Abstract
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most powerful tool for deep penetration and high-quality 3D imaging of tissues with anatomical details. However, the sensitivity of the MRI technique is not as good as that of the radioactive or optical imaging methods. Carbon-based nanomaterials have attracted significant attention in biomaterial research in recent decades due to their unique physical properties, versatile functionalization chemistry, as well as excellent biological compatibility. Researchers have employed various carbon nano-allotropes to develop hybrid MRI contrast agents for improved sensitivity. This review summarizes the new research progresses in carbon-based hybrid MRI contrast agents, especially those reported in the past five years. The review will only focus on T2-weighted MRI agents and will be categorized by the different carbon allotrope types and magnetic components. Considering the strong trend in recent bio-nanotechnology research towards multifunctional diagnosis and therapy, carbon-based MRI contrast agents integrated with other imaging modalities or therapeutic functions are also covered.
1. Introduction
1H magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), established on measuring the difference of the magnetization properties of hydrogen nuclei, has become one of the most powerful modern imaging tools for non-invasive biomedical diagnostics. In normal states, the hydrogen nuclei of the water or fat molecules in tissue are spinning in random orientations. MRI employs a powerful and uniform external magnetic field to align the randomly-spinning hydrogen nuclei, followed by applying another external radio frequency (RF) to perturb and perpendicularly rotate the spin orientation. By turning off the second RF energy while keeping the first main magnetic field retained, the disturbed spinning hydrogen nuclei return to their resting alignment through various relaxation processes including T1-longitudinal and T2-transverse relaxations, where T1 is the time constant for rotated hydrogen nuclei to re-align with the main external magnetic field, and T2 is the time constant for them to lose the phase coherence caused by the second RF energy. The image contrast in MRI primarily arises from the relaxation time differences of hydrogen nuclei in different environments of the studied tissues. In order to improve the sensitivity and diagnostic confidence, about 30% of the 60 million annually-performed MRI procedures employ chemical contrast agents (CAs) in the investigated area [1]. T1-shortening CAs are mainly based on transition metal ions, such as Gd3+ and Mn2+, and provide brighter images; whereas T2-shortening CAs usually contain superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), and produce darker images. The relaxivity parameters r1 and r2 are used to represent the relaxation rate enhancement in unit mM−1·s−1, which defines the efficacy of the MRI contrast agents.
In recent decades, the blossom of nanotechnology has strongly catalyzed the emergence of innovative functional biomaterials. Quite a few research reviews can be found in the area of biomedical nanomaterial applications, such as nanoparticles (NPs) for Alzheimer’s disease [2], NP contrast agents for molecular imaging [3], magnetic nanomaterials [4], or nanoparticles (MNPs) [5,6] for cancer therapy, as well as quantum dots (QDs) and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) for theranostic applications [7], where ‘theranostic’ describes the medical treatments combining therapy and diagnosis together in one procedure termed as ‘theranosis’ [8]. Specifically, in terms of MRI applications, magnetic nanoparticles need either further functionalization [9] or to be coupled with other nanocarriers [10] for improved biocompatibility, in vivo dispersion, and targeting-delivery capability.
Among numerous nano-structured materials, nanoscale carbon allotropes have emerged as highly potential candidates for biomedical applications due to their unique chemical, optical, thermal, optothermal properties, as well as good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity [11,12,13,14,15]. Hybrid materials containing magnetic components and various carbon nano-allotropes, such as CNTs [16] and nanodiamonds [17] have shown outstanding performances in drug delivery, hyperthermic anti-cancer therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging [18]. For example, we have recently designed and developed a Y-shaped synthetic peptide with the capability of targeting the tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). The Y-shaped peptide can be either grafted with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) for fluorescence-based bio-imaging or, as shown in Figure 1, grafted onto partially-oxidized carbon nanotubes (OCNTs) via the OCNT’s carboxylic group to form a novel tumor-targeting nanocarrier. The intrinsically-hydrophobic pristine SPIONs can be physically adsorbed onto the unmodified regions of the OCNTs and form SPION-CNT hybrid agents [19]. Intravenous injection of this Y-peptide-g-OCNT/Fe3O4 nano-assembly into 4T1 mammary tumor-bearing mice led to highly-efficient MR imaging of the TAM-infiltrated tumor microenvironment.
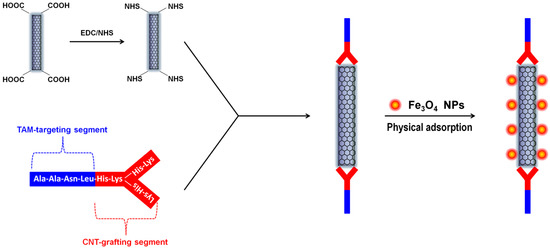
Figure 1.
Schematic of a CNT-based T2-weighted MRI contrast agent conjugated with our designed Y-shaped TAM-targeting peptide and loaded with Fe3O4 nanoparticles via physical adsorption.
Recently, new studies on the similar types of carbon-based hybrid MRI CAs are continuously increasing, with the system designs becoming more complex and multifunction-oriented. However, only a limited number of related reviews are available in the literature, either as a brief subsection of a wide topic, or only covering one carbon nanomaterial, such as multi-walled carbon nanotubes [20]. Thus, it is necessary to summarize the recent advances in carbon-based hybrid MRI CAs, especially those published in the past 3–5 years, with a full coverage of various types of carbon nano-allotropes, magnetic components, and the preparation strategies (Figure 2). Since the T1-category positive CAs usually have a better signal-enhancing ability and have been more widely used in clinical diagnosis, and the T2-category negative CAs intrinsically have lower imaging signal intensity, it is a more challenging mission for bio-nanomaterial researchers to explore T2-category CAs, improve their imaging contrast, and expand their multi-functionality. This review will only focus on T2-weighted MRI contrast agents. Other works using various carbon nano-allotropes for diffusion- or T1-weighted MRI applications are representatively selected and listed, but will not be discussed [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
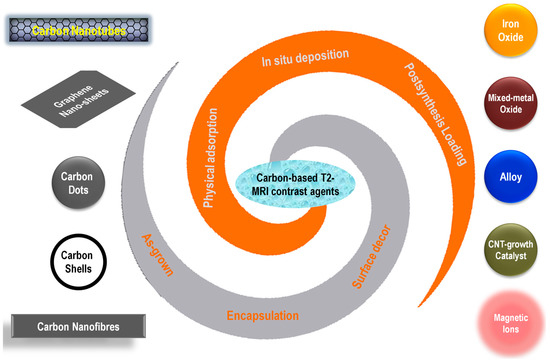
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of various carbon nano-allotropes, magnetic species, and their conjugation strategies used for the preparation of T2-weighted MRI contrast agents.
