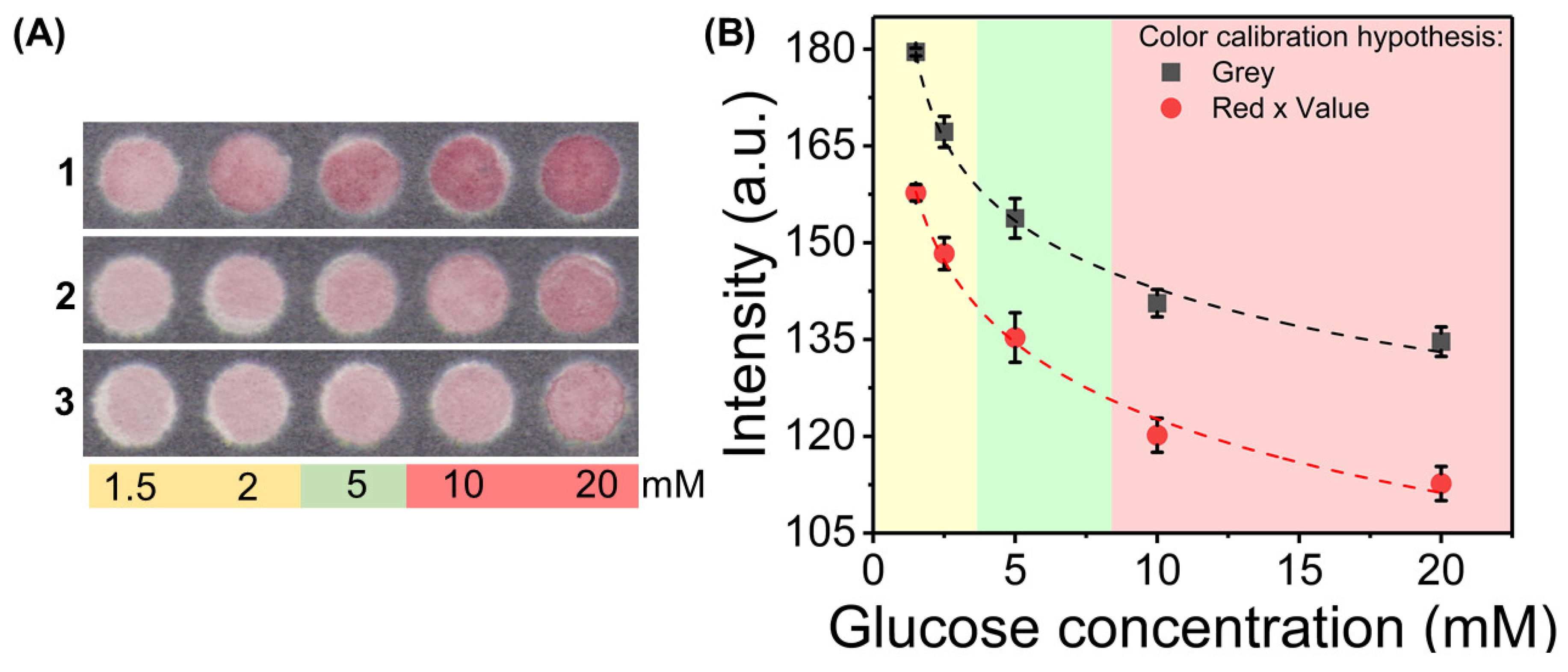
3.3. Color Feature Study and Calibration
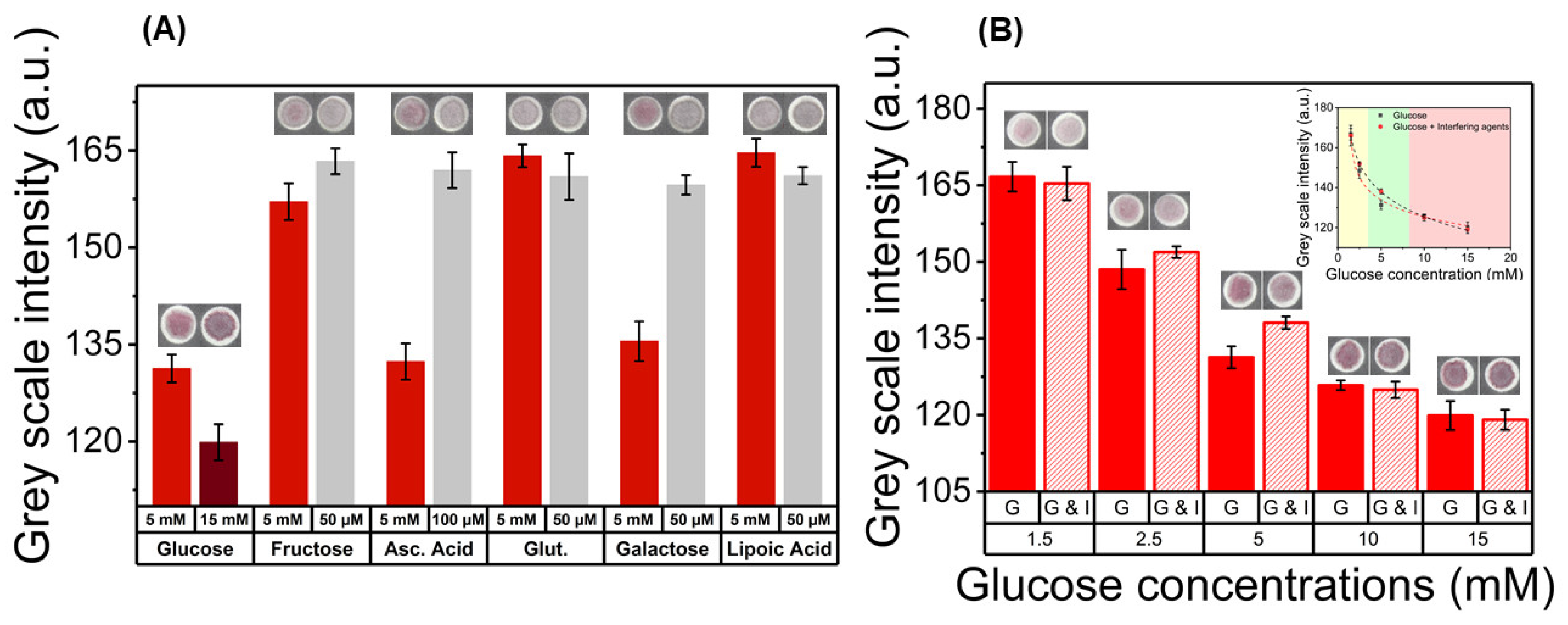
3.4. Interference Assay in the Paper Platform
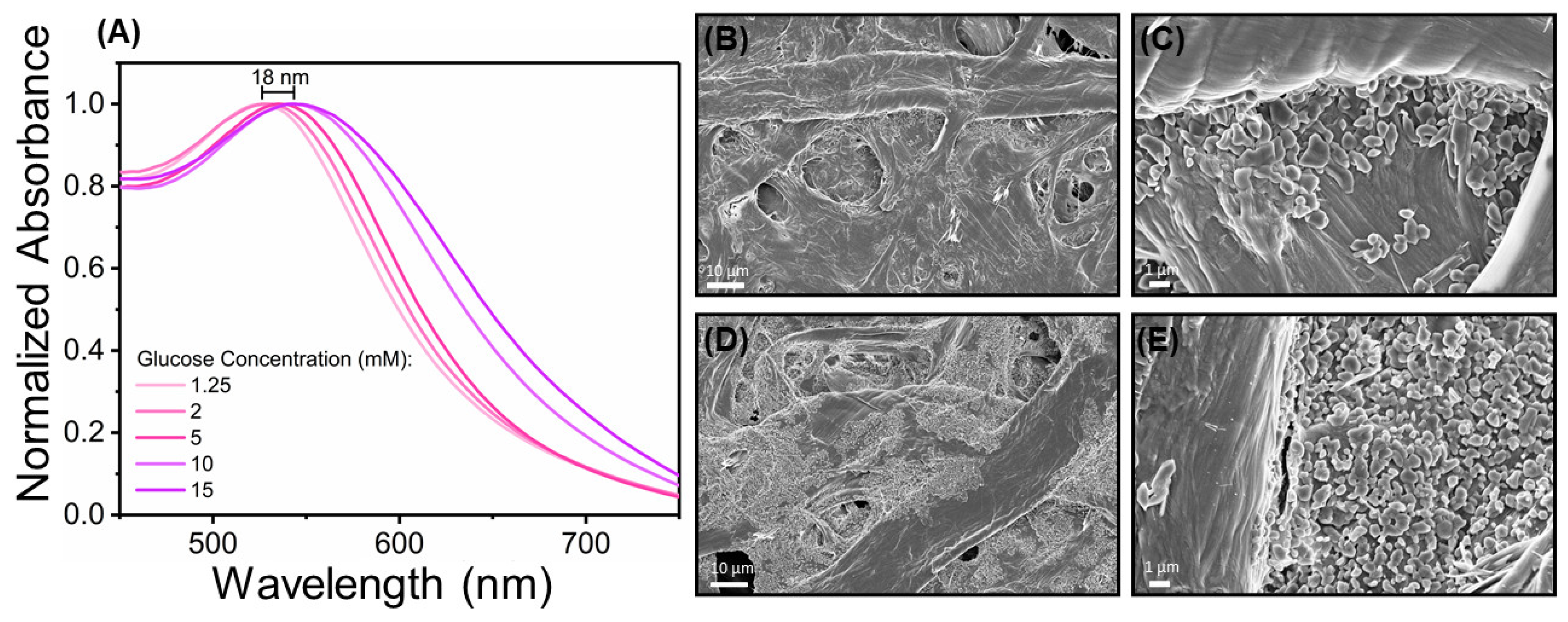
3.5. AuNPs Characterization in Paper Substrate
3.6. Colorimetric Sensing in Biological Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, M.N.; Veigas, B.; Jacob, J.M.; Santos, D.S.; Gomes, J.; Baptista, P.V.; Martins, R.; Inácio, J.; Fortunato, E. A Low Cost, Safe, Disposable, Rapid and Self-Sustainable Paper-Based Platform for Diagnostic Testing: Lab-on-Paper. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xiang, X.; Luo, M.; Ji, X.; He, Z. Determination of Glucose and Uric Acid with Bienzyme Colorimetry on Microfluidic Paper-Based Analysis Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, W.; Ding, X. A Review on Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Glucose Detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaurs, C.; Brun, J.F.; Bertrand, M.; Burcelin, R.; Du Rieu, M.C.; Anduze, Y.; Hanaire, H.; Ritz, P. Post-Prandial Hypoglycemia Results from a Non-Glucose-Dependent Inappropriate Insulin Secretion in Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypassed Patients. Metabolism 2016, 65, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems: A Review. Diagnostics 2013, 3, 385–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, D. Hyperglycemia and the Pathobiology of Diabetic Complications. In Cardiovascular Diabetology: Clinical, Metabolic and Inflammatory Facets; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 45, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Lee, A.R. Recent Developments in Blood Glucose Sensors. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, X.-L.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhu, Z.-G.; Qian, S.-H.; Flewitt, A. Current and Emerging Technology for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical Glucose Biosensors. In Chemical Reviews; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical Glucose Sensors and Their Applications in Diabetes Management. In Chemical Reviews; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the Developing World: Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Santos, L.; Costa, M.N.; Dantas, J.M.; Duarte, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Martins, R.; Salgueiro, C.A.; Fortunato, E. Office Paper Platform for Bioelectrochromic Detection of Electrochemically Active Bacteria Using Tungsten Trioxide Nanoprobes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, J. Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. RSC Adv. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, C.