Functional Compression Fabrics with Dual Scar-Suppressing and Antimicrobial Properties: Microencapsulation Design and Performance Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PDMS Microcapsules
2.3. Preparation of PDMS-M CGF
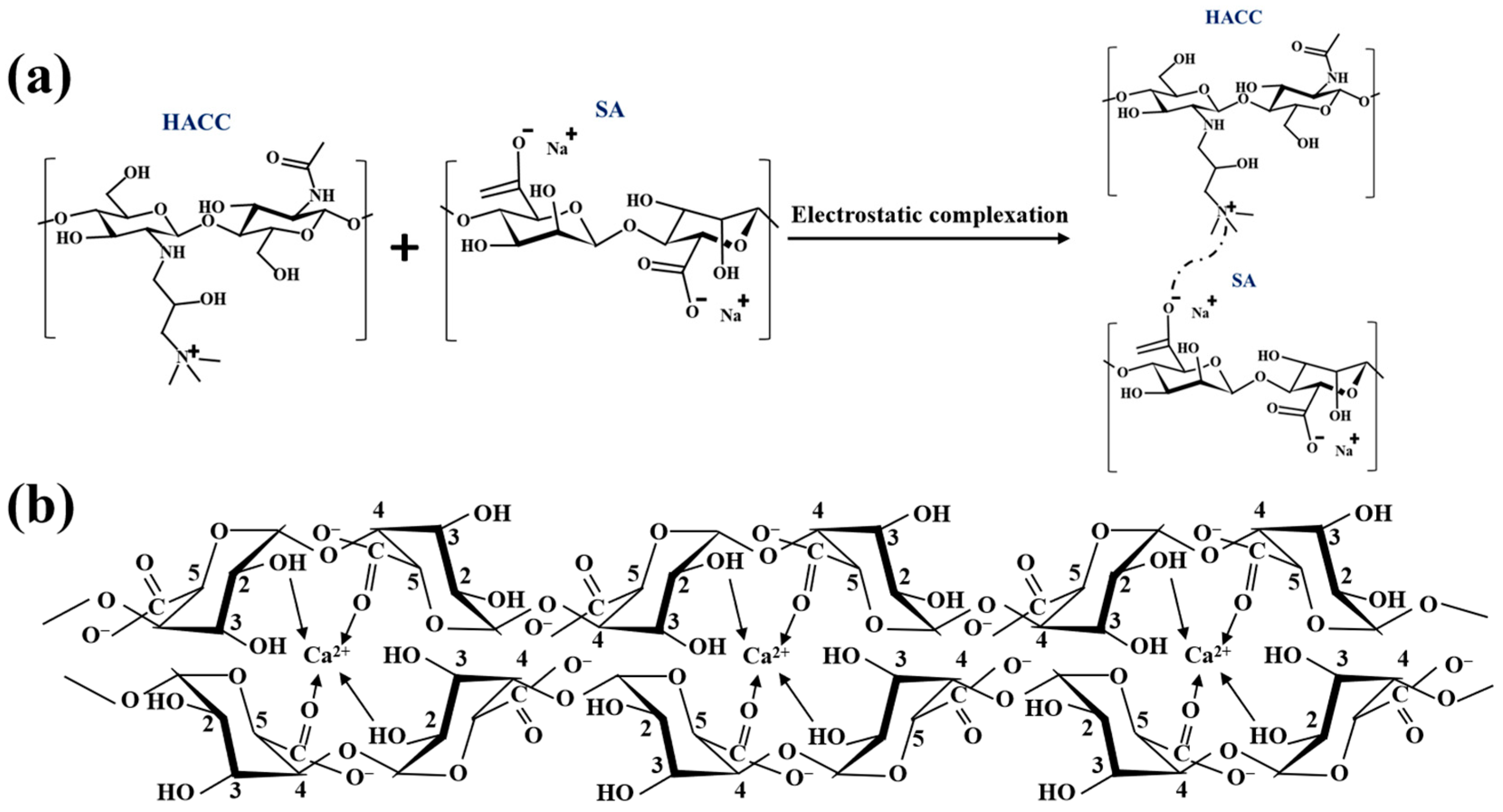
2.4. Preparation of PDMS-M-HACC CGF
2.5. Drug Loading Capacity, Encapsulation Efficiency, and In Vitro Drug Release of Microcapsules
2.6. Antibacterial Property Test
2.7. Washing Fastness Test
2.8. Wearability Test
2.9. Biocompatibility
2.9.1. Cell Viability Experiment
2.9.2. Skin Irritation Test—Direct Contact
2.10. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
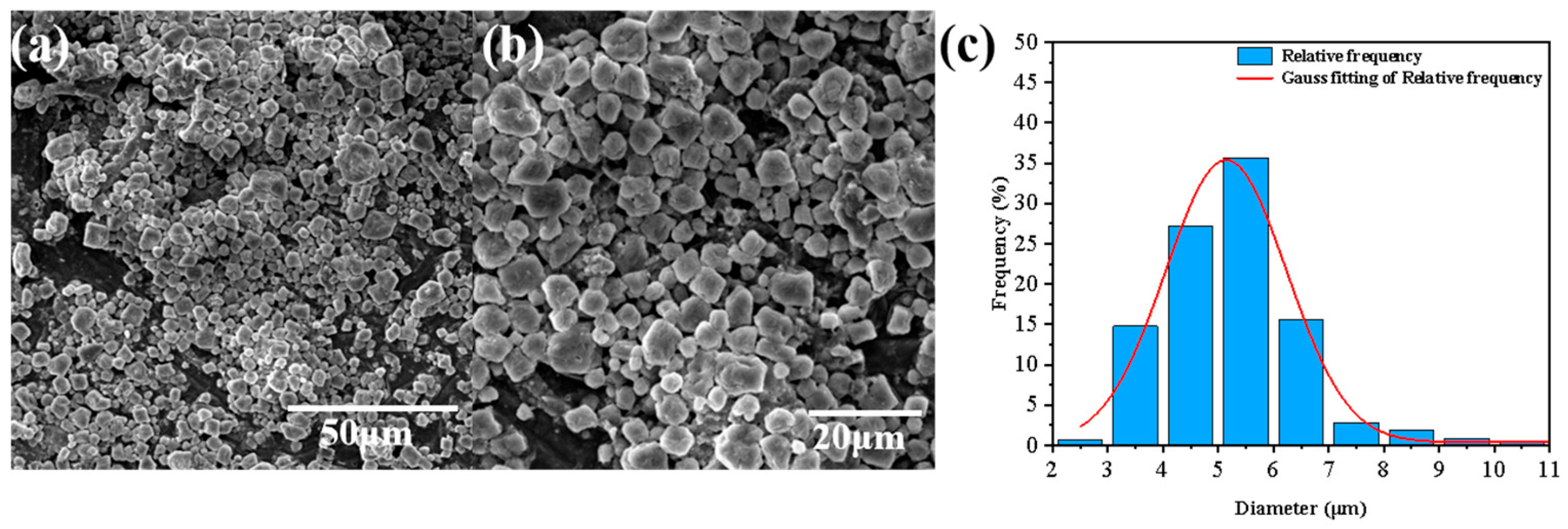
3.1. Characterization of PDMS-Ms
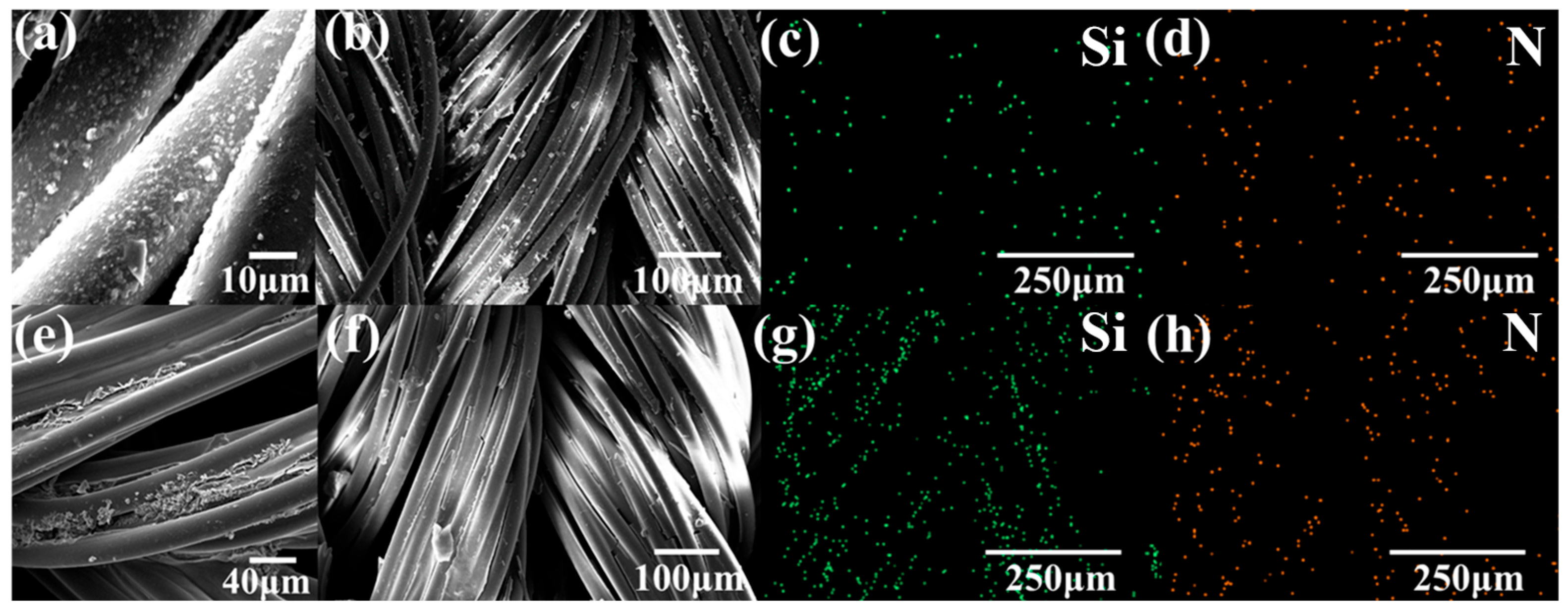
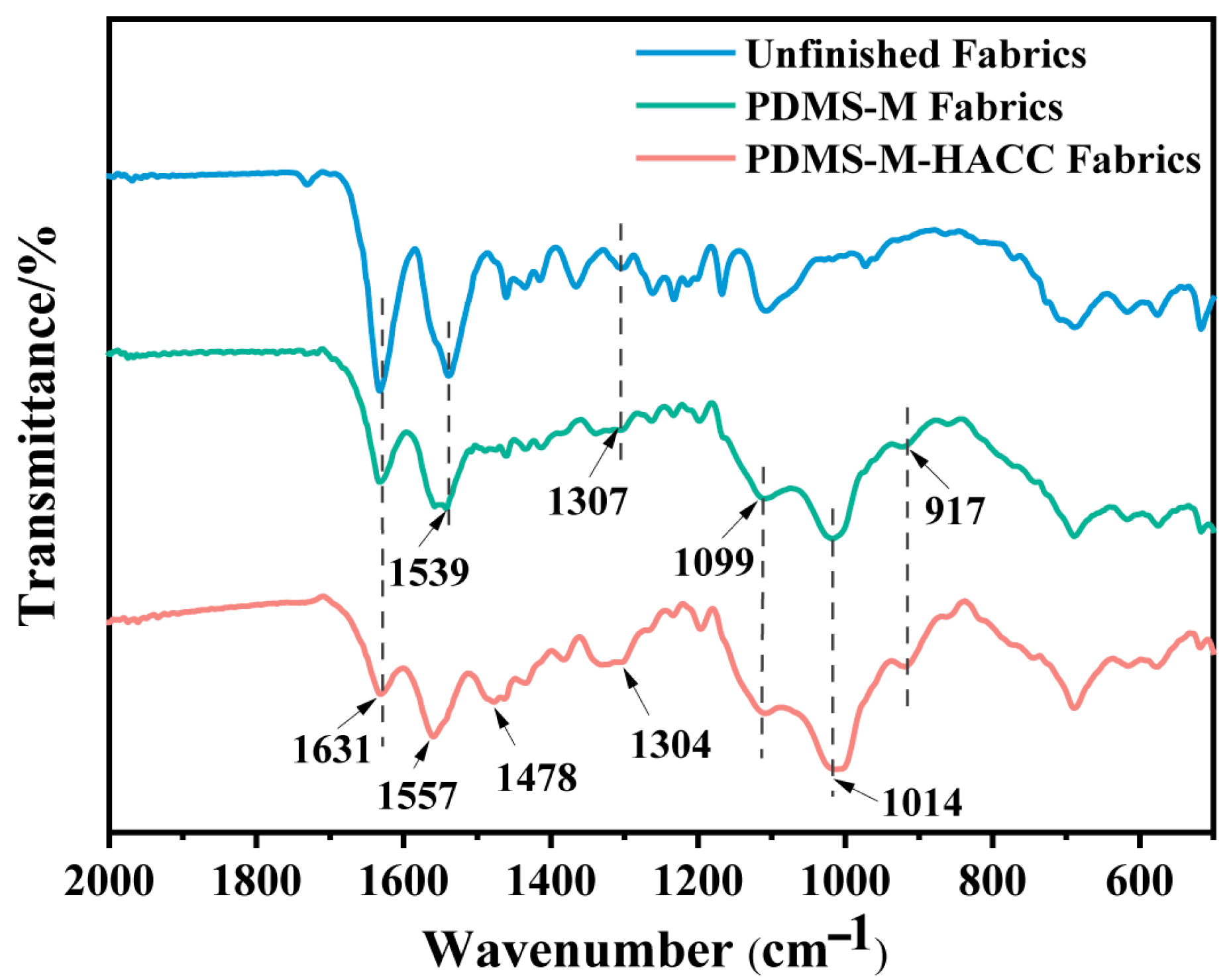
3.2. Characterization of PDMS-M CGF and PDMS-M-HACC CGF
3.3. Antimicrobial Effect and Washing Fastness of PDMS-M CGF and PDMS-M-HACC CGF
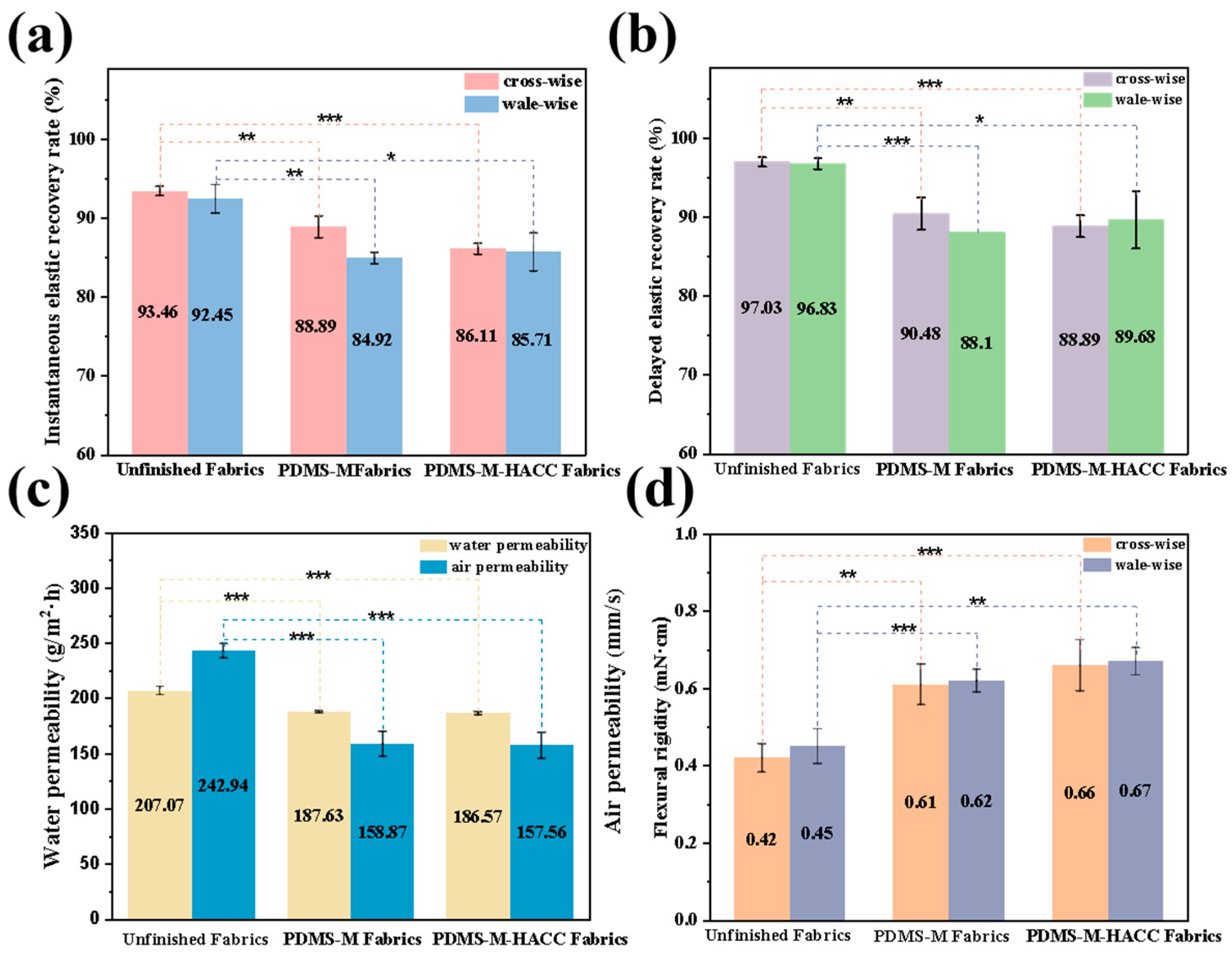
3.4. Wearing Performance of PDMS-M CGF and PDMS-M-HACC CGF
3.5. Biocompatibility of PDMS-M CGFs and PDMS-M-HACC CGFs
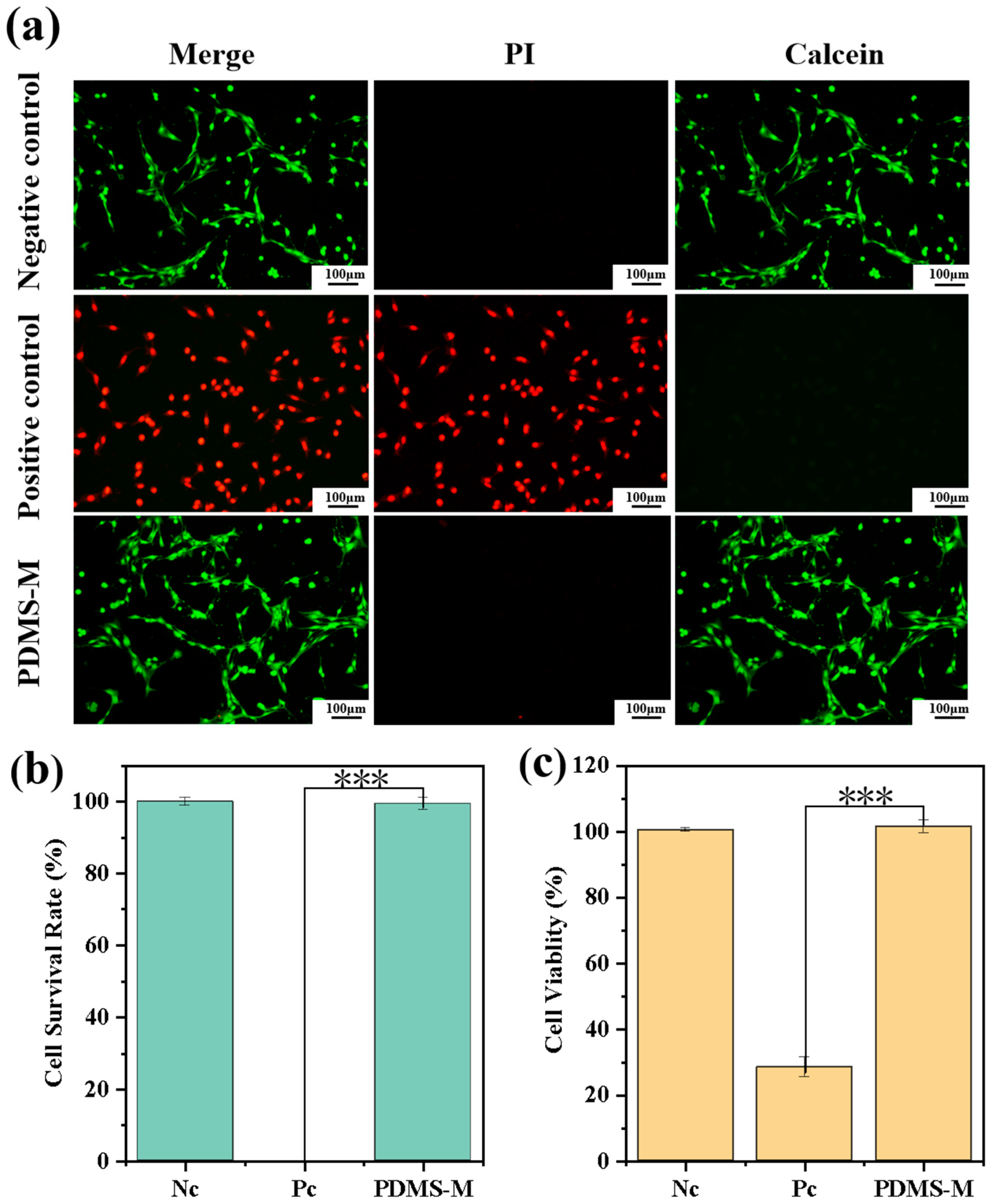
3.5.1. Cell Viability Experiment Results and Discussion
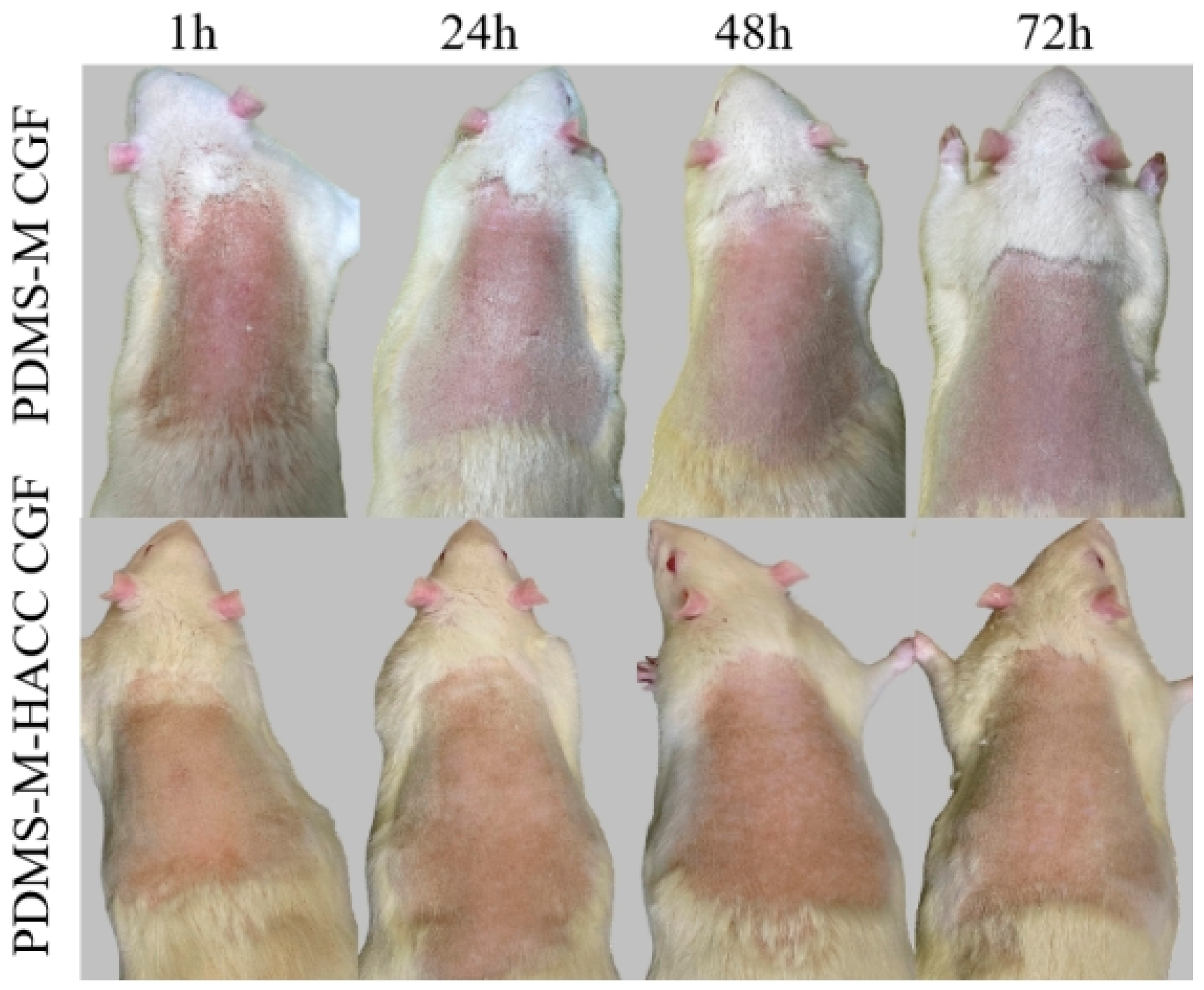
3.5.2. Skin Irritation Test Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chipp, E.; Charles, L.; Thomas, C.; Whiting, K.; Moiemen, N.; Wilson, Y. A prospective study of time to healing and hypertrophic scarring in paediatric burns: Every day counts. Burns Trauma 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. Antibacterial graphene oxide/chitosan composite compression garment fabric. