Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
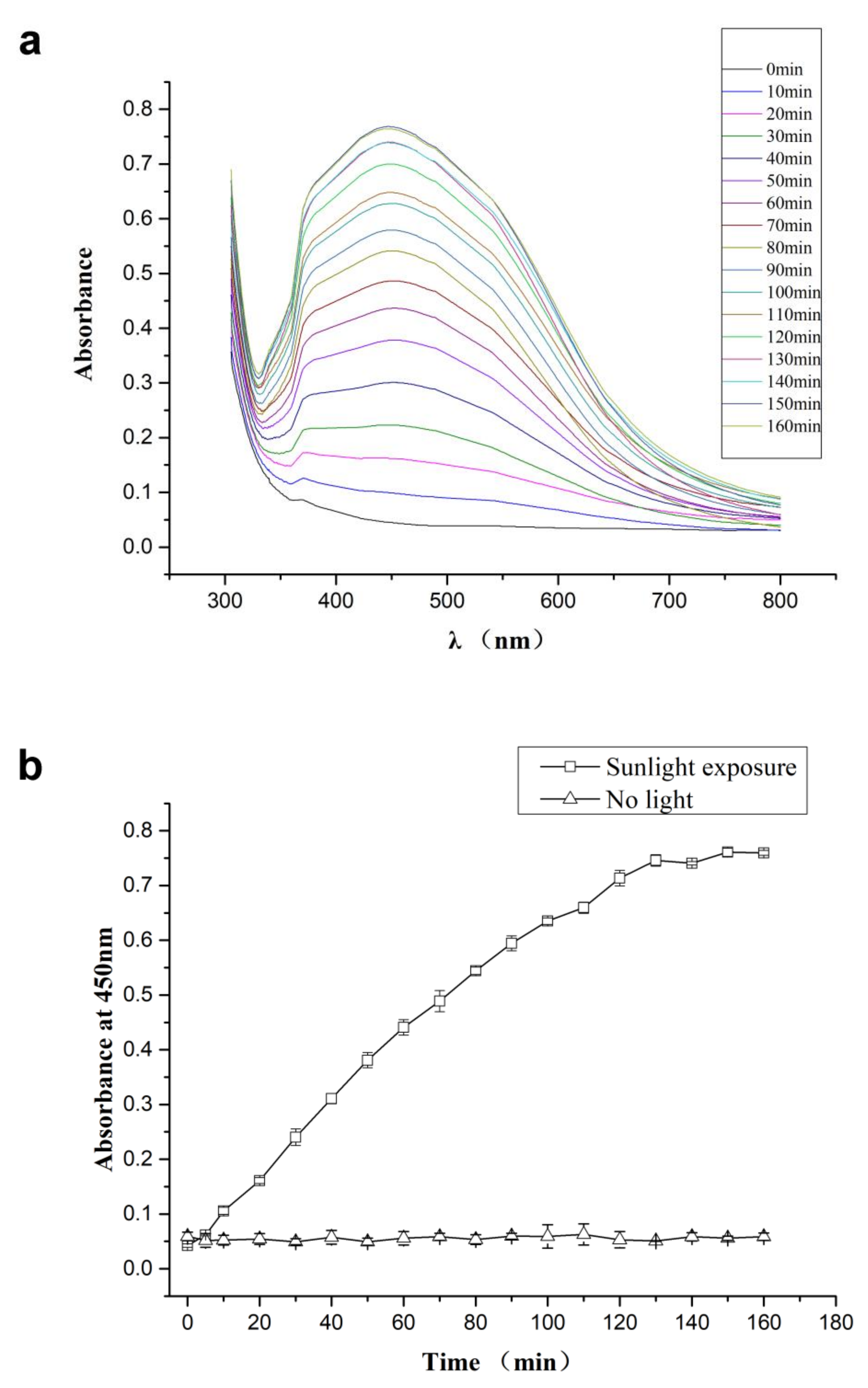
2.2. Natural Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of CMC-SNs
2.3. Characterization and Analysis
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
2.5. Morphological Analysis
2.6. Membrane Permeability Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Oxygen Free Radicals (ROS) in Bacterial Cells
2.8. Safety Evaluation to Non-Target Organisms
2.9. Cure of Rice Bacterial Diseases
3. Results and Discussion
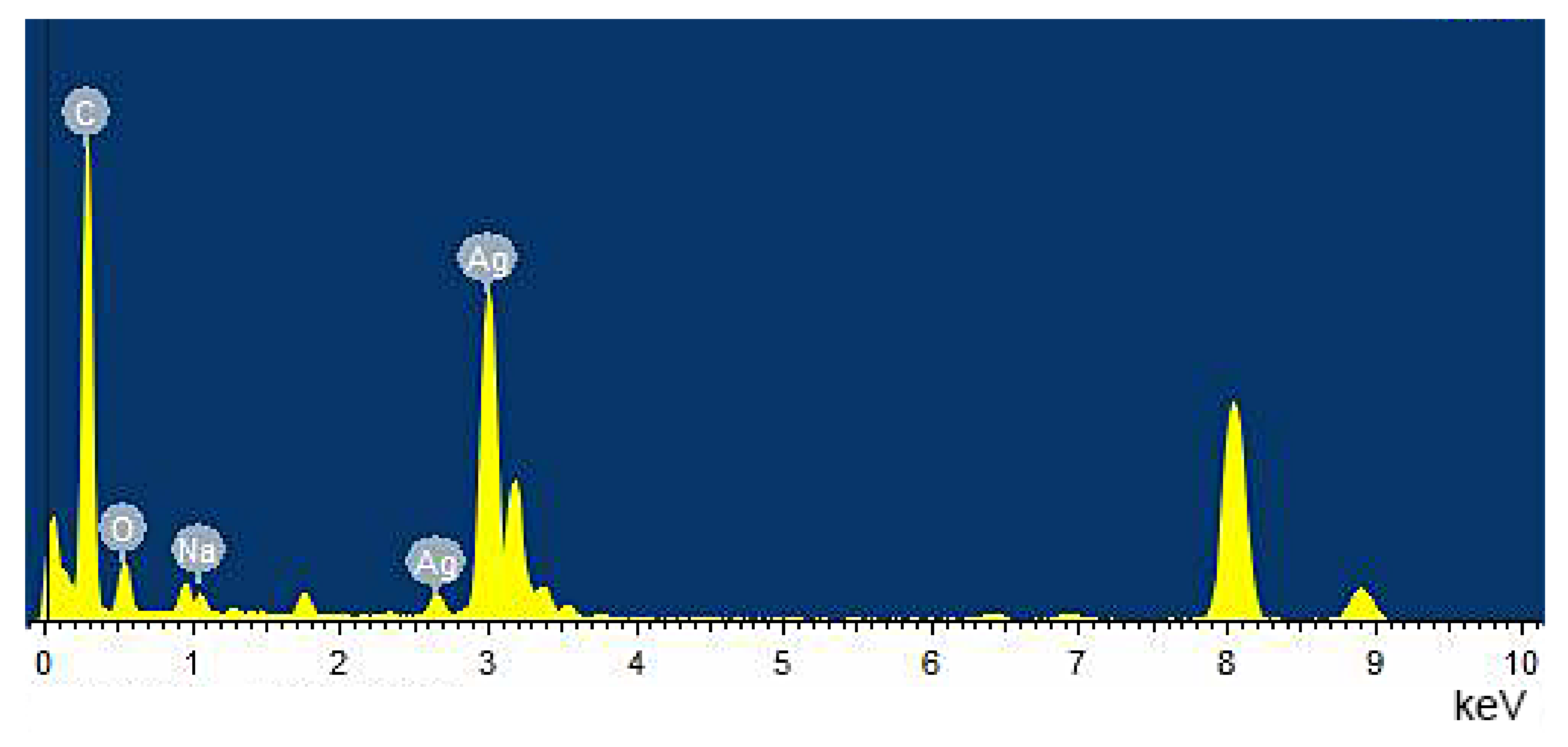
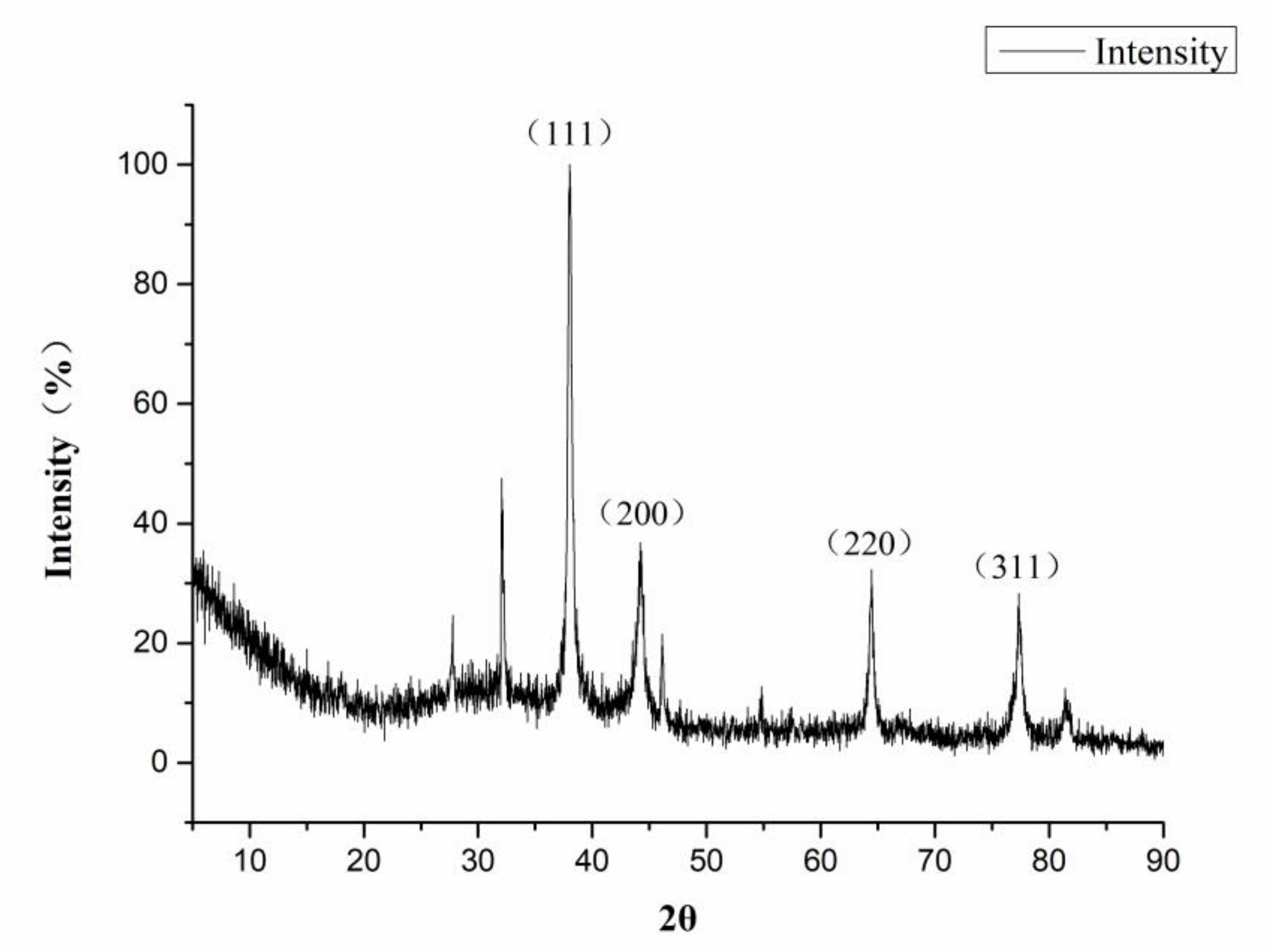
3.1. Characterization of CMC-SNs
3.2. Antibacterial Activity of CMC-SNs
3.2.1. Broth Dilution Method
3.2.2. Broth Dilution Method
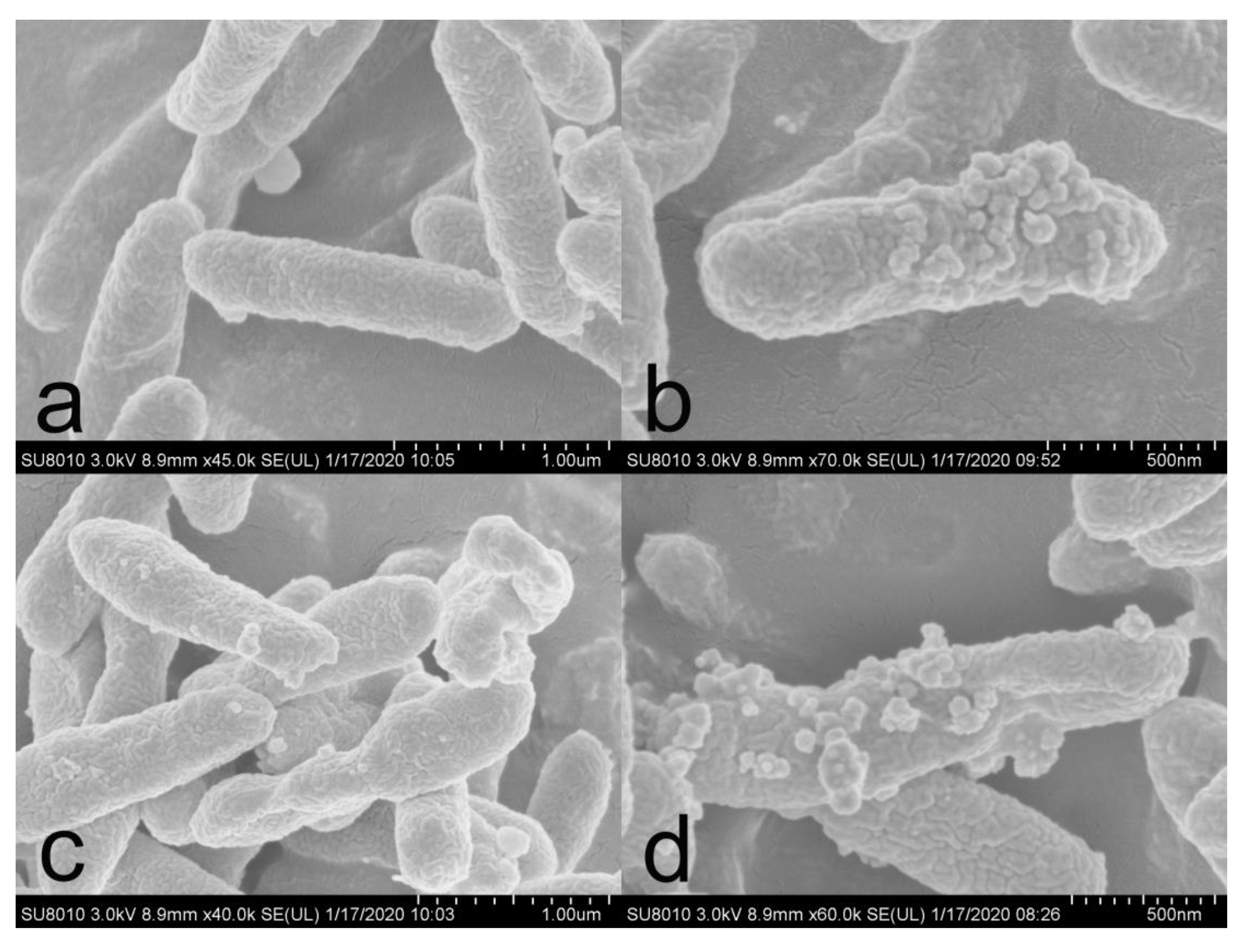
3.3. Morphological Analysis
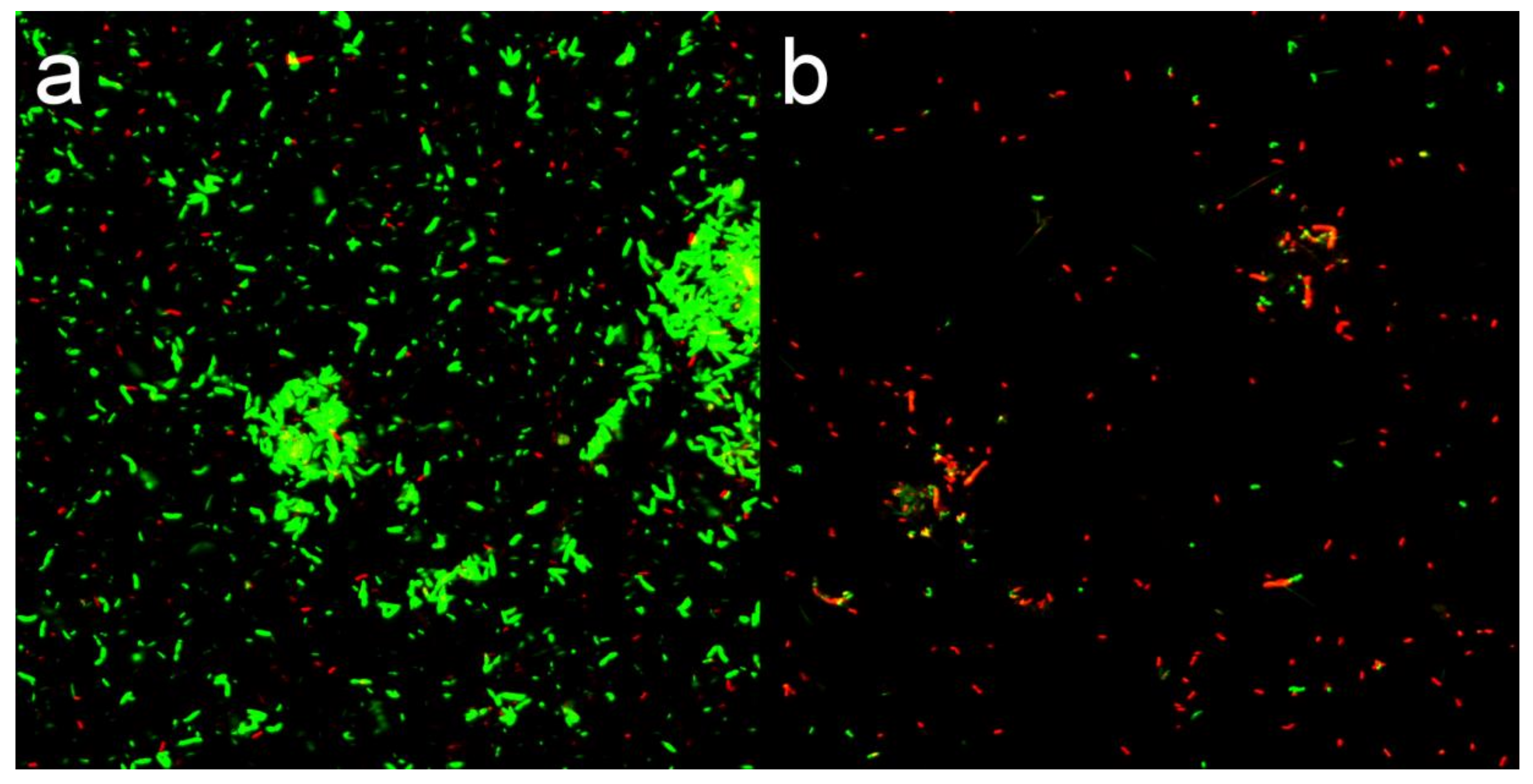
3.4. Membrane Permeability Analysis
Fluorescent Dye Analysis
3.5. Analysis of Oxygen Free Radicals (ROS)
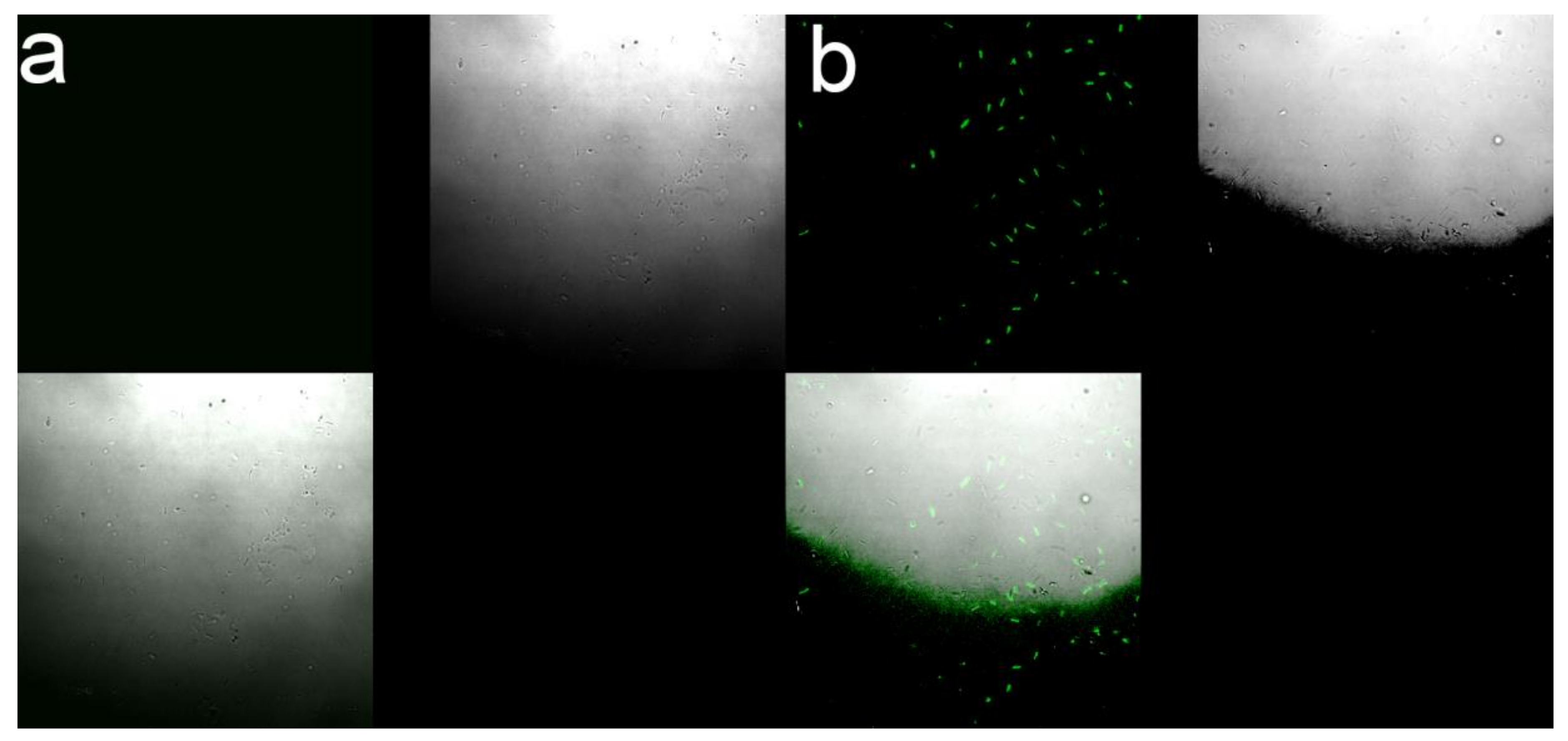
3.6. Safety Evaluation
3.7. Cure of Rice Bacterial Diseases
