Anti-Swelling Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Electrostatic Repulsion and Hydrophobic Interactions for Human Motion Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
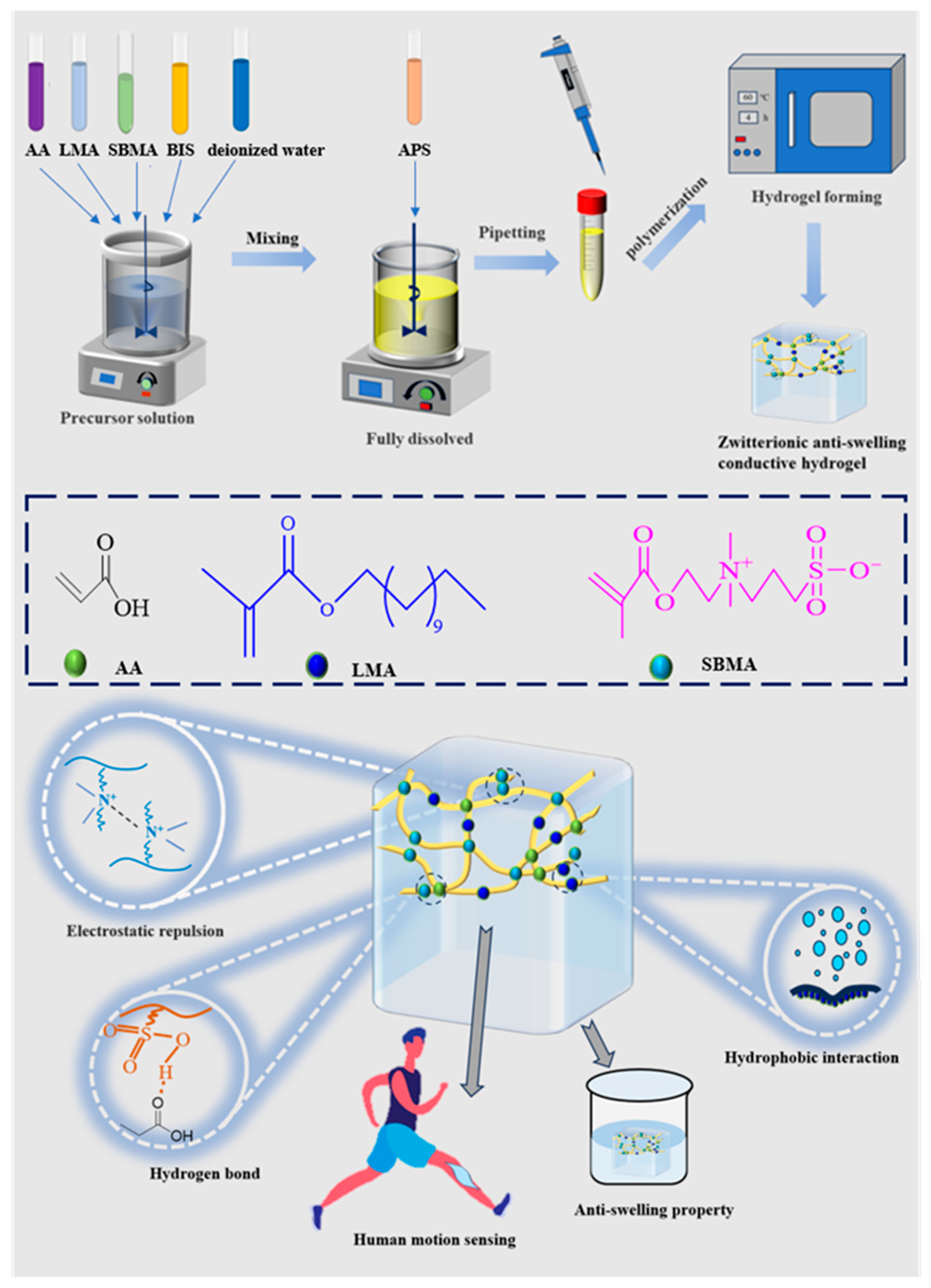
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. Characterization of Hydrogels
2.4. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
2.5. Anti-Swelling Properties of Hydrogels
2.6. Antibacterial Activities of Hydrogels
2.7. Biocompatibility Properties of Hydrogels
2.8. Sensing Properties of Hydrogels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Hydrogels
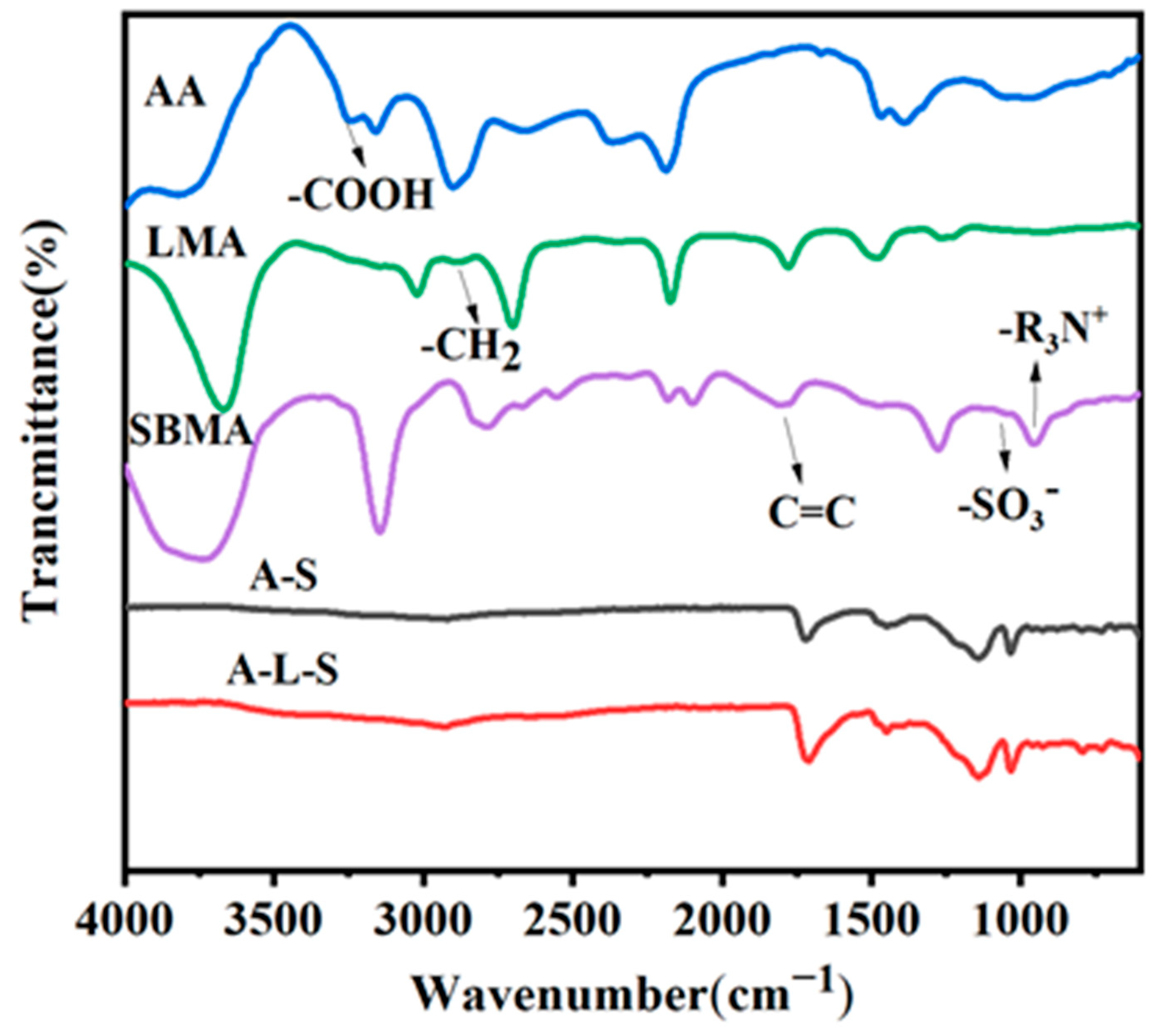
3.2. Characterization of Hydrogels
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogels
3.4. Swelling of Hydrogels
3.5. Antibacterial Performance of Hydrogels
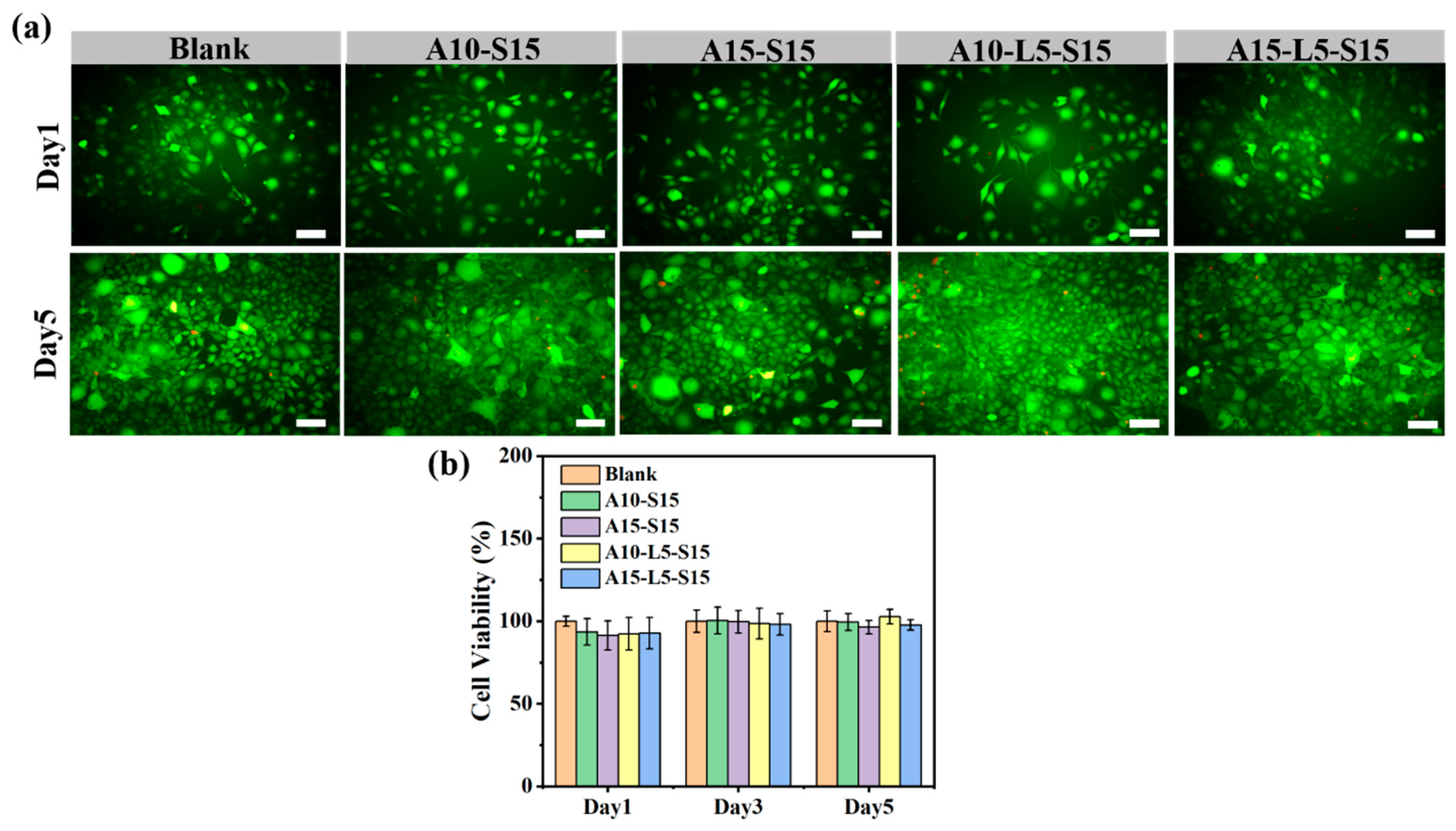
3.6. Biocompatibility of Hydrogels
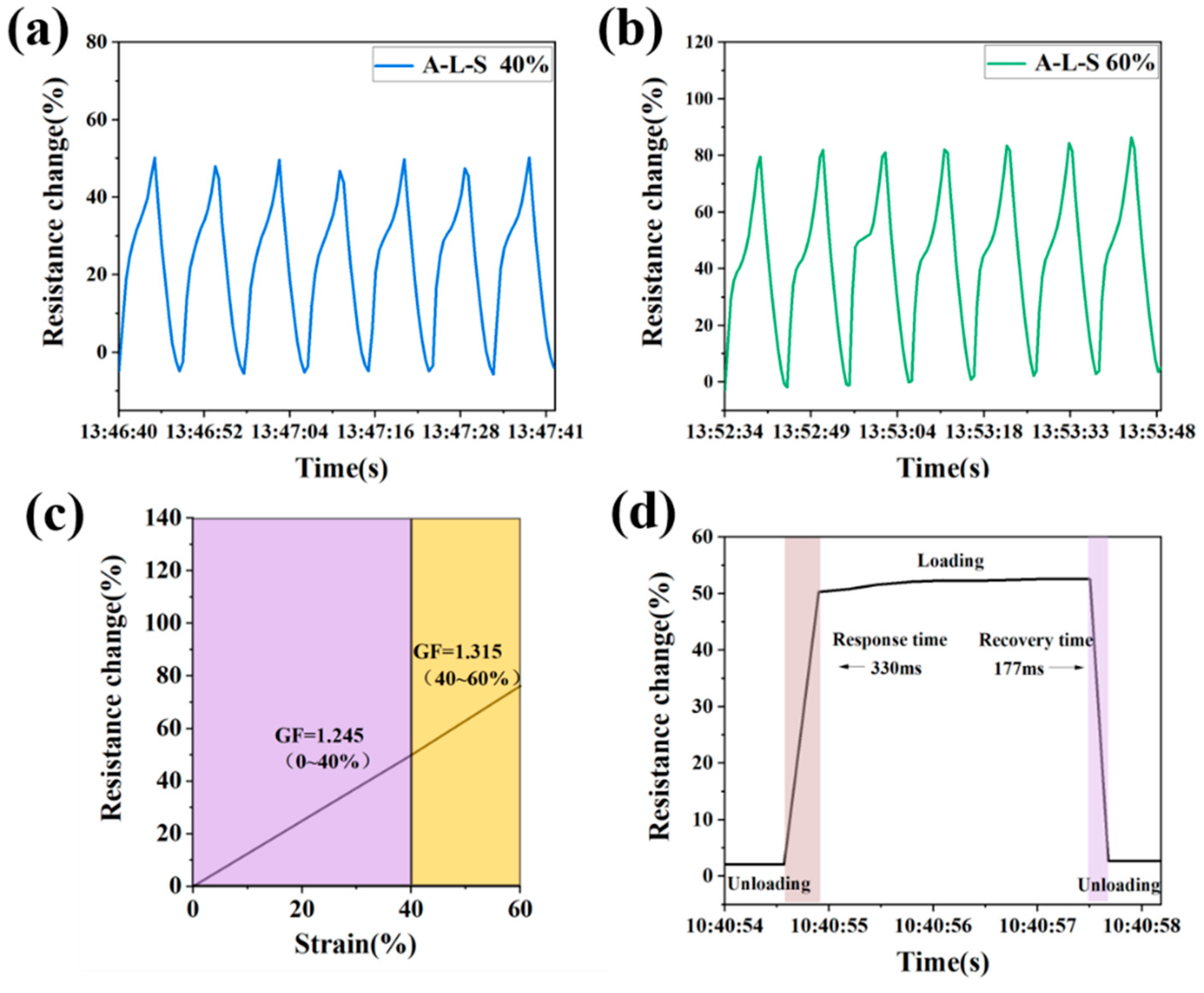
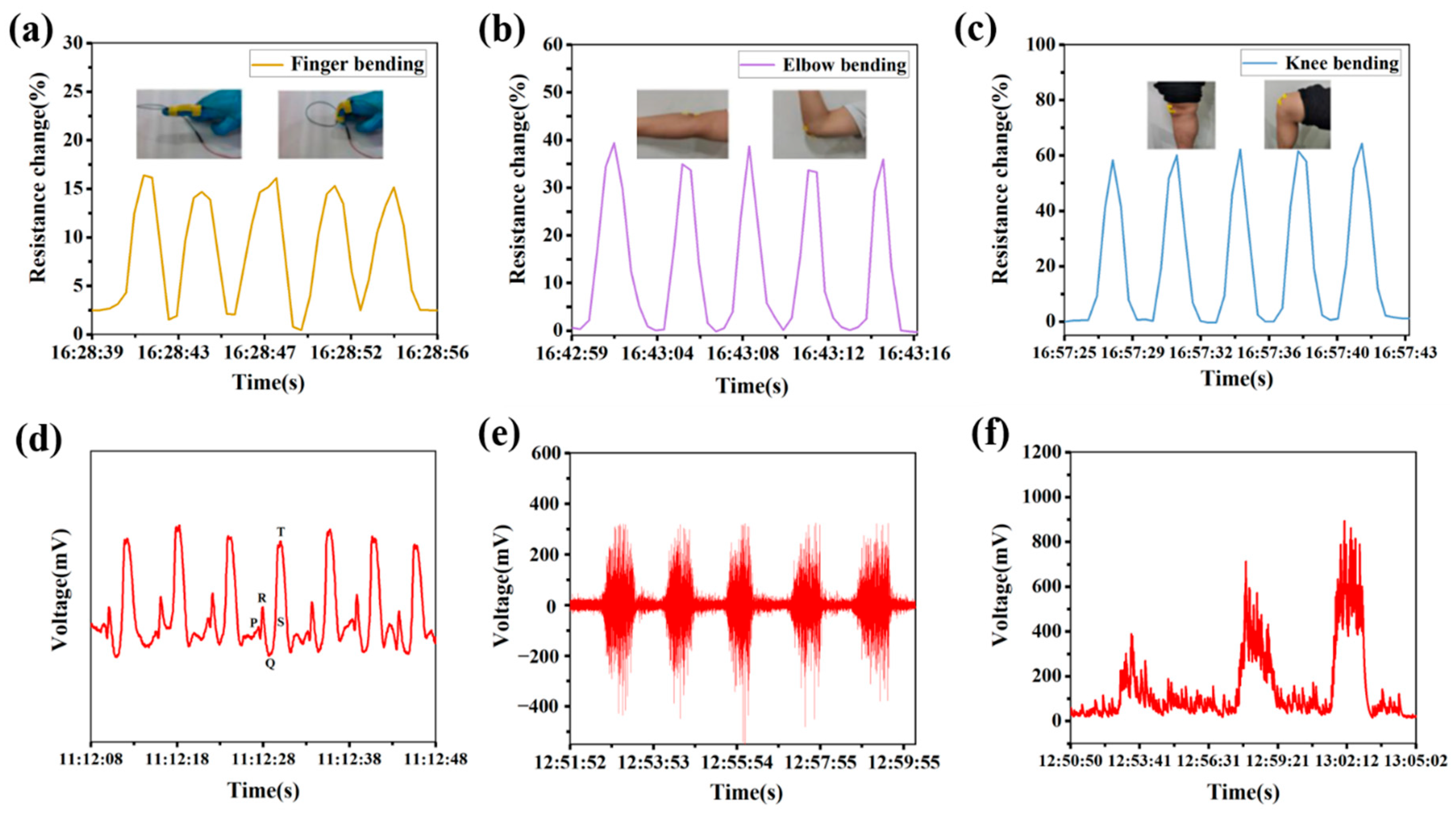
3.7. Sensing Properties of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhuo, S.W.; Deng, Z.X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B.L. Janus gels for biomedical applications Progress and future prospective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 155, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.P.; Mezzenga, R. Design principles of food gels. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofanica, B.-M.; Belosinschi, D.; Volf, I. Gels, aerogels and hydrogels: A challenge for the cellulose-based product industries. Gels 2022, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acet, Ö.; İnanan, T.; Acet, B.Ö.; Dikici, E.; Odabaşı, M. α-Amylase immobilized composite cryogels: Some studies on kinetic and adsorption factors. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.D.; Pan, J.J.; Wang, N.; Xia, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.S.; Fan, J.; Tao, L.; Shou, W.; Gao, Y. Cold-resistant, highly stretchable ionic conductive hydrogels for intelligent motion recognition in winter sports. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 1234–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Luo, J.B.; Jia, T.X.; Hou, C.