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Hydrogel loaded with components for therapeutic applications in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jang, Y. Recent understandings of biology, prophylaxis and treatment strategies for hypertrophic scars and keloids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engrav, L.H.; Heimbach, D.M.; Rivara, F.P.; Moore, M.L.; Wang, J.; Carrougher, G.J.; Costa, B.; Numhom, S.; Calderon, J.; Gibran, N.S. 12-Year within-wound study of the effectiveness of custom pressure garment therapy. Burns 2010, 36, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hou, C.; An, M. RNA-seq-based analysis of the hypertrophic scarring with and without pressure therapy in a Bama minipig model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Tsang, C.W.; Feng, B.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Shu, B.; Chan, Y.T.; Cheung, K.K. A histological study on the effect of pressure therapy on the activities of myofibroblasts and keratinocytes in hypertrophic scar tissues after burn. Burns. 2015, 41, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Barnes, S.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Moiemen, N.; Lord, J.M.; Sardeli, A.V. Influence of scar age, laser type and laser treatment intervals on paediatric burn scars: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Burns Trauma 2024, 12, tkad046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foppiani, J.A.; Khaity, A.; Al-Dardery, N.M.; Hasan, M.T.; El-Samahy, M.; Lee, D.; Abdelwahab, O.A.; Abd-Alwahed, A.E.; Khitti, H.M.; Albakri, K. Laser therapy in hypertrophic and keloid scars: A systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024, 48, 3988–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabe, R.M.; Choe, D.; Lin, T.J.; Pham, C.; Dang, J.; Madrigal, P.; Yenikomshian, H.A.; Gillenwater, T.J. Laser-assisted drug delivery in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: A systematic review. J. Burn Care Res. 2024, 45, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trace, A.P.; Enos, C.W.; Mantel, A.; Harvey, V.M. Keloids and hypertrophic scars: A spectrum of clinical challenges. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, K.; Davey, R.B.; Wallis, K.A. Silicone gel: A new treatment for burn scars and contractures. Burns 1983, 9, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frech, F.S.; Hernandez, L.; Urbonas, R.; Zaken, G.A.; Dreyfuss, I.; Nouri, K. Hypertrophic scars and keloids: Advances in treatment and review of established therapies. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Zouridaki, E.; Rosenberger, A.; Dalkowski, A. Current developments and uses of cryosurgery in the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Wound Repair Regen. 2002, 10, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.L.; Liu, M.Z.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yu, X.T.; Li, J.Q.; Guo, G.H. Research advances on pharmacological interventions for hypertrophic scar. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi 2022, 38, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Kafka, M.; Collins, V.; Kamolz, L.P.; Rappl, T.; Branski, L.K.; Wurzer, P. Evidence of invasive and noninvasive treatment modalities for hypertrophic scars: A systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. 2017, 25, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.A.; Mohammed, N.H.; Sotohy, M.; Abou-Taleb, D.A. Botulinum toxin type A versus 5-Fluorouracil in treatment of keloid. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2021, 313, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdeo, J.; Kerby, E.; Glass, D.A. Keloids. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, A. Comparing the efficacy of multiple drugs injection for the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloid: A network meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Tsang, C.W.P.; Zheng, Y.P.; Lau, J.C.M. A randomized clinical trial to study the effect of silicone gel dressing and pressure therapy on posttraumatic hypertrophic scars. J. Burn Care Res. 2010, 31, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, D.; Weissman, O.; Winkler, E.; Yankelson, L.; Millet, E.; Mushin, O.P.; Liran, A.; Haik, J. Silicone-based scar therapy: A review of the literature. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2010, 34, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Decker, I.; Beeckman, A.; Hoeksema, H.; De Mey, K.; Verbelen, J.; De Coninck, P.; Blondeel, P.; Speeckaert, M.M.; Monstrey, S.; Claes, K.E. Pressure therapy for scars: Myth or reality? A systematic review. Burns 2023, 49, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.; Yick, K.L.; Kwan, M.Y.; Yuen, C.F.; Ng, S.P.; Yu, A.; Yip, J. Customized fabrication approach for hypertrophic scar treatment: 3D printed fabric silicone composite. Int. J. Bioprinting 2020, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M. Antibacterial finishing of compression fabrics based on Ti3C2Tx-APTES material. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 671, 160765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittaya-areekul, S.; Kruenate, J.; Prahsarn, C. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of alginate/chitosan microparticles containing prednisolone. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 312, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsevinç, A.; Alkan, C. Polyurethane shell medicinal lavender release microcapsules for textile materials: An environmentally friendly preparation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, P.C.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Kan, C.W.; Ng, F.S.F.; Zhou, C.E.; Wat, E.; Zhang, V.X.; Chan, C.L.; Bik-San Lau, C.; Leung, P.C. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/sodium alginate (CSA) microcapsule containing Cortex Moutan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 434, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, H.; Yuan, T.; Yang, Z. Facile