2. CNT-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents
Carbon nanotubes, according to the number of their graphitic layers, can be classified as single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs), double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWNTs), and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs), among which SWNTs and MWNTs are the most widely used CNT species due to their relative economic and facile synthesis. CNTs represents one of the primary categories of carbon nano-allotropes that has been widely used for MRI applications.
2.1. CNTs with Inherent Magnetic Catalyst Residues
The catalysts used for CNT synthesis are usually magnetic nanoparticles, which after the CNT synthesis, remain physisorbed on the CNTs [38]. It has been demonstrated that the as-grown SWNTs non-covalently functionalized with DNA are potential for MRI CA applications [39]. On the other hand, SWNTs covalently functionalized with carboxylic acid groups (SWNT-COOH) are stable in biological media and cause strong T2 signal decreases in vitro [40]. The r2 relaxivity of SWNT-COOH without any postsynthesis MNP-loadings is as high as 1.54 mM−1·s−1 at 7 T. Another study also found that, when conjugated with a specific antibody, short SWNTs exhibited very high magnetic resonance r2 relaxivity and could be targeted on breast cancer cells for sensitive MRI detection [41].
Similarly, magnetic relaxation behavior was found on catalyst-containing MWNTs. PEGylated MWNTs carrying Fe-based catalyst particles were proved to be efficient T2-weighted MRI contrast agents in vitro [42]. By transplanting MWNT-labeled human islets into the subcutis of rats via a magnetic field and tracking with MRI, Marchetti et al. showed that MWNTs can be an alternative MRI labeling compound to be used with human islets for experimental and transplantation studies [43]. Vittorio et al. found that MWNTs with low metal impurities (2.57% iron from the growth catalyst) can be used as MRI contrast agents for tracking stem cells, which have a significant effect on the T2 transverse relaxation rate of water 1H nucleus [44]. Moreover, long Fe nanowires can be formed in the inner cavity of MWNTs under control during the nanotube synthesis process. Through surface functionalization (with folic acids), the MWNTs encapsulating Fe-nanowires can cause a strong decrease in T2 MRI signals by four-fifths, compared to MWNTs without the inner-encapsulated Fe nanowires [45]. Torti et al. explored the dose effect of the magnetic catalyst and found that the in vivo r2 relaxivity of the as-grown MWNTs increased with the mass content of the catalyst within the studied range, which maximized at 2.92% Fe [46]. Another in vitro study considered the effect of Fe dose in a wider range and showed that MWNTs with 10% Fe were less stable, but tended to agglomerate, and the best MRI contrast and biocompatibility was achieved at 2% Fe [47], which is very close to Torti’s results.
2.2. CNTs with Postsynthesis-Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
As discussed above, the as-grown CNTs usually contain trace amounts (2–3%) of magnetic nanoparticle catalyst, and will not be stable at high MNP contents. On the contrasts, attaching SPIONs on CNTs via postsynthesis methods may allow higher SPION-loading limits. As mentioned previously in the introduction section, simply taking advantage of the physical adsorption, we can load about 20% Fe3O4 nanoparticles on a TAM-targeting MWNT nanocarrier, which is stable in aqueous solution and gives excellent T2-weighted MRI contrast [19]. Other than physical adsorption, various postsynthesis methods for SPION-loading on CNTs have also been reported. The co-precipitating reaction of ferric and ferrous salts under anaerobic conditions was employed to deposit Fe3O4 NPs on MWNTs pre-functionalized with poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) for liver-targeting MRI applications [48]. Lamanna et al. explored two other approaches for decorating MWNTs with SPIONs: one was based on ligand exchanges between oleic acid-coated SPIONs and oxidized MWNTs, and the other employed a ‘click’ reaction between SPIONs bearing azide groups and functionalized MWNTs bearing alkyne groups. MWNT-SPION hybrid MRI CAs prepared with these chemistries were successfully internalized into tumor cells without showing cytotoxicity, and could be manipulated by a remote magnetic field [49]. Instead of being attached on the outer surface of CNTs, as another choice, SPIONs can be loaded inside CNTs in a postsynthesis manner. Ferrite nanoparticles have been successfully filled in pre-formed MWNTs by introducing an iron stearate precursor into the inner cavity of MWNTs via ultrasonication, followed by a thermo-decomposition [50]. The resulting SPION@MWNT system was proved to be a potential nano-agent for magnetic manipulation of cells, as well as MRI diagnostics. Finally, it is necessary to point out that, for biomaterial researchers working on the development of novel CNT-SPION hybrid MRI contrast agents, the length of CNTs is an important factor to be considered in the material design, because only shortened CNTs can be well-internalized by cells [51,52].
2.3. CNTs with Postsynthesis-Loaded Metal Ions, Metal Alloy, and Mixed-Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
Though SPIONs represent a major class of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for T2-weighted MRI CA applications, other types of magnetism sources such as paramagnetic metal ions, alloys, and mixed-metal oxides also received plenty of attention. It was found that even though the as-grown MWNTs-bearing catalyst residues could be used as T2-weighted MRI CAs, further coordinating paramagnetic Fe3+ ions on MWNTs pre-grafted with aminophenol ligands would enhance, or even triple, the r2 relativity, making the hybrid agents comparable to the commercial products [53]. Superparamagnetic alloy nanoparticles, such as FePt NPs have excellent stability and magnetic property for T2 negative contrast imaging [54]. Thus, FePt NPs with an average size of 3–4 nm have been deposited on both SWNTs and MWNTs to produce CNT-FePt hybrid CAs for MRI [55]. Magnetic mixed-metal oxide NPs are another class of nanoparticles found application in CNT-based T2-type MRI CAs. MWNT/cobalt ferrite (MWNT-CoFe2O4) can be prepared via a solvothermal approach, and show an r2 relaxivity of 152.8 mM−1·s−1 in aqueous solutions at 3.0 T [56]. Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn ferrite oxide (MIIFe2O4) nanoparticles can be deposited on CNTs when the relative precursors are calcinated via a simple microemulsion method [57].