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, H.Z. Water-resistant and underwater adhesive ion-conducting gel for motion-robust bioelectric monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogels and their applications as smart wearable devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2561–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.J.; Huo, H.L.; Jiang, B.X.; Yuan, H.; Lin, Z.D.; Zhang, P. A highly stretchable and sensitive carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel for flexible strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 15720–15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, P.C.; Yang, J.W.; Ji, Z.C.; Wang, Y. Advances in ionic conductive hydrogels for skin sensor applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2025, 165, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Han, L.; Fu, X.B.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Pan, L.K.; Xu, M. Multiple stimuli responsive and identifiable zwitterionic ionic conductive hydrogel for bionic electronic skin. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.Y.; Zhao, T.Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, B.-X.; Sun, H.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Yang, D.Z. Antifreezing, antidrying, and conductive hydrogels for electronic skin applications at ultralow temperatures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 21133–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratticò, D.; Laganà, F.; Oliva, G.; Fiorillo, A.S.; Pullano, S.A.; Calcagno, S.; De Carlo, D.; La Foresta, F. Integration of LSTM and U-Net models for monitoring electrical absorption with a system of sensors and electronic circuits. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2533311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zheng, C.C.; Zhu, L.X.; Yang, B.H.; Jin, X.K.; Wang, S.; Song, Z.K.; Liu, J.Y.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, F.Z.; et al. Machine learning enabled reusable adhesion, entangled network-based hydrogel for long-term, high-fidelity EEG recording and attention assessment. Nano-Micro Lett. 2025, 17, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, D.; Li, X.K.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, J.F.; Kang, Y.; Zeng, H.B.; Han, L.B. Recent advances in flexible hydrogel sensors: Enhancing data processing and machine learning for intelligent perception. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 261, 116499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, S.F.; Qian, L.W.; Wei, N.; Nica, V.; Coseri, S.; Han, F. Super stretchable, self-healing, adhesive ionic conductive hydrogels based on tailor-made ionic liquid for high-performance strain sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Sheng, N.; Wang, B.X.; Wu, Z.T.; Liang, Q.Q.; Wang, H.P. Anisotropic bacterial cellulose hydrogels with tunable high mechanical performances, non-swelling and bionic nanofluidic ion transmission behavior. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8126–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.J.; Liu, B.; Gao, G.H. Physically crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan-phytic acid hydrogels for wearable sensors with highly conductive, recyclable and antibacterial properties. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.H.; Kong, X.L.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, G.H.; Qu, W.R.; Shi, K. Ionic conductive soluble starch hydrogels for biocompatible and anti-freezing wearable sensors. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 210, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, C.X.; Fei, G.Q.; Yang, D.; Li, K.; Wang, M.X.; Yang, X.; Li, N.; Song, L.; et al. Conductive, adhesive, and biocompatible hydrogel sensor based on zwitterionic for effective wound healing and monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.L.; Shang, Y.H.; Shen, H.D.; Li, W.J.; Wang, Q.G. Highly transparent conductive ionohydrogel for all-climate wireless human-motion sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Ge, X.Y.; Zhong, Z.H.; Dong, X.L.; Xing, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Q.G. Robust and low swelling polyacrylamide/sodium alginate dual-network hydrogels via multiple freezing strategy toward amphibious motion sensors. Polymer 2024, 315, 127850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, A.S.; Yang, S.J.; Yin, J.B.; Wang, R. Phytic acid and carboxymethyl cellulose synergistically reinforced ionic conductive hydrogels for high-strength and low-swelling flexible sensor applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Tang, J.Y.; Feng, J.C. Robust hydrogel with significant swelling resistance via the synergy of hydrogen bond regulation and ionic cross-linking. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.F.; Wei, E.J.; Cui, C.K.; Xie, J.G. High tensile, antibacterial, and conductive hydrogel sensor with multiple cross-linked networks based on PVA/sodium alginate/zinc oxide. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 16851–16859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, F.-K.; Gong, C.; Xie, X.-M. Dual cross-linked networks hydrogels with unique swelling behavior and high mechanical strength: Based on silica nanoparticle and hydrophobic association. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 381, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Mu, Y.J.; Luo, Y.; Menon, C.; Zhou, Z.W.; Chu, P.K.; Feng, S.P. Hofmeister effect and electrostatic interaction enhanced ionic conductive organohydrogels for electronic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2110859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Igarashi, N.; Arazoe, Y.O.; Ishida, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Hikima, T.; Aida, T. Internal structure and mechanical property of an anisotropic hydrogel with electrostatic repulsion between nanosheets. Polymer 2019, 177, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mredha, M.T.I.; Le, H.H.; Cui, J.X.; Jeon, I. Double-hydrophobic-coating through quenching for hydrogels with strong resistance to both drying and swelling. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.L.; Wu, J.H.; Duan, T.F.; Tang, Z.M.; Li, N.; Xu, L.J.; Yang, P.P.; Xu, J.X. Cationic Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) antiswelling hydrogel sensor for underwater human motion detection and communication. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 5792–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, H.L.; Zhao, Z.C.; Guo, Y.H.; Kang, W.J.; Sun, J.; Jin, Z.H.; Ren, H.L.; Gao, Z.J. Preparation of environmental resistance and anti-swelling hydrogel through solvent displacement for monitoring human health and movement in amphibious environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Q.; Wang, S.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.F. Dual network zwitterionic hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties, anti-swelling, and shape memory behaviors. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 197, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.Y.; Yuan, W.Z. Highly adhesive and dual-crosslinking hydrogel via one-pot self-initiated polymerization for efficient antibacterial, antifouling and full-thickness wound healing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 230, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Lu, S.S.; Li, Q.S.; Ren, Y.W.; Ding, Y.Q.; Wu, H.L.; He, X.H.; Shang, Y.D. High strength zwitterionic nano-micelle hydrogels with superior self-healing, adhesive and ion conductive properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, M.L.; Feng, Y.K.; Zeng, Y.F.; Li, H.Q.; Sun, J.B.; Chen, X.L. Electrically conductive zwitterionic hydrogel with extraordinary antifreezing performance. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 9061–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.L.; Huang, S.S.; Gong, X.; King, J.A.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.C.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhai, G.X.; et al. Salt sensitive purely zwitterionic physical hydrogel for prevention of postoperative tissue adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2023, 158, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.Y.; Yan, S.P.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; He, D.; Wang, K.K.; Zhou, D.F.; Jia, Q.K.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, B.T.; et al. Ureido-ionic liquid mediated conductive hydrogel: Superior integrated properties for advanced biosensing applications. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.H.; Mei, L.; Liu, Q.; Fang, X.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, P.F.; Ding, W.P.; Luo, T.Z. High-performance conductive and antibacterial zwitterionic hydrogel for the design of flexible motion sensor. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 8065–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Ma, J.; Xu, L.B.; Lin, W.F.; Xue, W.L.; Huang, M.; Chen, S.F. An electrospun polyurethane scaffold-reinforced zwitterionic hydrogel as a biocompatible device. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, Q.S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.G.; Ji, F.; Dong, D.Y.; Gao, L.-N.; Cui, Y.