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daranas, N.; Rosello, G.; Cabrefiga, J.; Donati, I.; Frances, J.; Badosa, E.; Spinelli, F.; Montesinos, E.; Bonaterra, A. Biological control of bacterial plant diseases with Lactobacillus plantarum strains selected for their broad-spectrum activity. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2019, 174, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundin, G.W.; Castiblanco, L.F.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, C.H. Bacterial disease management: Challenges, experience, innovation and future prospects: Challenges in Bacterial Molecular Plant Pathology. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2016, 17, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.S.; Liu, L.W.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, P.Y.; Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. Fabrication of Furan-Functionalized Quinazoline Hybrids: Their Antibacterial Evaluation, Quantitative Proteomics, and Induced Phytopathogen Morphological Variation Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11005–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.Z.E., Jr. Multiple parameters for the comprehensive evaluation of the susceptibility of Escherichia coli to the silver ion. Biometals 1998, 11, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-R.; Sun, T.-L.; Zhou, S.-L.; Ma, Y.-K.; Shi, Q.-S.; Xie, X.-B.; Huang, X.-M. A comparative analysis of antibacterial activity, dynamics, and effects of silver ions and silver nanoparticles against four bacterial strains. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Ma, X.; Shi, H.; Ma, T.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Luo, K.; Cai, L.; et al. Green Synthesis of an Alginate-Coated Silver Nanoparticle Shows High Antifungal Activity by Enhancing Its Cell Membrane Penetrating Ability. ACS Appl. Biomater. 2019, 2, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Catechol-Functional Chitosan/Silver Nanoparticle Composite as a Highly Effective Antibacterial Agent with Species-Specific Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.J.B.; Bouwmeester, H.; Gottardo, S.; Amenta, V.; Arena, M.; Brandhoff, P.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Mech, A.; Moniz, F.B.; Pesudo, L.Q.; et al. Nanomaterials for products and application in agriculture, feed and food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Sunlight-Induced Reduction of Ionic Ag and Au to Metallic Nanoparticles by Dissolved Organic Matter. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7910–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Hussain, I.; Murtaza, G. Chemical synthesis and characterization of chitosan/silver nanocomposites films and their potential antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Motyka-Pomagruk, A.; Cyganowski, P.; Babinska, W.; Terefinko, D.; Jamroz, P.; Lojkowska, E.; Pohl, P.; Sledz, W. Antibacterial Activity of Fructose-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Direct Current Atmospheric Pressure Glow Discharge towards Quarantine Pests. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumari, M.; Giri, V.P.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, M.; Katiyar, R.; Nautiyal, C.S.; Mishra, A. An insight into the mechanism of antifungal activity of biogenic nanoparticles than their chemical counterparts. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 157, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, E.; Fouad, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B.; Mo, J.; Chen, J. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria and their role in inhibition of rice pathogenic bacteria and plant growth promotion. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29293–29299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Bhakya, S.; Senthil Kumar, T.; Rao, M.V. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Ceropegia thwaitesii—An endemic species. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohbatzadeh, F.; Hosseinzadeh Colagar, A.; Mirzanejhad, S.; Mahmodi, S. E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and B. cereus bacteria sterilization using afterglow of non-thermal plasma at atmospheric pressure. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Gallon, S.M.; Alpaslan, E.; Wang, M.; Larese-Casanova, P.; Londono, M.E.; Atehortua, L.; Pavon, J.J.; Webster, T.J. Characterization and study of the antibacterial mechanisms of silver nanoparticles prepared with microalgal exopolysaccharides. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Seo, J.; Kwon, D.; Park, J.; Yoon, T.-H.; Choi, K. Effects of Size, Impurities, and Citrate Capping on the Toxicity of Manufactured Silver Nano-particles to Larval Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Korean J. Environ. Health Sci. 2013, 39, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.-H.; Wei, L.-F.; He, Y.-Q.; Wu, Y.-P.; Bai, X.-H. Biological control of rice bacterial blight by Lysobacter antibioticus strain 13-1. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycenga, M.; Cobley, C.M.; Zeng, J.; Li, W.; Moran, C.H.