3. Graphene-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents
Graphene, a monolayer 2D material with hexagonally-arranged, tightly-packed, and sp2-hybridized carbon atoms in a honeycomb-like lattice, is the basal building block for all graphitic carbon allotropes, including SWNTs and MWNTs. Graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets can be stably dispersed in water or physiological environments. Their excellent biocompatibility and low toxicity make GO a very potential material for biomedical applications. Magnetic reduced-GO (RGO) nanosheets have been successfully synthesized via inverse chemical co-deposition of Fe3O4 NPs on the reduced GO sheets [58], or the RGO-Fe3O4 nanocomposites can be prepared via high-temperature decomposition of an iron precursor, iron(III) acetylacetonate (Fe(acac)3), in triethylene glycol in the present of RGO nanosheets [59]. Both methods result in efficient T2-type graphene-based MRI CAs. Moreover, Walsh and Hurt et al. showed that graphene oxide can encapsulate Fe3O4 NPs simultaneously with other nano-probes in the aerosol phase to form nano-cargos for multifunctional biomedical applications, with T2-weighted MRI as one of the integrated functions due to the encapsulated Fe3O4 NPs [60]. Preparation of the smaller-sized GO-SPIONs, or magnetic graphene quantum dots (MGQDs), can be achieved with a hydrothermal method that simultaneously reduces GO to RGO, deposits Fe3O4 NPs on the RGO, and shatters the graphene nanosheets to QD size [61]. Liu et al. functionalized RGO-SPION nanocomposites non-covalently with biocompatible polyethylene glycol (PEG) for MRI and multimodal-imaging guided photothermal therapy [62]. Similarly, covalently double-PEGylated RGO-SPIONs show dramatically improved in vivo blood circulation half-life and passive tumor targeting efficacy [63].
Except for iron oxides, combining graphene with other magnetic NPs, such as mixed-metal oxides, were also reported. Similar to what has been done on CNT nanocarriers, Wang et al. prepared a graphene oxide/cobalt ferrite (GO-CoFe2O4) composite through a facile sonochemical method, which showed strong T2-weighted MRI signal enhancement with an r2 relaxivity of 92.71 mM−1·s−1 at 3.0 T [64].
4. MNPs Loaded on Other Carbon Nano-Allotropes
Though graphene and CNTs are the two major carbon allotropes underwent intensive studies for carbon-based MRI CAs, other carbon structures also found their role in this application. Fe-core/C-shell magnetic nanoparticles can be synthesized using a one-step top-down approach, which was conducted between two closely-placed Fe electrodes during the electric-plasma discharge of toluene with the help of an ultrasonic horn [65]. The obtained NPs have improved biocompatibility and stability because of the carbon shell, and can be used as T2-weighted MRI contrast agents with a relaxivity of 70 mM−1·s−1 in a 7 T MRI scanner. Dai et al. synthesized FeCo-core/single-layer graphitic-carbon shell (FeCo-GC) nanocrystals that were soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. The 7 nm FeCo-GC nanocrystals internalized by mesenchymal stem cells exhibited an r2 relaxivity of 644 mM−1·s−1, one of the highest values in all reports at 1.5 T, and gave better T2 negative contrasts compared to commercial MRI CAs such as Feridex [66]. Another work reported a complex MNP-core/carbon-shell structure with the magnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals clustered in the core and fluorescent carbon dots embedded in the mesoporous carbon shell (Fe3O4-FCs). The Fe3O4-FC NPs can be assembled into stable 1D chains in an external magnetic field via the hydrogen bonding effect and π–π stacking between the carbon shells, which show much higher MRI contrast than the individual Fe3O4-FC NPs [67].
Carbon nanofiber (GNF) is another class of carbon nanostructures seen applications in MRI CAs. Lu et al. have employed graphitized GNFs as nanocarriers for Fe3O4 NPs. By coating the Fe3O4-GNF assembly with a SiO2 layer, Fe3O4-GNF@SiO2 nanocapsules were prepared for T2-weighted MRI applications [68]. In this work, the hollow GNF was initially filled with iron(III) acetylacetonate, a precursor for the formation of MNPs. Ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles were then synthesized inside the cavities of GNFs with a high density. The silica coating layer introduces many benefits, including preventing the leakage of the nanoparticles from the GNF hollow cavity, protecting the Fe3O4 NPs from damage in harsh acidic conditions, and increasing the biocompatibility and stability of the nanocomposites. In another work, Khlobystov et al. performed a detailed study on the controlled preparation of Fe3O4-GNF nanocomposites [69], in which hollow CNFs acted both as a template and a support for the nucleation and growth of Fe3O4 NPs. The influence of solvent type and the mass ratio of the magnetite precursor on the structures (size, dispersity, and morphology) and physical properties (magnetization and coercivity) of the Fe3O4-GNF products were systematically studied. The optimized magnetic hybrid composites were proved to be effective T2 negative MRI contrast agents with an excellent transverse relaxivity of 268 ± 13 mM−1·s−1 at 9.4 T, which surpasses most commercial MRI materials or state-of-the-art nanoscale CAs performing under such a high magnetic field.
5. Carbon-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents Integrated with Multiple Functions
Although MRI is the most powerful tool for deep penetration and high-quality 3D imaging of tissues with anatomical details, its sensitivity is not as good as that of the radioactive or optical methods. The application of multi-modality imaging probes could provide more accurate information in clinical settings. For example, fluorescence imaging is highly sensitive and has potential for real-time imaging, but it has limited depth perception; computed tomography (CT) imaging offers accurate and bright images; positron emission tomography (PET) uses signals emitted by compounds labeled with positron-emitting radioisotopes for bio-imaging. Combining the deep perception of MRI with other, more sensitive, imaging modals, the carbon-based T2 MRI contrast agents can provide highly accurate and detailed information associated with diseases. Indeed, plenty of efforts have been made to integrate multimodal bio-imaging techniques, such as fluorescence imaging, Raman imaging, microwave-induced thermoacoustic imaging (TAI), CT, PET, and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) on the carbon-based T2 MRA CAs, especially in the past 3–5 years.
Moreover, advanced clinical technologies are attempting to combine therapy and diagnosis functions together in one treatment for so-called “theranosis” applications. The therapy methods to be integrated include controlled drug delivery, targeted drug delivery, and hyperthermia (or thermotherapy). Hyperthermia exposes tumor tissues to high temperatures and kills cancer cells with minimal injury to the normal tissues.
In this section, representative new progress in carbon-MNP hybrid T2-type MRI CAs with integrated multimodal imaging capability, drug delivery, and hyperthermia functions will be summarized (Figure 3). All the carbon-based nanocomposites discussed in this section have MRI as a default function, and possess at least one more other function for either diagnosis or therapy purposes.