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T. Enzymatic and Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors. In Fundamentals and Sensing Applications of 2D Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 259–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; et al. “Gold Rush” in Modern Science: Fabrication Strategies and Typical Advanced Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Sensing. In Coordination Chemistry Reviews; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Plasmonic Colorimetric Sensors Based on Etching and Growth of Noble Metal Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. In Biosensors and Bioelectronics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Nawaz, M.H.; Latif, U.; Yaqub, M.; Hayat, A.; Rahim, A. An Overview on Enzyme-Mimicking Nanomaterials for Use in Electrochemical and Optical Assays. In Microchimica Acta; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2017; pp. 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors—A Review. In Analytica Chimica Acta; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, W. In Situ Formed Nanomaterials for Colorimetric and Fluorescent Sensing. In Coordination Chemistry Reviews; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, K.; He, S.; Xia, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. Sensitive Detection of Glucose Based on Gold Nanoparticles Assisted Silver Mirror Reaction. Analyst 2011, 136, 2893–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Ye, J.; Tan, K.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. Colorimetric Visualization of Glucose at the Submicromole Level in Serum by a Homogenous Silver Nanoprism-Glucose Oxidase System. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6241–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.A.; Sreenivasan, K. Non Enzymatic Colorimetric Detection of Glucose Using Cyanophenyl Boronic Acid Included β-Cyclodextrin Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Di, J. Colorimetric Detection of Glucose Based on Gold Nanoparticles Coupled with Silver Nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Gao, Y.; Yan, J.; Wu, Y.; Di, J. Visual Detection of Glucose Using Triangular Silver Nanoplates and Gold Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29122–29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Kalwar, N.H.; Abbas, M.W.; Soomro, R.A.; Saand, M.A.; Awan, F.R.; Avci, A.; Pehlivan, E.; Bajwa, S. Enzyme-Free Colorimetric Sensing of Glucose Using l-Cysteine Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juřík, T.; Podešva, P.; Farka, Z.; Kovář, D.; Skládal, P.; Foret, F. Nanostructured Gold Deposited in Gelatin Template Applied for Electrochemical Assay of Glucose in Serum. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandurra, A.; Ruffino, F.; Sanzaro, S.; Grimaldi, M.G. Laser and Thermal Dewetting of Gold Layer onto Graphene Paper for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Detection of Glucose and Fructose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buk, V.; Pemble, M.E.; Twomey, K. Fabrication and Evaluation of a Carbon Quantum Dot/Gold Nanoparticle Nanohybrid Material Integrated onto Planar Micro Gold Electrodes for Potential Bioelectrochemical Sensing Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 293, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buk, V.; Pemble, M.E. A Highly Sensitive Glucose Biosensor Based on a Micro Disk Array Electrode Design Modified with Carbon Quantum Dots and Gold Nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 298, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branagan, D.; Breslin, C.B. Electrochemical Detection of Glucose at Physiological PH Using Gold Nanoparticles Deposited on Carbon Nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, E.; Martinez, A.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Understanding Wax Printing: A Simple Micropatterning Process for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7091–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Van Den Berg, A. Lab on Paper. In Lab on a Chip; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2008; pp. 1988–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, C.; Koehne, J.; Ricco, A.J.; Crooks, R.M. Three-Dimensional Wax Patterning of Paper Fluidic Devices. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7030–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unser, S.; Campbell, I.; Jana, D.; Sagle, L. Direct Glucose Sensing in the Physiological Range through Plasmonic Nanoparticle Formation. Analyst 2015, 140, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. Completely “Green” Synthesis and Stabilization of Metal Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13940–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. A Simple and “Green” Method for the Synthesis of Au, Ag, and Au–Ag Alloy Nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The Human Serum Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.J.; Quaresma, P.; De Almeida, M.P.; Araújo, A.; Pereira, E.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Franco, R.; Águas, H. Office Paper Decorated with Silver Nanostars-an Alternative Cost Effective Platform for Trace Analyte Detection by SERS. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrekt, C.; Sørensen, K.H.; Zhang, J.; Welinder, A.C.; Jensen, P.S.; Ulstrup, J. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles with Starch-Glucose and Application in Bioelectrochemistry. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7839–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, S.; Das, U.; Sunil, K.C.; Mishra, S.; Sudarshan, M.; Saha, K.D.; Dey, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Narayana, Y. Synthesis of a Novel Glucose Capped Gold Nanoparticle as a Better Theranostic Candidate. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported Gold Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Organic Reactions. In Chemical Society Reviews; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2008; pp. 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Petit, C.; Pitchon, V. A New Preparation Method for the Formation of Gold Nanoparticles on an Oxide Support. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 267, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacławski, K.; Streszewski, B.; Jaworski, W.; Luty-Błocho, M.; Fitzner, K. Gold Nanoparticles Formation via Gold(III) Chloride Complex Ions Reduction with Glucose in the Batch and in the Flow Microreactor Systems. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 413, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzky, M.A.; Finke, R.G. Transition Metal Nanocluster Formation Kinetic and Mechanistic Studies. A New Mechanism When Hydrogen Is the Reductant: Slow, Continuous Nucleation and Fast Autocatalytic Surface Growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10382–10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luty-Błocho, M.; Wojnicki, M.; Fitzner, K. Gold Nanoparticles Formation via Au(III) Complex Ions Reduction with l-Ascorbic Acid. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2017, 49, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbgoo, F.; Nejabat, M.; Abnous, K.; Soltani, F.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Thomas Shier, W.; Steele, T.W.J.; Ramezani, M. Gold Nanoparticle Should Understand Protein Corona for Being a Clinical Nanomaterial. J. Control. Release 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Gao, N.; Li, J.F.; Wu, F.Y. Colorimetric Detection of Methionine Based on Anti-Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles in the Presence of Melamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2779–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksorn, J.; Teepoo, S. Development of the Simultaneous Colorimetric Enzymatic Detection of Sucrose, Fructose and Glucose Using a Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device. Talanta 2020, 207, 120302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, E.F.M.; Garcia, P.T.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; Lopes, F.M.; Martins, F.T.; Coltro, W.K.T. Highly Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Glucose and Uric Acid in Biological Fluids Using Chitosan-Modified Paper Microfluidic Devices. Analyst 2016, 141, 4749–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauerova, K.; Carneiro, M.C.C.G.