-L.; Yao, F.L. A Physical cross-linking starch-based zwitterionic hydrogel exhibiting excellent biocompatibility, protein resistance, and biodegradability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15710–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, S.Q.; Ma, Y.F.; Wei, H.; Lü, S.Y. An anti-swellable hydrogel strain sensor for underwater motion detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Duan, L.J.; Gao, G.H. The effect of methyl group on the mechanical properties of hydrophobic association hydrogel. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Huang, G.Q.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, M.M.; Feng, J.; Kan, K.; Shen, J. Novel uracil-functionalized Poly(ionic liquid) hydrogel: Highly stretchable and sensitive as a direct wearable ionic skin for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11062–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Liang, Y.Q.; Deng, Z.X.; Xu, H.R.; Zhang, H.L.; Guo, B.L.; Zhang, J. Adhesive ion-conducting hydrogel strain sensor with high sensitivity, long-term stability, and extreme temperature tolerance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 29902–29913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Lv, X.; Tian, S.; Xie, Y.H.; Lv, A.W.; Lv, Z.W.; Jiang, L.A.; Zhao, Y.H.; Sun, S.L. Simple fabrication of silica amino sphere-reinforced ionic liquids/graphene conductive hydrogel sensors with super toughness, self-healing, and strain sensitivity properties. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 6256–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Rahman, T.U.; Sher, M.; Shah, L.A.; Md Akil, H.; Fu, J.; Yoo, H.-M. Flexible ionic conductive hydrogels with wrinkled texture for flexible strain transducer with language identifying diversity. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 4703–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.G.; Jia, L.H.; Yu, J.Y.; Xu, H.R.; Guo, X.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, S.B. Environmentally tolerant multifunctional eutectogel for highly sensitive wearable sensors. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 2604–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Song, J.J.; Yang, G.; Shen, L.