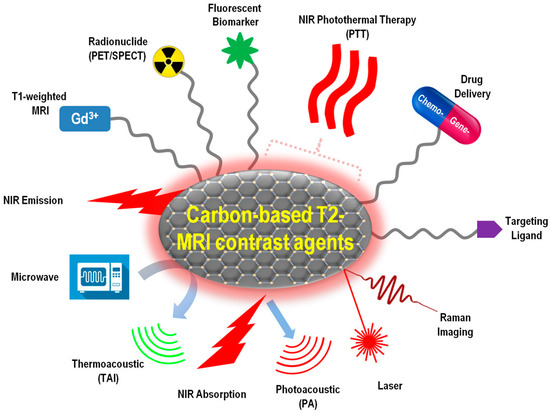
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of T2-type MRI contrast agents integrated with multiple theranostic functions.
5.1. Carbon-MNP Hybrid MRI Agents with both T1 and T2 Contrast
Although most gadolinium-based CAs are for T1-weighted MR imaging, recent studies have shown that gadolinium-loaded ultra-short SWNTs (GNTs) can be used as high-performance MRI CAs with both excellent T1 and T2 contrasts [70]. GNTs were prepared by encapsulating Gd3+ ion clusters within the hollow cavity of SWNTs. The prepared GNTs not only outperform the traditional Gd3+-chelate MRI CAs in r1 relaxivity by about 40 times at clinical field strengths, but also show strong T2-weighted MRI contrast. Other works also reported similar findings that Gd-SWNT nano-agents in solution have both high r1 and r2 relaxivity at either very low (0.01 MHz) or clinically-relevant (61 MHz) magnetic fields [71]. GNTs suspended in 1% Pluronic F127 solution gave a high r2 value of 578 mM−1∙s−1 at 9.4 T with excellent T2 negative contrast in vivo [72]. For Gd3+-functionalized nanodiamond, Meade et al. found that the dose of the loaded Gd3+ had significant influences on T2-weighted MRI signals. When the cellular concentration of Gd3+ exceeds a certain threshold, positive contrast diminishes to yield negative contrast, and T2 negative contrast becomes a predominant effect over T1 at the highest Gd3+ dose [73]. However, there are opposite cases in which Gd3+-functionalized MWNT nano-agents were studied, and it was found that the T2 effect was independent of Gd3+, but exclusively related to the presence of MWNTs [74].
Other than Gd3+-functionalization, Mn2+-CNTs were also prepared and shown both T1 and T2 effects. SWNTs functionalized with polydopamine, and further modified by PEG chelate Mn2+ ions to offer both T1- and T2-weighted contrasts for MR imaging [75].
As for non-ionic magnetism sources, LaF3:Eu:Gd nanocrystals have been coated on MWNTs to simultaneously provide both powerful T1- and T2-weighted signals for MR imaging [76]. The FeCo-GC hybrid nanocrystals reported by Dai et al. and reviewed in Section 4 of this review as a T2-type contrast agent show very high r1 relaxivity, as well, which enables both T1 positive-contrast and T2 negative-contrast [66].
5.2. Carbon-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents with Multimodal Imaging Capability
Multi-modal imaging provides multi-aspect, more accurate and complete information for biomedical diagnosis and therapy. Strano et al. demonstrated that the as-grown SWNTs containing residue-amounts of magnetic catalysts could be utilized as a multimodal bio-imaging probe due to their intrinsic near-infrared fluorescence and Raman scattering, in addition to the pre-existing MRI function established on their superparamagnetic catalysts [39]. Unlike SWNTs, MWNTs intrinsically do not emit fluorescence. However, PEGylated MWNT can be stained with external fluorescent organic dyes such as monodansylcadaverine (MDC), diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), or fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) to achieve MRI-fluorescence bimodal cellular imaging [42,55,77]. On the other hand, carbon QDs emitting violet fluorescence at 320 nm excitation can be used as an intrinsic source of photoluminescence. These QDs have been embedded in GO-Fe3O4 probes for MRI-fluorescence dual-modality imaging [61]. Similarly, another work conjugated carboxyl-terminated graphene quantum dots (GQD) on the outer surface of a Fe3O4-core/SiO2-shell hybrid system. The Fe3O4@SiO2@GQD hybrid nanoparticles functionalized with cancer-targeting molecule folic acid can be used for MRI-fluorescence duo-imaging of living Hela cells in vitro [78].
Liu et al. conjugated protamine with PEG-functionalized SWNTs and prepared an MRI CA exhibiting extremely efficient cell-entry into human mesenchymal stem cells without affecting their proliferation and differentiation. In addition to their inherent MRI capability, the strong Raman scattering from SWNTs enables ultrasensitive Raman imaging of as few as 500 stem cells administrated into mice [79]. The same research group later developed a multifunctional nano-platform based on PEGylated, mesoporous, silica-coated SWNTs, which could serve as a multimodal imaging probes simultaneously enabling MR, photoacoustic, Raman, and NIR imaging [80]. Microwave-induced thermoacoustic imaging (TAI) maps the microwave absorption distribution of the studied targets. Since MWNTs are outstanding electric absorption materials, while their magnetic absorption is negligible, they have been used to enhance the TAI signal of the tissue as a contrast to de-ionized water and blood [45]. Moreover, incorporating radioactive elements is an efficient way to introduce PET imaging capability. Double-PEGylated RGO-SPION nanoparticles labeled with 64Cu show multimodality in MR, PET, and photoacoustic imaging due to the strong superparamagnetism from SPIONs, radioactivity from 64Cu, and NIR absorbance from RGO [63]. Al-Jamal et al. designed another radio-labeled probe based on MWNT-SPION hybrid systems, where γ-Fe2O3 NPs were deposited in situ on the oxidized sites of MWNTs, and the radiolabel 99mTc were introduced via a functionalized bisphosphonate to enable 3D whole body SPECT/CT imaging and quantitative organ bio-distribution profiling in mice [81].
5.3. Carbon-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents with Drug Delivery Capability
Carbon-based MRI CAs integrated with drug delivery capability represents a new promising trend in nanomedicine research. A popular anti-cancer drug, doxorubicin (DOX), has been loaded onto an MWNT-CoFe2O4 hybrid system and achieved sustained and pH-responsive DOX release [56]. Similarly, the GO-CoFe2O4 composite prepared by a sonochemical method showed a high DOX loading capacity of 1.08 mg/mg and a sustained, PH-responsive drug releasing behavior [64]. More carbon-based MRI CAs with controlled DOX delivery function are reported on antibody-conjugated magnetic SWNTs [82,83] and GO-SPION systems [84]. Another anti-tumor model drug, 5-fluorouracil, was loaded onto the surface of RGO-Fe3O4 nanocomposites with a high loading capacity and showed pH-dependent release [58]. The colorectal cancer treatment drug, oxaliplatin, was encapsulated into the CNT cavity of a PEGylated MWNT-SPION MRI probe, which allowed sustained oxaliplatin release up to 96 hours with the MRI monitoring option [85]. Anesthetic lidocaine hydrochloride (LH) was loaded on RGO-SPION quantum dots through π–π stacking between the aromatic rings of LH and the RGO surfaces, and a steady, full drug release from the QDs was observed over 8 h [61].