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Nanocellulose- Based Biosensor for Colorimetric Detection of Glucose. Sens. Bio Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Feng, D.Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.D.; Zhu, R.; Fang, H.L.; Wang, W. Bienzyme Colorimetric Detection of Glucose with Self-Calibration Based on Tree-Shaped Paper Strip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, E.F.M.; Garcia, P.T.; Lopes, F.M.; Coltro, W.K.T. Paper-Based Colorimetric Biosensor for Tear Glucose Measurements. Micromachines 2017, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Platform Material | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic—GOx/HRP/4-aminoantipyrine | Chromatography paper | 0.5–10 mM | 0.9 mM | [50] |
| Enzymatic—GOx/HRP/3 different chromogenic indicators | Chromatography paper | 1.0–6.0 mM | 12 µM | [51] |
| Enzymatic—GOx/HRP/ABTS | Carboxyl nanocellulose | 1.5–13 mM | 1.5 mM | [52] |
| Enzymatic—GOD/HRP byenzyme system | Chromatography paper | 1.0–11 mM | 0.3 mM | [53] |
| Enzymatic—GOx/HRP/TMB | Chromatography paper | 0.1–1.0 mM | 50 µM | [54] |
| Non-enzymatic—AuNPs in-situ synthesis | Chromatography paper | 1.25–20 mM | 0.65 mM | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, T.; Ferrão, J.; Marques, A.C.; Oliveira, M.J.; Batra, N.M.; Costa, P.M.F.J.; Macedo, M.P.; Águas, H.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Paper-Based In-Situ Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis for Colorimetric, Non-Enzymatic Glucose Level Determination. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102027
Pinheiro T, Ferrão J, Marques AC, Oliveira MJ, Batra NM, Costa PMFJ, Macedo MP, Águas H, Martins R, Fortunato E. Paper-Based In-Situ Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis for Colorimetric, Non-Enzymatic Glucose Level Determination. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(10):2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102027
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Tomás, João Ferrão, Ana C. Marques, Maria J. Oliveira, Nitin M. Batra, Pedro M. F. J. Costa, M. Paula Macedo, Hugo Águas, Rodrigo Martins, and Elvira Fortunato. 2020. "Paper-Based In-Situ Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis for Colorimetric, Non-Enzymatic Glucose Level Determination" Nanomaterials 10, no. 10: 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102027
APA StylePinheiro, T., Ferrão, J., Marques, A. C., Oliveira, M. J., Batra, N. M., Costa, P. M. F. J., Macedo, M. P., Águas, H., Martins, R., & Fortunato, E. (2020). Paper-Based In-Situ Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis for Colorimetric, Non-Enzymatic Glucose Level Determination. Nanomaterials, 10(10), 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102027