fabrication of tea tree oil-loaded antibacterial microcapsules by complex coacervation of sodium alginate/quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 13032–13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Khan, G.; Bonde, G.V.; Bansal, M.; Mishra, B. Design, optimization and characterizations of chitosan fortified calcium alginate microspheres for the controlled delivery of dual drugs. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xing, Z.Y.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, B.; Ren, B.; Dong, X.; Yi, L. An environmental-friendly oil-based dust suppression microcapsules: Structure with chitosan derivative as capsule wall. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, H.; Vos, M.D.; Verbelen, J.A.; Pirayesh, S. Monstrey, Scar management by means of occlusion and hydration: A comparative study of silicones versus a hydrating gel-cream. Burns 2013, 39, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.; Haidari, H.; Cowin, A.J.; Wagstaff, M.; Dearman, B.; Kopecki, Z. Dermal substitutes for clinical management of severe burn injuries: current and future perspectives. Adv. Ther. 2025, 8, 2400455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salyer, C.E.; Bomholt, C.; Beckmann, N.; Bergmann, C.B.; Plattner, C.A.; Caldwell, C.C. Novel therapeutics for the treatment of burn infection. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Abbondanza, J.A.; Shahrokhi, S. Burn infection and burn sepsis. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 20944.3-2008; Textiles-Evaluation for Antibacterial Activity—Part 3: Shake Flask Method. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China location: Beijing, China, 2008.