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, D.; Xia, Y. Controlling the Synthesis and Assembly of Silver Nanostructures for Plasmonic Applications. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3669–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandbeck, D.J.S.; Inaba, M.; Quinson, J.; Bucher, J.; Zana, A.; Arenz, M.; Cherevko, S. Particle Size Effect on Platinum Dissolution: Practical Considerations for Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25718–25727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanema, N.S.V.; Carvalho, I.C.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Carvalho, S.M.; Lage, A.P.; Mansur, H.S. Hybrid Hydrogel Composed of Carboxymethylcellulose–Silver Nanoparticles–Doxorubicin for Anticancer and Antibacterial Therapies against Melanoma Skin Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7393–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Mai, B.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. Antibacterial effect of S-Porphin sodium photodynamic therapy on Staphylococcus aureus and multiple drug resistance Staphylococcus aureus. Photodiagnosis. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilberg, K.; Hovgaard, M.B.; Besenbacher, F.; Baatrup, E. In Vivo Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Toxicol. 2012, 2012, 293784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Ji, X.; Jing, J.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Yang, W. Synthesis of Triangular Silver Nanoprisms by Stepwise Reduction of Sodium Borohydride and Trisodium Citrate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocsoy, I.; Paret, M.L.; Ocsoy, M.A.; Kunwar, S.; Chen, T.; You, M.; Tan, W. Nanotechnology in plant disease management: DNA-directed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide as an antibacterial against Xanthomonas perforans. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8972–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


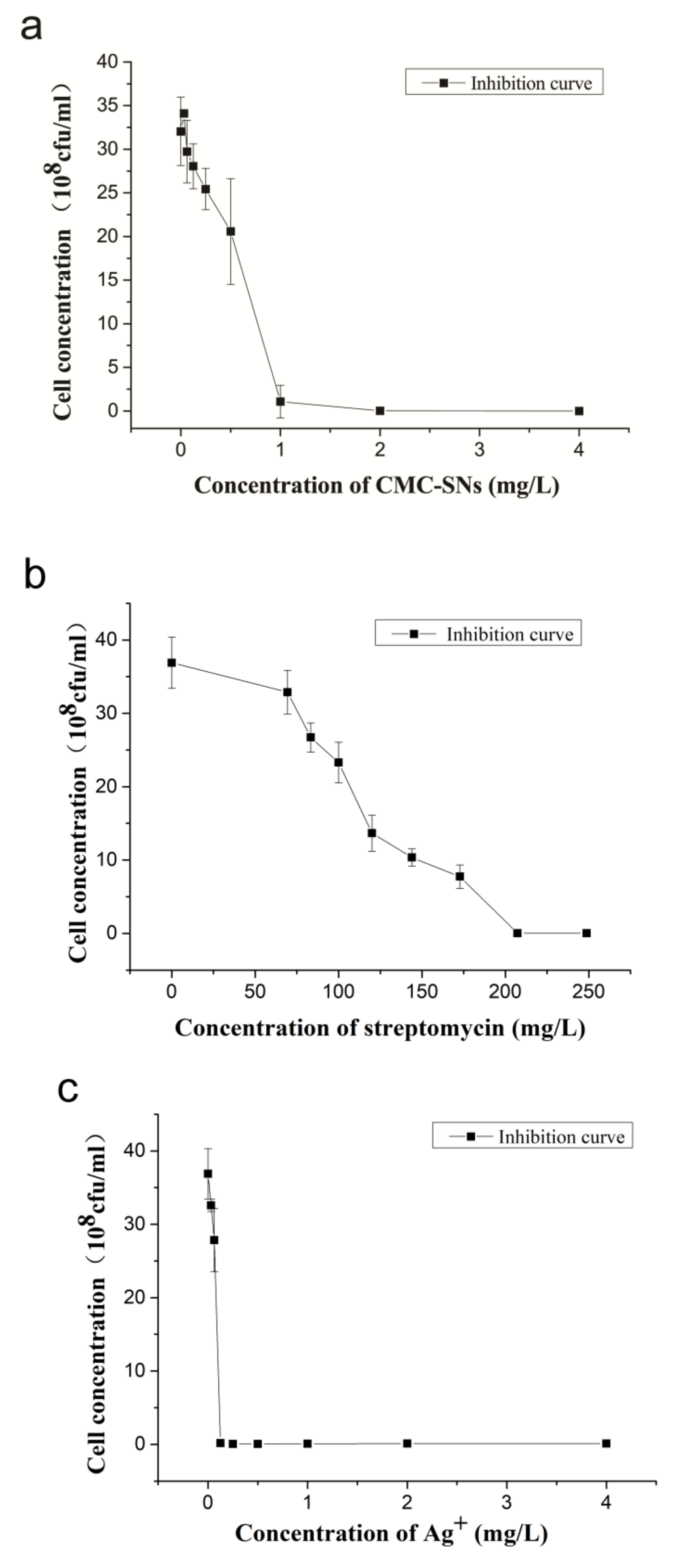

| Xoo | MIC (mg/L) | MBC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Silver nitrate | 0.125 | 0.125 |
| CMC-SNs | 1 | 2 |
| Streptomycin | 178.2 | 207 |
| Bacterial Diseases | Pathogenic Bacteria | MIC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas avenae Manns | P. yringae pv. panici (Elliott) Young et al. | 0.25 |
| Rice bacterial sheath rot | Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Van Holl | 0.5 |
| Test Drugs | Silver Nitrate | CMC-SNs | Streptomycin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure (h) | 96 | 96 | 96 |
| LC50 | 41.702 μg/L | >100 mg/L | >100 mg/L |
| R2 | 0.959 | - | - |
| Chi-square | 7.388 | - | - |
| 95% confidence interval | (39.601–43.694) | - | - |
| Treatment | Disease Index (DI) | Disease Suppression Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CK (control check) | 0 | - |
| 0 mg/L | 61.1 | 0 |
| 5 mg/L | 27.7 | 54.7 |
| 10 mg/L | 20 | 60.8 |
| 20 mg/L | 0 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102007
Shang H, Zhou Z, Wu X, Li X, Xu Y. Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(10):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102007
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Hongyi, Zehao Zhou, Xuemin Wu, Xuefeng Li, and Yong Xu. 2020. "Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases" Nanomaterials 10, no. 10: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102007
APA StyleShang, H., Zhou, Z., Wu, X., Li, X., & Xu, Y. (2020). Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases. Nanomaterials, 10(10), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102007