In addition to delivering traditional chemo-drugs, small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based gene delivery has become a new trend for cancer therapy in recent years [86]. Zhang et al. modified MWNT-Fe3O4 CAs with polyethyleneimine (PEI) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) to improve their solubility and biocompatibility. Then, human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) siRNA was adsorbed on the nanocarrier surface via electrostatic interaction. The obtained hybrid system MWNT-Fe3O4-PEI-PEG/siRNA efficiently delivered siRNAs into MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and significantly inhibited tumor cell growth via gene silencing, which can be monitored via the MRI function from the same agent [87].
5.4. Carbon-MNP Hybrid MRI Contrast Agents with Hypothermia Capability
In complement to chemotherapy and gene therapy, photothermal therapy (PTT) is another powerful technique that can be integrated on various carbon-based MRI CAs. Taking advantage of the broad NIR absorption of graphene, photosensitizer of any wavelength within 600–1200 nm will facilitate the light-induced phototherapy. Lin et al. adopted a simple non-covalent approach to immobilize a hydrophobic photosensitizer, silicon napthalocyanine bis (trihexylsilyloxide) (SiNc4), onto water-dispersible SPION-and-fluorescein-decorated graphene nanosheets via π–π stacking to yield an MRI-fluorescent dual-imaging probe with PTT capability [88]. The FeCo-GC hybrid nanocrystals reported by Dai et al. showed NIR absorbance at 808 nm and, thus, afforded the conversion of NIR photon energy into thermal energy for PTT applications [66]. Liu et al. utilized both the intrinsic high NIR optical absorbance of RGO and the strong magnetic property of SPIONs, and designed an efficient theranostic agent for in vivo MRI-guided PTT treatment. This RGO-based MRI contrast agent allows ultra-efficient tumor ablation using a laser power density as low as 0.5 W·cm−2 [62]. On a similar system, the same research group also loaded Au nanoparticles to further enhance the thermo-ablation capabilities of the nanocomposites [89]. Many other MRI CA systems based on RGO-SPIONs, CNT-SPIONs, and CNT-FePt have also been studied for simultaneously diagnosing and photothermal cancer treatments [50,55,90,91]. RGO-SPION quantum dots [61] and the fluorescent carbon dots embedded in the mesoporous carbon shell of the Fe3O4-FC MRI CAs [67] also efficiently convert NIR light to heat, and can be used for photothermal ablation of tumor cells under near-infrared irradiation.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
To summarize, carbon nano-allotropes are highly promising nano-carriers for the next-generation of MRI contrast agents. The main advantage lies in their relative low bio-toxicity, versatile surface modification strategies, unique structural cavities, and intrinsic NIR absorption/emission. This review covers the most recent research progresses in carbon-based T2-shortening MRI contrast agents, especially those published in the past 3–5 years. In terms of the allotrope species, a wide variety of novelly-structured carbon nanomaterials including single-walled/multi-walled carbon nanotubes, graphene and reduced graphene oxide nano-sheets, graphene quantum dots, carbon dots, carbon nanofibers, single-layer graphitic carbon nano-shells, and mesoporous carbon shells have all found their unique roles as efficient nano-carriers for MRI contrast agents. In terms of the magnetism origins, various magnetic species, such as iron oxide nanoparticles, mixed-metal oxide nanoparticles, metal alloys, and magnetic ions, have been successfully coupled with carbon nanomaterials for enhanced MR imaging. The coupling methods have versatile options from inner encapsulation to surface decoration, from in situ deposition to physical adsorption, and from real-time generation during the formation of the carbon structures to postsynthesis modification. Such rich possibilities in choosing the hybrid components and their combinations, as well as the versatile preparation strategies, endow the previous single-functional T2-shortening MRI contrast agents multiple functions. Due to the intrinsic near-infrared absorption and fluorescence of many carbon nanomaterials, NIR imaging and NIR-triggered photothermal therapy are the most commonly seen add-in functions to the carbon-based T2-type MRI contrast agents. Other imaging modals that have been successfully integrated include T1-weighted MR, bio-marker fluorescence, Raman, CT, PET, SPECT, thermoacoustic, and photoacoustic imaging. As for therapeutic functions, NIR-triggered hypothermia, drug-delivery-based chemotherapy, and siRNA-delivery-based gene therapy have also been successfully integrated, turning the carbon-based MRI contrast agents into more powerful all-in-one theranostic tools.