- FZ/T 73023-2006; Antibacterial Knitwear—Appendix 3: Laundering Test Method for Antibacterial Fabric Samples. The National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- FZ/T 70006-2022; Stretch and Recovery Testing Method for Knitted Fabrics. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB/T 5453-1997; Textiles-Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air. State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1997.
- GB/T 12704.2-2009; Textiles-Test Method for Water-Vapour Transmission of Fabrics—Part 2: Water Method. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 18318.1-2009; Textiles-Determination of Bending Behavior—Part1: Incline Method. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M. Antibacterial Finishing of Compression Garment Fabric Based on Ti3C2T x–Chitosan–APTES Material. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 21370–21378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 16886.5-2017; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China location: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Spano, A.; Monaco, G.; Barni, S.; Sciola, L. Cisplatin treatment of NIH/3T3 cultures induces a form of autophagic death in polyploid cells. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 717–730. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 16886.10-2017; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 10: Tests for Irritation and Skin Sensitization. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China location: Beijing, China, 2017.





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Nie, X.; Yan, B. Functional Compression Fabrics with Dual Scar-Suppressing and Antimicrobial Properties: Microencapsulation Design and Performance Evaluation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16080287
Zhao L, Li C, Yuan M, Zhang R, Liu X, Nie X, Yan B. Functional Compression Fabrics with Dual Scar-Suppressing and Antimicrobial Properties: Microencapsulation Design and Performance Evaluation. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(8):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16080287
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lihuan, Changjing Li, Mingzhu Yuan, Rong Zhang, Xinrui Liu, Xiuwen Nie, and Bowen Yan. 2025. "Functional Compression Fabrics with Dual Scar-Suppressing and Antimicrobial Properties: Microencapsulation Design and Performance Evaluation" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 8: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16080287
APA StyleZhao, L., Li, C., Yuan, M., Zhang, R., Liu, X., Nie, X., & Yan, B. (2025). Functional Compression Fabrics with Dual Scar-Suppressing and Antimicrobial Properties: Microencapsulation Design and Performance Evaluation. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(8), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16080287