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B.L.; Wang, W. Multiple crosslinked, self-healing, and shape-adaptable hydrogel laden with pain-relieving chitosan@borneol nanoparticles for infected burn wound healing. Theranostics 2025, 15, 1439–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dong, Q.L. Soybean protein isolate-incorporated zwitterionic hydrogel with rapid chlorine rechargeable biocidal and antifouling functions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 12843–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzl, G.; Walkner, S.; Hild, S.; Hassel, A.W.; Weber, H.K.; Paulik, C. Mechanistic approaches on the antibacterial activity of poly(acrylic acid) copolymers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Liang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Tian, Y. Skin-inspired ultra-tough supramolecular multifunctional hydrogel electronic skin for human-machine interaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, G. Amylopectin based hydrogel strain sensor with good biocompatibility, high toughness and stable anti-swelling in multiple liquid media. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, T. A fully hydrophobic ionogel enables highly efficient wearable underwater sensors and communicators. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Dong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Lei, C. Tough, anti-swelling supramolecular hydrogels mediated by surfactant-polymer interactions for underwater sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30385–30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Wei, Y. Chitosan-enhanced nonswelling hydrogel with stable mechanical properties for long-lasting underwater sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shen, J.; Wan, S.; Han, L.; Dou, G.; Sun, L. Wet-adhesive multifunctional hydrogel with anti-swelling and a skin-seamless interface for underwater electrophysiological monitoring and communication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11549–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; He, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zheng, S.Y.; Yang, J. Anti-swelling zwitterionic hydrogels as multi-modal underwater sensors and all-in-one supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 7498–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, H.