Although the carbon nano-allotrope/magnetic nanoparticle hybrid nanomaterials have been extensively studied for MRI applications, many more future efforts are still expected, especially in achieving better-defined and well-controlled parameters, such as agent size for real clinical setting applications. Moreover, humans’ ever-growing ambition in theranostic techniques requires more complex all-in-one nano-agents for challenging medical tasks. Developing novel carbon-based MRI agents with the capability of dynamically tracking pathological changes, or stimuli-responsively applying medical treatments, can potentially be significant for future studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviation
| Abbreviation | Label |
| CA | Contrast agent |
| CNF | Carbon nanofibre |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DAPI | Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| DWNT | Double-walled carbon nanotube |
| FC | Fluorescent carbon |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| GC | Graphitic carbon |
| GNT | Gadolinium-loaded CNT |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| GQD | Graphene quantum dot |
| hTERT | Human telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| LH | Lidocaine hydrochloride |
| MCF-7 | Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 |
| MDC | Monodansylcadaverine |
| MGQD | Magnetic graphene quantum dot |
| MNP | Magnetic nanoparticle |
| MR | Magnetic resonance |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MWNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| OCNT | Oxidized carbon nanotube |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PTT | Photothermal therapy |
| QD | Quantum dot |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| RGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| si-RNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SPECT | Single-photon emission computed tomography |
| SPION | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle |
| SWNT | Single-walled carbon nanotube |
| SWNT-COOH | SWNTs grafted with carboxylic acid groups |
| TAI | Thermoacoustic imaging |
| TAM | Tumor-associated macrophage |
References
- Sitharaman, B.; Kissell, K.R.; Hartman, K.B.; Tran, L.A.; Baikalov, A.; Rusakova, I.; Sun, Y.; Khant, H.A.; Ludtke, S.J.; Chiu, W.; et al. Superparamagnetic gadonanotubes are high-performance MRI contrast agents. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3915–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azria, D.; Blanquer, S.; Verdier, J.M.; Belamie, E. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for brain nuclear magnetic resonance imaging in alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7216–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Matham, M.V.; Su, H.B.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyas, B. Nanoparticulate contrast agents for multimodality molecular imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1553–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitanjali, A.; Brahmkhatri, V.P.; Atreya, H.S. Nanomaterial based magnetic resonance imaging of cancer. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2014, 94, 423–453. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.S.; Ali, Z.S.; Mou, X.B.; Wang, J.H.; Yi, H.; He, N.Y. Recent advances in magnetic nanoparticle design for cancer therapy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 9393–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajba, L.; Guttman, A. The use of magnetic nanoparticles in cancer theranostics: Toward handheld diagnostic devices. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Yildirimer, L.; Rajadas, J.; De La Pena, H.; Pastorin, G.; Seifalian, A. Quantum dots and carbon nanotubes in oncology: A review on emerging theranostic applications in nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Huh, M.S.; Sun, I.C.; Yuk, S.H.; Choi, K.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. In vivo targeted delivery of nanoparticles for theranosis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.R.; Wang, X.Y.; Yu, S.X.; Cao, J.B.; Li, S.H.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, X.Y. Co9Se8 nanoplates as a new theranostic platform for photoacoustic/magnetic resonance dual-modal-imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combination therapy. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, B.; Aswathy, R.G.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Mitcham, T.; Mitchel, K.A.; Nagaoka, Y.; Bouchard, R.R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Maekawa, T.; Sakthikumar, D.N. Highly versatile SPION encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles as photothermal ablators of cancer cells and as multimodal imaging agents. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Mukherjee, S.P.; Gallud, A.; Burkert, S.C.; Bistarelli, S.; Bellucci, S.; Bottini, M.; Star, A.; Fadeel, B. Biological interactions of carbon-based nanomaterials: From coronation to degradation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, Z. Carbon nanotubes in biology and medicine: An overview. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.A.; Yang, K.; Lee, S.T. Single-walled carbon nanotubes in biomedical imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q.; Dougherty, C.A.; Zhu, K.C.; Hong, H. Theranostic applications of carbon nanomaterials in cancer: Focus on imaging and cargo delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 210, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Carbon nanotubes for biomedical imaging: The recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2013, 65, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.W. Applications of functionalized carbon nanotubes for the therapy and diagnosis of cancer. Polymers 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeri, D.; Rinaldi, F.; Ingallina, C.; Carafa, M.; Rossi, M.; Terranova, M.L.; Marianecci, C. Biomedical applications of nanodiamonds: An overview. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncel, S.; Herman, A.P.; Walczak, K.Z. Magnetic carbon nanostructures in medicine. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Gao, Y.; Pierce, R.; Dai, L.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M. Development of Y-shaped peptide for constructing nanoparticle systems targeting tumor-associated macrophages in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Res. Express 2014, 1, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuznik, N.; Tomczyk, M.M. Multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrids as MRI contrast agents. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.F.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Zhuang, R.Q.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for therapy response monitoring and early treatment prediction of photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5137–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizzatov, A.; Keshishian, V.; Guven, A.; Dimiev, A.M.; Qu, F.F.; Muthupillai, R.; Decuzzi, P.; Bryant, R.G.; Tour, J.M.; Wilson, L.J. Enhanced MRI relaxivity of aquated Gd3+ ions by carboxyphenylated water-dispersed graphene nanoribbons. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3059–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Yang, X.M.; Ren, J.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, H.J.; Feng, Q.H.; Shi, Y.Y.; Shan, X.N.; Yuan, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.Z. A novel redox-sensitive system based on single-walled carbon nanotubes for chemo-photothermal therapy and magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 607–624. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, L.L.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, Z.Z. Hyaluronic acid-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes as tumor-targeting MRI contrast agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4507–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Tsuruoka, S.; Usui, Y.; Haniu, H.; Aoki, K.; Takanashi, S.; Okamoto, M.; Nomura, H.; Tanaka, M.; Aiso, S.; et al. An advanced in situ imaging method using heavy metal-doped hollow tubes to evaluate the biokinetics of carbon nanotubes in vivo. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalwani, G.; Sundararaj, J.L.; Schaefer, K.; Button, T.; Sitharaman, B. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro phantom imaging, and cytotoxicity of a novel graphene-based multimodal magnetic resonance imaging-X-ray computed tomography contrast agent. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3519–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, X.W.; Yao, Y.J.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, J.; Sun, G.; He, D.N. One-step synthesis of surface passivated carbon microspheres for enhanced photoluminescence and their application in multifunctional magnetic-fluorescent imaging. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24049–24055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Liu, G.X.; Dong, X.T.; Wang, J.X.; Yu, W.S. Multifunctional MWCNTs-NaGdF4:Yb3+,Er3+,Eu3+ hybrid nanocomposites with potential dual-mode luminescence, magnetism and photothermal properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 22659–22667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, I.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Beoutis, M.L.; Lartigue, L.; Alloyeau, D.; Pach, E.; Ballesteros, B.; Autret, G.; Ninjbadgar, T.; et al. Covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with a gadolinium chelate for efficient T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 7173–7186. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.H.; Zhao, Q.H.; An, X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Hou, W.X.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.P.; Shen, M.W.; Zhu, W.; Shi, X.Y. Multifunctional PEGylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes for enhanced blood pool and tumor MR imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, B.T.; Law, J.J.; Matson, M.L.; Azhdarinia, A.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M.; Wilson, L.J. Stable confinement of positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance agents within carbon nanotubes for bimodal imaging. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.L.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Guo, X.H.; Chang, Y.A.; Li, M.; Dong, J.Q.; Sun, B.Y.; Xing, G.M. Novel carbon nanohybrids as highly efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.L.; Shi, H.L.; Wu, H.X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.M.; An, L.; Yang, S.P. Prostate cancer targeted multifunctionalized graphene oxide for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Carbon 2016, 107, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitharaman, B.; Wilson, L.J. Gadofullerenes and gadonanotubes: A new paradigm for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent probes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, Q.J.; Chen, J.T.; Gao, H.L.; Fu, D.L.; Shen, S. Biocompatible polydopamine-encapsulated gadolinium-loaded carbon nanotubes for MRI and color mapping guided photothermal dissection of tumor metastasis. Carbon 2017, 112, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jia, X.H.; Yin, X.B.; He, X.W.; Zhang, Y.K. Carbon quantum dot stabilized gadolinium nanoprobe prepared via a one-pot hydrothermal approach for magnetic resonance and fluorescence dual-modality bioimaging. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12122–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.G.; Yang, S.P. Graphene oxide-BaGdF5 nanocomposites for multi-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2015, 42, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaev, P.; Bronikowski, M.J.; Bradley, R.K.; Rohmund, F.; Colbert, D.T.; Smith, K.A.; Smalley, R.E. Gas-phase catalytic growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes from carbon monoxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 313, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Nguyen, F.T.; Barone, P.W.; Heller, D.A.; Moll, A.E.; Patel, D.; Boppart, S.A.; Strano, M.S. Multimodal biomedical imaging with asymmetric single-walled carbon nanotube/iron oxide nanoparticle complexes. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, B.T.; Seguin, J.; Breton, M.; Le Beherec, R.; Bessodes, M.; Rodriguez-Manzo, J.A.; Banhart, F.; Beloeil, J.C.; Scherman, D.; Richard, C. Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes containing traces of iron as new negative MRI contrast agents for in vivo imaging. Contrast Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Faraj, A.; Shaik, A.S.; Al Sayed, B. Preferential magnetic targeting of carbon nanotubes to cancer sites: Noninvasive tracking using MRI in a murine breast cancer model. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska-Korczyc, A.; Jasiurkowska-Delaporte, M.; Maciejewska, B.M.; Warowicka, A.; Coy, L.E.; Zalewski, T.; Koziol, K.K.; Jurga, S. PEG-MWCNT/Fe hybrids as multi-modal contrast agents for MRI and optical imaging. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 49891–49902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.; Riggio, C.; Masini, M.; Bugliani, M.; Battaglia, V.; Novelli, M.; Suleiman, M.; Vittorio, O.; Boggi, U.; Filipponi, F.; et al. Labeling and tracking of human pancreatic islets using carbon nanotubes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittorio, O.; Duce, S.L.; Pietrabissa, A.; Cuschieri, A. Multiwall carbon nanotubes as MRI contrast agents for tracking stem cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 095706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.Z.; Lou, C.G.; Qiu, J.S.; Zhao, Z.B.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, M.J.; Ji, Z.; Yang, S.H.; Xing, D. Targeted Fe-filled carbon nanotube as a multifunctional contrast agent for thermoacoustic and magnetic resonance imaging of tumor in living mice. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.F.; Singh, R.; Burke, A.; Hatcher, H.; Olson, J.; Kraft, R.A.; Schmid, M.; Carroll, D.; Bourland, J.D.; Akman, S.; et al. Development of iron-containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes for MR-guided laser-induced thermotherapy. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewska, B.M.; Warowicka, A.; Baranowska-Korczyc, A.; Zaleski, K.; Zalewski, T.; Koziol, K.K.; Jurga, S. Magnetic and hydrophilic MWCNT/Fe composites as potential T2-weighted MRI contrast agents. Carbon 2015, 94, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hughes, T.C.; Muir, B.W.; Waddington, L.J.; Gengenbach, T.R.; Easton, C.D.; Hinton, T.M.; Moffat, B.A.; Hao, X.J.; Qiu, J.S. Water-dispersible magnetic carbon nanotubes as T2-weighted MRI contrast agents. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna, G.; Garofalo, A.; Popa, G.; Wilhelm, C.; Begin-Colin, S.; Felder-Flesch, D.; Bianco, A.; Gazeau, F.; Menard-Moyon, C. Endowing carbon nanotubes with superparamagnetic properties: Applications for cell labeling, MRI cell tracking and magnetic manipulations. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.J.; Marangon, I.; Melinte, G.; Wilhelm, C.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Pichon, B.P.; Ersen, O.; Aubertin, K.; Baaziz, W.; Pham-Huu, C.; et al. Design of covalently functionalized carbon nanotubes filled with metal oxide nanoparticles for imaging, therapy, and magnetic manipulation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11290–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Wang, M.L.; Miao, F.; Ji, Y.X.; Tian, Z.; Shen, H.B.; Jia, N.Q. Water-dispersible multiwalled carbon nanotube/iron oxide hybrids as contrast agents for cellular magnetic resonance imaging. Carbon 2012, 50, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, L.; Bourgognon, M.; Wang, J.T.W.; Protti, A.; Klippstein, R.; de Rosales, R.T.M.; Shah, A.M.; Fontcuberta, J.; Tobias-Rossell, E.; Sosabowski, J.K.; et al. The shortening of MWNT-SPION hybrids by steam treatment improves their magnetic resonance imaging properties in vitro and in vivo. Small 2016, 12, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznik, N.; Tomczyk, M.M.; Wyskocka, M.; Przypis, L.; Herman, A.P.; Jedrysiak, R.; Koziol, K.K.; Boncel, S. Amalgamation of complex iron(III) ions and iron nanoclusters with MWCNTs as a route to potential T2 MRI contrast agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3581–3591. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, S.W.; Shau, Y.H.; Wu, P.C.; Yang, Y.S.; Shieh, D.B.; Chen, C.C. In vitro and in vivo studies of FePt nanoparticles for dual modal CT/MRI molecular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13270–13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H.; Zheng, X.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.Z.; Wen, X.; Yue, L.D.; Wang, J.L. One-pot synthesis of FePt/CNTs nanocomposites for efficient cellular imaging and cancer therapy. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.L.; Yang, H.; Hu, H.; Yang, S.P. Solvothermal synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles loaded on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3496–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.D.; Hussain, S.T.; Gilani, S.R. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties of carbon nanotubes decorated with magnetic MIIFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 271, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Chen, G.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Dong, X.F.; Qi, M. Multifunctional Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.P.; He, J.J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S.H. Water-soluble magnetic-functionalized reduced graphene oxide sheets: In situ synthesis and magnetic resonance imaging applications. Small 2010, 6, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Guo, F.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, H.R.; Kulaots, I.; Walsh, E.; Hurt, R.H. Encapsulation of particle ensembles in graphene nanosacks as a new route to multifunctional materials. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3744–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justin, R.; Tao, K.; Roman, S.; Chen, D.X.; Xu, Y.W.; Geng, X.S.; Ross, I.M.; Grant, R.T.; Pearson, A.; Zhou, G.D.; et al. Photoluminescent and superparamagnetic reduced graphene oxide-iron oxide quantum dots for dual-modality imaging, drug delivery and photothermal therapy. Carbon 2016, 97, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Hu, L.L.; Ma, X.X.; Ye, S.Q.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.Z.; Li, C.H.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, Z. Multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy using functionalized graphene nanosheets anchored with magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Shi, S.X.; Feng, L.Z.; Chen, F.; Graves, S.A.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Goel, S.; Sun, H.Y.; England, C.G.; Nickles, R.J.; et al. Long circulating reduced graphene oxide-iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient tumor targeting and multimodality imaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12683–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.S.; Ma, Y.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Qi, M. Development of multifunctional cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and controlled drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.R.; Kangasniemi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Mohanty, K.S.; Koymen, R.A. Fe core–carbon shell nanoparticles as advanced MRI contrast enhancer. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Sun, X.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Mann, D.; Liu, Z.; Terashima, M.; Yang, P.C.; McConnell, M.V.; Nishimura, D.G.; et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mararenko, A.; Cao, G.X.; Gai, Z.; Hong, K.L.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S.Q. Multifunctional 1D magnetic and fluorescent nanoparticle chains for enhanced MRI, fluorescent cell imaging, and combined photothermal/chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15309–15317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.Y.; Sandoval, S.; Puig, T.; Obradors, X.; Tobias, G.; Ros, J.; Ricart, S. Novel Fe3O4@GNF@SiO2 nanocapsules fabricated through the combination of an in situ formation method and SiO2 coating process for magnetic resonance imaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24690–24697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelkina, O.N.; Lodge, R.W.; Rudakovskaya, P.G.; Gerasimov, V.M.; Lucas, C.H.; Grebennikov, I.S.; Shchetinin, I.V.; Savchenko, A.G.; Pavlovskaya, G.E.; Rance, G.A.; et al. Nanoscale engineering of hybrid magnetite-carbon nanofibre materials for magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitharaman, B.; Van Der Zande, M.; Ananta, J.S.; Shi, X.F.; Veltien, A.; Walboomers, X.F.; Wilson, L.J.; Mikos, A.G.; Heerschap, A.; Jansen, J.A. Magnetic resonance imaging studies on gadonanotube-reinforced biodegradable polymer nanocomposites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93A, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitharaman, B.; Jacobson, B.D.; Wadghiri, Y.Z.; Bryant, H.; Frank, J. The magnetic, relaxometric, and optical properties of gadolinium-catalyzed single walled carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 134308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.M.; Ananta, J.S.; Zhao, H.; Cisneros, B.T.; Lam, E.Y.; Wong, S.T.; Wilson, L.J.; Wong, K.K. Cellular uptake and imaging studies of gadolinium-loaded single-walled carbon nanotubes as MRI contrast agents. Contrast Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 6, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammohan, N.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Moore, L.K.; Parigi, G.; Mastarone, D.J.; Manus, L.M.; Lilley, L.M.; Preslar, A.T.; Waters, E.A.; Filicko, A.; et al. Nanodiamond-gadolinium(III) aggregates for tracking cancer growth in vivo at high field. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7551–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, C.; Doan, B.T.; Beloeil, J.C.; Bessodes, M.; Toth, E.; Scherman, D. Noncovalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes with amphiphilic Gd3+ chelates: Toward powerful T1 and T2 MRI contrast agents. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chao, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Huang, J.; Pan, J.; Guo, W.L.; Wu, J.Z.; Sheng, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; et al. Polydopamine coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as a versatile platform with radionuclide labeling for multimodal tumor imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.D.; Zhang, H.; Du, N.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.L.; Shi, D.L.; Yang, D.R. Magnetic-fluorescent nanohybrids of carbon nanotubes coated with Eu, Gd co-doped LaF3 as a multimodal imaging probe. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.L.; Li, J.; Sui, J.H.; Li, Z.G.; Cai, W. Synthesis and characterization of one-dimensional bifunctional carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4@SiO2 (FITC) nanohybrids. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.Q.; Chan, C.Y.; Shi, J.Y.; Tsang, M.K.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, C.M.; Gerile, O.; Yang, M. A graphene quantum dot@Fe3O4@SiO2 based nanoprobe for drug delivery sensing and dual-modal fluorescence and MRI imaging in cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ma, X.X.; Ye, S.Q.; Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Guo, L.; Li, C.H.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, Z. Protamine functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes for stem cell labeling and in vivo Raman/magnetic resonance/photoacoustic triple-modal imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as a multifunctional light-responsive platform for cancer combination therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.W.; Cabana, L.; Bourgognon, M.; Kafa, H.; Protti, A.; Venner, K.; Shah, A.M.; Sosabowski, J.K.; Mather, S.J.; Roig, A.; et al. Magnetically decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as dual MRI and SPECT contrast agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1880–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Faraj, A.; Shaik, A.P.; Shaik, A.S. Magnetic single-walled carbon nanotubes as efficient drug delivery nanocarriers in breast cancer murine model: Noninvasive monitoring using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as sensitive imaging biomarker. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Faraj, A.; Shaik, A.S.; Halwani, R.; Alfuraih, A. Magnetic targeting and delivery of drug-loaded SWCNTs theranostic nanoprobes to lung metastasis in breast cancer animal model: Noninvasive monitoring using magnetic resonance imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.X.; Tao, H.Q.; Yang, K.; Feng, L.Z.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.Z.; Li, Y.G.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z. A functionalized graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposite for magnetically targeted drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Peng, C.L.; Shieh, M.J. Development of a controlled-release drug delivery system by encapsulating oxaliplatin into SPIO/MWNT nanoparticles for effective colon cancer therapy and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1742–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Caja, K.; Zhao, B.; Kim, J.A. Non-viral nanoparticle delivers small interfering RNA to macrophages in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shi, J.J.; Hao, Y.W.; Zhang, P.P.; Zhao, Y.L.; Meng, D.H.; Li, D.; Chang, J.B.; Zhang, Z.Z. Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for tumor theranostics. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.C. Magnetic and fluorescent graphene for dual modal imaging and single light induced photothermal and photodynamic therapy of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4499–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.Z.; Gong, H.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Graphene-based magnetic plasmonic nanocomposite for dual bioimaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4786–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, X.F.; Li, J.; He, H.; Yang, F.; Di, Y.; Jin, C.; Jiang, X.G.; Shen, S.; et al. Magnetic graphene-based nanotheranostic agent for dual-modality mapping guided photothermal therapy in regional lymph nodal metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9473–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, P.; Yu, X.R.; Huang, L.Y.; Shen, S.; Cai, S.J. Manganese oxide-coated carbon nanotubes as dual-modality lymph mapping agents for photothermal therapy of tumor metastasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).