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wan, P.B. Flexible conformally bioadhesive MXene hydrogel electronics for machine learning-facilitated human-interactive Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pan, M.F.; Qiao, C.Y.; Ma, Y.H.; Yan, B.; Yang, W.S.; Peng, Q.Y.; Han, L.B.; Zeng, H.B. Ultra stretchable, tough, elastic and transparent hydrogel skins integrated with intelligent sensing functions enabled by machine learning algorithms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.M.; Liu, H.; Yuan, H.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, R.N.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, L.N.; Liu, M.H.; et al. Artificial intelligence-assisted conductive hydrogel dressings for refractory wounds monitoring. Nano-Micro Lett. 2025, 17, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Designation of Hydrogel | AA (μL) | LMA (μL) | SBMA (mg) | H2O (μL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A10 | 100 | / | / | 1000 |
| A10-S15 | 100 | / | 150 | 1000 |
| A15-S15 | 150 | / | 150 | 1000 |
| A10-L5-S15 | 100 | 50 | 150 | 1000 |
| A15-L5-S15 | 150 | 50 | 150 | 1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Shen, L.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Du, T.; Zhao, X. Anti-Swelling Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Electrostatic Repulsion and Hydrophobic Interactions for Human Motion Sensing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090346
Deng Z, Shen L, Cheng Q, Li Y, Du T, Zhao X. Anti-Swelling Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Electrostatic Repulsion and Hydrophobic Interactions for Human Motion Sensing. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(9):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090346
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zexing, Litong Shen, Qiwei Cheng, Ying Li, Tianming Du, and Xin Zhao. 2025. "Anti-Swelling Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Electrostatic Repulsion and Hydrophobic Interactions for Human Motion Sensing" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 9: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090346
APA StyleDeng, Z., Shen, L., Cheng, Q., Li, Y., Du, T., & Zhao, X. (2025). Anti-Swelling Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Electrostatic Repulsion and Hydrophobic Interactions for Human Motion Sensing. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(9), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16090346








